Assessment Schedule 2011 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (90521)
|
|
|
- Pauline McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NCEA Level 3 Physics (9052) 20 page of 5 Assessment Schedule 20 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (9052) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence ONE (a) f = = 75 Hz! = 2!f! = 2! " 75! = 47 rad s # 2 Correct. (b) = 2 I! 2 2 Correct kinetic energy. 2 Correct power. = 2 ".20 " 0#3 " 47 2 = 33 J P = t P = = 08 W he electric motor exerts a force on the axle holding the blade. he wood exerts a force on the teeth of the blade. he torque from this force balances the torque from the motor. Because the force from the wood acts at a much greater radius, the size of this force is much smaller. Both forces described. One torque described. orques on the blade stated to be balanced. Both torques described. Merit plus the torques are stated to be balanced.
2 NCEA Level 3 Physics (9052) 20 page 2 of 5 WO (a) = 2! L g 2 Correct working. his is a show question. = 2! = s! 4.70 s (b)(i) v max = A!! = 2" 4.70! =.337 rads # v max = A! = 0.90 $.337 =.20 m s # 2 Correct ω. 2 Correct answer. (ii) Equilibrium position shown. Correct. At all points the tension force has to provide the centripetal force required to keep the bag moving in a circle and balance a component of the force of gravity. At the equilibrium point, the tension is greatest because the speed is greatest and the gravity component is the full gravity force. At the extremes, the speed is zero, so there is no centripetal force, and as one component of the gravity force is providing the restoring force the other component, which must be balanced by the tension force is therefore less than the full gravity force. For both these reasons the tension force at the end positions has decreased. Recognition that the tension force provides the centripetal force. Recognition that tension force must provide both the centripetal force and must balance gravity. Explanation for why the centripetal force is greatest at the equilibrium position. or why the gravity component that tension must balance is greatest at the equilibrium position. Explanation for why the centripetal force AND the gravity component that tension must balance are both greatest at the equilibrium position. (d) = 2! l g = 2!! Angular frequency / frequency decreases because the time period is increases. v decreases because increases and angular frequency decreases.! = v r " l So increasing length makes v max decrease.
3 NCEA Level 3 Physics (9052) 20 page 3 of 5 (e) 2 Correct diagram. 2 Correct θ tot. Correct time consistent with using r = Correct time.! tot = sin " sin" 0.9 =.68 rad t =! tot # =.26 s $ 4.70' =.68 % & 2! ( ) HREE (a) Correct single force vector with correct label. (b) F g = GMm r 2 = 6.67! 0"! 5.974! 0 24!.08! 0 3 ( )! 0 7 = 60 N ( ) 2 2 Correct answer consistent with radius of earth not added. Correctly substituted equation. 2 Correct answer.
4 NCEA Level 3 Physics (9052) 20 page 4 of 5 F = mv2 r = 080v2 2.66! 0 7 v 2 =.498! 0 7 v = m s v = 2!r 2 Correct velocity. 2 Correct period in seconds. Correct period in hours consistent with incorrectly calculated velocity. 2 Calculated period compared with 2 hours. 2!! 2.66! = = 4382 s = 4382 (60! 60! 24) = days (d) Gravitational force must be equal to the Centripetal force required at that radius. Centripetal acceleration of any object must equal the acceleration due to gravity at that radius, regardless of its mass. F g = F C plus reason why mass has no effect. 2 Correct formula for v 2. Correct formula for v 2 plus reason why mass has no effect. 2 Correct relationship developed. Correct relationship developed plus reason why mass has no effect. F = mv2 r = GMm r 2 v 2 = GM r but v = 2!r! so " # 2!r $ % & 2 = GM r r 3 = GM 4! 2 ' 2 (e) For a satellite to be geostationary, it must orbit in the direction of the Earth s rotation, in the plane of the equator, and with an orbital period of one Earth day. Satellites must have this orbital period to be geostationary. Achievement plus either same direction or above the equator.
5 NCEA Level 3 Physics (9052) 20 page 5 of 5 Judgement Statement Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence 2 A + 2 A2 + 2 A M + M2 + 2 M + 3 A E + E2 + M + M2 + M + 2 A Note: where the criterion is not specified, the required grade(s) can be from either.
