The Cyclotron I. 1. Motion of the charges occurs in two semicircular containers, D 1. and D 2
|
|
|
- Norma Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Motion of the charges occurs in two semicircular containers, D 1 and D 2 referred to as the Dees 2. The Dees are evacuated in order to minimize energy loss from collisions 3. A high frrequency alternating voltage is applied to the Dees along with a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular to the plane of the Dees. 4. Positive ions released at the center of the magnet move in a semeicircular path and arrive back at the gap in a time T/2, where T is the period of revolution The Cyclotron I
2 1. The frequency of the applied voltage, V, is adjusted such that the polarity of the Dees is reverseed in the same time it takes the ions to complete one half of a revolution 2. If the phase of the applied voltage is adjusted such that D 2 is at a lower potential than D 1 by an amount V, the ion will accelerate across the gap to D 2 and its kinetic energy will increase by an amount qv 3. The ion continiues its semicircular path in D 2 but at a larger radius because of its increased velocity 4. After a time T/2, it is once more at the gap, the potential across the gap has been reversed (D 1 is now at a lower potential), and the ion is given another kick across the gap The Cyclotron II
3 The Cyclotron III 1. The process repeats itself and at each half revolution, the ion gains an additional qv of kinetic energy 2. Important to note that the operation of this device is based on the fact that the time for one revolution is independent of the speed or radius of the path of the ion 3. The maximum kinetic energy of the ion when it exits the cyclotron is in terms of the radius R, of the Dees. 4. Recall that the radius of circular orbit is given by from which we get
4 First successful cyclotron built by E. O. Lawrence and his graduate student M. Stanley Livingston, accelerated a few hydrogen molecule ions to an energy of 80,000 electron volts. Since each ion received an accelerating kick twice in a circuit as it entered and left the single flat semicircular electrode or 'dee', those that managed to reach full energy and fall into the collecting cup 4.50 cm from the center of the instrument had made no fewer than forty turns.
5
6
7 The Hall Effect: Reprise A conducting slab of width w carrying a current I is placed in a magnetic field B oriented perpendicular to the direction of the current. The magnetic force qv d B on the charge carriers pushes them to one edge of the slab. This separation of charge produces an electric field, which opposes any further separation of charge. Eventually these two forces come into equilibrium: qe = qv d B The electric field produces a potential difference V = Ew : r E q V w = qv d B V H = wv d B the "Hall voltage" measures v d
8 The Hall Effect II The drift velocity may be obtained by measuring the Hall voltage. Recall the expression for the drift velocity From a knowledge of the drift velocity, which came from an experimental measurement of the Hall voltage, we can obtain n the number of charge carriers per unit volume (charge density) Now, A is the cross sectional area of the conductor. Substitution of the expression for the drift velocity into our expression for the Hall voltage gives
9 The Hall Effect III Because A is equal to the width, w, times the thickness, t NOT to be confused with time in this case!!! We have A=wt. This gives us DO NOT confuse t with time here!!! The quantity 1/nq is what is known as the Hall Coefficient, R H Because all quantities other than n and q in the expression above can be measured the Hall coefficient is readily obtained. 1. The coefficient gives the sign of the charge carriers and their density 2. In most metals the values obtained from Hall effect measurements are in good agreement when n is approximately equal to the number of valence electrons per unit volume 3. This is a CLASSICAL model and for metals like Fe, Bi, and Cd or for semiconductors like silicon and germanium a model based on the quantum nature of solids is needed.
10 Example 1 Cyclotron Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of protons in a cyclotron of radius 0.50 m in a magnetic field of 0.35 T
11 Example 2 A copper wire of cross sectional area 3X10-6 m 2 carries a current of 10 A. Find the drift velocity of the electrons in the wire. (The molar mass of copper is 63.5 g/mole and the density of copper is 8.95 g/cm 3 )
12 Example 3 A rectangular copper strip 1.5 cm wide and 0.1 cm thick carries a current of 5 amperes. A 1.2 T magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the strip. Find the resulting Hall voltage. (The molar mass of copper is 63.5 g/mole and the density of copper is 8.95 g/cm3)
13 Example 4 The magnetic field of the earth at a certain location is directed vertically downward and has a magnitude of 0.5X10-4 T. A proton is moving horizontally towards the west in this field with a velocity of 6.2 X 10 6 m/s. 1. What are the direction and magnitude of the magnetic force the field exerts on this charge? 2. What is the radius of the circular arc followed by this proton?
14 Example 5 A singly charged positive ion has a mass of 3.2 X kg. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 833 V, the ion enters a magnetic field of 0.92 T along a direction perpendicular to the direction of the field. 1. Calculate the radius of the path of the ion in the field.
15 Example 7 Calculate the cyclotron frequency of a proton in a magnetic field of 5.2T.
16
17 Particle tracks from a Bubble Chamber
18 Example 8 A singly charged positive ion moving with a speed of 4.6 X 10 5 m/s leaves a spiral track of radius 7.94 mm in a photograph along a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field of a bubble chamber. The magnetic field applied for the photograph has a magnitude of 1.8T. Compute the mass (in atomic mass units) of this particle and from that, identify the particle
19 Example 9 The picture tube in a television uses magnetic deflection coils rather than electric deflection plates. Suppose an electron beam is accelerated though a 50-kV potential difference and then passes through a uniform magnetic field produced by these coils for 1 cm. The screen is located 10 cm from the center of the and is 50 cm wide. When the field is turned off, the electron beam hits the center of the screen. What field strength is necessary to deflect the beam to the side of the screen?
20 Example 10 The Hall effect can be used to measure the number of conduction electrons per unit volume, n, for an unknown sample. The sample is 15 mm thick, and when placed in a 1.8 T magnetic field produces a Hall voltage of µv while carrying a 12 A current. What is the value of n?
