Lecture 14: Randomized Computation (cont.)
|
|
|
- Mervin Banks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 200 Computability ad Complexity Wedesday, May 15, 2013 Lecture 14: Radomized Computatio (cot.) Istructor: Professor Shachar Lovett Scribe: Dogcai She 1 Radmized Algorithm Examples 1.1 The k-th Elemet Defiitio 1 (The k-th elemet) Iput: A def = {a 1, a 2,, a } ad k. Goal: Fid the k-th elemet (i the ordered set). (whe k = 2, it s fidig the media). The algorithm with low time complexity was iveted i But the algorithm was a little ucovetioal: it s a radomized algorithm. Algorithm 1 Elemet(A, k) [3] 1: Choose radom a i A (called pivot). 2: Partitio A to S {a j : a j a i }, ad H {a j : a j > a i }. 3: If S k, retur Elemet(S, k). If S < k, retur Elemet(H, k S ). Claim 2 The expected ruig time of Algorithm 1 is O(). Corollary 3 W.h.p., Algorithm 1 s ruig time is O(). Defiitio 4 (Expected ruig time) Let T (A, k) be the expected ruig time o iputs A ad k. A() def = max A = k [] T (A, k) Proof of Claim 2: {1,, }. We will prove T () c. Let l be the idex of a i i the order. l is uiform i T (A, k) + 1 max(t (l), T ( l)) l=1 + 2 T (l) l= 2 +1 By iductio o, T () + 2 = + 2c = + 2c l= 2 +1 cl [( ) ( )] 2 2 [ ( + 1) 2 ( 2 + 1) ]
2 = + 2c [ ] O() = + 3 c + O(c) 4 c Proof of Corollary 3: E [T ()] c. By Markov s iequality: Pr [T () > 10c] < Primality testig Defiitio 5 (PRIMALITY) Iput: a iteger. Goal: Is prime or composite? Theorem 6 (Fermat) If is a prime, the 1 a 1, a 1 1 (mod ) Algorithm 2 Miller-Rabi [5, 6] 1: Choose a radom a {1,, 1}. 2: If a 1 1 (mod ), retur NOT PRIME. Let S 1. 3: As log as a 1 1 (mod ), ad S is eve: S S 2. 4: If a S ±1 (mod ), retur PRIME, else retur NOT PRIME. We kow If is prime, Miller-Rabi returs PRIME always. If is composite, Miller-Rabi returs NOT PRIME w.p Before the AKS Algorithm, people foud some determiistic algorithms for PRIMALITY assumig some umber-theoretic cojectures (e.g., Geeralized Riema Hypothesis). The stadard trick to compute powers efficietly. Suppose we wat to compute a b mod. Cosider b s biary represetatio b log b b 1 b 0. Namely, b = b 0 + 2b 1 + 4b 2 + 8b 3 + where b l {0, 1} for ay l [log b]. The, a b = a b0 (a 2 ) b1 (a 4 ) b2. Compute a 2 mod, a 4 mod, a 8 mod,..., i order, ad the compute the multiplicatio, reducig modulo after each step. 1.3 Coectivity i Udirected Graphs Defiitio 7 (UCONN) Iput: a udirected graph G, vertices s, t. Goal: Is s, t i the same compoet? Algorithm 3 Radom walks o udirected graphs 1: Start a radom walk at s. At each step, choose eighbors with equal probability. 2: Stop util t is reached, or the radom walk made too may steps. Oe ca show that if s, t are coected the the expected ruig time of Algorithm 3 is O( 3 ). Hece, we ca set the algorithm to halt ad retur NO after O( 3 ) steps. The beefit of radom walks is it uses little space (O(log )). For example, it s very appealig for samplig pages o the Iteret. Google s Web 14-2
3 page crawler actually performs radom walks followig liks from a page to aother page. However, radom walks does ot solve the reachability problem i directed graphs i geeral. Cosider Figure 1, it takes the radom walk startig at ode 1 expected O(2 ) steps to reach ode. The reaso is that at each ode i, the walk goes back to its startig poit w. prob This makes the probability of reachig ode after 1 steps 2 ( 1), a expoetially small probability Figure 1: Radom walks do ot work o directed graphs 1.4 Polyomial idetity testig ad perfect matchig testig Defiitio 8 (Polyomial Idetity Testig) Iput: A real polyomial p(x 1,, x ) of a low degree; efficiet way to evaluate p o iputs. Goal: Is p 0 or ot? A simple method: evaluate the polyomial o a radom assigmet, retur whether it s 0 or ot. Lemma 9 (Schwartz-Zippel) If p(x 1,, x ) is a ozero degree D polyomial, S R, S > D. If choose a 1,, a S are chose uiformly ad idepedetly the Pr [p(a 1,, a ) = 0] D a 1,,a S S Lemma 9 was rediscovered may times i history. It s left as a problem i homework. The iequality is tight meaig that we ca actually costruct a polyomial by iterpolatio ad have correspodig poits to make it equality. A applicatio example for the above polyomial idetity testig is to fid the perfect matchig of a bipartite graph. Cosider a bipartite graph G = (V 1 V 2, E), V 1 = V 2 =. Defiitio 10 (Perfect matchig) A perfectio matchig is a permutatio π S s.t. (1, π(1)), (2, π(2)),, (, π()) E. Idea: Build a matrix A, A i,j def = { x i,j (i, j) E 0 (i, j) E Claim 11 G has a perfect matchig iff det(a) is a ozero polyomial. Proof det(a) = ( 1) sig(π) π S i=1 A i,π(i) = ( 1) sig(π) perfect matchig π i=1 We do t kow a determiistic way to do it. x i,π(i) 14-3
4 Questio 12 Ca we deradomize polyomial idetity testig? 2 Radomized Complexity Classes Defiitio 13 (Two-sided error algorithm) x L Pr [M(x) = 1] 2/3. x L Pr [M(x) = 1] 1/3. Defiitio 14 (Oe-sided error algorithm) x L Pr [M(x) = 1] 2/3. x L Pr [M(x) = 1] = 0. May atural radomized algorithms are oe-sided. For example, the primality testig ad polyomial idetity testig described above. Defiitio 15 (BPP, RP, co-rp) BPP def = Two-sided error polyomial time. RP def = Oe-sided error polyomial time (x L o error). co-rp def = Same as RP except for o error for x L. ZPP def = Algorithms ruig i expected polyomial time, but always retur correct aswers. Deradomizatio is itimately related to provig lowerbouds (e.g., [4]). Claim 16 ZPP = RP co-rp. Theorem 17 (Adelma [1]) BPP P/poly. Theorem 18 (Sipser-Gács [7]) BPP Σ 2 Π 2. It suffices to prove that BPP Σ 2 for the Sipser-Gács Theorem, sice BPP is closed uder complemet. Proof of Claim 16 (also see [2] Page 141, Exercise 7.6): ( ) Suppose L ZPP, there exists M s.t. M(x) = L(x). Ruig time i expectatio is c. Defie M (x): Ru M(x) for 3 c steps; If it did t halt, retur 0. If x L the M (x) returs 1 with probability 2/3. If x / L the M (x) returs 0 always. Hece L RP. Replacig 0 with 1 would show that also L co-rp. ( ) Suppose L RP co-rp, that is Machie M 1, x L, Pr [M 1 (x) = 1] 2 3 ad x L, Pr [M 1(x) = 0] = 1. Machie M 2, x L, Pr [M 2 (x) = 1] = 1 ad x L, Pr [M 2 (x) = 0] 2 3. Defie M (x) If M 1 (x) = 1, the retur x L. If M 2 (x) = 0, the retur x L. Retry. Say M 1, M 2 ru i c time, x, retur i first 2 lies of code w.p Pr [retry] 1 def 3. Let T = expected ruig time. The, T 2 c T. Hece, T O(c ). We will prove Theorem 17 ad Theorem 18 i the ext class. 14-4