Assessment Schedule 2016 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (91524)
 NCEA Level 3 Physics (91524) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (91524) Evidence Statement NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5 M6 E7 E8 No response; no relevant
NCEA Level 3 Physics (91524) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (91524) Evidence Statement NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5 M6 E7 E8 No response; no relevant
Assessment Schedule 2007 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanics (90255)
 NCEA Level Physics (9055) 007 page of 5 Assessment Schedule 007 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanics (9055) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
NCEA Level Physics (9055) 007 page of 5 Assessment Schedule 007 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanics (9055) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
Assessment Schedule 2013 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (91524)
 NCEA Level 3 Physics (91524) 2013 page 1 of 11 Assessment Schedule 2013 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (91524) Evidence Statement Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Physics (91524) 2013 page 1 of 11 Assessment Schedule 2013 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems (91524) Evidence Statement Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement
Level 3 Physics, 2011
 90521 905210 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2011 90521 Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems 9.30 am riday Friday 2 25 November 2011 Credits: Six Check that the National Student Number (NSN)
90521 905210 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2011 90521 Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems 9.30 am riday Friday 2 25 November 2011 Credits: Six Check that the National Student Number (NSN)
DEVIL CHAPTER 6 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 51 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 6 TEST REVIEW 1. A cyclist rides around a circular track at a uniform speed. Which of the following correctly gives
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 51 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 6 TEST REVIEW 1. A cyclist rides around a circular track at a uniform speed. Which of the following correctly gives
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level Physics: Mechanics Vectors Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the correct answer
Level Physics: Mechanics Vectors Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the correct answer
Award full marks for any solution which arrives at the correct answer by valid physics. Estimate because rope is not horizontal.
 Mark schemes 1 (a) (i) ω ( = 5.7 rad s 1 ) θ( = ωt ) = 5.7 0.40 =. (.9) (rad) = 60 = 10 (11) (degrees) [or s(( = vt) = 8.6 0.40 ( =.44 m) θ = 60 = 10 (11) (degrees) ] Award full marks for any solution
Mark schemes 1 (a) (i) ω ( = 5.7 rad s 1 ) θ( = ωt ) = 5.7 0.40 =. (.9) (rad) = 60 = 10 (11) (degrees) [or s(( = vt) = 8.6 0.40 ( =.44 m) θ = 60 = 10 (11) (degrees) ] Award full marks for any solution
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level Physics: Mechanics Circular Motion Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the correct
Level Physics: Mechanics Circular Motion Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the correct
Newton s Gravitational Law
 1 Newton s Gravitational Law Gravity exists because bodies have masses. Newton s Gravitational Law states that the force of attraction between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of
1 Newton s Gravitational Law Gravity exists because bodies have masses. Newton s Gravitational Law states that the force of attraction between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of
Ch 7 Homework. (a) Label physical quantities in this problem using letters you choose.
 Ch 7 Homework Name: Homework problems are from the Serway & Vuille 10 th edition. Follow the instructions and show your work clearly. 1. (Problem 7) A machine part rotates at an angular speed of 0.06 rad/s;
Ch 7 Homework Name: Homework problems are from the Serway & Vuille 10 th edition. Follow the instructions and show your work clearly. 1. (Problem 7) A machine part rotates at an angular speed of 0.06 rad/s;
Uniform Circular Motion
 Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Traveling with a constant speed in a circular path Even though the speed is constant, the acceleration is non-zero The acceleration responsible
Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Uniform Circular Motion Traveling with a constant speed in a circular path Even though the speed is constant, the acceleration is non-zero The acceleration responsible
Oscillations. Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Oscillations Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum Ref: 11-1,,3,4. Page 1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object oscillates
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Oscillations Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum Ref: 11-1,,3,4. Page 1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object oscillates
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems Linear Mechanics - Answers In 03, AS 954 replaced AS 905. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 905 there was an Evidence column
Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems Linear Mechanics - Answers In 03, AS 954 replaced AS 905. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 905 there was an Evidence column
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first
 Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Chapter 8. Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity
 Chapter 8 Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity Centripetal Acceleration An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration
Chapter 8 Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity Centripetal Acceleration An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Physics 12 January 1998 Provincial Examination
