The Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics
|
|
|
- Denis Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Joural of Fuzzy Mahemaics
2
3 THE JOURNL OF FUZZY MTHEMTICS Edior-i-Chief Hu Cheg-mig Volume 3 Number 05 INTERNTIONL FUZZY MTHEMTICS INSTITUTE Los geles US
4 THE JOURNL OF FUZZY MTHEMTICS Volume 3 Number March 05 Copyrigh 05 by Ieraioal Fuzzy Mahemaics Isiue ll Righs Reserved No par of his publicaio may be reproduced or rasmied i ay form or by ay meas elecroic mechaical phoocopyig recordig or ay iformaio sorage ad rerieval sysem or oherwise wihou he prior wrie permissio of he publisher Ieraioal Fuzzy Mahemaics Isiue 830 Broad Oak C delao C 930 US The appearace of he code a he boom of he firs page of a aricle i his joural idicaes he copyrigh ower s cose ha copies of he aricle may be made for persoal or ieral use or for he persoal or ieral use of specific clies This cose is give o he codiio ha he copier pays he per-copy fee saed i he code o he firs page of he aricle hrough he Copyrigh Clearace Ceer Ic (7 Cogress Sree Salem M 0970 US) for copyig beyod ha permied by Secios 07 or 08 of he US Copyrigh Law If o code appears i a aricle he auhor has o give broad cose o copy ad permissio o copy mus be obaied direcly form he auhor This cose does o exed o oher kids of copyig such as for geeral diibuio resale adverisig ad promoio purposes or for creaig ew collecive works Special wrie permissio mus be obaied from he publisher for such copyig Upo accepace of a aricle by he joural he auhor(s) will be asked o rasfer copyrigh of he aricle o he publisher The rasfer will esure he wides possible dissemiaio of iformaio /5 $850 This joural is pried o acid-free paper Pried i he Uied Saes of merica
5 The Joural of Fuzzy Mahemaics Vol 3 No 05 Los geles O (eriched) L -fuzzy Topologies: Decomposiio Theorem Guopeg Wag Ligqiag Li GuagwuMeg ad Qigxue Su School of Mahemaical Scieces Liaocheg Uiversiy Liaocheg 5059 Chia address: happywgp008@63com bac: To our kowledge he exised decomposiio heorems for L -fuzzy opologies are oly available i he case ha he laices o be compleely diibuive complee laice I his paper cosiderig L o be a arbirary complee Heyig algebra a decomposiio heorem for (eriched) L -fuzzy opologies is preseed Said precisely i is proved ha a (eriched) L -fuzzy opology ca be represeed as a family of (aified) L -opologies wih some lef-coiuous codiio Key words: Eriched L -fuzzy opology aified L -opology decomposiio heorem Iroducio The oio of fuzzy opologies was firs iiiaed by Chag [] He defied a fuzzy opology o a se X as a crisp subse of I -power se I X Laer Gogue [4] geeralized his oio from I o arbirary complee laice L Thus his kid of fuzzy opology is ofe called Chag-Gogue L -opology or L -opology for shor I a compleely differe direcio HÖhle [5] defied a fuzzy opology o a se X as a fuzzy subse of he power se X Yig [] sudied HÖhle s fuzzy opology from a logical poi of view ad called i fuzzifyig opology Kubiak [7] ad Šosak [9] exeded HÖhle s defiiio ad defied a fuzzy opology o a se X as a fuzzy subse of he L - power se L X This kid of fuzzy opology is usually called L -fuzzy opology The decomposiio heorems for L -fuzzy opologies are impora coe i he heory of fuzzy opologies Whe L o be a compleely diibuive complee laice we obai he saisfyig resuls Tha is a L -fuzzy opology ca decompose a family of L - opologies wih some addiioal codiio [33] Bu o our regre hese decompose heorems ca o be geeralized o he more geeral laice coexs I his paper we Received February 03 This work is suppored by he research award fud of Shadog provice middle aged ad youg scieiss (BS00SF004) /5 $ Ieraioal Fuzzy Mahemaics Isiue Los geles
6 Guopeg Wag Ligqiag Li Guagwu Meg ad Qigxue Su shall prese a decomposiio heorem for L -fuzzy opology i he case of ha L o be complee Heyig algebra Said precisely we shall prove ha a (eriched) L -fuzzy opology ca decompose a family of (aified) L -opologies wih some lef-coiuous codiio The eriched L -fuzzy opology ad aified L -opology meas hey coai all he cosa-valued fuzzy ses Le L o be a complee laice ad ab Œ L The we say a is wedge below b (resp a is way below b ) i symbol a b (resp a b ) if for each (direced) subse BÕ L b B implies a d for some dœ B For a compleely diibuive complee laice L i possesses he followig properies: () a b implies ha here exiss cœ L such ha a c b; a b implies ha here exiss cœ L such ha a c b () a = { b: b a} = { b: b a} Le d be a oempy subse of L X he i is said o be a L -opology o X if d saisfies he followig codiios: (T) 0Œ d B Œd fi ŸB Œ d (T) (T3) " Œ T Œd fi ŒT Œd The pair ( X d ) is called a L -opological space The d is said o be aified if for ay aœ L we have a Œ d Le ( X d ) ad ( Y e ) be L -opological spaces The mappig f : X Æ Y is said o f l = l f Œd for ay l Œ e be a coiuous mappig from ( ) X d o ( Y e ) if We use he symbol L -Top o dee he caegory composed by L -opological space ad coiuous mappig X Le : L Æ L be a fuzzy subse of L X The we call a L -fuzzy opology o X L if saisfies he followig codiios: 0 = = (FT) X X (FT) ( l Ÿm) ( l) Ÿ ( m) (FT3) ( Œ Tl) ŒT ( l) The pair ( X ) is called a L -fuzzy opological space The is said o be " Œ eriched if i furher saisfies: (FT4) a L a = Le ( X d ) ad ( Y e ) be L -fuzzy opological spaces The mappig f : X Æ Y is s l l for ay said o be a coiuous mappig from ( ) L ( f L ) X d o ( Y e ) if Y l Œ L Le L -FTop deoe caegory whose objec are L -fuzzy opological spaces ad morphisms are coiuous mappig The mai coclusios
7 O (eriched) L -fuzzy opologies: Decomposiio Theorem 3 Le LT ( X ) (resp o a oempy se X The LT ( X ) (resp LFT X ) deoes all L -opologies (resp L -fuzzy opologies) LFT X ) cosiue a complee laice uder he iclusio order (ie poi-by-poi order) Defiiio Le X be a oempy se The he mappig G: LÆ LT ( X) is called a layer L -fuzzy opology if i saisfies he followig codiios: () a bfi G( b) Õ G ( a) () G ( 0) is discree L -opology The pair ( X G ) is called a layer L -fuzzy opological space Furher if each G ( a) is aified L -opology he G is called aified layer L -fuzzy opology layer (aified) L -fuzzy opological space ( X G ) is said o be lef coiuous if i addiioally saisfies he followig codiio: l ŒG a iff here exiss B L l ŒG b ad B a for ay bœ B (3) à such ha Le CLT ( X ) deoe all he layer L -fuzzy opology o X Le GŒ CLT ( X) XŒ CLT ( Y ) mappig f : X X G ad ( ) G ad ( a) mappig bewee layer L -fuzzy opologies ( ) bewee L -opological spaces X ( a) Y Æ Y is said o be a coiuous Y X if f is coiuous X for ay aœ L Deoe L -CTop as caegory cosiuig by all he above objecs ad coiuous mappig Proposiio Le ( X ) be a L -fuzzy opological space The for ay aœ L X he se a = { l ŒL : ( l) a} is a L -opology o X I addiio for he mappig X G : LÆ LT ( X) defied by " aœ L G ( a) = a = { l ŒL : ( l) a} we have G Œ CLT ( X) Proof I is sufficie o check ha G saisfies he codiios ()-(3) i Defiiio () Le ab Œ L a b By he defiiio of G we have G ( a) = a G ( b) = b The i follows ha b Õ a ad so G ( b) Õ G ( a) { } () I is easily see ha ( 0 ) X X G = = l ŒL : ( l) 0 = L ie ( 0) discree L -opology o X So he lef- (3) Necessiy Noe ha if ( a) coiuous codiio holds by akig B { a} Sufficiecy: Suppose B bœ L ( b) 0 l ŒG he l a = Œ ie a l G is he à L saisfies he codiio (3) of Defiiio For all l ŒG we have ( l) b he { : } ( a) G combiaio of he above we have G Œ CLT ( X) l ŒG by he defiiio of l b bœb a I follows ha
8 4 Guopeg Wag Ligqiag Li Guagwu Meg ad Qigxue Su Proposiio If he mappig f :( X ) ( Y s) s f : X G Æ Y G is coiuous i L -CTop Æ is coiuous i L -FTop he Proof Noe ha we eed o prove he followig iclusio " aœ L l s ( a) s ŒG ( a) cually for each l ŒG ( a) by he coiuiy of he mappig :( ) ( Y s ) we obai ha ( l f) s ( l) a ie l f Œa ŒG ( a) by G ( a) = a Proposiio 3 Le CLT ( X) is a L -fuzzy opology o X ŒG fil f f X Æ The i follows ha l f X GŒ The he mappig G : L Æ L defied by { } X G " l Œ L ( l) = aœl: l ŒG( a) G G Proof (FT) For ay aœ L he 0 XX ŒG ( a) hus ( X) = ( 0X) = X (FT) Le lm Œ L Because a bfig( b) Õ G ( a) he G G ( l) Ÿ ( m) = ( { a : l ŒG( a)}) Ÿ( { b: m ŒG() b }) = { aÿb: l ŒG( a) m ŒG( b) } { aÿb: lm ŒG( a G Ÿ b)} { aÿb: l Ÿm ŒG( aÿb) } = { c: l Ÿm ŒG ( c) } = ( l Ÿm) where he secod iequaliy holds because G( aÿ b) is a L -opology hus i is closed wr fiie iersecios X (FT3) For ay { l : ŒT} Õ L le a = G ( l) = ( { a : l ŒG( a) }) The ŒT ŒT for ay Œ T we ge { a : l ŒG( a) } a ad hus l ŒG ( a) by Defiiio (3) l ŒG a By he defiiio of Furhermore because ( a) G G we obai l a ( l ) ŒT G is a L -opology hus Ê ˆ Á = Ë ŒT Proposiio 4 If he mappig f :( X ) ( Y ) G X ( ) ( ) f : X Æ Y is coiuous i L -FTop l ŒT X Y Proof Suppose ( l) = b for ay l Œ L he l ŒX ( b) G X G f ŒG( b) he ( l f) b = ( l) f X Y G Æ X is coiuous i L -CTop he ie For f is coiuous so X : Æ is coiuous Proposiio 5 (Decomposiio heorem) Le GŒ CLT ( X) Œ LFT ( X) () G = () LFT ( X ) he G G = G ie here exiss a oe-o-oe correspodece bewee CLT X ad
9 O (eriched) L -fuzzy opologies: Decomposiio Theorem 5 Proof () For all { a L : a } { a L : X G l Œ L we have a} ( l) () Noe ha we oly eed o check G ( a) ( a) = l = Œ l ŒG = Œ l G = G for ay aœ L For oe hig G G G ( a) ( ) { l L: ( l) a} { l L: l ( a) } ( a) a ay l ( G G Œ ) oe has a a ( l) = { bœl: l ŒG( b) } G = = Œ Œ ŒG = G For aoher for ccordig o Defiiio (3) we have l ŒG ( a) combiaio of he above we have G ( a) ( a) Corollary Caegories L -CTop isomorphic o L -FTop (( X )) ( X G - F G = ) ; ( ) ( X ) ( X ) F = G G = G Remark Some decomposiio heorems have bee preseed i [33] i he case of L beig compleely diibuive laice I is easily see ha hese heorems rely o he properies () ad () posed by compleely diibuive laice Thus i seems ha hose decomposiio heorems ca o be exeded o he more geeral laice coexs I addiio we ca obai a similar decomposiio heorem for he eriched L -fuzzy opologies Refereces [] J damek H Herrlich ad G E Srecker bac ad cocree caegories Wiley New York (990) [] C L Chag Fuzzy opological spaces J Mah al ppl 4 (968) 8-90 [3] J M F Caegories isomorphic o L -FTOP Fuzzy Se ad Sysems 57 (006) [4] J Gogue The fuzzy ychooff heorem J Mah a ppl 43 (973) [5] U Hohle Probabilisic merizaio of fuzzy uiformiies Fuzzy Ses ad Sysems 8 (98) [6] U Hohle ad P Sosak Mahemaics of fuzzy ses Logic Topology ad measure heory boso: Kluwer academic publishers (999) [7] T Kubiak O fuzzy opologies PhD Thesis dam mickiewicz Poza Polad (985) [8] Y Liu ad M Luo Fuzzy opology World scieific publishig Sigapore (997) [9] P Sosak O a fuzzy opological ucure Suppl Red Cirecc Ma Palermo Ser II (985) [0] G Wag Theory of L -fuzzy opological spaces Shaaxi ormal uiversiy press Xi a (988) (i Chiese) [] M Yig ew approach o fuzzy opology (I) Fuzzy Ses ad Sysems 39 (99) [] D X Z O he relaioship bewee several basil caegory i fuzzy opology Quesios Mahemaicae 5 (00) [3] J Z F G S ad C Y Z O L -fuzzy opological spaces Fuzzy Ses ad Sysems 49 (005)
10
11 The Joural of Fuzzy Mahemaics Vol 3 No 05 7 Los geles O Pairwise Iuiioisic Fuzzy Resolvable (Irresolvable) Spaces K Biljaa Isiue of Mahemaics Faculy of Mahemaics ad Naural Scieces Uiversiy S Cyril ad Mehodius P O Skopje Macedoia address: madob006@yahoocom N Rajesh Deparme of Mahemaics Rajah Serfoji Gov College Thajavur Tamiladu Idia address: rajesh_opology@yahoocoi V Vijayabharahi Deparme of Mahemaics Naioal Isiue of Techology Tiruchi-Rappalli Tamiladu Idia address: vijayabharahi_v@yahoocom bac: I his paper we iroduce ad sudy he coceps of iuiioisic fuzzy resolvabiliy iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvabiliy ad iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvabiliy i iuiioisic fuzzy biopological spaces Key words ad phrases: Iuiioisic fuzzy biopology pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable spaces Iroducio fer he iroducio of fuzzy ses by Zadeh [5] here have bee a umber of geeralizaios of his fudameal cocep The oio of iuiioisic fuzzy ses iroduced by aassov [] is oe amog hem Usig he oio of iuiioisic fuzzy ses Coker [3] iroduced he oio of iuiioisic fuzzy opological spaces I his paper we iroduce ad sudy he coceps of iuiioisic fuzzy resolvabiliy iuiioisidc fuzzy irresolvabiliy ad iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvabiliy i iuiioisic fuzzy biopological sapces Prelimiaries Received pril /5 $ Ieraioal Fuzzy Mahemaics Isiue Los geles
12 8 K Biljaa N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi Defiiio [] Le be a oempy fixed se iuiioisic fuzzy se ( IFS for shor) is a objec havig he form = { x m( x) g ( x) : xœ X} where he fucios m : X Æ I ad g : X Æ I deoe respecively he degree of membership (amely m ( x ) ) ad he degree of o-membership (amely g ( x ) ) of each eleme xœ X o he se ad 0 m( x) + g ( x) for each xœ X Obviously every fuzzy se o a oempy se X is a IFS havig he form = x m x g x : xœ X { } Defiiio [] Le X be a oempy se ad le he IFSs ad B i he form = { x m( x) g ( x) : xœ X} ad mb g B be a arbirary family of IFSs i ( X ) The () B if ad oly if x X = { : Œ } Le { j : jœ J} B x x x x X " Œ [ m( x) mb( x) ad g ( x) mb( x) () - = x g ( x) m ( x) : xœ X ; { } { : } { m g : } (3) m g = x x x xœx ; j j j (4) j = x ( x) j x xœx ; j (5) = { x0 : xœ X} ad 0 { x0 : x X} = Œ ]; Defiiio 3 iuiioisic fuzzy opology [3] ( IFT for shor) o a oempy se X is a family of IFSs i X saisfyig he followig axioms: (i) 0Œ ; (ii) (iii) «Œ for every j Œ for ay { j : } Œ ; jœj Õ I his case he ordered pair ( X ) is called a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space ( IFTS for shor) ad each IFS i is kow as a iuiioisic fuzzy ope se ( IFOS for shor) i X The compleme of a iuiioisic fuzzy ope se is called a iuiioisic fuzzy closed se ( IFCS for shor) The family of all IFOSs (resp IFC X ) IFCSs ) of ( X ) is deoed by IFO( X ) (resp Defiiio 4 riple ( ) X where X is a oempy se ad are wo arbirary iuiioisic fuzzy opologies o X is called he iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space (for shor IFBTS ) { : } Defiiio 5 [3] Le ( X ) be a IFTS ad m g = x x x xœ X be a IFS i X The he iuiioisic fuzzy ierior ad he iuiioisic fuzzy closure
