Enough Entropy? Justify It!
|
|
|
- Veronica Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enough Entropy? Justify It! Yi Mao, Ph.D., CISSP CST Lab Manager atsec information security corp.
2 Agenda Before IG 7.14 and IG 7.15 IG 7.14 Entropy Caveats IG 7.15 Entropy Assessment CPU Time Jitter as an Entropy Source Ring Oscillator as an Entropy Source After IG 7.14 and IG
3 Let It Go (RNG Edition) Before IG 7.14 and IG 7.15 Testing entropy is a chore Weak keys are out the door 3
4 FIPS DTR AS Guessing the seed value of an RNG (e.g. DRBG A) is at least as hard as guessing the generated key. The burden of proof is on the vendor. Vendor s wishes: We show you our design and data. You do the proof for us. 4
5 The Emotions of a CST Lab 5
6 Some Definitions of Key Strength NIST required minimum key strength: 112 bits Apparent key strength is determined by the key length according to the Table and formula in IG 7.5. Triple_DES: 112 bits of security AES 256: 256 bits of security RSA 3072: 128 bits of security RSA 4096: approximately 152 bits of security The real key strength is determined by the entropy in the RNG seed from which the key is generated. 6
7 How Much Entropy is Enough? At least 112 bits of entropy to seed the RNG that generates keys, and The amount of entropy in the RNG seed must be equal to or greater than all of the apparent strengths of the generated keys. 7
8 IG 7.14 Intended to answer the following questions: When is an entropy assessment necessary? How to handle cases when the entropy is insufficient? Entropy doesn t meet the minimum 112-bit strength, or Is not sufficient to account for an apparent strength of the generated keys 8
9 When must a lab perform the entropy assessment? The entropy source is within the module boundary Physical boundary for a hardware module Logical boundary for a software module Logical boundary for a sub-chip module (IG 1.20) The entropy source is outside the module boundary Assess the entropy strength whenever possible. 9
10 Outcomes of in-boundary Entropy Assessment Does not meet the minimum 112-bit strength STOP: The module CANNOT be validated. Is not sufficient to account for an apparent strength of the generated keys GO: The module CAN be validated. Caveat: The module generates cryptographic keys whose strengths are modified by available entropy. Sufficient entropy: No entropy caveat on the certificate 10
11 Outcomes of out-boundary Entropy Assessment (1) Vendor/tester knows the entropy does not meet the minimum 112-bit strength. STOP: The module CANNOT be validated. Vendor/tester doesn t know the minimum strength. GO: The module CAN be validated. Caveat: There is no assurance of the minimum strength of generated keys. In addition, knows that the entropy is NOT sufficient to account for an apparent strength of the generated keys Caveat: The module generates cryptographic keys whose strengths are modified by available entropy. 11
12 Outcomes of out-boundary Entropy Assessment (2) Vendor/tester knows there are at least 112 bits minimum strength, but also knows the entropy is NOT sufficient to account for an apparent strength of the generated keys or doesn t know if it s sufficient. GO: The module CAN be validated. Caveat: The module generates cryptographic keys whose strengths are modified by available entropy. Vendor/tester knows there are at least 112 bits minimum strength and also knows there is sufficient entropy: No entropy caveat on certificate 12
13 Summary of Caveats Is entropy source in or out of boundary? Is minimum strength at least 112 bits? Is sufficient to account for the apparent strength? Can be FIPS validated? If yes, what caveats are applicable? In, Out No No or Don t know No In, Out No Yes Not logically possible Out Don t know Don t know Yes. No Assurance caveat Out Don t know No Yes. No assurance and Modified Strength caveats Out Don t know Yes Not logically possible In, Out Yes No or Don t know Yes. Modified Strength caveat In, Out Yes Yes Yes. No Caveat 13
14 No assurance of minimum strength Caveat for Porting Caveat in the module s Security Policy: If porting to an untested platform is allowed when running a module on such an untested platform, the No assurance of the minimum strength of generated keys is applicable. 14
15 When I Know I Don t Know The entropy source is outside the module boundary. The entropy input is passively loaded into the module. The module does NOT have control over the entropy input. Warning sign to Federal Users: No assurance of the minimum strength caveat Not all FIPS certificates are equal. 15
16 Try to Know as Much as Possible Vendor: May I pretend I don t know the Entropy source? Within the module boundary: No No knowledge of the entropy source, no FIPS certificate. Outside the module boundary: Yes, if you wish. But caveats! Better off: Have some control over the entropy source: actively getting, sanity checking, safeguards 16
17 To Know is to Verify Vendor: in the Security Policy: State the minimum number of bits of entropy. State the entropy estimate of the RNG seed. Lab: in a separate PDF report: Confirm the entropy estimate by: Reviewing the design of entropy source Running statistical testing on the raw entropy data 17
18 7.15 Entropy Assessment Design Analysis First: Not the comparison between the length of the seed and the length of a generated key, But the comparison of the numbers of operations required to guess the seed and the generated key (i.e. the amount of entropy) Statistical Test Second: NIST STS (SP ) NIST Python Script (SP B) ENT /documentation_software.html
19 How to Report Entropy Estimation The lab shall provide a PDF addendum including: A detailed logical diagram illustrating all entropy sources, The tester s arguments in support of the accuracy of vendor-provided rationale, Results of statistical testing (optional but strongly recommended), Specification of definition of entropy used (e.g. minentropy, Shannon entropy). 19
20 NDRNG Approved for Use in Classified Applications The amount of entropy is assumed to be the length of the provided entropy string. No entropy estimation is required. The vendor may choose to claim a smaller amount of entropy. 20
21 CPU Time-Jitter Based Entropy Sampling frequency (e.g. once per second) Clock precision (e.g. nanosecond) How many bits are obtained from one clock reading (e.g. the least significant bit, the rightmost four bits) Note: The sampling frequency shall be much slower than the clock frequency to ensure the independency of time readings. 21
22 Ring Oscillator Based Entropy Number of ring oscillators Positions of ring oscillators: no harmony over time The frequencies of ring oscillators: relative prime Sampling frequency of the ring oscillators Note: The sampling frequency shall be much slower than the ring oscillators frequencies to allow the ring oscillators going through their full cycles. 22
