Two dimensional oscillator and central forces
|
|
|
- Whitney Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Two dimensional oscillator and central forces September 4, 04 Hooke s law in two dimensions Consider a radial Hooke s law force in -dimensions, F = kr where the force is along the radial unit vector and depends on the distance from the origin, r, where and therefore = et the initial position and velocity (at t 0 = 0 be î cos ϕ + ĵ sin ϕ r = x + y r = r = xî + yĵ x (0 = x 0 î v (0 = v 0 ĵ Find the motion, x (t, and determine whether this initial condition is sufficiently general. Solution in Cartesian coordinates In Cartesian coordinates, the solution is immediate. Writing the force and acceleration as ( F = k xî + yĵ a = ẍî + ÿĵ where the overdots denote time derivatives, e.g., ẍ d x, we have ( ( k xî + yĵ = m ẍî + ÿĵ Defining the frequency of oscillation by ω = k m, the equation decouples into two simple harmonic oscillators, mẍ + ω x = 0 mÿ + ω y = 0
2 with the immediate solution x = a cos ωt + b sin ωt = A cos ω (t t 0 y = C cos ωt + D sin ωt Since the force diverges as the motion moves off to infinity, we expect the motion to be bounded. We can check this with the energy theorem, and therefore k x 0 x 0 F dx = ( ( xî + yĵ dxî + dyĵ k x 0 (xdx + ydy = ˆy mv mv 0 = mv mv 0 mv mv 0 k xdx + ydy = mv mv 0 x 0 y 0 k ( x + y + k ( x 0 + y0 = mv mv 0 E = mv 0 + kx 0 = mv + kx remains constant. For finite initial conditions, E is finite, so both the velocity and position remain bounded at all times, x E k v E m This means there must be turning points for x, i.e., points where a positive velocity ẋ decreases to zero as x reaches a maximum x max begins to decrease. Notice also that the velocity cannot be zero for any position less than the maximum if E is nonzero. These observations allow us to choose the initial conditions so that ẋ = 0, and we may rotate the xy-axes until x-axis lies in the direction of the maximum vector x max. This means the initial x 0 = x max and ẋ 0 = 0. Since x is in the x-direction, y 0 = 0, and from the conservation of energy ẏ 0 = Choosing the initial time to be t 0 = 0 so that x (0 = x max, ẋ (0 = 0, we have The shape of the orbit is an ellipse, since x = x max cos ωt y = v min ω x x max + sin ωt y (v min /ω = m ( E kx max vmin.
3 3 Solution as a central force problem We may treat the problem in polar coordinates instead. This introduces complications which are unnecessary here, but which illustrate several of the general techniques used for the Kepler problem, or other central forces, F = f (r. We begin with the energy theorem. Taking the dot product with, we have F = kr F = kr To substitute into the second law, we need the acceleration in polar coordinates: Now, with we have so that The acceleration is then, d r = r v = d (r = d + r = î cos ϕ + ĵ sin ϕ ( dϕ = î sin ϕ + ĵ cos ϕ = ˆϕ ϕ v = d + r = ṙ + r ϕˆϕ a = d (ṙ + r ϕˆϕ = ( r + ṙ ϕˆϕ + ṙ ϕˆϕ + r ϕˆϕ + r ϕ d ˆϕ Then, using d ˆϕ = d ( î sin ϕ + ĵ cos ϕ = ϕ ( î cos ϕ ĵ sin ϕ = ϕ the acceleration becomes a = r + ṙ ϕˆϕ + ṙ ϕˆϕ + r ϕˆϕ r ϕ = ( r r ϕ + (ṙ ϕ + r ϕ ˆϕ Now Newton s second law gives kr = m ( r r ϕ + m (ṙ ϕ + r ϕ ˆϕ 3
4 so we have two independent equations, kr = m ( r r ϕ 0 = m (ṙ ϕ + r ϕ Define ω k m. We can integrate the second immediately: ṙ ϕ = r ϕ r = ϕ ˆ ϕ r = ln r r 0 ln r r 0 ϕ 0 d ϕ = ln ϕ ϕ 0 = ln ϕ 0 ϕ r ϕ = r 0 ϕ 0 Recognizing = mr ϕ, we see that this is conservation of angular momentum. We might have seen the constant more readily by multiplying the original equation by r, 0 = m ( rṙ ϕ + r ϕ = d ( mr ϕ agrangian techniques will let us find results like this quickly. Setting ϕ = mr with constant, the first equation now becomes ( ( ω r = r r mr ω r = r m r 3 ϕ d ϕ 0 = r + ω r m r 3 The energy theorem gives us the first integral. Multiplying by ṙ then by, 0 = ṙ r + ω rṙ m r 3 ṙ ˆṙ = ṙ dṙ + ω r m r 3 ṙdṙ = (ω r m r 3 ṙ 0 ṙdṙ = (ṙ ṙ 0 (ṙ + m r + ω r (ω r m r 3 ( = ω ( r r 0 m r m r0 = (ṙ 0 + ω + m r0 E m 4
5 Now solve for the radial velocity, ṙ, ṙ + m r + ω r = E m = E m m r ω r We can integrate this to find r (t, but it is more instructive to find the shape of the spatial orbit, r (ϕ. To do this, divide the whole equation by ϕ. Since /, we get dϕ/ = dϕ Then dϕ = ϕ E m ˆϕ 0 dϕ = ϕ = = mr = r E m m r k m r m r k m r + me r m ω r 4 r + me r m ω r 4 r + me r m ω r 4 et r = du u, so = u and ϕ = = du u + me u m ω u 4 udu u 4 + me u m ω We leave the limits in terms of r and substitute back later. Now with y = u, ϕ = dy y + me y m ω where we leave the limits in terms of u to substitute back later, and integrate by completing the square in the denominator. y + me y m ω ( = y + m E 4 m ω Then setting z = y, ϕ = = m E m ω 4 dz m E m ω z 4 5 ( y
6 = m E m ω dz 4 z m E m ω Now substitute sin θ = cos θdθ = z m E m ω dz m E m ω so that ϕ = m E m ω = dθ dz 4 z m E m ω r = θ = z r sin m E m ω = ( y r sin m E m ω = ( u r sin m E m ω = ( ( sin r m E m ω + sin r0 m E m ω Define ( ϕ 0 sin r0 m E m ω so that This gives the equation of the orbit, ϕ = ( sin r m E m ω + ϕ 0 r (ϕ ϕ 0 = sin ( me ( m E m ω sin (ϕ ϕ 0 = me r m ( E ω = me r m E ω E ω sin (ϕ ϕ 0 = E mr 6
7 Compare familiar equations for an ellipse: We have r = r = mr = E E ω sin (ϕ ϕ 0 r = me ω E sin (ϕ ϕ 0 A + ε sin θ B + ε sin θ + ε sin θ r = r kr sin ϕ cos ϕ = R x + y kxy = R x + y k (x cos ϕ + y sin ϕ (y cos ϕ x sin ϕ = R x + y k ( y x cos ϕ x cos ϕ sin ϕ + y sin ϕ cos ϕ x y sin ϕ = R R k sin (ϕ ϕ 0 et ϕ = π 4, x + y k ( x + y = R and this is of the same form as a general ellipse, ( + k x + ( k y = R x a + y b = 7
Question 1: Spherical Pendulum
 Question 1: Spherical Pendulum Consider a two-dimensional pendulum of length l with mass M at its end. It is easiest to use spherical coordinates centered at the pivot since the magnitude of the position
Question 1: Spherical Pendulum Consider a two-dimensional pendulum of length l with mass M at its end. It is easiest to use spherical coordinates centered at the pivot since the magnitude of the position