 Physics 12 January 1998 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
Physics 12 January 1998 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
[2] Explain why values of gravitational potential near to an isolated mass are all negative [3]
![[2] Explain why values of gravitational potential near to an isolated mass are all negative [3] [2] Explain why values of gravitational potential near to an isolated mass are all negative [3]](/thumbs/81/84541203.jpg) 1 (a) Define gravitational potential.... [2] (b) Explain why values of gravitational potential near to an isolated mass are all negative.... [3] (c) The Earth may be assumed to be an isolated sphere of
1 (a) Define gravitational potential.... [2] (b) Explain why values of gravitational potential near to an isolated mass are all negative.... [3] (c) The Earth may be assumed to be an isolated sphere of
Assessment Schedule 2011 Science: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics (90940)
 NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2011 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2011 Science: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics (90940) Evidence Statement Question Evidence with Merit with Excellence
NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2011 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2011 Science: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics (90940) Evidence Statement Question Evidence with Merit with Excellence
ω = k/m x = A cos (ωt + ϕ 0 ) L = I ω a x = ω 2 x P = F v P = de sys J = F dt = p w = m g F G = Gm 1m 2 D = 1 2 CρAv2 a r = v2
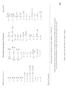 PHYS 2211 A, B, & C Final Exam Formulæ & Constants Spring 2017 Unless otherwise directed, drag is to be neglected and all problems take place on Earth, use the gravitational definition of weight, and all
PHYS 2211 A, B, & C Final Exam Formulæ & Constants Spring 2017 Unless otherwise directed, drag is to be neglected and all problems take place on Earth, use the gravitational definition of weight, and all
Chapter 9. Gravitation
 Chapter 9 Gravitation 9.1 The Gravitational Force For two particles that have masses m 1 and m 2 and are separated by a distance r, the force has a magnitude given by the same magnitude of force acts on
Chapter 9 Gravitation 9.1 The Gravitational Force For two particles that have masses m 1 and m 2 and are separated by a distance r, the force has a magnitude given by the same magnitude of force acts on
Chapter 8 continued. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.6 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.6 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation Exam-Style Questions 1 a) Calculate the angular velocity of a person standing on the Earth s surface at sea level. b) The summit of Mount Everest is 8848m above
Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation Exam-Style Questions 1 a) Calculate the angular velocity of a person standing on the Earth s surface at sea level. b) The summit of Mount Everest is 8848m above
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level Physics: Mechanics Equilibrium Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the correct answer
Level Physics: Mechanics Equilibrium Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column with the correct answer
(b) The period T and the angular frequency ω of uniform rotation are related to the cyclic frequency f as. , ω = 2πf =
 PHY 302 K. Solutions for problem set #9. Non-textbook problem #1: (a) Rotation frequency of 1 Hz means one revolution per second, or 60 revolutions per minute (RPM). The pre-lp vinyl disks rotated at 78
PHY 302 K. Solutions for problem set #9. Non-textbook problem #1: (a) Rotation frequency of 1 Hz means one revolution per second, or 60 revolutions per minute (RPM). The pre-lp vinyl disks rotated at 78
Physics A - PHY 2048C
 Physics A - PHY 2048C and 11/15/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapter 12 in the textbook on? 2 Must an object be rotating to have a moment
Physics A - PHY 2048C and 11/15/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapter 12 in the textbook on? 2 Must an object be rotating to have a moment
Lecture 6. Circular Motion. Pre-reading: KJF 6.1 and 6.2. Please take a clicker CIRCULAR MOTION KJF
 Lecture 6 Circular Motion Pre-reading: KJF 6.1 and 6.2 Please take a clicker CIRCULAR MOTION KJF 6.1 6.4 Angular position If an object moves in a circle of radius r, then after travelling a distance s
Lecture 6 Circular Motion Pre-reading: KJF 6.1 and 6.2 Please take a clicker CIRCULAR MOTION KJF 6.1 6.4 Angular position If an object moves in a circle of radius r, then after travelling a distance s
Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Chapter 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation To understand the dynamics of circular motion. To study the application of circular motion as it applies to Newton's law of gravitation. To examine the idea of
Chapter 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation To understand the dynamics of circular motion. To study the application of circular motion as it applies to Newton's law of gravitation. To examine the idea of
Assessment Schedule 2012 Science: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics (90940)
 NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2012 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2012 Science: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics (90940) Evidence Statement ONE v = Δd Δt = 600 90 = 6.67 m s 1 (rounding
NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2012 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2012 Science: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of mechanics (90940) Evidence Statement ONE v = Δd Δt = 600 90 = 6.67 m s 1 (rounding
Fig Explain how the lift force L maintains the aeroplane flying in a horizontal circle [2]