23 Let the Tests Go On After IG 7.14 and IG 7.15 An entropy test is a must The easy tester is gone Visit atsec media webpage to see the video clips: 23
24 Thank you for your attention! 24
The Entropy Bogeyman. Ed Morris and Khai Van November 5, 2015 International Crypto Module Conference
 The Entropy Bogeyman Ed Morris and Khai Van November 5, 2015 International Crypto Module Conference Topics Overview Background Design Problems Public Entropy Vulnerabilities Recommendations International
The Entropy Bogeyman Ed Morris and Khai Van November 5, 2015 International Crypto Module Conference Topics Overview Background Design Problems Public Entropy Vulnerabilities Recommendations International
Entropy. Finding Random Bits for OpenSSL. Denis Gauthier and Dr Paul Dale Network Security & Encryption May 19 th 2016
 Entropy Finding Random Bits for OpenSSL Denis Gauthier and Dr Paul Dale Network Security & Encryption May 19 th 2016 Program Agenda 1 2 3 4 OpenSSL s Entropy Finding Good Quality Entropy Designing an Entropy
Entropy Finding Random Bits for OpenSSL Denis Gauthier and Dr Paul Dale Network Security & Encryption May 19 th 2016 Program Agenda 1 2 3 4 OpenSSL s Entropy Finding Good Quality Entropy Designing an Entropy
/dev/random and SP800-90B
 /dev/random and SP800-90B Stephan Müller atsec information security 2015 atsec public atsec information security 2015 Agenda Linux RNG applied to concepts of SP800-90B chapter
/dev/random and SP800-90B Stephan Müller atsec information security 2015 atsec public atsec information security 2015 Agenda Linux RNG applied to concepts of SP800-90B chapter
Random Number Generation Is Getting Harder It s Time to Pay Attention
 SESSION ID: PDAC-F03 Random Number Generation Is Getting Harder It s Time to Pay Attention Richard Moulds General Manager Whitewood Richard Hughes Laboratory Fellow (Retired) Los Alamos National Laboratory
SESSION ID: PDAC-F03 Random Number Generation Is Getting Harder It s Time to Pay Attention Richard Moulds General Manager Whitewood Richard Hughes Laboratory Fellow (Retired) Los Alamos National Laboratory
Cryptanalysis of the Dual Elliptic Curve Pseudorandom Generator
 Cryptanalysis of the Dual Elliptic Curve Pseudorandom Generator Berry Schoenmakers and Andrey Sidorenko Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science, TU Eindhoven, P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
Cryptanalysis of the Dual Elliptic Curve Pseudorandom Generator Berry Schoenmakers and Andrey Sidorenko Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science, TU Eindhoven, P.O. Box 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
Random Bit Generation
 .. Random Bit Generation Theory and Practice Joshua E. Hill Department of Mathematics, University of California, Irvine Math 235B January 11, 2013 http://bit.ly/xwdbtv v. 1 / 47 Talk Outline 1 Introduction
.. Random Bit Generation Theory and Practice Joshua E. Hill Department of Mathematics, University of California, Irvine Math 235B January 11, 2013 http://bit.ly/xwdbtv v. 1 / 47 Talk Outline 1 Introduction
Entropy Estimation Methods for SW Environments in KCMVP. NSR: Seogchung Seo, Sangwoon Jang Kookmin University: Yewon Kim, Yongjin Yeom
 Entropy Estimation Methods for SW Environments in KCMVP NSR: Seogchung Seo, Sangwoon Jang Kookmin University: Yewon Kim, Yongjin Yeom Contents Brief Introduction to KCMVP Entropy Estimation Methods for
Entropy Estimation Methods for SW Environments in KCMVP NSR: Seogchung Seo, Sangwoon Jang Kookmin University: Yewon Kim, Yongjin Yeom Contents Brief Introduction to KCMVP Entropy Estimation Methods for
Entropy Estimation by Example
 Entropy Estimation by Example By David Cornwell, PhD Location: ICMC 2015 Date: November 2015 This document is for public distribution. 1 Table Of Contents 1. Introduction to Entropy 2. Unbiasing 3. Conditioning
Entropy Estimation by Example By David Cornwell, PhD Location: ICMC 2015 Date: November 2015 This document is for public distribution. 1 Table Of Contents 1. Introduction to Entropy 2. Unbiasing 3. Conditioning
Entropy Evaluation for Oscillator-based True Random Number Generators
 Entropy Evaluation for Oscillator-based True Random Number Generators Yuan Ma DCS Center Institute of Information Engineering Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline RNG Modeling method Experiment Entropy
Entropy Evaluation for Oscillator-based True Random Number Generators Yuan Ma DCS Center Institute of Information Engineering Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline RNG Modeling method Experiment Entropy
Elliptic Curve DRNGs. Çetin Kaya Koç Winter / 19
 Elliptic Curve DRNGs Çetin Kaya Koç koc@cs.ucsb.edu Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.org Winter 2017 1 / 19 Elliptic Curve DRNGs There are three existing proposals Linear Congruential Generator Power Generator
Elliptic Curve DRNGs Çetin Kaya Koç koc@cs.ucsb.edu Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.org Winter 2017 1 / 19 Elliptic Curve DRNGs There are three existing proposals Linear Congruential Generator Power Generator
Information Security
 SE 4472 / ECE 9064 Information Security Week 12: Random Number Generators and Picking Appropriate Key Lengths Fall 2015 Prof. Aleksander Essex Random Number Generation Where do keys come from? So far we
SE 4472 / ECE 9064 Information Security Week 12: Random Number Generators and Picking Appropriate Key Lengths Fall 2015 Prof. Aleksander Essex Random Number Generation Where do keys come from? So far we
FPGA based entropy source for cryptographic use
 AISFIPSKRAV 2013/8/12 19:15 page 1 #1 FPGA based entropy source for cryptographic use Emma Hilmersson Business Security Lund Advisor: Kennet Bckman at Business Security and Thomas Johansson at Electrical
AISFIPSKRAV 2013/8/12 19:15 page 1 #1 FPGA based entropy source for cryptographic use Emma Hilmersson Business Security Lund Advisor: Kennet Bckman at Business Security and Thomas Johansson at Electrical
Elliptic Curve DRNGs. Çetin Kaya Koç Winter / 21
 Elliptic Curve DRNGs http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Winter 2017 1 / 21 Elliptic Curve DRNGs Linear Congruential Generator Power Generator Naor-Reingold Generator Dual EC RNG http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya
Elliptic Curve DRNGs http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Winter 2017 1 / 21 Elliptic Curve DRNGs Linear Congruential Generator Power Generator Naor-Reingold Generator Dual EC RNG http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya
Design of Secure TRNGs for Cryptography Past, Present, and Future
