A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic
|
|
|
- Sherman Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx): 1 10 PII: (xxxx)-0x A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic Ma Li Philosophy Department, Peking University mq2828@126.com Abstract. Description Logics (DLs) model concepts, roles, and individuals. Especially, concept is the main modeling object. DLs describe the intension of concepts implicitly only by means of the subsuption relationship between concepts. As it is known, the intension of a concept not only involves the relationship with other concepts, but also some properties of its own. This paper extend the generic sentences to the basic description logic ALC, and get a new logic G-ALC. A kind of intensional semantics is provided to G-ALC, according to which a tableau algorithm is proposed for the reasoning problems of G-ALC. The important properties such as soundness and completeness of this algorithm are strictly proved. Keywords: Description Logic, Generic Sentence, Extension, Tableau Algorithm, Soundness, Completeness 1 Introduction This paper backgrounds on the concept descriptions in the description logics (DLs) [4]. DLs mainly model concepts, roles and individuals, and especially concepts are the important modeling elements. Though concepts extensions are explicitly interpreted by a collection of objects, the intensions are only dealed implicitly by the subsumption relationship between concepts. As a matter of fact, a concept has many intensions besides the relationship with other concepts. For instance, the concept bird has the intension being a subconcept of animal, as well as the intensions such as fly, feathered, lay eggs,. Hence, concepts also need to be interpreted intensionally. In order to describe the knowledge more precisely, DLs need to take care of the concepts intensions. To enhance the intensional expressive power of DLs, this paper extend a kind of intensional knowledge, generic sentences [1, 13], to the basic description logic ALC, and get a new logic denoted as G-ALC. G-ALC compounds ALC and the reasoning systems GAG and Gaa for generics [16]. We provide an intensional semantics for G-ALC, of which the frames preserve the properties of that of GAG and Gaa. In this Received xxxx-xx-xx This research is supported by the Major Project of National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 12 & ZD119).
2 2 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) semantics, a concept (a terminology precisely) has four-layer interpretation, namely, sense, extension, intension and concept [11]. Based on this intensional semantics, we propose a tableau algorithm for the reasoning problems of G-ALC. Because that all the typical reasoning problems can be reducted to the satisfiability of a formula w.r.t a knowledge base, it s suffice to ensure the tableau algorithm is effective for this reducted problem. The tableau algorithm provides a reasoning rule for each kind of G-ALC formula and each of the transforming rules holding intuitively. The important properties of this algorithm such as the soundness and completeness are strictly proved with help of induction method and some other technical ways. The termination property is relatively more obvious, therefore a proof in details is omitted in this paper. The body part of this article comprise five sections range from 2 to 6. In section 2, we introduces the generic extension G-ALC in syntax, semantics and the knowledge base. In section 3, the tableau algorithm is set up and some properties and notations are talked about. In section 4, the relationship between a G-ALC model and a tableau is shown. This is the basis of the proof the tableau algorithm. In section 5 and 6, the soundness and completeness are proved in details. 2 The generic extension of ALC In this part, we introduce G-ALC in three aspects: syntax, semantics and the knowledge base based on G-ALC. First, let us have a quick look at the syntax part. 2.1 G-ALC syntax Language G A L C. 1. symbols:enumerable variables x 1, x 2, ; constants c 1, c 2, ; concepts C 1, C 2, ; roles R 1, R 2,. 2. concept constructors:,,,,, N. 3. connectives:,,, G, >. 4. aux Symbols: (, ). Variable set is denoteds as V ar, constant set is denoted as Con, concept set is denoted as C A (means atomic concepts), role set is denoted as R. The term set T erm = V ar Con. Concept descriptions in G A L C are formed according to the following syntax rule: C, D ::= A C C D C D R.C R.C N(C, D) Particularly, A C A, R R, =, C D = ( C D), R.C = R. C, G A L C concept description set is denoted as C G A L C Formulae in G A L C are formed according to hte following syntax rule: α, β ::= C(t) R(t 1, t 2 ) C D C D G(C, D) α > β (α > β) Particularly, t, t 1, t 2 T erm, C, D C A, R R. The G A L C formula set is denoted as F G A L C.
3 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic G-ALC semantics Let s look into the G-ALC frame and structure first. Definition 1 A G-ALC frame is a tuple F = W, D, C, N,. W and D are nonempty sets, C is a map from (D) W to ( (D) W ) W called concept generating function. N is a function ranging over W and D called the normal individual collecting function. is a set sellect function over W. Definition 2 A G-ALC structure is a pair S = F, ε. F is a G-ALC frame, ε is the sense interpretation for G-ALC constants, concepts and roles on frame F : (1) For any constant c, ε(c) D W ε(c) is also written as c ε. (2) For any concept C, ε(c) (D) W. ε(c)is also written as C ε. And for any possible world w W, ε(c)(w) is defined as follow. (a) ε( )(w) = D. (b) ε( C)(w) = D ε(c)(w). (c) ε( )(w) = D ε( )(w) =. (d) ε(c 1 C 2 )(w) = ε(c 1 )(w) ε(c 2 )(w). (e) ε(c 1 C 2 )(w) = ε( ( C 1 C 2 ))(w) = D ε( C 1 C 2 )(w) = ε(c 1 )(w) ε(c 2 )(w). (f) ε( R.C)(w) = {a D b D((a, b) ε(r)(w) b ε(c)(w))}. (g) ε( R.C)(w) = ε( R. C)(w) = D ε( R. C)(w) = {a D b D((a, b) ε(r)(w) b ε(c)(w))}. (h) ε(n(c, D))(w) = N (C, D)(w) ε(c)(w) (3) For any role R, ε(r) ( (D D)) W. ε(r) is also written as R ε. Here now we go on to the G-ALC assignment and model. Definition 3 A G-ALC model is a pair M = S, σ. S is a G-ALC structure, σ is an assignment, which assigns an individual sense to each variable, σ : V ar D W. Let F = W, D, C, N, be a G-ALC frame, structure S = F, ε can be written as W, D, C, N,, ε ; model M = S, σ can be written as W, D, C, N,, ε, σ. Let M = W, D, C, N,, ε, σ be a G-ALC model, W M, D M, ε M, σ M be the elements of M, F M, S M be frame and stucture respectively. Definition 4 Let M be a model, σ M be the assignment of M, σ M (s/x) is a variant of σ M with respect to x, if and only if, σ M (s/x) : V ar DM W satisfies the following property. { s : y = x σ M (s/x)(y) = σ M (y) : y x
4 4 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) Let M =< S, σ > be a model, σ M (d/x) is a variant of σ M. Model < S, σ M (s/x) > is denoted as M (s/x). Definition 5 Let M be a G-ALC model, t is a term, the interpretation of t in M is t M, a map defined as follows: { t M εm (a) : t = c = σ M (x) : t = x Definition 6 Let M = W, D, C, N,, ε, σ be a G-ALC model, α be a G-ALC formula, α M is a set defined as follows: 1. C(t) M = {w W t M (w) C ε (w)} 2. R(t 1, t 2 ) M = {w W (t M 1 (w), tm 2 (w)) Rε (w)} 3. C D M = {w W C ε (w) D ε (w)} 4. C D M = C D M D C M 5. G(C, D) M = g (C ε, D ε ) = {w W D ε (C ε ) C } 6. α > β M = {X W (X, α M ) β M } 7. (α > β) M = W α > β M 2.3 G-ALC knowledge base Distinct from the ALC knowledge base, which comprises TBox and ABox, a knowledge base based on G-ALC comprises three sub-bases: TBox, ABox and G- Box. TBox is defined as usual in DL, which is a finite set of formulae with the form such as C D, C D. ABox is a finite set of formulae with the form such as C(t), R(t 1, t 2 ), N(C, D)(t). A GBox is a finite set of formuae with the form such as G(C, D), α > β, (α > β). 3 A tableau algorithm for G-ALC As we know, all the ALC reasoning problems can be reducted to the concept satisfiability problem. Similarly, all the G-ALC reasoning problems can be reducted to a kind of problem, that is the satisfiability of a G-ALC formula with respect to a knowledge base KB. Because of the page number restriction, the reduction proof is not given in details. The satisfiability of a G-ALC formula α with respect to a G-ALC knowledge base KB is just the consistance of set KB {α}, i.e., decide whether KB {α} has a G-ALC model. Let s call such problem restricted satisfiability. So, for G-ALC reasoning problems, it is suffice to provide an algorithm for the restricted satisfiability problem. The tableau algorithm specified below is just deserved.