Hamilton-Jacobi theory
 Hamilton-Jacobi theory November 9, 04 We conclude with the crowning theorem of Hamiltonian dynamics: a proof that for any Hamiltonian dynamical system there exists a canonical transformation to a set of
Hamilton-Jacobi theory November 9, 04 We conclude with the crowning theorem of Hamiltonian dynamics: a proof that for any Hamiltonian dynamical system there exists a canonical transformation to a set of
Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces
 Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces 21.1 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation According to Newton s Law of Universal Graviation, the force on a particle i of mass m i exerted by a particle j of
Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces 21.1 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation According to Newton s Law of Universal Graviation, the force on a particle i of mass m i exerted by a particle j of
Curvilinear Coordinates
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / LeClair Fall 2008 Curvilinear Coordinates Note that we use the convention that the cartesian unit vectors are ˆx, ŷ, and ẑ, rather than
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 106-4 / LeClair Fall 2008 Curvilinear Coordinates Note that we use the convention that the cartesian unit vectors are ˆx, ŷ, and ẑ, rather than
Solution to Homework 1. Vector Analysis (P201)
 Solution to Homework 1. Vector Analysis (P1) Q1. A = 3î + ĵ ˆk, B = î + 3ĵ + 4ˆk, C = 4î ĵ 6ˆk. The sides AB, BC and AC are, AB = 4î ĵ 6ˆk AB = 7.48 BC = 5î + 5ĵ + 1ˆk BC = 15 1.5 CA = î 3ĵ 4ˆk CA = 6
Solution to Homework 1. Vector Analysis (P1) Q1. A = 3î + ĵ ˆk, B = î + 3ĵ + 4ˆk, C = 4î ĵ 6ˆk. The sides AB, BC and AC are, AB = 4î ĵ 6ˆk AB = 7.48 BC = 5î + 5ĵ + 1ˆk BC = 15 1.5 CA = î 3ĵ 4ˆk CA = 6
Solution Set Two. 1 Problem #1: Projectile Motion Cartesian Coordinates Polar Coordinates... 3
 : Solution Set Two Northwestern University, Classical Mechanics Classical Mechanics, Third Ed.- Goldstein October 7, 2015 Contents 1 Problem #1: Projectile Motion. 2 1.1 Cartesian Coordinates....................................
: Solution Set Two Northwestern University, Classical Mechanics Classical Mechanics, Third Ed.- Goldstein October 7, 2015 Contents 1 Problem #1: Projectile Motion. 2 1.1 Cartesian Coordinates....................................
Chapter 6: Vector Analysis
 Chapter 6: Vector Analysis We use derivatives and various products of vectors in all areas of physics. For example, Newton s 2nd law is F = m d2 r. In electricity dt 2 and magnetism, we need surface and
Chapter 6: Vector Analysis We use derivatives and various products of vectors in all areas of physics. For example, Newton s 2nd law is F = m d2 r. In electricity dt 2 and magnetism, we need surface and
M2A2 Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics
 MA Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics. The particle in a cone. A particle slides under gravity, inside a smooth circular cone with a vertical axis, z = k x + y. Write down its Lagrangian in a) Cartesian,
MA Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics. The particle in a cone. A particle slides under gravity, inside a smooth circular cone with a vertical axis, z = k x + y. Write down its Lagrangian in a) Cartesian,
Gradient operator. In our calculation of dφ along the vector ds, we see that it can be described as the scalar product
 Gradient operator In our calculation of dφ along the vector ds, we see that it can be described as the scalar product ( φ dφ = x î + φ y ĵ + φ ) z ˆk ( ) u x dsî + u y dsĵ + u z dsˆk We take dφ = φ ds
Gradient operator In our calculation of dφ along the vector ds, we see that it can be described as the scalar product ( φ dφ = x î + φ y ĵ + φ ) z ˆk ( ) u x dsî + u y dsĵ + u z dsˆk We take dφ = φ ds
PHYSICS I. Lecture 1. Charudatt Kadolkar. Jul-Nov IIT Guwahati
 PHYSICS I Lecture 1 Charudatt Kadolkar IIT Guwahati Jul-Nov 2014 Section 1 Introduction to the Course Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics: Kinetic Energy rest mass energy Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics:
PHYSICS I Lecture 1 Charudatt Kadolkar IIT Guwahati Jul-Nov 2014 Section 1 Introduction to the Course Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics: Kinetic Energy rest mass energy Syllabus Topics Classical Mechanics:
Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
Question 1: A particle starts at rest and moves along a cycloid whose equation is. 2ay y a
 Stephen Martin PHYS 10 Homework #1 Question 1: A particle starts at rest and moves along a cycloid whose equation is [ ( ) a y x = ± a cos 1 + ] ay y a There is a gravitational field of strength g in the
Stephen Martin PHYS 10 Homework #1 Question 1: A particle starts at rest and moves along a cycloid whose equation is [ ( ) a y x = ± a cos 1 + ] ay y a There is a gravitational field of strength g in the
TP 3:Runge-Kutta Methods-Solar System-The Method of Least Squares
 TP :Runge-Kutta Methods-Solar System-The Method of Least Squares December 8, 2009 1 Runge-Kutta Method The problem is still trying to solve the first order differential equation dy = f(y, x). (1) dx In
TP :Runge-Kutta Methods-Solar System-The Method of Least Squares December 8, 2009 1 Runge-Kutta Method The problem is still trying to solve the first order differential equation dy = f(y, x). (1) dx In
PHYSICS - 1 (Lecture -1)
 PHYSICS - 1 (Lecture -1) Santabrata Das Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati sbdas@iitg.ernet.in, Room #: 006 30 July, 2014 Santabrata Das (IITG) PH 101, July-November 30 July,
PHYSICS - 1 (Lecture -1) Santabrata Das Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati sbdas@iitg.ernet.in, Room #: 006 30 July, 2014 Santabrata Das (IITG) PH 101, July-November 30 July,
