x +3y 2t = 1 2x +y +z +t = 2 3x y +z t = 7 2x +6y +z +t = a
|
|
|
- Leona Magdalen Moody
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UCM Final Exam, 05/8/014 Solutions 1 Given the parameter a R, consider the following linear system x +y t = 1 x +y +z +t = x y +z t = 7 x +6y +z +t = a (a (6 points Discuss the system depending on the values of the parameter a (b (4 points Solve the system whenever it is possible (a We use Gausian elimination to transform the augmented matrix of the system , a into an equivalent echelon matrix r r Two cases appear: a a + r r 1 r r 1 r 4 r 1 r4+r a a + 1 a = 1 The bottom line is null and the rank of the matrix of the system and of the augmented matrix coincides and equals, thus the system admits infinitely many solutions a 1 The bottom line is not null and the rank of the matrix of the system is, smaller than the rank of the augmented matrix, thus the system has no solutions (b The equivalent echelon system can be rewritten x +y = 1 t 5y +z = 5 t z = t After taking the parameter t = λ, the solutions are (x = 5 + λ, y =, z = 10 5λ, t = λ
2 Final Exam, 05/8/014 Page of 6 Consider the set A = {(x, y R : y 1 x, x 0, y 0} and the function f(x, y = x + (y 1 (a (5 points Draw the set A and prove that the function f attains global maximum and global minimum value in the set A (b (5 points Draw the level curves of f Using this information, find the points where the global maximum and global minimum value of f are obtained in A, and the value of f in those points (a The set A is the shadow region represented in the figure below The set A is closed, as it contains its boundary points It is also bounded, as can be enclosed by a finite ball, for instance the ball of center (0, 0 and radius in cosnequence, A is compact Function f is continuous in R because it is a polynomial Hence f is also continuous in A By the Theorem of Weierstrass, the function f attains global extrema (maximum and minimum in A (b The level curves of f are given by x + (y 1 = k, with k 0 They are circumferences with center in (0, 1 and radius k Obviously, the level increases with the radius of the circumferences Thus, the global minimum of f in A is (0, 1, with value f(0, 1 = 0 The global maximum of f in A is (1, 0, with value f(1, 0 =
3 Final Exam, 05/8/014 Page of 6 Given the parameter a R with a 0, consider the function f(x, y = x 4 ax y + (a (4 points Calculate the critical points of f depending on the value of a 0 (b (6 points Classify the critical points of f into local maxima, minima and saddle points, depending on the value of a 0 (a The function f is of class C in R since it is a polynomial The gradient of f is f(x, y = (4x 4ax, y The critical points are the solutions of the system of equations 4x 4ax = 0 and y = 0 The solutions are (0, 0 independently of the value of a and the additional points (± a, 0 when a > 0 In summary: If a > 0, then the critical points are (0, 0, ( a, 0 and ( a, 0 If a < 0, then (0, 0 is the only critical point (b We will study the character of the critical points through the sign of the Hessian matrix of f, which is given by ( 1x Hf(x, y = 4a 0 0 Note that the matrix is diagonal This fact makes quite easy to study the sign of the quadratic form Case i a > 0 We have three points to consider The Hessian matrices are Hf(0, 0 = ( 4a 0 0, Hf( ( 8a 0 a, 0 = 0, Hf( ( 8a 0 a, 0 = 0 The first matrix is negative definite because a > 0, hence (0, 0 a (strict local maximum of f in the two remaining cases, the matrix is indefinite, thus both critical points, (± a, 0, are saddle points of f Cas ii a < 0 The Hessian matrix is as before Hf(0, 0 = ( 4a 0 0 but now it is indefinite, as a < 0 In consequence (0, 0 is now a saddle point of f,
4 Final Exam, 05/8/014 Page 4 of 6 4 Consider a firm that produces a good by using labor and capital The production function of the firm is F (x, y = 60x 1 y, where x and y represent the cost of labor and capital (in thousands of euros, respectively (a (4 points Study whether the function F is concave or convex in the set A = {(x, y R : x > 0, y > 0} (b (6 points Suppose that the budget of the firm is 10 (thousands of euros and the firm s objective is to produce the greatest possible amount of good Write the optimization problem of the firm and solve the Lagrange equations (a It is clear that A is a convex set since it is intersection of two open semiplanes, which are convex sets The function F is of class C in A The gradient of F is (0x y, 40x 1 y 1 and the Hessian matrix is thus ( 40 HF (x, y = x 5 y 40 x y 1 40 x y 1 40 x 1 y 4 The first principal minor is negative for all (x, y A, 40 x 5 y < 0 The second principal minor is the determinant, that equals ( 40 x 4 y ( 40 x 4 y = 0 Thus the Hesian matrix is negative semidefinite for all (x, y A, hence F is concave (b The Lagrangian of the problem is L(x, y, λ = 60x 1 y + λ(10 x y The critical points of L are the solutions of the system L = 0, that is, 0x y λ = 0 40x 1 y 1 λ = 0 x + y = 10 After eliminating λ from the two first equations we find the relationship x y = x 1 y 1, or y = x By plugging it into the third equations we get the point (x, y = (40, 80 with multiplier λ = 0 4
5 Final Exam, 05/8/014 Page 5 of 6 5 Consider the equation x y + e zx = 1 (a (4 points Indicate in which of the following points p = (0, 1, 1 and q = (1, 0, 0 the Implicit Function Theorem can be applied, so that the equation above defines z as a function of x and y in a neighborhood of each point (b (6 points Calculate z z (x, y and (x, y at those points of part (a where the hypotheses of the Implicit Function Theorem were fulfilled (a Let f(x, y, z = x y + e zx 1 be the function that defines the equation The function f is formed by elementary functions (polynomial and exponential, thus it is of class C 1 It is easy to check that both points, p and q satisfy the equation The determinant of the matrix of partial derivatives with respect to z is f z (x, y = ezx x, a 1 1 matrix in this case The value at p is 0, thus the hypothesis of the theorem are not fulfilled for p The value at q is 1, different from 0, thus the hypotheses of the theorem are fulfilled for q (b By part (a we focus on q Deriving with respect to x in the equation we get and substituting q = (1, 0, 0 xy + e zx ( z (x, yx + z = e 0 1 ( z (1, = 0 Finally, z (1, 0 = 0 Deriving with respect to y in the equation we get x + e zx ( z (x, yx = 0 and substituting q = (1, 0, 0 Finally, z (1, 0 = e 0 1 ( z (1, 0 1 = 0