![Fig Explain how the lift force L maintains the aeroplane flying in a horizontal circle [2] Fig Explain how the lift force L maintains the aeroplane flying in a horizontal circle [2]](/thumbs/89/97996327.jpg) 1 (a) Fig. 2.1 shows an aeroplane flying in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The weight of the aeroplane is W and L is the lift force acting at right angles to the wings. L centre of circle aeroplane
1 (a) Fig. 2.1 shows an aeroplane flying in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The weight of the aeroplane is W and L is the lift force acting at right angles to the wings. L centre of circle aeroplane
A Level. A Level Physics. Circular Motion (Answers) Edexcel. Name: Total Marks: /30
 Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. Edexcel A Level A Level Physics Circular Motion (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. Total for
Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. Edexcel A Level A Level Physics Circular Motion (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. Total for
AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based
 018 AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary Inside: Free Response Question 1 RR Scoring Guideline RR Student Samples RR Scoring Commentary 018 The College Board. College
018 AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary Inside: Free Response Question 1 RR Scoring Guideline RR Student Samples RR Scoring Commentary 018 The College Board. College
Circular Motion. Gravitation
 Circular Motion Gravitation Circular Motion Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at constant speed. Centripetal force is the force that keeps an object moving in a circle. Centripetal acceleration,
Circular Motion Gravitation Circular Motion Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at constant speed. Centripetal force is the force that keeps an object moving in a circle. Centripetal acceleration,
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
Static Equilibrium, Gravitation, Periodic Motion
 This test covers static equilibrium, universal gravitation, and simple harmonic motion, with some problems requiring a knowledge of basic calculus. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. 60 A B 10 kg A mass of 10
This test covers static equilibrium, universal gravitation, and simple harmonic motion, with some problems requiring a knowledge of basic calculus. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. 60 A B 10 kg A mass of 10
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Newton s Second Law: in vector form Newton s Laws of Motion σ റF = m റa in component form σ F x = ma x σ F y = ma y in equilibrium and static situations a x = 0; a y = 0 Strategy for Solving
Chapter 4 Newton s Second Law: in vector form Newton s Laws of Motion σ റF = m റa in component form σ F x = ma x σ F y = ma y in equilibrium and static situations a x = 0; a y = 0 Strategy for Solving
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam
 Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves speed = distance time
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves speed = distance time
Physics 2211 M Quiz #2 Solutions Summer 2017
 Physics 2211 M Quiz #2 Solutions Summer 2017 I. (16 points) A block with mass m = 10.0 kg is on a plane inclined θ = 30.0 to the horizontal, as shown. A balloon is attached to the block to exert a constant
Physics 2211 M Quiz #2 Solutions Summer 2017 I. (16 points) A block with mass m = 10.0 kg is on a plane inclined θ = 30.0 to the horizontal, as shown. A balloon is attached to the block to exert a constant
Rotational Motion Examples:
 Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Center of Gravity Pearson Education, Inc.
 Center of Gravity = The center of gravity position is at a place where the torque from one end of the object is balanced by the torque of the other end and therefore there is NO rotation. Fulcrum Point
Center of Gravity = The center of gravity position is at a place where the torque from one end of the object is balanced by the torque of the other end and therefore there is NO rotation. Fulcrum Point
Topic 6 The Killers LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Topic 6. Circular Motion and Gravitation
 Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation LEARNING OBJECTIVES Topic 6 The Killers 1. Centripetal Force 2. Newton s Law of Gravitation 3. Gravitational Field Strength ROOKIE MISTAKE! Always remember. the
Topic 6 Circular Motion and Gravitation LEARNING OBJECTIVES Topic 6 The Killers 1. Centripetal Force 2. Newton s Law of Gravitation 3. Gravitational Field Strength ROOKIE MISTAKE! Always remember. the
AS91524: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems Level 3 Credits 6
 AS9154: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems Level 3 Credits 6 Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems. Demonstrate in-depth
AS9154: Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems Level 3 Credits 6 Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems. Demonstrate in-depth
10/21/2003 PHY Lecture 14 1
 Announcements. Second exam scheduled for Oct. 8 th -- practice exams now available -- http://www.wfu.edu/~natalie/f03phy3/extrapractice/. Thursday review of Chapters 9-4 3. Today s lecture Universal law
Announcements. Second exam scheduled for Oct. 8 th -- practice exams now available -- http://www.wfu.edu/~natalie/f03phy3/extrapractice/. Thursday review of Chapters 9-4 3. Today s lecture Universal law
Assessment Schedule 2011 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of wave systems (90520)
 NCEA Level 3 Physics (90520) 20 page of 5 Assessment Schedule 20 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of wave systems (90520) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence ONE (a)(i) The incident
NCEA Level 3 Physics (90520) 20 page of 5 Assessment Schedule 20 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of wave systems (90520) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence ONE (a)(i) The incident
Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004
 Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004 Problem 1 (10 points) - The Delivery A crate of mass M, which contains an expensive piece of scientific equipment, is being delivered to Caltech.
Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004 Problem 1 (10 points) - The Delivery A crate of mass M, which contains an expensive piece of scientific equipment, is being delivered to Caltech.
Rotational Motion. Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart
 Rotational Motion & Angular Momentum Rotational Motion Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angular Displacement
Rotational Motion & Angular Momentum Rotational Motion Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angular Displacement
A Ferris wheel in Japan has a radius of 50m and a mass of 1.2 x 10 6 kg. If a torque of 1 x 10 9 Nm is needed to turn the wheel when it starts at
 Option B Quiz 1. A Ferris wheel in Japan has a radius of 50m and a mass of 1. x 10 6 kg. If a torque of 1 x 10 9 Nm is needed to turn the wheel when it starts at rest, what is the wheel s angular acceleration?
Option B Quiz 1. A Ferris wheel in Japan has a radius of 50m and a mass of 1. x 10 6 kg. If a torque of 1 x 10 9 Nm is needed to turn the wheel when it starts at rest, what is the wheel s angular acceleration?
Its SI unit is rad/s and is an axial vector having its direction given by right hand thumb rule.
 Circular motion An object is said to be having circular motion if it moves along a circular path. For example revolution of moon around earth, the revolution of an artificial satellite in circular orbit
Circular motion An object is said to be having circular motion if it moves along a circular path. For example revolution of moon around earth, the revolution of an artificial satellite in circular orbit
Phys101 Lectures 19, 20 Rotational Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 19, 20 Rotational Motion Key points: Angular and Linear Quantities Rotational Dynamics; Torque and Moment of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Ref: 10-1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9. Page 1 Angular Quantities
Phys101 Lectures 19, 20 Rotational Motion Key points: Angular and Linear Quantities Rotational Dynamics; Torque and Moment of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Ref: 10-1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9. Page 1 Angular Quantities
AP Physics QUIZ Chapters 10
 Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
D. 2πmv 2 (Total 1 mark)
 1. A particle of mass m is moving with constant speed v in uniform circular motion. What is the total work done by the centripetal force during one revolution? A. Zero B. 2 mv 2 C. mv 2 D. 2πmv 2 2. A
1. A particle of mass m is moving with constant speed v in uniform circular motion. What is the total work done by the centripetal force during one revolution? A. Zero B. 2 mv 2 C. mv 2 D. 2πmv 2 2. A
a c = v2 R = ω2 R (1) in a horizontal direction towards the barrel s axis. The horizontal force providing for this acceleration is the normal force
 PHY 302 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem # 1: A rider in the barrel of fun appears motionless relative to the rotating barrel indeed, the whole point of this ride to stay stuck to the wall when
PHY 302 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem # 1: A rider in the barrel of fun appears motionless relative to the rotating barrel indeed, the whole point of this ride to stay stuck to the wall when
Rotational Kinematics
 Rotational Kinematics Rotational Coordinates Ridged objects require six numbers to describe their position and orientation: 3 coordinates 3 axes of rotation Rotational Coordinates Use an angle θ to describe
Rotational Kinematics Rotational Coordinates Ridged objects require six numbers to describe their position and orientation: 3 coordinates 3 axes of rotation Rotational Coordinates Use an angle θ to describe
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
Section I 20 marks (pages 3 6) Attempt Questions 1 20 Allow about 35 minutes for this section
 Sample Questions HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION This document shows the layout of the examination and provides some sample questions for each of the sections. Physics General Instructions Reading
Sample Questions HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION This document shows the layout of the examination and provides some sample questions for each of the sections. Physics General Instructions Reading
Sun Earth Moon Mars Mass kg kg kg kg Radius m m m 3.