5 Refereces [1] Leoard M. Adlema. Two theorems o radom polyomial time. I FOCS, pages 75 83, [2] Sajeev Arora ad Boaz Barak. Computatioal Complexity - A Moder Approach. Cambridge Uiversity Press, [3] Mauel Blum, Robert W. Floyd, Vaugha R. Pratt, Roald L. Rivest, ad Robert Edre Tarja. Time bouds for selectio. J. Comput. Syst. Sci., 7(4): , [4] Russell Impagliazzo ad Avi Wigderso. P = BPP if e requires expoetial circuits: Deradomizig the xor lemma. I STOC, pages , [5] Gary L. Miller. Riema s hypothesis ad tests for primality. I Proceedigs of seveth aual ACM symposium o Theory of computig, STOC 75, pages , New York, NY, USA, ACM. [6] Michael O Rabi. Probabilistic algorithm for testig primality. Joural of Number Theory, 12(1): , [7] Michael Sipser. A complexity theoretic approach to radomess. I STOC, pages ,
Lecture 2: Uncomputability and the Haling Problem
 CSE 200 Computability ad Complexity Wedesday, April 3, 2013 Lecture 2: Ucomputability ad the Halig Problem Istructor: Professor Shachar Lovett Scribe: Dogcai She 1 The Uiversal Turig Machie I the last
CSE 200 Computability ad Complexity Wedesday, April 3, 2013 Lecture 2: Ucomputability ad the Halig Problem Istructor: Professor Shachar Lovett Scribe: Dogcai She 1 The Uiversal Turig Machie I the last
Polynomial identity testing and global minimum cut
 CHAPTER 6 Polyomial idetity testig ad global miimum cut I this lecture we will cosider two further problems that ca be solved usig probabilistic algorithms. I the first half, we will cosider the problem
CHAPTER 6 Polyomial idetity testig ad global miimum cut I this lecture we will cosider two further problems that ca be solved usig probabilistic algorithms. I the first half, we will cosider the problem
Lecture 12: November 13, 2018
 Mathematical Toolkit Autum 2018 Lecturer: Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 12: November 13, 2018 1 Radomized polyomial idetity testig We will use our kowledge of coditioal probability to prove the followig lemma,
Mathematical Toolkit Autum 2018 Lecturer: Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 12: November 13, 2018 1 Radomized polyomial idetity testig We will use our kowledge of coditioal probability to prove the followig lemma,
Notes on the Combinatorial Nullstellensatz
 Notes o the Combiatorial Nullstellesatz Costructive ad Nocostructive Methods i Combiatorics ad TCS U. Chicago, Sprig 2018 Istructor: Adrew Drucker Scribe: Roberto Ferádez For the followig theorems ad examples
Notes o the Combiatorial Nullstellesatz Costructive ad Nocostructive Methods i Combiatorics ad TCS U. Chicago, Sprig 2018 Istructor: Adrew Drucker Scribe: Roberto Ferádez For the followig theorems ad examples
Lecture 9: Pseudo-random generators against space bounded computation,
 Lecture 9: Pseudo-radom geerators agaist space bouded computatio, Primality Testig Topics i Pseudoradomess ad Complexity (Sprig 2018) Rutgers Uiversity Swastik Kopparty Scribes: Harsha Tirumala, Jiyu Zhag
Lecture 9: Pseudo-radom geerators agaist space bouded computatio, Primality Testig Topics i Pseudoradomess ad Complexity (Sprig 2018) Rutgers Uiversity Swastik Kopparty Scribes: Harsha Tirumala, Jiyu Zhag
ACO Comprehensive Exam 9 October 2007 Student code A. 1. Graph Theory
 1. Graph Theory Prove that there exist o simple plaar triagulatio T ad two distict adjacet vertices x, y V (T ) such that x ad y are the oly vertices of T of odd degree. Do ot use the Four-Color Theorem.
1. Graph Theory Prove that there exist o simple plaar triagulatio T ad two distict adjacet vertices x, y V (T ) such that x ad y are the oly vertices of T of odd degree. Do ot use the Four-Color Theorem.
Notes for Lecture 11
 U.C. Berkeley CS78: Computatioal Complexity Hadout N Professor Luca Trevisa 3/4/008 Notes for Lecture Eigevalues, Expasio, ad Radom Walks As usual by ow, let G = (V, E) be a udirected d-regular graph with
U.C. Berkeley CS78: Computatioal Complexity Hadout N Professor Luca Trevisa 3/4/008 Notes for Lecture Eigevalues, Expasio, ad Radom Walks As usual by ow, let G = (V, E) be a udirected d-regular graph with
Lecture 11: Pseudorandom functions
 COM S 6830 Cryptography Oct 1, 2009 Istructor: Rafael Pass 1 Recap Lecture 11: Pseudoradom fuctios Scribe: Stefao Ermo Defiitio 1 (Ge, Ec, Dec) is a sigle message secure ecryptio scheme if for all uppt
COM S 6830 Cryptography Oct 1, 2009 Istructor: Rafael Pass 1 Recap Lecture 11: Pseudoradom fuctios Scribe: Stefao Ermo Defiitio 1 (Ge, Ec, Dec) is a sigle message secure ecryptio scheme if for all uppt
Recursive Algorithm for Generating Partitions of an Integer. 1 Preliminary
 Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma
 Staford Uiversity Sprig 208 Math 233A: No-costructive methods i combiatorics Istructor: Ja Vodrák Lecture date: Jauary 0, 208 Origial scribe: Apoorva Khare Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma 2. Itroductio
Staford Uiversity Sprig 208 Math 233A: No-costructive methods i combiatorics Istructor: Ja Vodrák Lecture date: Jauary 0, 208 Origial scribe: Apoorva Khare Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma 2. Itroductio
Lecture 2: Concentration Bounds
 CSE 52: Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms I Sprig 206 Lecture 2: Cocetratio Bouds Lecturer: Shaya Oveis Ghara March 30th Scribe: Syuzaa Sargsya Disclaimer: These otes have ot bee subjected to the usual scrutiy
CSE 52: Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms I Sprig 206 Lecture 2: Cocetratio Bouds Lecturer: Shaya Oveis Ghara March 30th Scribe: Syuzaa Sargsya Disclaimer: These otes have ot bee subjected to the usual scrutiy
Lecture 2 Clustering Part II
 COMS 4995: Usupervised Learig (Summer 8) May 24, 208 Lecture 2 Clusterig Part II Istructor: Nakul Verma Scribes: Jie Li, Yadi Rozov Today, we will be talkig about the hardess results for k-meas. More specifically,
COMS 4995: Usupervised Learig (Summer 8) May 24, 208 Lecture 2 Clusterig Part II Istructor: Nakul Verma Scribes: Jie Li, Yadi Rozov Today, we will be talkig about the hardess results for k-meas. More specifically,
Primality Test. Rong-Jaye Chen