6 Final Exam, 05/8/014 Page 6 of 6 6 Consider the function f(x, y = { x y x 4 +y, if (x, y (0, 0; 0, if (x, y = (0, 0 (a (5 points Study the continuity of f in (0, 0 (b (5 points Calculate the partial derivatives f f (0, 0, (0, 0 and the directional derivative of f at (0, 0 along the direction ( 1 1, In other words, compute D ( 1, 1 f(0, 0 (a The limits through lines y = mx passing through (0, 0 are all equal to 0 Now, if we compute the limit through the parabola y = x, then the limit is 1 0, thus the limit does not exist and then f is not continuous at (0, 0 Here is the computation: lim (x,y (0,0 y=x x y x 4 + y = lim x 0 x x x 4 + (x = 1, (b It is clear that both partial derivatives exist and are zero at (0, 0, since f(h, 0 = f(0, k = f(0, 0 = 0 To find the directional derivative at (0, 0, we compute the following limit: f( h lim, h f(0, 0 = lim h 0 h h 0 h h h h h = lim h 0 h h 5 + h = lim h 0 h + = Hence D ( 1, 1 f(0, 0 =
Optimization: Problem Set Solutions
 Optimization: Problem Set Solutions Annalisa Molino University of Rome Tor Vergata annalisa.molino@uniroma2.it Fall 20 Compute the maxima minima or saddle points of the following functions a. f(x y) =
Optimization: Problem Set Solutions Annalisa Molino University of Rome Tor Vergata annalisa.molino@uniroma2.it Fall 20 Compute the maxima minima or saddle points of the following functions a. f(x y) =
Math (P)refresher Lecture 8: Unconstrained Optimization
 Math (P)refresher Lecture 8: Unconstrained Optimization September 2006 Today s Topics : Quadratic Forms Definiteness of Quadratic Forms Maxima and Minima in R n First Order Conditions Second Order Conditions
Math (P)refresher Lecture 8: Unconstrained Optimization September 2006 Today s Topics : Quadratic Forms Definiteness of Quadratic Forms Maxima and Minima in R n First Order Conditions Second Order Conditions
EC /11. Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Problem Set 1 with Solutions. a11 a 12. x 2
 LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 2010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Problem Set 1 with Solutions 1. Show that the general
LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 2010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Problem Set 1 with Solutions 1. Show that the general
Review of Optimization Methods
 Review of Optimization Methods Prof. Manuela Pedio 20550 Quantitative Methods for Finance August 2018 Outline of the Course Lectures 1 and 2 (3 hours, in class): Linear and non-linear functions on Limits,
Review of Optimization Methods Prof. Manuela Pedio 20550 Quantitative Methods for Finance August 2018 Outline of the Course Lectures 1 and 2 (3 hours, in class): Linear and non-linear functions on Limits,
2x (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 2 2y. (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 4. 4xy. (1, 1)(x 1) + (1, 1)(y + 1) (1, 1)(x 1)(y + 1) 81 x y y + 7.
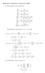 Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Math 10C - Fall Final Exam
 Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
CHAPTER 4: HIGHER ORDER DERIVATIVES. Likewise, we may define the higher order derivatives. f(x, y, z) = xy 2 + e zx. y = 2xy.
 April 15, 2009 CHAPTER 4: HIGHER ORDER DERIVATIVES In this chapter D denotes an open subset of R n. 1. Introduction Definition 1.1. Given a function f : D R we define the second partial derivatives as
April 15, 2009 CHAPTER 4: HIGHER ORDER DERIVATIVES In this chapter D denotes an open subset of R n. 1. Introduction Definition 1.1. Given a function f : D R we define the second partial derivatives as
Lecture 4: Optimization. Maximizing a function of a single variable
 Lecture 4: Optimization Maximizing or Minimizing a Function of a Single Variable Maximizing or Minimizing a Function of Many Variables Constrained Optimization Maximizing a function of a single variable
Lecture 4: Optimization Maximizing or Minimizing a Function of a Single Variable Maximizing or Minimizing a Function of Many Variables Constrained Optimization Maximizing a function of a single variable
MATH 5720: Unconstrained Optimization Hung Phan, UMass Lowell September 13, 2018
 MATH 57: Unconstrained Optimization Hung Phan, UMass Lowell September 13, 18 1 Global and Local Optima Let a function f : S R be defined on a set S R n Definition 1 (minimizers and maximizers) (i) x S
MATH 57: Unconstrained Optimization Hung Phan, UMass Lowell September 13, 18 1 Global and Local Optima Let a function f : S R be defined on a set S R n Definition 1 (minimizers and maximizers) (i) x S
September Math Course: First Order Derivative
 September Math Course: First Order Derivative Arina Nikandrova Functions Function y = f (x), where x is either be a scalar or a vector of several variables (x,..., x n ), can be thought of as a rule which
September Math Course: First Order Derivative Arina Nikandrova Functions Function y = f (x), where x is either be a scalar or a vector of several variables (x,..., x n ), can be thought of as a rule which
MATH Max-min Theory Fall 2016
 MATH 20550 Max-min Theory Fall 2016 1. Definitions and main theorems Max-min theory starts with a function f of a vector variable x and a subset D of the domain of f. So far when we have worked with functions
MATH 20550 Max-min Theory Fall 2016 1. Definitions and main theorems Max-min theory starts with a function f of a vector variable x and a subset D of the domain of f. So far when we have worked with functions
The general programming problem is the nonlinear programming problem where a given function is maximized subject to a set of inequality constraints.
