RADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR A NONPOSITONE PROBLEM IN AN ANNULUS
|
|
|
- Brendan Thornton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 04 (04), o. 9, pp. 0. ISS: UL: o ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS FO A OPOSITOE POBLEM I A AULUS SAID HAKIMI, ABDEAHIM ZETITI Abstact. The main pupose of this aticle is to pove the existence of adial positive solutions fo a nonpositone poblem in an annulus when the nonlineaity is supelinea and has moe than one zeo.. Intoduction In this aticle we study the existence of adial positive solutions fo the boundayvalue poblem u(x) = λf(u(x)) x Ω, (.) u(x) = 0 x Ω, whee λ > 0, f : [0, + ) is a continuous nonlinea function that has moe than one zeo, and Ω is the annulus: Ω = C(0,, ) = {x : < x < } ( >, 0 < < ). When f is a nondeceasing nonlineaity satisfying f(0) < 0 (the nonpositone case) and has only one zeo, poblem (.) has been studied by Acoya and Zetiti [ and by Hakimi and Zetiti in a ball when f has moe than one zeo [5. We obseve that the existence of adial positive solutions of (.) is equivalent to the existence of positive solutions of the poblem u () u () = λf(u()) < < (.) u() = u( ) = 0. Ou main objective in this aticle is to pove that the esult of existence of adial positive solutions of the poblem (.) emains valid when f has moe than one zeo and is not inceasing entiely on [0, + ); see [, Theoem.4. emak.. In this aticle, we assume (without loss of geneality) that f has exactly thee zeos. We assume that the map f : [0, + ) satisfies the following hypotheses: (F) f C ([0, + ), ) such that f has thee zeos β < β < β 3, with f (β i ) 0 fo all i {,, 3}. Moeove, f 0 on [β 3, + ). (F) f(0) < Mathematics Subject Classification. 35J5, 34B8. Key wods and phases. onpositone poblem; adial positive solutions. c 04 Texas State Univesity - San Macos. Submitted Apil, 03. Published Apil 5, 04.
2 S. HAKIMI, A. ZETITI EJDE-04/9 f(u) (F3) lim u + u = +. (F4) The function h(u) = F (u) f(u)u is bounded fom below in [0, + ), whee F (x) = x 0 f()d. emak.. We obseve that ou aguments also wok in the case Ω = B(O, ), impoving slightly the esults in [5. In fact in [5, besides imposing that f is inceasing, we need (F), (F), (F3) and that Fo some k (0, ), lim d + ( d f(d) ) / ( F (kd) df(d)) = +. On the othe hand, it is clea that ou hypothesis (F4) is moe geneal than this assumption. Fo a nonexistence esult of positive solutions fo supelineaities satisfying (F), (F) and (F3) see [6. Also see [3 fo existence and nonexistence of positive solutions fo a class of supelinea semipositone systems, and [4 fo existence and multiplicity esults fo semipositone poblems.. Main esult In this section, we give the main esult in this wok. Moe pecisely we shall pove the following theoem. Theoem.. Assume that the hypotheses (F) (F4) ae satisfied. Then thee exists a positive eal numbe λ such that if λ < λ, poblem (.) has at least one adial positive solution. To pove Theoem., we need the next fou technical lemmas. The fist lemma assues the existence of a unique solution u(., d, λ) of (.) in [, + ) fo all λ, d > 0. The thee last lemmas concen the behaviou of the solution of (.). emak.. In this aticle we follow the wok of Acoya and Zetiti [, and we note that the poofs of Lemmas.4 and.7 ae analogous with those of [, Lemmas. and.3. On the othe hand, the poofs of the second and thid lemmas ae diffeent fom that of [, Lemma. and.. This is so because ou f has moe than one zeo. So we apply the Shooting method. Fo this we conside the auxiliay bounday-value poblem u () u () = λf(u()), > (.) u() = 0, u () = d, whee d is the paamete of Shooting method. emak.3. Fo suitable d, poblem (.) has a solution u := u(., d, λ) such that u > 0 on (, ) and u( ) = 0. So, such solution u of (.) is also a positive solution of (.). In this sequel, we suppose that the nonlineaity f C ([0, + )) is always extended to by f (,0) f(0). Lemma.4. Let λ, d > 0 and f C ([0, + )) a function which is bounded fom below. Then poblem (.) has a unique solution u(., d, λ) defined in [, + ), In addition, fo evey d > 0 thee exist M = M(d) > 0 and λ = λ(d) > 0 such that max u(, d, λ) M, [, b λ (0, λ(d)).
3 EJDE-04/9 ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS 3 Poof. The poof of the existence is given in two steps. In fist, we show the existence and uniqueness of a local solution of (.); i.e, the existence a ε = ε(d, λ) > 0 such that (.) has a unique solution on [, + ε. In the second step we pove that this unique solution can be extended to [, + ). Step : (Local solution). Conside the poblem u () u () = λf(u()), > u( ) = a, u ( ) = b, (.) whee. Let u be a solution of (.). Multiplying the equation by and using the initial conditions, we obtain fom which u satisfies u() = a + b u () = { b λ ( ) λ s f(u(s))ds }. (.3) t s f(u(s))ds dt. (.4) Convesely, if u is a continuous function satisfying (.4), then u is a solution of (.). Hence, to pove the existence and uniqueness of a solution u of (.) defined in some inteval [, + ε, it is sufficient to show the existence of a unique fixed point of the opeato T defined on X (the Banach space of the eal continuous functions on [, + ε with the unifom nom), whee (T v)() = a+ b T : X = C([, + ε, ) X ( v T v, ) λ t s f(v(s))ds dt, (.5) fo all [, + ε and v X. To check this, Let δ > 0 such that δ > a and B(0, δ) = {u X : u δ}. Fo all u, v B(0, δ), we have (T u T v)() = λ t s {f(v(s)) f(u(s))}ds dt, then t (T u T v)() λ t [ λ Howeve, t t [ s dsdt = t s sup ζ (0,δ s ds t [t dt t dt f (ζ) v(s) u(s) dsdt dt sup ζ (0,δ dt t f (ζ) u v.