 Primality Test Rog-Jaye Che OUTLINE [1] Modular Arithmetic Algorithms [2] Quadratic Residues [3] Primality Testig p2. [1] Modular Arithmetic Algorithms 1. The itegers a divides b a b a{ 1, b} If b has
Primality Test Rog-Jaye Che OUTLINE [1] Modular Arithmetic Algorithms [2] Quadratic Residues [3] Primality Testig p2. [1] Modular Arithmetic Algorithms 1. The itegers a divides b a b a{ 1, b} If b has
Trial division, Pollard s p 1, Pollard s ρ, and Fermat s method. Christopher Koch 1. April 8, 2014
 Iteger Divisio Algorithm ad Cogruece Iteger Trial divisio,,, ad with itegers mod Iverses mod Multiplicatio ad GCD Iteger Christopher Koch 1 1 Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig CSE489/589 Algorithms
Iteger Divisio Algorithm ad Cogruece Iteger Trial divisio,,, ad with itegers mod Iverses mod Multiplicatio ad GCD Iteger Christopher Koch 1 1 Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egieerig CSE489/589 Algorithms
Lecture 16: Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy. 2 Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy
 15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
Lecture 9: Expanders Part 2, Extractors
 Lecture 9: Expaders Part, Extractors Topics i Complexity Theory ad Pseudoradomess Sprig 013 Rutgers Uiversity Swastik Kopparty Scribes: Jaso Perry, Joh Kim I this lecture, we will discuss further the pseudoradomess
Lecture 9: Expaders Part, Extractors Topics i Complexity Theory ad Pseudoradomess Sprig 013 Rutgers Uiversity Swastik Kopparty Scribes: Jaso Perry, Joh Kim I this lecture, we will discuss further the pseudoradomess
Davenport-Schinzel Sequences and their Geometric Applications
 Advaced Computatioal Geometry Sprig 2004 Daveport-Schizel Sequeces ad their Geometric Applicatios Prof. Joseph Mitchell Scribe: Mohit Gupta 1 Overview I this lecture, we itroduce the cocept of Daveport-Schizel
Advaced Computatioal Geometry Sprig 2004 Daveport-Schizel Sequeces ad their Geometric Applicatios Prof. Joseph Mitchell Scribe: Mohit Gupta 1 Overview I this lecture, we itroduce the cocept of Daveport-Schizel
Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems
 IAS/PCMI Summer Sessio 2000 Clay Mathematics Udergraduate Program Basic Course o Computatioal Complexity Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems David Mix Barrigto ad Alexis Maciel July 27, 2000 Most of this lecture
IAS/PCMI Summer Sessio 2000 Clay Mathematics Udergraduate Program Basic Course o Computatioal Complexity Lecture 9: Hierarchy Theorems David Mix Barrigto ad Alexis Maciel July 27, 2000 Most of this lecture
Lecture 5: April 17, 2013
 TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 5: April 7, 203 Scribe: Somaye Hashemifar Cheroff bouds recap We recall the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds we derived i the last lecture idepedet
TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 5: April 7, 203 Scribe: Somaye Hashemifar Cheroff bouds recap We recall the Cheroff/Hoeffdig bouds we derived i the last lecture idepedet
Math 609/597: Cryptography 1
 Math 609/597: Cryptography 1 The Solovay-Strasse Primality Test 12 October, 1993 Burt Roseberg Revised: 6 October, 2000 1 Itroductio We describe the Solovay-Strasse primality test. There is quite a bit
Math 609/597: Cryptography 1 The Solovay-Strasse Primality Test 12 October, 1993 Burt Roseberg Revised: 6 October, 2000 1 Itroductio We describe the Solovay-Strasse primality test. There is quite a bit
Randomized Algorithms I, Spring 2018, Department of Computer Science, University of Helsinki Homework 1: Solutions (Discussed January 25, 2018)
 Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
Radomized Algorithms I, Sprig 08, Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Helsiki Homework : Solutios Discussed Jauary 5, 08). Exercise.: Cosider the followig balls-ad-bi game. We start with oe black
Random assignment with integer costs
 Radom assigmet with iteger costs Robert Parviaie Departmet of Mathematics, Uppsala Uiversity P.O. Box 480, SE-7506 Uppsala, Swede robert.parviaie@math.uu.se Jue 4, 200 Abstract The radom assigmet problem
Radom assigmet with iteger costs Robert Parviaie Departmet of Mathematics, Uppsala Uiversity P.O. Box 480, SE-7506 Uppsala, Swede robert.parviaie@math.uu.se Jue 4, 200 Abstract The radom assigmet problem
An Introduction to Randomized Algorithms
 A Itroductio to Radomized Algorithms The focus of this lecture is to study a radomized algorithm for quick sort, aalyze it usig probabilistic recurrece relatios, ad also provide more geeral tools for aalysis
A Itroductio to Radomized Algorithms The focus of this lecture is to study a radomized algorithm for quick sort, aalyze it usig probabilistic recurrece relatios, ad also provide more geeral tools for aalysis
Quantum Computing Lecture 7. Quantum Factoring
 Quatum Computig Lecture 7 Quatum Factorig Maris Ozols Quatum factorig A polyomial time quatum algorithm for factorig umbers was published by Peter Shor i 1994. Polyomial time meas that the umber of gates
Quatum Computig Lecture 7 Quatum Factorig Maris Ozols Quatum factorig A polyomial time quatum algorithm for factorig umbers was published by Peter Shor i 1994. Polyomial time meas that the umber of gates
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Probabilistic aalysis ad Radomized algorithms Referece: CLRS Chapter 5 Topics: Hirig problem Idicatio radom variables Radomized algorithms Huo Hogwei 1 The hirig problem
Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Probabilistic aalysis ad Radomized algorithms Referece: CLRS Chapter 5 Topics: Hirig problem Idicatio radom variables Radomized algorithms Huo Hogwei 1 The hirig problem
SRC Technical Note June 17, Tight Thresholds for The Pure Literal Rule. Michael Mitzenmacher. d i g i t a l
 SRC Techical Note 1997-011 Jue 17, 1997 Tight Thresholds for The Pure Literal Rule Michael Mitzemacher d i g i t a l Systems Research Ceter 130 Lytto Aveue Palo Alto, Califoria 94301 http://www.research.digital.com/src/
SRC Techical Note 1997-011 Jue 17, 1997 Tight Thresholds for The Pure Literal Rule Michael Mitzemacher d i g i t a l Systems Research Ceter 130 Lytto Aveue Palo Alto, Califoria 94301 http://www.research.digital.com/src/
Intensive Algorithms Lecture 11. DFT and DP. Lecturer: Daniel A. Spielman February 20, f(n) O(g(n) log c g(n)).