 Sun Earth Moon Mars Mass 1.99 10 30 kg 5.97 10 24 kg 7.35 10 22 kg 6.42 10 23 kg Radius 6.96 10 8 m 6.38 10 6 m 1.74 10 6 m 3.40 10 6 m Orbital Radius - 1.50 10 11 m 3.84 10 8 m 2.28 10 11 m Orbital Period
Sun Earth Moon Mars Mass 1.99 10 30 kg 5.97 10 24 kg 7.35 10 22 kg 6.42 10 23 kg Radius 6.96 10 8 m 6.38 10 6 m 1.74 10 6 m 3.40 10 6 m Orbital Radius - 1.50 10 11 m 3.84 10 8 m 2.28 10 11 m Orbital Period
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
a = v2 R where R is the curvature radius and v is the car s speed. To provide this acceleration, the car needs static friction force f = ma = mv2
 PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #. Problem 1: The forces acting on the car comprise its weight mg, the normal force N from the road that cancels it, and the static friction force f that provides
PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #. Problem 1: The forces acting on the car comprise its weight mg, the normal force N from the road that cancels it, and the static friction force f that provides
Lecture 13 REVIEW. Physics 106 Spring What should we know? What should we know? Newton s Laws
 Lecture 13 REVIEW Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ What should we know? Vectors addition, subtraction, scalar and vector multiplication Trigonometric functions sinθ, cos θ, tan θ,
Lecture 13 REVIEW Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ What should we know? Vectors addition, subtraction, scalar and vector multiplication Trigonometric functions sinθ, cos θ, tan θ,
9.3 Worked Examples Circular Motion
 9.3 Worked Examples Circular Motion Example 9.1 Geosynchronous Orbit A geostationary satellite goes around the earth once every 3 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds, (a sidereal day, shorter than the noon-to-noon
9.3 Worked Examples Circular Motion Example 9.1 Geosynchronous Orbit A geostationary satellite goes around the earth once every 3 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds, (a sidereal day, shorter than the noon-to-noon
Level 3 Physics, 2013
 91524 915240 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2013 91524 Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems 2.00 pm Monday 25 November 2013 Credits: Six Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
91524 915240 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2013 91524 Demonstrate understanding of mechanical systems 2.00 pm Monday 25 November 2013 Credits: Six Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS
 31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS 1. Compare and contrast circular motion and rotation? Address the following Which involves an object and which involves a system? Does an object/system in circular motion have
31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS 1. Compare and contrast circular motion and rotation? Address the following Which involves an object and which involves a system? Does an object/system in circular motion have
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS OPTION B-1A: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Essential Idea: The basic laws of mechanics have an extension when equivalent principles are applied to rotation. Actual
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS OPTION B-1A: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Essential Idea: The basic laws of mechanics have an extension when equivalent principles are applied to rotation. Actual
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Steve Smith Tuition: Physics Notes
 Steve Smith Tuition: Physics Notes E = mc 2 F = GMm sin θ m = mλ d hν = φ + 1 2 mv2 Static Fields IV: Gravity Examples Contents 1 Gravitational Field Equations 3 1.1 adial Gravitational Field Equations.................................
Steve Smith Tuition: Physics Notes E = mc 2 F = GMm sin θ m = mλ d hν = φ + 1 2 mv2 Static Fields IV: Gravity Examples Contents 1 Gravitational Field Equations 3 1.1 adial Gravitational Field Equations.................................