4 4 S. HAKIMI, A. ZETITI EJDE-04/9 theefoe, Hence Similaly, = ( ) ( ( ) ) ( ) = + ( ). ( ) ( + ε), because [, + ε = ε( + ε) ; T u T v ε( + ε) λ sup f (ζ) u v ζ [0,δ T u T v λ ε( + ε) λ sup f (ζ) u v. ζ [0,δ sup f (ζ) ε( + ε) u v. (.6) ζ (0,δ ( T u a + b ) ( + ε) + λ sup f(ζ) ε( + ε). (.7) ζ [0,δ ow, by (.6) and (.7), we can choose ε = ε(δ) > 0 (depending on δ) sufficiently small such that T is a contaction fom B(0, δ) to B(0, δ). Consequently, T has a fixed point u in B(0, δ). The fixed point u is unique in X fo a δ as lage as we wanted. Step : Let u(.) = u(., d, λ) be the unique solution of (.) (we take a = 0, b = d and = in (.)), and denote by [, (d, λ)) its maximal domain. We shall pove by contadiction that (d, λ) = +. Fo it, assume := (d, λ) < +. u is bounded on [, ). In fact, using (.4) and that f is bounded fom below, we have d d = u() + λ u() + λ ( ) t inf f(ξ) ξ [0,+ ) s f(u(s))ds dt t s ds dt, [, ), then, thee exists K > 0 such that u() K fo all [, ). On the othe hand, using again (.4), we obtain ( u() d ) λ max f(ξ) ξ [0,K K, [, ), fo convenient K > 0. Hence u is bounded. t s ds dt
5 EJDE-04/9 ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS 5 By using this and (.3) and (.4), we deduce that {u( n )} and {u ( n )} ae the Cauchy sequence fo all sequence ( n ) [, ) conveging to. This is equivalent to the existence of the finite limits ow, conside the poblem lim u() = a and lim u () = b. v () v () = λf(v()), v( ) = a, v ( ) = b < (.8) and by step, we deduce the existence of a positive numbe ε > 0 and a solution v of this poblem in [, + ε. It is easy to see that { u(), if < w() = v(), if + ε, is a solution of (.) in [, + ε which is a contadiction, so = +. To pove the second pat of the lemma, we conside the opeato T defined by (.5) on X 0 = C([,, ) with =, a = 0 and b = d. Taking M = δ > d and λ(d) = min { M M max ξ [0,M f(ξ), M max ξ [0,M f (ξ) } with M = e t s ds dt. By (.6) and (.7), we deduce that T is a contaction fom B(0, M, X 0 ) into B(0, M, X 0 ), whee B(0, M, X 0 ) = {u X 0 : max u() M}. [, b So, the unique fixed point of T belongs to B(0, M, X 0 ). The lemma is poved. Lemma.5. Assume (F), (F) and let d 0 > 0. Then thee exists λ = λ (d 0 ) > 0 such that the unique solution u(, d 0, λ) of (.) satisfies Poof. Fo λ > 0, we conside the set u(, d 0, λ) > 0, (,, λ (0, λ ). Ψ = { (, ) : u(.) = u(., d 0, λ)is nondeceasing in (, )}. Since u () = d 0 > 0, Ψ is nonempty, and clealy bounded fom above. Let = sup Ψ (which depends on λ). We have two cases: Case. If =, the poof is complete. Case. If <, we shall pove u(.) = u(., d 0, λ) > 0, fo all (, fo all λ sufficiently small. In ode to show it, assume that <. Then u ( ) = 0, and since u () = [ d 0 λ s f(u(s))ds, then u( ) > β. Hence the set Γ = { [, : u(t) β and u (t) 0, t [, } is nonempty and bounded fom above. Let = sup Γ >. We shall pove that fo λ sufficiently small =. We obseve that u () 0 fo all Γ, then
6 6 S. HAKIMI, A. ZETITI EJDE-04/9 u() u( ), fo all [,. Theefoe, by the mean value theoem, thee exists c (, ) such that u( ) = u( ) + u (c)( ), but then u (c) = λ c u( ) > u( ) λ c t f(u(t))dt, sup f(ζ) ( ). [β,u( ) If M = M(d 0 ) > 0 and λ(d 0 ) > 0 (defined in Lemma.4), then β < u( ) M, λ (0, λ(d 0 )). Let K = K(d 0 ) > 0 such that f(ζ) < K(ζ β ) fo all ζ (β, M. We deduce that λk u( ) > u( ) ( )(u( ) β ), λ (0, λ(d 0 )), Thus, if λ (0, λ ) with λ = min{λ(d 0 ), K( b ) b } we have u( ) > β, which implies that =. Lemma.6. Assume (F) (F3). Let λ > 0. Then (i) lim d + (d, λ) = (ii) lim d + u(, d, λ) = + Poof. If (i) is not tue, then thee exists ε > 0 so that fo all n thee exists d n such that (d n, λ) ε, fom which (d n, λ) + ε (because (d n, λ) ), then thee exists 0 (, ) and a sequence (d n ) (0, + ) conveging to such that u n := u(., d n, λ) satisfies Let = +0. By the equality u n () = d n u n () > 0, u n() 0, (, 0, n. ( ) λ t s f(u n (s))ds dt, we obseve that (u n ()) is unbounded. Passing to a subsequence of (d n ), if it is necessay, we can suppose lim n + u n () = +. ow, conside M n = inf { f(u n ()) u n () : (, 0 ) }. By (F3), lim n + M n = +. Let n 0 such that λm n0 > µ 3 whee µ 3 is the thid eigenvalue of [ d d + d d in (, 0) with Diichlet bounday conditions. We take a nonzeo eigenfunction φ 3 associated to µ 3 ; i.e., φ 3() + φ 3() + µ 3 φ 3 () = 0, < < 0 φ 3 () = 0 = φ 3 ( 0 ).
7 EJDE-04/9 ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS 7 Since φ 3 has two zeos in (, 0 ), we deduce fom the Stum compaison Theoem [7 that u n0 has at least one zeo in (, 0 ). Which is a contadiction (because u n () > 0 fo all (, 0 and all n ). (ii) Let be the same numbe as in the poof of lemma.5. we have u ( ) = 0. Howeve, u ( ) = [ d λ t f(u(t))dt, then Hence d = λ t f(u(t))dt. lim u(, d, λ) = +. d + Lemma.7. Assume (F) (F4) and let γ be a positive numbe. Then thee exists a λ > 0 such that: (a) Fo all λ (0, λ ) the unique solution u(, d, λ) of (.) satisfies u (, d, λ) + u (, d, λ) > 0, [,, d γ. (b) Fo all λ (0, λ ), thee exists d > γ such that u(, d, λ) < 0 fo some (,. Poof. (a) Let λ, d > 0 and u(.) = u(., d, λ) the unique solution of (.). We define the auxiliay function H on [, + ) by setting H() = u () + λf (u()) + u()u (), [, + ). We can pove, as in [, 5 the next identity of Pohozaev-type: H() = t H(t)+λ t s [F (u(s)) f(u(s))u(s)ds, Taking t =, in this identity we obtain H() = d + λ s [ F (u(s)) f(u(s))u(s) ds, t [,. hence H() d ( ) + λm, (.9) whee m is a stictly negative eal such that F (u) f(u)u m fo all u, so H() γ ( ) + λm, [,, d γ. We note that m exists by (f 4 ). Hence thee exists λ > 0 such that Theefoe, H() > 0, [,, d γ, λ (0, λ ). (.0) u (, d, λ) + u (, d, λ) > 0, [,, d γ, λ (0, λ ). (b) We ague by contadiction: fix λ (0, λ ) and suppose that u(, d, λ) 0, [,, d γ.