13 O Pairwise Iuiioisic Fuzzy Resolvable (Irresolvable) Spaces 9 of is defied by I ( ) = { G\ G is a IFOS i X ad GÕ} ad Cl ( ) { G\ G is a IFCS i X ad G } = Remark 6 For ay IFS i ( X ) we have Cl ( ) I ( ) ( - ) = - ( ) I Cl - = - 3 Pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable ad iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable spaces Defiiio 3 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is called a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable space if here exiss a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se l such ha - l is a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se ad a -fuzzy dese se m such ha - m is a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se Oherwise ( X ) is called a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Example 3 Le X { a b} = ad B be iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied by a b a b = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë Le = { } ad = { B } The ( ) 0 fuzzy resolvable space Example 33 Le X { a b} 0 a b a b B = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë 03 0 X is a pairwise iuiioisic = ad B be iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied by a b a b = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë a b 03 0 a 05 b B = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë 05 Le = { } ad = { B } The ( ) 0 fuzzy irresolvable space 0 X is a pairwise iuiioisic Proposiio 34 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Proposiio 34 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable space if ad oly if ( ) dese se l ad -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se Proof Le ( X ) X is a pairwise X is a pairwise X has a -iuiioisic fuzzy l such ha l - l be a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable space Suppose ha for all -iuiioisic fuzzy dese ses l i ad -iuiioisic fuzzy dese ses l j l / - l Tha is l l Cl l > Cl - l Now l i is a -iui- i j i > - j The ( i) ( j)
14 0 K Biljaa N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi ioisic fuzzy dese se i ( X ) implies ha Tha is ( l j ) j i Cl l i = Hece Cl ( l ) j > - Cl - π lso we have l > - l The Cl ( l ) > Cl ( - l ) Sice j l j is a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se i ( ) Cl l j = Hece > Cl ( - l ) i The we have Cl ( -l ) i π Hece we have Cl ( l ) i = Cl ( - l ) i π ad Cl ( l ) j = Cl ( -l ) j π which is a coradicio o ( X ) beig a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable space Therefore ( ) -iuiioisic X implies ha X has a fuzzy dese se l ad a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se l such ha l - l Coversely suppose ha ( X ) has a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se l ad a - iui-ioisic fuzzy dese se l such ha l - l We wa o show ha ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable space Suppose ha ( X ) i is a pairwise iui-ioisic fuzzy irresolvable space The for all -iuiioisic fuzzy dese ses l i i ( X ) we have Cl ( -l ) i π I paricular Cl ( -l ) π Tha is here exiss a -iuiioisic fuzzy closed se m i ( X ) such ha ( - l ) < m < The ( - m) < l < ad ( - m) < l - l implies ha ( m) l l m which is a coradicio o l beig a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se i ( ) Hece ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable space - < - fi < < X Proposiio 35 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space if ad oly if for a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se l I l π 0 ad for a -iuiioc fuzzy dese se l I l π 0 Proof Le l be a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se ad l a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se i ( X ) Sice ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space - l is o a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se ad - l is o a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se i ( X ) Tha is Cl ( -l ) π ad Cl ( -l ) π The we have -I ( l ) π ad -I ( l ) π Hece we have I ( l ) π 0 ad I ( l ) π 0 Coversely le l be a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se ad l a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se i ( X ) By hypohesis I ( l ) π 0 ad I ( l ) π 0 The -I ( l ) π ad -I ( l ) π implies ha Cl ( -l ) π ad Cl ( -l ) π Tha is Cl ( l ) = implies ha Cl -l π ad Cl ( l ) = implies ha Cl ( - l ) π Hece ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Proposiio 36 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy resolvable if ad oly if here exiss a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se
15 O Pairwise Iuiioisic Fuzzy Resolvable (Irresolvable) Spaces l ad -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se I l = 0 Proof The proof follows from Proposiio 35 l i ( X ) such ha Defiiio 37 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) I l = 0 ad X is called a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy submaximal if each -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se is a - iuiioisic fuzzy ope se ad each -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se is a - iuiioisic fuzzy ope se Example 38 Le X { a b} = ad B be iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied by = a b a b x Ê Á Ë Á Ë C = a b a b x Ê Á Ë Á Ë a b a b B = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë 03 0 a b a b D = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë 0 03 Á Ë Le = { D } ad = { BC } The ( ) 0 fuzzy submaximal space 0 X is a pair-wise iuiioisic Proposiio 39 If a iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy submaximal he i is pairwise iuiioiaic fuzzy irresolvable Proof Le ( ) a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se i ( ) dese se i ( X ) Sice ( ) X be a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy submaximal space Le l be X ad m be a -iuiioisic fuzzy X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy submaximal l is -iuiioisic fuzzy ope ad m is -iuiioisic fuzzy ope The we have I ( l) = l π 0 ad I m = m π 0 Hece by he Proposiio 35 ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Defiiio 30 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable if I Cl 0 iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l implies ha I ( l) π 0 ad ( ) -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m implies ha I 0 m π X is called a l π for ay - I Cl m π 0 for ay Proposiio 3 If a iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediariy irresolue he i is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable Proof Le l be a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se ad m be a -iuiioisic fuzzy Cl I Cl l = I = π 0 ad dese se i ( X ) Now ( l ) = implies ha
16 K Biljaa N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi Cl ( m ) = implies ha I Cl m = I 0 = π Sice ( ) iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable I ( l) π 0 ad for a -iuiioisic fuzzy dese se l I ( l) π 0 ad for a dese se mi ( m) π 0 Therefore by Proposiio 35 ( ) X is pairwise I m π 0 Hece -iuiioisic fuzzy X is a pairise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Remark 3 I is clear ha every pairwsie iuiiosiic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable space is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable However he coverse eed o be rue Example 33 Le X { a b} = ad B be iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied by a b a b = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë a b 03 0 a 06 b B = x Ê Á ˆ Ê ˆ Ë Á Ë 05 Le = { 0 } ad { 0 B} ( ) = The he iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable bu o pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable Proposiio 34 If a iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( X ) is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable ad if I ( l ) = 0 for a - iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l ad I ( m ) = 0 for a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m he I ( Cl ) 0 l = ad I ( ) Cl 0 m = Proof Le l π 0 be a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se i ( X ) such ha I ( l ) = 0 ad m π 0 be a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se i ( X ) such ha I ( m ) = 0 We claim ha I ( ) Cl 0 l = ad I ( ) Cl 0 m = Suppose ha I ( Cl ) l π 0 ad I ( ) Cl 0 m π Sice ( X ) is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable we have I ( Cl ) 0 l π for ay -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l implies ha I ( l) π 0 ad I ( ) Cl 0 m π for ay - iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m implies ha I ( m) π 0 which is a coradicio o our hypohesis Hece we mus have I Cl ( l ) = 0 ad I Cl ( m ) = 0 Defiiio 35 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is called a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced if for every ozero -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l ad a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m such ha l + m >
17 O Pairwise Iuiioisic Fuzzy Resolvable (Irresolvable) Spaces 3 Proposiio 36 iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced if ad oly if for ay ozero iuiioisic fuzzy se Cl Cl - l = l i ( X ) eiher ( l ) = or Proof Le ( X ) be a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced space The for every -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l ( π 0) ad a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m ( π 0) such ha l + m > Suppose ha for a iuiioisic fuzzy se g Cl ( g ) π ad Cl ( -g ) π Now Cl g π implies ha -Cl 0 g π The I - g π 0 Hece here exiss a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se d i ( X ) such ha d - g lso Cl ( -g ) π implies ha here exiss a -iuiioisic fuzzy closed se h i ( X ) such ha - g h < Hece d - g h implies ha d h Tha is d -( - h) The d + ( - h) Tha is for a ozero -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se d ad a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se - h i ( X ) we have d + ( - h) which is a coradicio o our hypohesis Hece we have eiher Cl ( g ) = or Cl - g = for a ozero iuiioisic fuzzy se g i ( X ) Coversely le Cl ( g ) = or Cl - g = for ay ozero iuiioisic fuzzy se g i ( X ) Suppose ha for every -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se ( 0) - iuiioisic fuzzy ope se ( 0) Cl ( l ) l π ad a m π such ha l + m / The l + m implies ha Cl - m = - m (sice m is a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se fi- m is X ) Hece Cl ( l) - m < (sice Cl l π Now Cl - l = - I l = -l π (sice l π 0 ) Cl -l π Therefore for he ozero iuiioisic fuzzy se - l -iuiioisic fuzzy closed se i m π 0 ) Tha is Tha is Cl ( -l) π ad Cl ( [ ]) l Hece for every -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l ( π 0) ad a ope se m ( π 0) such ha l + m > which implies ha ( ) - - π which is a coradicio o our hypohesis -iuiioisic fuzzy X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced space Proposiio 37 If a iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced he i is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable space Proof Le l be a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se such ha a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se such ha I ( Cl ) 0 fuzzy hpercoeced space ( ) I Cl l π 0 ad m m π i a pairwise iuiioisic X The for he ozero -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l ad for he -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m we have l + m > Now l > - m fi I ( l) > I ( - m) The I ( l) > -Cl ( m) 0 Tha is I ( l) π 0 lso
18 4 K Biljaa N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi l + m > - l The I ( m) > I ( ) Cl 0 - l = - l Tha is Therefore I ( Cl ) 0 l π for ay I ( l) π 0 ad I ( ) Cl 0 m π for ay ha I ( m) π 0 Hece ( ) irresolvable space I m π 0 -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se l implies ha -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m implies X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily Proposiio 38 If a iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced ad pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space he Cl ( l ) = implies ha Cl -l π for ay iuiioisic fuzzy se l i X Proof Sice ( ) Proposiio 36 eiher Cl ( l ) = or Cl l fuzzy se l i ( X ) Suppose Cl ( l ) = Now ( ) iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space implies ha I ( l) π 0 The l Hece Cl ( -l) π X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced space by - = for ay o zero iuiioisic X is a pairwise -I π Proposiio 39 If a iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced ad pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space he ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable space Proof Le l be a -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se ad m be a -iuiioisic fuzzy X Sice ( X ) is pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced Cl l = or Cl - l = Suppose Cl l = The Cl -l π Now Cl ( ) () l = fi I Cl I 0 l = π X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space implies ha I ( l ) X is iuiioisic fuzzy hyper-coeced by Proposiio 36 -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m Suppose Cl m = im- ope se i by Proposiio 36 eiher by Proposiio 38 ad π 0 gai sice ( ) eiher Cl ( m ) = or Cl - m = for he Cl ( m ) = The by Proposiio 38 we have Cl -m π Now plies ha I ( Cl ) () m = I 0 π ad ( ) irresolvable space implies ha I ( m) π 0 Hece I Cl 0 l π for ay ioisic fuzzy ope se l implies ha I ( l) π 0 ad I ( Cl ) 0 iuiioisic fuzzy ope se m implies ha I ( m) π 0 Therefore ( ) X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy -iui- m π for ay - X is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable space