 Design of Secure TRNGs for Cryptography Past, Present, and Future Viktor FISCHER Univ Lyon, UJM-Saint-Etienne, CNRS Laboratoire Hubert Curien UMR 5516 F-42023, SAINT-ETIENNE, France fischer@univ-st-etienne.fr
Design of Secure TRNGs for Cryptography Past, Present, and Future Viktor FISCHER Univ Lyon, UJM-Saint-Etienne, CNRS Laboratoire Hubert Curien UMR 5516 F-42023, SAINT-ETIENNE, France fischer@univ-st-etienne.fr
Network Security (NetSec)
 Chair of Network Architectures and Services Department of Informatics Technical University of Munich Network Security (NetSec) IN2101 WS 16/17 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Cornelius Diekmann Version: October
Chair of Network Architectures and Services Department of Informatics Technical University of Munich Network Security (NetSec) IN2101 WS 16/17 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Cornelius Diekmann Version: October
Generation of True Random Numbers using quasi-monte Carlo methods
 Generation of True Random Numbers using quasi-monte Carlo methods Ana I Gomez, Domingo Gómez-Pérez, Florian Pausinger Universidad de Cantabria, Queen s University Belfast MCQMC 2018 Ana I Gomez, Domingo
Generation of True Random Numbers using quasi-monte Carlo methods Ana I Gomez, Domingo Gómez-Pérez, Florian Pausinger Universidad de Cantabria, Queen s University Belfast MCQMC 2018 Ana I Gomez, Domingo
A study of entropy transfers
 A study of entropy transfers in the Linux Random Number Generator Th. Vuillemin, F. Goichon, G. Salagnac, C. Lauradoux The need for random numbers Computers are built to be fully deterministic......but
A study of entropy transfers in the Linux Random Number Generator Th. Vuillemin, F. Goichon, G. Salagnac, C. Lauradoux The need for random numbers Computers are built to be fully deterministic......but
Network Security. Random Numbers. Cornelius Diekmann. Version: November 21, 2015
 Network Security Random Numbers Cornelius Diekmann Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik Version: November 21, 2015 IN2101, WS 15/16, Network Security 1 Fakulta t fu r
Network Security Random Numbers Cornelius Diekmann Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik Version: November 21, 2015 IN2101, WS 15/16, Network Security 1 Fakulta t fu r
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 19 November 8, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 19 1/37 Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs (ZKIP) ZKIP for graph isomorphism Feige-Fiat-Shamir
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 19 November 8, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 19 1/37 Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs (ZKIP) ZKIP for graph isomorphism Feige-Fiat-Shamir
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 18 November 3, 2014 CPSC 467, Lecture 18 1/43 Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs (ZKIP) Secret cave protocol ZKIP for graph isomorphism
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 18 November 3, 2014 CPSC 467, Lecture 18 1/43 Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs (ZKIP) Secret cave protocol ZKIP for graph isomorphism
The Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic RBG
 / The Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic RBG Background, Specification, Security and Notes Joshua E Hill Department of Mathematics, University of California, Irvine Math C Mathematical Cryptography June,
/ The Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic RBG Background, Specification, Security and Notes Joshua E Hill Department of Mathematics, University of California, Irvine Math C Mathematical Cryptography June,
BLOCK CIPHERS KEY-RECOVERY SECURITY
 BLOCK CIPHERS and KEY-RECOVERY SECURITY Mihir Bellare UCSD 1 Notation Mihir Bellare UCSD 2 Notation {0, 1} n is the set of n-bit strings and {0, 1} is the set of all strings of finite length. By ε we denote
BLOCK CIPHERS and KEY-RECOVERY SECURITY Mihir Bellare UCSD 1 Notation Mihir Bellare UCSD 2 Notation {0, 1} n is the set of n-bit strings and {0, 1} is the set of all strings of finite length. By ε we denote
1 Cryptographic hash functions
 CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 23 February 2011 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 23 February 2011 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
DVClub Europe Formal fault analysis for ISO fault metrics on real world designs. Jörg Große Product Manager Functional Safety November 2016
 DVClub Europe Formal fault analysis for ISO 26262 fault metrics on real world designs Jörg Große Product Manager Functional Safety November 2016 Page 1 11/27/2016 Introduction Functional Safety The objective
DVClub Europe Formal fault analysis for ISO 26262 fault metrics on real world designs Jörg Große Product Manager Functional Safety November 2016 Page 1 11/27/2016 Introduction Functional Safety The objective
Introduction to Side Channel Analysis. Elisabeth Oswald University of Bristol
 Introduction to Side Channel Analysis Elisabeth Oswald University of Bristol Outline Part 1: SCA overview & leakage Part 2: SCA attacks & exploiting leakage and very briefly Part 3: Countermeasures Part
Introduction to Side Channel Analysis Elisabeth Oswald University of Bristol Outline Part 1: SCA overview & leakage Part 2: SCA attacks & exploiting leakage and very briefly Part 3: Countermeasures Part
Message Authentication Codes (MACs)
 Message Authentication Codes (MACs) Tung Chou Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands October 8, 2015 1 / 22 About Me 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) Ph.D.
Message Authentication Codes (MACs) Tung Chou Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands October 8, 2015 1 / 22 About Me 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) 2 / 22 About Me Tung Chou (Tony) Ph.D.
Survey of Hardware Random Number Generators (RNGs) Dr. Robert W. Baldwin Plus Five Consulting, Inc.
 Survey of Hardware Random Number Generators (RNGs) Dr. Robert W. Baldwin Plus Five Consulting, Inc. Outline True vs. Pseudo Randomness Radiation Noise RNG Removing Bit-Bias Thermal Resistive Noise RNG
Survey of Hardware Random Number Generators (RNGs) Dr. Robert W. Baldwin Plus Five Consulting, Inc. Outline True vs. Pseudo Randomness Radiation Noise RNG Removing Bit-Bias Thermal Resistive Noise RNG
Tutorial: Device-independent random number generation. Roger Colbeck University of York
 Tutorial: Device-independent random number generation Roger Colbeck University of York Outline Brief motivation of random number generation Discuss what we mean by a random number Discuss some ways of
Tutorial: Device-independent random number generation Roger Colbeck University of York Outline Brief motivation of random number generation Discuss what we mean by a random number Discuss some ways of
What is the Q in QRNG?