 Itesive Algorithms Lecture 11 DFT ad DP Lecturer: Daiel A. Spielma February 20, 2018 11.1 Itroductio The purpose of this lecture is to lear how use the Discrete Fourier Trasform to save space i Dyamic
Itesive Algorithms Lecture 11 DFT ad DP Lecturer: Daiel A. Spielma February 20, 2018 11.1 Itroductio The purpose of this lecture is to lear how use the Discrete Fourier Trasform to save space i Dyamic
Math 216A Notes, Week 5
 Math 6A Notes, Week 5 Scribe: Ayastassia Sebolt Disclaimer: These otes are ot early as polished (ad quite possibly ot early as correct) as a published paper. Please use them at your ow risk.. Thresholds
Math 6A Notes, Week 5 Scribe: Ayastassia Sebolt Disclaimer: These otes are ot early as polished (ad quite possibly ot early as correct) as a published paper. Please use them at your ow risk.. Thresholds
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 CS271 Radomess & Computatio, Sprig 2018 Problem Set 2 Solutios Poit totals are i the margi; the maximum total umber of poits was 52. 1. Probabilistic method for domiatig sets 6pts Pick a radom subset S
CS271 Radomess & Computatio, Sprig 2018 Problem Set 2 Solutios Poit totals are i the margi; the maximum total umber of poits was 52. 1. Probabilistic method for domiatig sets 6pts Pick a radom subset S
ECE 6980 An Algorithmic and Information-Theoretic Toolbox for Massive Data
 ECE 6980 A Algorithmic ad Iformatio-Theoretic Toolbo for Massive Data Istructor: Jayadev Acharya Lecture # Scribe: Huayu Zhag 8th August, 017 1 Recap X =, ε is a accuracy parameter, ad δ is a error parameter.
ECE 6980 A Algorithmic ad Iformatio-Theoretic Toolbo for Massive Data Istructor: Jayadev Acharya Lecture # Scribe: Huayu Zhag 8th August, 017 1 Recap X =, ε is a accuracy parameter, ad δ is a error parameter.
Sequences and Series of Functions
 Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
w (1) ˆx w (1) x (1) /ρ and w (2) ˆx w (2) x (2) /ρ.
 2 5. Weighted umber of late jobs 5.1. Release dates ad due dates: maximimizig the weight of o-time jobs Oce we add release dates, miimizig the umber of late jobs becomes a sigificatly harder problem. For
2 5. Weighted umber of late jobs 5.1. Release dates ad due dates: maximimizig the weight of o-time jobs Oce we add release dates, miimizig the umber of late jobs becomes a sigificatly harder problem. For
Lecture 11: Hash Functions and Random Oracle Model
 CS 7810 Foudatios of Cryptography October 16, 017 Lecture 11: Hash Fuctios ad Radom Oracle Model Lecturer: Daiel Wichs Scribe: Akshar Varma 1 Topic Covered Defiitio of Hash Fuctios Merkle-Damgaård Theorem
CS 7810 Foudatios of Cryptography October 16, 017 Lecture 11: Hash Fuctios ad Radom Oracle Model Lecturer: Daiel Wichs Scribe: Akshar Varma 1 Topic Covered Defiitio of Hash Fuctios Merkle-Damgaård Theorem
On Algorithm for the Minimum Spanning Trees Problem with Diameter Bounded Below
 O Algorithm for the Miimum Spaig Trees Problem with Diameter Bouded Below Edward Kh. Gimadi 1,2, Alexey M. Istomi 1, ad Ekateria Yu. Shi 2 1 Sobolev Istitute of Mathematics, 4 Acad. Koptyug aveue, 630090
O Algorithm for the Miimum Spaig Trees Problem with Diameter Bouded Below Edward Kh. Gimadi 1,2, Alexey M. Istomi 1, ad Ekateria Yu. Shi 2 1 Sobolev Istitute of Mathematics, 4 Acad. Koptyug aveue, 630090
Math778P Homework 2 Solution
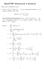 Math778P Homework Solutio Choose ay 5 problems to solve. 1. Let S = X i where X 1,..., X are idepedet uiform { 1, 1} radom variables. Prove that E( S = 1 ( 1 1 Proof by Day Rorabaugh: Let S = X i where
Math778P Homework Solutio Choose ay 5 problems to solve. 1. Let S = X i where X 1,..., X are idepedet uiform { 1, 1} radom variables. Prove that E( S = 1 ( 1 1 Proof by Day Rorabaugh: Let S = X i where
A Simple Derivation for the Frobenius Pseudoprime Test
 A Simple Derivatio for the Frobeius Pseudoprime Test Daiel Loebeberger Bo-Aache Iteratioal Ceter for Iformatio Techology March 17, 2008 Abstract Probabilistic compositeess tests are of great practical
A Simple Derivatio for the Frobeius Pseudoprime Test Daiel Loebeberger Bo-Aache Iteratioal Ceter for Iformatio Techology March 17, 2008 Abstract Probabilistic compositeess tests are of great practical
Last time, we talked about how Equation (1) can simulate Equation (2). We asserted that Equation (2) can also simulate Equation (1).
 6896 Quatum Complexity Theory Sept 23, 2008 Lecturer: Scott Aaroso Lecture 6 Last Time: Quatum Error-Correctio Quatum Query Model Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm (Computes x y i oe query) Today: Berstei-Vazirii
6896 Quatum Complexity Theory Sept 23, 2008 Lecturer: Scott Aaroso Lecture 6 Last Time: Quatum Error-Correctio Quatum Query Model Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm (Computes x y i oe query) Today: Berstei-Vazirii
Solutions for the Exam 9 January 2012
 Mastermath ad LNMB Course: Discrete Optimizatio Solutios for the Exam 9 Jauary 2012 Utrecht Uiversity, Educatorium, 15:15 18:15 The examiatio lasts 3 hours. Gradig will be doe before Jauary 23, 2012. Studets
Mastermath ad LNMB Course: Discrete Optimizatio Solutios for the Exam 9 Jauary 2012 Utrecht Uiversity, Educatorium, 15:15 18:15 The examiatio lasts 3 hours. Gradig will be doe before Jauary 23, 2012. Studets
Ma/CS 6b Class 19: Extremal Graph Theory
 /9/05 Ma/CS 6b Class 9: Extremal Graph Theory Paul Turá By Adam Sheffer Extremal Graph Theory The subfield of extremal graph theory deals with questios of the form: What is the maximum umber of edges that
/9/05 Ma/CS 6b Class 9: Extremal Graph Theory Paul Turá By Adam Sheffer Extremal Graph Theory The subfield of extremal graph theory deals with questios of the form: What is the maximum umber of edges that
Fundamenta Informaticae XXI (2001) IOS Press
 Fudameta Iformaticae XXI (2001) 1001 1006 1001 IOS Press Approximate Sortig Joachim Giese Max Plak Istitute for Computer Sciece Saarbrücke, Germay Eva Schuberth Istitute for Theoretical Computer Sciece
Fudameta Iformaticae XXI (2001) 1001 1006 1001 IOS Press Approximate Sortig Joachim Giese Max Plak Istitute for Computer Sciece Saarbrücke, Germay Eva Schuberth Istitute for Theoretical Computer Sciece
MA131 - Analysis 1. Workbook 3 Sequences II
 MA3 - Aalysis Workbook 3 Sequeces II Autum 2004 Cotets 2.8 Coverget Sequeces........................ 2.9 Algebra of Limits......................... 2 2.0 Further Useful Results........................