19 O Pairwise Iuiioisic Fuzzy Resolvable (Irresolvable) Spaces 5 Proposiio 30 For ay iuiioisic fuzzy biopological space ( ) X he followig are equivale: () ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced ad pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space () For every ozero iuiioisic fuzzy se l i ( X ) eiher Cl I l = or Cl ( I ( )) - l = Proof () fi () Le ( X ) be a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced ad pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Suppose ha Cl ( I ) l π ad Cl ( I ( )) -l π The -Cl ( ) I 0 l π ad -Cl ( ) I 0 -l π Hece I ( Cl ( )) 0 -l π ad I ( ( [ ])) Cl 0 - -l π Tha is I ( ) Cl 0 -l π ad I ( Cl ) 0 l π Sice ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy ope herediarily irresolvable space we have I ( -l) π 0 ad I l π 0 The -Cl 0 l π ad -I ( l) π- 0= Tha is Cl l π ad Cl -l π which is a coradicio o ( X ) beig a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced space Hece we have eiher Cl ( I ) l = or Cl ( ) I - l = () fi () Le eiher Cl ( I ) l = or Cl ( ) I - l = for every ozero iuiioisic fuzzy se l i ( X ) The I ( l) π 0 or I -l π 0 Therefore for a -dese iuiioisic fuzzy se I ( l ) I ( ) I l = I l π 0 ad for a -dese iuiioisic fuzzy se I ( - l) I ( ) I - l = I - l π 0 Hece by Proposiio 35 ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy irresolvable space Now I ( l) l implies ha Cl I l Cl l The Cl l Tha is Cl ( l ) = lso I - l - l implies ha Cl I - l Cl - l The Cl ( - l) Tha is Cl - l = Therefore Cl l = or Cl - l = for ay iuiioisic fuzzy se l i ( X ) Hece by Proposiio 36 ( X ) is a pairwise iuiioisic fuzzy hypercoeced space Refereces [] K aassov Iuiioisic fuzzy ses Fuzzy Ses ad Sysems 0 (986) [] D Coker iroducio o fuzzy subspaces i iuiioisic fuzzy opological spaces J Fuzzy Mah 4 () (996) [3] D Coker iroducio o iuiioisic fuzzy opological spaces Fuzzy Ses ad Sysems 88 (997) 8-89 [4] D Coker ad M Demirci O iuiioisic fuzzy pois Noes o Iuiioisic Fuzzy Ses (995) 79-84
20 6 K Biljaa N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi [5] L Zadeh Fuzzy ses Iformaio ad Corol 8 (965)
21 The Joural of Fuzzy Mahemaics Vol 3 No 05 7 Los geles O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology N Gowrisakar 70/3 6B Kollupeai Sree M Chavady Thajavur-6300 Tamil-adu Idia address: gowrisakarj@gmailcom N Rajesh Deparme of Mahemaics Rajah Serfoji Gov College Thajavur Tamiladu Idia address: rajesh_opology@yahoocoi V Vijayabharahi Deparme of Mahemaics Naioal Isiue of Techology Tiruchi-Rapalli Tamiladu Idia address: vijayabharahi_v@yahoocom bac: The aim of his paper is o prese a commo approach allowig o obai familes of iuiioisic fuzzy ses i a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space Key words ad phrases: Geeralzied Iuiioisic fuzzy opology g -iuiioisic fuzzy ope se Iroducio fer he iroducio of fuzzy ses by Zadeh [7] here have bee a umber of geeralizaios of his fudameal cocep The oio of iuiioisic fuzzy ses iroduced by aassov [] is oe amog hem Usig he oio of iuiioisic fuzzy ses Coker [3] iroduced he oio of iuiioisic fuzzy opological spaces The aim of his paper is o prese a commo approach allowig o obai familes of iuiioisic fuzzy ses i a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space Prelimiaries Received pril /5 $ Ieraioal Fuzzy Mahemaics Isiue Los geles
22 8 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi Defiiio [] Le be a oempy fixed se iuiioisic fuzzy se ( IFS for shor) is a objec havig he form = { x m( x) g ( x) : xœ X} where he fucios m : X Æ I ad g : X Æ I deoe respecively he degree of membership (amely m ( x ) ) ad he degree of o-membership (amely g ( x ) ) of each eleme xœ X o he se ad 0 m( x) + g ( x) for each xœ X Obviously every fuzzy se o a oempy se X is a IFS havig he form = x m x g x : xœ X { } Defiiio [] Le X be a oempy se ad le he IFS ' s ad B i he form = { x m( x) g ( x) : xœ X} B { x mb( x) g B( x) : x X} a arbirary family of IFS s i ( X ) The () B if ad oly if " xœ X [ m( x) mb( x) ad g ( x) mb( x) () = x g ( x) m ( x) : xœ X ; { } { : } { m g : } (3) m g = x x x xœx ; j j j (4) j = x ( x) j x xœx ; j (5) X = { x0 : xœ X} ad 0 X { x0 : x X} = Œ Le { j : j J} = Œ ]; Œ be Defiiio 3 iuiioisic fuzzy opology [3] ( IFT for shor) o a oempy se X is a family of IFSs i X saisfyig he followig axioms: (i) 0 XX Œ ; (ii) (iii) «Œ for every j Œ for ay { j : } Œ ; jœj Õ I his case he ordered pair ( X ) is called a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space ( IFTS for shro) ad each IFS i is kow as a iuiioisic fuzzy ope se ( IFOS for shor) i X The compleme of a iuiioisic fuzzy ope se is called a iuiioisic fuzzy closed se ( IFCS for shro) The family of all IFOSs (resp IFC X ) IFCSs ) of ( X ) is deoed by IFO( X ) (resp { : } Defiiio 4 [3] Le ( X ) be a IFTS ad le m g = x x x xœ X be a IFS i X The he iuiioisic fuzzy ierior ad iuiioisic fuzzy closure of I = G\ G is a IFOS i X ad GÕ Cl = G\ G is defied by { } ad { is a IFCS i X ad G }
23 O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology 9 Remark 5 For ay IFS i ( X ) we have Cl( - ) = - I ( ) I ( - ) = - Cl( ) Defiiio 6 iuiioisic fuzzy poi [4] ( IFP for shor) wrie p ( a b ) is defied o be a IFS i X give by Ï Ô a b if x = p p( a b ) = Ì Ô Ó( 0 ) oherwise { } Le X be a oempy se ad = ll: X Æ[ 0] iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X Le g : F be he family of all F Æ F be a fucio such ha l m implies ha g ( l) g ( m) for every lmœf Tha is g is a moooic fucio defied o F by G ( F ) or simpily G We will defied he followig subclasses of G () For every a Œ [ 0] defie G a = { g ŒG g ( a) = a} where a is he iuiioisic fuzzy se defied by a ( x) = a for every xœ X () G = g ŒG g ( l) = g ( l) l ŒF { } { g l g l for every l } { g g l l for every } for every (3) G + = ŒG ŒF ad (4) G - = ŒG F If  is a collecio of some of he symbols - + ad a Œ [ 0] { g g i for every i } G = ŒG ŒG ŒÂ  he 3 Properies of g -iuiioisic fuzzy ope ses Defiiio 3 Le X be a oempy se g ŒG iuiioisic fuzzy se l ŒF is said o be g -iuiioisic fuzzy ope (for shor -IF l g l g ) if Theorem 3 Le X be a oempy se F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG The he followig hold () rbirary uio of g -IF ope ses is a g -IF ope se () is g -IF ope if ad oly if g ŒG (3) If g ŒG he every iuiioisic fuzzy se of he form g ( l ) lf is a ope se (4) If g ŒG + he every iuiioisic fuzzy subse is g -IF ope (5) g ŒG - he l is g -IF ope if ad oly if l = g ( l) g -IF
24 0 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi i (6) 0 is always g -IF ope se he for all Proof () Le { li : iœj} Õ F If li g ( li) for all iœ J ad li = l Œ J l g ( l ) fi g ( l ) g ( l) fi g ( l ) g ( l) fi l = l g ( l ) i i i () is -IF g ope if ad oly if g g ( g l ) g ( l) i if ad oly if g ŒG = by hypo- (3) If g ŒG he = for every l ŒF ad so g ( l ) is a (4) If g ŒG + he l g ( l) for every l ŒF is g -IF ope (5) Suppose g ŒG - If l is g -IF ope he l g ( l) ad so l g ( l) hesis If l = g ( l) he clearly l is g -IF ope i i g l g -IF ope se (6) Clear Le X be a oempy se ad F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X subfamily G of F is called geeralized iuiioisic fuzzy opology if 0 ŒG l a ŒD ŒG wheever la ŒG for every a ŒD ad { a } Remark 33 If g ŒG by Theorem 3 () i follows ha he family of all g -IF ope ses is a geeralized iuiioisic fuzzy opology g Defiiio 34 For l ŒF he g -ierior of l deoe by ig ( l ) is give by = { Œ } i l m m l Proposiio 35 Le g ŒG l ŒF ad ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space The for he g -ierior operaor I ii ( l) = I ( l) for all l ŒF The followig Theorem 36 gives all he properies of ig ( l ) Theorem 36 Le X be a oempy se F he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG The he followig properies hold () For every l ŒF ig ( l ) is he larges g -IF ope se coaied i l () l is g -IF ope if ad oly if i ( l) = l (3) ig ŒG 0- for every g ŒG (4) ig ŒG if ad oly if g ŒG (5) If g Œ l0 - he g = i (6) l is -IF g i ope if ad oly if g i l = l g Proof () By defiiio ad Theorem 3 () ig ( l ) is a g -IF ope se By defiiio ig ( l) l If b is g -IF ope such ha b l he b ig ( l) l ad so ig ( l ) is he larges g -IF ope se coaied i l
25 O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology () If a is -IF coverse par is clear i g 0 = 0 ad so g 0 g ope he by defiiio l i ( l) ad so (3) Clearly l ŒF ad so by () ig ( ig ( l) ) ig ( l) g (4) g ŒG if ad oly if g ŒG if ad oly if if ad oly if i g = if ad oly if ig ŒG (5) Le l ŒF Sice g ŒG g ( g ( l) ) g ( l) se Sice g - m l is -IF i ŒG By () g g i l = l by () The g i l is a g -IF ope se for every = ad so i ŒG By () i follows ha i g ŒG - g = if ad oly if is g -IF ope by () Therefore g = if ad oly if is g -IF ope by () Therefore g ŒG = Therefore g ( l ) is a ŒG g ( l) l Thus g ( l ) is a g -IF ope se such ha g ( l) g ope he m g ( m) g ( l) ad so by () g ( l) i ( l) g -IF ope l If g = i = g ad so g Remark 37 Le X be a oempy se ad ( X ) a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space Le I represe he ierior operaor ad C deoe he closure operaor of he X The iuiioisic fuzzy opological space () for g = I g -IF ope ses coicide wih iuiioisic fuzzy ope ses () for g = I Cl g -IF ope ses coicide wih iuiioisic fuzzy preope ses [5] (3) for g = Cl I g -IF ope ses coicide wih iuiioisic fuzzy semiope ses [5] (4) for g = I Cl I g -IF ope ses coicide wih iuiioisic fuzzy a -ses i [5] (5) for g = Cl I Cl g -IF ope ses coicide wih iuiioisic fuzzy semiprope ses i [5] (6) for g = I Cl Cl I g -IF ope ses coicide wih iuiioisic fuzzy g - ope ses [6] i l is he iui- Moreover ii Cl ( l ) is he iuiioisic fuzzy preierior [6] Cl I ioisic fuzzy semiierior [6] icl I Cl ( l ) is he iuiioisic fuzzy semipreierior [5] i ( l ) is he iuiioisic fuzzy a -ierior [5] ad i ( l) I Cl I fuzzy g ierior [6] of ( l) ŒF Theorem 38 Le g g ŒG () g g ŒG () If g g ŒG for all { 0 } Œ + - he g g ŒG is he iuiioisic I Cl Cl I Proof Oe ca easily prove his heorem by meas of he defiiios of G for all Œ { 0 + -}
26 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi Proposiio 39 Le i k ŒG ad for all l ŒF ik ( l) k ( l) () ad ik ( l ) kik ( l ) () If g is a composiio of aleraig facors i ad k he g ŒG excep for he case g = ki Proof Le l ŒF For g = ik we have kik ( l) kk ( l) = k ( l) by () Hece we obai ikik ( l) ik ( l) O he oherhad by () we ger ik ( l) kik ( l) implyig ha ik = iik ( l) ikik ( l) Hece we obai ikik ( l) = ik ha is g = ik ŒG For g = iki we have ( iki ( iki) )( l) = ikiki ( l) = ( ikik ) i ( l) Hece g = iki ŒG For g = kik we have ( kik )( kik )( l) = kikik ( l) = k ( ikik )( l) = kik ( l) implyig ha g = kik ŒG For g = kiki we have ( kiki)( kiki)( l) = k ( ikik ) iki ( l) = k ( ikik) i( l ) = kiki ( l ) Hece g = kiki ŒG For g = ikik we have ( ikik )( ikik )( l) = ikik ( l) Hece g = kiki ŒG O ca easily show ha g ŒG for ay g -composed of more ha four facors Proposiio 30 Le saisfied for all l ŒF The g = ki ŒG i k ŒG he iequaliy () ad i ( l) ki( l) () are Proof Le l ŒF If i ( l) ki( l) he i ( l) iki( l) implyig ha ki ( l) kiki ( l) If i () we replace l by i ( l ) he we ge iki ( l) ki ( l) Hece we obai kiki ( l ) ki ( l) Thus kiki ( l) ki ( l) ki ŒG = ha is Corollary 3 Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space If i ad k are chose as he ierior ad closure operaor respecively sice ICl ŒG ad () () ad () are saisfied by I ad Cl operaors ay composiio of aleraig Cl I facors Cl ad I is equal o oe of he mappigs I Cl I ( Cl ) I Cl( I ) or Cl I ( Cl ) by Proposiio 39 ad 30 Corollary 3 If i ŒG - ad ŒG i ad k is a eleme of G k + he ay composiio of aleraig facors Proof I follows from he fac ha iequaliies () () () are verified by i ad k Proposiio 33 Le g ŒG Every g -IF ope se is g -IF ope for all Œ N If g ŒG - he g -IF ope ses coicide wih g -IF ope ses Proof Le g ŒG ad l ŒF is a g -IF ope se The l g ( l) gg ( l) - g l g l Therefore l is a g -IF ope se For he case g ŒG - assume