 What is the Q in QRNG? IN ORDER TO GUARANTEE ABSOLUTELY RANDOM NUMBERS, RNGS (RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS) MUST NOT BE VULNERABLE TO PREDICTION OR BIAS, AND THUS DICTATED BY TRUE RANDOMNESS. BUT HOW CAN WE
What is the Q in QRNG? IN ORDER TO GUARANTEE ABSOLUTELY RANDOM NUMBERS, RNGS (RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS) MUST NOT BE VULNERABLE TO PREDICTION OR BIAS, AND THUS DICTATED BY TRUE RANDOMNESS. BUT HOW CAN WE
True Random Number Generation on FPGA
 TRNG Design TRNG Classes Conclusions True Random Number Generation on FPGA Viktor FISCHER and Milos DRUTAROVSKY fischer@univ-st-etienne.fr; milos.drutarovsky@tuke.sk Training School on Trustworthy Manufacturing
TRNG Design TRNG Classes Conclusions True Random Number Generation on FPGA Viktor FISCHER and Milos DRUTAROVSKY fischer@univ-st-etienne.fr; milos.drutarovsky@tuke.sk Training School on Trustworthy Manufacturing
Logic gates. Quantum logic gates. α β 0 1 X = 1 0. Quantum NOT gate (X gate) Classical NOT gate NOT A. Matrix form representation
 Quantum logic gates Logic gates Classical NOT gate Quantum NOT gate (X gate) A NOT A α 0 + β 1 X α 1 + β 0 A N O T A 0 1 1 0 Matrix form representation 0 1 X = 1 0 The only non-trivial single bit gate
Quantum logic gates Logic gates Classical NOT gate Quantum NOT gate (X gate) A NOT A α 0 + β 1 X α 1 + β 0 A N O T A 0 1 1 0 Matrix form representation 0 1 X = 1 0 The only non-trivial single bit gate
Equalities and Uninterpreted Functions. Chapter 3. Decision Procedures. An Algorithmic Point of View. Revision 1.0
 Equalities and Uninterpreted Functions Chapter 3 Decision Procedures An Algorithmic Point of View D.Kroening O.Strichman Revision 1.0 Outline Decision Procedures Equalities and Uninterpreted Functions
Equalities and Uninterpreted Functions Chapter 3 Decision Procedures An Algorithmic Point of View D.Kroening O.Strichman Revision 1.0 Outline Decision Procedures Equalities and Uninterpreted Functions
LED Lighting Facts: Manufacturer Guide
 LED Lighting Facts: Manufacturer Guide 2018 1 P a g e L E D L i g h t i n g F a c t s : M a n u f a c t u r e r G u i d e TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1) Accessing your account and managing your products...
LED Lighting Facts: Manufacturer Guide 2018 1 P a g e L E D L i g h t i n g F a c t s : M a n u f a c t u r e r G u i d e TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1) Accessing your account and managing your products...
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Institute of Informatics TU München Prof. Carle. Network Security. Chapter 2 Basics
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Institute of Informatics TU München Prof. Carle Network Security Chapter 2 Basics 2.4 Random Number Generation for Cryptographic Protocols Motivation It is
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Institute of Informatics TU München Prof. Carle Network Security Chapter 2 Basics 2.4 Random Number Generation for Cryptographic Protocols Motivation It is
Random number generators
 s generators Comp Sci 1570 Introduction to Outline s 1 2 s generator s The of a sequence of s or symbols that cannot be reasonably predicted better than by a random chance, usually through a random- generator
s generators Comp Sci 1570 Introduction to Outline s 1 2 s generator s The of a sequence of s or symbols that cannot be reasonably predicted better than by a random chance, usually through a random- generator
NP-Completeness I. Lecture Overview Introduction: Reduction and Expressiveness
 Lecture 19 NP-Completeness I 19.1 Overview In the past few lectures we have looked at increasingly more expressive problems that we were able to solve using efficient algorithms. In this lecture we introduce
Lecture 19 NP-Completeness I 19.1 Overview In the past few lectures we have looked at increasingly more expressive problems that we were able to solve using efficient algorithms. In this lecture we introduce
1 Cryptographic hash functions
 CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 24 October 2012 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 24 October 2012 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS
 CST.2014.2.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IA Tuesday 3 June 2014 1.30 to 4.30 pm COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 2 Answer one question from each of Sections A, B and C, and two questions from Section D. Submit
CST.2014.2.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IA Tuesday 3 June 2014 1.30 to 4.30 pm COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 2 Answer one question from each of Sections A, B and C, and two questions from Section D. Submit
Topics in Computer Mathematics
 Random Number Generation (Uniform random numbers) Introduction We frequently need some way to generate numbers that are random (by some criteria), especially in computer science. Simulations of natural
Random Number Generation (Uniform random numbers) Introduction We frequently need some way to generate numbers that are random (by some criteria), especially in computer science. Simulations of natural
Secret Sharing CPT, Version 3
 Secret Sharing CPT, 2006 Version 3 1 Introduction In all secure systems that use cryptography in practice, keys have to be protected by encryption under other keys when they are stored in a physically
Secret Sharing CPT, 2006 Version 3 1 Introduction In all secure systems that use cryptography in practice, keys have to be protected by encryption under other keys when they are stored in a physically
Cosc 412: Cryptography and complexity Lecture 7 (22/8/2018) Knapsacks and attacks
 1 Cosc 412: Cryptography and complexity Lecture 7 (22/8/2018) Knapsacks and attacks Michael Albert michael.albert@cs.otago.ac.nz 2 This week Arithmetic Knapsack cryptosystems Attacks on knapsacks Some
1 Cosc 412: Cryptography and complexity Lecture 7 (22/8/2018) Knapsacks and attacks Michael Albert michael.albert@cs.otago.ac.nz 2 This week Arithmetic Knapsack cryptosystems Attacks on knapsacks Some
Pseudorandom Generators
 Principles of Construction and Usage of Pseudorandom Generators Alexander Vakhitov June 13, 2005 Abstract In this report we try to talk about the main concepts and tools needed in pseudorandom generators
Principles of Construction and Usage of Pseudorandom Generators Alexander Vakhitov June 13, 2005 Abstract In this report we try to talk about the main concepts and tools needed in pseudorandom generators
8 Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 8 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 8.1 Elliptic Curves over a Finite Field For the purposes of cryptography, we want to consider an elliptic curve defined over a finite field F p = Z/pZ for p a prime. Given