8 8 S. HAKIMI, A. ZETITI EJDE-04/9 Choose ϱ > 0 such that thee exists a solution of ω + ω + ϱω = 0, whee ω(0) =, ω (0) = 0, is the fist zeo of ω. 4 We note (see [8) that ω() 0 and ω () < 0, fo all (0, b 4. By (F3), thee exists d 0 = d 0 (λ) > γ such that f(u) u ϱ λ, u d 0. (.) On the othe hand, let = (d, λ) and = (d, λ) be the same numbes as in the poof of Lemma.5. By Lemma.6, we can assume that = (d, λ) < + < 4 and u(, d, λ) > d 0, d d 0, the definitions of and imply u (, d, λ) 0, [,, d d 0. (.) Define v() = u( )ω( ), hence v () + v () + ϱv() = 0, fo all (, + b 4 ) with u( ) = v( ), v ( ) = 0, v( + b 4 ) = 0, v() > 0 and v () 0, fo all (, + b 4 ), thus v () + v () + ϱv() 0, (, + ), 4 if u() d 0, fo all (, + b 4 ), hence by (.) and the Stum compaison theoem (see [7), u have a zeo in (, + b 4 ). Which is a contadiction. Hence, thee exists (, + b 4 ) such that u(, d, λ) = d 0. ow, conside the enegy function E(, d, λ) = u (, d, λ) + λf (u(, d, λ)),. By (.9), (.) and the equality H() = E() + u()u (), we obtain E(, d, λ) H(, d, λ) d ( + λm hence, thee exists d = d (λ) d 0 such that Howeve, hence thus E(, d, λ) λf (d 0 ) + ), [,, ( ) d 0, [,, d d. E () = u () 0, E( ) E(), [,, [,, u () d 0 ( ), [,, d d,
9 EJDE-04/9 ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS 9 and by (.), we deduce u () d 0, [,, d d. The mean value theoem implies that thee exists a c (, + b ) such that ( u + ) u( ) = u (c). Hence ( u + ) 0. Which is a contadiction (because u ( + b ) < 0). Poof of theoem.. Let d 0 > 0. By Lemmas.5 and.7, thee exists λ > 0 such that, if λ (0, λ ) then (i) u(, d 0, λ) > 0 fo all (, (ii) u (, d, λ) + u(, d, λ) > 0 fo all [, and all d d 0, (iii) thee exist d > d 0 and (, such that u(, d, λ) < 0. Define Γ = {d d 0 u(, d, λ) > 0, (, ), d [d 0, d}. By (i), d 0 Γ then Γ is nonempty. In addition, by (iii) Γ is bounded fom above by d. Take d = sup Γ. it is clea that u(, d, λ) 0, Since d < d, we deduce (using (ii)) that [,. u(, d, λ) > 0, (, ). (.3) u(., d, λ) will be a solution seaching, if we pove u(, d, λ) = 0. Assume that u(, d, λ) > 0. Then by (.3) and the fact that u (, d, λ) = d > 0, we have that u(, d, λ) > 0, (,, d [d, d + δ, whee δ is sufficiently small. Hence d + δ Γ, which is a contadiction. Theefoe, u(, d, λ) = 0. efeences [ D. Acoya, A. Zetiti; Existence and non-existence of adially symmetic non-negative solutions fo a class of semi-positone poblems in annulus, endiconti di Mathematica, seie VII, Volume 4, oma (994), [ A. Casto,. Shivaji; onnegative solutions fo a class of nonpositone poblems, Poc. oy. Soc. Edin., 08(A)(988), pp [3 M. Chheti, P. Gig; Existence and and nonexistence of positive solutions fo a class of supelinea semipositone systems, onlinea Analysis, 7 (009), [4 D. G. Costa, H. Tehani, J. Yang; On a vaiational appoach to existence and multiplicity esults fo semi positone poblems, Electon. J. Diff. Equ., Vol. (006), o., -0. [5 Said Hakimi, Abdeahim Zetiti; adial positive solutions fo a nonpositone poblem in a ball, Eletonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 009(009), o. 44, pp. -6. [6 Said Hakimi, Abdeahim Zetiti; onexistence of adial positive solutions fo a nonpositone poblem, Eletonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 0(0), o. 6, pp. -7. [7 Hatman; Odinay Diffeential equations, Baltimoe, 973. [8 B. Gidas, W. M. i, L. ienbeg; Symmety and elated popeties via the maximum pinciple, Commun. Maths Phys., 68 (979),
10 0 S. HAKIMI, A. ZETITI EJDE-04/9 Said Hakimi Univesité Sultan Moulay Slimane, Faculté polydisciplinaie, Dépatement de Mathématiques, Béni Mellal, Moocco addess: h saidhakimi@yahoo.f Abdeahim Zetiti Univesité Abdelmalek Essaadi, Faculté des sciences, Dépatement de Mathématiques, BP, Tétouan, Moocco addess: zetitia@hotmail.com
Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Radial Solutions for a Class of Quasilinear Elliptic Systems
 JOURAL OF PARTIAL DIFFERETIAL EQUATIOS J Pat Diff Eq, Vol 8, o 4, pp 37-38 doi: 48/jpdev8n46 Decembe 5 Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Radial Solutions fo a Class of Quasilinea Elliptic Systems LI
JOURAL OF PARTIAL DIFFERETIAL EQUATIOS J Pat Diff Eq, Vol 8, o 4, pp 37-38 doi: 48/jpdev8n46 Decembe 5 Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Radial Solutions fo a Class of Quasilinea Elliptic Systems LI
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM
 A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
The first nontrivial curve in the fučĺk spectrum of the dirichlet laplacian on the ball consists of nonradial eigenvalues
 enedikt et al. ounday Value Poblems 2011, 2011:27 RESEARCH Open Access The fist nontivial cuve in the fučĺk spectum of the diichlet laplacian on the ball consists of nonadial eigenvalues Jiřĺ enedikt 1*,
enedikt et al. ounday Value Poblems 2011, 2011:27 RESEARCH Open Access The fist nontivial cuve in the fučĺk spectum of the diichlet laplacian on the ball consists of nonadial eigenvalues Jiřĺ enedikt 1*,
A proof of the binomial theorem
 A poof of the binomial theoem If n is a natual numbe, let n! denote the poduct of the numbes,2,3,,n. So! =, 2! = 2 = 2, 3! = 2 3 = 6, 4! = 2 3 4 = 24 and so on. We also let 0! =. If n is a non-negative
A poof of the binomial theoem If n is a natual numbe, let n! denote the poduct of the numbes,2,3,,n. So! =, 2! = 2 = 2, 3! = 2 3 = 6, 4! = 2 3 4 = 24 and so on. We also let 0! =. If n is a non-negative
Brief summary of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 2014 Applied Analysis
 Bief summay of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 014 Applied Analysis Stephen Becke, stephen.becke@coloado.edu Standad theoems. When necessay, I used Royden s and Keyzsig s books as a efeence. Vesion
Bief summay of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 014 Applied Analysis Stephen Becke, stephen.becke@coloado.edu Standad theoems. When necessay, I used Royden s and Keyzsig s books as a efeence. Vesion
 This aticle was oiginally published in a jounal published by Elsevie, the attached copy is povided by Elsevie fo the autho s benefit fo the benefit of the autho s institution, fo non-commecial eseach educational
This aticle was oiginally published in a jounal published by Elsevie, the attached copy is povided by Elsevie fo the autho s benefit fo the benefit of the autho s institution, fo non-commecial eseach educational
Numerical approximation to ζ(2n+1)
 Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
THE CONE THEOREM JOEL A. TROPP. Abstract. We prove a fixed point theorem for functions which are positive with respect to a cone in a Banach space.