27 O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology 3 ha l is a -IF l is a - g ope se The l g ( l) g ( l) g ( l) g ( l) g -IF ope se Hece Proposiio 34 Le i k ŒG - ad i k saisfy he iequaliy () The ay composiio of facors i ad k is a eleme of G - Moreover if g ŒG is a arbirary composiio of facors i ad k he () a g -IF ope se is a ik -IF ope se where g = ig k () a g -IF ope se is a iki -IF ope se where g = ig i (3) a g -IF ope se is a ki -IF ope se where g = kg i (4) a g -IF ope se is a kik -IF ope se where g = kg k The coverse implicaios hold if o facor i is immediaely followed by aoher facor i Proof Le l ŒF I ca be easily see ha if i k - i l i l ad k ( l) k ( l) ad by () we obai ik ( l) k ( l) k ( l) for all Œ N Sice for all Œ N - gg l = i i l ii l = i i ( l) = i ( l) = g ( l) we have g ŒG - for g = i Now le g = gkg where g g are ay (may be empy) composiios of gg l = g kg g kg l If ŒG he facors i ad k ha is g has a leas oe facor k The i is replaced isead of each i m facors ad k is replaced isead of k facors ad k is replaced isead of each ( ik ) p facors i he composiio kg g k we ge gg ( l ) = g kggkg ( l) gkg ( l) = g( l) Hece g ŒG - () Le g = ig k ad l ŒF is a g -IF ope se For a suiable m N l g l = m m - m - = = m Œ ig k l ik l ik ik l ikk l ik l ik l by similar subsiuios i he above maer Hece l is a ik -IF ope se Coversely suppose ha o facor i is immediaely followed by aoher facor i ad l is ik -IF ope se We have l ik ( l) implyig ha l ( ik) ( l) where is he umber of he facors k i g ad also we ge l ik ( l) k ( l) The by he iequaliy () ad l k ( l) we l g l Hece l is a g -IF ope se obai () Le g = ig i ad l is a -IF m - m - ik ik i l ik k i( l) ik m i( l) iki( l) m g ope se By () we obai l ig i( l) ( ik) i( l) = for a suiable mœ N Hece l is a iki -IF ope se Coversely if o facor i is immediaedly followed by aoher facor i ad l is iki -IF ope se he for mœ N m m m m+ l iki( l) fi ( ik) i( l) ( ik) iiki ( l) ( ik ) iki ( l) ( ik ) i ( l) he iequaliy () l iki( l) ( ik) i( l) g ( l) facors k i g Thus l is a g -IF ope se = Therefore by where is he umber of he
28 4 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi (3) Leg = kg i ad l is a g -IF ope se For m ad m N m m - m - ki l k ik i l kk i( l) k m i( l) ki( l) Œ we have lgl = = Hece l is a ki -IF ope se Coversely if o facor i is immediaely followed by aoher facor i ad l is ki -IF ope se he by he iequaliy () we have l ki( l) fi l ( ki) ( l) g ( l) where is he umber of facors k i g Hece l is a g -IF ope se (4) Le g = kg k ad l is a g -IF ope se For a suiable mœ N we have l m m - m - = m kg k l ki k l k ik ik l kk ik l k ik l kik l Thus l is a kik -IF ope se Coversely if o facor i is immediaely followed by aoher facor i ad l is -IF m m l kik l fi ki k l ki kik ope se he we ge m m+ kkik ( l) ( ki) kik ( l) ( ki) k ( l) - obai l kik ( l) ( ki) k ( l) g ( l) = for all mœ N Thus by he iequaliy () we where is he umber of facors k i g Hece l is a g -IF ope se Corollary 35 Le i ŒG - ad k ŒG - The he saemes of Proposiio 34 are valid Furhermore () Every iki -IF ope se is iki -IF ope se () Every iki -IF ope se is ki -IF ope se (3) Every ik -IF ope se is kik -IF ope se (4) Every ki -IF ope se is kik -IF ope se (5) Every kik -IF ope se is k -IF ope se (6) Every iki -IF ope se is iki -IF ope se (7) If l ŒF is a ik -IF ope se ad ki -IF ope se he i is iki -IF ope se Proof Le l ŒF I is clear from he fac ha he iequaliy () ad i ŒG - are saisfied uder hese codiios () Le l is a -IF l i ki l ki l implyig ha l is a iki ope se Hece ki -IF ope se If l ( ik) i( l) ik ( l) he l is a -IF l is a ik -IF ope se or ki -ope se he l ik( l) ikik( l) kik( l) or l ki( l) ( kik ) i ( l) kik ( l) respecively Tha is l is a -IF For he case l kik ( l) we ge l kik ( l) kk ( l) k ( l) k -IF ope se () Suppose ha l is a -IF ik ope se Providig ha kik ope se i boh cases implyig ha l is a ik ope se ad ki -ope se Hece we obai likl ik ( ki)( l) iki( l) Thus l is a iki -IF ope se Remark 36 If i ad k are choose as he ierior ad closure operaor respecively ad Remark 37 cosidered he we have he followig () ik -IF ope se eed o be a iki -IF ope se () ki -IF ope se eed o be a iki -IF ope se
29 O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology 5 (3) kik -IF ope se eed o be a ki -IF ope se (4) kik -IF ope se eed o be a ik -IF ope se (5) iuiioisic fuzzy se eed o be a kik -IF ope se (6) The ik -IF ope ses ad ki -ope ses are idepede oios X be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space We deoe he family of all Le ( ) g ŒG ( X) saisfyig he propery "Œ " l ŒF ; m g ( l) g ( m l) clear ha for a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space ( X ) Ÿ Ÿ by G 3 I i he ierior operaor I ŒG 3 O he oher had a closure operaor may o be a eleme of G 3 Proposiio 37 If g g ŒG 3 he g g ŒG3 Proof Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space 3 l ŒF Sice ( ) g ( m l) g g ŒG g g ŒG m Œ ad ( ) m Ÿ g g l = mÿ g g l g mÿ g l g g mÿ l = g Ÿ we have 3 Proposiio 38 Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space ad g ŒG 3 If m Œ ad l ŒF is a g -IF ope se he m Ÿ l is a g -IF ope se Proof Sice m m m Ÿ l is a g -IF ope se ad l g ( l) we have m l m g ( l) g ( m l) Ÿ Ÿ Ÿ Hece Proposiio 39 Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space If g ŒG 3 ad m is a iuiioisic fuzzy ope se such ha m g se Proof Le m Œ ad m g g -IF ope se he m is a g -IF ope Sice m m g g ( m ) g ( m) = Ÿ Ÿ = m is a Corollary 30 Le g ŒG 3 The every iuiioisic fuzzy ope se is a g -IF ope se Proof Le m a g -IF ope es Œ The m m g m g g ( m ) g ( m) = Ÿ = Ÿ Ÿ = Hece m is Corollary 3 Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space If g ŒG 3 ad m is a iuiioisic fuzzy ope se such ha here exiss a g -IF ope se l coaiig m he m is a g -IF ope se Proof Le l ŒF l g ( l) ad m l g -IF ope se from Proposiio 39 Sice m l g ( l) g m is a
30 6 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi Proposiio 3 If g ŒG 3 he i g ŒG 3 Proof Le m Œ ad l ŒF Sice m i g ( l) 38 ad m Ÿ ( l) mÿ l we have m i ( l) i ( m f) i g Proposiio 33 Le Ÿ is a g -IF ope se by Proposiio Ÿ g g Ÿ Hece we have i g ŒG 3 g ŒG if ad oly if I ( l) g ( l) for all l ŒF Proof Le l ŒF g ŒG 3 we have I ( l) g I ( l) I ( l) ( I Ÿ ) = ( I ) Sice I = g we ge g ŒG g l g l g l Ÿ = Ÿ = Remark 34 Cosider he fucio g cosisig of aleraig composiios of I ad g where g ŒG 3 I is clear ha g ŒG3 by Proposiio 37 Proposiio 35 Le g ŒG 3 ad g cosis of aleraig composiios of I ad g The g ŒG excep for he codiio g = g I Proof Sice he iequaliies () ad () are saisfied for he cases i = I ad k = g we have g ŒG by Proposiio 39 Remark 36 If g ŒG 3 he he case I g Ig g I Ig I g Ig g Ig I are eough o be cosidered Proposiio 37 If g ŒG 3 he () Ig I Ig g Ig () Ig I g Ig I g Ig (3) g Ig g (4) g I g Proof (3) ad (4) are clear from he fac ha g ŒG ad I ŒG - We eed o show Ig l g Ig l Ig l Ig g Ig l is a ha g -IF ope se by Proposiio 39 Hece we have Ig ( l) g Ig ( l) for all l ŒF Sice complees for he proofs of () ad () which Proposiio 38 Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space If g ŒG 3 he for all l ŒF I ( l) Ig I ( l) g I ( l) = g Ig I ( l) g ( l) Proof Le l ŒF If 3 I l g I l Sice he iequaliies () ad () are saisfied for he case k = g ad i = I we ge g I ŒG Thus we obai I I ( l) = I ( l) Ig I ( l) g I ( l) = g Ig I ( l) gg l = g l g ŒG he by Proposiio 39 we have
31 O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology 7 Corollary 39 If g ŒG 3 he he implicaios i he followig diagram hold: I g - IF ope ope Æ Ig I- IF ope g Ig - IF ope g I- IF ope g Ig I- IF ope Theorem 330 Le g ŒG - The for Œ N l ŒF is () Ig -IF ope Ig -IF ope () ( I ) (3) g I-IF ope Ig I-IF ope g I -IF ope g I-IF ope (4) g I g -IF ope g Ig -IF ope (5) Ig I-IF ope Ig ad g I-IF ope ÏIg - IF ope (6) Ì fig Ig - IF ope fi g - IF ope Óg I- IF ope Proof () () (3) ad (4) are clear from Proposiio 33 (5) ad (6) are obvious from Corollary 35 Theorem 33 Le ( X ) be a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space ad g ŒG 3 The he family O of all () If l Œ he l ŒO g -IF ope ses saisfies he followig properies: () If li ŒO for all iœ J he i Jfi ŒO Œ (3) If m Œ ad l ŒO he l Ÿf ŒO Coversely if O is a subse of a iuiioisic fuzzy opological spaces saisfyig he properies from () o (3) he here exiss a fucio g ŒG 03- such ha O cosiss of all g -IF ope ses Proof () () ad (3) are obvious from Corollary 30 Proposiio 3 () ad 38 respecively Coversely le O be a subse of a iuiioisic fuzzy opological space saisfyig he properies from () o (3) Defie g : Æ l Æ g l = m ŒO F F { g ŒG - Le m ŒO ad l ŒF Sice mÿg ( l) ŒO Ÿ Ÿ we have m Ÿ g ( l) g ( mÿ l) Hece g ŒG 3 Now i is g -IF ope ses Le l ŒO The we have g ( l ) g ope se Coversely l g ( l) he l = g ( l) ŒO f} by (3) ad m g ( l) m l m I is clear o see ha eough o show ha O cosiss of all = l implyig ha l is a -IF
32 8 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi Defiiio 33 Le X be a oempy se F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG iuiioisicd fuzzy subse l ŒF is said o be a g -IF closed se if - l is a g -IF ope se Defiiio 333 The iersecio of all g -IF closed ses coaiig l ŒF is called he g -closure of l ad is deoed by c g ( l ) The followig Theorem 334 gives some properies of g -IF closed se ad he g - closure operaor The easy proof of he heorem is omied Theorem 334 Le X be a oempy se F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG The he followig hold () is a g -IF closed se () rbirary iersecio of g -IF closed ses is a g -IF closed se (3) 0 is g -IF closed if ad oly if g ŒG (4) If g ŒG + he every l ŒF is g -IF closed (5) For every l ŒF c g ( l ) is he smalles g -IF closed subse coaiig l (6) l is -IF c g l = l g closed if ad oly if (7) c g ŒG + for every g ŒG (8) c g ŒG 0 if ad oly if g ŒG (9) l is i g -IF closed if ad oly if c g ( l) = l Le X be a oempy se F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG Defie g : F Æ F by g ( l) = -g ( - l) for every l ŒF The followig Theorem 335 gives properies of g Theorem 335 () g ŒG () ( g ) = g (3) g ŒG 0 if ad oly if g ŒG (4) g ŒG if ad oly if g ŒG 0 (5) g ŒG if ad oly if g ŒG (6) g ŒG + if ad oly if g ŒG - (7) ( i g ) = c g (8) ( c g ) = i g (9) i ( l) c ( l) g - = - for every l ŒF g
33 O Geeralized Iuiioisic Fuzzy Topology 9 (0) ( l) i ( l) c g - = - for every l ŒF g Proof () Le lmœf such ha l m The -g ( - l) -g ( - m) ad so g l g m Hece g ŒG () For l ŒF ( ( )) (3) g ŒG if ad oly if ( 0) 0 (4) The proof follows form (3) g l = -g -g - - l = g l g = if ad oly if g ŒG 0 (5) For l ŒF g ŒG if ad oly if ( g ) ( l) g ( l) ( - ( - )) = - if ad oly if g ( g ( l) ) g ( l) g g l g l g ( l ) if ad oly if g ŒG (6) For l ŒF g - ( g ( l) ) - l ŒG if ad oly if - if ad oly if l g ( l) - = - if ad oly if - - = - ad so if ad oly if g ŒG + g g l = g - l - l if ad oly if (7) ig ( - l) is he larges g -IF ope se coaied i - l Hece i g ( l) g closed se coaig l ad so i ( l) i ( l) c ( l) is he smalles -IF c g = i g (8) The proof follows from (7) i - l = c - l = - c l (9) For l ŒF from (8) g g g g g g = = Hece (0) The proof follows from (9) By Theorem 335 () above g ŒG ad so we ca defie he collecio of all g -IF ope ses ad g -IF closed ses Hece we ca defie he g -closure for a l ŒF The followig Theorem 336 gives a characerizaio of g -IF 337 below gives a propery of g -closure operaor c g closed ses ad Theorem Theorem 336 Le X be a oempy se F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG The l is a -IF g l l g closed se if ad oly if Proof l is a g -IF closed se if ad if - l is a g -IF ope se if ad oly l g l l g l g l l ( ) if ad oly if - - if ad oly if Theorem 337 Le X be a oempy se F be he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g ŒG + The g = c g Proof Le l ŒF Sice g g l g l is a g -IF closed se Sice g ŒG + l g ( l) g ŒG = Therefore by Theorem 336 g ( l ) Thus g ( l ) is a g -IF closed se such
34 30 N Gowrisakar N Rajesh ad V Vijayabharahi ha l g ( l) If m is -IF so by Theorem 334 (5) g ( l) ( l) g closed se such ha l m = ad so g = c g c g he l g ( l) g ( m) ad Theorem 338 Le X be a oempy se F he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad g g ŒG The he followig hold () g g ŒG () If i (3) ( g g ) g g ŒG for i s { } gg = Œ - he g g ŒG i Proof () Le l m ŒF such ha l m Sice g ( g l ) g( g ( m) ) Therefore g g ŒG () The proof is clear g ŒG g ŒG g ( l) g ( m) Sice (3) For l ŒF ( gg ) ( l) gg ( l) g ( g ( l) ) ( - ) = ( ) Therefore ( g g ) = gg g g l g g l = - - = = - Theorem 339 Le X be a oempy se F he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X ad i k ŒG Suppose ik ( l) k ( l) ad ik ( l) kik ( l) for every l ŒF If g is a produc of aleraig facors i ad k excep g = ki he g ŒG I addiio if i ( l) ki( l) for every l ŒF ad g = ki he g ŒG Proof i k ŒG implies ha i k ŒG ad so by Theorem 338 () g ŒG Le l ŒF By hypohesis ik ( l) k ( l) ad so kik ( l) kk ( l) = k ( l) Therefore ikik ( l ) ik ( l ) gai by hypohesis ik ( l) kik ( l) ad so iik ikik ( l) which implies ha ik l ikik l ikik l = ik l ad so ikik ik iki iki = Hece = Furher ( ikiki) = ( ikik ) i = iki ( kik )( kik ) = kikik = ( k ) ikik = kik ( ikik ) = ( ik )( ik ) = ikik ( kiki)( kiki) = k ( ikik ) iki = k ( ik ) iki = ik ( ikik ) i = kik Thus he saeme is valid for hree or four facors Sice ikik = ik a aleraig produc of 5 facors is equal o aoher produc of - facors ad he saeme holds for i Suppose g = ki Sice by hypohesis ik ( l) k ( l) we have iki ( l) ki ( l) ad so kiki ( l) ki ( l) Sice i ( l) ki( l) by hypohesis we have i ( l) iki( l) ad so ki ( l) kiki ( l) Hece i follows ha ki = kki Corollary 340 Le X be a oempy se F he family of all iuiioisic fuzzy ses defied o X i ŒG - ad k ŒG + If g is a produc of facors of i ad k he g ŒG 4 O g -iuiioisic fuzzy semiope ses
FIXED FUZZY POINT THEOREMS IN FUZZY METRIC SPACE
 Mohia & Samaa, Vol. 1, No. II, December, 016, pp 34-49. ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS FIED FUZZY POINT THEOREMS IN FUZZY METRIC SPACE 1 Mohia S. *, Samaa T. K. 1 Deparme of Mahemaics, Sudhir Memorial