8 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 8.1 Elliptic Curves over a Finite Field For the purposes of cryptography, we want to consider an elliptic curve defined over a finite field F p = Z/pZ for p a prime. Given
YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE CPSC 467a: Cryptography and Computer Security Notes 23 (rev. 1) Professor M. J. Fischer November 29, 2005 1 Oblivious Transfer Lecture Notes 23 In the locked
YALE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE CPSC 467a: Cryptography and Computer Security Notes 23 (rev. 1) Professor M. J. Fischer November 29, 2005 1 Oblivious Transfer Lecture Notes 23 In the locked
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 16 March 19, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 16 1/58 Authentication While Preventing Impersonation Challenge-response authentication protocols
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 16 March 19, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 16 1/58 Authentication While Preventing Impersonation Challenge-response authentication protocols
Cryptanalysis on An ElGamal-Like Cryptosystem for Encrypting Large Messages
 Cryptanalysis on An ElGamal-Like Cryptosystem for Encrypting Large Messages MEI-NA WANG Institute for Information Industry Networks and Multimedia Institute TAIWAN, R.O.C. myrawang@iii.org.tw SUNG-MING
Cryptanalysis on An ElGamal-Like Cryptosystem for Encrypting Large Messages MEI-NA WANG Institute for Information Industry Networks and Multimedia Institute TAIWAN, R.O.C. myrawang@iii.org.tw SUNG-MING
Pseudo-Random Generators
 Pseudo-Random Generators Why do we need random numbers? Simulation Sampling Numerical analysis Computer programming (e.g. randomized algorithm) Elementary and critical element in many cryptographic protocols
Pseudo-Random Generators Why do we need random numbers? Simulation Sampling Numerical analysis Computer programming (e.g. randomized algorithm) Elementary and critical element in many cryptographic protocols
How to Evaluate Side-Channel Leakages
 How to Evaluate Side-Channel Leakages 7. June 2017 Ruhr-Universität Bochum Acknowledgment Tobias Schneider 2 Motivation Security Evaluation Attack based Testing Information theoretic Testing Testing based
How to Evaluate Side-Channel Leakages 7. June 2017 Ruhr-Universität Bochum Acknowledgment Tobias Schneider 2 Motivation Security Evaluation Attack based Testing Information theoretic Testing Testing based
Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography Real World Issues
 Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography Real World Issues Michael Naehrig Cryptography Research Group Microsoft Research UW Number Theory Seminar Seattle, 28 April 2015 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 1985:
Selecting Elliptic Curves for Cryptography Real World Issues Michael Naehrig Cryptography Research Group Microsoft Research UW Number Theory Seminar Seattle, 28 April 2015 Elliptic Curve Cryptography 1985:
Pseudo-Random Generators
 Pseudo-Random Generators Topics Why do we need random numbers? Truly random and Pseudo-random numbers. Definition of pseudo-random-generator What do we expect from pseudorandomness? Testing for pseudo-randomness.
Pseudo-Random Generators Topics Why do we need random numbers? Truly random and Pseudo-random numbers. Definition of pseudo-random-generator What do we expect from pseudorandomness? Testing for pseudo-randomness.
Pseudo-random Number Generation. Qiuliang Tang
 Pseudo-random Number Generation Qiuliang Tang Random Numbers in Cryptography The keystream in the one-time pad The secret key in the DES encryption The prime numbers p, q in the RSA encryption The private
Pseudo-random Number Generation Qiuliang Tang Random Numbers in Cryptography The keystream in the one-time pad The secret key in the DES encryption The prime numbers p, q in the RSA encryption The private
True & Deterministic Random Number Generators
 True & Deterministic Random Number Generators Çetin Kaya Koç http://cs.ucsb.edu/~koc koc@cs.ucsb.edu 1.0 0.5 1.0 0.5 0.5 1.0 0.5 1.0 Koç (http://cs.ucsb.edu/~koc) HRL RNG April 11, 2013 1 / 47 Random Numbers
True & Deterministic Random Number Generators Çetin Kaya Koç http://cs.ucsb.edu/~koc koc@cs.ucsb.edu 1.0 0.5 1.0 0.5 0.5 1.0 0.5 1.0 Koç (http://cs.ucsb.edu/~koc) HRL RNG April 11, 2013 1 / 47 Random Numbers
Cryptographic Hash Function. Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Trondheim, Norway
 Cryptographic Hash Function BLUE MIDNIGHT WISH Norwegian University of Science and Technology Trondheim, Norway Danilo Gligoroski Vlastimil Klima Svein Johan Knapskog Mohamed El-Hadedy Jørn Amundsen Stig
Cryptographic Hash Function BLUE MIDNIGHT WISH Norwegian University of Science and Technology Trondheim, Norway Danilo Gligoroski Vlastimil Klima Svein Johan Knapskog Mohamed El-Hadedy Jørn Amundsen Stig
Modern elliptic curve cryptography
 Modern elliptic curve cryptography Ivo Kubjas 1 Introduction Elliptic curve cryptography has raised attention as it allows for having shorter keys and ciphertexts. For example, to obtain similar security
Modern elliptic curve cryptography Ivo Kubjas 1 Introduction Elliptic curve cryptography has raised attention as it allows for having shorter keys and ciphertexts. For example, to obtain similar security
Chapter 2. Reductions and NP. 2.1 Reductions Continued The Satisfiability Problem (SAT) SAT 3SAT. CS 573: Algorithms, Fall 2013 August 29, 2013
 Chapter 2 Reductions and NP CS 573: Algorithms, Fall 2013 August 29, 2013 2.1 Reductions Continued 2.1.1 The Satisfiability Problem SAT 2.1.1.1 Propositional Formulas Definition 2.1.1. Consider a set of
Chapter 2 Reductions and NP CS 573: Algorithms, Fall 2013 August 29, 2013 2.1 Reductions Continued 2.1.1 The Satisfiability Problem SAT 2.1.1.1 Propositional Formulas Definition 2.1.1. Consider a set of
You separate binary numbers into columns in a similar fashion. 2 5 = 32
 RSA Encryption 2 At the end of Part I of this article, we stated that RSA encryption works because it s impractical to factor n, which determines P 1 and P 2, which determines our private key, d, which
RSA Encryption 2 At the end of Part I of this article, we stated that RSA encryption works because it s impractical to factor n, which determines P 1 and P 2, which determines our private key, d, which
Topics. Pseudo-Random Generators. Pseudo-Random Numbers. Truly Random Numbers
 Topics Pseudo-Random Generators Why do we need random numbers? Truly random and Pseudo-random numbers. Definition of pseudo-random-generator What do we expect from pseudorandomness? Testing for pseudo-randomness.