 1 Optimization Mathematical programming refers to the basic mathematical problem of finding a maximum to a function, f, subject to some constraints. 1 In other words, the objective is to find a point,
1 Optimization Mathematical programming refers to the basic mathematical problem of finding a maximum to a function, f, subject to some constraints. 1 In other words, the objective is to find a point,
Solutions to Homework 7
 Solutions to Homework 7 Exercise #3 in section 5.2: A rectangular box is inscribed in a hemisphere of radius r. Find the dimensions of the box of maximum volume. Solution: The base of the rectangular box
Solutions to Homework 7 Exercise #3 in section 5.2: A rectangular box is inscribed in a hemisphere of radius r. Find the dimensions of the box of maximum volume. Solution: The base of the rectangular box
Lecture 2 - Unconstrained Optimization Definition[Global Minimum and Maximum]Let f : S R be defined on a set S R n. Then
![Lecture 2 - Unconstrained Optimization Definition[Global Minimum and Maximum]Let f : S R be defined on a set S R n. Then Lecture 2 - Unconstrained Optimization Definition[Global Minimum and Maximum]Let f : S R be defined on a set S R n. Then](/thumbs/86/93291808.jpg) Lecture 2 - Unconstrained Optimization Definition[Global Minimum and Maximum]Let f : S R be defined on a set S R n. Then 1. x S is a global minimum point of f over S if f (x) f (x ) for any x S. 2. x S
Lecture 2 - Unconstrained Optimization Definition[Global Minimum and Maximum]Let f : S R be defined on a set S R n. Then 1. x S is a global minimum point of f over S if f (x) f (x ) for any x S. 2. x S
Basics of Calculus and Algebra
 Monika Department of Economics ISCTE-IUL September 2012 Basics of linear algebra Real valued Functions Differential Calculus Integral Calculus Optimization Introduction I A matrix is a rectangular array
Monika Department of Economics ISCTE-IUL September 2012 Basics of linear algebra Real valued Functions Differential Calculus Integral Calculus Optimization Introduction I A matrix is a rectangular array
MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICS: OPTIMIZATION. Contents
 MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICS: OPTIMIZATION JOÃO LOPES DIAS Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1. Preliminaries 2 1.2. Optimal points and values 2 1.3. The optimization problems 3 1.4. Existence of optimal points 4
MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICS: OPTIMIZATION JOÃO LOPES DIAS Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1. Preliminaries 2 1.2. Optimal points and values 2 1.3. The optimization problems 3 1.4. Existence of optimal points 4
Week 4: Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A2)
 Week 4: Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A2) Tsun-Feng Chiang *School of Economics, Henan University, Kaifeng, China September 27, 2015 Microeconomic Theory Week 4: Calculus and Optimization
Week 4: Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A2) Tsun-Feng Chiang *School of Economics, Henan University, Kaifeng, China September 27, 2015 Microeconomic Theory Week 4: Calculus and Optimization
EC /11. Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Lecture Notes. Course Outline
 LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 20010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Lecture Notes Course Outline Lecture 1: Tools for
LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 20010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Lecture Notes Course Outline Lecture 1: Tools for
Examination paper for TMA4180 Optimization I
 Department of Mathematical Sciences Examination paper for TMA4180 Optimization I Academic contact during examination: Phone: Examination date: 26th May 2016 Examination time (from to): 09:00 13:00 Permitted
Department of Mathematical Sciences Examination paper for TMA4180 Optimization I Academic contact during examination: Phone: Examination date: 26th May 2016 Examination time (from to): 09:00 13:00 Permitted
Calculus 2502A - Advanced Calculus I Fall : Local minima and maxima
 Calculus 50A - Advanced Calculus I Fall 014 14.7: Local minima and maxima Martin Frankland November 17, 014 In these notes, we discuss the problem of finding the local minima and maxima of a function.
Calculus 50A - Advanced Calculus I Fall 014 14.7: Local minima and maxima Martin Frankland November 17, 014 In these notes, we discuss the problem of finding the local minima and maxima of a function.