Mohia & Samaa, Vol. 1, No. II, December, 016, pp 34-49. ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS FIED FUZZY POINT THEOREMS IN FUZZY METRIC SPACE 1 Mohia S. *, Samaa T. K. 1 Deparme of Mahemaics, Sudhir Memorial
Some Properties of Semi-E-Convex Function and Semi-E-Convex Programming*
 The Eighh Ieraioal Symposium o Operaios esearch ad Is Applicaios (ISOA 9) Zhagjiajie Chia Sepember 2 22 29 Copyrigh 29 OSC & APOC pp 33 39 Some Properies of Semi-E-Covex Fucio ad Semi-E-Covex Programmig*
The Eighh Ieraioal Symposium o Operaios esearch ad Is Applicaios (ISOA 9) Zhagjiajie Chia Sepember 2 22 29 Copyrigh 29 OSC & APOC pp 33 39 Some Properies of Semi-E-Covex Fucio ad Semi-E-Covex Programmig*
Comparison between Fourier and Corrected Fourier Series Methods
 Malaysia Joural of Mahemaical Scieces 7(): 73-8 (13) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES Joural homepage: hp://eispem.upm.edu.my/oural Compariso bewee Fourier ad Correced Fourier Series Mehods 1
Malaysia Joural of Mahemaical Scieces 7(): 73-8 (13) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES Joural homepage: hp://eispem.upm.edu.my/oural Compariso bewee Fourier ad Correced Fourier Series Mehods 1
An interesting result about subset sums. Nitu Kitchloo. Lior Pachter. November 27, Abstract
 A ieresig resul abou subse sums Niu Kichloo Lior Pacher November 27, 1993 Absrac We cosider he problem of deermiig he umber of subses B f1; 2; : : :; g such ha P b2b b k mod, where k is a residue class
A ieresig resul abou subse sums Niu Kichloo Lior Pacher November 27, 1993 Absrac We cosider he problem of deermiig he umber of subses B f1; 2; : : :; g such ha P b2b b k mod, where k is a residue class
Extremal graph theory II: K t and K t,t
 Exremal graph heory II: K ad K, Lecure Graph Theory 06 EPFL Frak de Zeeuw I his lecure, we geeralize he wo mai heorems from he las lecure, from riagles K 3 o complee graphs K, ad from squares K, o complee
Exremal graph heory II: K ad K, Lecure Graph Theory 06 EPFL Frak de Zeeuw I his lecure, we geeralize he wo mai heorems from he las lecure, from riagles K 3 o complee graphs K, ad from squares K, o complee
The analysis of the method on the one variable function s limit Ke Wu
 Ieraioal Coferece o Advaces i Mechaical Egieerig ad Idusrial Iformaics (AMEII 5) The aalysis of he mehod o he oe variable fucio s i Ke Wu Deparme of Mahemaics ad Saisics Zaozhuag Uiversiy Zaozhuag 776
Ieraioal Coferece o Advaces i Mechaical Egieerig ad Idusrial Iformaics (AMEII 5) The aalysis of he mehod o he oe variable fucio s i Ke Wu Deparme of Mahemaics ad Saisics Zaozhuag Uiversiy Zaozhuag 776
Common Fixed Point Theorem in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metric Space via Compatible Mappings of Type (K)
 Ieraioal Joural of ahemaics Treds ad Techology (IJTT) Volume 35 umber 4- July 016 Commo Fixed Poi Theorem i Iuiioisic Fuzzy eric Sace via Comaible aigs of Tye (K) Dr. Ramaa Reddy Assisa Professor De. of
Ieraioal Joural of ahemaics Treds ad Techology (IJTT) Volume 35 umber 4- July 016 Commo Fixed Poi Theorem i Iuiioisic Fuzzy eric Sace via Comaible aigs of Tye (K) Dr. Ramaa Reddy Assisa Professor De. of
Ideal Amplifier/Attenuator. Memoryless. where k is some real constant. Integrator. System with memory
 Liear Time-Ivaria Sysems (LTI Sysems) Oulie Basic Sysem Properies Memoryless ad sysems wih memory (saic or dyamic) Causal ad o-causal sysems (Causaliy) Liear ad o-liear sysems (Lieariy) Sable ad o-sable
Liear Time-Ivaria Sysems (LTI Sysems) Oulie Basic Sysem Properies Memoryless ad sysems wih memory (saic or dyamic) Causal ad o-causal sysems (Causaliy) Liear ad o-liear sysems (Lieariy) Sable ad o-sable
1 Notes on Little s Law (l = λw)
 Copyrigh c 26 by Karl Sigma Noes o Lile s Law (l λw) We cosider here a famous ad very useful law i queueig heory called Lile s Law, also kow as l λw, which assers ha he ime average umber of cusomers i
Copyrigh c 26 by Karl Sigma Noes o Lile s Law (l λw) We cosider here a famous ad very useful law i queueig heory called Lile s Law, also kow as l λw, which assers ha he ime average umber of cusomers i
ODEs II, Supplement to Lectures 6 & 7: The Jordan Normal Form: Solving Autonomous, Homogeneous Linear Systems. April 2, 2003
 ODEs II, Suppleme o Lecures 6 & 7: The Jorda Normal Form: Solvig Auoomous, Homogeeous Liear Sysems April 2, 23 I his oe, we describe he Jorda ormal form of a marix ad use i o solve a geeral homogeeous
ODEs II, Suppleme o Lecures 6 & 7: The Jorda Normal Form: Solvig Auoomous, Homogeeous Liear Sysems April 2, 23 I his oe, we describe he Jorda ormal form of a marix ad use i o solve a geeral homogeeous
EXISTENCE THEORY OF RANDOM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS D. S. Palimkar
 Ieraioal Joural of Scieific ad Research Publicaios, Volue 2, Issue 7, July 22 ISSN 225-353 EXISTENCE THEORY OF RANDOM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS D S Palikar Depare of Maheaics, Vasarao Naik College, Naded
Ieraioal Joural of Scieific ad Research Publicaios, Volue 2, Issue 7, July 22 ISSN 225-353 EXISTENCE THEORY OF RANDOM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS D S Palikar Depare of Maheaics, Vasarao Naik College, Naded
A New Functional Dependency in a Vague Relational Database Model
 Ieraioal Joural of Compuer pplicaios (0975 8887 olume 39 No8, February 01 New Fucioal Depedecy i a ague Relaioal Daabase Model Jaydev Mishra College of Egieerig ad Maageme, Kolagha Wes egal, Idia Sharmisha
Ieraioal Joural of Compuer pplicaios (0975 8887 olume 39 No8, February 01 New Fucioal Depedecy i a ague Relaioal Daabase Model Jaydev Mishra College of Egieerig ad Maageme, Kolagha Wes egal, Idia Sharmisha
BEST LINEAR FORECASTS VS. BEST POSSIBLE FORECASTS
 BEST LINEAR FORECASTS VS. BEST POSSIBLE FORECASTS Opimal ear Forecasig Alhough we have o meioed hem explicily so far i he course, here are geeral saisical priciples for derivig he bes liear forecas, ad
BEST LINEAR FORECASTS VS. BEST POSSIBLE FORECASTS Opimal ear Forecasig Alhough we have o meioed hem explicily so far i he course, here are geeral saisical priciples for derivig he bes liear forecas, ad
Online Supplement to Reactive Tabu Search in a Team-Learning Problem
 Olie Suppleme o Reacive abu Search i a eam-learig Problem Yueli She School of Ieraioal Busiess Admiisraio, Shaghai Uiversiy of Fiace ad Ecoomics, Shaghai 00433, People s Republic of Chia, she.yueli@mail.shufe.edu.c
Olie Suppleme o Reacive abu Search i a eam-learig Problem Yueli She School of Ieraioal Busiess Admiisraio, Shaghai Uiversiy of Fiace ad Ecoomics, Shaghai 00433, People s Republic of Chia, she.yueli@mail.shufe.edu.c
A Note on Random k-sat for Moderately Growing k
 A Noe o Radom k-sat for Moderaely Growig k Ju Liu LMIB ad School of Mahemaics ad Sysems Sciece, Beihag Uiversiy, Beijig, 100191, P.R. Chia juliu@smss.buaa.edu.c Zogsheg Gao LMIB ad School of Mahemaics
A Noe o Radom k-sat for Moderaely Growig k Ju Liu LMIB ad School of Mahemaics ad Sysems Sciece, Beihag Uiversiy, Beijig, 100191, P.R. Chia juliu@smss.buaa.edu.c Zogsheg Gao LMIB ad School of Mahemaics
The Central Limit Theorem
 The Ceral Limi Theorem The ceral i heorem is oe of he mos impora heorems i probabiliy heory. While here a variey of forms of he ceral i heorem, he mos geeral form saes ha give a sufficiely large umber,
The Ceral Limi Theorem The ceral i heorem is oe of he mos impora heorems i probabiliy heory. While here a variey of forms of he ceral i heorem, he mos geeral form saes ha give a sufficiely large umber,
Some Newton s Type Inequalities for Geometrically Relative Convex Functions ABSTRACT. 1. Introduction
 Malaysia Joural of Mahemaical Scieces 9(): 49-5 (5) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES Joural homepage: hp://eispem.upm.edu.my/joural Some Newo s Type Ieualiies for Geomerically Relaive Covex Fucios
Malaysia Joural of Mahemaical Scieces 9(): 49-5 (5) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES Joural homepage: hp://eispem.upm.edu.my/joural Some Newo s Type Ieualiies for Geomerically Relaive Covex Fucios
A note on deviation inequalities on {0, 1} n. by Julio Bernués*
 A oe o deviaio iequaliies o {0, 1}. by Julio Berués* Deparameo de Maemáicas. Faculad de Ciecias Uiversidad de Zaragoza 50009-Zaragoza (Spai) I. Iroducio. Le f: (Ω, Σ, ) IR be a radom variable. Roughly
A oe o deviaio iequaliies o {0, 1}. by Julio Berués* Deparameo de Maemáicas. Faculad de Ciecias Uiversidad de Zaragoza 50009-Zaragoza (Spai) I. Iroducio. Le f: (Ω, Σ, ) IR be a radom variable. Roughly
Calculus Limits. Limit of a function.. 1. One-Sided Limits...1. Infinite limits 2. Vertical Asymptotes...3. Calculating Limits Using the Limit Laws.
 Limi of a fucio.. Oe-Sided..... Ifiie limis Verical Asympoes... Calculaig Usig he Limi Laws.5 The Squeeze Theorem.6 The Precise Defiiio of a Limi......7 Coiuiy.8 Iermediae Value Theorem..9 Refereces..
Limi of a fucio.. Oe-Sided..... Ifiie limis Verical Asympoes... Calculaig Usig he Limi Laws.5 The Squeeze Theorem.6 The Precise Defiiio of a Limi......7 Coiuiy.8 Iermediae Value Theorem..9 Refereces..
On The Eneström-Kakeya Theorem
 Applied Mahemaics,, 3, 555-56 doi:436/am673 Published Olie December (hp://wwwscirporg/oural/am) O The Eesröm-Kakeya Theorem Absrac Gulsha Sigh, Wali Mohammad Shah Bharahiar Uiversiy, Coimbaore, Idia Deparme
Applied Mahemaics,, 3, 555-56 doi:436/am673 Published Olie December (hp://wwwscirporg/oural/am) O The Eesröm-Kakeya Theorem Absrac Gulsha Sigh, Wali Mohammad Shah Bharahiar Uiversiy, Coimbaore, Idia Deparme
CLOSED FORM EVALUATION OF RESTRICTED SUMS CONTAINING SQUARES OF FIBONOMIAL COEFFICIENTS
 PB Sci Bull, Series A, Vol 78, Iss 4, 2016 ISSN 1223-7027 CLOSED FORM EVALATION OF RESTRICTED SMS CONTAINING SQARES OF FIBONOMIAL COEFFICIENTS Emrah Kılıc 1, Helmu Prodiger 2 We give a sysemaic approach
PB Sci Bull, Series A, Vol 78, Iss 4, 2016 ISSN 1223-7027 CLOSED FORM EVALATION OF RESTRICTED SMS CONTAINING SQARES OF FIBONOMIAL COEFFICIENTS Emrah Kılıc 1, Helmu Prodiger 2 We give a sysemaic approach
Dynamic h-index: the Hirsch index in function of time
 Dyamic h-idex: he Hirsch idex i fucio of ime by L. Egghe Uiversiei Hassel (UHassel), Campus Diepebeek, Agoralaa, B-3590 Diepebeek, Belgium ad Uiversiei Awerpe (UA), Campus Drie Eike, Uiversieisplei, B-260
Dyamic h-idex: he Hirsch idex i fucio of ime by L. Egghe Uiversiei Hassel (UHassel), Campus Diepebeek, Agoralaa, B-3590 Diepebeek, Belgium ad Uiversiei Awerpe (UA), Campus Drie Eike, Uiversieisplei, B-260
Big O Notation for Time Complexity of Algorithms
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of he Ciy Uiversiy of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CSI 33 Secio E01 Hadou 1 Fall 2014 Sepember 3, 2014 Big O Noaio for Time Complexiy of Algorihms Time
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of he Ciy Uiversiy of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CSI 33 Secio E01 Hadou 1 Fall 2014 Sepember 3, 2014 Big O Noaio for Time Complexiy of Algorihms Time
Fermat Numbers in Multinomial Coefficients
 1 3 47 6 3 11 Joural of Ieger Sequeces, Vol. 17 (014, Aricle 14.3. Ferma Numbers i Muliomial Coefficies Shae Cher Deparme of Mahemaics Zhejiag Uiversiy Hagzhou, 31007 Chia chexiaohag9@gmail.com Absrac
1 3 47 6 3 11 Joural of Ieger Sequeces, Vol. 17 (014, Aricle 14.3. Ferma Numbers i Muliomial Coefficies Shae Cher Deparme of Mahemaics Zhejiag Uiversiy Hagzhou, 31007 Chia chexiaohag9@gmail.com Absrac
Math 6710, Fall 2016 Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 67, Fall 6 Fial Exam Soluios. Firs, a sude poied ou a suble hig: if P (X i p >, he X + + X (X + + X / ( evaluaes o / wih probabiliy p >. This is roublesome because a radom variable is supposed o be
Mah 67, Fall 6 Fial Exam Soluios. Firs, a sude poied ou a suble hig: if P (X i p >, he X + + X (X + + X / ( evaluaes o / wih probabiliy p >. This is roublesome because a radom variable is supposed o be
FORBIDDING HAMILTON CYCLES IN UNIFORM HYPERGRAPHS
 FORBIDDING HAMILTON CYCLES IN UNIFORM HYPERGRAPHS JIE HAN AND YI ZHAO Absrac For d l
FORBIDDING HAMILTON CYCLES IN UNIFORM HYPERGRAPHS JIE HAN AND YI ZHAO Absrac For d l
STK4080/9080 Survival and event history analysis
 STK48/98 Survival ad eve hisory aalysis Marigales i discree ime Cosider a sochasic process The process M is a marigale if Lecure 3: Marigales ad oher sochasic processes i discree ime (recap) where (formally
STK48/98 Survival ad eve hisory aalysis Marigales i discree ime Cosider a sochasic process The process M is a marigale if Lecure 3: Marigales ad oher sochasic processes i discree ime (recap) where (formally
A TAUBERIAN THEOREM FOR THE WEIGHTED MEAN METHOD OF SUMMABILITY
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 78, Iss. 2, 206 ISSN 223-7027 A TAUBERIAN THEOREM FOR THE WEIGHTED MEAN METHOD OF SUMMABILITY İbrahim Çaak I his paper we obai a Tauberia codiio i erms of he weighed classical
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 78, Iss. 2, 206 ISSN 223-7027 A TAUBERIAN THEOREM FOR THE WEIGHTED MEAN METHOD OF SUMMABILITY İbrahim Çaak I his paper we obai a Tauberia codiio i erms of he weighed classical
TAKA KUSANO. laculty of Science Hrosh tlnlersty 1982) (n-l) + + Pn(t)x 0, (n-l) + + Pn(t)Y f(t,y), XR R are continuous functions.