21 Example 11 In an experiment designed to measure the earth s magnetic field using the Hall effect, a copper bar 0.5 cm in thickness is positioned along an east-west direction. If a current of 8 A in the conductor results in a measured Hall voltage of 5.1 X V, what is the calculated value of the earth s magnetic field? (Assume that n=8.48 X electrons/m 3 and that the plane of the bar is rotated to be perpendicular to the direction of B)
22 Example 12 A cyclotron designed to accelerate protons is a provided with a magnetic field of 0.45 T and has a radius of 1.2 m. 1. What is the cyclotron frequency? 2. What is the maximum speed acquired by the protons?
23 Example 13 A certain cyclotron designed to accelerate alpha particles has a diameter of 1.52 m and operates at a frequency of 9.37 MHz. 1. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the alpha particles?
24 stop
v = E B FXA 2008 UNIT G485 Module Magnetic Fields BQv = EQ THE MASS SPECTROMETER
 UNIT G485 Module 1 5.1.2 Magnetic Fields 11 Thus, in order for the particle to suffer NO DEFLECTION and so exit the device at Y : From which : MAGNETIC FORCE UP = ELECTRIC FORCE DOWN BQv = EQ THE MASS
UNIT G485 Module 1 5.1.2 Magnetic Fields 11 Thus, in order for the particle to suffer NO DEFLECTION and so exit the device at Y : From which : MAGNETIC FORCE UP = ELECTRIC FORCE DOWN BQv = EQ THE MASS
Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles
 Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles 1. In the arrangement shown below, 2 C of positive charge is moved from plate S, which is at a potential of 250 V, to plate T, which is at a potential of 750 V.
Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles 1. In the arrangement shown below, 2 C of positive charge is moved from plate S, which is at a potential of 250 V, to plate T, which is at a potential of 750 V.
P ROBL E M S. 10. A current-carrying conductor experiences no magnetic force when placed in a certain manner in a uniform magnetic field. Explain. 11.
 918 C HAPTER 29 Magnetic Fields 10. A current-carrying conductor experiences no magnetic force when placed in a certain manner in a uniform magnetic field. Explain. 11. s it possible to orient a current
918 C HAPTER 29 Magnetic Fields 10. A current-carrying conductor experiences no magnetic force when placed in a certain manner in a uniform magnetic field. Explain. 11. s it possible to orient a current
4. An electron moving in the positive x direction experiences a magnetic force in the positive z direction. If B x
 Magnetic Fields 3. A particle (q = 4.0 µc, m = 5.0 mg) moves in a uniform magnetic field with a velocity having a magnitude of 2.0 km/s and a direction that is 50 away from that of the magnetic field.
Magnetic Fields 3. A particle (q = 4.0 µc, m = 5.0 mg) moves in a uniform magnetic field with a velocity having a magnitude of 2.0 km/s and a direction that is 50 away from that of the magnetic field.
Chapter 28. Magnetic Fields. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Copyright 28-1 Magnetic Fields and the Definition of B The Definition of B The Field. We can define a magnetic field B to be a vector quantity that exists when it exerts a force
Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Copyright 28-1 Magnetic Fields and the Definition of B The Definition of B The Field. We can define a magnetic field B to be a vector quantity that exists when it exerts a force
MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT
 MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q.1 Who designed cyclotron? Q.2 What is the magnetic field at a point on the axis of the current element? Q.3 Can the path of integration around which
MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q.1 Who designed cyclotron? Q.2 What is the magnetic field at a point on the axis of the current element? Q.3 Can the path of integration around which
Physics Tutorial MF1 Magnetic Forces
 Physics Tutorial MF1 Magnetic Forces 1 Magnetic Forces The force F on a charge q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field is: F = qv The force F on a straight conductor of length L carrying a current
Physics Tutorial MF1 Magnetic Forces 1 Magnetic Forces The force F on a charge q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field is: F = qv The force F on a straight conductor of length L carrying a current
University Physics Volume II Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 11: Magnetic Forces and Fields
 University Physics Volume II 1. Discuss the similarities and differences between the electrical force on a charge and the magnetic force on a charge. Both are field dependent. Electrical force is dependent
University Physics Volume II 1. Discuss the similarities and differences between the electrical force on a charge and the magnetic force on a charge. Both are field dependent. Electrical force is dependent
Chapter 28. Magnetic Fields. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Copyright 28-2 What Produces a Magnetic Field? 1. Moving electrically charged particles ex: current in a wire makes an electromagnet. The current produces a magnetic field that
Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Copyright 28-2 What Produces a Magnetic Field? 1. Moving electrically charged particles ex: current in a wire makes an electromagnet. The current produces a magnetic field that
CHAPTER 4: MAGNETIC FIELD
 CHAPTER 4: MAGNETIC FIELD PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 4 4. FIGURE 3 A copper rod of mass 0.08 kg and length 0.20 m is attached to two thin current carrying wires, as shown in FIGURE 3. The rod is perpendicular
CHAPTER 4: MAGNETIC FIELD PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 4 4. FIGURE 3 A copper rod of mass 0.08 kg and length 0.20 m is attached to two thin current carrying wires, as shown in FIGURE 3. The rod is perpendicular
Chapter 20. Magnetism
 Ch-20-1 Chapter 20 Magnetism Questions 1. A compass needle is not always balanced parallel to the Earth s surface, but one end may dip downward. Explain. 2. Explain why the Earth s north pole is really
Ch-20-1 Chapter 20 Magnetism Questions 1. A compass needle is not always balanced parallel to the Earth s surface, but one end may dip downward. Explain. 2. Explain why the Earth s north pole is really
Physics. Student Materials Advanced Higher. Tutorial Problems Electrical Phenomena HIGHER STILL. Spring 2000
 Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Electrical Phenomena TUTORIAL 1 Coulomb's Inverse Square Law 1 A charge of 2.0 x 10-8 C is placed a distance of 2.0
Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Electrical Phenomena TUTORIAL 1 Coulomb's Inverse Square Law 1 A charge of 2.0 x 10-8 C is placed a distance of 2.0
Physics 212 Question Bank III 2010
 A negative charge moves south through a magnetic field directed north. The particle will be deflected (A) North. () Up. (C) Down. (D) East. (E) not at all.. A positive charge moves West through a magnetic
A negative charge moves south through a magnetic field directed north. The particle will be deflected (A) North. () Up. (C) Down. (D) East. (E) not at all.. A positive charge moves West through a magnetic
Set of sure shot questions of Magnetic effect of Current for class XII CBSE Board Exam Reg.