5 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 5 Before proposing the G-ALC tableau algorithm formally, we first show what s tableau algorithm and some important terminologies and notations of it. Tableau algorithm uses a tableau, which indicate the relationship between the semantics and syntax of the problem domain, to decide whether the problem holds. A tableau algorithm comprises a group of rules to build a tableau, as well as a group rules to decide whether the tableau is open or closed. A tableau is a pair T = < N, S >, while N is a set of nodes, and S a directed binary relation between the nodes called deriving relation, which is irreflexive, asymmetry and intransitive. For every node, there is a set K of two kind of node expressions with forms of [i, α] and r(i, α, j). Particularly, α is a G-ALC formula,and i, j are natural numbers. The number i in [i, α] called the tab 1 for α. A tableau for the restriced satisfiability of formula α w.r.t knowledge KB is denoted as T (KB,α). Each tableau is built using the tableau rules step by step. The tableau T (KB,α) built by n steps, that is to say, using n rules can be denoted as T (KB,α) (n). Especially, T (KB,α) (0) only has one node, and the node-expression set is K (KB,α) (0) = {[0, α] α KB} {[0, α]}. For every tableau T (KB,α) = < N, S >, there are two kinds of special nodes named root-node and end-node. The root-node is the node with K (KB,α) (0) as node-expression set. For any x N, if there is no y N such that Sxy, then x is a end-node of T (KB,α). Let T = < N, S > be a tableau, B = < N, S > a sub-tableau of T (N N, S S). If N contains the root-node u and an end-node v of T, satisfying that S n uv (n 0) and B contains no other end-node of T, then B is a branch of T. S n uv means that there are x 1,, x n 1, such that S ux 1 S x 1 x 2 S x n 1 v. n is the length of B. In convention, n = 0 when S =. Let K be a node-expression set of an end-node. All the formulae in K are of negative normal form. The formula-rules are given below. 1. [ ]:If [i, (C 1 C 2 )(t)] K and [i, C 1 (t)] / K or [i, C 2 (t)] / K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, C 1 (t)], [i, C 2 (t)]}. 2. [ ]:If [i, (C 1 C 2 )(t)] K and [i, C 1 (t)] / K, [i, C 2 (t)] / K, then this node derives two new nodes such that K = K {[i, C 1 (t)]}, and K = K {[i, C 2 (t)]}. (In this case, one branch forks two branches. ) 3. [ ]:If [i, R.C(t)] K, [i, R(t, t )] K, and [i, C(t )] / K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, C(t )]}. 4. [ ]:If [i, R.C(t)] K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, R(t, c)], [i, C(c)]}. (c is a new constant haven t occurred in K.) 5. [ ]:If [i, C 1 C 2 ] K and [i, C 1 (t)] K, [i, C 2 (t)] / K, then this node de- 1 i, j represent possible worlds, and the intuitionistic meaning of [i, α] is that α is true on possible world i. r(i, α, j) is a ternary relation obtained according to the set collection function in G-ALC frame. The meaning of r(i, α, j) is w j ({w i }, α M ) [16].
6 6 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) rives a new node such that K = K {[i, C 2 (t)], [i, G(C 2, D) > G(C 1, D)]}. (D is any concept occurred in K.) 6. [ ]:If [i, C 1 C 2 ] K, and [i, C 1 C 2 ] / K or [i, C 2 C 1 ] / K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, C 1 C 2 ], [i, C 2 C 1 ]}. 7. [N]: If [i, N(C, D)(t)] K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, C(t)]}. 8. [G]: If [i, G(C, D)] K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, N(C, D)t > D(t)], [i, C(t) > N(C, D)(t)]} (t is a term occurred in K). 9. [>]: If [i, α > β] K and r(i, α, j) K, [j, β] / Kthen this node derives a new node such that K = K {[j, β]}. 10. [ >]: If [i, (α > β)] K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {r(i, α, j), [j, β]}. (j = m + 1, m is the largest tab in K). The r-rules are given below. 1. [r ]: If r(i, C 1 C 2, j) K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {r(i, G(C 2, D) > G(C 1, D), j)}. (D is any concept occurred in K). 2. [r > ]: If r(i, α, j), r(i, α > β, j) K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[j, β], r(i, β, j)}. 3. [r ]: If r(i, (C D)(t), j) K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {r(i, C(t), j), r(i, D(t), j)}. 4. [r ]: If r(i, (C D)(t), j) K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {r(i, C(t), j)}, K = K {r(i, D(t), j)}. 5. [r ]: If r(i, R.C(t), j), r(i, R(t, t ), j) K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {r(i, C(t ), j)}. 6. [r ]: If r(i, R.C(t), j) K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {r(i, R(t, c), j), r(i, C(c), j)}. (c is a new constant haven t occurred in K). 7. [r GAG ]: If {[i, C 1 C 2 ], [i, G(C 2, D)], r(i, C 1 C 2, j), r(i, G(C 2, D), j)} K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[j, G(C 1, D)]}. 8. [r ID ]: If {r(i, α, j)} K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[j, α]}. 9. [r T T ]: If {[i, α > β], [i, β > γ]} K, then this node derives a new node such that K = K {[i, α > γ]}. 10. [r Gaa ]: If {[i, G(C, D)], [i, C(t)], r(i, G(C, D), j), r(i, C(t), j)} K, then this node derives a new node such thatk = K {[j, D(t)]}. Regulation of the usage of abovementioned tableau rules: each rule can t be used repeatedly, namely, we can t use a used rule for the same formula more than once. Definition 7 Let K be a node-expression set. K is clashed if there is i, t such that