ECON 186 Class Notes: Optimization Part 2
 ECON 186 Class Notes: Optimization Part 2 Jijian Fan Jijian Fan ECON 186 1 / 26 Hessians The Hessian matrix is a matrix of all partial derivatives of a function. Given the function f (x 1,x 2,...,x n ),
ECON 186 Class Notes: Optimization Part 2 Jijian Fan Jijian Fan ECON 186 1 / 26 Hessians The Hessian matrix is a matrix of all partial derivatives of a function. Given the function f (x 1,x 2,...,x n ),
Transpose & Dot Product
 Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
Chapter 7. Extremal Problems. 7.1 Extrema and Local Extrema
 Chapter 7 Extremal Problems No matter in theoretical context or in applications many problems can be formulated as problems of finding the maximum or minimum of a function. Whenever this is the case, advanced
Chapter 7 Extremal Problems No matter in theoretical context or in applications many problems can be formulated as problems of finding the maximum or minimum of a function. Whenever this is the case, advanced
Math 118, Fall 2014 Final Exam
 Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
Math 8, Fall 4 Final Exam True or false Please circle your choice; no explanation is necessary True There is a linear transformation T such that T e ) = e and T e ) = e Solution Since T is linear, if T
March 5, 2012 MATH 408 FINAL EXAM SAMPLE
 March 5, 202 MATH 408 FINAL EXAM SAMPLE Partial Solutions to Sample Questions (in progress) See the sample questions for the midterm exam, but also consider the following questions. Obviously, a final
March 5, 202 MATH 408 FINAL EXAM SAMPLE Partial Solutions to Sample Questions (in progress) See the sample questions for the midterm exam, but also consider the following questions. Obviously, a final
Transpose & Dot Product
 Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
Transpose & Dot Product Def: The transpose of an m n matrix A is the n m matrix A T whose columns are the rows of A. So: The columns of A T are the rows of A. The rows of A T are the columns of A. Example:
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS. MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2 Fall 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2 Fall 208 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up. Version A. A particle
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2 Fall 208 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up. Version A. A particle
1 Overview. 2 A Characterization of Convex Functions. 2.1 First-order Taylor approximation. AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016
 AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016 Prof. Yaron Singer Lecture 8 February 22nd 1 Overview In the previous lecture we saw characterizations of optimality in linear optimization, and we reviewed the
AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016 Prof. Yaron Singer Lecture 8 February 22nd 1 Overview In the previous lecture we saw characterizations of optimality in linear optimization, and we reviewed the
5x 2 = 10. x 1 + 7(2) = 4. x 1 3x 2 = 4. 3x 1 + 9x 2 = 8
 1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
Functions of Several Variables
 Jim Lambers MAT 419/519 Summer Session 2011-12 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1.2 in the text. Functions of Several Variables We now generalize the results from the previous section,
Jim Lambers MAT 419/519 Summer Session 2011-12 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1.2 in the text. Functions of Several Variables We now generalize the results from the previous section,
Paul Schrimpf. October 18, UBC Economics 526. Unconstrained optimization. Paul Schrimpf. Notation and definitions. First order conditions
 Unconstrained UBC Economics 526 October 18, 2013 .1.2.3.4.5 Section 1 Unconstrained problem x U R n F : U R. max F (x) x U Definition F = max x U F (x) is the maximum of F on U if F (x) F for all x U and
Unconstrained UBC Economics 526 October 18, 2013 .1.2.3.4.5 Section 1 Unconstrained problem x U R n F : U R. max F (x) x U Definition F = max x U F (x) is the maximum of F on U if F (x) F for all x U and
1 Directional Derivatives and Differentiability
 Wednesday, January 18, 2012 1 Directional Derivatives and Differentiability Let E R N, let f : E R and let x 0 E. Given a direction v R N, let L be the line through x 0 in the direction v, that is, L :=
Wednesday, January 18, 2012 1 Directional Derivatives and Differentiability Let E R N, let f : E R and let x 0 E. Given a direction v R N, let L be the line through x 0 in the direction v, that is, L :=
Math Maximum and Minimum Values, I
 Math 213 - Maximum and Minimum Values, I Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky October 8, 218 Homework Re-read section 14.7, pp. 959 965; read carefully pp. 965 967 Begin homework on section 14.7, problems
Math 213 - Maximum and Minimum Values, I Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky October 8, 218 Homework Re-read section 14.7, pp. 959 965; read carefully pp. 965 967 Begin homework on section 14.7, problems
Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013
 Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013 1 Rectangular Space Coordinates; Vectors in the Three-Dimensional Space (a) Cartesian coordinates of a point (b) sphere (c) symmetry about a point, a line, and a
Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013 1 Rectangular Space Coordinates; Vectors in the Three-Dimensional Space (a) Cartesian coordinates of a point (b) sphere (c) symmetry about a point, a line, and a
E 600 Chapter 4: Optimization
 E 600 Chapter 4: Optimization Simona Helmsmueller August 8, 2018 Goals of this lecture: Every theorem in these slides is important! You should understand, remember and be able to apply each and every one
E 600 Chapter 4: Optimization Simona Helmsmueller August 8, 2018 Goals of this lecture: Every theorem in these slides is important! You should understand, remember and be able to apply each and every one
OR MSc Maths Revision Course
 OR MSc Maths Revision Course Tom Byrne School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh t.m.byrne@sms.ed.ac.uk 15 September 2017 General Information Today JCMB Lecture Theatre A, 09:30-12:30 Mathematics revision
OR MSc Maths Revision Course Tom Byrne School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh t.m.byrne@sms.ed.ac.uk 15 September 2017 General Information Today JCMB Lecture Theatre A, 09:30-12:30 Mathematics revision
Math 164-1: Optimization Instructor: Alpár R. Mészáros
 Math 164-1: Optimization Instructor: Alpár R. Mészáros First Midterm, April 20, 2016 Name (use a pen): Student ID (use a pen): Signature (use a pen): Rules: Duration of the exam: 50 minutes. By writing
Math 164-1: Optimization Instructor: Alpár R. Mészáros First Midterm, April 20, 2016 Name (use a pen): Student ID (use a pen): Signature (use a pen): Rules: Duration of the exam: 50 minutes. By writing
Lecture 8: Maxima and Minima
 Lecture 8: Maxima and Minima Rafikul Alam Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Local extremum of f : R n R Let f : U R n R be continuous, where U is open. Then f has a local maximum at p if there exists
Lecture 8: Maxima and Minima Rafikul Alam Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Local extremum of f : R n R Let f : U R n R be continuous, where U is open. Then f has a local maximum at p if there exists
II. An Application of Derivatives: Optimization
 Anne Sibert Autumn 2013 II. An Application of Derivatives: Optimization In this section we consider an important application of derivatives: finding the minimum and maximum points. This has important applications
Anne Sibert Autumn 2013 II. An Application of Derivatives: Optimization In this section we consider an important application of derivatives: finding the minimum and maximum points. This has important applications
STUDY MATERIALS. (The content of the study material is the same as that of Chapter I of Mathematics for Economic Analysis II of 2011 Admn.