airplanes need Air Rocket Propulsion, 2 Rocket Propulsion Recap: conservation of Momentum
 Announcements. HW6 due March 4.. Prof. Reitze office hour this week: Friday 3 5 pm 3. Midterm: grades posted in e-learning solutions and grade distribution posted on website if you want to look at your
Announcements. HW6 due March 4.. Prof. Reitze office hour this week: Friday 3 5 pm 3. Midterm: grades posted in e-learning solutions and grade distribution posted on website if you want to look at your
AP Physics 1 Chapter 7 Circular Motion and Gravitation
 AP Physics 1 Chapter 7 Circular Motion and Gravitation Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Angular Measure Gravitation Angular Speed and Velocity Uniform Circular Motion and Centripetal Acceleration Angular
AP Physics 1 Chapter 7 Circular Motion and Gravitation Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Angular Measure Gravitation Angular Speed and Velocity Uniform Circular Motion and Centripetal Acceleration Angular
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 12 January 2001 Provincial Examination
 Physics 12 January 2001 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
Physics 12 January 2001 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
Chapter 13. Gravitation
 Chapter 13 Gravitation e = c/a A note about eccentricity For a circle c = 0 à e = 0 a Orbit Examples Mercury has the highest eccentricity of any planet (a) e Mercury = 0.21 Halley s comet has an orbit
Chapter 13 Gravitation e = c/a A note about eccentricity For a circle c = 0 à e = 0 a Orbit Examples Mercury has the highest eccentricity of any planet (a) e Mercury = 0.21 Halley s comet has an orbit
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006
 Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
Apr 14, Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 20More physics Aprapplications
 Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 20 More physics applications Apr 14, 2015 14, 2015 1 / 14 Motion in two dimensions A particle s motion can be described by specifying how the coordinates
Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 20 More physics applications Apr 14, 2015 14, 2015 1 / 14 Motion in two dimensions A particle s motion can be described by specifying how the coordinates
Use a BLOCK letter to answer each question: A, B, C, or D (not lower case such a b or script such as D)
 Physics 23 Spring 212 Answer Sheet Print LAST Name: Rec Sec Letter EM Mini-Test First Name: Recitation Instructor & Final Exam Student ID: Gently remove this page from your exam when you begin. Write clearly
Physics 23 Spring 212 Answer Sheet Print LAST Name: Rec Sec Letter EM Mini-Test First Name: Recitation Instructor & Final Exam Student ID: Gently remove this page from your exam when you begin. Write clearly
Physics. Student Materials Advanced Higher. Tutorial Problems Mechanics HIGHER STILL. Spring 2000
 Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Gravitation. chapter 9
 chapter 9 Gravitation Circular orbits (Section 9.3) 1, 2, and 3 are simple exercises to supplement the quantitative calculations of Examples 4, 5, and 6 in Section 9.3. 1. Satellite near Earth s surface
chapter 9 Gravitation Circular orbits (Section 9.3) 1, 2, and 3 are simple exercises to supplement the quantitative calculations of Examples 4, 5, and 6 in Section 9.3. 1. Satellite near Earth s surface
Simple and Physical Pendulums Challenge Problem Solutions
 Simple and Physical Pendulums Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1 Solutions: For this problem, the answers to parts a) through d) will rely on an analysis of the pendulum motion. There are two conventional
Simple and Physical Pendulums Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1 Solutions: For this problem, the answers to parts a) through d) will rely on an analysis of the pendulum motion. There are two conventional
2009 Assessment Report Physics GA 1: Written examination 1
 2009 Physics GA 1: Written examination 1 GENERAL COMMENTS The number of students who sat for the 2009 Physics examination 1 was 6868. With a mean score of 68 per cent, students generally found the paper
2009 Physics GA 1: Written examination 1 GENERAL COMMENTS The number of students who sat for the 2009 Physics examination 1 was 6868. With a mean score of 68 per cent, students generally found the paper
Practice Test 3. Name: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Date: _ Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20
Name: Date: _ Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20
Physics 207 Lecture 10. Lecture 10. Employ Newton s Laws in 2D problems with circular motion
 Lecture 10 Goals: Employ Newton s Laws in 2D problems with circular motion Assignment: HW5, (Chapters 8 & 9, due 3/4, Wednesday) For Tuesday: Finish reading Chapter 8, start Chapter 9. Physics 207: Lecture
Lecture 10 Goals: Employ Newton s Laws in 2D problems with circular motion Assignment: HW5, (Chapters 8 & 9, due 3/4, Wednesday) For Tuesday: Finish reading Chapter 8, start Chapter 9. Physics 207: Lecture
CIRCULAR MOTION, HARMONIC MOTION, ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CIRCULAR MOTION, HARMONIC MOTION, ROTATIONAL MOTION 1 UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION path circle distance arc Definition: An object which moves on a circle, travels equal arcs in equal times. Periodic motion
CIRCULAR MOTION, HARMONIC MOTION, ROTATIONAL MOTION 1 UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION path circle distance arc Definition: An object which moves on a circle, travels equal arcs in equal times. Periodic motion
AP Physics 1 Lesson 10.a Law of Universal Gravitation Homework Outcomes
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 10.a Law of Universal Gravitation Homework Outcomes 1. Use Law of Universal Gravitation to solve problems involving different masses. 2. Determine changes in gravitational and kinetic
AP Physics 1 Lesson 10.a Law of Universal Gravitation Homework Outcomes 1. Use Law of Universal Gravitation to solve problems involving different masses. 2. Determine changes in gravitational and kinetic
Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009
 ame: Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this figure of a roller coaster: At which of these
ame: Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this figure of a roller coaster: At which of these
AP Physics 1 Second Semester Final Exam Review
 AP Physics 1 Second Semester Final Exam Review Chapter 7: Circular Motion 1. What does centripetal mean? What direction does it indicate?. Does the centripetal force do work on the object it is rotating?