7 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 7 {[i, (t)]} K, or i, α such that {[i, α], [i, α]} K. Otherwise, K is consistent. Definition 8 Let T be a tableau, B is a branch of T. If there exists clashed nodeexpression set in B, then B is a closed branch, otherwise it s open. If all the branched of T are closed, then T is closed tableau, otherwise, it s open. Definition 9 A branch which is closed or has no rules can be used is called finished. A tableau with all branches finished is a finished tableau. Proposition 1 Let T be a tableau, u is a node of T, v is derived directly from u, K, K are node-expression set of u, v respectively, then K K. Proof It can be proved easily according to the tableau rules. Proof in details is omitted here. Corollary 1 Let T be a tableau, B is a branch of T with length of n. K 0, K 1,, K n are the node-expression sets of B from the root-node to the end-node. Then K 0 K 1 K n. Proof here. It can be obtained from proposition 1 obviously. Proof in details is omitted Proposition 2 Let T be a tableau, B is a branch of T with length of n. K 0, K 1,, K n are the node-expression sets of B from the root-node to the end-node. B is open, iff, the node-expression set of end-node K n is consistent. Proof = : If B is open, then K 0, K 1,, K n are consistent. Therefore, K n is consistent holds obviously. =:If B is closed, then there is an inconsistent node-expression set K i, (0 i n). According to the corollary 1, K i K n. So K n is inconsistent. From this proposition, we can infer that whether a branch B is open correspondence to the consistency of the end-node expression set. So we call the end-node expression set K n the characteristic set for branch B, denoded as K B. G-ALC tableau algorithm comprises the tableau rules, the regulation of rules and the definition of open (closed) tableau. 4 The relationship between the G-ALC model and tableau As mentioned above, tableau bridges the syntax aspect and the semantics aspect. In the following part, we will show how it bridges the two sides. This question leads to two branches, with (1) is to construct a G-ALC model according to a end-node expression set on a tableau, and (2) is to unfold the fact that the restricted satisfiablility of a formula α w.r.t a knowledge base KB correspondence to the open (closed)
8 8 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) property of the tableau T (KB,α). As for (2), it s in nature the soundness and completeness of the G-ALC tableau algorithm. Soundness: if formula α is satisfiable w.r.t a knowledge base KB, then the tableau T (KB,α) is open. Completeness is the converse proposition of soundness: if the tableau T (KB,α) is open, then formula α is satisfiable w.r.t a knowledge base KB. In this section, we will look into the subquestion (1), and the subquesetion (2) will be left to the two coming sections. Definition 10 Let T be a finished tableau, K a consistent end-node expression set on it. M K = < W K, D K, N K, K, ε K, C K, σ K > ia called a model based on K, for short, K-model, if M K satisfies the following conditions. 1. W K = I(K), i.e. the set of all the tabs in K. 2. D K = {t i [i, α(t)] K, i I(K)}. t is a term in K. 3. K : (W K ) (W K ) (W K ) is the set sellection function on (W K ). r(i, α, j) K, iff, j ({i}, α ). 4. N K (D K ) (D K ) (D K ). For any C ε K, D ε K (D K ), i W K, N K (C ε K, D ε K)(i) = {t i [i, N(C, D)(t)] K}. 5. ε K is the interpretation of constants, concepts and roles on frame F K :(1) for any constant c, c ε K W D K K, for any i W K, c ε K(i) = c i, iff, there is a formula α such that [i, α(c)] K; (2) for any concept C, C ε K (D K ) W K, for any i W K, C ε K(i) = {t i [i, C(t)] K}; (3) for any role R, R ε K ( (D K D K )) W K, for any i W K, R ε K(i) = {< t M K(i), t M K(i) > [i, R(t, t )] K}. 6. C K is the concept generating function from (D K ) W K to ( (D K ) W K) W K. If [i, G(C, D)] K, then (D) ε K C ε KC K (i), or else (D) ε K / C ε KC K (i). For any sense s, s (D K ) W K, any i W K, if s(i) s (i), then for any sense s, ({i}, g (s, s )) g (s, s ). 7. σ K is an assignment for the variables. For any variable x, x σ K W D K K. For any i W K, x σ K(i) = x i. Definition 11 For any G-ALC formula α, α M K is a set defined as follow. 1. C(t) M K= {w W K t M K(w) C ε K(w)} 2. R(t 1, t 2 ) M K= {w W K (t M K 1 (w), t M K 2 (w)) R ε K(w)} 3. C D M K= {w W K C ε K(w) D ε K(w)} 4. C D M K= C D M K D C M K 5. G(C, D) M K= g (C ε K, D ε K) = {w W K D ε K (C ε K) C K} 6. α > β M K= {X M K (X, α M K) β M K} 7. (α > β) M K= M K α > β M K In conclusion, this section provide a method to construct a G-ALC model from a consistent end-node expression set. Then, let s switch to the subquestion (2), the soundeness and completeness of the G-ALC tableau algorithm.
9 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 9 5 The soundness of the G-ALC tableau algorithm Let B be a branch, I(B) is the tab set of B. For any i I(B), let F (B, i) = {α [i, α] occurs on B} called the formula set of tab i. Let C(B) = {F (B, i) i I(B)}, namely the set of formula set of all the tabs on B, denoted as B characteristics. Let K be a node-expression set, I(K) is the tab set of K. For any i I(K), let F (K, i) = {α [i, α] occurs in K} be the formula set of tab i. Let C(K) = {F (K, i) i I(K)} be the set of formula set of all the tabs of K, denoted as K characteristics. According to the proposition 1, it s obvious that C(B) = C(K B ). Proposition 3 Let K be a node-expression set. K is consistent, iff, for all i I(K), neither there is a formula α such that α F (K, i) and α F (K, i), nor there is a term t such that (t) F (K, i). Proof It can be proved by the definition of the consistency of node-expression set. Proof in details is omitted here. Definition 12 Let α be a G-ALC formula, K a node-expression set. (1)α is satisfiable, iff, there is a G-ALC model M and a possible world w W M such that w α M.(Also denoted as M, w = α. (2)C(K) is satisfiable, iff, there is a G-ALC model M, for any i I(K) thereis a possible world w W M such that M, w = F (K, i). ( F (K, i) means the conjunction of all the formulae in F (K, i)) Let K be a node-expression set. C(K) is satisfiable, iff, K is consis- Proposition 4 tent. Proof It can be proved according to proposition 4 and definition 19, 20. Proof in details is omitted here. Proposition 5 Let K be a node-expression set. C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, I(K) = {0,, k}. Let K be the node-expression set obtained by the application of a tableau rule to K. (1) Except for [ >], all the other tableau rules can not generate new tabs, i.e., I(K ) = I(K) = {0,, k}. (2) Except for [>], [ >], [r > ], [r GAG ], [r Gaa, [r ID ], all the other tableau rules only add new formulae to F (K, i), i.e., F (K, j) = F (K, j), if j i. (3) [ >] can generate new tabs. If the rule [ >] is used to [i, (β > γ)] in K, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k), F (K, k + 1)}, and F (K, k + 1) = { γ}, I(K ) = {0,, k, k + 1}. (4) Only the rule [ ] derives two new nodes.