Chemistry 532 Practice Final Exam Fall 2012 Solutions
 Chemistry 53 Practice Final Exam Fall Solutions x e ax dx π a 3/ ; π sin 3 xdx 4 3 π cos nx dx π; sin θ cos θ + K x n e ax dx n! a n+ ; r r r r ˆL h r ˆL z h i φ ˆL x i hsin φ + cot θ cos φ θ φ ) ˆLy i
Chemistry 53 Practice Final Exam Fall Solutions x e ax dx π a 3/ ; π sin 3 xdx 4 3 π cos nx dx π; sin θ cos θ + K x n e ax dx n! a n+ ; r r r r ˆL h r ˆL z h i φ ˆL x i hsin φ + cot θ cos φ θ φ ) ˆLy i
21.60 Worksheet 8 - preparation problems - question 1:
 Dynamics 190 1.60 Worksheet 8 - preparation problems - question 1: A particle of mass m moes under the influence of a conseratie central force F (r) =g(r)r where r = xˆx + yŷ + zẑ and r = x + y + z. A.
Dynamics 190 1.60 Worksheet 8 - preparation problems - question 1: A particle of mass m moes under the influence of a conseratie central force F (r) =g(r)r where r = xˆx + yŷ + zẑ and r = x + y + z. A.
1 Summary of Chapter 2
 General Astronomy (9:61) Fall 01 Lecture 7 Notes, September 10, 01 1 Summary of Chapter There are a number of items from Chapter that you should be sure to understand. 1.1 Terminology A number of technical
General Astronomy (9:61) Fall 01 Lecture 7 Notes, September 10, 01 1 Summary of Chapter There are a number of items from Chapter that you should be sure to understand. 1.1 Terminology A number of technical
Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress
 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic mass unit ) = 1 1.66
1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic mass unit ) = 1 1.66
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy. PH 125 / LeClair Spring A Short Math Guide. Cartesian (x, y) Polar (r, θ)
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Spring 2009 A Short Math Guide 1 Definition of coordinates Relationship between 2D cartesian (, y) and polar (r, θ) coordinates.
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Spring 2009 A Short Math Guide 1 Definition of coordinates Relationship between 2D cartesian (, y) and polar (r, θ) coordinates.
Laplace equation in polar coordinates
 Laplace equation in polar coordinates The Laplace equation is given by 2 F 2 + 2 F 2 = 0 We have x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, and also r 2 = x 2 + y 2, tan θ = y/x We have for the partials with respect to
Laplace equation in polar coordinates The Laplace equation is given by 2 F 2 + 2 F 2 = 0 We have x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, and also r 2 = x 2 + y 2, tan θ = y/x We have for the partials with respect to
Fun With Carbon Monoxide. p. 1/2
 Fun With Carbon Monoxide p. 1/2 p. 1/2 Fun With Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results p. 1/2 Fun With Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results C V (J/K-mole) 35 30 25
Fun With Carbon Monoxide p. 1/2 p. 1/2 Fun With Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results p. 1/2 Fun With Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results C V (J/K-mole) 35 30 25
Additional Mathematical Tools: Detail
 Additional Mathematical Tools: Detail September 9, 25 The material here is not required, but gives more detail on the additional mathmatical tools: coordinate systems, rotations, the Dirac delta function
Additional Mathematical Tools: Detail September 9, 25 The material here is not required, but gives more detail on the additional mathmatical tools: coordinate systems, rotations, the Dirac delta function
Problem Set 5 Solution
 Problem Set 5 Solution Friday, 14 October 011 Physics 111 Proble The Setup For a pair of point masses, and m, interacting via a conservative force directed along the line joining the masses, show that
Problem Set 5 Solution Friday, 14 October 011 Physics 111 Proble The Setup For a pair of point masses, and m, interacting via a conservative force directed along the line joining the masses, show that
SOLUTIONS, PROBLEM SET 11
 SOLUTIONS, PROBLEM SET 11 1 In this problem we investigate the Lagrangian formulation of dynamics in a rotating frame. Consider a frame of reference which we will consider to be inertial. Suppose that
SOLUTIONS, PROBLEM SET 11 1 In this problem we investigate the Lagrangian formulation of dynamics in a rotating frame. Consider a frame of reference which we will consider to be inertial. Suppose that
Vectors. J.R. Wilson. September 28, 2017
 Vectors J.R. Wilson September 28, 2017 This chapter introduces vectors that are used in many areas of physics (needed for classical physics this year). One complication is that a number of different forms
Vectors J.R. Wilson September 28, 2017 This chapter introduces vectors that are used in many areas of physics (needed for classical physics this year). One complication is that a number of different forms
The Calculus of Vec- tors
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Phys 7221 Homework # 8
 Phys 71 Homework # 8 Gabriela González November 15, 6 Derivation 5-6: Torque free symmetric top In a torque free, symmetric top, with I x = I y = I, the angular velocity vector ω in body coordinates with
Phys 71 Homework # 8 Gabriela González November 15, 6 Derivation 5-6: Torque free symmetric top In a torque free, symmetric top, with I x = I y = I, the angular velocity vector ω in body coordinates with
Lagrangian Dynamics: Derivations of Lagrange s Equations
 Constraints and Degrees of Freedom 1.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 007 Professor Thomas Peacock 4/9/007 Lecture 15 Lagrangian Dynamics: Derivations of Lagrange s Equations Constraints and
Constraints and Degrees of Freedom 1.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 007 Professor Thomas Peacock 4/9/007 Lecture 15 Lagrangian Dynamics: Derivations of Lagrange s Equations Constraints and
More On Carbon Monoxide
 More On Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results Jerry Gilfoyle The Configurations of CO 1 / 26 More On Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results Jerry Gilfoyle The Configurations