 STUDY MATERIALS MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR ECONOMICS III (The content of the study material is the same as that of Chapter I of Mathematics for Economic Analysis II of 2011 Admn.) & MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR
STUDY MATERIALS MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR ECONOMICS III (The content of the study material is the same as that of Chapter I of Mathematics for Economic Analysis II of 2011 Admn.) & MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR
Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. P. Duysinx and P. Tossings
 Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization P. Duysinx and P. Tossings 2018-2019 CONTACTS Pierre Duysinx Institut de Mécanique et du Génie Civil (B52/3) Phone number: 04/366.91.94 Email: P.Duysinx@uliege.be
Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization P. Duysinx and P. Tossings 2018-2019 CONTACTS Pierre Duysinx Institut de Mécanique et du Génie Civil (B52/3) Phone number: 04/366.91.94 Email: P.Duysinx@uliege.be
There are six more problems on the next two pages
 Math 435 bg & bu: Topics in linear algebra Summer 25 Final exam Wed., 8/3/5. Justify all your work to receive full credit. Name:. Let A 3 2 5 Find a permutation matrix P, a lower triangular matrix L with
Math 435 bg & bu: Topics in linear algebra Summer 25 Final exam Wed., 8/3/5. Justify all your work to receive full credit. Name:. Let A 3 2 5 Find a permutation matrix P, a lower triangular matrix L with
Math 1314 Week #14 Notes
 Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Convex Functions and Optimization
 Chapter 5 Convex Functions and Optimization 5.1 Convex Functions Our next topic is that of convex functions. Again, we will concentrate on the context of a map f : R n R although the situation can be generalized
Chapter 5 Convex Functions and Optimization 5.1 Convex Functions Our next topic is that of convex functions. Again, we will concentrate on the context of a map f : R n R although the situation can be generalized
Optimization Theory. Lectures 4-6
 Optimization Theory Lectures 4-6 Unconstrained Maximization Problem: Maximize a function f:ú n 6 ú within a set A f ú n. Typically, A is ú n, or the non-negative orthant {x0ú n x$0} Existence of a maximum:
Optimization Theory Lectures 4-6 Unconstrained Maximization Problem: Maximize a function f:ú n 6 ú within a set A f ú n. Typically, A is ú n, or the non-negative orthant {x0ú n x$0} Existence of a maximum:
Constrained Optimization Theory
 Constrained Optimization Theory Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Constrained Optimization Theory IMA, August
Constrained Optimization Theory Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Constrained Optimization Theory IMA, August
This exam will be over material covered in class from Monday 14 February through Tuesday 8 March, corresponding to sections in the text.
 Math 275, section 002 (Ultman) Spring 2011 MIDTERM 2 REVIEW The second midterm will be held in class (1:40 2:30pm) on Friday 11 March. You will be allowed one half of one side of an 8.5 11 sheet of paper
Math 275, section 002 (Ultman) Spring 2011 MIDTERM 2 REVIEW The second midterm will be held in class (1:40 2:30pm) on Friday 11 March. You will be allowed one half of one side of an 8.5 11 sheet of paper
SOLUTIONS FOR PRACTICE FINAL EXAM
 SOLUTIONS FOR PRACTICE FINAL EXAM ANDREW J. BLUMBERG. Solutions () Short answer questions: (a) State the mean value theorem. Proof. The mean value theorem says that if f is continuous on (a, b) and differentiable
SOLUTIONS FOR PRACTICE FINAL EXAM ANDREW J. BLUMBERG. Solutions () Short answer questions: (a) State the mean value theorem. Proof. The mean value theorem says that if f is continuous on (a, b) and differentiable
January 29, Introduction to optimization and complexity. Outline. Introduction. Problem formulation. Convexity reminder. Optimality Conditions
 Olga Galinina olga.galinina@tut.fi ELT-53656 Network Analysis Dimensioning II Department of Electronics Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finl January 29, 2014 1 2 3
Olga Galinina olga.galinina@tut.fi ELT-53656 Network Analysis Dimensioning II Department of Electronics Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finl January 29, 2014 1 2 3
Boston College. Math Review Session (2nd part) Lecture Notes August,2007. Nadezhda Karamcheva www2.bc.
 Boston College Math Review Session (2nd part) Lecture Notes August,2007 Nadezhda Karamcheva karamche@bc.edu www2.bc.edu/ karamche 1 Contents 1 Quadratic Forms and Definite Matrices 3 1.1 Quadratic Forms.........................
Boston College Math Review Session (2nd part) Lecture Notes August,2007 Nadezhda Karamcheva karamche@bc.edu www2.bc.edu/ karamche 1 Contents 1 Quadratic Forms and Definite Matrices 3 1.1 Quadratic Forms.........................
MATH2070 Optimisation
 MATH2070 Optimisation Nonlinear optimisation with constraints Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The full nonlinear optimisation problem with equality constraints
MATH2070 Optimisation Nonlinear optimisation with constraints Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The full nonlinear optimisation problem with equality constraints
HW3 - Due 02/06. Each answer must be mathematically justified. Don t forget your name. 1 2, A = 2 2
 HW3 - Due 02/06 Each answer must be mathematically justified Don t forget your name Problem 1 Find a 2 2 matrix B such that B 3 = A, where A = 2 2 If A was diagonal, it would be easy: we would just take
HW3 - Due 02/06 Each answer must be mathematically justified Don t forget your name Problem 1 Find a 2 2 matrix B such that B 3 = A, where A = 2 2 If A was diagonal, it would be easy: we would just take
Introduction Linear system Nonlinear equation Interpolation
 Interpolation Interpolation is the process of estimating an intermediate value from a set of discrete or tabulated values. Suppose we have the following tabulated values: y y 0 y 1 y 2?? y 3 y 4 y 5 x
Interpolation Interpolation is the process of estimating an intermediate value from a set of discrete or tabulated values. Suppose we have the following tabulated values: y y 0 y 1 y 2?? y 3 y 4 y 5 x
minimize x subject to (x 2)(x 4) u,
 Math 6366/6367: Optimization and Variational Methods Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. Suppose that f : [, L] R is a C 2 -function with f () on (, L) and that you have explicit formulae for
Math 6366/6367: Optimization and Variational Methods Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. Suppose that f : [, L] R is a C 2 -function with f () on (, L) and that you have explicit formulae for
Constrained Optimization and Lagrangian Duality
 CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 02, 2017 Constrained Optimization and Lagrangian Duality Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may or may
CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 02, 2017 Constrained Optimization and Lagrangian Duality Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may or may
2015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution
 015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
Workshop I The R n Vector Space. Linear Combinations
 Workshop I Workshop I The R n Vector Space. Linear Combinations Exercise 1. Given the vectors u = (1, 0, 3), v = ( 2, 1, 2), and w = (1, 2, 4) compute a) u + ( v + w) b) 2 u 3 v c) 2 v u + w Exercise 2.