10 10 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) Proof here. It can be easily proved according to tableau rules. Proof in details is omitted According to proposition 6, all the tableau rules can be devided into three kinds: 1. [ ], [r ], which result in forks and do not change the formula set of other tabs; 2. [ ], [ ], [ ], [ ], [ ], [N], [G], [r ], [r ], [r ], [r ], [r T T ], which neither result in forks nor change the formula set of other tabs; 3. [>], [ >], [r > ], [r GAG ], [r Gaa ], [r ID ], which do not result in forks, but change the formula set of other certain tab. Three propositions will be proved below to show all the tableau rules are satisfiable preseving. Proposition 6 Let K be a node-expression set, K and K are obtained after the application of [ ]. If C(K) is satisfiable, then so is C(K ) or C(K ). Proof Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}. K and K are obtained after the application of the rule [ ] to [i, (C D)(t)] in K. So C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {C(t)}. C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {D(t)}. By the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M and possible world w such that M, w = (C D)(t). By the G-ALC semantics, M, w = C(t) or M, w = D(t). In addition, the rule [ ] do not change the other tab s formula set, so C(K ) is satisfiable or C(K ) is satisfiable. Proposition 7 Let K be a node-expression set. K is obtained after the application of one of the following rules [ ], [ ], [ ], [ ], [ ], [N], [G], [r T T ]. If C(K) is satisfiable, then so is C(K ). Proof Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, and I(K) = {0,, k}. K is the result counterpart after the application of one of the above rules. As for [ ]. Suppose that the rule [ ] is applied to [i, (C D)(t)] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {C(t), D(t)}. If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ > and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because (C D)(t) F (K, i), M, w = C(t), M, w = D(t). Therefore, M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [ ] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [ ]. Suppose that the rule [ ] is allpied to [i, R.C(t)] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}. For any term t, if R(t, t ) F (K, i), then C(t ) F (K, i). If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because R.C(t) F (K, i), M, w = R.C(t), i.e., t M (w) ( R.C) ε (w) = {d D d D(< d, d > R ε (w) d C ε (w))}. For any term t, if R(t, t ) F (K, i), then M, w = R(t, t ), namely, < t, t > R ε (w). Thus t C ε (w), i.e.,
11 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 11 M, w = C(t ). As a result, M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [ ] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [ ]. Suppose that the rule [ ] is allpied to [i, R.C(t)] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {R(t, c), C(c)}. If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because R.C(t) F (K, i), M, w = R.C(t), i.e., t M (w) ( R.C) ε (w) = {d D d D(< d, d > R ε (w) d C ε (w))}. Let M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and c ε {d D < t ε (w), d ε (w) > R ε (w) d ε (w) C ε (w))}, all the other interpretations coincide with ε. So M, w = R(t, c), and M, w = C(c), i.e., M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [ ] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [ ]. Suppose that the rule [ ] is allpied to [i, C D] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}. For any term t, if C(t) F (K, i), then F (K, i) = F (K, i) {D(t)}. If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because C D F (K, i), M, w = C D, i.e., C ε (w) D ε (w). For any term t, if C(t) F (K, i), then M, w = C(t), i.e., t ε (w) C ε (w) D ε (w). Therefore, M, w = D(t), and M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [ ] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [ ]. Suppose that the rule [ ] is allpied to [i, C D] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {C D, D C}. If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because C D F (K, i), M, w = C D, i.e., C ε (w) D ε (w) and D ε (w) C ε (w). Thus M, w = C D and M, w = D C. So M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [ ] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [N]. Suppose that the rule [N] is allpied to [i, N(C, D)(t)] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {C(t)}. If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because N(C, D)(t) F (K, i), M, w = N(C, D)(t), i.e., t ε (w) N (C ε, D ε )(w) C ε (w). Therefore M, w = C(t), and M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [N] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [G]. Suppose that the rule [G] is allpied to [i, G(C, D)] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}. For any term t, if t occurs in F (K, i), then N(C, D)t > D(t), C(t) > N(C, D)(t) F (K, i). If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because G(C, D) F (K, i), M, w = G(C, D), i.e., w G(C, D) M = g (C ε, D ε ). According to the G-ALC frame condition N G : g (C ε, D ε ) g(c ε, D ε ) = {w W t, ({w}, N(C, D)(t) M ) D(t) M }, M, w = N(C, D)(t) > D(t). In addition for the G-ALC frame condi-
12 12 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) tion D N æg (C ε, D ε ) {w W t, ({w}, C(t) M ) N(C, D)(t) M }, M, w = C(t) > N(C, D)(t). Thus M, w = F (K, i). For the rule [G] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. As for [r T T ]. Suppose that the rule [r T T ] is allpied to [i, α > β], [i, β > γ] K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {[i, α > γ]}. According to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is satisfiable, then there is a model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and a possible world w W such that M, w = F (K, i). Because α > β, β > γ F (K, i), M, w = α > β, M, w = β > γ. In addition for transitivity of the G-ALC frame, M, w = α > γ. Thus M = C(K ). For the rule [r T T ] do not change the formula set of other tabs, thus C(K ) is satisfiable. Definition 13 Let K be a node-expression set, M is a model of C(K). M is called a RS model, if R(i, α, j) K, then there are possible worlds w i, w j W K, such that w j ({w i }, α M ). If a RS model models C(K), then C(K) is called RS-satisfiable. K models are such RS-models. Proposition 8 Let K be a node-expression set, K is obtained by applying one of the following rules [>], [ >], [r ], [r ], [r ], [r ], [r > ], [r ], [r GAG ], [r ID ], [r Gaa ]. If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, then so is C(K ). Proof As for [>]. Suppose that the rule [>] is allpied to [i, α > β], r(i, α, j) K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}. Particularly, F (K, j) = F (K, j) {β}, 0 j k, and F (K, l) = F (K, l), l j. If C(K) is RSsatisfiable, for α > β F (K, i), so there is a RS-model M and a possible world w i such that M, w i = α > β. Thus ({w i }, α M ) β M. Because M is a RS-model, and R(i, α, j) K, w j ({w i }, α M ). Therefore w j β M, i.e., M K, w j = β. So M K is a RS-model of C(K ). According to the construcure of M K, in fact, w i and w j are i and j respectively. Let i and j replace w i and w j respectively in below. As for [ >]. Suppose that the rule [ >] is allpied to [i, (α > β)] K. Then R(i, α, j), [j, β] K, and j = k+1 is a new tab. Because C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k), F (K, k + 1)}, and F (K, k + 1) = { β}. If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, so there is a RS-model M, for i, (0 i k), M = F (K, i). For (α > β) F (K, i), so there is an i such that M, i = (α > β). So ({i}, α M ) β M, i.e., there is a w ({i}, α M ), and w / β M. Thus w β M. Let w = w k+1, so M = F (K, k + 1). Therefore M = C(K ). Now that j = k + 1, so there are i, j W K such that j ({i}, α M ). So C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r ]. Suppose that the rule [r ] is allpied to r(i, (C D)(t), j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, Kß and K are obtained after the application of rule [r ]. So C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i)