More On Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results Jerry Gilfoyle The Configurations of CO 1 / 26 More On Carbon Monoxide E = 0.25 ± 0.05 ev Electron beam results Jerry Gilfoyle The Configurations
Physics 8, Fall 2013, equation sheet work in progress
 (Chapter 1: foundations) 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2013, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic
(Chapter 1: foundations) 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2013, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
Lecture Notes for PHY 405 Classical Mechanics
 Lecture Notes for PHY 405 Classical Mechanics From Thorton & Marion s Classical Mechanics Prepared by Dr. Joseph M. Hahn Saint Mary s University Department of Astronomy & Physics September 1, 2005 Chapter
Lecture Notes for PHY 405 Classical Mechanics From Thorton & Marion s Classical Mechanics Prepared by Dr. Joseph M. Hahn Saint Mary s University Department of Astronomy & Physics September 1, 2005 Chapter
Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals
 A. Line Integrals MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOY Department of Physics Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals The line integral of a scalar function f ( xyz),, along a path C is
A. Line Integrals MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOY Department of Physics Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals The line integral of a scalar function f ( xyz),, along a path C is
FROM NEWTON TO KEPLER. One simple derivation of Kepler s laws from Newton s ones.
 italian journal of pure and applied mathematics n. 3 04 (393 400) 393 FROM NEWTON TO KEPLER. One simple derivation of Kepler s laws from Newton s ones. František Mošna Department of Mathematics Technical
italian journal of pure and applied mathematics n. 3 04 (393 400) 393 FROM NEWTON TO KEPLER. One simple derivation of Kepler s laws from Newton s ones. František Mošna Department of Mathematics Technical
Final Examination Solutions
 Math. 5, Sections 5 53 (Fulling) 7 December Final Examination Solutions Test Forms A and B were the same except for the order of the multiple-choice responses. This key is based on Form A. Name: Section:
Math. 5, Sections 5 53 (Fulling) 7 December Final Examination Solutions Test Forms A and B were the same except for the order of the multiple-choice responses. This key is based on Form A. Name: Section:
PHY321 Homework Set 10
 PHY321 Homework Set 10 1. [5 pts] A small block of mass m slides without friction down a wedge-shaped block of mass M and of opening angle α. Thetriangular block itself slides along a horizontal floor,
PHY321 Homework Set 10 1. [5 pts] A small block of mass m slides without friction down a wedge-shaped block of mass M and of opening angle α. Thetriangular block itself slides along a horizontal floor,
Central Forces. c 2007 Corinne Manogue. March 1999, last revised February 2009
 Central Forces Corinne A. Manogue with Tevian Dray, Kenneth S. Krane, Jason Janesky Department of Physics Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331, USA corinne@physics.oregonstate.edu c 2007 Corinne
Central Forces Corinne A. Manogue with Tevian Dray, Kenneth S. Krane, Jason Janesky Department of Physics Oregon State University Corvallis, OR 97331, USA corinne@physics.oregonstate.edu c 2007 Corinne
MET 4301 LECTURE SEP17
 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Objectives: To review essential mathematics for Meteorological Dynamics
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Objectives: To review essential mathematics for Meteorological Dynamics
MATH H53 : Final exam
 MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
ENGI Duffing s Equation Page 4.65
 ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
ENGI 940 4. - Duffing s Equation Page 4.65 4. Duffing s Equation Among the simplest models of damped non-linear forced oscillations of a mechanical or electrical system with a cubic stiffness term is Duffing
Two- and Three-Dimensional Motion (Symon Chapter Three)
 Two- and Three-Dimensional Motion (Symon Chapter Three) Physics A300 Fall 2003 Contents 1 Vector Analysis 2 1.1 Definitions..................................... 2 1.1.1 Notation..................................
Two- and Three-Dimensional Motion (Symon Chapter Three) Physics A300 Fall 2003 Contents 1 Vector Analysis 2 1.1 Definitions..................................... 2 1.1.1 Notation..................................
2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review
 2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review September 10, 2018 These notes are to help you through the math used in this class. This is just a refresher, so if you never learned one of these topics you should look more
2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review September 10, 2018 These notes are to help you through the math used in this class. This is just a refresher, so if you never learned one of these topics you should look more
Qualifying Exam. Aug Part II. Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets!
 Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Two-Body Problem. Central Potential. 1D Motion
 Two-Body Problem. Central Potential. D Motion The simplest non-trivial dynamical problem is the problem of two particles. The equations of motion read. m r = F 2, () We already know that the center of
Two-Body Problem. Central Potential. D Motion The simplest non-trivial dynamical problem is the problem of two particles. The equations of motion read. m r = F 2, () We already know that the center of
The Equipartition Theorem
 Chapter 8 The Equipartition Theorem Topics Equipartition and kinetic energy. The one-dimensional harmonic oscillator. Degrees of freedom and the equipartition theorem. Rotating particles in thermal equilibrium.