Topics Pseudo-Random Generators Why do we need random numbers? Truly random and Pseudo-random numbers. Definition of pseudo-random-generator What do we expect from pseudorandomness? Testing for pseudo-randomness.
The BB84 cryptologic protocol
 The cryptologic protocol of quantum key distribution Dimitri Petritis Institut de recherche mathématique de Rennes Université de Rennes 1 et CNRS (UMR 6625) Vernam s ciphering Principles of coding and
The cryptologic protocol of quantum key distribution Dimitri Petritis Institut de recherche mathématique de Rennes Université de Rennes 1 et CNRS (UMR 6625) Vernam s ciphering Principles of coding and
Lecture Notes. Advanced Discrete Structures COT S
 Lecture Notes Advanced Discrete Structures COT 4115.001 S15 2015-01-27 Recap ADFGX Cipher Block Cipher Modes of Operation Hill Cipher Inverting a Matrix (mod n) Encryption: Hill Cipher Example Multiple
Lecture Notes Advanced Discrete Structures COT 4115.001 S15 2015-01-27 Recap ADFGX Cipher Block Cipher Modes of Operation Hill Cipher Inverting a Matrix (mod n) Encryption: Hill Cipher Example Multiple
Better proofs for rekeying
 Better proofs for rekeying 1 D. J. Bernstein Security of AES-256 key k is far below 2 256 in most protocols: (AES k (0); : : : ; AES k (n 1)) is distinguishable from uniform with probability n(n 1)=2 129,
Better proofs for rekeying 1 D. J. Bernstein Security of AES-256 key k is far below 2 256 in most protocols: (AES k (0); : : : ; AES k (n 1)) is distinguishable from uniform with probability n(n 1)=2 129,
Other Public-Key Cryptosystems
 Other Public-Key Cryptosystems Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 10-1 Overview 1. How to exchange
Other Public-Key Cryptosystems Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 10-1 Overview 1. How to exchange
AM02 - Texas A&M University. Purchase Order
 Page 1 of 8 AM02 - Texas A&M University Purchase Order P.O. Date: 8/23/2016 Purchase Order Number AM02-17-P029331 SHOW THIS NUMBER ON ALL PACKAGES, INVOICES AND SHIPPING PAPERS. V E N D O R Vendor Number:
Page 1 of 8 AM02 - Texas A&M University Purchase Order P.O. Date: 8/23/2016 Purchase Order Number AM02-17-P029331 SHOW THIS NUMBER ON ALL PACKAGES, INVOICES AND SHIPPING PAPERS. V E N D O R Vendor Number:
RSA Key Extraction via Low- Bandwidth Acoustic Cryptanalysis. Daniel Genkin, Adi Shamir, Eran Tromer
 RSA Key Extraction via Low- Bandwidth Acoustic Cryptanalysis Daniel Genkin, Adi Shamir, Eran Tromer Mathematical Attacks Input Crypto Algorithm Key Output Goal: recover the key given access to the inputs
RSA Key Extraction via Low- Bandwidth Acoustic Cryptanalysis Daniel Genkin, Adi Shamir, Eran Tromer Mathematical Attacks Input Crypto Algorithm Key Output Goal: recover the key given access to the inputs
Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS)
 Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) New Mexico SDC Meeting Chris Wingate Geography Division U.S. Census Bureau 1 Agenda Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) BAS Overview American Community Survey (ACS)
Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) New Mexico SDC Meeting Chris Wingate Geography Division U.S. Census Bureau 1 Agenda Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) BAS Overview American Community Survey (ACS)
ON SITE SYSTEMS Chemical Safety Assistant
 ON SITE SYSTEMS Chemical Safety Assistant CS ASSISTANT WEB USERS MANUAL On Site Systems 23 N. Gore Ave. Suite 200 St. Louis, MO 63119 Phone 314-963-9934 Fax 314-963-9281 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION
ON SITE SYSTEMS Chemical Safety Assistant CS ASSISTANT WEB USERS MANUAL On Site Systems 23 N. Gore Ave. Suite 200 St. Louis, MO 63119 Phone 314-963-9934 Fax 314-963-9281 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION
POLICY ISSUE (INFORMATION)
 POLICY ISSUE (INFORMATION) August 12, 2011 SECY-11-0112 FOR: FROM: SUBJECT: The Commissioners Michael R. Johnson, Director /RA/ Office of New Reactors STAFF ASSESSMENT OF SELECTED SMALL MODULAR REACTOR
POLICY ISSUE (INFORMATION) August 12, 2011 SECY-11-0112 FOR: FROM: SUBJECT: The Commissioners Michael R. Johnson, Director /RA/ Office of New Reactors STAFF ASSESSMENT OF SELECTED SMALL MODULAR REACTOR
PC100 Memory Driver Competitive Comparisons
 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note March 1999 Revised December 2000 PC100 Memory Driver Competitive Comparisons Introduction The latest developments in chipset and motherboard design have taken memory
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note March 1999 Revised December 2000 PC100 Memory Driver Competitive Comparisons Introduction The latest developments in chipset and motherboard design have taken memory
Stream Ciphers. Çetin Kaya Koç Winter / 20
 Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.cs.ucsb.edu Winter 2016 1 / 20 Linear Congruential Generators A linear congruential generator produces a sequence of integers x i for i = 1,2,... starting with the given initial
Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.cs.ucsb.edu Winter 2016 1 / 20 Linear Congruential Generators A linear congruential generator produces a sequence of integers x i for i = 1,2,... starting with the given initial
CPE 776:DATA SECURITY & CRYPTOGRAPHY. Some Number Theory and Classical Crypto Systems
 CPE 776:DATA SECURITY & CRYPTOGRAPHY Some Number Theory and Classical Crypto Systems Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Computer Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Jordan Some Number Theory
CPE 776:DATA SECURITY & CRYPTOGRAPHY Some Number Theory and Classical Crypto Systems Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Computer Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Jordan Some Number Theory
EXPERIMENT MEASUREMENT
 PHYS 1401 General Physics I EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT and UNITS I. OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the measurement of the basic quantities of mechanics and to become
PHYS 1401 General Physics I EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT and UNITS I. OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the measurement of the basic quantities of mechanics and to become
Pseudorandom Generators
 Outlines Saint Petersburg State University, Mathematics and Mechanics 2nd April 2005 Outlines Part I: Main Approach Part II: Blum-Blum-Shub Generator Part III: General Concepts of Pseudorandom Generator
Outlines Saint Petersburg State University, Mathematics and Mechanics 2nd April 2005 Outlines Part I: Main Approach Part II: Blum-Blum-Shub Generator Part III: General Concepts of Pseudorandom Generator
Batch Verification of ECDSA Signatures AfricaCrypt 2012 Ifrane, Morocco
 Batch Verification of ECDSA Signatures AfricaCrypt 2012 Ifrane, Morocco Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, West Bengal, India. Outline Introduction
Batch Verification of ECDSA Signatures AfricaCrypt 2012 Ifrane, Morocco Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, West Bengal, India. Outline Introduction
A Grey Pseudo Random Number Generator
 A Grey Pseudo Random Numer Generator Yi-Fung Huang 1 Kun-Li Wen 2 Chu-Hsing Lin 3 Jen-Chieh Chang 4 1, 3, 4 Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering Tunghai University, Taichung, Taiwan