13 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 13 {r(i, C(t), j)}, C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, F (K, i) = F (K, i) {r(i, D(t), j)}. According to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, for r(i, (C D)(t), j) F (K, i), so there is a RS-model M and a possible worlds i, j such that j ({i}, (C D)(t) M ) = ({i}, C(t) M ) ({i}, D(t) M ). Therefore, j ({i}, C(t) M ) or j ({i}, D(t) M ). Thus C(K ) is RS-satisfiable, or C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r ]. Suppose that the rule [r ] is allpied to r(i, (C D)(t), j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {r(i, C(t), j), r(i, D(t), j)}. According to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, for r(i, (C D)(t), j) C(K), then there is a RS-model M and possible worlds i, j such that j ({i}, (C D)(t) M ) = ({i}, C(t) M ) ({i}, D(t) M ). Thus j ({i}, C(t) M ), and j ({i}, D(t) M ). So C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r ]. Suppose that the rule [r ] is allpied to r(i, R.C(t), j), r(i, R(t, t ), j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {r(i, C(t ), j)}. According to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, for r(i, R.C(t), j), r(i, R(t, t ), j) C(K), so there is a RS-model M and possible worlds i, j such that j ( ({i}, R.C(t) M ) ({i}, R(t, t ) M )) ({i}, C(t ) M ). Thus j ({i}, C(t ) M ), and C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r ]. Suppose that the rule [r ] is allpied to r(i, R.C(t), j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {r(i, R(t, c), j), C(c)}. According to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, for r(i, R.C(t), j) C(K), so there is a RS-model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ > and possible worlds i, j such that j ( ({i}, R.C(t) M ). Let M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and conincides with except for j ({i}, R(t, c)), j ({i}, C(c)). Therefore M is also a RS-model, and M = C(K ). So C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r ]. Suppose that the rule [r ] is allpied to r(i, C 1 C 2, j) K. Then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, i),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {G(C 2, D) > G(C 1, D)} with D being any concept occurs in K. If C(K) is RSsatisfiable, then there is a RS-model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ >, and possible worlds i, j W such that j ({i}, C 1 C 2 M ). Because C 1 C 2 F (K, i), M, w = C 1 C 2, i.e., C1 ε(w) Cε 2 (w). By the inverse proportion between the concept extension and intension in the G-ALC semantics, we know that (C2 ε)c (w) (C1 ε)c (w). So for any concept D, G(C 2, D) M G(C 1, D) M. Thanks to the I D condition of the G-ALC frame, {w W ({w}, G(C 2, D) M )} G(C 2, D) M G(C 1, D) M. So C 1 C 2 M G(C 2, D) > G(C 1, D) M. In addition to the monotonicity of the set sellection function, we get that ({w}, C 1 C 2 M ) ({w}, G(C 2, D) > G(C 1, D) M ). Because that j ({i}, C 1 C 2 M ), w j ({i}, G(C 2, D) > G(C 1, D) M ). So C(K ) is RS-
14 14 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) satisfiable. As for [r > ]. Suppose that the rule [r > ] is allpied to r(i, α, j), r(i, α > β, j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {[j, β], r(i, β, j)}. Accordint to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, because r(i, α, j), r(i, α > β, j) C(K), there is a RS-model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ > and possible worlds i, j such that j ( ({i}, α M ) ({i}, α > β M ) α M α > β M ). By the property of the set sellection, we know that α M α > β M ) β M. So M = C(K ), i.e., C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r ID ]. Suppose that the rule [r ID ] is allpied to r(i, α, j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {[j, α]}. According to the proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K)is RS-satisfiable, and r(i, α, j) C(K), so there is a RS-model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ > and possible worlds i, j such that j ({i}, α M. By the ID property of the G-ALC frame, we know that ({i}, α M α M. So j α M, therefore, M = C(K ). Consequently C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r Gaa ]. Suppose that the rule [r Gaa ] is allpied to [i, G(C, D)], [i, C(t)], r(i, G(C, D), j), r(i, C(t), j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {[j, D(t)]}. For the reason of proposition 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, as G(C, D), C(t), r(i, G(C, D), j), r(i, C(t), j) C(K), so there is a RS-model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ > and possible worlds i, j such that M, i = G(C, D), M, i = C(t), j ( ({i}, G(C, D) M ({i}, C(t) M ). On the grounds of the Gaa property of G-ALC frame, ( ({i}, G(C, D) M ({i}, C(t) M ) α M. Hence j D(t) M, and M = C(K ). Consequenctly C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. As for [r GAG ]. Suppose that the rule [r GAG ] is allpied to [i, C 1 C 2 ], [i, G(C 2, D)], r(i, C 1 C 2, j), r(i, G(C 2, D), j) K. Let C(K) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, then C(K ) = {F (K, 0),, F (K, k)}, and F (K, i) = F (K, i) {[j, G(C 1, D)]}. According to 6.(2), for any j i, F (K, j) = F (K, j). If C(K) is RS-satisfiable, for the reason that [i, C 1 C 2 ], [i, G(C 2, D)], r(i, C 1 C 2, j), r(i, G(C 2, D), j) C(K), so there is a RS-model M =< W, D, N,, C, ε, σ > and possible worlds i, j such that M, i = C 1 C 2, M, i = G(C 2, D), j ( ({i}, C 1 C 2 M ({i}, G(C 2, D) M ). In addition to the GAG property of the G-ALC frame, ( ({i}, C 1 C 2 M ({i}, G(C 2, D) M ) α M. Hence j G(C 1, D) M and M = C(K ). Consequently C(K ) is RS-satisfiable. Proposition 9 Let α be a G-ALC formula. If α is satisfiable w.r.t the knowledge base KB, then the tableau T (KB,α) is open.
