arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 12 Mar 2015
|
|
|
- Sylvia Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 axiv: v [math.ca] 2 Ma 205 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS TRISTRAM DE PIRO Abstact. We develop a method fo calculating Riemann sums using Fouie analysis.. Poisson Summation Fomula Definition.. If f L (R), we define; (f) (y) = f(x)e 2πixy (f) (y) = f( y) (f) (y) = f(x)e2πixy and, if g L ([0,]), m Z, we define; (g) (m) = 0 g(x)e 2πixm Remaks.2. If f S(R), we have that; f(x) = (f) (y)e 2πixy dy, (x R) and, if g C ([0,]), ( ), the seies; m Z (g) (m)e 2πixm conveges unifomly to g on [0,]. See [4],[2] and [3]. Also obseve that (f) = (f ) and (f) = (f ). Theoem.3. Let f S(R), and let; By which we mean that g (0,) C (0,), and thee exist {g k C[0,] : k Z 0 }, such that g k (0,) = g (k), and g k (0) = g k ().
2 2 TRISTRAM DE PIRO g(y) = m Z f(y +m), (y [0,]) Then g C ([0,]) and the seies m Z (f) (m)e 2πiym conveges unifomly to g on [0,]. In paticula; m Z f(m) = m Z (f) (m) Poof. Obseve that, as f S(R), fo y 0 [0,], Z 0, n 2; m Z d f dy y0 +m m Z m Z C,n (+ y 0 +m n ) C,n (+ m n ) C,n +2C,n m m n C,n +2C,n (+[ y n+ n+ ] = C,n (+2(+ n ) 5C,n ( ) whee C,n = sup w R ( w nd f w ) Suppose, inductively, that d g dy y0 = d f m Z dy y0 +m, fo y 0 [0,], ( 2 ), then, using ( ), we have, fo, that; d + g = d ( d f m dy + m Z ) = d + f m dy m Z dy + whee f m (x) = f(x+m), fo m Z. Moeove, fo 0; d g dy 0 = d f m m Z dy 0 = d f m m Z dy = d g dy It follows that g C [0,]. Moeove, we have that, fo n Z; 2 Given d g dy, we intepet d+ g dy + 0 = lim h 0,+ h (d g dy h d g dy 0 )
3 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS 3 (g) (n) = 0 g(y)e 2πiyn = 0 ( m Z f(y +m))e 2πiyn = 0 ( m Z f(y +m))e 2πi(y+m)n = f(y)e 2πiyn = (f) (n) Using Remak.2, the seies; m Z ˆf(m)e 2πiym conveges unifomly to g on [0,] as equied. Lemma.4. If h C 2 (R), and thee exists C R, with; sup x R ( x 2 h(x), x 2 h (x), x 2 h (x) ) C then the Invesion theoem holds fo h. That is (h) L (R) and; h(x) = R (h) (y)e 2πixy dy (x R) Poof. The esult follows fom inspection of the poof in[2], see Remak 0.4. Lemma.5. If h satisfies the conditions of Lemma.4, and f = (h), then (f) = h. Poof. As h satisfies the conditions of Lemma.4, so does h, and, theefoe, the invesion theoem holds fo h. Then; ((h ) ) = (((h ) ) ) = (h ) theefoe; (((h ) ) ) = h. As f = h = (h ), we have that; (f) = (h ) ) = h
4 4 TRISTRAM DE PIRO Lemma.6. Let f be given by Lemma.5. Then, if thee exists D R, with; sup x R ( x 4 h(x), x 4 h (x), x 4 h (x) ) D we have that f C 2 (R), and, moeove, thee exists a constant F R, such that; sup y R ( y 2 f(y), y 2 f (y), y 2 f (y) ) F. Poof. Letting E = h [,] C[,], we have that, fo y R, x ; h(x)e 2πixy = h(x) D x 4 D x 2 2πixh(x)e 2πixy = 2π x h(x) 2πD 2πD x 3 x 2 4π 2 x 2 h(x)e 2πixy = 4π 2 x 2 h(x) 4π2 D 4π2 D x 2 x 2 and, fo y R, x ; x 2 h(x)e 2πixy h(x) E x 2 2πixh(x)e 2πixy 2π h(x) 2πE x 2 4π 2 x 2 h(x)e 2πixy 4π 2 h(x) 4π 2 E Hence; sup x R { x 2 h(x)e 2πixy, x 2 2πixh(x)e 2πixy, x 2 4π 2 x 2 h(x)e 2πixy } 4π 2 max(d,e) and {h(x)e 2πixy,2πixh(x)e 2πixy, 4π 2 x 2 h(x)e 2πixy } C(R). It follows that, fo y 0 R, we can diffeentiate unde the integal sign, to obtain that {f(y 0 ),f (y 0 ),f (y 0 )} ae all defined. By the DCT, using the fact that 4π 2 x 2 h(x) L (R), we obtain that f C(R), hence, f C 2 (R). Diffeentiating by pats, using the fact that; {h,h,h,xh,xh,xh,x 2 h,x 2 h,x 2 h } (L (R) C 0 (R))
5 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS 5 by the hypotheses of Lemma.4 and this Lemma, we have that; (h ) = 4πy 2 (h) = 4πy 2 f (4πih +2πixh ) = ((2πixh) ) = 4πy 2 (2πixh) = 4πy 2 f (8π 2 h+6π 2 xh +4π 2 x 2 h ) = ((4π 2 x 2 h) ) = 4πy 2 (4π 2 x 2 h) = 4πy 2 f, ( ) We have, by ( ), fo y, that; f(y) (h ) (y) 4πy 2 h L (R) 4πy 2 2D 3 +2E 4πy 2 f (y) (4πih +2πixh ) (y) 4πy 2 (4πih +2πixh ) L (R) 4πy 2 2 h L (R) + xh L (R) 2y 2 2(2D 3 +2E )+D+2E 2y 2 f (y) (8π2 h+6π 2 xh +4π 2 x 2 h ) (y) 4πy 2 (8π2 h+6π 2 xh +4π 2 x 2 h ) L (R) 4πy 2 2π h L (R) +4π xh L (R) +π x 2 h L (R) y 2 2π(2D 3 +2E)+4π(D+2E )+π(2d+2e ) y 2 whee E = h [,] C[,] and E = h [,] C[,] Fo y, we have that; f(y) h L (R) 2D 3 +E f (y) (2πixh) L (R) 2πD +2E f (y) 4π 2 x 2 h L (R) 8π 2 D +2E Hence, we can take F = max(8π 2 D+2E, 22πD 3 +4πE+8πE +2πE )