 THE ONE THEOEM JOEL A. TOPP Abstact. We pove a fixed point theoem fo functions which ae positive with espect to a cone in a Banach space. 1. Definitions Definition 1. Let X be a eal Banach space. A subset
THE ONE THEOEM JOEL A. TOPP Abstact. We pove a fixed point theoem fo functions which ae positive with espect to a cone in a Banach space. 1. Definitions Definition 1. Let X be a eal Banach space. A subset
A STABILITY RESULT FOR p-harmonic SYSTEMS WITH DISCONTINUOUS COEFFICIENTS. Bianca Stroffolini. 0. Introduction
 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Method for Approximating Irrational Numbers
 Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS
 Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR ON THE UNIT BALL. Juntao Du and Xiangling Zhu
 Opuscula Math. 38, no. 6 (8), 89 839 https://doi.og/.7494/opmath.8.38.6.89 Opuscula Mathematica ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR FROM ω-bloch SPACES TO µ-zygmund SPACES ON THE UNIT BALL Juntao
Opuscula Math. 38, no. 6 (8), 89 839 https://doi.og/.7494/opmath.8.38.6.89 Opuscula Mathematica ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR FROM ω-bloch SPACES TO µ-zygmund SPACES ON THE UNIT BALL Juntao
On uniqueness for nonlinear elliptic equation involving the Pucci s extremal operator
 On uniqueness fo nonlinea elliptic equation involving the Pucci s extemal opeato Paticio L. Felme a,, Alexande Quaas b, Moxun Tang c a Depatamento de Ing. Matemática, F.C.F.M. Univesidad de Chile, Casilla
On uniqueness fo nonlinea elliptic equation involving the Pucci s extemal opeato Paticio L. Felme a,, Alexande Quaas b, Moxun Tang c a Depatamento de Ing. Matemática, F.C.F.M. Univesidad de Chile, Casilla
Asymptotically Lacunary Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convergence and an Orlicz Function
 "Science Stays Tue Hee" Jounal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, 335-35 Science Signpost Publishing Asymptotically Lacunay Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convegence and an
"Science Stays Tue Hee" Jounal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, 335-35 Science Signpost Publishing Asymptotically Lacunay Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convegence and an
Compactly Supported Radial Basis Functions
 Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Regularity for Fully Nonlinear Elliptic Equations with Neumann Boundary Data
 Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 31: 1227 1252, 2006 Copyight Taylo & Fancis Goup, LLC ISSN 0360-5302 pint/1532-4133 online DOI: 10.1080/03605300600634999 Regulaity fo Fully Nonlinea Elliptic
Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 31: 1227 1252, 2006 Copyight Taylo & Fancis Goup, LLC ISSN 0360-5302 pint/1532-4133 online DOI: 10.1080/03605300600634999 Regulaity fo Fully Nonlinea Elliptic
Integral operator defined by q-analogue of Liu-Srivastava operator
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013, No. 4, 529 537 Integal opeato defined by q-analogue of Liu-Sivastava opeato Huda Aldweby and Maslina Daus Abstact. In this pape, we shall give an application of q-analogues
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013, No. 4, 529 537 Integal opeato defined by q-analogue of Liu-Sivastava opeato Huda Aldweby and Maslina Daus Abstact. In this pape, we shall give an application of q-analogues
GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS HAVING THE SAME LOGARITHMIC ORDER
 UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA doi: 104467/20843828AM170027078 542017, 15 32 STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS
UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA doi: 104467/20843828AM170027078 542017, 15 32 STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS
On absence of solutions of a semi-linear elliptic equation with biharmonic operator in the exterior of a ball
 Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36, 63-69 016. Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. On absence of solutions of a semi-linea elliptic euation with bihamonic opeato
Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36, 63-69 016. Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. On absence of solutions of a semi-linea elliptic euation with bihamonic opeato
Fixed Point Results for Multivalued Maps
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 3, 119-1136 Fixed Point Results fo Multivalued Maps Abdul Latif Depatment of Mathematics King Abdulaziz Univesity P.O. Box 8003, Jeddah 1589 Saudi Aabia
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 3, 119-1136 Fixed Point Results fo Multivalued Maps Abdul Latif Depatment of Mathematics King Abdulaziz Univesity P.O. Box 8003, Jeddah 1589 Saudi Aabia
ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS
 STUDIA UNIV BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume XLVIII, Numbe 4, Decembe 2003 ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS VATAN KARAKAYA AND NECIP SIMSEK Abstact The
STUDIA UNIV BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume XLVIII, Numbe 4, Decembe 2003 ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS VATAN KARAKAYA AND NECIP SIMSEK Abstact The
SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF 2 2 OPERATOR MATRICES
 italian jounal of pue and applied mathematics n. 35 015 (433 44) 433 SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF OPERATOR MATRICES Watheq Bani-Domi Depatment of Mathematics
italian jounal of pue and applied mathematics n. 35 015 (433 44) 433 SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF OPERATOR MATRICES Watheq Bani-Domi Depatment of Mathematics
Lacunary I-Convergent Sequences
 KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 52(2012), 473-482 http://dx.doi.og/10.5666/kmj.2012.52.4.473 Lacunay I-Convegent Sequences Binod Chanda Tipathy Mathematical Sciences Division, Institute of Advanced Study in Science
KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 52(2012), 473-482 http://dx.doi.og/10.5666/kmj.2012.52.4.473 Lacunay I-Convegent Sequences Binod Chanda Tipathy Mathematical Sciences Division, Institute of Advanced Study in Science
ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS. D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi
 Opuscula Math. 37, no. 3 (017), 447 456 http://dx.doi.og/10.7494/opmath.017.37.3.447 Opuscula Mathematica ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi Communicated
Opuscula Math. 37, no. 3 (017), 447 456 http://dx.doi.og/10.7494/opmath.017.37.3.447 Opuscula Mathematica ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi Communicated
Chaos and bifurcation of discontinuous dynamical systems with piecewise constant arguments