A Grey Pseudo Random Numer Generator Yi-Fung Huang 1 Kun-Li Wen 2 Chu-Hsing Lin 3 Jen-Chieh Chang 4 1, 3, 4 Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering Tunghai University, Taichung, Taiwan
Sharing a Secret in Plain Sight. Gregory Quenell
 Sharing a Secret in Plain Sight Gregory Quenell 1 The Setting: Alice and Bob want to have a private conversation using email or texting. Alice Bob 2 The Setting: Alice and Bob want to have a private conversation
Sharing a Secret in Plain Sight Gregory Quenell 1 The Setting: Alice and Bob want to have a private conversation using email or texting. Alice Bob 2 The Setting: Alice and Bob want to have a private conversation
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
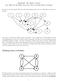 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LIMITATIONS OF A TRUE RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR IN A FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY THESIS Jennifer L. Brady AFIT/GE/ENG/08-01 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
LIMITATIONS OF A TRUE RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR IN A FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY THESIS Jennifer L. Brady AFIT/GE/ENG/08-01 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE AIR UNIVERSITY AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Lecture 18: P & NP. Revised, May 1, CLRS, pp
 Lecture 18: P & NP Revised, May 1, 2003 CLRS, pp.966-982 The course so far: techniques for designing efficient algorithms, e.g., divide-and-conquer, dynamic-programming, greedy-algorithms. What happens
Lecture 18: P & NP Revised, May 1, 2003 CLRS, pp.966-982 The course so far: techniques for designing efficient algorithms, e.g., divide-and-conquer, dynamic-programming, greedy-algorithms. What happens
Try the assignment f(1) = 2; f(2) = 1; f(3) = 4; f(4) = 3;.
 I. Precisely complete the following definitions: 1. A natural number n is composite whenever... See class notes for the precise definitions 2. Fix n in N. The number s(n) represents... 3. For A and B sets,
I. Precisely complete the following definitions: 1. A natural number n is composite whenever... See class notes for the precise definitions 2. Fix n in N. The number s(n) represents... 3. For A and B sets,
Overview. Background / Context. CSC 580 Cryptography and Computer Security. March 21, 2017
 CSC 580 Cryptography and Computer Security Math for Public Key Crypto, RSA, and Diffie-Hellman (Sections 2.4-2.6, 2.8, 9.2, 10.1-10.2) March 21, 2017 Overview Today: Math needed for basic public-key crypto
CSC 580 Cryptography and Computer Security Math for Public Key Crypto, RSA, and Diffie-Hellman (Sections 2.4-2.6, 2.8, 9.2, 10.1-10.2) March 21, 2017 Overview Today: Math needed for basic public-key crypto
LED Lighting Facts: Product Submission Guide
 LED Lighting Facts: Product Submission Guide NOVEMBER 2017 1 P a g e L E D L i g h t i n g F a c t s : M a n u f a c t u r e r P r o d u c t S u b m i s s i o n G u i d e TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1) Accessing
LED Lighting Facts: Product Submission Guide NOVEMBER 2017 1 P a g e L E D L i g h t i n g F a c t s : M a n u f a c t u r e r P r o d u c t S u b m i s s i o n G u i d e TABLE OF CONTENTS Section 1) Accessing
An Introduction. Dr Nick Papanikolaou. Seminar on The Future of Cryptography The British Computer Society 17 September 2009
 An Dr Nick Papanikolaou Research Fellow, e-security Group International Digital Laboratory University of Warwick http://go.warwick.ac.uk/nikos Seminar on The Future of Cryptography The British Computer
An Dr Nick Papanikolaou Research Fellow, e-security Group International Digital Laboratory University of Warwick http://go.warwick.ac.uk/nikos Seminar on The Future of Cryptography The British Computer
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 16 October 30, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 16 1/52 Properties of Hash Functions Hash functions do not always look random Relations among
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 16 October 30, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 16 1/52 Properties of Hash Functions Hash functions do not always look random Relations among
Elliptic curve cryptography: Generation and validation of domain parameters in binary Galois Fields
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 2008 Elliptic curve cryptography: Generation and validation of domain parameters in binary Galois Fields Peter
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 2008 Elliptic curve cryptography: Generation and validation of domain parameters in binary Galois Fields Peter
Design of S-Box using Combination of Chaotic Functions
 129 Design of S-Box using Combination of Chaotic Functions Tanu Wadhera 1, Gurmeet Kaur 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 2 Department of Electronics
129 Design of S-Box using Combination of Chaotic Functions Tanu Wadhera 1, Gurmeet Kaur 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 2 Department of Electronics
COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS
 CST0.2017.2.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IA Thursday 8 June 2017 1.30 to 4.30 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 2 Answer one question from each of Sections A, B and C, and two questions from Section D. Submit the
CST0.2017.2.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Part IA Thursday 8 June 2017 1.30 to 4.30 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 2 Answer one question from each of Sections A, B and C, and two questions from Section D. Submit the
} } } Lecture 23: Computational Complexity. Lecture Overview. Definitions: EXP R. uncomputable/ undecidable P C EXP C R = = Examples
 Lecture 23 Computational Complexity 6.006 Fall 2011 Lecture 23: Computational Complexity Lecture Overview P, EXP, R Most problems are uncomputable NP Hardness & completeness Reductions Definitions: P =
Lecture 23 Computational Complexity 6.006 Fall 2011 Lecture 23: Computational Complexity Lecture Overview P, EXP, R Most problems are uncomputable NP Hardness & completeness Reductions Definitions: P =
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION
 ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION 1 / 1 Recommended Book Steven Levy. Crypto. Penguin books. 2001. A non-technical account of the history of public-key cryptography and the colorful characters involved. 2 / 1 Recall
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION 1 / 1 Recommended Book Steven Levy. Crypto. Penguin books. 2001. A non-technical account of the history of public-key cryptography and the colorful characters involved. 2 / 1 Recall
Lesson 8: Graphs of Simple Non Linear Functions
 Student Outcomes Students examine the average rate of change for non linear functions and learn that, unlike linear functions, non linear functions do not have a constant rate of change. Students determine
Student Outcomes Students examine the average rate of change for non linear functions and learn that, unlike linear functions, non linear functions do not have a constant rate of change. Students determine
Dan Boneh. Stream ciphers. The One Time Pad
 Online Cryptography Course Stream ciphers The One Time Pad Symmetric Ciphers: definition Def: a cipher defined over is a pair of efficient algs (E, D) where E is often randomized. D is always deterministic.