6 6 TRISTRAM DE PIRO Definition.7. Let f be given by satisfying the conditions of Lemmas.5 and.6, we let; g(y) = m Z f(y +m), (y [0,]) Lemma.8. Let g be given by Definition.7, then g C 2 [0,]. Poof. Using Lemma.6 and Weiestass M-test, we have that the seies; m Z f(y +m), m Z f (y +m), m Z f (y +m) ae unifomly convegent on [0,]. It follows, that g C 2 (0,), and clealy; g + (0) = m Z f (m) = m Z f (m+) = g () hence, g C 2 [0,]. Lemma.9. Let f L (R), such that; g(y) = m Z f(y +m) is defined, fo y [0,]. Then, if g C 2 [0,], we have that the seies m Z (f) (m)e 2πiym conveges unifomly to g on [0,]. In paticula; m Z f(m) = m Z (f) (m) Poof. Following though the calculation in Theoem.3, we have that g L ([0,]), and (g) (m) = (f) (m), fo m Z. Using the esult of [3] o [4], we obtain the second pat, the final claim is clea. Lemma.0. Let f be given by satisfying the conditions of Lemmas.5 and.6, with espect to h, then; m Z f(m) = m Z h(m) Poof. Using Lemmas.5 and.6, we have that g C 2 [0,], whee g is defined by.8, and (f) (m) = h(m), fo m Z. By Lemmas.8
7 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS 7 and.9, we have that; m Z f(m) = m Z (f) (m) Hence; m Z f(m) = m Z h(m) as equied. Lemma.. If s Z 2, s even, then; n= = ( ) s+2 2 (2π) s B s n s 2(s!) Poof. The poof of this esult can be found in [4]. Definition.2. If s C, with Re(s) 4, and Z, we define; h s, (x) = x s, (x ) h s, (x) = ( )s x s = e iπs x s, (x ) Remaks.3. h s, is symmetic, that is h s, (x) = h s, ( x), fo x. Lemma.4. Thee exists a polynomial p s, of degee 2 + 3, with the popeties; (i). p s, is symmetic, that is p s, (x) = p s, ( x), fo x R. (ii). p s, (n) = n s, fo n. (iii). p (k) s,() = h (k),+ s, (), (0 k 2) (iv). p (k) s,( ) = h (k), s, ( ), (0 k 2) Poof. We let, fo j +, k ;
8 8 TRISTRAM DE PIRO j (+)... A = k 2... k 2j... k 2(+) j... 2(+) j 2j... 2( +) j(2j ) 2j ( +)(2+) 2 s 2 s... b s, = k s... s s (+s) s(s+) (2+s) Wehavethatdet(A ) 0,hence, wecansolvetheequationa (a s, ) = b s,. Let p s, (x) = + j=0 (a s,) (j+) x 2j. We have, by constuction, that p s, ( x) = p s, (x), and p (k) s,() = h s, (k),+ (). As both p s, and h s, ae symmetic, we also have that, p (k) s,() = h s, (k), ( ), as equied. Definition.5. We define; g s, (x) = h s, (x), (if x ) g s, (x) = p s, (x), (if x ) Lemma.6. We have that g s, C 2 (R), g s, is symmetic, and, moeove, the hypotheses of Lemmas.4 and.6 hold fo g s,. Poof. The fact that g s, C 2 (R) follows immediately fomconditions (iii) and(iv) of Lemma.4. The symmety condition is a consequence of Condition (i). If x, we have that; g s, (x) x Re(s) x Im(s) x 4 Hence, as g s, is symmetic, g s, (x) x 4, fo x.
9 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS 9 If x ; g s, (x) = p s, (x) j=0 (a s,) (j+) a s, It follows that sup x R ( x 4 g s, (x) ) max(, a s, ). Similaly, as g s, s (x) =, g s(s+) x s+ s (x) =, x >, then, if x >, we x s+2 have that; g s, (x) s x 5 g s,(x) s s x 6 and, if x ; g s,(x) = p s,(x) 2+2 ( + j= 2j(a s,) (j+) ) 2(+) a s, g s (x) = p s (x) 2+2 ( + j= 2j(2j )(a s,) (j+) ) (2+2)(2+ ) a s so that; sup x R ( x 5 g s,(x) ) max( s,2( +) a s ) sup x R ( x 6 g s, (x) ) max( s s,(2+2)(2+) a s ) ( ) It follows that Lemmas.4 and.6 holds fo g s,, with C = D = max( s s,(2+2)(2+) a s. Definition.7. We let f s, (y) = R g s,(x)e 2πixy. R s,, = n Z 0 ( R s,,2 = n Z 0 ( R s, = R s,, +R s,,2 e 2πinx ) x s e 2πinx ) x s P s,, = n Z 0 ( 0 p s,(x)e 2πinx )
10 0 TRISTRAM DE PIRO P s,,2 = n Z 0 ( 0 p s,(x)e 2πinx ) P s, = P s,, +P s,,2 Lemma.8. We have that f s, is symmetic, and f s, satisfies the conclusions of Lemmas.5 and.6. Moeove; f s, (0)+P s, +R s, = p s, (0)+2 n= n s Poof. The second pat follows immediately fom Definition.7, and Lemmas.6,.5 and.6. It follows that f s, L (R), and; f s, ( y) = R g s,(x)e 2πixy = R g s,( x)e 2πixy = R g s,(x)e 2πixy = f s, (y) Hence, f s, is symmetic. By Lemma.0, we have that; n Z f s,(n) = n Z g s,(n) As both f s, and g s, ae symmetic, using Definition.5 and popety (ii) of Lemma.4, we obtain; f s, (0)+P s, +R s, = f s, (0)+ n Z 0 f s, (n) = g s, (0)+2( n= g s,(n)) = p s, (0)+2( n= n s ) Lemma.9. We have that; R s, 2 s 2 3(Re(s)+) Re(s)+
11 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS P s, = p s, (0)+p s, ()+2 l= p s,(l) 2 0 p s,(x) Poof. We have that; R s,, = n Z 0 2πin s + n Z 0 s e 2πinx 2πin x s+ = s + s(s+) e 2πinx n Z 0 s+ (2πin) 2 n Z 0 (2πin) 2 x s+2 = 2s 4 s+ π 2 n= = s 2 s+ π 2 π 2 6 +D s,, = s 2 s+ +D s,, whee; D s,, s(s+) C s,, 4π 2 and C s,, = = x Re(s)+2 (Re(s)+) Re(s)+ It follows that; R s,, n 2 +D s,, x s+2 = s(s+) C s,, n Z 0 n 2 2 s s(s+) + 2 Re(s)+ 2(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ s (Re(s)+) s(s+) + 2(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ 2(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ = s (Re(s)+)+ s(s+) 2(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ 2 s(s+) 2(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ s 2 3(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ Similaly, R s,,2 We have that; s 2 3(Re(s)+) Re(s)+, so that R s, 2 s 2 3(Re(s)+) Re(s)+.