AP Physics 1 Second Semester Final Exam Review Chapter 7: Circular Motion 1. What does centripetal mean? What direction does it indicate?. Does the centripetal force do work on the object it is rotating?
Sept 30 QUIZ ONE: Fundamental Concepts; Kinematics; Newton s Laws. 7:30-9:30 pm Oct 1 No class
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 4: Uniform Circular Motion Available on-line September 24; Due: October 5 at 4:00 p.m. Please write
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 4: Uniform Circular Motion Available on-line September 24; Due: October 5 at 4:00 p.m. Please write
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Physics 111. Tuesday, November 2, Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy
 ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
Physics 12 August 1998 Provincial Examination
 Physics 12 August 1998 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
Physics 12 August 1998 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE Organizers CURRICULUM: Sub-Organizers 1. Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions A, B and Dynamics and Vector Dynamics C, D 2. Work,
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 Level Physics: Mechanics Newton s Laws, Momentum and Energy Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column
Level Physics: Mechanics Newton s Laws, Momentum and Energy Answers The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. Level Physics: AS 97 replaced AS 9055. In 9055, from 003 to 0, there was an Evidence column
Assessment Schedule 2014 Geography: Demonstrate understanding of how interacting natural processes shape a New Zealand geographic environment (91426)
 NCEA Level 3 Geography (91426) 2014 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2014 Geography: Demonstrate understanding of how interacting natural processes shape a New Zealand geographic environment (91426) Evidence
NCEA Level 3 Geography (91426) 2014 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2014 Geography: Demonstrate understanding of how interacting natural processes shape a New Zealand geographic environment (91426) Evidence
Angular Momentum. Objectives CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM
 Angular Momentum CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM Objectives Calculate the angular momentum vector for a moving particle Calculate the angular momentum vector for a rotating rigid object where angular
Angular Momentum CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM Objectives Calculate the angular momentum vector for a moving particle Calculate the angular momentum vector for a rotating rigid object where angular
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system
7 - GRAVITATION Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 7 - GRAVITATION Page 1 1 ) The change in the value of g at a height h above the surface of the earth is the same as at a depth d below the surface of earth. When both d and h are much smaller than the
7 - GRAVITATION Page 1 1 ) The change in the value of g at a height h above the surface of the earth is the same as at a depth d below the surface of earth. When both d and h are much smaller than the
AP Physics. Harmonic Motion. Multiple Choice. Test E
 AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
A = 6561 times greater. B. 81 times greater. C. equally strong. D. 1/81 as great. E. (1/81) 2 = 1/6561 as great Pearson Education, Inc.
 Q13.1 The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on the Moon, the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on the Earth is A. 81 2
Q13.1 The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on the Moon, the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on the Earth is A. 81 2
Chapter 5 Centripetal Force and Gravity. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Centripetal Force and Gravity v Centripetal Acceleration v Velocity is a Vector v It has Magnitude and Direction v If either changes, the velocity vector changes. Tumble Buggy Demo v Centripetal
Chapter 5 Centripetal Force and Gravity v Centripetal Acceleration v Velocity is a Vector v It has Magnitude and Direction v If either changes, the velocity vector changes. Tumble Buggy Demo v Centripetal
Linear vs. Rotational Motion
 Linear vs. Rotational Motion Every term in a linear equation has a similar term in the analogous rotational equation. Displacements: s = r θ v t ω Speeds: v t = ω r Accelerations: a t = α r Every point
Linear vs. Rotational Motion Every term in a linear equation has a similar term in the analogous rotational equation. Displacements: s = r θ v t ω Speeds: v t = ω r Accelerations: a t = α r Every point
Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY
 Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY Question 2. Question 3. Question 4. Two stars, each of mass M, form a binary system. The stars orbit about a point a distance R from the center of each star, as
Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY Question 2. Question 3. Question 4. Two stars, each of mass M, form a binary system. The stars orbit about a point a distance R from the center of each star, as
General Definition of Torque, final. Lever Arm. General Definition of Torque 7/29/2010. Units of Chapter 10
 Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
