MCS 341 Probability Theory Name. Final Exam: Probability Theory 17 December 2010
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MCS 341 Probability Theory Name. Final Exam: Probability Theory 17 December 2010 This is a closed-book test. You may, however, use one new 3 -by-5 note card, your previous note cards, the tables provided, and a calculator (for calculation/graphing only). As usual, show support as appropriate. Do FIVE problems. Cross out the number of the one you do not want graded. Honor pledge: On my honor, I pledge that I have not given, received, or tolerated others use of unauthorized aid in completing this work. Please sign when you are finished: (signed) 1. (20%) BASIC CONCEPTS (a) What are the components of the basic probability space model (S, F,P)? (b) What are the postulates (of Kolmogorov) for the probability measure? (c) What is a random variable? (d) What is the distribution of a random variable?
2 2. (20%) In the Poisson process, the random number N t of arrivals during the time interval [0,t] (or any interval of duration t) has a Poisson distribution with parameter λt, where λ is a positive parameter (the average arrival rate). Also, the numbers of arrivals in nonoverlapping time intervals are independent random variables. (a) Let T 1 be the time (after t = 0) until the first arrival. Let t > 0. P(T 1 > t) =? (b) Let f(t) be the density function of the random time T 1. Using the previous part, deduce the simple formula for f(t) for t > 0, showing that T 1 has an Exponential distribution. (c) Let T 2 be the length of time after T 1 until the next arrival. Then T 1 and T 2 are independent random variables, and T 1 + T 2 is the time of the second arrival. What is the distribution of T 1 + T 2? Explain, or calculate the density.
3 3. (20%) (Jointly distributed discrete r.v.s) Assume that X and Y are discrete random variables whose joint probability function s nonzero values are given in the following table. x y (a) What is the (marginal) probability function of X? (b) What is the (marginal) probability function of Y? (c) What is the conditional probability function of Y given X? (Give defined non-zero values only.) (d) Are X and Y independent random variables? Explain. Continue on the next page.
4 The problem continues. Here, again, is the joint probability table. x y (e) Calculate the expected values of X and Y. (f) Calculate the variances of X and Y. (g) Calculate the variance of X Y.
5 4. (20%) Let X 1,X 2,X 3,... be independent random variables all having the Gamma(α,λ) distribution for some fixed α > 0 and λ > 0. (a) Show the calculation that leads to this formula for the moment generating function: for s < λ. m Xj (s) = ( λ ) α λ s (b) For n = 1,2,3,..., let S n = X 1 + X X n. Deduce the formula for the moment generating function of S n, and thence deduce the distribution of S n. (c) Now assume α = 4, λ = 0.1, and n = 49. Calculate a good approximation of the value of P(37 S n n 44).
6 5. (20%) (Probability calculations) The dice game craps is played with two presumably fair dice as follows: The player rolls the two dice. If the result is 7 or 11, the player wins, while if the result is 2, 3, or 12, the player loses. If the result is 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, or 10, then the player rolls the dice again, repeatedly if necessary, until the first result is matched a win for the player or a 7 is obtained a loss for the player. (a) Let X be the result of one roll of the two dice. Complete the following table giving the probability function of X, p X (x) = P(X = x) x p X (x) (b) Give a formula for the conditional probability that the player wins on the k th roll after the initial roll if 4 was the result of the initial roll. (c) Calculate the probability that the player first rolls a 4 and then ultimately wins. (d) (Extra credit) Show that the probability that the player wins is 244/495. (There s a relatively easy way to do it, and there s an arduous way.)
7 6. (20%) (Stochastic processes) (a) Suppose that X 1,X 2,X 3,... are independent identically distributed random variables, and suppose that P(X 1 = 1) = p, P(X 1 = 0) = q, P(X 1 = 1) = r where p,q,r are nonnegative numbers whose sum is 1. Let S 0 = X 0 and, for n > 0, let S n = X 0 + X 1 + X X n. Let T 0 denote the first time that S n = 0, i.e., T 0 = min{n : S n = 0}. Likewise, given a positive integer c, let T c denote the first time that S n = c, i.e., T c = min{n : S n = c}. (If S n is never c, we allow T c = ; likewise for T 0.) Let R k = P(T 0 < T c S 0 = k), which may be interpreted as the probability, starting at k, of getting to 0 before getting to c Deduce a recurrence equation for R k valid for integers k satisfying 0 < k < c. (b) Suppose that an electronic component has two states, zero (0), and one (1). Furthermore, at each tick of a clock, it may change state, depending on its current state. Let X n denote the state at time n, and assume that for n = 0,1,2,..., [ P(Xn+1 = 0 X n = 0) P(X n+1 = 1 X n = 0) P(X n+1 = 0 X n = 1) P(X n+1 = 1 X n = 1) Calculate [ P(X4 = 0 X 0 = 0) P(X 4 = 1 X 0 = 0) P(X 4 = 0 X 0 = 1) P(X 4 = 1 X 0 = 1) ] = ] [ ].
8 (Extra page) Merry Christmas! Happy Hanukkah! Habari Gani! Have a great break! References [1] Evans and Rosenthal, Probability and Statistics: The Science of Uncertainty 2/e, W.H. Freeman, New York, 2009.