12 2 TRISTRAM DE PIRO P s,, = ( p n Z 0 0 s,(x)e 2πinx = n Z 0 ( l=0 l+ l p s, (x)e 2πinx ) = l=0 ( ( l+ p n Z 0 s, (x)e 2πinx )) l = l=0 ( n Z 0 ( 0 p s,(x+l)e 2πin(x+l) )) = l=0 ( n Z 0 ( 0 p s,(x+l)e 2πinx )) = l=0 ( n Z 0 (p l s, ) (n)) = l=0 ( n Z (pl s, ) (n) 0 pl s, ), (3 ) 3 If f (C[0,] C 2 (0,)), and thee exist {a +,j,a,j : 0 j 2} C, with lim x 0 +f (j) (x) = a +,j and lim x f (j) (x) = a,j, ( ), fo 0 j 2, then a classical esult in the theoy of Fouie seies, says that; lim N N n= N (f)( ) (n)e 2πinx = f(x) (x (0,)) lim N N n= N (f)( ) (n) = a+,0+a,0 2 We give a simple poofofthis esult. Fist obsevethat thee exists a polynomial p C[x], with deg(p) = 5, such that p (j) (0) = 0 and p (j) () = a,j a +,j, fo 0 j 2. This follows fom the fact that we can find c C 3, such that M c = a, whee a(j) = a,j a +,j, fo j 3, and; M = as det(m) 0, and, setting p(x) = 2 k=0 c kx 3+k. We have that p+f C 2 (S ), in which case the esult follows fom [3]. Hence, it is sufficient to veify the esult fo the powes {x k : 0 k 5}. We have that, fo k, n Z 0 ; 0 xk e 2πinx [ xk e 2πinx 2πin ] 0 + k 2πin 2πin + k 2πin 0 xk e 2πinx 0 xk e 2πinx 0 xk e 2πinx = ( k k! l= )+ (k l+)!(2πin) l 0 e 2πinx = ( k l= k! (k l+)!(2πin) l )
13 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS 3 = l=0 (pl s, ()+pl s, (0) 2 0 pl s, ) = l=0 (ps,(l+)+ps,(l) p 2 0 s,(x+l)) = l=0 (ps,(l+)+ps,(l) l+ 2 l p s, (x)) = ps,(0)+ps,() 2 + l= p s,(l) 0 p s,(x) Similaly; P s,,2 = ps,(0)+ps,() 2 + l= p s,(l) 0 p s,(x) so that; P s, = P s,, +P s,,2 lim N N n= N (xk ) (n) = k+ 2 k l= n= k! (k l+)!(2πin) l Case k =, we obtain S k = 2 k = 2, S k = π 2 ( n= n 2 ) k = 3, S k = π 2 ( n= n 2 ) k = 4, S k = π 2 ( n= n 2 ) π 4 ( n= n 4 ) k = 5, S k = π 2 ( n= n 2 ) π 4 ( n= n 4 ) Using Lemma., we have that; n= n = π[cot(πz)z](2) ! = π. 4π 6.2.2! = π2 6 n= n = π[cot(πz)z](4) ! = π. 48π ! = π4 90 S 2 = π 2 ( π2 6 ) = = 2 S 3 = π 2 π 2 6 = = 2 S 4 = π 2 π π 4 π 4 90 = 2 S 5 = π 2 π π 4 π 4 90 = 2
14 4 TRISTRAM DE PIRO = p s, (0)+p s, ()+2 l= p s,(l) 2 0 p s,(x) Lemma.20. If Re(s) 4,, we have that; n= = n s + ps,() + Rs, x s 2 2 = + Rs, + s (s ) s 2 2 If 2; n= n s = + j=0 (a s,) j+ ( B 2j+() 2j+ ) Poof. The fist claim is just a simple eaangement of the claim in Lemma.8, using Lemma.9. We have that; x s = (s ) s and ps,() = s 2 2 Moeove; n= n s = l= p s,(l) = + l=0 j=0 (a s,) j+ l 2j = + j=0 (a s,) j+ ( l=0 l2j ), by popety (ii) in Lemma.4. = + j=0 (a s,) j+ ( B 2j+() B 2j+ (0) 2j+ ) = + j=0 (a s,) j+ ( B 2j+() 2j+ ) Remaks.2. Using Lemma.9, we have that lim R s, = 0, hence, Lemma.20 educes the calculation of n= to a calculation n s
15 AN APPLICATION OF FOURIER ANALYSIS TO RIEMANN SUMS 5 involving Benoulli polynomials. Moeove, letting A s, = n=, we n s have that; A x s s, x s A x Re(s) s, x s (Re(s) ) Re(s) A s, 3( ) 3 Obseving that; s 2 3(Re(s)+) Re(s)+ (Re(s) ) if s (Re(s) ) Re(s) 3(Re(s)+), we havethatthe estimate + j=0 (a s,) j+ ( B 2j+() 2j+ )+ (s ) s + 2 s impoves upon + j=0 (a s,) j+ ( B 2j+() 2j+ ), fo sufficiently lage values of. The coefficients (a s, ) j, j +2 can be computed using simple linea algeba. The computation of absolutely convegent Riemann sums, and thei diffeences, occus in the evaluation of ζ(s), fo 0 < Re(s) <, it is well known that ζ(s) 0, fo Re(s). It is hoped that the above method might lead to some pogess in the diection of solving the famous Riemann hypothesis, that, ζ(s) = 0 iff Re(s) = 2 o s = 2w, fo w Z, see []. Refeences [] Intoduction to Analytical Numbe Theoy, Spinge, T. Apostol, (976) [2] A Simple Poof of the Invesion Theoem using Nonstandad Analysis, available at T. de Pio, (203). [3] A Simple Poof of the Unifom Convegence of Fouie Seies using Nonstandad Analysis, available at T.de Pio, (203). [4] Fouie Analysis: An Intoduction, Pinceton Lectue Seies, E. Stein, R. Shakachi, (2003). Mathematics Depatment, Haison Building, Steatham Campus, Univesity of Exete, Noth Pak Road, Exete, Devon, EX4 4QF, United Kingdom
Method for Approximating Irrational Numbers
 Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
On the Poisson Approximation to the Negative Hypergeometric Distribution
 BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://mathusmmy/bulletin Bull Malays Math Sci Soc (2) 34(2) (2011), 331 336 On the Poisson Appoximation to the Negative Hypegeometic Distibution
BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://mathusmmy/bulletin Bull Malays Math Sci Soc (2) 34(2) (2011), 331 336 On the Poisson Appoximation to the Negative Hypegeometic Distibution
Numerical approximation to ζ(2n+1)
 Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
New problems in universal algebraic geometry illustrated by boolean equations
 New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE
 ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
A generalization of the Bernstein polynomials
 A genealization of the Benstein polynomials Halil Ouç and Geoge M Phillips Mathematical Institute, Univesity of St Andews, Noth Haugh, St Andews, Fife KY16 9SS, Scotland Dedicated to Philip J Davis This
A genealization of the Benstein polynomials Halil Ouç and Geoge M Phillips Mathematical Institute, Univesity of St Andews, Noth Haugh, St Andews, Fife KY16 9SS, Scotland Dedicated to Philip J Davis This
SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017](/thumbs/88/114976486.jpg) On The Numbe Of Unlabeled Bipatite Gaphs Abdullah Atmaca and A Yavuz Ouç axiv:7050800v [mathco] 4 May 207 Abstact This pape solves a poblem that was stated by M A Haison in 973 [] This poblem, that has
On The Numbe Of Unlabeled Bipatite Gaphs Abdullah Atmaca and A Yavuz Ouç axiv:7050800v [mathco] 4 May 207 Abstact This pape solves a poblem that was stated by M A Haison in 973 [] This poblem, that has
Compactly Supported Radial Basis Functions
 Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Mar 2008](/thumbs/94/118262240.jpg) An uppe bound fo the numbe of pefect matchings in gaphs Shmuel Fiedland axiv:0803.0864v [math.co] 6 Ma 2008 Depatment of Mathematics, Statistics, and Compute Science, Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Chicago,
An uppe bound fo the numbe of pefect matchings in gaphs Shmuel Fiedland axiv:0803.0864v [math.co] 6 Ma 2008 Depatment of Mathematics, Statistics, and Compute Science, Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Chicago,
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 28 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 28 Oct 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 28 Oct 2017](/thumbs/94/119001059.jpg) ON th COEFFICIENT OF DIVISORS OF x n axiv:70049v [mathnt] 28 Oct 207 SAI TEJA SOMU Abstact Let,n be two natual numbes and let H(,n denote the maximal absolute value of th coefficient of divisos of x n