 Malaya Jounal of Matematik ()(22) 4 8 Chaos and bifucation of discontinuous dynamical systems with piecewise constant aguments A.M.A. El-Sayed, a, and S. M. Salman b a Faculty of Science, Aleandia Univesity,
Malaya Jounal of Matematik ()(22) 4 8 Chaos and bifucation of discontinuous dynamical systems with piecewise constant aguments A.M.A. El-Sayed, a, and S. M. Salman b a Faculty of Science, Aleandia Univesity,
Lecture 28: Convergence of Random Variables and Related Theorems
 EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
Analytical solutions to the Navier Stokes equations
 JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS 49, 113102 2008 Analytical solutions to the avie Stokes equations Yuen Manwai a Depatment of Applied Mathematics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univesity, Hung Hom, Kowloon,
JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS 49, 113102 2008 Analytical solutions to the avie Stokes equations Yuen Manwai a Depatment of Applied Mathematics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univesity, Hung Hom, Kowloon,
Do Managers Do Good With Other People s Money? Online Appendix
 Do Manages Do Good With Othe People s Money? Online Appendix Ing-Haw Cheng Haison Hong Kelly Shue Abstact This is the Online Appendix fo Cheng, Hong and Shue 2013) containing details of the model. Datmouth
Do Manages Do Good With Othe People s Money? Online Appendix Ing-Haw Cheng Haison Hong Kelly Shue Abstact This is the Online Appendix fo Cheng, Hong and Shue 2013) containing details of the model. Datmouth
Research Article On Alzer and Qiu s Conjecture for Complete Elliptic Integral and Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent Function
 Abstact and Applied Analysis Volume 011, Aticle ID 697547, 7 pages doi:10.1155/011/697547 Reseach Aticle On Alze and Qiu s Conjectue fo Complete Elliptic Integal and Invese Hypebolic Tangent Function Yu-Ming
Abstact and Applied Analysis Volume 011, Aticle ID 697547, 7 pages doi:10.1155/011/697547 Reseach Aticle On Alze and Qiu s Conjectue fo Complete Elliptic Integal and Invese Hypebolic Tangent Function Yu-Ming
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Unobserved Correlation in Ascending Auctions: Example And Extensions
 Unobseved Coelation in Ascending Auctions: Example And Extensions Daniel Quint Univesity of Wisconsin Novembe 2009 Intoduction In pivate-value ascending auctions, the winning bidde s willingness to pay
Unobseved Coelation in Ascending Auctions: Example And Extensions Daniel Quint Univesity of Wisconsin Novembe 2009 Intoduction In pivate-value ascending auctions, the winning bidde s willingness to pay
Numerical Integration
 MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
15 Solving the Laplace equation by Fourier method
 5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
k. s k=1 Part of the significance of the Riemann zeta-function stems from Theorem 9.2. If s > 1 then 1 p s
 9 Pimes in aithmetic ogession Definition 9 The Riemann zeta-function ζs) is the function which assigns to a eal numbe s > the convegent seies k s k Pat of the significance of the Riemann zeta-function
9 Pimes in aithmetic ogession Definition 9 The Riemann zeta-function ζs) is the function which assigns to a eal numbe s > the convegent seies k s k Pat of the significance of the Riemann zeta-function
AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 ENTIRE BLOW-UP SOLUTIONS OF SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS AND SYSTEMS THESIS Jesse D. Peteson, Second Lieutenant, USAF AFIT/GAM/ENC/8-2 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF
ENTIRE BLOW-UP SOLUTIONS OF SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS AND SYSTEMS THESIS Jesse D. Peteson, Second Lieutenant, USAF AFIT/GAM/ENC/8-2 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF
Quasi-Randomness and the Distribution of Copies of a Fixed Graph
 Quasi-Randomness and the Distibution of Copies of a Fixed Gaph Asaf Shapia Abstact We show that if a gaph G has the popety that all subsets of vetices of size n/4 contain the coect numbe of tiangles one
Quasi-Randomness and the Distibution of Copies of a Fixed Gaph Asaf Shapia Abstact We show that if a gaph G has the popety that all subsets of vetices of size n/4 contain the coect numbe of tiangles one
New Singular Standing Wave Solutions Of The Nonlinear Schrodinger Equation
 New Singula Standing Wave Solutions Of The Nonlinea Schodinge Equation W. C. Toy Abstact We pove existence, and asymptotic behavio as, of a family of singula solutions of 1) y + y +y y p 1 y = 0, 0 <
New Singula Standing Wave Solutions Of The Nonlinea Schodinge Equation W. C. Toy Abstact We pove existence, and asymptotic behavio as, of a family of singula solutions of 1) y + y +y y p 1 y = 0, 0 <
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
Hölder Continuity for Local Minimizers of a Nonconvex Variational Problem
 Jounal of Convex Analysis Volume 10 003), No., 389 408 Hölde Continuity fo Local Minimizes of a Nonconvex Vaiational Poblem Giovanni Cupini Dipatimento di Matematica U. Dini, Univesità di Fienze, Viale
Jounal of Convex Analysis Volume 10 003), No., 389 408 Hölde Continuity fo Local Minimizes of a Nonconvex Vaiational Poblem Giovanni Cupini Dipatimento di Matematica U. Dini, Univesità di Fienze, Viale
A Multivariate Normal Law for Turing s Formulae
 A Multivaiate Nomal Law fo Tuing s Fomulae Zhiyi Zhang Depatment of Mathematics and Statistics Univesity of Noth Caolina at Chalotte Chalotte, NC 28223 Abstact This pape establishes a sufficient condition
A Multivaiate Nomal Law fo Tuing s Fomulae Zhiyi Zhang Depatment of Mathematics and Statistics Univesity of Noth Caolina at Chalotte Chalotte, NC 28223 Abstact This pape establishes a sufficient condition
Mean Curvature and Shape Operator of Slant Immersions in a Sasakian Space Form
 Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
f h = u, h g = v, we have u + v = f g. So, we wish
 Answes to Homewok 4, Math 4111 (1) Pove that the following examples fom class ae indeed metic spaces. You only need to veify the tiangle inequality. (a) Let C be the set of continuous functions fom [0,
Answes to Homewok 4, Math 4111 (1) Pove that the following examples fom class ae indeed metic spaces. You only need to veify the tiangle inequality. (a) Let C be the set of continuous functions fom [0,
Uniqueness of Positive Ground State Solutions of the Logarithmic Schrodinger Equation
 Achive fo Rational Mechanics and Analysis manuscipt No. will be inseted by the edito) William C. Toy Uniqueness of Positive Gound State Solutions of the Logaithmic Schodinge Equation Dedicated To The Memoy
Achive fo Rational Mechanics and Analysis manuscipt No. will be inseted by the edito) William C. Toy Uniqueness of Positive Gound State Solutions of the Logaithmic Schodinge Equation Dedicated To The Memoy