Chapter 8 The Equipartition Theorem Topics Equipartition and kinetic energy. The one-dimensional harmonic oscillator. Degrees of freedom and the equipartition theorem. Rotating particles in thermal equilibrium.
Symmetries 2 - Rotations in Space
 Symmetries 2 - Rotations in Space This symmetry is about the isotropy of space, i.e. space is the same in all orientations. Thus, if we continuously rotated an entire system in space, we expect the system
Symmetries 2 - Rotations in Space This symmetry is about the isotropy of space, i.e. space is the same in all orientations. Thus, if we continuously rotated an entire system in space, we expect the system
Phys 7221, Fall 2006: Midterm exam
 Phys 7221, Fall 2006: Midterm exam October 20, 2006 Problem 1 (40 pts) Consider a spherical pendulum, a mass m attached to a rod of length l, as a constrained system with r = l, as shown in the figure.
Phys 7221, Fall 2006: Midterm exam October 20, 2006 Problem 1 (40 pts) Consider a spherical pendulum, a mass m attached to a rod of length l, as a constrained system with r = l, as shown in the figure.
MATHEMATICAL PROBLEM SOLVING, MECHANICS AND MODELLING MTHA4004Y
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2014 2015 MATHEMATICAL PROBLEM SOLVING, MECHANICS AND MODELLING MTHA4004Y Time allowed: 2 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 AND 2 and
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2014 2015 MATHEMATICAL PROBLEM SOLVING, MECHANICS AND MODELLING MTHA4004Y Time allowed: 2 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 AND 2 and
Prelim 2 Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 90 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck!
 April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
Department of Physics, Korea University Page 1 of 8
 Name: Department: Student ID #: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer No penalty for an unanswered question Fill the blank ( ) with ( ) if the statement is correct (incorrect) : corrections
Name: Department: Student ID #: Notice +2 ( 1) points per correct (incorrect) answer No penalty for an unanswered question Fill the blank ( ) with ( ) if the statement is correct (incorrect) : corrections
Work and kinetic energy. If a net force is applied on an object, the object may
 Work and kinetic energy If a net force is applied on an object, the object may CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY experience a change in position, i.e., a displacement. When a net force is applied over a distance,
Work and kinetic energy If a net force is applied on an object, the object may CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY experience a change in position, i.e., a displacement. When a net force is applied over a distance,
1/30. Rigid Body Rotations. Dave Frank
 . 1/3 Rigid Body Rotations Dave Frank A Point Particle and Fundamental Quantities z 2/3 m v ω r y x Angular Velocity v = dr dt = ω r Kinetic Energy K = 1 2 mv2 Momentum p = mv Rigid Bodies We treat a rigid
. 1/3 Rigid Body Rotations Dave Frank A Point Particle and Fundamental Quantities z 2/3 m v ω r y x Angular Velocity v = dr dt = ω r Kinetic Energy K = 1 2 mv2 Momentum p = mv Rigid Bodies We treat a rigid
A645/A445: Exercise #1. The Kepler Problem
 A645/A445: Exercise #1 The Kepler Problem Due: 2017 Sep 26 1 Numerical solution to the one-degree-of-freedom implicit equation The one-dimensional implicit solution is: t = t o + x x o 2(E U(x)). (1) The
A645/A445: Exercise #1 The Kepler Problem Due: 2017 Sep 26 1 Numerical solution to the one-degree-of-freedom implicit equation The one-dimensional implicit solution is: t = t o + x x o 2(E U(x)). (1) The
Math Review Night: Work and the Dot Product
 Math Review Night: Work and the Dot Product Dot Product A scalar quantity Magnitude: A B = A B cosθ The dot product can be positive, zero, or negative Two types of projections: the dot product is the parallel
Math Review Night: Work and the Dot Product Dot Product A scalar quantity Magnitude: A B = A B cosθ The dot product can be positive, zero, or negative Two types of projections: the dot product is the parallel
Errata Instructor s Solutions Manual Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed Author: David Griffiths Date: September 1, 2004
 Errata Instructor s Solutions Manual Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed Author: David Griffiths Date: September, 004 Page 4, Prob..5 (b): last expression should read y +z +3x. Page 4, Prob..6: at
Errata Instructor s Solutions Manual Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed Author: David Griffiths Date: September, 004 Page 4, Prob..5 (b): last expression should read y +z +3x. Page 4, Prob..6: at
7 Curvilinear coordinates
 7 Curvilinear coordinates Read: Boas sec. 5.4, 0.8, 0.9. 7. Review of spherical and cylindrical coords. First I ll review spherical and cylindrical coordinate systems so you can have them in mind when
7 Curvilinear coordinates Read: Boas sec. 5.4, 0.8, 0.9. 7. Review of spherical and cylindrical coords. First I ll review spherical and cylindrical coordinate systems so you can have them in mind when
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #2. Due at start of class, Friday, January 27, 2017
 Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #2. Due at start of class, Friday, January 27, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #2. Due at start of class, Friday, January 27, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING, MECHANICS AND MOD- ELLING MTHA4004Y
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017 18 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING, MECHANICS AND MOD- ELLING MTHA4004Y Time allowed: 2 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and ONE other
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017 18 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING, MECHANICS AND MOD- ELLING MTHA4004Y Time allowed: 2 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and ONE other
Physics 351 Wednesday, February 14, 2018
 Physics 351 Wednesday, February 14, 2018 HW4 due Friday. For HW help, Bill is in DRL 3N6 Wed 4 7pm. Grace is in DRL 2C2 Thu 5:30 8:30pm. Respond at pollev.com/phys351 or text PHYS351 to 37607 once to join,
Physics 351 Wednesday, February 14, 2018 HW4 due Friday. For HW help, Bill is in DRL 3N6 Wed 4 7pm. Grace is in DRL 2C2 Thu 5:30 8:30pm. Respond at pollev.com/phys351 or text PHYS351 to 37607 once to join,