MCS 256 Discrete Calculus and Probability Exam 5: Final Examination 22 May 2007
 MCS 256 Discrete Calculus and Probability SOLUTIONS Exam 5: Final Examination 22 May 2007 Instructions: This is a closed-book examination. You may, however, use one 8.5 -by-11 page of notes, your note
MCS 256 Discrete Calculus and Probability SOLUTIONS Exam 5: Final Examination 22 May 2007 Instructions: This is a closed-book examination. You may, however, use one 8.5 -by-11 page of notes, your note
HW1 (due 10/6/05): (from textbook) 1.2.3, 1.2.9, , , (extra credit) A fashionable country club has 100 members, 30 of whom are
 HW1 (due 10/6/05): (from textbook) 1.2.3, 1.2.9, 1.2.11, 1.2.12, 1.2.16 (extra credit) A fashionable country club has 100 members, 30 of whom are lawyers. Rumor has it that 25 of the club members are liars
HW1 (due 10/6/05): (from textbook) 1.2.3, 1.2.9, 1.2.11, 1.2.12, 1.2.16 (extra credit) A fashionable country club has 100 members, 30 of whom are lawyers. Rumor has it that 25 of the club members are liars
Math 493 Final Exam December 01
 Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
You may use a calculator. Translation: Show all of your work; use a calculator only to do final calculations and/or to check your work.
 GROUND RULES: Print your name at the top of this page. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You may use a calculator. Translation: Show all of your work; use a calculator only to do final calculations
GROUND RULES: Print your name at the top of this page. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You may use a calculator. Translation: Show all of your work; use a calculator only to do final calculations
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2015 MODULE 1 : Probability distributions Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2015 MODULE 1 : Probability distributions Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
MAS108 Probability I
 1 BSc Examination 2008 By Course Units 2:30 pm, Thursday 14 August, 2008 Duration: 2 hours MAS108 Probability I Do not start reading the question paper until you are instructed to by the invigilators.
1 BSc Examination 2008 By Course Units 2:30 pm, Thursday 14 August, 2008 Duration: 2 hours MAS108 Probability I Do not start reading the question paper until you are instructed to by the invigilators.
December 2010 Mathematics 302 Name Page 2 of 11 pages
 December 2010 Mathematics 302 Name Page 2 of 11 pages [9] 1. An urn contains red balls, 10 green balls and 1 yellow balls. You randomly select balls, without replacement. (a What ( is( the probability
December 2010 Mathematics 302 Name Page 2 of 11 pages [9] 1. An urn contains red balls, 10 green balls and 1 yellow balls. You randomly select balls, without replacement. (a What ( is( the probability
FINAL EXAM: Monday 8-10am
 ECE 30: Probabilistic Methods in Electrical and Computer Engineering Fall 016 Instructor: Prof. A. R. Reibman FINAL EXAM: Monday 8-10am Fall 016, TTh 3-4:15pm (December 1, 016) This is a closed book exam.
ECE 30: Probabilistic Methods in Electrical and Computer Engineering Fall 016 Instructor: Prof. A. R. Reibman FINAL EXAM: Monday 8-10am Fall 016, TTh 3-4:15pm (December 1, 016) This is a closed book exam.
Probability Midterm Exam 2:15-3:30 pm Thursday, 21 October 1999
 Name: 2:15-3:30 pm Thursday, 21 October 1999 You may use a calculator and your own notes but may not consult your books or neighbors. Please show your work for partial credit, and circle your answers.
Name: 2:15-3:30 pm Thursday, 21 October 1999 You may use a calculator and your own notes but may not consult your books or neighbors. Please show your work for partial credit, and circle your answers.
Probability Models. 4. What is the definition of the expectation of a discrete random variable?
 1 Probability Models The list of questions below is provided in order to help you to prepare for the test and exam. It reflects only the theoretical part of the course. You should expect the questions
1 Probability Models The list of questions below is provided in order to help you to prepare for the test and exam. It reflects only the theoretical part of the course. You should expect the questions
1. Consider a random independent sample of size 712 from a distribution with the following pdf. c 1+x. f(x) =
 1. Consider a random independent sample of size 712 from a distribution with the following pdf f(x) = c 1+x 0
1. Consider a random independent sample of size 712 from a distribution with the following pdf f(x) = c 1+x 0
Math 407: Probability Theory 5/10/ Final exam (11am - 1pm)
 Math 407: Probability Theory 5/10/2013 - Final exam (11am - 1pm) Name: USC ID: Signature: 1. Write your name and ID number in the spaces above. 2. Show all your work and circle your final answer. Simplify
Math 407: Probability Theory 5/10/2013 - Final exam (11am - 1pm) Name: USC ID: Signature: 1. Write your name and ID number in the spaces above. 2. Show all your work and circle your final answer. Simplify
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY (formerly the Examinations of the Institute of Statisticians) GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2004
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY (formerly the Examinations of the Institute of Statisticians) GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 004 Statistical Theory and Methods I Time Allowed: Three Hours Candidates should
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY (formerly the Examinations of the Institute of Statisticians) GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 004 Statistical Theory and Methods I Time Allowed: Three Hours Candidates should
December 2010 Mathematics 302 Name Page 2 of 11 pages
 December 2010 Mathematics 302 Name Page 2 of 11 pages [9] 1. An urn contains 5 red balls, 10 green balls and 15 yellow balls. You randomly select 5 balls, without replacement. What is the probability that