MA3 - Aalysis Workbook 3 Sequeces II Autum 2004 Cotets 2.8 Coverget Sequeces........................ 2.9 Algebra of Limits......................... 2 2.0 Further Useful Results........................
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutions
 CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
CS / MCS 401 Homework 3 grader solutios assigmet due July 6, 016 writte by Jāis Lazovskis maximum poits: 33 Some questios from CLRS. Questios marked with a asterisk were ot graded. 1 Use the defiitio of
COMP760, SUMMARY OF LECTURE 16.
 COMP760, SUMMARY OF LECTURE 16. HAMED HATAMI 1. Direct product ad direct sum theorems Oe class of the most iterestig ad fudametal questios of theoretical computer sciece are the closely related direct
COMP760, SUMMARY OF LECTURE 16. HAMED HATAMI 1. Direct product ad direct sum theorems Oe class of the most iterestig ad fudametal questios of theoretical computer sciece are the closely related direct
Some special clique problems
 Some special clique problems Reate Witer Istitut für Iformatik Marti-Luther-Uiversität Halle-Witteberg Vo-Seckedorff-Platz, D 0620 Halle Saale Germay Abstract: We cosider graphs with cliques of size k
Some special clique problems Reate Witer Istitut für Iformatik Marti-Luther-Uiversität Halle-Witteberg Vo-Seckedorff-Platz, D 0620 Halle Saale Germay Abstract: We cosider graphs with cliques of size k
The Discrete Fourier Transform
 The Discrete Fourier Trasform Complex Fourier Series Represetatio Recall that a Fourier series has the form a 0 + a k cos(kt) + k=1 b k si(kt) This represetatio seems a bit awkward, sice it ivolves two
The Discrete Fourier Trasform Complex Fourier Series Represetatio Recall that a Fourier series has the form a 0 + a k cos(kt) + k=1 b k si(kt) This represetatio seems a bit awkward, sice it ivolves two
M A T H F A L L CORRECTION. Algebra I 1 4 / 1 0 / U N I V E R S I T Y O F T O R O N T O
 M A T H 2 4 0 F A L L 2 0 1 4 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 CORRECTION Algebra I 1 4 / 1 0 / 2 0 1 4 U N I V E R S I T Y O F T O R O N T O P r o f e s s o r : D r o r B a r - N a t a Correctio Homework Assigmet
M A T H 2 4 0 F A L L 2 0 1 4 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 CORRECTION Algebra I 1 4 / 1 0 / 2 0 1 4 U N I V E R S I T Y O F T O R O N T O P r o f e s s o r : D r o r B a r - N a t a Correctio Homework Assigmet
Approximate Sorting. Institute for Theoretical Computer Science, ETH Zürich, CH-8092 Zürich
 Approximate Sortig Joachim Giese, Eva Schuberth, ad Miloš Stojaković Istitute for Theoretical Computer Sciece, ETH Zürich, CH-809 Zürich Abstract. We show that ay radomized algorithm to approximate ay
Approximate Sortig Joachim Giese, Eva Schuberth, ad Miloš Stojaković Istitute for Theoretical Computer Sciece, ETH Zürich, CH-809 Zürich Abstract. We show that ay radomized algorithm to approximate ay
6 Integers Modulo n. integer k can be written as k = qn + r, with q,r, 0 r b. So any integer.
 6 Itegers Modulo I Example 2.3(e), we have defied the cogruece of two itegers a,b with respect to a modulus. Let us recall that a b (mod ) meas a b. We have proved that cogruece is a equivalece relatio
6 Itegers Modulo I Example 2.3(e), we have defied the cogruece of two itegers a,b with respect to a modulus. Let us recall that a b (mod ) meas a b. We have proved that cogruece is a equivalece relatio
Infinite Sequences and Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
MA131 - Analysis 1. Workbook 2 Sequences I
 MA3 - Aalysis Workbook 2 Sequeces I Autum 203 Cotets 2 Sequeces I 2. Itroductio.............................. 2.2 Icreasig ad Decreasig Sequeces................ 2 2.3 Bouded Sequeces..........................
MA3 - Aalysis Workbook 2 Sequeces I Autum 203 Cotets 2 Sequeces I 2. Itroductio.............................. 2.2 Icreasig ad Decreasig Sequeces................ 2 2.3 Bouded Sequeces..........................