 Iera. J. Mah. & Mah. Si. Vol. 6 No. 3 (1983) 559-566 559 ASYMPTOTIC RELATIOHIPS BETWEEN TWO HIGHER ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS TAKA KUSANO laculy of Sciece Hrosh llersy 1982) ABSTRACT. Some asympoic
Iera. J. Mah. & Mah. Si. Vol. 6 No. 3 (1983) 559-566 559 ASYMPTOTIC RELATIOHIPS BETWEEN TWO HIGHER ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS TAKA KUSANO laculy of Sciece Hrosh llersy 1982) ABSTRACT. Some asympoic
COS 522: Complexity Theory : Boaz Barak Handout 10: Parallel Repetition Lemma
 COS 522: Complexiy Theory : Boaz Barak Hadou 0: Parallel Repeiio Lemma Readig: () A Parallel Repeiio Theorem / Ra Raz (available o his websie) (2) Parallel Repeiio: Simplificaios ad he No-Sigallig Case
COS 522: Complexiy Theory : Boaz Barak Hadou 0: Parallel Repeiio Lemma Readig: () A Parallel Repeiio Theorem / Ra Raz (available o his websie) (2) Parallel Repeiio: Simplificaios ad he No-Sigallig Case
Research Article Generalized Equilibrium Problem with Mixed Relaxed Monotonicity
 e Scieific World Joural, Aricle ID 807324, 4 pages hp://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/807324 Research Aricle Geeralized Equilibrium Problem wih Mixed Relaxed Moooiciy Haider Abbas Rizvi, 1 Adem KJlJçma, 2 ad
e Scieific World Joural, Aricle ID 807324, 4 pages hp://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/807324 Research Aricle Geeralized Equilibrium Problem wih Mixed Relaxed Moooiciy Haider Abbas Rizvi, 1 Adem KJlJçma, 2 ad
λiv Av = 0 or ( λi Av ) = 0. In order for a vector v to be an eigenvector, it must be in the kernel of λi
 Liear lgebra Lecure #9 Noes This week s lecure focuses o wha migh be called he srucural aalysis of liear rasformaios Wha are he irisic properies of a liear rasformaio? re here ay fixed direcios? The discussio
Liear lgebra Lecure #9 Noes This week s lecure focuses o wha migh be called he srucural aalysis of liear rasformaios Wha are he irisic properies of a liear rasformaio? re here ay fixed direcios? The discussio
Approximately Quasi Inner Generalized Dynamics on Modules. { } t t R
 Joural of Scieces, Islamic epublic of Ira 23(3): 245-25 (22) Uiversiy of Tehra, ISSN 6-4 hp://jscieces.u.ac.ir Approximaely Quasi Ier Geeralized Dyamics o Modules M. Mosadeq, M. Hassai, ad A. Nikam Deparme
Joural of Scieces, Islamic epublic of Ira 23(3): 245-25 (22) Uiversiy of Tehra, ISSN 6-4 hp://jscieces.u.ac.ir Approximaely Quasi Ier Geeralized Dyamics o Modules M. Mosadeq, M. Hassai, ad A. Nikam Deparme
Fuzzy Dynamic Equations on Time Scales under Generalized Delta Derivative via Contractive-like Mapping Principles
 Idia Joural of Sciece ad echology Vol 9(5) DOI: 7485/ijs/6/v9i5/8533 July 6 ISSN (Pri) : 974-6846 ISSN (Olie) : 974-5645 Fuzzy Dyamic Euaios o ime Scales uder Geeralized Dela Derivaive via Coracive-lie
Idia Joural of Sciece ad echology Vol 9(5) DOI: 7485/ijs/6/v9i5/8533 July 6 ISSN (Pri) : 974-6846 ISSN (Olie) : 974-5645 Fuzzy Dyamic Euaios o ime Scales uder Geeralized Dela Derivaive via Coracive-lie
L-functions and Class Numbers
 L-fucios ad Class Numbers Sude Number Theory Semiar S. M.-C. 4 Sepember 05 We follow Romyar Sharifi s Noes o Iwasawa Theory, wih some help from Neukirch s Algebraic Number Theory. L-fucios of Dirichle
L-fucios ad Class Numbers Sude Number Theory Semiar S. M.-C. 4 Sepember 05 We follow Romyar Sharifi s Noes o Iwasawa Theory, wih some help from Neukirch s Algebraic Number Theory. L-fucios of Dirichle
AN EXTENSION OF LUCAS THEOREM. Hong Hu and Zhi-Wei Sun. (Communicated by David E. Rohrlich)
 Proc. Amer. Mah. Soc. 19(001, o. 1, 3471 3478. AN EXTENSION OF LUCAS THEOREM Hog Hu ad Zhi-Wei Su (Commuicaed by David E. Rohrlich Absrac. Le p be a prime. A famous heorem of Lucas saes ha p+s p+ ( s (mod
Proc. Amer. Mah. Soc. 19(001, o. 1, 3471 3478. AN EXTENSION OF LUCAS THEOREM Hog Hu ad Zhi-Wei Su (Commuicaed by David E. Rohrlich Absrac. Le p be a prime. A famous heorem of Lucas saes ha p+s p+ ( s (mod
Lecture 15 First Properties of the Brownian Motion
 Lecure 15: Firs Properies 1 of 8 Course: Theory of Probabiliy II Term: Sprig 2015 Isrucor: Gorda Zikovic Lecure 15 Firs Properies of he Browia Moio This lecure deals wih some of he more immediae properies
Lecure 15: Firs Properies 1 of 8 Course: Theory of Probabiliy II Term: Sprig 2015 Isrucor: Gorda Zikovic Lecure 15 Firs Properies of he Browia Moio This lecure deals wih some of he more immediae properies
Completeness of Random Exponential System in Half-strip
 23-24 Prepri for School of Mahemaical Scieces, Beijig Normal Uiversiy Compleeess of Radom Expoeial Sysem i Half-srip Gao ZhiQiag, Deg GuaTie ad Ke SiYu School of Mahemaical Scieces, Laboraory of Mahemaics
23-24 Prepri for School of Mahemaical Scieces, Beijig Normal Uiversiy Compleeess of Radom Expoeial Sysem i Half-srip Gao ZhiQiag, Deg GuaTie ad Ke SiYu School of Mahemaical Scieces, Laboraory of Mahemaics
Moment Generating Function
 1 Mome Geeraig Fucio m h mome m m m E[ ] x f ( x) dx m h ceral mome m m m E[( ) ] ( ) ( x ) f ( x) dx Mome Geeraig Fucio For a real, M () E[ e ] e k x k e p ( x ) discree x k e f ( x) dx coiuous Example
1 Mome Geeraig Fucio m h mome m m m E[ ] x f ( x) dx m h ceral mome m m m E[( ) ] ( ) ( x ) f ( x) dx Mome Geeraig Fucio For a real, M () E[ e ] e k x k e p ( x ) discree x k e f ( x) dx coiuous Example
The Connection between the Basel Problem and a Special Integral
 Applied Mahemaics 4 5 57-584 Published Olie Sepember 4 i SciRes hp://wwwscirporg/joural/am hp://ddoiorg/436/am45646 The Coecio bewee he Basel Problem ad a Special Iegral Haifeg Xu Jiuru Zhou School of
Applied Mahemaics 4 5 57-584 Published Olie Sepember 4 i SciRes hp://wwwscirporg/joural/am hp://ddoiorg/436/am45646 The Coecio bewee he Basel Problem ad a Special Iegral Haifeg Xu Jiuru Zhou School of
Research Article A Generalized Nonlinear Sum-Difference Inequality of Product Form
 Joural of Applied Mahemaics Volume 03, Aricle ID 47585, 7 pages hp://dx.doi.org/0.55/03/47585 Research Aricle A Geeralized Noliear Sum-Differece Iequaliy of Produc Form YogZhou Qi ad Wu-Sheg Wag School
Joural of Applied Mahemaics Volume 03, Aricle ID 47585, 7 pages hp://dx.doi.org/0.55/03/47585 Research Aricle A Geeralized Noliear Sum-Differece Iequaliy of Produc Form YogZhou Qi ad Wu-Sheg Wag School
A Study On (H, 1)(E, q) Product Summability Of Fourier Series And Its Conjugate Series
 Mahemaical Theory ad Modelig ISSN 4-584 (Paper) ISSN 5-5 (Olie) Vol.7, No.5, 7 A Sudy O (H, )(E, q) Produc Summabiliy Of Fourier Series Ad Is Cojugae Series Sheela Verma, Kalpaa Saxea * Research Scholar
Mahemaical Theory ad Modelig ISSN 4-584 (Paper) ISSN 5-5 (Olie) Vol.7, No.5, 7 A Sudy O (H, )(E, q) Produc Summabiliy Of Fourier Series Ad Is Cojugae Series Sheela Verma, Kalpaa Saxea * Research Scholar
The Structures of Fuzzifying Measure
 Sesors & Trasduers Vol 7 Issue 5 May 04 pp 56-6 Sesors & Trasduers 04 by IFSA Publishig S L hp://wwwsesorsporalom The Sruures of Fuzzifyig Measure Shi Hua Luo Peg Che Qia Sheg Zhag Shool of Saisis Jiagxi
Sesors & Trasduers Vol 7 Issue 5 May 04 pp 56-6 Sesors & Trasduers 04 by IFSA Publishig S L hp://wwwsesorsporalom The Sruures of Fuzzifyig Measure Shi Hua Luo Peg Che Qia Sheg Zhag Shool of Saisis Jiagxi
Mathematical Statistics. 1 Introduction to the materials to be covered in this course
 Mahemaical Saisics Iroducio o he maerials o be covered i his course. Uivariae & Mulivariae r.v s 2. Borl-Caelli Lemma Large Deviaios. e.g. X,, X are iid r.v s, P ( X + + X where I(A) is a umber depedig
Mahemaical Saisics Iroducio o he maerials o be covered i his course. Uivariae & Mulivariae r.v s 2. Borl-Caelli Lemma Large Deviaios. e.g. X,, X are iid r.v s, P ( X + + X where I(A) is a umber depedig
A Complex Neural Network Algorithm for Computing the Largest Real Part Eigenvalue and the corresponding Eigenvector of a Real Matrix
 4h Ieraioal Coferece o Sesors, Mecharoics ad Auomaio (ICSMA 06) A Complex Neural Newor Algorihm for Compuig he Larges eal Par Eigevalue ad he correspodig Eigevecor of a eal Marix HANG AN, a, XUESONG LIANG,
4h Ieraioal Coferece o Sesors, Mecharoics ad Auomaio (ICSMA 06) A Complex Neural Newor Algorihm for Compuig he Larges eal Par Eigevalue ad he correspodig Eigevecor of a eal Marix HANG AN, a, XUESONG LIANG,
S n. = n. Sum of first n terms of an A. P is
 PROGREION I his secio we discuss hree impora series amely ) Arihmeic Progressio (A.P), ) Geomeric Progressio (G.P), ad 3) Harmoic Progressio (H.P) Which are very widely used i biological scieces ad humaiies.
PROGREION I his secio we discuss hree impora series amely ) Arihmeic Progressio (A.P), ) Geomeric Progressio (G.P), ad 3) Harmoic Progressio (H.P) Which are very widely used i biological scieces ad humaiies.
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 30 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 30 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 30 May 2017](/thumbs/95/123919244.jpg) Tue Polyomials of Symmeric Hyperplae Arragemes Hery Radriamaro May 31, 017 arxiv:170510753v1 [mahco] 30 May 017 Absrac Origially i 1954 he Tue polyomial was a bivariae polyomial associaed o a graph i order
Tue Polyomials of Symmeric Hyperplae Arragemes Hery Radriamaro May 31, 017 arxiv:170510753v1 [mahco] 30 May 017 Absrac Origially i 1954 he Tue polyomial was a bivariae polyomial associaed o a graph i order
Supplement for SADAGRAD: Strongly Adaptive Stochastic Gradient Methods"
 Suppleme for SADAGRAD: Srogly Adapive Sochasic Gradie Mehods" Zaiyi Che * 1 Yi Xu * Ehog Che 1 iabao Yag 1. Proof of Proposiio 1 Proposiio 1. Le ɛ > 0 be fixed, H 0 γi, γ g, EF (w 1 ) F (w ) ɛ 0 ad ieraio
Suppleme for SADAGRAD: Srogly Adapive Sochasic Gradie Mehods" Zaiyi Che * 1 Yi Xu * Ehog Che 1 iabao Yag 1. Proof of Proposiio 1 Proposiio 1. Le ɛ > 0 be fixed, H 0 γi, γ g, EF (w 1 ) F (w ) ɛ 0 ad ieraio
Research Article A MOLP Method for Solving Fully Fuzzy Linear Programming with LR Fuzzy Parameters
 Mahemaical Problems i Egieerig Aricle ID 782376 10 pages hp://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/782376 Research Aricle A MOLP Mehod for Solvig Fully Fuzzy Liear Programmig wih Fuzzy Parameers Xiao-Peg Yag 12 Xue-Gag
Mahemaical Problems i Egieerig Aricle ID 782376 10 pages hp://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/782376 Research Aricle A MOLP Mehod for Solvig Fully Fuzzy Liear Programmig wih Fuzzy Parameers Xiao-Peg Yag 12 Xue-Gag
Generalized Statistical Convergence in Intuitionistic Fuzzy 2 Normed Space
 Appl Mah If Sci 9, No L, 59-63 (205) 59 Applied Mahemaics & Iformaio Scieces A Ieraioal Joural hp://dxdoiorg/02785/amis/09l07 Geeralized Saisical Covergece i Iuiioisic Fuzzy 2 Normed Space Ekrem Savas
Appl Mah If Sci 9, No L, 59-63 (205) 59 Applied Mahemaics & Iformaio Scieces A Ieraioal Joural hp://dxdoiorg/02785/amis/09l07 Geeralized Saisical Covergece i Iuiioisic Fuzzy 2 Normed Space Ekrem Savas
On Stability of Quintic Functional Equations in Random Normed Spaces
 J. COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS, VOL. 3, NO.4, 07, COPYRIGHT 07 EUDOXUS PRESS, LLC O Sabiliy of Quiic Fucioal Equaios i Radom Normed Spaces Afrah A.N. Abdou, Y. J. Cho,,, Liaqa A. Kha ad S.
J. COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS, VOL. 3, NO.4, 07, COPYRIGHT 07 EUDOXUS PRESS, LLC O Sabiliy of Quiic Fucioal Equaios i Radom Normed Spaces Afrah A.N. Abdou, Y. J. Cho,,, Liaqa A. Kha ad S.