 Set of sure shot questions of Magnetic effect of Current for class XII CBSE Board Exam. 2016- Reg. 1 Two Parallel Conducting wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other.why? I 1 A B
Set of sure shot questions of Magnetic effect of Current for class XII CBSE Board Exam. 2016- Reg. 1 Two Parallel Conducting wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other.why? I 1 A B
2R R R 2R. Phys Test 1
 Group test. You want to calculate the electric field at position (x o, 0, z o ) due to a charged ring. The ring is centered at the origin, and lies on the xy plane. ts radius is and its charge density
Group test. You want to calculate the electric field at position (x o, 0, z o ) due to a charged ring. The ring is centered at the origin, and lies on the xy plane. ts radius is and its charge density
Chapter 23 Electric Potential. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential Units of Chapter 23 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field Electric Potential Due to Point Charges Potential
Chapter 23 Electric Potential Units of Chapter 23 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field Electric Potential Due to Point Charges Potential
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Magnetic Field and Force
 NAME: Magnetic Field and Force 1. An aircraft whose wingspan is 15 m carries a static charge of 0.60 C. It travels at 240 m/s perpendicular to a 1.5x10-4 T magnetic field. What magnetic force does the
NAME: Magnetic Field and Force 1. An aircraft whose wingspan is 15 m carries a static charge of 0.60 C. It travels at 240 m/s perpendicular to a 1.5x10-4 T magnetic field. What magnetic force does the
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Review Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 21 The force that a magnetic field exerts on a charge moving with velocity v is given by! F B = q v!! B! The magnitude of the force
Review Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 21 The force that a magnetic field exerts on a charge moving with velocity v is given by! F B = q v!! B! The magnitude of the force
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT-3
 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT-3 [Motion of a charged particle in Magnetic field] Force On a Charged Particle in Magnetic Field If a particle carrying a positie charge q and moing with elocity enters a magnetic
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT-3 [Motion of a charged particle in Magnetic field] Force On a Charged Particle in Magnetic Field If a particle carrying a positie charge q and moing with elocity enters a magnetic
Physics 12 Final exam review key
 Physics 12 Final exam review key 1) A scalar field differs from a vector field in that A. a scalar field acts in only one direction B. a vector field acts in only one direction C. direction is irrelevant
Physics 12 Final exam review key 1) A scalar field differs from a vector field in that A. a scalar field acts in only one direction B. a vector field acts in only one direction C. direction is irrelevant
Chapter 12. Magnetism and Electromagnetism
 Chapter 12 Magnetism and Electromagnetism 167 168 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Magnetism and Electromagnetism SECTION A Magnetostatics 1. Four infinitely long wires are arranged as shown in the
Chapter 12 Magnetism and Electromagnetism 167 168 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Magnetism and Electromagnetism SECTION A Magnetostatics 1. Four infinitely long wires are arranged as shown in the
Three particles, a, b, and c, enter a magnetic field as shown in the figure. What can you say about the charge on each particle?
 1 Three particles, a, b, and c, enter a magnetic field as shown in the figure. What can you say about the charge on each particle? 6 Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on an electron traveling
1 Three particles, a, b, and c, enter a magnetic field as shown in the figure. What can you say about the charge on each particle? 6 Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on an electron traveling
Physics 212 Question Bank III 2006
 A negative charge moves south through a magnetic field directed north. The particle will be deflected (A) North. () Up. (C) Down. (D) East. (E) not at all. The magnetic force on a moving charge is (A)
A negative charge moves south through a magnetic field directed north. The particle will be deflected (A) North. () Up. (C) Down. (D) East. (E) not at all. The magnetic force on a moving charge is (A)
Homework (lecture 11): 3, 5, 9, 13, 21, 25, 29, 31, 40, 45, 49, 51, 57, 62
 Homework (lecture ): 3, 5, 9, 3,, 5, 9, 3, 4, 45, 49, 5, 57, 6 3. An electron that has velocity: moves through the uniform magnetic field (a) Find the force on the electron. (b) Repeat your calculation
Homework (lecture ): 3, 5, 9, 3,, 5, 9, 3, 4, 45, 49, 5, 57, 6 3. An electron that has velocity: moves through the uniform magnetic field (a) Find the force on the electron. (b) Repeat your calculation
Magnetic Fields & Forces
 Magnetic Fields & Forces Oersted discovered that an electric current will produce a magnetic field around conductor only a moving charge creates a magnetic field the magnetic field is circular around the
Magnetic Fields & Forces Oersted discovered that an electric current will produce a magnetic field around conductor only a moving charge creates a magnetic field the magnetic field is circular around the
12:40-2:40 3:00-4:00 PM
 PHY294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 handwritten problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40 Monday
PHY294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 handwritten problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40 Monday
Chapter 27 Magnetism 1/20/ Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnets and Magnetic Fields
 Chapter 27 Magnetism Magnets have two ends poles called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. However, if you cut a magnet in half, you don t get a north pole and a south pole you get
Chapter 27 Magnetism Magnets have two ends poles called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. However, if you cut a magnet in half, you don t get a north pole and a south pole you get
Question Bank 4-Magnetic effects of current
 Question Bank 4-Magnetic effects of current LEVEL A 1 Mark Questions 1) State Biot-Savart s law in vector form. 2) What is the SI unit of magnetic flux density? 3) Define Tesla. 4) A compass placed near