2 High-level Complexity vs. Concrete Complexity
 COMS 6998: Advaced Complexity Sprig 2017 Lecture 1: Course Itroductio ad Boolea Formulas Lecturer: Rocco Servedio Scribes: Jiahui Liu, Kailash Karthik Meiyappa 1 Overview of Topics 1. Boolea formulas (examples,
COMS 6998: Advaced Complexity Sprig 2017 Lecture 1: Course Itroductio ad Boolea Formulas Lecturer: Rocco Servedio Scribes: Jiahui Liu, Kailash Karthik Meiyappa 1 Overview of Topics 1. Boolea formulas (examples,
Test One (Answer Key)
 CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
CS395/Ma395 (Sprig 2005) Test Oe Name: Page 1 Test Oe (Aswer Key) CS395/Ma395: Aalysis of Algorithms This is a closed book, closed otes, 70 miute examiatio. It is worth 100 poits. There are twelve (12)
n outcome is (+1,+1, 1,..., 1). Let the r.v. X denote our position (relative to our starting point 0) after n moves. Thus X = X 1 + X 2 + +X n,
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2008 David Wager Note 9 Variace Questio: At each time step, I flip a fair coi. If it comes up Heads, I walk oe step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk oe
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2008 David Wager Note 9 Variace Questio: At each time step, I flip a fair coi. If it comes up Heads, I walk oe step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk oe
Lecture 19: Convergence
 Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
Lecture 19: Covergece Asymptotic approach I statistical aalysis or iferece, a key to the success of fidig a good procedure is beig able to fid some momets ad/or distributios of various statistics. I may
MAT1026 Calculus II Basic Convergence Tests for Series
 MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
Element sampling: Part 2
 Chapter 4 Elemet samplig: Part 2 4.1 Itroductio We ow cosider uequal probability samplig desigs which is very popular i practice. I the uequal probability samplig, we ca improve the efficiecy of the resultig
Chapter 4 Elemet samplig: Part 2 4.1 Itroductio We ow cosider uequal probability samplig desigs which is very popular i practice. I the uequal probability samplig, we ca improve the efficiecy of the resultig
62. Power series Definition 16. (Power series) Given a sequence {c n }, the series. c n x n = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +
 62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
Lecture 2: April 3, 2013
 TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 2: April 3, 203 Scribe: Shubhedu Trivedi Coi tosses cotiued We retur to the coi tossig example from the last lecture agai: Example. Give,
TTIC/CMSC 350 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 203 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 2: April 3, 203 Scribe: Shubhedu Trivedi Coi tosses cotiued We retur to the coi tossig example from the last lecture agai: Example. Give,
Frequentist Inference
 Frequetist Iferece The topics of the ext three sectios are useful applicatios of the Cetral Limit Theorem. Without kowig aythig about the uderlyig distributio of a sequece of radom variables {X i }, for
Frequetist Iferece The topics of the ext three sectios are useful applicatios of the Cetral Limit Theorem. Without kowig aythig about the uderlyig distributio of a sequece of radom variables {X i }, for
Hashing and Amortization
 Lecture Hashig ad Amortizatio Supplemetal readig i CLRS: Chapter ; Chapter 7 itro; Sectio 7.. Arrays ad Hashig Arrays are very useful. The items i a array are statically addressed, so that isertig, deletig,
Lecture Hashig ad Amortizatio Supplemetal readig i CLRS: Chapter ; Chapter 7 itro; Sectio 7.. Arrays ad Hashig Arrays are very useful. The items i a array are statically addressed, so that isertig, deletig,
The multiplicative structure of finite field and a construction of LRC
 IERG6120 Codig for Distributed Storage Systems Lecture 8-06/10/2016 The multiplicative structure of fiite field ad a costructio of LRC Lecturer: Keeth Shum Scribe: Zhouyi Hu Notatios: We use the otatio
IERG6120 Codig for Distributed Storage Systems Lecture 8-06/10/2016 The multiplicative structure of fiite field ad a costructio of LRC Lecturer: Keeth Shum Scribe: Zhouyi Hu Notatios: We use the otatio
1. By using truth tables prove that, for all statements P and Q, the statement
 Author: Satiago Salazar Problems I: Mathematical Statemets ad Proofs. By usig truth tables prove that, for all statemets P ad Q, the statemet P Q ad its cotrapositive ot Q (ot P) are equivalet. I example.2.3
Author: Satiago Salazar Problems I: Mathematical Statemets ad Proofs. By usig truth tables prove that, for all statemets P ad Q, the statemet P Q ad its cotrapositive ot Q (ot P) are equivalet. I example.2.3
How to walk home drunk. Some Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science for. Probability Refresher. Probability Refresher.
 15251 Some Great Theoretical Ideas i Computer Sciece for "My frieds keep askig me what 251 is like. I lik them to this video: http://youtube.com/watch?v=m275pjvwrli" Probability Refresher What s a Radom
15251 Some Great Theoretical Ideas i Computer Sciece for "My frieds keep askig me what 251 is like. I lik them to this video: http://youtube.com/watch?v=m275pjvwrli" Probability Refresher What s a Radom
YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE CPSC 467a: Crytograhy ad Comuter Security Notes 16 (rev. 1 Professor M. J. Fischer November 3, 2008 68 Legedre Symbol Lecture Notes 16 ( Let be a odd rime,
YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE CPSC 467a: Crytograhy ad Comuter Security Notes 16 (rev. 1 Professor M. J. Fischer November 3, 2008 68 Legedre Symbol Lecture Notes 16 ( Let be a odd rime,
Model of Computation and Runtime Analysis
 Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
Model of Computatio ad Rutime Aalysis Model of Computatio Model of Computatio Specifies Set of operatios Cost of operatios (ot ecessarily time) Examples Turig Machie Radom Access Machie (RAM) PRAM Map
# fixed points of g. Tree to string. Repeatedly select the leaf with the smallest label, write down the label of its neighbour and remove the leaf.
 Combiatorics Graph Theory Coutig labelled ad ulabelled graphs There are 2 ( 2) labelled graphs of order. The ulabelled graphs of order correspod to orbits of the actio of S o the set of labelled graphs.
Combiatorics Graph Theory Coutig labelled ad ulabelled graphs There are 2 ( 2) labelled graphs of order. The ulabelled graphs of order correspod to orbits of the actio of S o the set of labelled graphs.
Square-Congruence Modulo n
 Square-Cogruece Modulo Abstract This paper is a ivestigatio of a equivalece relatio o the itegers that was itroduced as a exercise i our Discrete Math class. Part I - Itro Defiitio Two itegers are Square-Cogruet
Square-Cogruece Modulo Abstract This paper is a ivestigatio of a equivalece relatio o the itegers that was itroduced as a exercise i our Discrete Math class. Part I - Itro Defiitio Two itegers are Square-Cogruet
1 Last time: similar and diagonalizable matrices
 Last time: similar ad diagoalizable matrices Let be a positive iteger Suppose A is a matrix, v R, ad λ R Recall that v a eigevector for A with eigevalue λ if v ad Av λv, or equivaletly if v is a ozero
Last time: similar ad diagoalizable matrices Let be a positive iteger Suppose A is a matrix, v R, ad λ R Recall that v a eigevector for A with eigevalue λ if v ad Av λv, or equivaletly if v is a ozero
Some remarks for codes and lattices over imaginary quadratic
 Some remarks for codes ad lattices over imagiary quadratic fields Toy Shaska Oaklad Uiversity, Rochester, MI, USA. Caleb Shor Wester New Eglad Uiversity, Sprigfield, MA, USA. shaska@oaklad.edu Abstract
Some remarks for codes ad lattices over imagiary quadratic fields Toy Shaska Oaklad Uiversity, Rochester, MI, USA. Caleb Shor Wester New Eglad Uiversity, Sprigfield, MA, USA. shaska@oaklad.edu Abstract
Math 4400/6400 Homework #7 solutions
 MATH 4400 problems. Math 4400/6400 Homewor #7 solutios 1. Let p be a prime umber. Show that the order of 1 + p modulo p 2 is exactly p. Hit: Expad (1 + p) p by the biomial theorem, ad recall from MATH
MATH 4400 problems. Math 4400/6400 Homewor #7 solutios 1. Let p be a prime umber. Show that the order of 1 + p modulo p 2 is exactly p. Hit: Expad (1 + p) p by the biomial theorem, ad recall from MATH
Solutions to Math 347 Practice Problems for the final
 Solutios to Math 347 Practice Problems for the fial 1) True or False: a) There exist itegers x,y such that 50x + 76y = 6. True: the gcd of 50 ad 76 is, ad 6 is a multiple of. b) The ifiimum of a set is
Solutios to Math 347 Practice Problems for the fial 1) True or False: a) There exist itegers x,y such that 50x + 76y = 6. True: the gcd of 50 ad 76 is, ad 6 is a multiple of. b) The ifiimum of a set is
Lecture 4: April 10, 2013
 TTIC/CMSC 1150 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 01 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 4: April 10, 01 Scribe: Haris Agelidakis 1 Chebyshev s Iequality recap I the previous lecture, we used Chebyshev s iequality to get a
TTIC/CMSC 1150 Mathematical Toolkit Sprig 01 Madhur Tulsiai Lecture 4: April 10, 01 Scribe: Haris Agelidakis 1 Chebyshev s Iequality recap I the previous lecture, we used Chebyshev s iequality to get a
7.1 Convergence of sequences of random variables
 Chapter 7 Limit Theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Chapter 7 Limit Theorems Throughout this sectio we will assume a probability space (, F, P), i which is defied a ifiite sequece of radom variables (X ) ad a radom variable X. The fact that for every ifiite
Lecture 2: Monte Carlo Simulation
 STAT/Q SCI 43: Itroductio to Resamplig ethods Sprig 27 Istructor: Ye-Chi Che Lecture 2: ote Carlo Simulatio 2 ote Carlo Itegratio Assume we wat to evaluate the followig itegratio: e x3 dx What ca we do?