ON th COEFFICIENT OF DIVISORS OF x n axiv:70049v [mathnt] 28 Oct 207 SAI TEJA SOMU Abstact Let,n be two natual numbes and let H(,n denote the maximal absolute value of th coefficient of divisos of x n
12th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Cairo, Egypt, December 29-31,
 th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Caio, Egypt, Decembe 9-3, 7 5 Magnetostatic Field calculations associated with thick Solenoids in the Pesence of Ion using a Powe Seies expansion and the Complete
th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Caio, Egypt, Decembe 9-3, 7 5 Magnetostatic Field calculations associated with thick Solenoids in the Pesence of Ion using a Powe Seies expansion and the Complete
Construction and Analysis of Boolean Functions of 2t + 1 Variables with Maximum Algebraic Immunity
 Constuction and Analysis of Boolean Functions of 2t + 1 Vaiables with Maximum Algebaic Immunity Na Li and Wen-Feng Qi Depatment of Applied Mathematics, Zhengzhou Infomation Engineeing Univesity, Zhengzhou,
Constuction and Analysis of Boolean Functions of 2t + 1 Vaiables with Maximum Algebaic Immunity Na Li and Wen-Feng Qi Depatment of Applied Mathematics, Zhengzhou Infomation Engineeing Univesity, Zhengzhou,
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS
 6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
6 PROBABILITY GENERATING FUNCTIONS Cetain deivations pesented in this couse have been somewhat heavy on algeba. Fo example, detemining the expectation of the Binomial distibution (page 5.1 tuned out to
SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF 2 2 OPERATOR MATRICES
 italian jounal of pue and applied mathematics n. 35 015 (433 44) 433 SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF OPERATOR MATRICES Watheq Bani-Domi Depatment of Mathematics
italian jounal of pue and applied mathematics n. 35 015 (433 44) 433 SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF OPERATOR MATRICES Watheq Bani-Domi Depatment of Mathematics
ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS
 STUDIA UNIV BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume XLVIII, Numbe 4, Decembe 2003 ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS VATAN KARAKAYA AND NECIP SIMSEK Abstact The
STUDIA UNIV BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume XLVIII, Numbe 4, Decembe 2003 ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS VATAN KARAKAYA AND NECIP SIMSEK Abstact The
KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS
 Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
A Multivariate Normal Law for Turing s Formulae
 A Multivaiate Nomal Law fo Tuing s Fomulae Zhiyi Zhang Depatment of Mathematics and Statistics Univesity of Noth Caolina at Chalotte Chalotte, NC 28223 Abstact This pape establishes a sufficient condition
A Multivaiate Nomal Law fo Tuing s Fomulae Zhiyi Zhang Depatment of Mathematics and Statistics Univesity of Noth Caolina at Chalotte Chalotte, NC 28223 Abstact This pape establishes a sufficient condition
k. s k=1 Part of the significance of the Riemann zeta-function stems from Theorem 9.2. If s > 1 then 1 p s
 9 Pimes in aithmetic ogession Definition 9 The Riemann zeta-function ζs) is the function which assigns to a eal numbe s > the convegent seies k s k Pat of the significance of the Riemann zeta-function
9 Pimes in aithmetic ogession Definition 9 The Riemann zeta-function ζs) is the function which assigns to a eal numbe s > the convegent seies k s k Pat of the significance of the Riemann zeta-function
Research Article On Alzer and Qiu s Conjecture for Complete Elliptic Integral and Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent Function
 Abstact and Applied Analysis Volume 011, Aticle ID 697547, 7 pages doi:10.1155/011/697547 Reseach Aticle On Alze and Qiu s Conjectue fo Complete Elliptic Integal and Invese Hypebolic Tangent Function Yu-Ming
Abstact and Applied Analysis Volume 011, Aticle ID 697547, 7 pages doi:10.1155/011/697547 Reseach Aticle On Alze and Qiu s Conjectue fo Complete Elliptic Integal and Invese Hypebolic Tangent Function Yu-Ming
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Integral operator defined by q-analogue of Liu-Srivastava operator
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013, No. 4, 529 537 Integal opeato defined by q-analogue of Liu-Sivastava opeato Huda Aldweby and Maslina Daus Abstact. In this pape, we shall give an application of q-analogues
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013, No. 4, 529 537 Integal opeato defined by q-analogue of Liu-Sivastava opeato Huda Aldweby and Maslina Daus Abstact. In this pape, we shall give an application of q-analogues
Lecture 28: Convergence of Random Variables and Related Theorems
 EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
EE50: Pobability Foundations fo Electical Enginees July-Novembe 205 Lectue 28: Convegence of Random Vaiables and Related Theoems Lectue:. Kishna Jagannathan Scibe: Gopal, Sudhasan, Ajay, Swamy, Kolla An
Lacunary I-Convergent Sequences
 KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 52(2012), 473-482 http://dx.doi.og/10.5666/kmj.2012.52.4.473 Lacunay I-Convegent Sequences Binod Chanda Tipathy Mathematical Sciences Division, Institute of Advanced Study in Science
KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 52(2012), 473-482 http://dx.doi.og/10.5666/kmj.2012.52.4.473 Lacunay I-Convegent Sequences Binod Chanda Tipathy Mathematical Sciences Division, Institute of Advanced Study in Science
STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS HAVING THE SAME LOGARITHMIC ORDER
 UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA doi: 104467/20843828AM170027078 542017, 15 32 STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS
UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA doi: 104467/20843828AM170027078 542017, 15 32 STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS
Brief summary of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 2014 Applied Analysis
 Bief summay of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 014 Applied Analysis Stephen Becke, stephen.becke@coloado.edu Standad theoems. When necessay, I used Royden s and Keyzsig s books as a efeence. Vesion
Bief summay of functional analysis APPM 5440 Fall 014 Applied Analysis Stephen Becke, stephen.becke@coloado.edu Standad theoems. When necessay, I used Royden s and Keyzsig s books as a efeence. Vesion
On the ratio of maximum and minimum degree in maximal intersecting families
 On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Mach 6, 013 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Mach 6, 013 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
Σk=1. g r 3/2 z. 2 3-z. g 3 ( 3/2 ) g r 2. = 1 r = 0. () z = ( a ) + Σ. c n () a = ( a) 3-z -a. 3-z. z - + Σ. z 3, 5, 7, z ! = !