Question Bank 4-Magnetic effects of current LEVEL A 1 Mark Questions 1) State Biot-Savart s law in vector form. 2) What is the SI unit of magnetic flux density? 3) Define Tesla. 4) A compass placed near
Chapter 29 The Magnetic Field
 Chapter 9 The Magnetic Field y analogy with electrostatics, why don t we study magnetostatics first? Due to complicated mathematics (lack of magnetic monopole). In 80, Oersted established the link between
Chapter 9 The Magnetic Field y analogy with electrostatics, why don t we study magnetostatics first? Due to complicated mathematics (lack of magnetic monopole). In 80, Oersted established the link between
AP Physics Electromagnetic Wrap Up
 AP Physics Electromagnetic Wrap Up Here are the glorious equations for this wonderful section. This is the equation for the magnetic force acting on a moving charged particle in a magnetic field. The angle
AP Physics Electromagnetic Wrap Up Here are the glorious equations for this wonderful section. This is the equation for the magnetic force acting on a moving charged particle in a magnetic field. The angle
2. Draw the Magnetic Field lines created by the below two bar magnets. Homework 3. Draw the Magnetic Field lines created by the below bar magnets.
 Chapter Problems Magnetic Fields 1. Draw the Magnetic Field lines created by the below bar magnet. S N 2. Draw the Magnetic Field lines created by the below two bar magnets S N N S 3. Draw the Magnetic
Chapter Problems Magnetic Fields 1. Draw the Magnetic Field lines created by the below bar magnet. S N 2. Draw the Magnetic Field lines created by the below two bar magnets S N N S 3. Draw the Magnetic
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. An electron orbits a nucleus which carries a charge of +9.6 x10-19 C. If the electron s orbital radius is 2.0 x10-10 m, what is its electric potential energy? A. -6.9 x10-18
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. An electron orbits a nucleus which carries a charge of +9.6 x10-19 C. If the electron s orbital radius is 2.0 x10-10 m, what is its electric potential energy? A. -6.9 x10-18
Magnetic Fields & Forces
 Magnetic Fields & Forces Oersted discovered that an electric current will produce a magnetic field around conductor only a moving charge creates a magnetic field the magnetic field is circular around the
Magnetic Fields & Forces Oersted discovered that an electric current will produce a magnetic field around conductor only a moving charge creates a magnetic field the magnetic field is circular around the
An electron follows a circular path when it is moving at right angles to. uniform electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular.
 Q1.Which one of the following statements is correct? n electron follows a circular path when it is moving at right angles to D a uniform magnetic field. a uniform electric field. uniform electric and magnetic
Q1.Which one of the following statements is correct? n electron follows a circular path when it is moving at right angles to D a uniform magnetic field. a uniform electric field. uniform electric and magnetic
Cyclotron motion. Lecture 16. Chapter 29. Physics II. Course website:
 Lecture 16 Chapter 29 Physics II Cyclotron motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 29: Section 29.7 (Skip the Hall effect)
Lecture 16 Chapter 29 Physics II Cyclotron motion Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 29: Section 29.7 (Skip the Hall effect)
PH 222-2C Fall Magnetic Field. Lecture 13. Chapter 28 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Magnetic Field Lecture 13 Chapter 28 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields In this chapter we will cover the following topics:
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Magnetic Field Lecture 13 Chapter 28 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields In this chapter we will cover the following topics:
Downloaded from
 Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Magnetism. Permanent magnets Earth s magnetic field Magnetic force Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields
 Magnetism Permanent magnets Earth s magnetic field Magnetic force Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Magnetism Permanent magnets Earth s magnetic field Magnetic force Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
SECTION B Induction. 1. The rate of change of flux has which of the following units A) farads B) joules C) volts D) m/s E) webers
 SECTION B Induction 1. The rate of change of flux has which of the following units ) farads B) joules C) volts D) m/s E) webers 2. For the solenoids shown in the diagram (which are assumed to be close
SECTION B Induction 1. The rate of change of flux has which of the following units ) farads B) joules C) volts D) m/s E) webers 2. For the solenoids shown in the diagram (which are assumed to be close
Chapter 27 Magnetism. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 27 Magnetism 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnets have two ends poles called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields However, if you cut a
Chapter 27 Magnetism 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnets have two ends poles called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields However, if you cut a
Lab 4: The Classical Hall Effect
 Lab 4: The Classical Hall Effect Background A particle with charge q moving with a velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B will experience a force F, F = q( v B ) (1) 1 Introduction Understanding the
Lab 4: The Classical Hall Effect Background A particle with charge q moving with a velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B will experience a force F, F = q( v B ) (1) 1 Introduction Understanding the
week 8 The Magnetic Field
 week 8 The Magnetic Field General Principles General Principles Applications Start with magnetic forces on moving charges and currents A positive charge enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is
week 8 The Magnetic Field General Principles General Principles Applications Start with magnetic forces on moving charges and currents A positive charge enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is
Ch 17 Problem Set 31. A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a 120-V source. What current does the toaster carry, and what is its resistance?