Workshop I Workshop I The R n Vector Space. Linear Combinations Exercise 1. Given the vectors u = (1, 0, 3), v = ( 2, 1, 2), and w = (1, 2, 4) compute a) u + ( v + w) b) 2 u 3 v c) 2 v u + w Exercise 2.
ECON 5111 Mathematical Economics
 Test 1 October 1, 2010 1. Construct a truth table for the following statement: [p (p q)] q. 2. A prime number is a natural number that is divisible by 1 and itself only. Let P be the set of all prime numbers
Test 1 October 1, 2010 1. Construct a truth table for the following statement: [p (p q)] q. 2. A prime number is a natural number that is divisible by 1 and itself only. Let P be the set of all prime numbers
Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema
 Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema Math 368 c Copyright 2012, 2013 R Clark Robinson May 22, 2013 Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema 1 Types of Sets Definition For p R n and r > 0, the open ball about p of
Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema Math 368 c Copyright 2012, 2013 R Clark Robinson May 22, 2013 Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema 1 Types of Sets Definition For p R n and r > 0, the open ball about p of
EC9A0: Pre-sessional Advanced Mathematics Course. Lecture Notes: Unconstrained Optimisation By Pablo F. Beker 1
 EC9A0: Pre-sessional Advanced Mathematics Course Lecture Notes: Unconstrained Optimisation By Pablo F. Beker 1 1 Infimum and Supremum Definition 1. Fix a set Y R. A number α R is an upper bound of Y if
EC9A0: Pre-sessional Advanced Mathematics Course Lecture Notes: Unconstrained Optimisation By Pablo F. Beker 1 1 Infimum and Supremum Definition 1. Fix a set Y R. A number α R is an upper bound of Y if
Partial Derivatives. w = f(x, y, z).
 Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of Several Variables So far we have focused our attention of functions of one variable. These functions model situations in which a variable depends on another independent
Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of Several Variables So far we have focused our attention of functions of one variable. These functions model situations in which a variable depends on another independent
1. Find and classify the extrema of h(x, y) = sin(x) sin(y) sin(x + y) on the square[0, π] [0, π]. (Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out).
![1. Find and classify the extrema of h(x, y) = sin(x) sin(y) sin(x + y) on the square[0, π] [0, π]. (Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out). 1. Find and classify the extrema of h(x, y) = sin(x) sin(y) sin(x + y) on the square[0, π] [0, π]. (Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out).](/thumbs/87/97246100.jpg) . Find and classify the extrema of hx, y sinx siny sinx + y on the square[, π] [, π]. Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out. Solution: h x cos x sin y sinx + y + sin x sin y cosx + y h y sin x
. Find and classify the extrema of hx, y sinx siny sinx + y on the square[, π] [, π]. Keep in mind there is a boundary to check out. Solution: h x cos x sin y sinx + y + sin x sin y cosx + y h y sin x
Two hours. To be provided by Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables. THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. xx xxxx 2017 xx:xx xx.
 Two hours To be provided by Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables. THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER CONVEX OPTIMIZATION - SOLUTIONS xx xxxx 27 xx:xx xx.xx Answer THREE of the FOUR questions. If
Two hours To be provided by Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables. THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER CONVEX OPTIMIZATION - SOLUTIONS xx xxxx 27 xx:xx xx.xx Answer THREE of the FOUR questions. If
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid
 Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Question 1 3 4 5 6 Total Grade Economics Department Final Exam, Mathematics I January 14, 011 Total length: hours. SURNAME: NAME: DNI: Degree: Group: { 4(x 4) if 3 x 4
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Question 1 3 4 5 6 Total Grade Economics Department Final Exam, Mathematics I January 14, 011 Total length: hours. SURNAME: NAME: DNI: Degree: Group: { 4(x 4) if 3 x 4
STATE COUNCIL OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING TNCF DRAFT SYLLABUS.