 09 Maclauin Seies of Completed Riemann Zeta 9. Maclauin Seies of Lemma 9.. ( Maclauin seies of gamma function ) When is the gamma function, n is the polygamma function and B n,kf, f, ae Bell polynomials,
09 Maclauin Seies of Completed Riemann Zeta 9. Maclauin Seies of Lemma 9.. ( Maclauin seies of gamma function ) When is the gamma function, n is the polygamma function and B n,kf, f, ae Bell polynomials,
Exceptional regular singular points of second-order ODEs. 1. Solving second-order ODEs
 (May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
(May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
On the ratio of maximum and minimum degree in maximal intersecting families
 On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Septembe 5, 011 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Septembe 5, 011 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On a generalization of Eulerian numbers
 Notes on Numbe Theoy and Discete Mathematics Pint ISSN 1310 513, Online ISSN 367 875 Vol, 018, No 1, 16 DOI: 10756/nntdm018116- On a genealization of Euleian numbes Claudio Pita-Ruiz Facultad de Ingenieía,
Notes on Numbe Theoy and Discete Mathematics Pint ISSN 1310 513, Online ISSN 367 875 Vol, 018, No 1, 16 DOI: 10756/nntdm018116- On a genealization of Euleian numbes Claudio Pita-Ruiz Facultad de Ingenieía,
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
A Bijective Approach to the Permutational Power of a Priority Queue
 A Bijective Appoach to the Pemutational Powe of a Pioity Queue Ia M. Gessel Kuang-Yeh Wang Depatment of Mathematics Bandeis Univesity Waltham, MA 02254-9110 Abstact A pioity queue tansfoms an input pemutation
A Bijective Appoach to the Pemutational Powe of a Pioity Queue Ia M. Gessel Kuang-Yeh Wang Depatment of Mathematics Bandeis Univesity Waltham, MA 02254-9110 Abstact A pioity queue tansfoms an input pemutation
Enumerating permutation polynomials
 Enumeating pemutation polynomials Theodoulos Gaefalakis a,1, Giogos Kapetanakis a,, a Depatment of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics, Univesity of Cete, 70013 Heaklion, Geece Abstact We conside thoblem
Enumeating pemutation polynomials Theodoulos Gaefalakis a,1, Giogos Kapetanakis a,, a Depatment of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics, Univesity of Cete, 70013 Heaklion, Geece Abstact We conside thoblem
Application of Parseval s Theorem on Evaluating Some Definite Integrals
 Tukish Jounal of Analysis and Numbe Theoy, 4, Vol., No., -5 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/tjant/// Science and Education Publishing DOI:.69/tjant--- Application of Paseval s Theoem on Evaluating
Tukish Jounal of Analysis and Numbe Theoy, 4, Vol., No., -5 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/tjant/// Science and Education Publishing DOI:.69/tjant--- Application of Paseval s Theoem on Evaluating
GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
Measure Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyharmonic Functions
 Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, 97 93 DOI: 0.007/s40-08-004-6 Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of
Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, 97 93 DOI: 0.007/s40-08-004-6 Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of
3.1 Random variables
 3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017](/thumbs/93/113642317.jpg) SEQUENCES OF CONSECUTIVE HAPPY NUMBERS IN NEGATIVE BASES HELEN G. GRUNDMAN AND PAMELA E. HARRIS axiv:1705.04648v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017 ABSTRACT. Fo b 2 and e 2, let S e,b : Z Z 0 be the function taking
SEQUENCES OF CONSECUTIVE HAPPY NUMBERS IN NEGATIVE BASES HELEN G. GRUNDMAN AND PAMELA E. HARRIS axiv:1705.04648v1 [math.nt] 12 May 2017 ABSTRACT. Fo b 2 and e 2, let S e,b : Z Z 0 be the function taking
< 1. max x B(0,1) f. ν ds(y) Use Poisson s formula for the ball to prove. (r x ) x y n ds(y) (x B0 (0, r)). 1 nα(n)r n 1
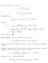 7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Aug 2009
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Aug 2009 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Aug 2009](/thumbs/92/108818336.jpg) axiv:98.4578v [math.ca] 3 Aug 9 On L-convegence of tigonometic seies Bogdan Szal Univesity of Zielona Góa, Faculty of Mathematics, Compute Science and Econometics, 65-56 Zielona Góa, ul. Szafana 4a, Poland
axiv:98.4578v [math.ca] 3 Aug 9 On L-convegence of tigonometic seies Bogdan Szal Univesity of Zielona Góa, Faculty of Mathematics, Compute Science and Econometics, 65-56 Zielona Góa, ul. Szafana 4a, Poland
arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013](/thumbs/96/127989960.jpg) A mixed method fo Diichlet poblems with adial basis functions axiv:1302.2079v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 Nobet Heue Thanh Tan Abstact We pesent a simple discetization by adial basis functions fo the Poisson
A mixed method fo Diichlet poblems with adial basis functions axiv:1302.2079v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 Nobet Heue Thanh Tan Abstact We pesent a simple discetization by adial basis functions fo the Poisson
of the contestants play as Falco, and 1 6
 JHMT 05 Algeba Test Solutions 4 Febuay 05. In a Supe Smash Bothes tounament, of the contestants play as Fox, 3 of the contestants play as Falco, and 6 of the contestants play as Peach. Given that thee
JHMT 05 Algeba Test Solutions 4 Febuay 05. In a Supe Smash Bothes tounament, of the contestants play as Fox, 3 of the contestants play as Falco, and 6 of the contestants play as Peach. Given that thee
An Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation
 An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
Journal of Number Theory
 Jounal of umbe Theoy 3 2 2259 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDiect Jounal of umbe Theoy www.elsevie.com/locate/jnt Sums of poducts of hypegeometic Benoulli numbes Ken Kamano Depatment of Geneal
Jounal of umbe Theoy 3 2 2259 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDiect Jounal of umbe Theoy www.elsevie.com/locate/jnt Sums of poducts of hypegeometic Benoulli numbes Ken Kamano Depatment of Geneal
ON SPARSELY SCHEMMEL TOTIENT NUMBERS. Colin Defant 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida
 #A8 INTEGERS 5 (205) ON SPARSEL SCHEMMEL TOTIENT NUMBERS Colin Defant Depatment of Mathematics, Univesity of Floida, Gainesville, Floida cdefant@ufl.edu Received: 7/30/4, Revised: 2/23/4, Accepted: 4/26/5,
#A8 INTEGERS 5 (205) ON SPARSEL SCHEMMEL TOTIENT NUMBERS Colin Defant Depatment of Mathematics, Univesity of Floida, Gainesville, Floida cdefant@ufl.edu Received: 7/30/4, Revised: 2/23/4, Accepted: 4/26/5,
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
Using Laplace Transform to Evaluate Improper Integrals Chii-Huei Yu
 Available at https://edupediapublicationsog/jounals Volume 3 Issue 4 Febuay 216 Using Laplace Tansfom to Evaluate Impope Integals Chii-Huei Yu Depatment of Infomation Technology, Nan Jeon Univesity of
Available at https://edupediapublicationsog/jounals Volume 3 Issue 4 Febuay 216 Using Laplace Tansfom to Evaluate Impope Integals Chii-Huei Yu Depatment of Infomation Technology, Nan Jeon Univesity of