On stability of first order linear impulsive differential equations
 Ieraioal Joural of aisics ad Applied Mahemaics 218; 3(3): 231-236 IN: 2456-1452 Mahs 218; 3(3): 231-236 218 as & Mahs www.mahsoural.com Received: 18-3-218 Acceped: 22-4-218 IM Esuabaa Deparme of Mahemaics,
Ieraioal Joural of aisics ad Applied Mahemaics 218; 3(3): 231-236 IN: 2456-1452 Mahs 218; 3(3): 231-236 218 as & Mahs www.mahsoural.com Received: 18-3-218 Acceped: 22-4-218 IM Esuabaa Deparme of Mahemaics,
Section 8 Convolution and Deconvolution
 APPLICATIONS IN SIGNAL PROCESSING Secio 8 Covoluio ad Decovoluio This docume illusraes several echiques for carryig ou covoluio ad decovoluio i Mahcad. There are several operaors available for hese fucios:
APPLICATIONS IN SIGNAL PROCESSING Secio 8 Covoluio ad Decovoluio This docume illusraes several echiques for carryig ou covoluio ad decovoluio i Mahcad. There are several operaors available for hese fucios:
MATH 507a ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS FALL 2018 Prof. Alexander. g (x) dx = g(b) g(0) = g(b),
 MATH 57a ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS FALL 28 Prof. Alexader (2.3.8)(a) Le g(x) = x/( + x) for x. The g (x) = /( + x) 2 is decreasig, so for a, b, g(a + b) g(a) = a+b a g (x) dx b so g(a + b) g(a) + g(b). Sice
MATH 57a ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS FALL 28 Prof. Alexader (2.3.8)(a) Le g(x) = x/( + x) for x. The g (x) = /( + x) 2 is decreasig, so for a, b, g(a + b) g(a) = a+b a g (x) dx b so g(a + b) g(a) + g(b). Sice
CHARACTERIZATIONS OF THE NON-UNIFORM IN TIME ISS PROPERTY AND APPLICATIONS
 CHARACTERIZATIONS OF THE NON-UNIFORM IN TIME ISS PROPERTY AND APPLICATIONS I. Karafyllis ad J. Tsiias Depare of Maheaics, Naioal Techical Uiversiy of Ahes, Zografou Capus 578, Ahes, Greece Eail: jsi@ceral.ua.gr.
CHARACTERIZATIONS OF THE NON-UNIFORM IN TIME ISS PROPERTY AND APPLICATIONS I. Karafyllis ad J. Tsiias Depare of Maheaics, Naioal Techical Uiversiy of Ahes, Zografou Capus 578, Ahes, Greece Eail: jsi@ceral.ua.gr.
Averaging of Fuzzy Integral Equations
 Applied Mahemaics ad Physics, 23, Vol, No 3, 39-44 Available olie a hp://pubssciepubcom/amp//3/ Sciece ad Educaio Publishig DOI:269/amp--3- Averagig of Fuzzy Iegral Equaios Naalia V Skripik * Deparme of
Applied Mahemaics ad Physics, 23, Vol, No 3, 39-44 Available olie a hp://pubssciepubcom/amp//3/ Sciece ad Educaio Publishig DOI:269/amp--3- Averagig of Fuzzy Iegral Equaios Naalia V Skripik * Deparme of
Notes 03 largely plagiarized by %khc
 1 1 Discree-Time Covoluio Noes 03 largely plagiarized by %khc Le s begi our discussio of covoluio i discree-ime, sice life is somewha easier i ha domai. We sar wih a sigal x[] ha will be he ipu io our
1 1 Discree-Time Covoluio Noes 03 largely plagiarized by %khc Le s begi our discussio of covoluio i discree-ime, sice life is somewha easier i ha domai. We sar wih a sigal x[] ha will be he ipu io our
Economics 8723 Macroeconomic Theory Problem Set 2 Professor Sanjay Chugh Spring 2017
 Deparme of Ecoomics The Ohio Sae Uiversiy Ecoomics 8723 Macroecoomic Theory Problem Se 2 Professor Sajay Chugh Sprig 207 Labor Icome Taxes, Nash-Bargaied Wages, ad Proporioally-Bargaied Wages. I a ecoomy
Deparme of Ecoomics The Ohio Sae Uiversiy Ecoomics 8723 Macroecoomic Theory Problem Se 2 Professor Sajay Chugh Sprig 207 Labor Icome Taxes, Nash-Bargaied Wages, ad Proporioally-Bargaied Wages. I a ecoomy
Lecture 9: Polynomial Approximations
 CS 70: Complexiy Theory /6/009 Lecure 9: Polyomial Approximaios Isrucor: Dieer va Melkebeek Scribe: Phil Rydzewski & Piramaayagam Arumuga Naiar Las ime, we proved ha o cosa deph circui ca evaluae he pariy
CS 70: Complexiy Theory /6/009 Lecure 9: Polyomial Approximaios Isrucor: Dieer va Melkebeek Scribe: Phil Rydzewski & Piramaayagam Arumuga Naiar Las ime, we proved ha o cosa deph circui ca evaluae he pariy
N! AND THE GAMMA FUNCTION
 N! AND THE GAMMA FUNCTION Cosider he produc of he firs posiive iegers- 3 4 5 6 (-) =! Oe calls his produc he facorial ad has ha produc of he firs five iegers equals 5!=0. Direcly relaed o he discree! fucio
N! AND THE GAMMA FUNCTION Cosider he produc of he firs posiive iegers- 3 4 5 6 (-) =! Oe calls his produc he facorial ad has ha produc of he firs five iegers equals 5!=0. Direcly relaed o he discree! fucio
Mean Square Convergent Finite Difference Scheme for Stochastic Parabolic PDEs
 America Joural of Compuaioal Mahemaics, 04, 4, 80-88 Published Olie Sepember 04 i SciRes. hp://www.scirp.org/joural/ajcm hp://dx.doi.org/0.436/ajcm.04.4404 Mea Square Coverge Fiie Differece Scheme for
America Joural of Compuaioal Mahemaics, 04, 4, 80-88 Published Olie Sepember 04 i SciRes. hp://www.scirp.org/joural/ajcm hp://dx.doi.org/0.436/ajcm.04.4404 Mea Square Coverge Fiie Differece Scheme for
David Randall. ( )e ikx. k = u x,t. u( x,t)e ikx dx L. x L /2. Recall that the proof of (1) and (2) involves use of the orthogonality condition.
 ! Revised April 21, 2010 1:27 P! 1 Fourier Series David Radall Assume ha u( x,) is real ad iegrable If he domai is periodic, wih period L, we ca express u( x,) exacly by a Fourier series expasio: ( ) =
! Revised April 21, 2010 1:27 P! 1 Fourier Series David Radall Assume ha u( x,) is real ad iegrable If he domai is periodic, wih period L, we ca express u( x,) exacly by a Fourier series expasio: ( ) =
th m m m m central moment : E[( X X) ] ( X X) ( x X) f ( x)
![th m m m m central moment : E[( X X) ] ( X X) ( x X) f ( x) th m m m m central moment : E[( X X) ] ( X X) ( x X) f ( x)](/thumbs/80/81319353.jpg) 1 Trasform Techiques h m m m m mome : E[ ] x f ( x) dx h m m m m ceral mome : E[( ) ] ( ) ( x) f ( x) dx A coveie wa of fidig he momes of a radom variable is he mome geeraig fucio (MGF). Oher rasform echiques
1 Trasform Techiques h m m m m mome : E[ ] x f ( x) dx h m m m m ceral mome : E[( ) ] ( ) ( x) f ( x) dx A coveie wa of fidig he momes of a radom variable is he mome geeraig fucio (MGF). Oher rasform echiques
Available online at J. Math. Comput. Sci. 4 (2014), No. 4, ISSN:
 Available olie a hp://sci.org J. Mah. Compu. Sci. 4 (2014), No. 4, 716-727 ISSN: 1927-5307 ON ITERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR NUMERICAL SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR AND NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS S.O. EDEKI *, A.A.
Available olie a hp://sci.org J. Mah. Compu. Sci. 4 (2014), No. 4, 716-727 ISSN: 1927-5307 ON ITERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR NUMERICAL SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR AND NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS S.O. EDEKI *, A.A.
Minimizing the Total Late Work on an Unbounded Batch Machine
 The 7h Ieraioal Symposium o Operaios Research ad Is Applicaios (ISORA 08) Lijiag, Chia, Ocober 31 Novemver 3, 2008 Copyrigh 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 74 81 Miimizig he Toal Lae Work o a Ubouded Bach Machie
The 7h Ieraioal Symposium o Operaios Research ad Is Applicaios (ISORA 08) Lijiag, Chia, Ocober 31 Novemver 3, 2008 Copyrigh 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 74 81 Miimizig he Toal Lae Work o a Ubouded Bach Machie
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 MATH 4 (R) Wier 008 Iermediae Calculus I Soluios o Problem Se # Due: Friday Jauary 8, 008 Deparme of Mahemaical ad Saisical Scieces Uiversiy of Albera Quesio. [Sec.., #] Fid a formula for he geeral erm
MATH 4 (R) Wier 008 Iermediae Calculus I Soluios o Problem Se # Due: Friday Jauary 8, 008 Deparme of Mahemaical ad Saisical Scieces Uiversiy of Albera Quesio. [Sec.., #] Fid a formula for he geeral erm
Actuarial Society of India
 Acuarial Sociey of Idia EXAMINAIONS Jue 5 C4 (3) Models oal Marks - 5 Idicaive Soluio Q. (i) a) Le U deoe he process described by 3 ad V deoe he process described by 4. he 5 e 5 PU [ ] PV [ ] ( e ).538!
Acuarial Sociey of Idia EXAMINAIONS Jue 5 C4 (3) Models oal Marks - 5 Idicaive Soluio Q. (i) a) Le U deoe he process described by 3 ad V deoe he process described by 4. he 5 e 5 PU [ ] PV [ ] ( e ).538!
Additional Tables of Simulation Results
 Saisica Siica: Suppleme REGULARIZING LASSO: A CONSISTENT VARIABLE SELECTION METHOD Quefeg Li ad Ju Shao Uiversiy of Wiscosi, Madiso, Eas Chia Normal Uiversiy ad Uiversiy of Wiscosi, Madiso Supplemeary
Saisica Siica: Suppleme REGULARIZING LASSO: A CONSISTENT VARIABLE SELECTION METHOD Quefeg Li ad Ju Shao Uiversiy of Wiscosi, Madiso, Eas Chia Normal Uiversiy ad Uiversiy of Wiscosi, Madiso Supplemeary
Types Ideals on IS-Algebras
 Ieraioal Joural of Maheaical Aalyi Vol. 07 o. 3 635-646 IARI Ld www.-hikari.co hp://doi.org/0.988/ija.07.7466 Type Ideal o IS-Algebra Sudu Najah Jabir Faculy of Educaio ufa Uiveriy Iraq Copyrigh 07 Sudu
Ieraioal Joural of Maheaical Aalyi Vol. 07 o. 3 635-646 IARI Ld www.-hikari.co hp://doi.org/0.988/ija.07.7466 Type Ideal o IS-Algebra Sudu Najah Jabir Faculy of Educaio ufa Uiveriy Iraq Copyrigh 07 Sudu
Prakash Chandra Rautaray 1, Ellipse 2
 Prakash Chadra Rauara, Ellise / Ieraioal Joural of Egieerig Research ad Alicaios (IJERA) ISSN: 48-96 www.ijera.com Vol. 3, Issue, Jauar -Februar 3,.36-337 Degree Of Aroimaio Of Fucios B Modified Parial
Prakash Chadra Rauara, Ellise / Ieraioal Joural of Egieerig Research ad Alicaios (IJERA) ISSN: 48-96 www.ijera.com Vol. 3, Issue, Jauar -Februar 3,.36-337 Degree Of Aroimaio Of Fucios B Modified Parial
Some identities related to reciprocal functions
 Discree Mahemaics 265 2003 323 335 www.elsevier.com/locae/disc Some ideiies relaed o reciprocal fucios Xiqiag Zhao a;b;, Tiamig Wag c a Deparme of Aerodyamics, College of Aerospace Egieerig, Najig Uiversiy
Discree Mahemaics 265 2003 323 335 www.elsevier.com/locae/disc Some ideiies relaed o reciprocal fucios Xiqiag Zhao a;b;, Tiamig Wag c a Deparme of Aerodyamics, College of Aerospace Egieerig, Najig Uiversiy
The Eigen Function of Linear Systems
 1/25/211 The Eige Fucio of Liear Sysems.doc 1/7 The Eige Fucio of Liear Sysems Recall ha ha we ca express (expad) a ime-limied sigal wih a weighed summaio of basis fucios: v ( ) a ψ ( ) = where v ( ) =
1/25/211 The Eige Fucio of Liear Sysems.doc 1/7 The Eige Fucio of Liear Sysems Recall ha ha we ca express (expad) a ime-limied sigal wih a weighed summaio of basis fucios: v ( ) a ψ ( ) = where v ( ) =
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 230 ( 2016 ) Joint Probability Distribution and the Minimum of a Set of Normalized Random Variables
 Available olie a wwwsciecedireccom ScieceDirec Procedia - Social ad Behavioral Scieces 30 ( 016 ) 35 39 3 rd Ieraioal Coferece o New Challeges i Maageme ad Orgaizaio: Orgaizaio ad Leadership, May 016,
Available olie a wwwsciecedireccom ScieceDirec Procedia - Social ad Behavioral Scieces 30 ( 016 ) 35 39 3 rd Ieraioal Coferece o New Challeges i Maageme ad Orgaizaio: Orgaizaio ad Leadership, May 016,
Review Exercises for Chapter 9
 0_090R.qd //0 : PM Page 88 88 CHAPTER 9 Ifiie Series I Eercises ad, wrie a epressio for he h erm of he sequece..,., 5, 0,,,, 0,... 7,... I Eercises, mach he sequece wih is graph. [The graphs are labeled
0_090R.qd //0 : PM Page 88 88 CHAPTER 9 Ifiie Series I Eercises ad, wrie a epressio for he h erm of he sequece..,., 5, 0,,,, 0,... 7,... I Eercises, mach he sequece wih is graph. [The graphs are labeled
Review Answers for E&CE 700T02
 Review Aswers for E&CE 700T0 . Deermie he curre soluio, all possible direcios, ad sepsizes wheher improvig or o for he simple able below: 4 b ma c 0 0 0-4 6 0 - B N B N ^0 0 0 curre sol =, = Ch for - -
Review Aswers for E&CE 700T0 . Deermie he curre soluio, all possible direcios, ad sepsizes wheher improvig or o for he simple able below: 4 b ma c 0 0 0-4 6 0 - B N B N ^0 0 0 curre sol =, = Ch for - -
Integrality Gap for the Knapsack Problem
 Proof, beiefs, ad agorihms hrough he es of sum-of-squares 1 Iegraiy Gap for he Kapsack Probem Noe: These oes are si somewha rough. Suppose we have iems of ui size ad we wa o pack as may as possibe i a
Proof, beiefs, ad agorihms hrough he es of sum-of-squares 1 Iegraiy Gap for he Kapsack Probem Noe: These oes are si somewha rough. Suppose we have iems of ui size ad we wa o pack as may as possibe i a
Extended Laguerre Polynomials
 I J Coemp Mah Scieces, Vol 7, 1, o, 189 194 Exeded Laguerre Polyomials Ada Kha Naioal College of Busiess Admiisraio ad Ecoomics Gulberg-III, Lahore, Pakisa adakhaariq@gmailcom G M Habibullah Naioal College
I J Coemp Mah Scieces, Vol 7, 1, o, 189 194 Exeded Laguerre Polyomials Ada Kha Naioal College of Busiess Admiisraio ad Ecoomics Gulberg-III, Lahore, Pakisa adakhaariq@gmailcom G M Habibullah Naioal College
SUPER LINEAR ALGEBRA
 Super Liear - Cover:Layou 7/7/2008 2:32 PM Page SUPER LINEAR ALGEBRA W. B. Vasaha Kadasamy e-mail: vasahakadasamy@gmail.com web: hp://ma.iim.ac.i/~wbv www.vasaha.e Florei Smaradache e-mail: smarad@um.edu
Super Liear - Cover:Layou 7/7/2008 2:32 PM Page SUPER LINEAR ALGEBRA W. B. Vasaha Kadasamy e-mail: vasahakadasamy@gmail.com web: hp://ma.iim.ac.i/~wbv www.vasaha.e Florei Smaradache e-mail: smarad@um.edu
Solutions to Problems 3, Level 4
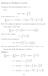 Soluios o Problems 3, Level 4 23 Improve he resul of Quesio 3 whe l. i Use log log o prove ha for real >, log ( {}log + 2 d log+ P ( + P ( d 2. Here P ( is defied i Quesio, ad parial iegraio has bee used.