15 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 15 Proof If the formula α is satisfiable w.r.t the knowledge base KB, namely the rootnode expression set K 0 of the tableau T (KB,α) is satisfiable. For the reason of the proposition 7,8,9, we know that there must be a branch B on tableau T (KB,α) such that its end-node expression set K B is satisfiable. Thanks to the proposition 2, B is open, iff, K B is satisfiable. Hence T (KB,α) must have an open branch, that is to say, T (KB,α) is open. 6 The completeness of the G-ALC tableau algorithm Lemma 1 Let α be a G-ALC formula, T (KB,α) a finished open tableau, B a open branch of T (KB,α), and K B the end-node expression set of B. For any G-ALC formula β, if there is i I(K B ) such that β F (K B, i), then M KB, i = β. Proof To prove by the induction on the formula structure. 1. In case β = C(t). In this case, [i, C(t)] K B, by the definition 18, t M K B (i) = t i and C ε K B (i) = {t i [i, C(t)] K B }. Hence t M K B (i) C ε K B (i). In addition to the definition 19, M KB, i = C(t). 2. In case β = R(t, t ). In this case, [i, R(t, t )] K B, by the definition 18, R ε K B (i) = {< t M K B (i), t M K B (i) > [i, R(t, t )] K B }. According to the definition 19, i R(t, t ) M K B, i.e., M KB, i = R(t, t ). 3. In case β = C D. In this case, [i, C D] K B, and T (KB,α) is a finished open tableau, so there is a term t such that [i, C(t)] K B. And the rule [ ] is used to [i, C D]. Hence [i, D(t)] K B. According to the definition 18, C ε K B (i) D ε K B (i). Again by the definition 19, we get i C D M K B, i.e., M KB, i = C D. 4. In case β = C D. In this case, [i, C D] K B, and T (KB,α) is a finished open tableau, so the rule [ ] is used to [i, C D]. Hence {[i, C D], [i, D C]} K B. According to the definition 18, we get that C ε K B (i) D ε K B (i). In addition to the definition 19, there goes that i C D M K B, i.e., M KB, i = C D. 5. In case β = G(C, D). For [i, G(C, D)] K B. According to the definition 18, we get that D ε K B (C ε K B ) C K B (i). In additon to the definition 19, we get that i G(C, D) M K B. Hence, M KB, i = G(C, D). 6. In case β = α > γ. In this case, [i, α > γ] K B, and M KB is a RS-model, then r(i, α, j) K B, iff, j ({i}, α M K B ). Because T (KB,α) is a finished open tableau, if r(i, α, j) K B, then [i, α > γ] must use the rule [>]. Hence [j, γ] K B, namely j γ M K B. So if j ({i}, α M K B ), then j γ M K B. Therefore ({i}, α M K B ) γ M K B. According to the definition 19, i α > γ M K B, i.e., M KB, i = α > γ. 7. In case β = (α > γ). In this case, [i, (α > γ)] K B. Because T (KB,α) is finished and open, [i, (α > γ)] must use the rule [ >]. Hence
16 16 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) {r(i, α, j), [j, γ]} K B. By the induction hypothesis, we know that j γ M K B. By the definition 19, j / γ M K B. Because M KB is a RS-model, r(i, α, j) K B, iff, j ({i}, α M K B ). Hence, j ({i}, α M K B ), j / γ M K B, and ({i}, α M K B ) γ M K B.By the definition 19, i (α > γ) M K B, consequently M KB, i = (α > γ). Proposition 10 Let α be a G-ALC formula. If T (KB,α) is a finished opem tableau, then α is satisfiable w.r.t. the knowledge base KB. Proof If T (KB,α) is open, then there is an open branch B. If T (KB,α) is finished, then according to the lemma 1, for the reason that α F (K B, 0), so M B, 0 = α. For M B is a G-ALC model, so α is satisfiable w.r.t. the knowledge base KB. 7 Conclusion This paper extends generic sentences to the basic description logic ALC, and get a new logic G-ALC. As a matter of fact, we compound ALC and the term logic systems GAG and Gaa, for the reasoning of generic sentences, in syntax and semantics. Then a tableau agorithm is given for the reasoning problems of G-ALC, and the important properties such as the soundness and completeness of it are strictly proved. The future work following this paper is to research the algorithm s computational complexity and the application of G-ALC in some certaim knowledge fields. References [1] Ariel Cohen, Think Generic! The Meaning and Use of Gerneric Sentences,CSLI Publications, 1996 [2] Asher, N. and Morreau, M., 1991, Commonsense entailment: A modal theory of non-monotonic reasoning, Proceedings of the Twelfth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, J. Mylopoulos and R. Reiter (eds), Morgan Kauffman, Los Altos, California, pp [3] Boutilier, C., Conditional logics of normality: A modal approach, Artificial Intelligence, VOl (68): [4] Franz Baader, Deborah L. McGuinness,Daniele Nardi, Peter F.Patel-Schneider, The description logic handbook: Theory, implementation and application, Cambridge University Press, 2007 [5] Mao, Yi., 2003, A Formalism for Non-monotonic Reasoning Encoded Generics, Ph.D. dissertation, The University of Texas at Austin. [6] McCarthy, J., 1980, Circumscription-a form of non-monotonic reasoning, Artificial Intelligence, VOl (13): [7] McCarthy, J., 1986, Applications of circumscription to formalizing commonsense knowledge, Artificial Intelligence, VOl (28), [8] Priest, G., 2001, An Introduction to Non-Classical Logic, Cambridge University Press, [9] Reiter, R., 1980, A logic for default reasoning, Artificial Intelligence, VOl (13 (1, 2)):
17 Ma Li / A Tableau Algorithm for the Generic Extension of Description Logic 17 [10] Reiter, R., 1987, Non-monotonic Reasoning, Annual Review of Computer Science, VOl (2): [11] Zhou, Beihai, and Mao, Yi, 2010, Four semantic layers of common nouns, Synthese,VOl (175(1)): [12] 周北海, 毛翊, 2003, 一个关于常识推理的基础逻辑, 哲学研究, 2003 年增刊 : 1-10 [13] 周北海, 概称句的本质与概念, 北京大学学报 ( 哲学社会科学版 ), [14] 张立英, 周北海, 基于主谓项涵义联系的概称句推理的几个逻辑, 哲学动态 2004 年增刊 [15] 张立英, 一种类型的概称句推理, 哲学动态, 增刊,2005. [16] 周北海, 2008, 涵义语义与关于概称句推理的词项逻辑, 逻辑学研究, 2008 年第 1 期 : 37-48
18 18 Studies in Logic, Vol. x, No. x (xxxx) 描述逻辑的概称句扩张及其 Tableau 判定算法 马丽 北京大学哲学系 mq2828@126.com 摘 要 描述逻辑主要刻画概念 角色和个体, 特别地, 概念是描述逻辑主要的刻画对象 描述逻辑对概念的外延有确定的解释, 是个体域的一个子集 描述逻辑对概念的内涵也有处理, 但是只是通过概念与其上下位概念之间的外延包含关系来体现 事实上, 一个概念的内涵不仅是它与上下位概念之间的关系, 而且还有它自己独特的性质 比如 鸟 这个概念不仅是 动物 的子概念, 而且它还有 会飞 有羽毛 生蛋 等等一些内涵项 既然描述逻辑的初衷是为了更好地刻画知识, 那么就要更好地刻画知识的内涵 本文把一种表达概念内涵的句子概称句扩张到基本描述逻辑 ALC 中去, 扩张后的逻辑记为 G-ALC 把概称句推理的系统 GAG 和 Gaa 与 ALC 相结合, 为 G-ALC 提供了内涵语义, 并且基于此语义为其推理问题提供了 tabeau ( 树图 ) 算法 算法的的可靠性和完全性在本文中得到了细致的 严谨的技术化证明 本文的工作对描述逻辑处理自然语言 构建语义本体都有理论意义, 希望这一研究能够在语义网即相关研究中能够得到应用 关键词 : 描述逻辑, 概称句, 扩张, 树图算法, 可靠性, 完全性
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤
 The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤 2016.12.26 研究背景 RNA 甲基化作为表观遗传学研究的重要内容之一, 是指发生在 RNA 分子上不同位置的甲基化修饰现象 RNA 甲基化在调控基因表达 剪接 RNA 编辑 RNA 稳定性 控制 mrna 寿命和降解等方面可能扮演重要角色
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤 2016.12.26 研究背景 RNA 甲基化作为表观遗传学研究的重要内容之一, 是指发生在 RNA 分子上不同位置的甲基化修饰现象 RNA 甲基化在调控基因表达 剪接 RNA 编辑 RNA 稳定性 控制 mrna 寿命和降解等方面可能扮演重要角色
d) There is a Web page that includes links to both Web page A and Web page B.
 P403-406 5. Determine whether the relation R on the set of all eb pages is reflexive( 自反 ), symmetric( 对 称 ), antisymmetric( 反对称 ), and/or transitive( 传递 ), where (a, b) R if and only if a) Everyone who
P403-406 5. Determine whether the relation R on the set of all eb pages is reflexive( 自反 ), symmetric( 对 称 ), antisymmetric( 反对称 ), and/or transitive( 传递 ), where (a, b) R if and only if a) Everyone who
On the Quark model based on virtual spacetime and the origin of fractional charge
 On the Quark model based on virtual spacetime and the origin of fractional charge Zhi Cheng No. 9 Bairong st. Baiyun District, Guangzhou, China. 510400. gzchengzhi@hotmail.com Abstract: The quark model
On the Quark model based on virtual spacetime and the origin of fractional charge Zhi Cheng No. 9 Bairong st. Baiyun District, Guangzhou, China. 510400. gzchengzhi@hotmail.com Abstract: The quark model
Integrated Algebra. Simplified Chinese. Problem Solving
 Problem Solving algebraically concept conjecture constraint equivalent formulate generalization graphically multiple representations numerically parameter pattern relative efficiency strategy verbally
Problem Solving algebraically concept conjecture constraint equivalent formulate generalization graphically multiple representations numerically parameter pattern relative efficiency strategy verbally