Vectors. J.R. Wilson. September 27, 2018
 Vectors J.R. Wilson September 27, 2018 This chapter introduces vectors that are used in many areas of physics (needed for classical physics this year). One complication is that a number of different forms
Vectors J.R. Wilson September 27, 2018 This chapter introduces vectors that are used in many areas of physics (needed for classical physics this year). One complication is that a number of different forms
Central force motion/kepler problem. 1 Reducing 2-body motion to effective 1-body, that too with 2 d.o.f and 1st order differential equations
 Central force motion/kepler problem This short note summarizes our discussion in the lectures of various aspects of the motion under central force, in particular, the Kepler problem of inverse square-law
Central force motion/kepler problem This short note summarizes our discussion in the lectures of various aspects of the motion under central force, in particular, the Kepler problem of inverse square-law
Module 12: Work and the Scalar Product
 Module 1: Work and the Scalar Product 1.1 Scalar Product (Dot Product) We shall introduce a vector operation, called the dot product or scalar product that takes any two vectors and generates a scalar
Module 1: Work and the Scalar Product 1.1 Scalar Product (Dot Product) We shall introduce a vector operation, called the dot product or scalar product that takes any two vectors and generates a scalar
Name: Date: 12/06/2018. M20550 Calculus III Tutorial Worksheet 11
 1. ompute the surface integral M255 alculus III Tutorial Worksheet 11 x + y + z) d, where is a surface given by ru, v) u + v, u v, 1 + 2u + v and u 2, v 1. olution: First, we know x + y + z) d [ ] u +
1. ompute the surface integral M255 alculus III Tutorial Worksheet 11 x + y + z) d, where is a surface given by ru, v) u + v, u v, 1 + 2u + v and u 2, v 1. olution: First, we know x + y + z) d [ ] u +
Maxima/minima with constraints
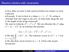 Maxima/minima with constraints Very often we want to find maxima/minima but subject to some constraint Example: A wire is bent to a shape y = 1 x 2. If a string is stretched from the origin to the wire,
Maxima/minima with constraints Very often we want to find maxima/minima but subject to some constraint Example: A wire is bent to a shape y = 1 x 2. If a string is stretched from the origin to the wire,
Problem Set 2 Solution
 Problem Set Solution Friday, September 13 Physics 111 Problem 1 Tautochrone A particle slides without friction on a cycloidal track given by x = a(θ sinθ y = a(1 cosθ where y is oriented vertically downward
Problem Set Solution Friday, September 13 Physics 111 Problem 1 Tautochrone A particle slides without friction on a cycloidal track given by x = a(θ sinθ y = a(1 cosθ where y is oriented vertically downward
The Two -Body Central Force Problem
 The Two -Body Central Force Problem Physics W3003 March 6, 2015 1 The setup 1.1 Formulation of problem The two-body central potential problem is defined by the (conserved) total energy E = 1 2 m 1Ṙ2 1
The Two -Body Central Force Problem Physics W3003 March 6, 2015 1 The setup 1.1 Formulation of problem The two-body central potential problem is defined by the (conserved) total energy E = 1 2 m 1Ṙ2 1
Methods of Integration
 Methods of Integration Professor D. Olles January 8, 04 Substitution The derivative of a composition of functions can be found using the chain rule form d dx [f (g(x))] f (g(x)) g (x) Rewriting the derivative
Methods of Integration Professor D. Olles January 8, 04 Substitution The derivative of a composition of functions can be found using the chain rule form d dx [f (g(x))] f (g(x)) g (x) Rewriting the derivative
Constraints. Noninertial coordinate systems
 Chapter 8 Constraints. Noninertial codinate systems 8.1 Constraints Oftentimes we encounter problems with constraints. F example, f a ball rolling on a flo without slipping, there is a constraint linking
Chapter 8 Constraints. Noninertial codinate systems 8.1 Constraints Oftentimes we encounter problems with constraints. F example, f a ball rolling on a flo without slipping, there is a constraint linking
1. (13%) Find the orthogonal trajectories of the family of curves y = tan 1 (kx), where k is an arbitrary constant. Solution: For the original curves:
 5 微甲 6- 班期末考解答和評分標準. (%) Find the orthogonal trajectories of the family of curves y = tan (kx), where k is an arbitrary constant. For the original curves: dy dx = tan y k = +k x x sin y cos y = +tan y
5 微甲 6- 班期末考解答和評分標準. (%) Find the orthogonal trajectories of the family of curves y = tan (kx), where k is an arbitrary constant. For the original curves: dy dx = tan y k = +k x x sin y cos y = +tan y
Two- and Three-Dimensional Motion (Symon Chapter Three)
 Two- and Three-Dimensional Motion (Symon Chapter Three) Physics A300 Spring 2006 Contents 1 Vector Analysis 3 11 Definitions 3 111 Notation 3 12 Basic Vector Arithmetic 3 121 Equality 3 122 Magnitude 4
Two- and Three-Dimensional Motion (Symon Chapter Three) Physics A300 Spring 2006 Contents 1 Vector Analysis 3 11 Definitions 3 111 Notation 3 12 Basic Vector Arithmetic 3 121 Equality 3 122 Magnitude 4
3 Space curvilinear motion, motion in non-inertial frames
 3 Space curvilinear motion, motion in non-inertial frames 3.1 In-class problem A rocket of initial mass m i is fired vertically up from earth and accelerates until its fuel is exhausted. The residual mass
3 Space curvilinear motion, motion in non-inertial frames 3.1 In-class problem A rocket of initial mass m i is fired vertically up from earth and accelerates until its fuel is exhausted. The residual mass
0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 4
 0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 4 Dynamics II Forces and motion in 2D and 3D This is the generalisation of Dynamics I to 2D and 3D. We shall use vectors and vector algebra including the scalar (dot) product.
0J2 - Mechanics Lecture Notes 4 Dynamics II Forces and motion in 2D and 3D This is the generalisation of Dynamics I to 2D and 3D. We shall use vectors and vector algebra including the scalar (dot) product.
PHY6426/Fall 07: CLASSICAL MECHANICS HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #1 due by 9:35 a.m. Wed 09/05 Instructor: D. L. Maslov Rm.