Online Cryptography Course Stream ciphers The One Time Pad Symmetric Ciphers: definition Def: a cipher defined over is a pair of efficient algs (E, D) where E is often randomized. D is always deterministic.
5 Pseudorandom Generators
 5 Pseudorandom Generators We have already seen that randomness is essential for cryptographic security. Following Kerckhoff s principle, we assume that an adversary knows everything about our cryptographic
5 Pseudorandom Generators We have already seen that randomness is essential for cryptographic security. Following Kerckhoff s principle, we assume that an adversary knows everything about our cryptographic
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics. Mathematical Induction
 Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Mathematical Induction Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall 2018
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Mathematical Induction Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall 2018
Random Number Generation. Stephen Booth David Henty
 Random Number Generation Stephen Booth David Henty Introduction Random numbers are frequently used in many types of computer simulation Frequently as part of a sampling process: Generate a representative
Random Number Generation Stephen Booth David Henty Introduction Random numbers are frequently used in many types of computer simulation Frequently as part of a sampling process: Generate a representative
Assembly and Operation Manual. April 2016
 Assembly and Operation Manual April 2016 Table of Contents What is in the OurWeather Box? 3 Step by Step Assembly 13 Building the Weather Sensors 18 Testing the OurWeather Weather Station 28 Power Up OurWeather
Assembly and Operation Manual April 2016 Table of Contents What is in the OurWeather Box? 3 Step by Step Assembly 13 Building the Weather Sensors 18 Testing the OurWeather Weather Station 28 Power Up OurWeather
Solutions to the Midterm Test (March 5, 2011)
 MATC16 Cryptography and Coding Theory Gábor Pete University of Toronto Scarborough Solutions to the Midterm Test (March 5, 2011) YOUR NAME: DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. INSTRUCTIONS:
MATC16 Cryptography and Coding Theory Gábor Pete University of Toronto Scarborough Solutions to the Midterm Test (March 5, 2011) YOUR NAME: DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. INSTRUCTIONS:
Asymmetric Encryption
 -3 s s Encryption Comp Sci 3600 Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Function Using Bitwise XOR -3 s s Key Properties for -3 s s The most important property of a hash function
-3 s s Encryption Comp Sci 3600 Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Outline -3 s s 1-3 2 3 4 5 s s Function Using Bitwise XOR -3 s s Key Properties for -3 s s The most important property of a hash function
Tips Geared Towards R. Adam J. Suarez. Arpil 10, 2015
 Tips Geared Towards R Departments of Statistics North Carolina State University Arpil 10, 2015 1 / 30 Advantages of R As an interpretive and interactive language, developing an algorithm in R can be done
Tips Geared Towards R Departments of Statistics North Carolina State University Arpil 10, 2015 1 / 30 Advantages of R As an interpretive and interactive language, developing an algorithm in R can be done
CHAPTER 4 SOME METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 SOME METHODS OF PROOF In all sciences, general theories usually arise from a number of observations. In the experimental sciences, the validity of the theories can only be tested by carefully
CHAPTER 4 SOME METHODS OF PROOF In all sciences, general theories usually arise from a number of observations. In the experimental sciences, the validity of the theories can only be tested by carefully
Mechanizing Elliptic Curve Associativity
 Mechanizing Elliptic Curve Associativity Why a Formalized Mathematics Challenge is Useful for Verification of Crypto ARM Machine Code Joe Hurd Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge Galois Connections
Mechanizing Elliptic Curve Associativity Why a Formalized Mathematics Challenge is Useful for Verification of Crypto ARM Machine Code Joe Hurd Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge Galois Connections
Solutions for week 1, Cryptography Course - TDA 352/DIT 250
 Solutions for week, Cryptography Course - TDA 352/DIT 250 In this weekly exercise sheet: you will use some historical ciphers, the OTP, the definition of semantic security and some combinatorial problems.
Solutions for week, Cryptography Course - TDA 352/DIT 250 In this weekly exercise sheet: you will use some historical ciphers, the OTP, the definition of semantic security and some combinatorial problems.
IndiFrag v2.1: An Object-based Fragmentation Analysis Software Tool
 IndiFrag v2.1: An Object-based Fragmentation Analysis Software Tool Geo-Environmental Cartography and Remote Sensing Group http://cgat.webs.upv.es/software/ Universitat Politècnica de València Introduction
IndiFrag v2.1: An Object-based Fragmentation Analysis Software Tool Geo-Environmental Cartography and Remote Sensing Group http://cgat.webs.upv.es/software/ Universitat Politècnica de València Introduction