 STATE COUNCIL OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING TNCF 2017 - DRAFT SYLLABUS Subject :Mathematics Class : XI TOPIC CONTENT Unit 1 : Real Numbers - Revision : Rational, Irrational Numbers, Basic Algebra
STATE COUNCIL OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING TNCF 2017 - DRAFT SYLLABUS Subject :Mathematics Class : XI TOPIC CONTENT Unit 1 : Real Numbers - Revision : Rational, Irrational Numbers, Basic Algebra
Chapter 13. Convex and Concave. Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 13 Convex and Concave 1 / 44
 Chapter 13 Convex and Concave Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 13 Convex and Concave 1 / 44 Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if x 1 x 2 f (x 1 ) f (x 2 ) It
Chapter 13 Convex and Concave Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 13 Convex and Concave 1 / 44 Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if x 1 x 2 f (x 1 ) f (x 2 ) It
Chapter 2: Preliminaries and elements of convex analysis
 Chapter 2: Preliminaries and elements of convex analysis Edoardo Amaldi DEIB Politecnico di Milano edoardo.amaldi@polimi.it Website: http://home.deib.polimi.it/amaldi/opt-14-15.shtml Academic year 2014-15
Chapter 2: Preliminaries and elements of convex analysis Edoardo Amaldi DEIB Politecnico di Milano edoardo.amaldi@polimi.it Website: http://home.deib.polimi.it/amaldi/opt-14-15.shtml Academic year 2014-15
Math Camp Notes: Linear Algebra I
 Math Camp Notes: Linear Algebra I Basic Matrix Operations and Properties Consider two n m matrices: a a m A = a n a nm Then the basic matrix operations are as follows: a + b a m + b m A + B = a n + b n
Math Camp Notes: Linear Algebra I Basic Matrix Operations and Properties Consider two n m matrices: a a m A = a n a nm Then the basic matrix operations are as follows: a + b a m + b m A + B = a n + b n
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 16
 Mathematical Economics: Lecture 16 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University November 26, 2012 Outline 1 Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions New Section Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions Concave
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 16 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University November 26, 2012 Outline 1 Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions New Section Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions Concave
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 10550
 SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 0550. Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 6 x2 x /3. We have f (x) = 3 x 3 x 2/3 = [ x 5/3 ] 3 x 2/3. So x = 0 is a critical point. For x 0, the equation f (x) = 0 can be written
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 0550. Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 6 x2 x /3. We have f (x) = 3 x 3 x 2/3 = [ x 5/3 ] 3 x 2/3. So x = 0 is a critical point. For x 0, the equation f (x) = 0 can be written
Ca Foscari University of Venice - Department of Management - A.A Luciano Battaia. December 14, 2017
 Ca Foscari University of Venice - Department of Management - A.A.27-28 Mathematics Luciano Battaia December 4, 27 Brief summary for second partial - Sample Exercises Two variables functions Here and in
Ca Foscari University of Venice - Department of Management - A.A.27-28 Mathematics Luciano Battaia December 4, 27 Brief summary for second partial - Sample Exercises Two variables functions Here and in
V. Graph Sketching and Max-Min Problems
 V. Graph Sketching and Max-Min Problems The signs of the first and second derivatives of a function tell us something about the shape of its graph. In this chapter we learn how to find that information.
V. Graph Sketching and Max-Min Problems The signs of the first and second derivatives of a function tell us something about the shape of its graph. In this chapter we learn how to find that information.
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES. 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) ax 2 + bx + c = 0. x = b ± b 2 4ac 2a. i = 1.
 MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
4.1 Analysis of functions I: Increase, decrease and concavity
 4.1 Analysis of functions I: Increase, decrease and concavity Definition Let f be defined on an interval and let x 1 and x 2 denote points in that interval. a) f is said to be increasing on the interval
4.1 Analysis of functions I: Increase, decrease and concavity Definition Let f be defined on an interval and let x 1 and x 2 denote points in that interval. a) f is said to be increasing on the interval
5. Duality. Lagrangian
 5. Duality Convex Optimization Boyd & Vandenberghe Lagrange dual problem weak and strong duality geometric interpretation optimality conditions perturbation and sensitivity analysis examples generalized
5. Duality Convex Optimization Boyd & Vandenberghe Lagrange dual problem weak and strong duality geometric interpretation optimality conditions perturbation and sensitivity analysis examples generalized
Exam in TMA4180 Optimization Theory
 Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences Page 1 of 11 Contact during exam: Anne Kværnø: 966384 Exam in TMA418 Optimization Theory Wednesday May 9, 13 Tid: 9. 13.
Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences Page 1 of 11 Contact during exam: Anne Kværnø: 966384 Exam in TMA418 Optimization Theory Wednesday May 9, 13 Tid: 9. 13.
Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics
 Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Mathematical Economics (ECON 471) Lecture 3 Calculus of Several Variables & Implicit Functions
 Mathematical Economics (ECON 471) Lecture 3 Calculus of Several Variables & Implicit Functions Teng Wah Leo 1 Calculus of Several Variables 11 Functions Mapping between Euclidean Spaces Where as in univariate
Mathematical Economics (ECON 471) Lecture 3 Calculus of Several Variables & Implicit Functions Teng Wah Leo 1 Calculus of Several Variables 11 Functions Mapping between Euclidean Spaces Where as in univariate
g(x,y) = c. For instance (see Figure 1 on the right), consider the optimization problem maximize subject to
 1 of 11 11/29/2010 10:39 AM From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers (named after Joseph Louis Lagrange) provides a strategy for finding the
1 of 11 11/29/2010 10:39 AM From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers (named after Joseph Louis Lagrange) provides a strategy for finding the
BEEM103 UNIVERSITY OF EXETER. BUSINESS School. January 2009 Mock Exam, Part A. OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR ECONOMISTS solutions
 BEEM03 UNIVERSITY OF EXETER BUSINESS School January 009 Mock Exam, Part A OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR ECONOMISTS solutions Duration : TWO HOURS The paper has 3 parts. Your marks on the rst part will be
BEEM03 UNIVERSITY OF EXETER BUSINESS School January 009 Mock Exam, Part A OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR ECONOMISTS solutions Duration : TWO HOURS The paper has 3 parts. Your marks on the rst part will be
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 2007
 Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Lagrange Multipliers
 Lagrange Multipliers (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Nov 9, 2017 1 Introduction We turn now to the study of minimization with constraints. More specifically, we will tackle the following problem: minimize
Lagrange Multipliers (Com S 477/577 Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Nov 9, 2017 1 Introduction We turn now to the study of minimization with constraints. More specifically, we will tackle the following problem: minimize
Chapter 1: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 : Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
Nonlinear Optimization: What s important?