 Ch 17 Problem Set 31. A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a 120-V source. What current does the toaster carry, and what is its resistance? 33. How many 100-W lightbulbs can you use in a 120-V
Ch 17 Problem Set 31. A toaster is rated at 600 W when connected to a 120-V source. What current does the toaster carry, and what is its resistance? 33. How many 100-W lightbulbs can you use in a 120-V
Chapter 29. Magnetic Fields
 Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields Outline 29.1 Magnetic Fields and Forces 29.2 Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-Carrying Conductor 29.4 Motion of a Charged Particle in a Uniform Magnetic Field 29.5 Applications
Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields Outline 29.1 Magnetic Fields and Forces 29.2 Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-Carrying Conductor 29.4 Motion of a Charged Particle in a Uniform Magnetic Field 29.5 Applications
(Total for Question = 5 marks) PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 1 Rutherford designed an experiment to see what happened when alpha particles were directed at a piece of gold foil. Summarise the observations and state the conclusions Rutherford reached about the structure
1 Rutherford designed an experiment to see what happened when alpha particles were directed at a piece of gold foil. Summarise the observations and state the conclusions Rutherford reached about the structure
Chapter 4 - Moving Charges and Magnetism. Magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the coil is given by the relation,
 Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Magnetic force and magnetic fields
 magnetar Magnetic force and magnetic fields Feb 28, 2012 Magnetic field Iron filings may be used to show the pattern of the magnetic field lines. A compass can be used to trace the field lines. The lines
magnetar Magnetic force and magnetic fields Feb 28, 2012 Magnetic field Iron filings may be used to show the pattern of the magnetic field lines. A compass can be used to trace the field lines. The lines
 1. Write the relation for the force acting on a charge carrier q moving with velocity through a magnetic field in vector notation. Using this relation, deduce the conditions under which this force will
1. Write the relation for the force acting on a charge carrier q moving with velocity through a magnetic field in vector notation. Using this relation, deduce the conditions under which this force will
Phys102 Lecture 16/17 Magnetic fields
 Phys102 Lecture 16/17 Magnetic fields Key Points Electric Currents Produce Magnetic Fields Force on an Electric Current in a Magnetic Field; Definition of B Force on an Electric Charge Moving in a Magnetic
Phys102 Lecture 16/17 Magnetic fields Key Points Electric Currents Produce Magnetic Fields Force on an Electric Current in a Magnetic Field; Definition of B Force on an Electric Charge Moving in a Magnetic
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. Which line, to, correctly describes the trajectory of charged particles which enter, at right angles, (a) a uniform electric field, and (b) a uniform magnetic field? (a) uniform
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. Which line, to, correctly describes the trajectory of charged particles which enter, at right angles, (a) a uniform electric field, and (b) a uniform magnetic field? (a) uniform
P Q 2 = -3.0 x 10-6 C
 1. Which one of the following represents correct units for electric field strength? A. T B. N/C C. J / C D. N m 2 /C 2 2. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. P Q 2Q Which
1. Which one of the following represents correct units for electric field strength? A. T B. N/C C. J / C D. N m 2 /C 2 2. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. P Q 2Q Which
Unit 8: Electromagnetism
 Multiple Choice Portion Unit 8: Electromagnetism 1. Four compasses are placed around a conductor carrying a current into the page, as shown below. Which compass correctly shows the direction of the magnetic
Multiple Choice Portion Unit 8: Electromagnetism 1. Four compasses are placed around a conductor carrying a current into the page, as shown below. Which compass correctly shows the direction of the magnetic
10/24/2012 PHY 102. (FAWOLE O.G.) Good day. Here we go..
 Good day. Here we go.. 1 PHY102- GENERAL PHYSICS II Text Book: Fundamentals of Physics Authors: Halliday, Resnick & Walker Edition: 8 th Extended Lecture Schedule TOPICS: Dates Ch. 28 Magnetic Fields 12
Good day. Here we go.. 1 PHY102- GENERAL PHYSICS II Text Book: Fundamentals of Physics Authors: Halliday, Resnick & Walker Edition: 8 th Extended Lecture Schedule TOPICS: Dates Ch. 28 Magnetic Fields 12
Physics 2220 Fall 2010 George Williams THIRD MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 2220 Fall 2010 George Williams THIRD MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS Solution sets are available on the course web site. A data sheet is provided. Problems marked by "*" do not have solutions. 1. An
Physics 2220 Fall 2010 George Williams THIRD MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS Solution sets are available on the course web site. A data sheet is provided. Problems marked by "*" do not have solutions. 1. An
CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTORS / MOVING CHARGES / CHARGED PARTICLES IN CIRCULAR ORBITS
 PHYSICS A2 UNIT 4 SECTION 4: MAGNETIC FIELDS CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTORS / MOVING CHARGES / CHARGED PARTICLES IN CIRCULAR ORBITS # Questions MAGNETIC FLUX DENSITY 1 What is a magnetic field? A region in
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 4 SECTION 4: MAGNETIC FIELDS CURRENT-CARRYING CONDUCTORS / MOVING CHARGES / CHARGED PARTICLES IN CIRCULAR ORBITS # Questions MAGNETIC FLUX DENSITY 1 What is a magnetic field? A region in
Physics 2112 Unit 12
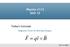 Physics 2112 Unit 12 Today s Concept: Magnetic Force on Moving Charges F qv B Unit 12, Slide 1 Where we are E fields B fields Stuff You asked about.. This is crazy. But also really cool. What is that "K"
Physics 2112 Unit 12 Today s Concept: Magnetic Force on Moving Charges F qv B Unit 12, Slide 1 Where we are E fields B fields Stuff You asked about.. This is crazy. But also really cool. What is that "K"
where the magnetic field is directed from south to north. It will be deflected:
 Section: Magnetic Field Take Home Test Due Tues. Apr. 2----all work should be shown on test---you will hand in the scantron for scoring 1. A hydrogen atom that has lost its electron is moving east in a
Section: Magnetic Field Take Home Test Due Tues. Apr. 2----all work should be shown on test---you will hand in the scantron for scoring 1. A hydrogen atom that has lost its electron is moving east in a
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 8, 2012 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 8, 2012 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
Tridib s Physics Tutorials. NCERT-XII / Unit- 4 Moving charge and magnetic field
 MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO A CURRENT ELEMENT The relation between current and the magnetic field, produced by it is magnetic effect of currents. The magnetic fields that we know are due to currents or moving
MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO A CURRENT ELEMENT The relation between current and the magnetic field, produced by it is magnetic effect of currents. The magnetic fields that we know are due to currents or moving
MAGNETIC PROBLEMS. (d) Sketch B as a function of d clearly showing the value for maximum value of B.
 PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
FXA 2008 ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) 1. Candidates should be able to : Electric charge is a property possessed by protons and electrons.
 ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) 1 Candidates should be able to : Explain that electric current is a net flow of charged particles. Explain that electric current in a metal is due to the movement of electrons, whereas
ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) 1 Candidates should be able to : Explain that electric current is a net flow of charged particles. Explain that electric current in a metal is due to the movement of electrons, whereas
Brown University PHYS 0060 Physics Department LAB B -190
 Physics Department LAB B -190 THE FORCE OF A MAGNETIC FIELD ON A MOVING ELECTRIC CHARGE DETERMINATION OF THE RATIO OF CHARGE TO MASS, e/m, FOR ELECTRONS References: H.D. Young, University Physics, Eleventh
Physics Department LAB B -190 THE FORCE OF A MAGNETIC FIELD ON A MOVING ELECTRIC CHARGE DETERMINATION OF THE RATIO OF CHARGE TO MASS, e/m, FOR ELECTRONS References: H.D. Young, University Physics, Eleventh
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM
 UNIT III MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM Weightage 8 Marks Concept of magnetic field and Oersted s experiment Biot-savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere s law
UNIT III MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM Weightage 8 Marks Concept of magnetic field and Oersted s experiment Biot-savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere s law
a) head-on view b) side view c) side view Use the right hand rule for forces to confirm the direction of the force in each case.
 Electromagnetism Magnetic Force on a Wire Magnetic Field around a Bar Magnet Direction of magnetic field lines: the direction that the North pole of a small test compass would point if placed in the field
Electromagnetism Magnetic Force on a Wire Magnetic Field around a Bar Magnet Direction of magnetic field lines: the direction that the North pole of a small test compass would point if placed in the field
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS XII CHAPTER 4 and 5 Magnetic Effects of Electric current and Magnetism WORKSHEET 4
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS XII CHAPTER 4 and 5 Magnetic Effects of Electric current and Magnetism WORKSHEET 4 SECTION A CONCEPTUAL AND APPLICATION TYPE QUESTIONS 1
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS XII CHAPTER 4 and 5 Magnetic Effects of Electric current and Magnetism WORKSHEET 4 SECTION A CONCEPTUAL AND APPLICATION TYPE QUESTIONS 1
Electric_Field_core_P1
 Electric_Field_core_P1 1. [1 mark] An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel to the plates. The electromagnetic force acting on the electron A. causes
Electric_Field_core_P1 1. [1 mark] An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel to the plates. The electromagnetic force acting on the electron A. causes
Electromagnetism IB 12
 Electromagnetism Magnetic Field around a Bar Magnet Direction of magnetic field lines: the direction that the North pole of a small test compass would point if placed in the field (N to S) What is the
Electromagnetism Magnetic Field around a Bar Magnet Direction of magnetic field lines: the direction that the North pole of a small test compass would point if placed in the field (N to S) What is the
A 12-V battery does 1200 J of work transferring charge. How much charge is transferred? A source of 1.0 µc is meters is from a positive test
 1 A source of 1.0 µc is 0.030 meters is from a positive test charge of 2.0 µc. (a) What is the force on the test charge? (b) What is the potential energy of the test charge? (c) What is the strength of
1 A source of 1.0 µc is 0.030 meters is from a positive test charge of 2.0 µc. (a) What is the force on the test charge? (b) What is the potential energy of the test charge? (c) What is the strength of
Other Formulae for Electromagnetism. Biot's Law Force on moving charges
 Other Formulae for Electromagnetism Biot's Law Force on moving charges 1 Biot's Law. Biot's Law states that the magnetic field strength (B) is directly proportional to the current in a straight conductor,
Other Formulae for Electromagnetism Biot's Law Force on moving charges 1 Biot's Law. Biot's Law states that the magnetic field strength (B) is directly proportional to the current in a straight conductor,
Class XII- Physics - Assignment Topic: - Magnetic Effect of Current
 LJPS Gurgaon 1. An electron beam projected along +X axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along +Y axis. What is the direction of the magnetic field? Class XII- Physics - Assignment Topic:
LJPS Gurgaon 1. An electron beam projected along +X axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along +Y axis. What is the direction of the magnetic field? Class XII- Physics - Assignment Topic:
Lecture 26: WED 18 MAR
 Physics 2113 Aurora Borealis Jonathan Dowling Lecture 26: WED 18 MAR Magnetic fields I ll be back. The Hall Effect Charge Flow in Conductors is From Electrons: Benjamin Franklin s Biggest Blunder! 28.5:
Physics 2113 Aurora Borealis Jonathan Dowling Lecture 26: WED 18 MAR Magnetic fields I ll be back. The Hall Effect Charge Flow in Conductors is From Electrons: Benjamin Franklin s Biggest Blunder! 28.5:
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 11, 2009 Time: 3 hours NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 11, 2009 Time: 3 hours NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print
Sample Examination Questions
 Sample Examination Questions Contents NB. Material covered by the AS papers may also appear in A2 papers. Question Question type Question focus number (section A or B) 1 A Ideal transformer 2 A Induced
Sample Examination Questions Contents NB. Material covered by the AS papers may also appear in A2 papers. Question Question type Question focus number (section A or B) 1 A Ideal transformer 2 A Induced
Chapter 29. Magnetic Fields
 Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields A Brief History of Magnetism 13 th century BC Chinese used a compass Uses a magnetic needle Probably an invention of Arabic or Indian origin 800 BC Greeks Discovered magnetite
Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields A Brief History of Magnetism 13 th century BC Chinese used a compass Uses a magnetic needle Probably an invention of Arabic or Indian origin 800 BC Greeks Discovered magnetite
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX. First Pre-Board Examination, Physics
 Series SSO Code No. 55/1/B Roll No. Candidates must write the code on the title page of the answer book General Instructions: Please check that this question paper contains 6 printed pages. Code number
Series SSO Code No. 55/1/B Roll No. Candidates must write the code on the title page of the answer book General Instructions: Please check that this question paper contains 6 printed pages. Code number
Unit 3 Electromagnetism. Class Questions
 Unit 3 Electromagnetism Class Questions Contents TUTORIAL 1 TUTORIAL 2 TUTORIAL 3 Coulomb's Inverse Square Law Electric Field Strength Electrostatic Potential PAST PAPERS 2012 Q5, 2011 Q5, 2010 Q6, 2009
Unit 3 Electromagnetism Class Questions Contents TUTORIAL 1 TUTORIAL 2 TUTORIAL 3 Coulomb's Inverse Square Law Electric Field Strength Electrostatic Potential PAST PAPERS 2012 Q5, 2011 Q5, 2010 Q6, 2009
(D) Blv/R Counterclockwise
 1. There is a counterclockwise current I in a circular loop of wire situated in an external magnetic field directed out of the page as shown above. The effect of the forces that act on this current is
1. There is a counterclockwise current I in a circular loop of wire situated in an external magnetic field directed out of the page as shown above. The effect of the forces that act on this current is
MOTION OF A CHARGED PARTICLE IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD
 MOTION OF A CHARGED PARTICLE IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD When the velocity of a charged particle is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, the particle moves in a circular path in a plane perpendicular
MOTION OF A CHARGED PARTICLE IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD When the velocity of a charged particle is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, the particle moves in a circular path in a plane perpendicular
Chapter 27 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces
 Chapter 27 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 27 To study magnets and the forces they exert on each other To calculate the force that a magnetic field exerts on
Chapter 27 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 27 To study magnets and the forces they exert on each other To calculate the force that a magnetic field exerts on
Physics Week 5(Sem. 2) Name. Magnetism. Chapter Summary. Magnetic Fields
 Physics Week 5(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Magnetism Magnetic Fields Permanent magnets have long been used in navigational compasses. The needle in a compass is supported to allow it to freely rotate
Physics Week 5(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Magnetism Magnetic Fields Permanent magnets have long been used in navigational compasses. The needle in a compass is supported to allow it to freely rotate
Section 4 : Accelerators
 Section 4 : Accelerators In addition to their critical role in the evolution of nuclear science, nuclear particle accelerators have become an essential tool in both industry and medicine. Table 4.1 summarizes
Section 4 : Accelerators In addition to their critical role in the evolution of nuclear science, nuclear particle accelerators have become an essential tool in both industry and medicine. Table 4.1 summarizes
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Define electric field strength at a point in space....... [Total 1 marks] 2. Fig. 1 shows a square flat coil of insulated wire placed in a region of a uniform magnetic field
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Define electric field strength at a point in space....... [Total 1 marks] 2. Fig. 1 shows a square flat coil of insulated wire placed in a region of a uniform magnetic field
Direct-Current Accelerator
 Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 11 Accelerators One of the most important tools of nuclear science is the
Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 11 Accelerators One of the most important tools of nuclear science is the
Chapter 4: Magnetic Field
 Chapter 4: Magnetic Field 4.1 Magnetic Field 4.1.1 Define magnetic field Magnetic field is defined as the region around a magnet where a magnetic force can be experienced. Magnetic field has two poles,
Chapter 4: Magnetic Field 4.1 Magnetic Field 4.1.1 Define magnetic field Magnetic field is defined as the region around a magnet where a magnetic force can be experienced. Magnetic field has two poles,
Chapter 21. Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fields
 Chapter 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fields 21.1 Magnetic Fields The needle of a compass is permanent magnet that has a north magnetic pole (N) at one end and a south magnetic pole (S) at the other.
Chapter 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fields 21.1 Magnetic Fields The needle of a compass is permanent magnet that has a north magnetic pole (N) at one end and a south magnetic pole (S) at the other.
Magnetic Fields; Sources of Magnetic Field
 This test covers magnetic fields, magnetic forces on charged particles and current-carrying wires, the Hall effect, the Biot-Savart Law, Ampère s Law, and the magnetic fields of current-carrying loops
This test covers magnetic fields, magnetic forces on charged particles and current-carrying wires, the Hall effect, the Biot-Savart Law, Ampère s Law, and the magnetic fields of current-carrying loops
Magnetic Fields. or I in the filed. ! F = q! E. ! F = q! v! B. q! v. Charge q as source. Current I as source. Gauss s Law. Ampere s Law.