STAT/Q SCI 43: Itroductio to Resamplig ethods Sprig 27 Istructor: Ye-Chi Che Lecture 2: ote Carlo Simulatio 2 ote Carlo Itegratio Assume we wat to evaluate the followig itegratio: e x3 dx What ca we do?
Lecture 11: Channel Coding Theorem: Converse Part
 EE376A/STATS376A Iformatio Theory Lecture - 02/3/208 Lecture : Chael Codig Theorem: Coverse Part Lecturer: Tsachy Weissma Scribe: Erdem Bıyık I this lecture, we will cotiue our discussio o chael codig
EE376A/STATS376A Iformatio Theory Lecture - 02/3/208 Lecture : Chael Codig Theorem: Coverse Part Lecturer: Tsachy Weissma Scribe: Erdem Bıyık I this lecture, we will cotiue our discussio o chael codig
ORIE 633 Network Flows September 27, Lecture 8
 ORIE 633 Network Flows September 7, 007 Lecturer: David P. Williamso Lecture 8 Scribe: Gema Plaza-Martíez 1 Global mi-cuts i udirected graphs 1.1 Radom cotractio Recall from last time we itroduced the
ORIE 633 Network Flows September 7, 007 Lecturer: David P. Williamso Lecture 8 Scribe: Gema Plaza-Martíez 1 Global mi-cuts i udirected graphs 1.1 Radom cotractio Recall from last time we itroduced the
2.1. The Algebraic and Order Properties of R Definition. A binary operation on a set F is a function B : F F! F.
 CHAPTER 2 The Real Numbers 2.. The Algebraic ad Order Properties of R Defiitio. A biary operatio o a set F is a fuctio B : F F! F. For the biary operatios of + ad, we replace B(a, b) by a + b ad a b, respectively.
CHAPTER 2 The Real Numbers 2.. The Algebraic ad Order Properties of R Defiitio. A biary operatio o a set F is a fuctio B : F F! F. For the biary operatios of + ad, we replace B(a, b) by a + b ad a b, respectively.
Mathematical Foundation. CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai
 Mathematical Foudatio CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai Complexity of Algorithms Aalysis of algorithm: to predict the ruig time required by a algorithm. Elemetary operatios: arithmetic & boolea operatios:
Mathematical Foudatio CSE 6331 Algorithms Steve Lai Complexity of Algorithms Aalysis of algorithm: to predict the ruig time required by a algorithm. Elemetary operatios: arithmetic & boolea operatios:
HOMEWORK 2 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS CSE 55 RANDOMIZED AND APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS 1. Questio 1. a) The larger the value of k is, the smaller the expected umber of days util we get all the coupos we eed. I fact if = k
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS CSE 55 RANDOMIZED AND APPROXIMATION ALGORITHMS 1. Questio 1. a) The larger the value of k is, the smaller the expected umber of days util we get all the coupos we eed. I fact if = k
Solution. 1 Solutions of Homework 1. Sangchul Lee. October 27, Problem 1.1
 Solutio Sagchul Lee October 7, 017 1 Solutios of Homework 1 Problem 1.1 Let Ω,F,P) be a probability space. Show that if {A : N} F such that A := lim A exists, the PA) = lim PA ). Proof. Usig the cotiuity
Solutio Sagchul Lee October 7, 017 1 Solutios of Homework 1 Problem 1.1 Let Ω,F,P) be a probability space. Show that if {A : N} F such that A := lim A exists, the PA) = lim PA ). Proof. Usig the cotiuity
Lecture 1. January 8, 2018
 Lecture 1 Jauary 8, 018 1 Primes A prime umber p is a positive iteger which caot be writte as ab for some positive itegers a, b > 1. A prime p also have the property that if p ab, the p a or p b. This
Lecture 1 Jauary 8, 018 1 Primes A prime umber p is a positive iteger which caot be writte as ab for some positive itegers a, b > 1. A prime p also have the property that if p ab, the p a or p b. This
If a subset E of R contains no open interval, is it of zero measure? For instance, is the set of irrationals in [0, 1] is of measure zero?
![If a subset E of R contains no open interval, is it of zero measure? For instance, is the set of irrationals in [0, 1] is of measure zero? If a subset E of R contains no open interval, is it of zero measure? For instance, is the set of irrationals in [0, 1] is of measure zero?](/thumbs/89/99848926.jpg) 2 Lebesgue Measure I Chapter 1 we defied the cocept of a set of measure zero, ad we have observed that every coutable set is of measure zero. Here are some atural questios: If a subset E of R cotais a
2 Lebesgue Measure I Chapter 1 we defied the cocept of a set of measure zero, ad we have observed that every coutable set is of measure zero. Here are some atural questios: If a subset E of R cotais a
ALG 2.2 Search Algorithms
 Algorithms Professor Joh Reif ALG 2.2 Search Algorithms (a Biary Search: average case (b Biary Search with Errors (homework (c Iterpolatio Search (d Ubouded Search Biary Search Trees (i sorted Table of
Algorithms Professor Joh Reif ALG 2.2 Search Algorithms (a Biary Search: average case (b Biary Search with Errors (homework (c Iterpolatio Search (d Ubouded Search Biary Search Trees (i sorted Table of
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2007 Luca Trevisan Lecture 22
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2007 Luca Trevisa Lecture 22 Aother Importat Distributio The Geometric Distributio Questio: A biased coi with Heads probability p is tossed repeatedly util the first
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Sprig 2007 Luca Trevisa Lecture 22 Aother Importat Distributio The Geometric Distributio Questio: A biased coi with Heads probability p is tossed repeatedly util the first
1 Approximating Integrals using Taylor Polynomials
 Seughee Ye Ma 8: Week 7 Nov Week 7 Summary This week, we will lear how we ca approximate itegrals usig Taylor series ad umerical methods. Topics Page Approximatig Itegrals usig Taylor Polyomials. Defiitios................................................