 Nonlinear Optimization: What s important? Julian Hall 10th May 2012 Convexity: convex problems A local minimizer is a global minimizer A solution of f (x) = 0 (stationary point) is a minimizer A global
Nonlinear Optimization: What s important? Julian Hall 10th May 2012 Convexity: convex problems A local minimizer is a global minimizer A solution of f (x) = 0 (stationary point) is a minimizer A global
Higher order derivative
 2 Î 3 á Higher order derivative Î 1 Å Iterated partial derivative Iterated partial derivative Suppose f has f/ x, f/ y and ( f ) = 2 f x x x 2 ( f ) = 2 f x y x y ( f ) = 2 f y x y x ( f ) = 2 f y y y
2 Î 3 á Higher order derivative Î 1 Å Iterated partial derivative Iterated partial derivative Suppose f has f/ x, f/ y and ( f ) = 2 f x x x 2 ( f ) = 2 f x y x y ( f ) = 2 f y x y x ( f ) = 2 f y y y
Monotone Function. Function f is called monotonically increasing, if. x 1 x 2 f (x 1 ) f (x 2 ) x 1 < x 2 f (x 1 ) < f (x 2 ) x 1 x 2
 Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if Chapter 3 x x 2 f (x ) f (x 2 ) It is called strictly monotonically increasing, if f (x 2) f (x ) Convex and Concave x < x 2 f (x )
Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if Chapter 3 x x 2 f (x ) f (x 2 ) It is called strictly monotonically increasing, if f (x 2) f (x ) Convex and Concave x < x 2 f (x )
Generalization to inequality constrained problem. Maximize
 Lecture 11. 26 September 2006 Review of Lecture #10: Second order optimality conditions necessary condition, sufficient condition. If the necessary condition is violated the point cannot be a local minimum
Lecture 11. 26 September 2006 Review of Lecture #10: Second order optimality conditions necessary condition, sufficient condition. If the necessary condition is violated the point cannot be a local minimum
UNDERGROUND LECTURE NOTES 1: Optimality Conditions for Constrained Optimization Problems
 UNDERGROUND LECTURE NOTES 1: Optimality Conditions for Constrained Optimization Problems Robert M. Freund February 2016 c 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. All rights reserved. 1 1 Introduction
UNDERGROUND LECTURE NOTES 1: Optimality Conditions for Constrained Optimization Problems Robert M. Freund February 2016 c 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. All rights reserved. 1 1 Introduction
Modern Optimization Theory: Concave Programming
 Modern Optimization Theory: Concave Programming 1. Preliminaries 1 We will present below the elements of modern optimization theory as formulated by Kuhn and Tucker, and a number of authors who have followed
Modern Optimization Theory: Concave Programming 1. Preliminaries 1 We will present below the elements of modern optimization theory as formulated by Kuhn and Tucker, and a number of authors who have followed
UNC Charlotte Super Competition Level 3 Test March 4, 2019 Test with Solutions for Sponsors
 . Find the minimum value of the function f (x) x 2 + (A) 6 (B) 3 6 (C) 4 Solution. We have f (x) x 2 + + x 2 + (D) 3 4, which is equivalent to x 0. x 2 + (E) x 2 +, x R. x 2 + 2 (x 2 + ) 2. How many solutions
. Find the minimum value of the function f (x) x 2 + (A) 6 (B) 3 6 (C) 4 Solution. We have f (x) x 2 + + x 2 + (D) 3 4, which is equivalent to x 0. x 2 + (E) x 2 +, x R. x 2 + 2 (x 2 + ) 2. How many solutions
1 Lagrange Multiplier Method
 1 Lagrange Multiplier Method Near a maximum the decrements on both sides are in the beginning only imperceptible. J. Kepler When a quantity is greatest or least, at that moment its flow neither increases
1 Lagrange Multiplier Method Near a maximum the decrements on both sides are in the beginning only imperceptible. J. Kepler When a quantity is greatest or least, at that moment its flow neither increases
a x a y = a x+y a x a = y ax y (a x ) r = a rx and log a (xy) = log a (x) + log a (y) log a ( x y ) = log a(x) log a (y) log a (x r ) = r log a (x).
 You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
McGill University December Intermediate Calculus. Tuesday December 17, 2014 Time: 14:00-17:00
 McGill University December 214 Faculty of Science Final Examination Intermediate Calculus Math 262 Tuesday December 17, 214 Time: 14: - 17: Examiner: Dmitry Jakobson Associate Examiner: Neville Sancho
McGill University December 214 Faculty of Science Final Examination Intermediate Calculus Math 262 Tuesday December 17, 214 Time: 14: - 17: Examiner: Dmitry Jakobson Associate Examiner: Neville Sancho
Tutorial 3: Optimisation
 Tutorial : Optimisation ECO411F 011 1. Find and classify the extrema of the cubic cost function C = C (Q) = Q 5Q +.. Find and classify the extreme values of the following functions (a) y = x 1 + x x 1x
Tutorial : Optimisation ECO411F 011 1. Find and classify the extrema of the cubic cost function C = C (Q) = Q 5Q +.. Find and classify the extreme values of the following functions (a) y = x 1 + x x 1x
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM
 THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2. No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit.
 Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2 No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit. 1. ( 4 pts) Say which matrix is in row echelon form and which is not.
Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2 No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit. 1. ( 4 pts) Say which matrix is in row echelon form and which is not.
School of Business. Blank Page
 Maxima and Minima 9 This unit is designed to introduce the learners to the basic concepts associated with Optimization. The readers will learn about different types of functions that are closely related
Maxima and Minima 9 This unit is designed to introduce the learners to the basic concepts associated with Optimization. The readers will learn about different types of functions that are closely related
Tangent spaces, normals and extrema
 Chapter 3 Tangent spaces, normals and extrema If S is a surface in 3-space, with a point a S where S looks smooth, i.e., without any fold or cusp or self-crossing, we can intuitively define the tangent
Chapter 3 Tangent spaces, normals and extrema If S is a surface in 3-space, with a point a S where S looks smooth, i.e., without any fold or cusp or self-crossing, we can intuitively define the tangent
Microeconomics I. September, c Leopold Sögner
 Microeconomics I c Leopold Sögner Department of Economics and Finance Institute for Advanced Studies Stumpergasse 56 1060 Wien Tel: +43-1-59991 182 soegner@ihs.ac.at http://www.ihs.ac.at/ soegner September,
Microeconomics I c Leopold Sögner Department of Economics and Finance Institute for Advanced Studies Stumpergasse 56 1060 Wien Tel: +43-1-59991 182 soegner@ihs.ac.at http://www.ihs.ac.at/ soegner September,