 Magnetic Fields Charge q as source Gauss s Law Electric field E F = q E Faraday s Law Ampere-Maxwell Law Current I as source Magnetic field B Ampere s Law F = q v B Force on q in the field Force on q v
Magnetic Fields Charge q as source Gauss s Law Electric field E F = q E Faraday s Law Ampere-Maxwell Law Current I as source Magnetic field B Ampere s Law F = q v B Force on q in the field Force on q v
1 Written and composed by: Prof. Muhammad Ali Malik (M. Phil. Physics), Govt. Degree College, Naushera
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Q # 1. Describe the properties of magnetic field due to current in a long straight conductor. Ans. When the heavy current is passed through a straight conductor: i. A magnetic field is
ELECTROMAGNETISM Q # 1. Describe the properties of magnetic field due to current in a long straight conductor. Ans. When the heavy current is passed through a straight conductor: i. A magnetic field is
Problems set # 7 Physics 169 March 31, 2015
 Prof. Anchordoqui Problems set # 7 Physics 69 March 3, 05. (i) Determine the initial direction of the deflection of charged particles as they enter the magnetic fields as shown in Fig.. (ii) At the Equator
Prof. Anchordoqui Problems set # 7 Physics 69 March 3, 05. (i) Determine the initial direction of the deflection of charged particles as they enter the magnetic fields as shown in Fig.. (ii) At the Equator
Advanced Higher Physics. Electromagnetism
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Electromagnetism Problems AH Physics: Electromagnetism 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Electromagnetism Problems AH Physics: Electromagnetism 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
224 g (Total 1 mark) A straight line in a direction opposite to that of the field.
 Q1. The diagram shows a rigidly-clamped straight horizontal current-carrying wire held mid-way between the poles of a magnet on a top pan balance. The wire is perpendicular to the magnetic field direction.
Q1. The diagram shows a rigidly-clamped straight horizontal current-carrying wire held mid-way between the poles of a magnet on a top pan balance. The wire is perpendicular to the magnetic field direction.
PHYSICS 30 ELECTROMAGNETISM ASSIGNMENT 3 VERSION:0
 Communication includes statement of the physics concept used and how it is applied in the situation along with diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well laid out formula, substitution, answer
Communication includes statement of the physics concept used and how it is applied in the situation along with diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well laid out formula, substitution, answer
6.013 Lecture 12: Magnetic Forces and Devices
 6.013 Lecture 12: Magnetic Forces and Devices A. Overview Magnetic forces are central to a wide array of actuators and sensors. These forces can be calculated using either energy methods or the Lorentz
6.013 Lecture 12: Magnetic Forces and Devices A. Overview Magnetic forces are central to a wide array of actuators and sensors. These forces can be calculated using either energy methods or the Lorentz
CHARGE TO MASS RATIO FOR THE ELECTRON
 CHARGE TO MASS RATIO FOR THE ELECTRON OBJECTIVE: To measure the ratio of the charge of an electron to its mass. METHOD: A stream of electrons is accelerated by having them "fall" through a measured potential
CHARGE TO MASS RATIO FOR THE ELECTRON OBJECTIVE: To measure the ratio of the charge of an electron to its mass. METHOD: A stream of electrons is accelerated by having them "fall" through a measured potential
Determining the Charge to Mass Ratio (e/m) for an Electron
 Determining the Charge to Mass Ratio (e/m) for an Electron Introduction In order to determine the charge to mass ratio (e/m) for an electron we create a beam of electrons by heating a metal filament in
Determining the Charge to Mass Ratio (e/m) for an Electron Introduction In order to determine the charge to mass ratio (e/m) for an electron we create a beam of electrons by heating a metal filament in
Chapter 27 Magnetism. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 27 Magnetism 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnets have two ends poles called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields However, if you cut a
Chapter 27 Magnetism 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnets have two ends poles called north and south. Like poles repel; unlike poles attract. 27-1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields However, if you cut a
Problem Fig
 Problem 27.15 An electron at point A has a speed of 1.41 x 10 6 m/s. Find (a) the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field that will cause the electron to follow the semicircular path from A to B,
Problem 27.15 An electron at point A has a speed of 1.41 x 10 6 m/s. Find (a) the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field that will cause the electron to follow the semicircular path from A to B,
1 (a) Define magnetic flux [1]
![1 (a) Define magnetic flux [1] 1 (a) Define magnetic flux [1]](/thumbs/85/92556381.jpg) 1 (a) Define magnetic flux..... [1] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows a generator coil of 5 turns and cross-sectional area 2.5 1 3 m 2 placed in a magnetic field of magnetic flux density.35 T. The plane of the coil is
1 (a) Define magnetic flux..... [1] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows a generator coil of 5 turns and cross-sectional area 2.5 1 3 m 2 placed in a magnetic field of magnetic flux density.35 T. The plane of the coil is
Magnetism Chapter Questions
 Magnetism Chapter Questions 1. Both Electric and Magnetic Forces will cause objects to repel and attract each other. What is a difference in the origin of these forces? 2. A Magnet has a north and a south
Magnetism Chapter Questions 1. Both Electric and Magnetic Forces will cause objects to repel and attract each other. What is a difference in the origin of these forces? 2. A Magnet has a north and a south
MAGNETIC DEFLECTION. OBJECTIVE: To observe the effect of a magnetic field on an electron beam. To measure the Earth s magnetic field.
 MAGNETIC DEFLECTION OBJECTIVE: To observe the effect of a magnetic field on an electron beam. To measure the Earth s magnetic field. THEORY: Moving charges exert forces on one another that are not observed
MAGNETIC DEFLECTION OBJECTIVE: To observe the effect of a magnetic field on an electron beam. To measure the Earth s magnetic field. THEORY: Moving charges exert forces on one another that are not observed