There are only 92 stable elements in nature
 There are only stable elements in nature Jiang Chun-xuan P. O. Box, Beijing 0, P. R. China jcxxxx@.com Abstract Using mathematical method we prove that there are only stable elements in nature and obtain
There are only stable elements in nature Jiang Chun-xuan P. O. Box, Beijing 0, P. R. China jcxxxx@.com Abstract Using mathematical method we prove that there are only stable elements in nature and obtain
能源化学工程专业培养方案. Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香
 能源化学工程专业培养方案 Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香 Director of Specialty: He Ping Executive Dean: Liao Qilong Academic Committee Director:
能源化学工程专业培养方案 Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香 Director of Specialty: He Ping Executive Dean: Liao Qilong Academic Committee Director:
三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用
 申请上海交通大学博士学位论文 三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用 博士生 : 苏惠荞 导师 : 万国华教授 专业 : 管理科学与工程 研究方向 : 运作管理 学校代码 : 10248 上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院 2017 年 6 月 Dissertation Submitted to Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the Degree of
申请上海交通大学博士学位论文 三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用 博士生 : 苏惠荞 导师 : 万国华教授 专业 : 管理科学与工程 研究方向 : 运作管理 学校代码 : 10248 上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院 2017 年 6 月 Dissertation Submitted to Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the Degree of
Source mechanism solution
 Source mechanism solution Contents Source mechanism solution 1 1. A general introduction 1 2. A step-by-step guide 1 Step-1: Prepare data files 1 Step-2: Start GeoTaos or GeoTaos_Map 2 Step-3: Convert
Source mechanism solution Contents Source mechanism solution 1 1. A general introduction 1 2. A step-by-step guide 1 Step-1: Prepare data files 1 Step-2: Start GeoTaos or GeoTaos_Map 2 Step-3: Convert
Type and Propositions
 Fall 2018 Type and Propositions Yu Zhang Course web site: http://staff.ustc.edu.cn/~yuzhang/tpl Yu Zhang: Types and Propositions 1 Outline Curry-Howard Isomorphism - Constructive Logic - Classical Logic
Fall 2018 Type and Propositions Yu Zhang Course web site: http://staff.ustc.edu.cn/~yuzhang/tpl Yu Zhang: Types and Propositions 1 Outline Curry-Howard Isomorphism - Constructive Logic - Classical Logic
Concurrent Engineering Pdf Ebook Download >>> DOWNLOAD
 1 / 6 Concurrent Engineering Pdf Ebook Download >>> DOWNLOAD 2 / 6 3 / 6 Rozenfeld, WEversheim, HKroll - Springer.US - 1998 WDuring 2005 年 3 月 1 日 - For.the.journal,.see.Conc urrent.engineering.(journal)verhagen
1 / 6 Concurrent Engineering Pdf Ebook Download >>> DOWNLOAD 2 / 6 3 / 6 Rozenfeld, WEversheim, HKroll - Springer.US - 1998 WDuring 2005 年 3 月 1 日 - For.the.journal,.see.Conc urrent.engineering.(journal)verhagen
Design, Development and Application of Northeast Asia Resources and Environment Scientific Expedition Data Platform
 September, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(3) 266-271 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.03.010 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.3 NE Asia Design, Development and Application of Northeast
September, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(3) 266-271 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.03.010 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.3 NE Asia Design, Development and Application of Northeast
系统生物学. (Systems Biology) 马彬广
 系统生物学 (Systems Biology) 马彬广 通用建模工具 ( 第十四讲 ) 梗概 (Synopsis) 通用建模工具 ( 数学计算软件 ) 专用建模工具 ( 细胞生化体系建模 ) 通用建模工具 主要是各种数学计算软件, 有些是商业软件, 有些是自由软件 商业软件, 主要介绍 : MatLab, Mathematica, Maple, 另有 MuPAD, 现已被 MatLab 收购 自由软件
系统生物学 (Systems Biology) 马彬广 通用建模工具 ( 第十四讲 ) 梗概 (Synopsis) 通用建模工具 ( 数学计算软件 ) 专用建模工具 ( 细胞生化体系建模 ) 通用建模工具 主要是各种数学计算软件, 有些是商业软件, 有些是自由软件 商业软件, 主要介绍 : MatLab, Mathematica, Maple, 另有 MuPAD, 现已被 MatLab 收购 自由软件
A proof of the 3x +1 conjecture
 A proof of he 3 + cojecure (Xjag, Cha Rado ad Televso Uversy) (23..) Su-fawag Absrac: Fd a soluo o 3 + cojecures a mahemacal ool o fd ou he codo 3 + cojecures gve 3 + cojecure became a proof. Keywords:
A proof of he 3 + cojecure (Xjag, Cha Rado ad Televso Uversy) (23..) Su-fawag Absrac: Fd a soluo o 3 + cojecures a mahemacal ool o fd ou he codo 3 + cojecures gve 3 + cojecure became a proof. Keywords:
XING Sheng-Kai LI Yun ZHAO Xue-Zhuang * CAI Zun-Sheng SHANG Zhen-Feng WANG Gui-Chang *
 1000 物理化学学报 (Wuli Huaxue Xuebao) Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2011, 27 (5), 1000-1004 May [Communication] www.whxb.pku.edu.cn Möbius 环并苯的分子对称性 * 邢生凯李云赵学庄 ( 南开大学化学学院, 天津 300071) * 蔡遵生尚贞锋王贵昌 摘要 : 一般来说, 点群理论认为 Möbius
1000 物理化学学报 (Wuli Huaxue Xuebao) Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2011, 27 (5), 1000-1004 May [Communication] www.whxb.pku.edu.cn Möbius 环并苯的分子对称性 * 邢生凯李云赵学庄 ( 南开大学化学学院, 天津 300071) * 蔡遵生尚贞锋王贵昌 摘要 : 一般来说, 点群理论认为 Möbius
2004 Journal of Software 软件学报
 000-9825/2004/5(07)0977 2004 Journal of Software 软件学报 Vol5, No7 如何测量 SMP 机群可扩放性 何家华 +, 陈国良, 单久龙 ( 中国科学技术大学计算机科学技术系国家高性能计算中心 ( 合肥 ), 安徽合肥 230027) How to Measure Scalability of SMP Cluster HE Jia-Hua +,
000-9825/2004/5(07)0977 2004 Journal of Software 软件学报 Vol5, No7 如何测量 SMP 机群可扩放性 何家华 +, 陈国良, 单久龙 ( 中国科学技术大学计算机科学技术系国家高性能计算中心 ( 合肥 ), 安徽合肥 230027) How to Measure Scalability of SMP Cluster HE Jia-Hua +,
Theory of Water-Proton Spin Relaxation in Complex Biological Systems
 Theory of Water-Proton Spin Relaxation in Complex Biological Systems Zhiwei Chang Doctoral Thesis by due permission of the Faculty of Engineering LTH, Lund University, Sweden. The thesis will be publicly
Theory of Water-Proton Spin Relaxation in Complex Biological Systems Zhiwei Chang Doctoral Thesis by due permission of the Faculty of Engineering LTH, Lund University, Sweden. The thesis will be publicly
Riemann s Hypothesis and Conjecture of Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer are False
 Riemann s Hypothesis and Conjecture of Birch and Swinnerton-yer are False Chun-Xuan Jiang. O. Box 3924, Beijing 854 China jcxuan@sina.com Abstract All eyes are on the Riemann s hypothesis, zeta and L-functions,
Riemann s Hypothesis and Conjecture of Birch and Swinnerton-yer are False Chun-Xuan Jiang. O. Box 3924, Beijing 854 China jcxuan@sina.com Abstract All eyes are on the Riemann s hypothesis, zeta and L-functions,
( 选出不同类别的单词 ) ( 照样子完成填空 ) e.g. one three
 Contents 目录 TIPS: 对于数量的问答 - How many + 可数名词复数 + have you/i/we/they got? has he/she/it/kuan got? - I/You/We/They have got + 数字 (+ 可数名词复数 ). He/She/It/Kuan has got + 数字 (+ 可数名词复数 ). e.g. How many sweets
Contents 目录 TIPS: 对于数量的问答 - How many + 可数名词复数 + have you/i/we/they got? has he/she/it/kuan got? - I/You/We/They have got + 数字 (+ 可数名词复数 ). He/She/It/Kuan has got + 数字 (+ 可数名词复数 ). e.g. How many sweets
Lecture 2. Random variables: discrete and continuous
 Lecture 2 Random variables: discrete and continuous Random variables: discrete Probability theory is concerned with situations in which the outcomes occur randomly. Generically, such situations are called
Lecture 2 Random variables: discrete and continuous Random variables: discrete Probability theory is concerned with situations in which the outcomes occur randomly. Generically, such situations are called
Lecture Note on Linear Algebra 14. Linear Independence, Bases and Coordinates