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM
 A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
RADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR A NONPOSITONE PROBLEM IN AN ANNULUS
 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 04 (04), o. 9, pp. 0. ISS: 07-669. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS FO A OPOSITOE
Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 04 (04), o. 9, pp. 0. ISS: 07-669. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ADIAL POSITIVE SOLUTIOS FO A OPOSITOE
ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS. D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi
 Opuscula Math. 37, no. 3 (017), 447 456 http://dx.doi.og/10.7494/opmath.017.37.3.447 Opuscula Mathematica ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi Communicated
Opuscula Math. 37, no. 3 (017), 447 456 http://dx.doi.og/10.7494/opmath.017.37.3.447 Opuscula Mathematica ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi Communicated
A STABILITY RESULT FOR p-harmonic SYSTEMS WITH DISCONTINUOUS COEFFICIENTS. Bianca Stroffolini. 0. Introduction
 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Multiple Criteria Secretary Problem: A New Approach
 J. Stat. Appl. Po. 3, o., 9-38 (04 9 Jounal of Statistics Applications & Pobability An Intenational Jounal http://dx.doi.og/0.785/jsap/0303 Multiple Citeia Secetay Poblem: A ew Appoach Alaka Padhye, and
J. Stat. Appl. Po. 3, o., 9-38 (04 9 Jounal of Statistics Applications & Pobability An Intenational Jounal http://dx.doi.og/0.785/jsap/0303 Multiple Citeia Secetay Poblem: A ew Appoach Alaka Padhye, and
Supplementary information Efficient Enumeration of Monocyclic Chemical Graphs with Given Path Frequencies
 Supplementay infomation Efficient Enumeation of Monocyclic Chemical Gaphs with Given Path Fequencies Masaki Suzuki, Hioshi Nagamochi Gaduate School of Infomatics, Kyoto Univesity {m suzuki,nag}@amp.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Supplementay infomation Efficient Enumeation of Monocyclic Chemical Gaphs with Given Path Fequencies Masaki Suzuki, Hioshi Nagamochi Gaduate School of Infomatics, Kyoto Univesity {m suzuki,nag}@amp.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn Tribonacci numbers with indices in arithmetic progression and their sums. Nurettin Irmak and Murat Alp
 Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 8- Vol. (0), No, pp. 5- DOI 0.85/MMN.0.5 Tibonacci numbes with indices in aithmetic pogession and thei sums Nuettin Imak and Muat Alp Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU
Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 8- Vol. (0), No, pp. 5- DOI 0.85/MMN.0.5 Tibonacci numbes with indices in aithmetic pogession and thei sums Nuettin Imak and Muat Alp Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU
Solving Some Definite Integrals Using Parseval s Theorem
 Ameican Jounal of Numeical Analysis 4 Vol. No. 6-64 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajna///5 Science and Education Publishing DOI:.69/ajna---5 Solving Some Definite Integals Using Paseval s
Ameican Jounal of Numeical Analysis 4 Vol. No. 6-64 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajna///5 Science and Education Publishing DOI:.69/ajna---5 Solving Some Definite Integals Using Paseval s
Fixed Point Results for Multivalued Maps
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 3, 119-1136 Fixed Point Results fo Multivalued Maps Abdul Latif Depatment of Mathematics King Abdulaziz Univesity P.O. Box 8003, Jeddah 1589 Saudi Aabia
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 3, 119-1136 Fixed Point Results fo Multivalued Maps Abdul Latif Depatment of Mathematics King Abdulaziz Univesity P.O. Box 8003, Jeddah 1589 Saudi Aabia
Dynamic Visualization of Complex Integrals with Cabri II Plus
 Dynamic Visualiation of omplex Integals with abi II Plus Sae MIKI Kawai-juu, IES Japan Email: sand_pictue@hotmailcom Abstact: Dynamic visualiation helps us undestand the concepts of mathematics This pape
Dynamic Visualiation of omplex Integals with abi II Plus Sae MIKI Kawai-juu, IES Japan Email: sand_pictue@hotmailcom Abstact: Dynamic visualiation helps us undestand the concepts of mathematics This pape
Problems with Mannheim s conformal gravity program
 Poblems with Mannheim s confomal gavity pogam June 4, 18 Youngsub Yoon axiv:135.163v6 [g-qc] 7 Jul 13 Depatment of Physics and Astonomy Seoul National Univesity, Seoul 151-747, Koea Abstact We show that
Poblems with Mannheim s confomal gavity pogam June 4, 18 Youngsub Yoon axiv:135.163v6 [g-qc] 7 Jul 13 Depatment of Physics and Astonomy Seoul National Univesity, Seoul 151-747, Koea Abstact We show that
Do Managers Do Good With Other People s Money? Online Appendix
 Do Manages Do Good With Othe People s Money? Online Appendix Ing-Haw Cheng Haison Hong Kelly Shue Abstact This is the Online Appendix fo Cheng, Hong and Shue 2013) containing details of the model. Datmouth
Do Manages Do Good With Othe People s Money? Online Appendix Ing-Haw Cheng Haison Hong Kelly Shue Abstact This is the Online Appendix fo Cheng, Hong and Shue 2013) containing details of the model. Datmouth
Quasi-Randomness and the Distribution of Copies of a Fixed Graph
 Quasi-Randomness and the Distibution of Copies of a Fixed Gaph Asaf Shapia Abstact We show that if a gaph G has the popety that all subsets of vetices of size n/4 contain the coect numbe of tiangles one
Quasi-Randomness and the Distibution of Copies of a Fixed Gaph Asaf Shapia Abstact We show that if a gaph G has the popety that all subsets of vetices of size n/4 contain the coect numbe of tiangles one
arxiv: v2 [math.ag] 4 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [math.ag] 4 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [math.ag] 4 Jul 2012](/thumbs/75/72065206.jpg) SOME EXAMPLES OF VECTOR BUNDLES IN THE BASE LOCUS OF THE GENERALIZED THETA DIVISOR axiv:0707.2326v2 [math.ag] 4 Jul 2012 SEBASTIAN CASALAINA-MARTIN, TAWANDA GWENA, AND MONTSERRAT TEIXIDOR I BIGAS Abstact.
SOME EXAMPLES OF VECTOR BUNDLES IN THE BASE LOCUS OF THE GENERALIZED THETA DIVISOR axiv:0707.2326v2 [math.ag] 4 Jul 2012 SEBASTIAN CASALAINA-MARTIN, TAWANDA GWENA, AND MONTSERRAT TEIXIDOR I BIGAS Abstact.
Vanishing lines in generalized Adams spectral sequences are generic
 ISSN 364-0380 (on line) 465-3060 (pinted) 55 Geomety & Topology Volume 3 (999) 55 65 Published: 2 July 999 G G G G T T T G T T T G T G T GG TT G G G G GG T T T TT Vanishing lines in genealized Adams spectal
ISSN 364-0380 (on line) 465-3060 (pinted) 55 Geomety & Topology Volume 3 (999) 55 65 Published: 2 July 999 G G G G T T T G T T T G T G T GG TT G G G G GG T T T TT Vanishing lines in genealized Adams spectal
Convergence of Quotients of Consecutive Terms of a Generalized Secondary Fibonacci Sequence
 Intenational Mathematical Foum, Vol. 6, 2011, no. 40, 1955-1964 Convegence of Quotients of Consecutive Tems of a Genealized Seconday Fibonacci Seuence Loenzo J. Matínez Univesidad de Caldas loenzo.matinez
Intenational Mathematical Foum, Vol. 6, 2011, no. 40, 1955-1964 Convegence of Quotients of Consecutive Tems of a Genealized Seconday Fibonacci Seuence Loenzo J. Matínez Univesidad de Caldas loenzo.matinez
Goodness-of-fit for composite hypotheses.
 Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
Section 11 Goodness-of-fit fo composite hypotheses. Example. Let us conside a Matlab example. Let us geneate 50 obsevations fom N(1, 2): X=nomnd(1,2,50,1); Then, unning a chi-squaed goodness-of-fit test
The Congestion of n-cube Layout on a Rectangular Grid S.L. Bezrukov J.D. Chavez y L.H. Harper z M. Rottger U.-P. Schroeder Abstract We consider the pr
 The Congestion of n-cube Layout on a Rectangula Gid S.L. Bezukov J.D. Chavez y L.H. Hape z M. Rottge U.-P. Schoede Abstact We conside the poblem of embedding the n-dimensional cube into a ectangula gid
The Congestion of n-cube Layout on a Rectangula Gid S.L. Bezukov J.D. Chavez y L.H. Hape z M. Rottge U.-P. Schoede Abstact We conside the poblem of embedding the n-dimensional cube into a ectangula gid
Weighted least-squares estimators of parametric functions of the regression coefficients under a general linear model
 Ann Inst Stat Math (2010) 62:929 941 DOI 10.1007/s10463-008-0199-8 Weighted least-squaes estimatos of paametic functions of the egession coefficients unde a geneal linea model Yongge Tian Received: 9 Januay
Ann Inst Stat Math (2010) 62:929 941 DOI 10.1007/s10463-008-0199-8 Weighted least-squaes estimatos of paametic functions of the egession coefficients unde a geneal linea model Yongge Tian Received: 9 Januay
6 Matrix Concentration Bounds
 6 Matix Concentation Bounds Concentation bounds ae inequalities that bound pobabilities of deviations by a andom vaiable fom some value, often its mean. Infomally, they show the pobability that a andom
6 Matix Concentation Bounds Concentation bounds ae inequalities that bound pobabilities of deviations by a andom vaiable fom some value, often its mean. Infomally, they show the pobability that a andom
Asymptotically Lacunary Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convergence and an Orlicz Function
 "Science Stays Tue Hee" Jounal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, 335-35 Science Signpost Publishing Asymptotically Lacunay Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convegence and an
"Science Stays Tue Hee" Jounal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, 335-35 Science Signpost Publishing Asymptotically Lacunay Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convegence and an
SPECTRAL SEQUENCES. im(er
 SPECTRAL SEQUENCES MATTHEW GREENBERG. Intoduction Definition. Let a. An a-th stage spectal (cohomological) sequence consists of the following data: bigaded objects E = p,q Z Ep,q, a diffeentials d : E
SPECTRAL SEQUENCES MATTHEW GREENBERG. Intoduction Definition. Let a. An a-th stage spectal (cohomological) sequence consists of the following data: bigaded objects E = p,q Z Ep,q, a diffeentials d : E
Perturbation to Symmetries and Adiabatic Invariants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of Relative Motion
 Commun. Theo. Phys. Beijing, China) 43 25) pp. 577 581 c Intenational Academic Publishes Vol. 43, No. 4, Apil 15, 25 Petubation to Symmeties and Adiabatic Invaiants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of
Commun. Theo. Phys. Beijing, China) 43 25) pp. 577 581 c Intenational Academic Publishes Vol. 43, No. 4, Apil 15, 25 Petubation to Symmeties and Adiabatic Invaiants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of
BEST CONSTANTS FOR UNCENTERED MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS. Loukas Grafakos and Stephen Montgomery-Smith University of Missouri, Columbia
 BEST CONSTANTS FOR UNCENTERED MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS Loukas Gafakos and Stehen Montgomey-Smith Univesity of Missoui, Columbia Abstact. We ecisely evaluate the oeato nom of the uncenteed Hady-Littlewood maximal
BEST CONSTANTS FOR UNCENTERED MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS Loukas Gafakos and Stehen Montgomey-Smith Univesity of Missoui, Columbia Abstact. We ecisely evaluate the oeato nom of the uncenteed Hady-Littlewood maximal
NOTE. Some New Bounds for Cover-Free Families
 Jounal of Combinatoial Theoy, Seies A 90, 224234 (2000) doi:10.1006jcta.1999.3036, available online at http:.idealibay.com on NOTE Some Ne Bounds fo Cove-Fee Families D. R. Stinson 1 and R. Wei Depatment
Jounal of Combinatoial Theoy, Seies A 90, 224234 (2000) doi:10.1006jcta.1999.3036, available online at http:.idealibay.com on NOTE Some Ne Bounds fo Cove-Fee Families D. R. Stinson 1 and R. Wei Depatment
TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS
 Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics: Advances and Applications Volume 4, Numbe, 200, Pages 97-4 TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS Dépatement de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences de
Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics: Advances and Applications Volume 4, Numbe, 200, Pages 97-4 TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS Dépatement de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences de
THE NUMBER OF TWO CONSECUTIVE SUCCESSES IN A HOPPE-PÓLYA URN
 TH NUMBR OF TWO CONSCUTIV SUCCSSS IN A HOPP-PÓLYA URN LARS HOLST Depatment of Mathematics, Royal Institute of Technology S 100 44 Stocholm, Sweden -mail: lholst@math.th.se Novembe 27, 2007 Abstact In a
TH NUMBR OF TWO CONSCUTIV SUCCSSS IN A HOPP-PÓLYA URN LARS HOLST Depatment of Mathematics, Royal Institute of Technology S 100 44 Stocholm, Sweden -mail: lholst@math.th.se Novembe 27, 2007 Abstact In a
On decompositions of complete multipartite graphs into the union of two even cycles
 On decompositions of complete multipatite gaphs into the union of two even cycles A. Su, J. Buchanan, R. C. Bunge, S. I. El-Zanati, E. Pelttai, G. Rasmuson, E. Spaks, S. Tagais Depatment of Mathematics
On decompositions of complete multipatite gaphs into the union of two even cycles A. Su, J. Buchanan, R. C. Bunge, S. I. El-Zanati, E. Pelttai, G. Rasmuson, E. Spaks, S. Tagais Depatment of Mathematics
Unobserved Correlation in Ascending Auctions: Example And Extensions
 Unobseved Coelation in Ascending Auctions: Example And Extensions Daniel Quint Univesity of Wisconsin Novembe 2009 Intoduction In pivate-value ascending auctions, the winning bidde s willingness to pay
Unobseved Coelation in Ascending Auctions: Example And Extensions Daniel Quint Univesity of Wisconsin Novembe 2009 Intoduction In pivate-value ascending auctions, the winning bidde s willingness to pay
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL CHAPTER 7 A (2 ) B. a x + bx + c dx
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 613 7.6.3 CHAPTER 7 ( px + q) a x + bx + c dx. We choose constants A and B such that d px + q A ( ax + bx + c) + B dx A(ax + b) + B Compaing the coefficients of x and the constant
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 613 7.6.3 CHAPTER 7 ( px + q) a x + bx + c dx. We choose constants A and B such that d px + q A ( ax + bx + c) + B dx A(ax + b) + B Compaing the coefficients of x and the constant
Moment-free numerical approximation of highly oscillatory integrals with stationary points
 Moment-fee numeical appoximation of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points Sheehan Olve Abstact We pesent a method fo the numeical quadatue of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points.
Moment-fee numeical appoximation of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points Sheehan Olve Abstact We pesent a method fo the numeical quadatue of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points.