3.1 Random variables
 3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
Results on the Commutative Neutrix Convolution Product Involving the Logarithmic Integral li(
 Intenational Jounal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Reseach (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2014, PP 736-741 ISSN 2347-307X (Pint) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) www.acjounals.og Results on the
Intenational Jounal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Reseach (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2014, PP 736-741 ISSN 2347-307X (Pint) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) www.acjounals.og Results on the
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017](/thumbs/93/113642317.jpg) SEQUENCES OF CONSECUTIVE HAPPY NUMBERS IN NEGATIVE BASES HELEN G. GRUNDMAN AND PAMELA E. HARRIS axiv:1705.04648v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017 ABSTRACT. Fo b 2 and e 2, let S e,b : Z Z 0 be the function taking
SEQUENCES OF CONSECUTIVE HAPPY NUMBERS IN NEGATIVE BASES HELEN G. GRUNDMAN AND PAMELA E. HARRIS axiv:1705.04648v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017 ABSTRACT. Fo b 2 and e 2, let S e,b : Z Z 0 be the function taking
On the ratio of maximum and minimum degree in maximal intersecting families
 On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Septembe 5, 011 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Septembe 5, 011 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
BEST CONSTANTS FOR UNCENTERED MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS. Loukas Grafakos and Stephen Montgomery-Smith University of Missouri, Columbia
 BEST CONSTANTS FOR UNCENTERED MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS Loukas Gafakos and Stehen Montgomey-Smith Univesity of Missoui, Columbia Abstact. We ecisely evaluate the oeato nom of the uncenteed Hady-Littlewood maximal
BEST CONSTANTS FOR UNCENTERED MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS Loukas Gafakos and Stehen Montgomey-Smith Univesity of Missoui, Columbia Abstact. We ecisely evaluate the oeato nom of the uncenteed Hady-Littlewood maximal
Connectedness of Ordered Rings of Fractions of C(X) with the m-topology
 Filomat 31:18 (2017), 5685 5693 https://doi.og/10.2298/fil1718685s Published by Faculty o Sciences and Mathematics, Univesity o Niš, Sebia Available at: http://www.pm.ni.ac.s/ilomat Connectedness o Odeed
Filomat 31:18 (2017), 5685 5693 https://doi.og/10.2298/fil1718685s Published by Faculty o Sciences and Mathematics, Univesity o Niš, Sebia Available at: http://www.pm.ni.ac.s/ilomat Connectedness o Odeed
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Doubling property for the Laplacian and its applications (Course Chengdu 2007)
 Doubling popety fo the Laplacian and its applications Couse Chengdu 007) K.-D. PHUNG The oiginal appoach of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin Fo simplicity, we epoduce the poof of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin in the
Doubling popety fo the Laplacian and its applications Couse Chengdu 007) K.-D. PHUNG The oiginal appoach of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin Fo simplicity, we epoduce the poof of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin in the
Divisibility. c = bf = (ae)f = a(ef) EXAMPLE: Since 7 56 and , the Theorem above tells us that
 Divisibility DEFINITION: If a and b ae integes with a 0, we say that a divides b if thee is an intege c such that b = ac. If a divides b, we also say that a is a diviso o facto of b. NOTATION: d n means
Divisibility DEFINITION: If a and b ae integes with a 0, we say that a divides b if thee is an intege c such that b = ac. If a divides b, we also say that a is a diviso o facto of b. NOTATION: d n means
A generalization of the Bernstein polynomials
 A genealization of the Benstein polynomials Halil Ouç and Geoge M Phillips Mathematical Institute, Univesity of St Andews, Noth Haugh, St Andews, Fife KY16 9SS, Scotland Dedicated to Philip J Davis This
A genealization of the Benstein polynomials Halil Ouç and Geoge M Phillips Mathematical Institute, Univesity of St Andews, Noth Haugh, St Andews, Fife KY16 9SS, Scotland Dedicated to Philip J Davis This
Surveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces
 Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 38
 Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE
 ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE. We consider second order constant coefficient scalar linear PDEs on R n. These have the form
 MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
MATH 220: SECOND ORDER CONSTANT COEFFICIENT PDE ANDRAS VASY We conside second ode constant coefficient scala linea PDEs on R n. These have the fom Lu = f L = a ij xi xj + b i xi + c i whee a ij b i and
CENTRAL INDEX BASED SOME COMPARATIVE GROWTH ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE ENTIRE FUNCTIONS FROM THE VIEW POINT OF L -ORDER. Tanmay Biswas
 J Koean Soc Math Educ Se B: Pue Appl Math ISSNPint 16-0657 https://doiog/107468/jksmeb01853193 ISSNOnline 87-6081 Volume 5, Numbe 3 August 018, Pages 193 01 CENTRAL INDEX BASED SOME COMPARATIVE GROWTH
J Koean Soc Math Educ Se B: Pue Appl Math ISSNPint 16-0657 https://doiog/107468/jksmeb01853193 ISSNOnline 87-6081 Volume 5, Numbe 3 August 018, Pages 193 01 CENTRAL INDEX BASED SOME COMPARATIVE GROWTH
< 1. max x B(0,1) f. ν ds(y) Use Poisson s formula for the ball to prove. (r x ) x y n ds(y) (x B0 (0, r)). 1 nα(n)r n 1
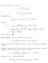 7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
A CHARACTERIZATION ON BREAKDOWN OF SMOOTH SPHERICALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS OF THE ISENTROPIC SYSTEM OF COMPRESSIBLE NAVIER STOKES EQUATIONS
 Huang, X. and Matsumua, A. Osaka J. Math. 52 (215), 271 283 A CHARACTRIZATION ON BRAKDOWN OF SMOOTH SPHRICALLY SYMMTRIC SOLUTIONS OF TH ISNTROPIC SYSTM OF COMPRSSIBL NAVIR STOKS QUATIONS XIANGDI HUANG
Huang, X. and Matsumua, A. Osaka J. Math. 52 (215), 271 283 A CHARACTRIZATION ON BRAKDOWN OF SMOOTH SPHRICALLY SYMMTRIC SOLUTIONS OF TH ISNTROPIC SYSTM OF COMPRSSIBL NAVIR STOKS QUATIONS XIANGDI HUANG
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Mar 2008](/thumbs/94/118262240.jpg) An uppe bound fo the numbe of pefect matchings in gaphs Shmuel Fiedland axiv:0803.0864v [math.co] 6 Ma 2008 Depatment of Mathematics, Statistics, and Compute Science, Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Chicago,
An uppe bound fo the numbe of pefect matchings in gaphs Shmuel Fiedland axiv:0803.0864v [math.co] 6 Ma 2008 Depatment of Mathematics, Statistics, and Compute Science, Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Chicago,