 PHY646/Fall 07: CLASSICAL MECHANICS HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT # due by 9:35 a.m. Wed 09/05 Instructor: D. L. Maslov maslov@phys.ufl.edu 39-053 Rm. 4 Please help your instructor by doing your work neatly.. Goldstein,
PHY646/Fall 07: CLASSICAL MECHANICS HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT # due by 9:35 a.m. Wed 09/05 Instructor: D. L. Maslov maslov@phys.ufl.edu 39-053 Rm. 4 Please help your instructor by doing your work neatly.. Goldstein,
on an open connected region D, then F is conservative on D. (c) If curl F=curl G on R 3, then C F dr = C G dr for all closed path C.
 . (5%) Determine the statement is true ( ) or false ( ). 微甲 -4 班期末考解答和評分標準 (a) If f(x, y) is continuous on the rectangle R = {(x, y) a x b, c y d} except for finitely many points, then f(x, y) is integrable
. (5%) Determine the statement is true ( ) or false ( ). 微甲 -4 班期末考解答和評分標準 (a) If f(x, y) is continuous on the rectangle R = {(x, y) a x b, c y d} except for finitely many points, then f(x, y) is integrable
Math Assignment 5
 Math 2280 - Assignment 5 Dylan Zwick Fall 2013 Section 3.4-1, 5, 18, 21 Section 3.5-1, 11, 23, 28, 35, 47, 56 Section 3.6-1, 2, 9, 17, 24 1 Section 3.4 - Mechanical Vibrations 3.4.1 - Determine the period
Math 2280 - Assignment 5 Dylan Zwick Fall 2013 Section 3.4-1, 5, 18, 21 Section 3.5-1, 11, 23, 28, 35, 47, 56 Section 3.6-1, 2, 9, 17, 24 1 Section 3.4 - Mechanical Vibrations 3.4.1 - Determine the period
First Year Physics: Prelims CP1. Classical Mechanics: Prof. Neville Harnew. Problem Set III : Projectiles, rocket motion and motion in E & B fields
 HT017 First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: Prof Neville Harnew Problem Set III : Projectiles, rocket motion and motion in E & B fields Questions 1-10 are standard examples Questions 11-1
HT017 First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: Prof Neville Harnew Problem Set III : Projectiles, rocket motion and motion in E & B fields Questions 1-10 are standard examples Questions 11-1
PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall September 28 th, 2015 Midterm Exam # 1
 Name: SOLUTIONS PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall 2015 September 28 th, 2015 Mierm Exam # 1 Always remember to write full work for what you do. This will help your grade in case of incomplete or wrong
Name: SOLUTIONS PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall 2015 September 28 th, 2015 Mierm Exam # 1 Always remember to write full work for what you do. This will help your grade in case of incomplete or wrong
xy 2 e 2z dx dy dz = 8 3 (1 e 4 ) = 2.62 mc. 12 x2 y 3 e 2z 2 m 2 m 2 m Figure P4.1: Cube of Problem 4.1.
 Problem 4.1 A cube m on a side is located in the first octant in a Cartesian coordinate system, with one of its corners at the origin. Find the total charge contained in the cube if the charge density
Problem 4.1 A cube m on a side is located in the first octant in a Cartesian coordinate system, with one of its corners at the origin. Find the total charge contained in the cube if the charge density
Problem Set 1 solutions
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 301 / LeClair Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 solutions 1. If a(t), b(t), and c(t) are functions of t, verify the following results: ( d [a (b c)] =
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 301 / LeClair Fall 2018 Problem Set 1 solutions 1. If a(t), b(t), and c(t) are functions of t, verify the following results: ( d [a (b c)] =
Module 24: Angular Momentum of a Point Particle
 24.1 Introduction Module 24: Angular Momentum of a Point Particle When we consider a system of objects, we have shown that the external force, acting at the center of mass of the system, is equal to the
24.1 Introduction Module 24: Angular Momentum of a Point Particle When we consider a system of objects, we have shown that the external force, acting at the center of mass of the system, is equal to the
Lecture 9: Kinetic Energy and Work 1
 Lecture 9: Kinetic Energy and Work 1 CHAPTER 6: Work and Kinetic Energy The concept of WORK has a very precise definition in physics. Work is a physical quantity produced when a Force moves an object through
Lecture 9: Kinetic Energy and Work 1 CHAPTER 6: Work and Kinetic Energy The concept of WORK has a very precise definition in physics. Work is a physical quantity produced when a Force moves an object through
Week 7: Integration: Special Coordinates
 Week 7: Integration: Special Coordinates Introduction Many problems naturally involve symmetry. One should exploit it where possible and this often means using coordinate systems other than Cartesian coordinates.
Week 7: Integration: Special Coordinates Introduction Many problems naturally involve symmetry. One should exploit it where possible and this often means using coordinate systems other than Cartesian coordinates.
V (r,t) = i ˆ u( x, y,z,t) + ˆ j v( x, y,z,t) + k ˆ w( x, y, z,t)
 IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
Potential-Density pair: Worked Problem In a spherical galaxy, the density of matter varies with radius as. a r 2 (r+a) 2, ρ(r) = M 4π
 15 Potential-Density pair: Worked Problem In a spherical galaxy, the density of matter varies with radius as where M and a are constants. ρ(r) = M 4π a r 2 (r+a) 2, (a) Verify that the total mass of the
15 Potential-Density pair: Worked Problem In a spherical galaxy, the density of matter varies with radius as where M and a are constants. ρ(r) = M 4π a r 2 (r+a) 2, (a) Verify that the total mass of the
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page dt dt dt
 ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page 2-01 2. Parametric Vector Functions (continued) Any non-zero vector r can be decomposed into its magnitude r and its direction: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vector:
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page 2-01 2. Parametric Vector Functions (continued) Any non-zero vector r can be decomposed into its magnitude r and its direction: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vector:
28. Pendulum phase portrait Draw the phase portrait for the pendulum (supported by an inextensible rod)
 28. Pendulum phase portrait Draw the phase portrait for the pendulum (supported by an inextensible rod) θ + ω 2 sin θ = 0. Indicate the stable equilibrium points as well as the unstable equilibrium points.