Seughee Ye Ma 8: Week 7 Nov Week 7 Summary This week, we will lear how we ca approximate itegrals usig Taylor series ad umerical methods. Topics Page Approximatig Itegrals usig Taylor Polyomials. Defiitios................................................
Monte Carlo Integration
 Mote Carlo Itegratio I these otes we first review basic umerical itegratio methods (usig Riema approximatio ad the trapezoidal rule) ad their limitatios for evaluatig multidimesioal itegrals. Next we itroduce
Mote Carlo Itegratio I these otes we first review basic umerical itegratio methods (usig Riema approximatio ad the trapezoidal rule) ad their limitatios for evaluatig multidimesioal itegrals. Next we itroduce
1 Review and Overview
 DRAFT a fial versio will be posted shortly CS229T/STATS231: Statistical Learig Theory Lecturer: Tegyu Ma Lecture #3 Scribe: Migda Qiao October 1, 2013 1 Review ad Overview I the first half of this course,
DRAFT a fial versio will be posted shortly CS229T/STATS231: Statistical Learig Theory Lecturer: Tegyu Ma Lecture #3 Scribe: Migda Qiao October 1, 2013 1 Review ad Overview I the first half of this course,
Commutativity in Permutation Groups
 Commutativity i Permutatio Groups Richard Wito, PhD Abstract I the group Sym(S) of permutatios o a oempty set S, fixed poits ad trasiet poits are defied Prelimiary results o fixed ad trasiet poits are
Commutativity i Permutatio Groups Richard Wito, PhD Abstract I the group Sym(S) of permutatios o a oempty set S, fixed poits ad trasiet poits are defied Prelimiary results o fixed ad trasiet poits are
Bertrand s Postulate
 Bertrad s Postulate Lola Thompso Ross Program July 3, 2009 Lola Thompso (Ross Program Bertrad s Postulate July 3, 2009 1 / 33 Bertrad s Postulate I ve said it oce ad I ll say it agai: There s always a
Bertrad s Postulate Lola Thompso Ross Program July 3, 2009 Lola Thompso (Ross Program Bertrad s Postulate July 3, 2009 1 / 33 Bertrad s Postulate I ve said it oce ad I ll say it agai: There s always a
Lecture Chapter 6: Convergence of Random Sequences
 ECE5: Aalysis of Radom Sigals Fall 6 Lecture Chapter 6: Covergece of Radom Sequeces Dr Salim El Rouayheb Scribe: Abhay Ashutosh Doel, Qibo Zhag, Peiwe Tia, Pegzhe Wag, Lu Liu Radom sequece Defiitio A ifiite
ECE5: Aalysis of Radom Sigals Fall 6 Lecture Chapter 6: Covergece of Radom Sequeces Dr Salim El Rouayheb Scribe: Abhay Ashutosh Doel, Qibo Zhag, Peiwe Tia, Pegzhe Wag, Lu Liu Radom sequece Defiitio A ifiite
Seunghee Ye Ma 8: Week 5 Oct 28
 Week 5 Summary I Sectio, we go over the Mea Value Theorem ad its applicatios. I Sectio 2, we will recap what we have covered so far this term. Topics Page Mea Value Theorem. Applicatios of the Mea Value
Week 5 Summary I Sectio, we go over the Mea Value Theorem ad its applicatios. I Sectio 2, we will recap what we have covered so far this term. Topics Page Mea Value Theorem. Applicatios of the Mea Value
Polynomial reduction. Outline Lecture. Non deterministic polynomial time. Example 1 : discrete log. Lecture: Polynomial reduction.
 Outlie Lecture Part 1 : Asymmetric cryptography, oe way fuctio, complexity Part 2 : arithmetic complexity ad lower bouds : expoetiatio Part 3 : Provable security ad polyomial time reductio : P, NP classes.
Outlie Lecture Part 1 : Asymmetric cryptography, oe way fuctio, complexity Part 2 : arithmetic complexity ad lower bouds : expoetiatio Part 3 : Provable security ad polyomial time reductio : P, NP classes.
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE
 COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
Homework 3. = k 1. Let S be a set of n elements, and let a, b, c be distinct elements of S. The number of k-subsets of S is
 Homewor 3 Chapter 5 pp53: 3 40 45 Chapter 6 p85: 4 6 4 30 Use combiatorial reasoig to prove the idetity 3 3 Proof Let S be a set of elemets ad let a b c be distict elemets of S The umber of -subsets of
Homewor 3 Chapter 5 pp53: 3 40 45 Chapter 6 p85: 4 6 4 30 Use combiatorial reasoig to prove the idetity 3 3 Proof Let S be a set of elemets ad let a b c be distict elemets of S The umber of -subsets of
SOME TRIBONACCI IDENTITIES
 Mathematics Today Vol.7(Dec-011) 1-9 ISSN 0976-38 Abstract: SOME TRIBONACCI IDENTITIES Shah Devbhadra V. Sir P.T.Sarvajaik College of Sciece, Athwalies, Surat 395001. e-mail : drdvshah@yahoo.com The sequece
Mathematics Today Vol.7(Dec-011) 1-9 ISSN 0976-38 Abstract: SOME TRIBONACCI IDENTITIES Shah Devbhadra V. Sir P.T.Sarvajaik College of Sciece, Athwalies, Surat 395001. e-mail : drdvshah@yahoo.com The sequece
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
On Random Line Segments in the Unit Square
 O Radom Lie Segmets i the Uit Square Thomas A. Courtade Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Califoria Los Ageles, Califoria 90095 Email: tacourta@ee.ucla.edu I. INTRODUCTION Let Q = [0, 1] [0,
O Radom Lie Segmets i the Uit Square Thomas A. Courtade Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Califoria Los Ageles, Califoria 90095 Email: tacourta@ee.ucla.edu I. INTRODUCTION Let Q = [0, 1] [0,
Sequences III. Chapter Roots
 Chapter 4 Sequeces III 4. Roots We ca use the results we ve established i the last workbook to fid some iterestig limits for sequeces ivolvig roots. We will eed more techical expertise ad low cuig tha
Chapter 4 Sequeces III 4. Roots We ca use the results we ve established i the last workbook to fid some iterestig limits for sequeces ivolvig roots. We will eed more techical expertise ad low cuig tha
ITEC 360 Data Structures and Analysis of Algorithms Spring for n 1
 ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
ITEC 360 Data Structures ad Aalysis of Algorithms Sprig 006 1. Prove that f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is Θ ( ). 60 + 5 + 1 60 + 5 + = 66 for 1 Take C 1 = 66 f () = 60 + 5 + 1 is O( ) Sice 60 + 5 + 1 60 for 1 If
Homework 2 January 19, 2006 Math 522. Direction: This homework is due on January 26, In order to receive full credit, answer
 Homework 2 Jauary 9, 26 Math 522 Directio: This homework is due o Jauary 26, 26. I order to receive full credit, aswer each problem completely ad must show all work.. What is the set of the uits (that
Homework 2 Jauary 9, 26 Math 522 Directio: This homework is due o Jauary 26, 26. I order to receive full credit, aswer each problem completely ad must show all work.. What is the set of the uits (that