December 2010 Mathematics 302 Name Page 2 of 11 pages [9] 1. An urn contains 5 red balls, 10 green balls and 15 yellow balls. You randomly select 5 balls, without replacement. What is the probability that
Math 218 Supplemental Instruction Spring 2008 Final Review Part A
 Spring 2008 Final Review Part A SI leaders: Mario Panak, Jackie Hu, Christina Tasooji Chapters 3, 4, and 5 Topics Covered: General probability (probability laws, conditional, joint probabilities, independence)
Spring 2008 Final Review Part A SI leaders: Mario Panak, Jackie Hu, Christina Tasooji Chapters 3, 4, and 5 Topics Covered: General probability (probability laws, conditional, joint probabilities, independence)
Exercises in Probability Theory Paul Jung MA 485/585-1C Fall 2015 based on material of Nikolai Chernov
 Exercises in Probability Theory Paul Jung MA 485/585-1C Fall 2015 based on material of Nikolai Chernov Many of the exercises are taken from two books: R. Durrett, The Essentials of Probability, Duxbury
Exercises in Probability Theory Paul Jung MA 485/585-1C Fall 2015 based on material of Nikolai Chernov Many of the exercises are taken from two books: R. Durrett, The Essentials of Probability, Duxbury
Final Exam. Math Su10. by Prof. Michael Cap Khoury
 Final Exam Math 45-0 Su0 by Prof. Michael Cap Khoury Name: Directions: Please print your name legibly in the box above. You have 0 minutes to complete this exam. You may use any type of conventional calculator,
Final Exam Math 45-0 Su0 by Prof. Michael Cap Khoury Name: Directions: Please print your name legibly in the box above. You have 0 minutes to complete this exam. You may use any type of conventional calculator,
STAT 414: Introduction to Probability Theory
 STAT 414: Introduction to Probability Theory Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical Exercises
STAT 414: Introduction to Probability Theory Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical Exercises
STAT 418: Probability and Stochastic Processes
 STAT 418: Probability and Stochastic Processes Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical
STAT 418: Probability and Stochastic Processes Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical
4 Branching Processes
 4 Branching Processes Organise by generations: Discrete time. If P(no offspring) 0 there is a probability that the process will die out. Let X = number of offspring of an individual p(x) = P(X = x) = offspring
4 Branching Processes Organise by generations: Discrete time. If P(no offspring) 0 there is a probability that the process will die out. Let X = number of offspring of an individual p(x) = P(X = x) = offspring
Edexcel past paper questions
 Edexcel past paper questions Statistics 1 Discrete Random Variables Past examination questions Discrete Random variables Page 1 Discrete random variables Discrete Random variables Page 2 Discrete Random
Edexcel past paper questions Statistics 1 Discrete Random Variables Past examination questions Discrete Random variables Page 1 Discrete random variables Discrete Random variables Page 2 Discrete Random
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/86/94002861.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 8 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 8 Notes Goals for Today Counting Partitions
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 8 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 8 Notes Goals for Today Counting Partitions
MAT 271E Probability and Statistics
 MAT 271E Probability and Statistics Spring 2011 Instructor : Class Meets : Office Hours : Textbook : Supp. Text : İlker Bayram EEB 1103 ibayram@itu.edu.tr 13.30 16.30, Wednesday EEB? 10.00 12.00, Wednesday
MAT 271E Probability and Statistics Spring 2011 Instructor : Class Meets : Office Hours : Textbook : Supp. Text : İlker Bayram EEB 1103 ibayram@itu.edu.tr 13.30 16.30, Wednesday EEB? 10.00 12.00, Wednesday
CME 106: Review Probability theory
 : Probability theory Sven Schmit April 3, 2015 1 Overview In the first half of the course, we covered topics from probability theory. The difference between statistics and probability theory is the following:
: Probability theory Sven Schmit April 3, 2015 1 Overview In the first half of the course, we covered topics from probability theory. The difference between statistics and probability theory is the following:
MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS July 1, 2011 FINAL EXAM
 MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS July 1, 2011 FINAL EXAM YOUR NAME: KEY: Answers in blue Show all your work. Answers out of the blue and without any supporting work may receive no credit even if they are
MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS July 1, 2011 FINAL EXAM YOUR NAME: KEY: Answers in blue Show all your work. Answers out of the blue and without any supporting work may receive no credit even if they are
Conditional Probability and Independence
 Conditional Probability and Independence September 3, 2009 1 Restricting the Sample Space - Conditional Probability How do we modify the probability of an event in light of the fact that something is known?
Conditional Probability and Independence September 3, 2009 1 Restricting the Sample Space - Conditional Probability How do we modify the probability of an event in light of the fact that something is known?
Is this a fair game? Great Expectations. win $1 for each match lose $1 if no match
 Mathematics for Computer Science MIT 6.042J/18.062J Great Expectations Choose a number from 1 to 6, then roll 3 fair dice: win $1 for each match lose $1 if no match expect_intro.1 expect_intro.3 Example:
Mathematics for Computer Science MIT 6.042J/18.062J Great Expectations Choose a number from 1 to 6, then roll 3 fair dice: win $1 for each match lose $1 if no match expect_intro.1 expect_intro.3 Example:
(b) What is the variance of the time until the second customer arrives, starting empty, assuming that we measure time in minutes?
 IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
MATH 151, FINAL EXAM Winter Quarter, 21 March, 2014
 Time: 3 hours, 8:3-11:3 Instructions: MATH 151, FINAL EXAM Winter Quarter, 21 March, 214 (1) Write your name in blue-book provided and sign that you agree to abide by the honor code. (2) The exam consists
Time: 3 hours, 8:3-11:3 Instructions: MATH 151, FINAL EXAM Winter Quarter, 21 March, 214 (1) Write your name in blue-book provided and sign that you agree to abide by the honor code. (2) The exam consists
452 FINAL- VERSION E Do not open this exam until you are told. Read these instructions:
 1 452 FINAL- VERSION E Do not open this exam until you are told. Read these instructions: 1. This is a closed book exam, though one sheet of notes is allowed. No calculators, or other aids are allowed.
1 452 FINAL- VERSION E Do not open this exam until you are told. Read these instructions: 1. This is a closed book exam, though one sheet of notes is allowed. No calculators, or other aids are allowed.
Math 20 Spring Discrete Probability. Midterm Exam
 Math 20 Spring 203 Discrete Probability Midterm Exam Thursday April 25, 5:00 7:00 PM Your name (please print): Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. Use of calculators is not permitted.
Math 20 Spring 203 Discrete Probability Midterm Exam Thursday April 25, 5:00 7:00 PM Your name (please print): Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. Use of calculators is not permitted.
MAT 135B Midterm 1 Solutions
 MAT 35B Midterm Solutions Last Name (PRINT): First Name (PRINT): Student ID #: Section: Instructions:. Do not open your test until you are told to begin. 2. Use a pen to print your name in the spaces above.
MAT 35B Midterm Solutions Last Name (PRINT): First Name (PRINT): Student ID #: Section: Instructions:. Do not open your test until you are told to begin. 2. Use a pen to print your name in the spaces above.
Question Paper Code : AEC11T03
 Hall Ticket No Question Paper Code : AEC11T03 VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Affiliated to JNTUH, Hyderabad Four Year B Tech III Semester Tutorial Question Bank 2013-14 (Regulations: VCE-R11)
Hall Ticket No Question Paper Code : AEC11T03 VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Affiliated to JNTUH, Hyderabad Four Year B Tech III Semester Tutorial Question Bank 2013-14 (Regulations: VCE-R11)
2. Suppose (X, Y ) is a pair of random variables uniformly distributed over the triangle with vertices (0, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1).
 Name M362K Final Exam Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. There is a table of formulae on the last page. 1. Suppose X 1,..., X 1 are independent
Name M362K Final Exam Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. There is a table of formulae on the last page. 1. Suppose X 1,..., X 1 are independent
Name of the Student: Problems on Discrete & Continuous R.Vs
 Engineering Mathematics 08 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Random Processes SUBJECT CODE : MA645 MATERIAL NAME : University Questions REGULATION : R03 UPDATED ON : November 07 (Upto N/D 07 Q.P) (Scan the
Engineering Mathematics 08 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Random Processes SUBJECT CODE : MA645 MATERIAL NAME : University Questions REGULATION : R03 UPDATED ON : November 07 (Upto N/D 07 Q.P) (Scan the
Name of the Student:
 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes Midterm Quiz April 6, 2010 There are 5 questions, each with several parts.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes Midterm Quiz April 6, 2010 There are 5 questions, each with several parts.
MAS275 Probability Modelling Exercises
 MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
Stat 426 : Homework 1.
 Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
Math 510 midterm 3 answers
 Math 51 midterm 3 answers Problem 1 (1 pts) Suppose X and Y are independent exponential random variables both with parameter λ 1. Find the probability that Y < 7X. P (Y < 7X) 7x 7x f(x, y) dy dx e x e
Math 51 midterm 3 answers Problem 1 (1 pts) Suppose X and Y are independent exponential random variables both with parameter λ 1. Find the probability that Y < 7X. P (Y < 7X) 7x 7x f(x, y) dy dx e x e
n(1 p i ) n 1 p i = 1 3 i=1 E(X i p = p i )P(p = p i ) = 1 3 p i = n 3 (p 1 + p 2 + p 3 ). p i i=1 P(X i = 1 p = p i )P(p = p i ) = p1+p2+p3
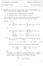 Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
MATH 19B FINAL EXAM PROBABILITY REVIEW PROBLEMS SPRING, 2010
 MATH 9B FINAL EXAM PROBABILITY REVIEW PROBLEMS SPRING, 00 This handout is meant to provide a collection of exercises that use the material from the probability and statistics portion of the course The
MATH 9B FINAL EXAM PROBABILITY REVIEW PROBLEMS SPRING, 00 This handout is meant to provide a collection of exercises that use the material from the probability and statistics portion of the course The
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Spring 2015 Abhay Parekh February 17, 2015.
 EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Spring 2015 Abhay Parekh February 17, 2015 Midterm Exam Last name First name SID Rules. You have 80 mins (5:10pm - 6:30pm)
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Spring 2015 Abhay Parekh February 17, 2015 Midterm Exam Last name First name SID Rules. You have 80 mins (5:10pm - 6:30pm)
Discrete Random Variable
 Discrete Random Variable Outcome of a random experiment need not to be a number. We are generally interested in some measurement or numerical attribute of the outcome, rather than the outcome itself. n
Discrete Random Variable Outcome of a random experiment need not to be a number. We are generally interested in some measurement or numerical attribute of the outcome, rather than the outcome itself. n
What is Probability? Probability. Sample Spaces and Events. Simple Event
 What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2016 MODULE 1 : Probability distributions Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2016 MODULE 1 : Probability distributions Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models. Professor Whitt. SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2
 IEOR 316: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2 More Probability Review: In the Ross textbook, Introduction to Probability Models, read
IEOR 316: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2 More Probability Review: In the Ross textbook, Introduction to Probability Models, read
Course: ESO-209 Home Work: 1 Instructor: Debasis Kundu
 Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Discrete Random Variables
 CPSC 53 Systems Modeling and Simulation Discrete Random Variables Dr. Anirban Mahanti Department of Computer Science University of Calgary mahanti@cpsc.ucalgary.ca Random Variables A random variable is
CPSC 53 Systems Modeling and Simulation Discrete Random Variables Dr. Anirban Mahanti Department of Computer Science University of Calgary mahanti@cpsc.ucalgary.ca Random Variables A random variable is
FINAL EXAM: 3:30-5:30pm
 ECE 30: Probabilistic Methods in Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 016 Instructor: Prof. A. R. Reibman FINAL EXAM: 3:30-5:30pm Spring 016, MWF 1:30-1:0pm (May 6, 016) This is a closed book exam.
ECE 30: Probabilistic Methods in Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 016 Instructor: Prof. A. R. Reibman FINAL EXAM: 3:30-5:30pm Spring 016, MWF 1:30-1:0pm (May 6, 016) This is a closed book exam.
Chapter 5. Chapter 5 sections
 1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
*Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2016
 *Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2016 Name (Print): uniqname (Print): Instructions. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. You may have two page of notes (8.5x11.5 two-sided) but may not use any other
*Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2016 Name (Print): uniqname (Print): Instructions. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. You may have two page of notes (8.5x11.5 two-sided) but may not use any other
University of Illinois ECE 313: Final Exam Fall 2014
 University of Illinois ECE 313: Final Exam Fall 2014 Monday, December 15, 2014, 7:00 p.m. 10:00 p.m. Sect. B, names A-O, 1013 ECE, names P-Z, 1015 ECE; Section C, names A-L, 1015 ECE; all others 112 Gregory
University of Illinois ECE 313: Final Exam Fall 2014 Monday, December 15, 2014, 7:00 p.m. 10:00 p.m. Sect. B, names A-O, 1013 ECE, names P-Z, 1015 ECE; Section C, names A-L, 1015 ECE; all others 112 Gregory
1 Presessional Probability
 1 Presessional Probability Probability theory is essential for the development of mathematical models in finance, because of the randomness nature of price fluctuations in the markets. This presessional
1 Presessional Probability Probability theory is essential for the development of mathematical models in finance, because of the randomness nature of price fluctuations in the markets. This presessional
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models. Winter Midterm Exam Friday, Feb 8, 2013
 Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Friday, Feb 8, 2013 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Friday, Feb 8, 2013 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Math st Homework. First part of Chapter 2. Due Friday, September 17, 1999.
 Math 447. 1st Homework. First part of Chapter 2. Due Friday, September 17, 1999. 1. How many different seven place license plates are possible if the first 3 places are to be occupied by letters and the
Math 447. 1st Homework. First part of Chapter 2. Due Friday, September 17, 1999. 1. How many different seven place license plates are possible if the first 3 places are to be occupied by letters and the
6.041/6.431 Spring 2009 Quiz 1 Wednesday, March 11, 7:30-9:30 PM. SOLUTIONS
 6.0/6.3 Spring 009 Quiz Wednesday, March, 7:30-9:30 PM. SOLUTIONS Name: Recitation Instructor: Question Part Score Out of 0 all 0 a 5 b c 5 d 5 e 5 f 5 3 a b c d 5 e 5 f 5 g 5 h 5 Total 00 Write your solutions
6.0/6.3 Spring 009 Quiz Wednesday, March, 7:30-9:30 PM. SOLUTIONS Name: Recitation Instructor: Question Part Score Out of 0 all 0 a 5 b c 5 d 5 e 5 f 5 3 a b c d 5 e 5 f 5 g 5 h 5 Total 00 Write your solutions
Computations - Show all your work. (30 pts)
 Math 1012 Final Name: Computations - Show all your work. (30 pts) 1. Fractions. a. 1 7 + 1 5 b. 12 5 5 9 c. 6 8 2 16 d. 1 6 + 2 5 + 3 4 2.a Powers of ten. i. 10 3 10 2 ii. 10 2 10 6 iii. 10 0 iv. (10 5