Results on the Commutative Neutrix Convolution Product Involving the Logarithmic Integral li(
 Intenational Jounal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Reseach (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2014, PP 736-741 ISSN 2347-307X (Pint) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) www.acjounals.og Results on the
Intenational Jounal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Reseach (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2014, PP 736-741 ISSN 2347-307X (Pint) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) www.acjounals.og Results on the
Stanford University CS259Q: Quantum Computing Handout 8 Luca Trevisan October 18, 2012
 Stanfod Univesity CS59Q: Quantum Computing Handout 8 Luca Tevisan Octobe 8, 0 Lectue 8 In which we use the quantum Fouie tansfom to solve the peiod-finding poblem. The Peiod Finding Poblem Let f : {0,...,
Stanfod Univesity CS59Q: Quantum Computing Handout 8 Luca Tevisan Octobe 8, 0 Lectue 8 In which we use the quantum Fouie tansfom to solve the peiod-finding poblem. The Peiod Finding Poblem Let f : {0,...,
Semicanonical basis generators of the cluster algebra of type A (1)
 Semicanonical basis geneatos of the cluste algeba of type A (1 1 Andei Zelevinsky Depatment of Mathematics Notheasten Univesity, Boston, USA andei@neu.edu Submitted: Jul 7, 006; Accepted: Dec 3, 006; Published:
Semicanonical basis geneatos of the cluste algeba of type A (1 1 Andei Zelevinsky Depatment of Mathematics Notheasten Univesity, Boston, USA andei@neu.edu Submitted: Jul 7, 006; Accepted: Dec 3, 006; Published:
Lecture 18: Graph Isomorphisms
 INFR11102: Computational Complexity 22/11/2018 Lectue: Heng Guo Lectue 18: Gaph Isomophisms 1 An Athu-Melin potocol fo GNI Last time we gave a simple inteactive potocol fo GNI with pivate coins. We will
INFR11102: Computational Complexity 22/11/2018 Lectue: Heng Guo Lectue 18: Gaph Isomophisms 1 An Athu-Melin potocol fo GNI Last time we gave a simple inteactive potocol fo GNI with pivate coins. We will
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 38
 Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Long-range stress re-distribution resulting from damage in heterogeneous media
 Long-ange stess e-distibution esulting fom damage in heteogeneous media Y.L.Bai (1), F.J.Ke (1,2), M.F.Xia (1,3) X.H.Zhang (1) and Z.K. Jia (1) (1) State Key Laboatoy fo Non-linea Mechanics (LNM), Institute
Long-ange stess e-distibution esulting fom damage in heteogeneous media Y.L.Bai (1), F.J.Ke (1,2), M.F.Xia (1,3) X.H.Zhang (1) and Z.K. Jia (1) (1) State Key Laboatoy fo Non-linea Mechanics (LNM), Institute
SMT 2013 Team Test Solutions February 2, 2013
 1 Let f 1 (n) be the numbe of divisos that n has, and define f k (n) = f 1 (f k 1 (n)) Compute the smallest intege k such that f k (013 013 ) = Answe: 4 Solution: We know that 013 013 = 3 013 11 013 61
1 Let f 1 (n) be the numbe of divisos that n has, and define f k (n) = f 1 (f k 1 (n)) Compute the smallest intege k such that f k (013 013 ) = Answe: 4 Solution: We know that 013 013 = 3 013 11 013 61
Chebyshev Polynomial Based Numerical Inverse Laplace Transform Solutions of Linear Volterra Integral and Integro-Differential Equations
 Ameican Reseach Jounal of Mathematics ISSN 378-74X Oiginal Aticle Volume, Issue, Feb-5 Chebyshev Polynomial Based Numeical Invese Laplace Tansfom Solutions of Linea Voltea Integal and Intego-Diffeential
Ameican Reseach Jounal of Mathematics ISSN 378-74X Oiginal Aticle Volume, Issue, Feb-5 Chebyshev Polynomial Based Numeical Invese Laplace Tansfom Solutions of Linea Voltea Integal and Intego-Diffeential
Some Remarks on the Boundary Behaviors of the Hardy Spaces
 Soe Reaks on the Bounday Behavios of the Hady Spaces Tao Qian and Jinxun Wang In eoy of Jaie Kelle Abstact. Soe estiates and bounday popeties fo functions in the Hady spaces ae given. Matheatics Subject
Soe Reaks on the Bounday Behavios of the Hady Spaces Tao Qian and Jinxun Wang In eoy of Jaie Kelle Abstact. Soe estiates and bounday popeties fo functions in the Hady spaces ae given. Matheatics Subject
QIP Course 10: Quantum Factorization Algorithm (Part 3)
 QIP Couse 10: Quantum Factoization Algoithm (Pat 3 Ryutaoh Matsumoto Nagoya Univesity, Japan Send you comments to yutaoh.matsumoto@nagoya-u.jp Septembe 2018 @ Tokyo Tech. Matsumoto (Nagoya U. QIP Couse
QIP Couse 10: Quantum Factoization Algoithm (Pat 3 Ryutaoh Matsumoto Nagoya Univesity, Japan Send you comments to yutaoh.matsumoto@nagoya-u.jp Septembe 2018 @ Tokyo Tech. Matsumoto (Nagoya U. QIP Couse
THE MAXIMUM SIZE OF A PARTIAL SPREAD II: UPPER BOUNDS
 THE MAXIMUM SIZE OF A PARTIAL SPREAD II: UPPER BOUNDS ESMERALDA NĂSTASE MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT XAVIER UNIVERSITY CINCINNATI, OHIO 4507, USA PAPA SISSOKHO MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT ILLINOIS STATE UNIVERSITY
THE MAXIMUM SIZE OF A PARTIAL SPREAD II: UPPER BOUNDS ESMERALDA NĂSTASE MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT XAVIER UNIVERSITY CINCINNATI, OHIO 4507, USA PAPA SISSOKHO MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT ILLINOIS STATE UNIVERSITY
Lecture 16 Root Systems and Root Lattices
 1.745 Intoduction to Lie Algebas Novembe 1, 010 Lectue 16 Root Systems and Root Lattices Pof. Victo Kac Scibe: Michael Cossley Recall that a oot system is a pai (V, ), whee V is a finite dimensional Euclidean
1.745 Intoduction to Lie Algebas Novembe 1, 010 Lectue 16 Root Systems and Root Lattices Pof. Victo Kac Scibe: Michael Cossley Recall that a oot system is a pai (V, ), whee V is a finite dimensional Euclidean
On the Quasi-inverse of a Non-square Matrix: An Infinite Solution
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
LET a random variable x follows the two - parameter
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS AND SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING ISSN: 2231-5330, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 2015 19 Shinkage Bayesian Appoach in Item - Failue Gamma Data In Pesence of Pio Point Guess Value Gyan Pakash
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS AND SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING ISSN: 2231-5330, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 2015 19 Shinkage Bayesian Appoach in Item - Failue Gamma Data In Pesence of Pio Point Guess Value Gyan Pakash
Mean Curvature and Shape Operator of Slant Immersions in a Sasakian Space Form
 Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
A proof of the binomial theorem
 A poof of the binomial theoem If n is a natual numbe, let n! denote the poduct of the numbes,2,3,,n. So! =, 2! = 2 = 2, 3! = 2 3 = 6, 4! = 2 3 4 = 24 and so on. We also let 0! =. If n is a non-negative
A poof of the binomial theoem If n is a natual numbe, let n! denote the poduct of the numbes,2,3,,n. So! =, 2! = 2 = 2, 3! = 2 3 = 6, 4! = 2 3 4 = 24 and so on. We also let 0! =. If n is a non-negative
TESTING THE VALIDITY OF THE EXPONENTIAL MODEL BASED ON TYPE II CENSORED DATA USING TRANSFORMED SAMPLE DATA
 STATISTICA, anno LXXVI, n. 3, 2016 TESTING THE VALIDITY OF THE EXPONENTIAL MODEL BASED ON TYPE II CENSORED DATA USING TRANSFORMED SAMPLE DATA Hadi Alizadeh Noughabi 1 Depatment of Statistics, Univesity
STATISTICA, anno LXXVI, n. 3, 2016 TESTING THE VALIDITY OF THE EXPONENTIAL MODEL BASED ON TYPE II CENSORED DATA USING TRANSFORMED SAMPLE DATA Hadi Alizadeh Noughabi 1 Depatment of Statistics, Univesity
A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol3 15 2007, 41 45 A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LI JULING AND GAO HONGYA Abstact We pove a new a pioi estimate fo vey weak
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol3 15 2007, 41 45 A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LI JULING AND GAO HONGYA Abstact We pove a new a pioi estimate fo vey weak
Random Variables and Probability Distribution Random Variable
 Random Vaiables and Pobability Distibution Random Vaiable Random vaiable: If S is the sample space P(S) is the powe set of the sample space, P is the pobability of the function then (S, P(S), P) is called
Random Vaiables and Pobability Distibution Random Vaiable Random vaiable: If S is the sample space P(S) is the powe set of the sample space, P is the pobability of the function then (S, P(S), P) is called
Surveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces
 Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Tools fo decision help since 995 Suveillance Points in High Dimensional Spaces by Benad Beauzamy Januay 06 Abstact Let us conside any compute softwae, elying upon a lage