9.1 The multiplicative group of a finite field. Theorem 9.1. The multiplicative group F of a finite field is cyclic.
 Chapte 9 Pimitive Roots 9.1 The multiplicative goup of a finite fld Theoem 9.1. The multiplicative goup F of a finite fld is cyclic. Remak: In paticula, if p is a pime then (Z/p) is cyclic. In fact, this
Chapte 9 Pimitive Roots 9.1 The multiplicative goup of a finite fld Theoem 9.1. The multiplicative goup F of a finite fld is cyclic. Remak: In paticula, if p is a pime then (Z/p) is cyclic. In fact, this
POSITIVE AND OSCILLATORY RADIAL SOLUTIONS OF SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 Jounal of Applied Mathematics and Stochastic Analysis, 0: (997), 95-08. POSITIVE AND OSCILLATORY RADIAL SOLUTIONS OF SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS SHAOHUA CHEN and WILLIAM R. DERRICK Univesity of Montana,
Jounal of Applied Mathematics and Stochastic Analysis, 0: (997), 95-08. POSITIVE AND OSCILLATORY RADIAL SOLUTIONS OF SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS SHAOHUA CHEN and WILLIAM R. DERRICK Univesity of Montana,
12th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Cairo, Egypt, December 29-31,
 th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Caio, Egypt, Decembe 9-3, 7 5 Magnetostatic Field calculations associated with thick Solenoids in the Pesence of Ion using a Powe Seies expansion and the Complete
th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Caio, Egypt, Decembe 9-3, 7 5 Magnetostatic Field calculations associated with thick Solenoids in the Pesence of Ion using a Powe Seies expansion and the Complete
Measure Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyharmonic Functions
 Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, 97 93 DOI: 0.007/s40-08-004-6 Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of
Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, 97 93 DOI: 0.007/s40-08-004-6 Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of
TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS
 Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics: Advances and Applications Volume 4, Numbe, 200, Pages 97-4 TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS Dépatement de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences de
Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics: Advances and Applications Volume 4, Numbe, 200, Pages 97-4 TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS Dépatement de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences de
NONLINEAR OSCILLATIONS OF SECOND ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF EULER TYPE
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 124, Numbe 1, Octobe 1996 NONLINEAR OSCILLATIONS OF SECOND ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF EULER TYPE JITSURO SUGIE AND TADAYUKI HARA (Communicated
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 124, Numbe 1, Octobe 1996 NONLINEAR OSCILLATIONS OF SECOND ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF EULER TYPE JITSURO SUGIE AND TADAYUKI HARA (Communicated
An Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation
 An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol3 15 2007, 41 45 A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LI JULING AND GAO HONGYA Abstact We pove a new a pioi estimate fo vey weak
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol3 15 2007, 41 45 A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LI JULING AND GAO HONGYA Abstact We pove a new a pioi estimate fo vey weak
RADIALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS TO THE GRAPHIC WILLMORE SURFACE EQUATION
 RADIALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS TO THE GRAPHIC WILLMORE SURFACE EQUATION JINGYI CHEN AND YUXIANG LI Abstact. We show that a smooth adially symmetic solution u to the gaphic Willmoe suface equation is eithe
RADIALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS TO THE GRAPHIC WILLMORE SURFACE EQUATION JINGYI CHEN AND YUXIANG LI Abstact. We show that a smooth adially symmetic solution u to the gaphic Willmoe suface equation is eithe
An analytical proof of Hardy-like inequalities related to the Dirac operator
 An analytical poof of Hady-like inequalities elated to the Diac opeato Jean Dolbeault a,1 Maia J. Esteban a,1 Michael Loss b,2 Luis Vega c,1 a CEREMADE, Univesité Pais-Dauphine, 75775 Pais Cedex 16, Fance
An analytical poof of Hady-like inequalities elated to the Diac opeato Jean Dolbeault a,1 Maia J. Esteban a,1 Michael Loss b,2 Luis Vega c,1 a CEREMADE, Univesité Pais-Dauphine, 75775 Pais Cedex 16, Fance
Large Solutions for a System of Elliptic Equations Arising from Fluid Dynamics
 Lage Solutions fo a System of Elliptic Equations Aising fom Fluid Dynamics J. I. Díaz, M. Lazzo and P. G. Schmidt Abstact. This pape is concened with the elliptic system v = φ, φ = v 2, (.1) posed in a
Lage Solutions fo a System of Elliptic Equations Aising fom Fluid Dynamics J. I. Díaz, M. Lazzo and P. G. Schmidt Abstact. This pape is concened with the elliptic system v = φ, φ = v 2, (.1) posed in a
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5
 Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
15.081J/6.251J Introduction to Mathematical Programming. Lecture 6: The Simplex Method II
 15081J/6251J Intoduction to Mathematical Pogamming ectue 6: The Simplex Method II 1 Outline Revised Simplex method Slide 1 The full tableau implementation Anticycling 2 Revised Simplex Initial data: A,
15081J/6251J Intoduction to Mathematical Pogamming ectue 6: The Simplex Method II 1 Outline Revised Simplex method Slide 1 The full tableau implementation Anticycling 2 Revised Simplex Initial data: A,
ON VON NEUMANN-JORDAN TYPE CONSTANT AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR FIXED POINTS OF MULTIVALUED NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS
 Gulf Jounal of Mathematics Vol 4, Issue 06) - ON VON NEUMANN-JORDAN TYPE CONSTANT AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR FIXED POINTS OF MULTIVALUED NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS MINA DINARVAND Abstact In the pesent pape,
Gulf Jounal of Mathematics Vol 4, Issue 06) - ON VON NEUMANN-JORDAN TYPE CONSTANT AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR FIXED POINTS OF MULTIVALUED NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS MINA DINARVAND Abstact In the pesent pape,
18.06 Problem Set 4 Solution
 8.6 Poblem Set 4 Solution Total: points Section 3.5. Poblem 2: (Recommended) Find the lagest possible numbe of independent vectos among ) ) ) v = v 4 = v 5 = v 6 = v 2 = v 3 =. Solution (4 points): Since
8.6 Poblem Set 4 Solution Total: points Section 3.5. Poblem 2: (Recommended) Find the lagest possible numbe of independent vectos among ) ) ) v = v 4 = v 5 = v 6 = v 2 = v 3 =. Solution (4 points): Since
A Bijective Approach to the Permutational Power of a Priority Queue
 A Bijective Appoach to the Pemutational Powe of a Pioity Queue Ia M. Gessel Kuang-Yeh Wang Depatment of Mathematics Bandeis Univesity Waltham, MA 02254-9110 Abstact A pioity queue tansfoms an input pemutation
A Bijective Appoach to the Pemutational Powe of a Pioity Queue Ia M. Gessel Kuang-Yeh Wang Depatment of Mathematics Bandeis Univesity Waltham, MA 02254-9110 Abstact A pioity queue tansfoms an input pemutation
SPREADING SPEED AND PROFILE FOR NONLINEAR STEFAN PROBLEMS IN HIGH SPACE DIMENSIONS
 SPREADING SPEED AND PROFILE FOR NONLINEAR STEFAN PROBLEMS IN HIGH SPACE DIMENSIONS YIHONG DU, HIROSHI MATSUZAWA AND MAOLIN ZHOU Abstact. We conside nonlinea diffusion poblems of the fom u t = u + f(u)
SPREADING SPEED AND PROFILE FOR NONLINEAR STEFAN PROBLEMS IN HIGH SPACE DIMENSIONS YIHONG DU, HIROSHI MATSUZAWA AND MAOLIN ZHOU Abstact. We conside nonlinea diffusion poblems of the fom u t = u + f(u)
Boundedness for Marcinkiewicz integrals associated with Schrödinger operators
 Poc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci. Vol. 24, No. 2, May 24, pp. 93 23. c Indian Academy of Sciences oundedness fo Macinkiewicz integals associated with Schödinge opeatos WENHUA GAO and LIN TANG 2 School
Poc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci. Vol. 24, No. 2, May 24, pp. 93 23. c Indian Academy of Sciences oundedness fo Macinkiewicz integals associated with Schödinge opeatos WENHUA GAO and LIN TANG 2 School
On the global uniform asymptotic stability of time-varying dynamical systems
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 59014), No. 1, 57 67 On the global unifom asymptotic stability of time-vaying dynamical systems Zaineb HajSalem, Mohamed Ali Hammami and Mohamed Mabouk Abstact. The objective
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 59014), No. 1, 57 67 On the global unifom asymptotic stability of time-vaying dynamical systems Zaineb HajSalem, Mohamed Ali Hammami and Mohamed Mabouk Abstact. The objective
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Journal of Number Theory
 Jounal of umbe Theoy 3 2 2259 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDiect Jounal of umbe Theoy www.elsevie.com/locate/jnt Sums of poducts of hypegeometic Benoulli numbes Ken Kamano Depatment of Geneal
Jounal of umbe Theoy 3 2 2259 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDiect Jounal of umbe Theoy www.elsevie.com/locate/jnt Sums of poducts of hypegeometic Benoulli numbes Ken Kamano Depatment of Geneal
On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theorem that relates to it
 Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
Goodness-of-fit for composite hypotheses.
 Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 12 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 12 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 12 Mar 2015](/thumbs/71/65747658.jpg) axiv:503.0356v [math.ca] 2 Ma 205 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS TRISTRAM DE PIRO Abstact. We develop a method fo calculating Riemann sums using Fouie analysis.. Poisson Summation Fomula
axiv:503.0356v [math.ca] 2 Ma 205 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS TRISTRAM DE PIRO Abstact. We develop a method fo calculating Riemann sums using Fouie analysis.. Poisson Summation Fomula
Nuclear size corrections to the energy levels of single-electron atoms
 Nuclea size coections to the enegy levels of single-electon atoms Babak Nadii Nii a eseach Institute fo Astonomy and Astophysics of Maagha (IAAM IAN P. O. Box: 554-44. Abstact A study is made of nuclea
Nuclea size coections to the enegy levels of single-electon atoms Babak Nadii Nii a eseach Institute fo Astonomy and Astophysics of Maagha (IAAM IAN P. O. Box: 554-44. Abstact A study is made of nuclea
Projection Gravitation, a Projection Force from 5-dimensional Space-time into 4-dimensional Space-time
 Intenational Jounal of Physics, 17, Vol. 5, No. 5, 181-196 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/5/6 Science and ducation Publishing DOI:1.1691/ijp-5-5-6 Pojection Gavitation, a Pojection Foce
Intenational Jounal of Physics, 17, Vol. 5, No. 5, 181-196 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/5/5/6 Science and ducation Publishing DOI:1.1691/ijp-5-5-6 Pojection Gavitation, a Pojection Foce
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 2013](/thumbs/86/93353853.jpg) A VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A GAUGED NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION ALESSIO POMPONIO 1 AND DAVID RUIZ axiv:136.51v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 13 ABSTRACT. This pape is motivated by a gauged Schödinge equation in dimension
A VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A GAUGED NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION ALESSIO POMPONIO 1 AND DAVID RUIZ axiv:136.51v1 [math.ap] 9 Jun 13 ABSTRACT. This pape is motivated by a gauged Schödinge equation in dimension
Introduction Common Divisors. Discrete Mathematics Andrei Bulatov
 Intoduction Common Divisos Discete Mathematics Andei Bulatov Discete Mathematics Common Divisos 3- Pevious Lectue Integes Division, popeties of divisibility The division algoithm Repesentation of numbes
Intoduction Common Divisos Discete Mathematics Andei Bulatov Discete Mathematics Common Divisos 3- Pevious Lectue Integes Division, popeties of divisibility The division algoithm Repesentation of numbes
JENSEN S INEQUALITY FOR DISTRIBUTIONS POSSESSING HIGHER MOMENTS, WITH APPLICATION TO SHARP BOUNDS FOR LAPLACE-STIELTJES TRANSFORMS
 J. Austal. Math. Soc. Se. B 40(1998), 80 85 JENSEN S INEQUALITY FO DISTIBUTIONS POSSESSING HIGHE MOMENTS, WITH APPLICATION TO SHAP BOUNDS FO LAPLACE-STIELTJES TANSFOMS B. GULJAŠ 1,C.E.M.PEACE 2 and J.
J. Austal. Math. Soc. Se. B 40(1998), 80 85 JENSEN S INEQUALITY FO DISTIBUTIONS POSSESSING HIGHE MOMENTS, WITH APPLICATION TO SHAP BOUNDS FO LAPLACE-STIELTJES TANSFOMS B. GULJAŠ 1,C.E.M.PEACE 2 and J.
Exceptional regular singular points of second-order ODEs. 1. Solving second-order ODEs
 (May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
(May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
Bounds for Codimensions of Fitting Ideals
 Ž. JOUNAL OF ALGEBA 194, 378 382 1997 ATICLE NO. JA966999 Bounds fo Coensions of Fitting Ideals Michał Kwiecinski* Uniwesytet Jagiellonski, Instytut Matematyki, ul. eymonta 4, 30-059, Kakow, Poland Communicated
Ž. JOUNAL OF ALGEBA 194, 378 382 1997 ATICLE NO. JA966999 Bounds fo Coensions of Fitting Ideals Michał Kwiecinski* Uniwesytet Jagiellonski, Instytut Matematyki, ul. eymonta 4, 30-059, Kakow, Poland Communicated
ON SPARSELY SCHEMMEL TOTIENT NUMBERS. Colin Defant 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida
 #A8 INTEGERS 5 (205) ON SPARSEL SCHEMMEL TOTIENT NUMBERS Colin Defant Depatment of Mathematics, Univesity of Floida, Gainesville, Floida cdefant@ufl.edu Received: 7/30/4, Revised: 2/23/4, Accepted: 4/26/5,
#A8 INTEGERS 5 (205) ON SPARSEL SCHEMMEL TOTIENT NUMBERS Colin Defant Depatment of Mathematics, Univesity of Floida, Gainesville, Floida cdefant@ufl.edu Received: 7/30/4, Revised: 2/23/4, Accepted: 4/26/5,
Infinitely many solutions and Morse index for non-autonomous elliptic problems
 Infinitely many solutions and Mose index fo non-autonomous elliptic poblems Philip Koman Depatment of Mathematical Sciences Univesity of Cincinnati Cincinnati Ohio 45221-0025 Abstact Ou fist esult is a
Infinitely many solutions and Mose index fo non-autonomous elliptic poblems Philip Koman Depatment of Mathematical Sciences Univesity of Cincinnati Cincinnati Ohio 45221-0025 Abstact Ou fist esult is a
On the Quasi-inverse of a Non-square Matrix: An Infinite Solution
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
Functions Defined on Fuzzy Real Numbers According to Zadeh s Extension
 Intenational Mathematical Foum, 3, 2008, no. 16, 763-776 Functions Defined on Fuzzy Real Numbes Accoding to Zadeh s Extension Oma A. AbuAaqob, Nabil T. Shawagfeh and Oma A. AbuGhneim 1 Mathematics Depatment,
Intenational Mathematical Foum, 3, 2008, no. 16, 763-776 Functions Defined on Fuzzy Real Numbes Accoding to Zadeh s Extension Oma A. AbuAaqob, Nabil T. Shawagfeh and Oma A. AbuGhneim 1 Mathematics Depatment,