Math 1012 Final Name: Computations - Show all your work. (30 pts) 1. Fractions. a. 1 7 + 1 5 b. 12 5 5 9 c. 6 8 2 16 d. 1 6 + 2 5 + 3 4 2.a Powers of ten. i. 10 3 10 2 ii. 10 2 10 6 iii. 10 0 iv. (10 5
ORF 245 Fundamentals of Engineering Statistics. Final Exam
 Princeton University Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering ORF 45 Fundamentals of Engineering Statistics Final Exam May 15, 009 1:30pm-4:30pm PLEASE DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE AND START
Princeton University Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering ORF 45 Fundamentals of Engineering Statistics Final Exam May 15, 009 1:30pm-4:30pm PLEASE DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE AND START
Math 16 - Practice Final
 Math 16 - Practice Final May 28th 2007 Name: Instructions 1. In Part A, attempt every question. In Part B, attempt two of the five questions. If you attempt more you will only receive credit for your best
Math 16 - Practice Final May 28th 2007 Name: Instructions 1. In Part A, attempt every question. In Part B, attempt two of the five questions. If you attempt more you will only receive credit for your best
Lecture 10: Probability distributions TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019
 Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
The exponential distribution and the Poisson process
 The exponential distribution and the Poisson process 1-1 Exponential Distribution: Basic Facts PDF f(t) = { λe λt, t 0 0, t < 0 CDF Pr{T t) = 0 t λe λu du = 1 e λt (t 0) Mean E[T] = 1 λ Variance Var[T]
The exponential distribution and the Poisson process 1-1 Exponential Distribution: Basic Facts PDF f(t) = { λe λt, t 0 0, t < 0 CDF Pr{T t) = 0 t λe λu du = 1 e λt (t 0) Mean E[T] = 1 λ Variance Var[T]
Exam III #1 Solutions
 Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 10120 Finite Math Fall 2017 Name: Instructors: Basit & Migliore Exam III #1 Solutions November 14, 2017 This exam is in two parts on 11 pages and
Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 10120 Finite Math Fall 2017 Name: Instructors: Basit & Migliore Exam III #1 Solutions November 14, 2017 This exam is in two parts on 11 pages and
Işık University Math 230 Exam I Exam Duration : 1 hr 30 min Nov. 12, Last Name : First Name : Student Number : Section :
 Işık University Math 230 Exam I Exam Duration : 1 hr 30 min Nov. 12, 2012 Last Name : First Name : Student Number : Section : 1 2 3 Instructor :Deniz Karlı Row #: / Sinan Özeren Directions. Please read
Işık University Math 230 Exam I Exam Duration : 1 hr 30 min Nov. 12, 2012 Last Name : First Name : Student Number : Section : 1 2 3 Instructor :Deniz Karlı Row #: / Sinan Özeren Directions. Please read
*Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2016
 *Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2016 Name (Print): uniqname (Print): Instructions. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. You may have two pages of notes (8.5x11.5 two-sided) but may not use any other
*Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2016 Name (Print): uniqname (Print): Instructions. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. You may have two pages of notes (8.5x11.5 two-sided) but may not use any other
Math 447. Introduction to Probability and Statistics I. Fall 1998.
 Math 447. Introduction to Probability and Statistics I. Fall 1998. Schedule: M. W. F.: 08:00-09:30 am. SW 323 Textbook: Introduction to Mathematical Statistics by R. V. Hogg and A. T. Craig, 1995, Fifth
Math 447. Introduction to Probability and Statistics I. Fall 1998. Schedule: M. W. F.: 08:00-09:30 am. SW 323 Textbook: Introduction to Mathematical Statistics by R. V. Hogg and A. T. Craig, 1995, Fifth
Statistics for Economists. Lectures 3 & 4
 Statistics for Economists Lectures 3 & 4 Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University 1 CHAPTER 2- Discrete Distributions 2.1. Random variables of the Discrete Type Definition 2.1.1: Given a random experiment with
Statistics for Economists Lectures 3 & 4 Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University 1 CHAPTER 2- Discrete Distributions 2.1. Random variables of the Discrete Type Definition 2.1.1: Given a random experiment with
Math Fall 2010 Some Old Math 302 Exams There is always a danger when distributing old exams for a class that students will rely on them
 Math 302.102 Fall 2010 Some Old Math 302 Exams There is always a danger when distributing old exams for a class that students will rely on them solely for their final exam preparations. The final exam
Math 302.102 Fall 2010 Some Old Math 302 Exams There is always a danger when distributing old exams for a class that students will rely on them solely for their final exam preparations. The final exam
(b). What is an expression for the exact value of P(X = 4)? 2. (a). Suppose that the moment generating function for X is M (t) = 2et +1 3
 Math 511 Exam #2 Show All Work 1. A package of 200 seeds contains 40 that are defective and will not grow (the rest are fine). Suppose that you choose a sample of 10 seeds from the box without replacement.
Math 511 Exam #2 Show All Work 1. A package of 200 seeds contains 40 that are defective and will not grow (the rest are fine). Suppose that you choose a sample of 10 seeds from the box without replacement.