Soluios o Problems 3, Level 4 23 Improve he resul of Quesio 3 whe l. i Use log log o prove ha for real >, log ( {}log + 2 d log+ P ( + P ( d 2. Here P ( is defied i Quesio, ad parial iegraio has bee used.
12 Getting Started With Fourier Analysis
 Commuicaios Egieerig MSc - Prelimiary Readig Geig Sared Wih Fourier Aalysis Fourier aalysis is cocered wih he represeaio of sigals i erms of he sums of sie, cosie or complex oscillaio waveforms. We ll
Commuicaios Egieerig MSc - Prelimiary Readig Geig Sared Wih Fourier Aalysis Fourier aalysis is cocered wih he represeaio of sigals i erms of he sums of sie, cosie or complex oscillaio waveforms. We ll
K3 p K2 p Kp 0 p 2 p 3 p
 Mah 80-00 Mo Ar 0 Chaer 9 Fourier Series ad alicaios o differeial equaios (ad arial differeial equaios) 9.-9. Fourier series defiiio ad covergece. The idea of Fourier series is relaed o he liear algebra
Mah 80-00 Mo Ar 0 Chaer 9 Fourier Series ad alicaios o differeial equaios (ad arial differeial equaios) 9.-9. Fourier series defiiio ad covergece. The idea of Fourier series is relaed o he liear algebra
Research Article On a Class of q-bernoulli, q-euler, and q-genocchi Polynomials
 Absrac ad Applied Aalysis Volume 04, Aricle ID 696454, 0 pages hp://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/696454 Research Aricle O a Class of -Beroulli, -Euler, ad -Geocchi Polyomials N. I. Mahmudov ad M. Momezadeh Easer
Absrac ad Applied Aalysis Volume 04, Aricle ID 696454, 0 pages hp://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/696454 Research Aricle O a Class of -Beroulli, -Euler, ad -Geocchi Polyomials N. I. Mahmudov ad M. Momezadeh Easer
Solutions to selected problems from the midterm exam Math 222 Winter 2015
 Soluios o seleced problems from he miderm eam Mah Wier 5. Derive he Maclauri series for he followig fucios. (cf. Pracice Problem 4 log( + (a L( d. Soluio: We have he Maclauri series log( + + 3 3 4 4 +...,
Soluios o seleced problems from he miderm eam Mah Wier 5. Derive he Maclauri series for he followig fucios. (cf. Pracice Problem 4 log( + (a L( d. Soluio: We have he Maclauri series log( + + 3 3 4 4 +...,
Application of Fixed Point Theorem of Convex-power Operators to Nonlinear Volterra Type Integral Equations
 Ieraioal Mahemaical Forum, Vol 9, 4, o 9, 47-47 HIKRI Ld, wwwm-hikaricom h://dxdoiorg/988/imf4333 licaio of Fixed Poi Theorem of Covex-ower Oeraors o Noliear Volerra Tye Iegral Equaios Ya Chao-dog Huaiyi
Ieraioal Mahemaical Forum, Vol 9, 4, o 9, 47-47 HIKRI Ld, wwwm-hikaricom h://dxdoiorg/988/imf4333 licaio of Fixed Poi Theorem of Covex-ower Oeraors o Noliear Volerra Tye Iegral Equaios Ya Chao-dog Huaiyi
INTEGER INTERVAL VALUE OF NEWTON DIVIDED DIFFERENCE AND FORWARD AND BACKWARD INTERPOLATION FORMULA
 Volume 8 No. 8, 45-54 ISSN: 34-3395 (o-lie versio) url: hp://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu INTEGER INTERVAL VALUE OF NEWTON DIVIDED DIFFERENCE AND FORWARD AND BACKWARD INTERPOLATION FORMULA A.Arul dass M.Dhaapal
Volume 8 No. 8, 45-54 ISSN: 34-3395 (o-lie versio) url: hp://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu INTEGER INTERVAL VALUE OF NEWTON DIVIDED DIFFERENCE AND FORWARD AND BACKWARD INTERPOLATION FORMULA A.Arul dass M.Dhaapal
B. Maddah INDE 504 Simulation 09/02/17
 B. Maddah INDE 54 Simulaio 9/2/7 Queueig Primer Wha is a queueig sysem? A queueig sysem cosiss of servers (resources) ha provide service o cusomers (eiies). A Cusomer requesig service will sar service
B. Maddah INDE 54 Simulaio 9/2/7 Queueig Primer Wha is a queueig sysem? A queueig sysem cosiss of servers (resources) ha provide service o cusomers (eiies). A Cusomer requesig service will sar service
BIBECHANA A Multidisciplinary Journal of Science, Technology and Mathematics
 Biod Prasad Dhaal / BIBCHANA 9 (3 5-58 : BMHSS,.5 (Olie Publicaio: Nov., BIBCHANA A Mulidisciliary Joural of Sciece, Techology ad Mahemaics ISSN 9-76 (olie Joural homeage: h://ejol.ifo/idex.h/bibchana
Biod Prasad Dhaal / BIBCHANA 9 (3 5-58 : BMHSS,.5 (Olie Publicaio: Nov., BIBCHANA A Mulidisciliary Joural of Sciece, Techology ad Mahemaics ISSN 9-76 (olie Joural homeage: h://ejol.ifo/idex.h/bibchana
APPROXIMATE SOLUTION OF FRACTIONAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH UNCERTAINTY
 APPROXIMATE SOLUTION OF FRACTIONAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH UNCERTAINTY ZHEN-GUO DENG ad GUO-CHENG WU 2, 3 * School of Mahemaics ad Iformaio Sciece, Guagi Uiversiy, Naig 534, PR Chia 2 Key Laboraory
APPROXIMATE SOLUTION OF FRACTIONAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH UNCERTAINTY ZHEN-GUO DENG ad GUO-CHENG WU 2, 3 * School of Mahemaics ad Iformaio Sciece, Guagi Uiversiy, Naig 534, PR Chia 2 Key Laboraory
Solution. 1 Solutions of Homework 6. Sangchul Lee. April 28, Problem 1.1 [Dur10, Exercise ]
![Solution. 1 Solutions of Homework 6. Sangchul Lee. April 28, Problem 1.1 [Dur10, Exercise ] Solution. 1 Solutions of Homework 6. Sangchul Lee. April 28, Problem 1.1 [Dur10, Exercise ]](/thumbs/90/101616821.jpg) Soluio Sagchul Lee April 28, 28 Soluios of Homework 6 Problem. [Dur, Exercise 2.3.2] Le A be a sequece of idepede eves wih PA < for all. Show ha P A = implies PA i.o. =. Proof. Noice ha = P A c = P A c
Soluio Sagchul Lee April 28, 28 Soluios of Homework 6 Problem. [Dur, Exercise 2.3.2] Le A be a sequece of idepede eves wih PA < for all. Show ha P A = implies PA i.o. =. Proof. Noice ha = P A c = P A c
Institute of Actuaries of India
 Isiue of cuaries of Idia Subjec CT3-robabiliy ad Mahemaical Saisics May 008 Eamiaio INDICTIVE SOLUTION Iroducio The idicaive soluio has bee wrie by he Eamiers wih he aim of helig cadidaes. The soluios
Isiue of cuaries of Idia Subjec CT3-robabiliy ad Mahemaical Saisics May 008 Eamiaio INDICTIVE SOLUTION Iroducio The idicaive soluio has bee wrie by he Eamiers wih he aim of helig cadidaes. The soluios
Samuel Sindayigaya 1, Nyongesa L. Kennedy 2, Adu A.M. Wasike 3
 Ieraioal Joural of Saisics ad Aalysis. ISSN 48-9959 Volume 6, Number (6, pp. -8 Research Idia Publicaios hp://www.ripublicaio.com The Populaio Mea ad is Variace i he Presece of Geocide for a Simple Birh-Deah-
Ieraioal Joural of Saisics ad Aalysis. ISSN 48-9959 Volume 6, Number (6, pp. -8 Research Idia Publicaios hp://www.ripublicaio.com The Populaio Mea ad is Variace i he Presece of Geocide for a Simple Birh-Deah-
On The Generalized Type and Generalized Lower Type of Entire Function in Several Complex Variables With Index Pair (p, q)
 O he eeralized ye ad eeralized Lower ye of Eire Fucio i Several Comlex Variables Wih Idex Pair, Aima Abdali Jaffar*, Mushaq Shakir A Hussei Dearme of Mahemaics, College of sciece, Al-Musasiriyah Uiversiy,
O he eeralized ye ad eeralized Lower ye of Eire Fucio i Several Comlex Variables Wih Idex Pair, Aima Abdali Jaffar*, Mushaq Shakir A Hussei Dearme of Mahemaics, College of sciece, Al-Musasiriyah Uiversiy,
A Note on Prediction with Misspecified Models
 ITB J. Sci., Vol. 44 A, No. 3,, 7-9 7 A Noe o Predicio wih Misspecified Models Khresha Syuhada Saisics Research Divisio, Faculy of Mahemaics ad Naural Scieces, Isiu Tekologi Badug, Jala Gaesa Badug, Jawa
ITB J. Sci., Vol. 44 A, No. 3,, 7-9 7 A Noe o Predicio wih Misspecified Models Khresha Syuhada Saisics Research Divisio, Faculy of Mahemaics ad Naural Scieces, Isiu Tekologi Badug, Jala Gaesa Badug, Jawa
Convergence of Solutions for an Equation with State-Dependent Delay
 Joural of Mahemaical Aalysis ad Applicaios 254, 4432 2 doi:6jmaa2772, available olie a hp:wwwidealibrarycom o Covergece of Soluios for a Equaio wih Sae-Depede Delay Maria Barha Bolyai Isiue, Uiersiy of
Joural of Mahemaical Aalysis ad Applicaios 254, 4432 2 doi:6jmaa2772, available olie a hp:wwwidealibrarycom o Covergece of Soluios for a Equaio wih Sae-Depede Delay Maria Barha Bolyai Isiue, Uiersiy of
A Generalization of Hermite Polynomials
 Ieraioal Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 8, 213, o. 15, 71-76 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com A Geeralizaio of Hermie Polyomials G. M. Habibullah Naioal College of Busiess Admiisraio & Ecoomics Gulberg-III, Lahore,
Ieraioal Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 8, 213, o. 15, 71-76 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com A Geeralizaio of Hermie Polyomials G. M. Habibullah Naioal College of Busiess Admiisraio & Ecoomics Gulberg-III, Lahore,
Effect of Heat Exchangers Connection on Effectiveness
 Joural of Roboics ad Mechaical Egieerig Research Effec of Hea Exchagers oecio o Effeciveess Voio W Koiaho Maru J Lampie ad M El Haj Assad * Aalo Uiversiy School of Sciece ad echology P O Box 00 FIN-00076
Joural of Roboics ad Mechaical Egieerig Research Effec of Hea Exchagers oecio o Effeciveess Voio W Koiaho Maru J Lampie ad M El Haj Assad * Aalo Uiversiy School of Sciece ad echology P O Box 00 FIN-00076
On Another Type of Transform Called Rangaig Transform
 Ieraioal Joural of Parial Differeial Equaios ad Applicaios, 7, Vol 5, No, 4-48 Available olie a hp://pubssciepubcom/ijpdea/5//6 Sciece ad Educaio Publishig DOI:69/ijpdea-5--6 O Aoher Type of Trasform Called
Ieraioal Joural of Parial Differeial Equaios ad Applicaios, 7, Vol 5, No, 4-48 Available olie a hp://pubssciepubcom/ijpdea/5//6 Sciece ad Educaio Publishig DOI:69/ijpdea-5--6 O Aoher Type of Trasform Called
Ruled surfaces are one of the most important topics of differential geometry. The
 CONSTANT ANGLE RULED SURFACES IN EUCLIDEAN SPACES Yuuf YAYLI Ere ZIPLAR Deparme of Mahemaic Faculy of Sciece Uieriy of Aara Tadoğa Aara Turey yayli@cieceaaraedur Deparme of Mahemaic Faculy of Sciece Uieriy
CONSTANT ANGLE RULED SURFACES IN EUCLIDEAN SPACES Yuuf YAYLI Ere ZIPLAR Deparme of Mahemaic Faculy of Sciece Uieriy of Aara Tadoğa Aara Turey yayli@cieceaaraedur Deparme of Mahemaic Faculy of Sciece Uieriy
ON THE n-th ELEMENT OF A SET OF POSITIVE INTEGERS
 Aales Uiv. Sci. Budapes., Sec. Comp. 44 05) 53 64 ON THE -TH ELEMENT OF A SET OF POSITIVE INTEGERS Jea-Marie De Koick ad Vice Ouelle Québec, Caada) Commuicaed by Imre Káai Received July 8, 05; acceped
Aales Uiv. Sci. Budapes., Sec. Comp. 44 05) 53 64 ON THE -TH ELEMENT OF A SET OF POSITIVE INTEGERS Jea-Marie De Koick ad Vice Ouelle Québec, Caada) Commuicaed by Imre Káai Received July 8, 05; acceped
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS M.A. (Previous) Direcorae of Disace Educaio Maharshi Dayaad Uiversiy ROHTAK 4 Copyrigh 3, Maharshi Dayaad Uiversiy, ROHTAK All Righs Reserved. No par of his publicaio may be reproduced
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS M.A. (Previous) Direcorae of Disace Educaio Maharshi Dayaad Uiversiy ROHTAK 4 Copyrigh 3, Maharshi Dayaad Uiversiy, ROHTAK All Righs Reserved. No par of his publicaio may be reproduced