28. Pendulum phase portrait Draw the phase portrait for the pendulum (supported by an inextensible rod) θ + ω 2 sin θ = 0. Indicate the stable equilibrium points as well as the unstable equilibrium points.
22.2. Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Consider a particle in 1D at position x(t), subject to a force F (x), so that mẍ = F (x). Define the kinetic energy to be.
 Chapter 4 Energy and Stability 4.1 Energy in 1D Consider a particle in 1D at position x(t), subject to a force F (x), so that mẍ = F (x). Define the kinetic energy to be T = 1 2 mẋ2 and the potential energy
Chapter 4 Energy and Stability 4.1 Energy in 1D Consider a particle in 1D at position x(t), subject to a force F (x), so that mẍ = F (x). Define the kinetic energy to be T = 1 2 mẋ2 and the potential energy
Celestial Orbits. Adrienne Carter Ottopaskal Rice May 18, 2001
 Celestial Orbits Adrienne Carter sillyajc@yahoo.com Ottopaskal Rice ottomanbuski@hotmail.com May 18, 2001 1. Tycho Brache, a Danish astronomer of the late 1500s, had collected large amounts of raw data
Celestial Orbits Adrienne Carter sillyajc@yahoo.com Ottopaskal Rice ottomanbuski@hotmail.com May 18, 2001 1. Tycho Brache, a Danish astronomer of the late 1500s, had collected large amounts of raw data
P321(b), Assignement 1
 P31(b), Assignement 1 1 Exercise 3.1 (Fetter and Walecka) a) The problem is that of a point mass rotating along a circle of radius a, rotating with a constant angular velocity Ω. Generally, 3 coordinates
P31(b), Assignement 1 1 Exercise 3.1 (Fetter and Walecka) a) The problem is that of a point mass rotating along a circle of radius a, rotating with a constant angular velocity Ω. Generally, 3 coordinates
Conservation of Linear Momentum : If a force F is acting on particle of mass m, then according to Newton s second law of motion, we have F = dp /dt =
 Conservation of Linear Momentum : If a force F is acting on particle of mass m, then according to Newton s second law of motion, we have F = dp /dt = d (mv) /dt where p =mv is linear momentum of particle
Conservation of Linear Momentum : If a force F is acting on particle of mass m, then according to Newton s second law of motion, we have F = dp /dt = d (mv) /dt where p =mv is linear momentum of particle
29.3. Integral Vector Theorems. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Integral ector Theorems 9. Introduction arious theorems exist relating integrals involving vectors. Those involving line, surface and volume integrals are introduced here. They are the multivariable calculus
Integral ector Theorems 9. Introduction arious theorems exist relating integrals involving vectors. Those involving line, surface and volume integrals are introduced here. They are the multivariable calculus
POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION
 7 POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 7.. IDENTIFY: U grav = mgy so ΔU grav = mg( y y ) SET UP: + y is upward. EXECUTE: (a) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(4 m 5 m) = +6.6 5 J (b) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(35
7 POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 7.. IDENTIFY: U grav = mgy so ΔU grav = mg( y y ) SET UP: + y is upward. EXECUTE: (a) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(4 m 5 m) = +6.6 5 J (b) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(35
MATH2000 Flux integrals and Gauss divergence theorem (solutions)
 DEPARTMENT O MATHEMATIC MATH lux integrals and Gauss divergence theorem (solutions ( The hemisphere can be represented as We have by direct calculation in terms of spherical coordinates. = {(r, θ, φ r,
DEPARTMENT O MATHEMATIC MATH lux integrals and Gauss divergence theorem (solutions ( The hemisphere can be represented as We have by direct calculation in terms of spherical coordinates. = {(r, θ, φ r,
The central force problem
 1 The central force problem Moment. Das Moment des Eindrucks, den ein Mann auf das gemeine Volk macht, ist ein Produkt aus dem Wert des Rocks in den Titel. Georg Christoph Lichtenberg We start by dealing
1 The central force problem Moment. Das Moment des Eindrucks, den ein Mann auf das gemeine Volk macht, ist ein Produkt aus dem Wert des Rocks in den Titel. Georg Christoph Lichtenberg We start by dealing
Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 2016
 MA34 Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 26 Example Sheet d n+ = d n cot θ n r θ n r = Θθ n i. 2. 3. 4. Possible answers include: and with opposite orientation: 5..
MA34 Geometry and Motion Selected answers to Sections A and C Dwight Barkley 26 Example Sheet d n+ = d n cot θ n r θ n r = Θθ n i. 2. 3. 4. Possible answers include: and with opposite orientation: 5..
Potential/density pairs and Gauss s law
 Potential/density pairs and Gauss s law We showed last time that the motion of a particle in a cluster will evolve gradually, on the relaxation time scale. This time, however, is much longer than the typical
Potential/density pairs and Gauss s law We showed last time that the motion of a particle in a cluster will evolve gradually, on the relaxation time scale. This time, however, is much longer than the typical
1.11 Some Higher-Order Differential Equations
 page 99. Some Higher-Order Differential Equations 99. Some Higher-Order Differential Equations So far we have developed analytical techniques only for solving special types of firstorder differential equations.
page 99. Some Higher-Order Differential Equations 99. Some Higher-Order Differential Equations So far we have developed analytical techniques only for solving special types of firstorder differential equations.
Lecture 41: Highlights
 Lecture 41: Highlights The goal of this lecture is to remind you of some of the key points that we ve covered this semester Note that this is not the complete set of topics that may appear on the final
Lecture 41: Highlights The goal of this lecture is to remind you of some of the key points that we ve covered this semester Note that this is not the complete set of topics that may appear on the final
PHZ 6607 Fall 2004 Midterm exam, Due Monday, November 8.
 PHZ 6607 Fall 2004 Mierm exam, Due Monday, November 8. This is a take-home exam. You may use your class notes, your textbook and any algebra program, such as Maple or Mathematica, for assistance. If you
PHZ 6607 Fall 2004 Mierm exam, Due Monday, November 8. This is a take-home exam. You may use your class notes, your textbook and any algebra program, such as Maple or Mathematica, for assistance. If you