3.5. First step analysis
 12 3.5. First step analysis A journey of a thousand miles begins with the first step. Lao Tse Example 3.6. (Coin Tossing) Repeatedly toss a fair coin a number of times. What s the expected number of tosses
12 3.5. First step analysis A journey of a thousand miles begins with the first step. Lao Tse Example 3.6. (Coin Tossing) Repeatedly toss a fair coin a number of times. What s the expected number of tosses
Math , Fall 2012: HW 5 Solutions
 Math 230.0, Fall 202: HW 5 Solutions Due Thursday, October 4th, 202. Problem (p.58 #2). Let X and Y be the numbers obtained in two draws at random from a box containing four tickets labeled, 2, 3, 4. Display
Math 230.0, Fall 202: HW 5 Solutions Due Thursday, October 4th, 202. Problem (p.58 #2). Let X and Y be the numbers obtained in two draws at random from a box containing four tickets labeled, 2, 3, 4. Display
DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO
 QUESTION BOOKLET EE 126 Spring 26 Midterm #2 Thursday, April 13, 11:1-12:3pm DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO You have 8 minutes to complete the midterm. The midterm consists
QUESTION BOOKLET EE 126 Spring 26 Midterm #2 Thursday, April 13, 11:1-12:3pm DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO You have 8 minutes to complete the midterm. The midterm consists
for valid PSD. PART B (Answer all five units, 5 X 10 = 50 Marks) UNIT I
 Code: 15A04304 R15 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R15) Regular Examinations November/December 016 PROBABILITY THEY & STOCHASTIC PROCESSES (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Code: 15A04304 R15 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R15) Regular Examinations November/December 016 PROBABILITY THEY & STOCHASTIC PROCESSES (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
1. Let X and Y be independent exponential random variables with rate α. Find the densities of the random variables X 3, X Y, min(x, Y 3 )
 1 Introduction These problems are meant to be practice problems for you to see if you have understood the material reasonably well. They are neither exhaustive (e.g. Diffusions, continuous time branching
1 Introduction These problems are meant to be practice problems for you to see if you have understood the material reasonably well. They are neither exhaustive (e.g. Diffusions, continuous time branching
Solutionbank S1 Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics
 Heinemann Solutionbank: Statistics S Page of Solutionbank S Exercise A, Question Write down whether or not each of the following is a discrete random variable. Give a reason for your answer. a The average
Heinemann Solutionbank: Statistics S Page of Solutionbank S Exercise A, Question Write down whether or not each of the following is a discrete random variable. Give a reason for your answer. a The average
Probability & Statistics - FALL 2008 FINAL EXAM
 550.3 Probability & Statistics - FALL 008 FINAL EXAM NAME. An urn contains white marbles and 8 red marbles. A marble is drawn at random from the urn 00 times with replacement. Which of the following is
550.3 Probability & Statistics - FALL 008 FINAL EXAM NAME. An urn contains white marbles and 8 red marbles. A marble is drawn at random from the urn 00 times with replacement. Which of the following is
ECE 302 Division 2 Exam 2 Solutions, 11/4/2009.
 NAME: ECE 32 Division 2 Exam 2 Solutions, /4/29. You will be required to show your student ID during the exam. This is a closed-book exam. A formula sheet is provided. No calculators are allowed. Total
NAME: ECE 32 Division 2 Exam 2 Solutions, /4/29. You will be required to show your student ID during the exam. This is a closed-book exam. A formula sheet is provided. No calculators are allowed. Total
Statistics for Economists Lectures 6 & 7. Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University
 Statistics for Economists Lectures 6 & 7 Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University 1 Chapter 4- Bivariate Distributions 41 Distributions of two random variables Definition 41-1: Let X and Y be two random variables
Statistics for Economists Lectures 6 & 7 Asrat Temesgen Stockholm University 1 Chapter 4- Bivariate Distributions 41 Distributions of two random variables Definition 41-1: Let X and Y be two random variables
Lecture 4 - Random walk, ruin problems and random processes
 Lecture 4 - Random walk, ruin problems and random processes Jan Bouda FI MU April 19, 2009 Jan Bouda (FI MU) Lecture 4 - Random walk, ruin problems and random processesapril 19, 2009 1 / 30 Part I Random
Lecture 4 - Random walk, ruin problems and random processes Jan Bouda FI MU April 19, 2009 Jan Bouda (FI MU) Lecture 4 - Random walk, ruin problems and random processesapril 19, 2009 1 / 30 Part I Random
Lecture 4. David Aldous. 2 September David Aldous Lecture 4
 Lecture 4 David Aldous 2 September 2015 The specific examples I m discussing are not so important; the point of these first lectures is to illustrate a few of the 100 ideas from STAT134. Ideas used in
Lecture 4 David Aldous 2 September 2015 The specific examples I m discussing are not so important; the point of these first lectures is to illustrate a few of the 100 ideas from STAT134. Ideas used in
Brief Review of Probability
 Brief Review of Probability Nuno Vasconcelos (Ken Kreutz-Delgado) ECE Department, UCSD Probability Probability theory is a mathematical language to deal with processes or experiments that are non-deterministic
Brief Review of Probability Nuno Vasconcelos (Ken Kreutz-Delgado) ECE Department, UCSD Probability Probability theory is a mathematical language to deal with processes or experiments that are non-deterministic
TMA4265 Stochastic processes ST2101 Stochastic simulation and modelling
 Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences Page of 7 English Contact during examination: Øyvind Bakke Telephone: 73 9 8 26, 99 4 673 TMA426 Stochastic processes
Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences Page of 7 English Contact during examination: Øyvind Bakke Telephone: 73 9 8 26, 99 4 673 TMA426 Stochastic processes
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. Joint probability distributions
 Universit of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 100A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Joint probabilit distributions So far we have considered onl distributions with one random variable.
Universit of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 100A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Joint probabilit distributions So far we have considered onl distributions with one random variable.
Discrete Random Variables
 Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan 2014 Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random
Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan 2014 Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random
Discrete Random Variables
 Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random processes,
Discrete Random Variables An Undergraduate Introduction to Financial Mathematics J. Robert Buchanan Introduction The markets can be thought of as a complex interaction of a large number of random processes,
Multivariate distributions
 CHAPTER Multivariate distributions.. Introduction We want to discuss collections of random variables (X, X,..., X n ), which are known as random vectors. In the discrete case, we can define the density
CHAPTER Multivariate distributions.. Introduction We want to discuss collections of random variables (X, X,..., X n ), which are known as random vectors. In the discrete case, we can define the density
*Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2015
 *Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2015 Name (Print): uniqname (Print): Instructions. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. You may have one page of notes (8.5x11.5 two-sided) but may not use any other
*Final Exam* EECS 203 Spring 2015 Name (Print): uniqname (Print): Instructions. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. You may have one page of notes (8.5x11.5 two-sided) but may not use any other
IE 230 Probability & Statistics in Engineering I. Closed book and notes. 60 minutes.
 Closed book and notes. 60 minutes. A summary table of some univariate continuous distributions is provided. Four Pages. In this version of the Key, I try to be more complete than necessary to receive full
Closed book and notes. 60 minutes. A summary table of some univariate continuous distributions is provided. Four Pages. In this version of the Key, I try to be more complete than necessary to receive full
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS June 15, 2011 MIDTERM EXAM
 MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS June 15, 2011 MIDTERM EXAM YOUR NAME: KEY: Answers in Blue Show all your work. Answers out of the blue and without any supporting work may receive no credit even if they
MATH 3510: PROBABILITY AND STATS June 15, 2011 MIDTERM EXAM YOUR NAME: KEY: Answers in Blue Show all your work. Answers out of the blue and without any supporting work may receive no credit even if they
18.05 Final Exam. Good luck! Name. No calculators. Number of problems 16 concept questions, 16 problems, 21 pages
 Name No calculators. 18.05 Final Exam Number of problems 16 concept questions, 16 problems, 21 pages Extra paper If you need more space we will provide some blank paper. Indicate clearly that your solution
Name No calculators. 18.05 Final Exam Number of problems 16 concept questions, 16 problems, 21 pages Extra paper If you need more space we will provide some blank paper. Indicate clearly that your solution
Lynch 2017 Page 1 of 5. Math 150, Fall 2017 Exam 1 Form A Multiple Choice
 Lynch 017 Page 1 of 5 Math 150, Fall 017 Exam 1 Form A Multiple Choice Last Name: First Name: Section Number: Student ID number: Directions: 1. No calculators, cell phones, or other electronic devices
Lynch 017 Page 1 of 5 Math 150, Fall 017 Exam 1 Form A Multiple Choice Last Name: First Name: Section Number: Student ID number: Directions: 1. No calculators, cell phones, or other electronic devices
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models. Professor Whitt. SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 1
 IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 1 Probability Review: Read Chapters 1 and 2 in the textbook, Introduction to Probability
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 1 Probability Review: Read Chapters 1 and 2 in the textbook, Introduction to Probability
Things to remember when learning probability distributions:
 SPECIAL DISTRIBUTIONS Some distributions are special because they are useful They include: Poisson, exponential, Normal (Gaussian), Gamma, geometric, negative binomial, Binomial and hypergeometric distributions
SPECIAL DISTRIBUTIONS Some distributions are special because they are useful They include: Poisson, exponential, Normal (Gaussian), Gamma, geometric, negative binomial, Binomial and hypergeometric distributions
 IE 361 EXAM #3 FALL 2013 Show your work: Partial credit can only be given for incorrect answers if there is enough information to clearly see what you were trying to do. There are two additional blank
IE 361 EXAM #3 FALL 2013 Show your work: Partial credit can only be given for incorrect answers if there is enough information to clearly see what you were trying to do. There are two additional blank
No books, no notes, only SOA-approved calculators. Please put your answers in the spaces provided!
 Math 447 Final Exam Fall 2015 No books, no notes, only SOA-approved calculators. Please put your answers in the spaces provided! Name: Section: Question Points Score 1 8 2 6 3 10 4 19 5 9 6 10 7 14 8 14
Math 447 Final Exam Fall 2015 No books, no notes, only SOA-approved calculators. Please put your answers in the spaces provided! Name: Section: Question Points Score 1 8 2 6 3 10 4 19 5 9 6 10 7 14 8 14
STAT 516 Midterm Exam 2 Friday, March 7, 2008
 STAT 516 Midterm Exam 2 Friday, March 7, 2008 Name Purdue student ID (10 digits) 1. The testing booklet contains 8 questions. 2. Permitted Texas Instruments calculators: BA-35 BA II Plus BA II Plus Professional
STAT 516 Midterm Exam 2 Friday, March 7, 2008 Name Purdue student ID (10 digits) 1. The testing booklet contains 8 questions. 2. Permitted Texas Instruments calculators: BA-35 BA II Plus BA II Plus Professional
Midterm Exam Business Statistics Fall 2001 Russell
 Name Midterm Exam Business Statistics Fall 001 Russell Do not turn over this page until you are told to do so. You will have 1 hour and 0 minutes to complete the exam. There are a total of 100 points divided
Name Midterm Exam Business Statistics Fall 001 Russell Do not turn over this page until you are told to do so. You will have 1 hour and 0 minutes to complete the exam. There are a total of 100 points divided
18.05 Practice Final Exam
 No calculators. 18.05 Practice Final Exam Number of problems 16 concept questions, 16 problems. Simplifying expressions Unless asked to explicitly, you don t need to simplify complicated expressions. For
No calculators. 18.05 Practice Final Exam Number of problems 16 concept questions, 16 problems. Simplifying expressions Unless asked to explicitly, you don t need to simplify complicated expressions. For
Physics 201, Exam 3 -- Summer 2017
 Physics 201, Exam 3 -- Summer 2017 Name (printed) On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam. The fill-in-the-blank and multiple-choice
Physics 201, Exam 3 -- Summer 2017 Name (printed) On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam. The fill-in-the-blank and multiple-choice