 Lecture Note on Linear Algebra 14 Linear Independence, Bases and Coordinates Wei-Shi Zheng, wszheng@ieeeorg, 211 November 3, 211 1 What Do You Learn from This Note Do you still remember the unit vectors
Lecture Note on Linear Algebra 14 Linear Independence, Bases and Coordinates Wei-Shi Zheng, wszheng@ieeeorg, 211 November 3, 211 1 What Do You Learn from This Note Do you still remember the unit vectors
沙强 / 讲师 随时欢迎对有机化学感兴趣的同学与我交流! 理学院化学系 从事专业 有机化学. 办公室 逸夫楼 6072 实验室 逸夫楼 6081 毕业院校 南京理工大学 电子邮箱 研 究 方 向 催化不对称合成 杂环骨架构建 卡宾化学 生物活性分子设计
 沙强 / 讲师 随时欢迎对有机化学感兴趣的同学与我交流! 院系 理学院化学系 从事专业 有机化学 学历 博士研究生 学位 博士 办公室 逸夫楼 6072 实验室 逸夫楼 6081 毕业院校 南京理工大学 电子邮箱 qsha@njau.edu.cn 研 究 方 向 催化不对称合成 杂环骨架构建 卡宾化学 生物活性分子设计 研究方向汇总图个人简介 2010 年毕业于南京理工大学制药工程专业, 获得工学学士学位,
沙强 / 讲师 随时欢迎对有机化学感兴趣的同学与我交流! 院系 理学院化学系 从事专业 有机化学 学历 博士研究生 学位 博士 办公室 逸夫楼 6072 实验室 逸夫楼 6081 毕业院校 南京理工大学 电子邮箱 qsha@njau.edu.cn 研 究 方 向 催化不对称合成 杂环骨架构建 卡宾化学 生物活性分子设计 研究方向汇总图个人简介 2010 年毕业于南京理工大学制药工程专业, 获得工学学士学位,
2012 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷
 0 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷 北京新东方罗勇 luoyong@df.cn 0-3- 说明 : 请严格按照实际考试时间进行模拟, 考试时间共 95 分钟 Multiple-Choice section A 部分 : 无计算器 B 部分 : 有计算器 Free-response section A 部分 : 有计算器 B 部分 : 无计算器 总计 45 题 /05 分钟 8 题,55 分钟
0 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷 北京新东方罗勇 luoyong@df.cn 0-3- 说明 : 请严格按照实际考试时间进行模拟, 考试时间共 95 分钟 Multiple-Choice section A 部分 : 无计算器 B 部分 : 有计算器 Free-response section A 部分 : 有计算器 B 部分 : 无计算器 总计 45 题 /05 分钟 8 题,55 分钟
Synthesis of PdS Au nanorods with asymmetric tips with improved H2 production efficiency in water splitting and increased photostability
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 407 412 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue of
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 407 412 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue of
USTC SNST 2014 Autumn Semester Lecture Series
 USTC SNST 2014 Autumn Semester Lecture Series Title: Introduction to Tokamak Fusion Energy Nuclear Science and Technology Research and Development (R&D) L8 A: Putting it all together: the box and thinking
USTC SNST 2014 Autumn Semester Lecture Series Title: Introduction to Tokamak Fusion Energy Nuclear Science and Technology Research and Development (R&D) L8 A: Putting it all together: the box and thinking
An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R
 An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R Tan Xi Department of Statistics, NUFE Nov 6, 2009 2009-2-5 Contents: A brief introduction to Grey Methods An analysis of Degree of Grey Incidence Grey GM(, )
An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R Tan Xi Department of Statistics, NUFE Nov 6, 2009 2009-2-5 Contents: A brief introduction to Grey Methods An analysis of Degree of Grey Incidence Grey GM(, )
上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍
 上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍 Pan Qiangyan for SLEGS collaborators 一. 引言二. 装置布局三. 实验及其结果四. 结论 一, 引言 为建设 SLEGS 光束线提供参考和研制依据, 中科院上海应用物理研究所于 2005 年成立了以徐望研究员为组长的 SLEGS 小组, 开展 SLEGS 样机的实验工作 ; 在中科院知识创新工程方向性项目 (
上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍 Pan Qiangyan for SLEGS collaborators 一. 引言二. 装置布局三. 实验及其结果四. 结论 一, 引言 为建设 SLEGS 光束线提供参考和研制依据, 中科院上海应用物理研究所于 2005 年成立了以徐望研究员为组长的 SLEGS 小组, 开展 SLEGS 样机的实验工作 ; 在中科院知识创新工程方向性项目 (
Microbiology. Zhao Liping 赵立平 Chen Feng. School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Microbiology By Zhao Liping 赵立平 Chen Feng 陈峰 School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn 1896 1920 1987 2006 Preface : Introduction
1896 1920 1987 2006 Microbiology By Zhao Liping 赵立平 Chen Feng 陈峰 School of Life Science and Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn 1896 1920 1987 2006 Preface : Introduction
Lecture 4-1 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 4-1 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms CHAPTER 4 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS Zhao Liping, Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology
1896 1920 1987 2006 Lecture 4-1 Nutrition, Laboratory Culture and Metabolism of Microorganisms CHAPTER 4 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS Zhao Liping, Chen Feng School of Life Science and Biotechnology
A new approach to inducing Ti 3+ in anatase TiO2 for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 510 516 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article (Special Issue of Photocatalysis
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 510 516 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article (Special Issue of Photocatalysis
STUDIES ON CLITICS OF CHINESE - THE GRAMMATICALIZATION APPROACH
 汉语的附着成分研究 从语法化的角度考察 STUDIES ON CLITICS OF CHINESE - THE GRAMMATICALIZATION APPROACH 林尔嵘 LIM NI ENG (B.A. Hons, NUS) 新加坡国立大学中文系硕士学位论文 A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTERS OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF CHINESE
汉语的附着成分研究 从语法化的角度考察 STUDIES ON CLITICS OF CHINESE - THE GRAMMATICALIZATION APPROACH 林尔嵘 LIM NI ENG (B.A. Hons, NUS) 新加坡国立大学中文系硕士学位论文 A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTERS OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF CHINESE
Galileo Galilei ( ) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632.
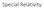 Special Relativity Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632. 2 Galilean Transformation z z!!! r ' = r
Special Relativity Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632. 2 Galilean Transformation z z!!! r ' = r
Effect of lengthening alkyl spacer on hydroformylation performance of tethered phosphine modified Rh/SiO2 catalyst
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 268 272 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Effect of lengthening alkyl
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 268 272 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Effect of lengthening alkyl
TKP students will be guided by the revised school values, PR IDE: ride espect esponsibility ntegrity iscipline mpathy
 K i i I 6 i i K I i i Ci k K Pii f j K Pi i k f i i i i i I i j K Pi (KP) i i i 14-- H i ii i i i f 3 Fi Pi( f Fi) Hi B M Pi i f KP i 2001 I f f ff i 3 L i i f i KP i i i i i i i i ii Wi i k i i i i f
K i i I 6 i i K I i i Ci k K Pii f j K Pi i k f i i i i i I i j K Pi (KP) i i i 14-- H i ii i i i f 3 Fi Pi( f Fi) Hi B M Pi i f KP i 2001 I f f ff i 3 L i i f i KP i i i i i i i i ii Wi i k i i i i f
ArcGIS 10.1 for Server OGC 标准支持. Esri 中国信息技术有限公司
 ArcGIS 10.1 for Server OGC 标准支持 Esri 中国信息技术有限公司 李光辉 DEMO OpenLayers GoogleEarth Map Services udig OWS Image Service 商业 GIS 软件 ArcGIS for Server GP Services Globe Services GeoCoding Services GeoData Services
ArcGIS 10.1 for Server OGC 标准支持 Esri 中国信息技术有限公司 李光辉 DEMO OpenLayers GoogleEarth Map Services udig OWS Image Service 商业 GIS 软件 ArcGIS for Server GP Services Globe Services GeoCoding Services GeoData Services
生物統計教育訓練 - 課程. Introduction to equivalence, superior, inferior studies in RCT 謝宗成副教授慈濟大學醫學科學研究所. TEL: ext 2015
 生物統計教育訓練 - 課程 Introduction to equivalence, superior, inferior studies in RCT 謝宗成副教授慈濟大學醫學科學研究所 tchsieh@mail.tcu.edu.tw TEL: 03-8565301 ext 2015 1 Randomized controlled trial Two arms trial Test treatment
生物統計教育訓練 - 課程 Introduction to equivalence, superior, inferior studies in RCT 謝宗成副教授慈濟大學醫學科學研究所 tchsieh@mail.tcu.edu.tw TEL: 03-8565301 ext 2015 1 Randomized controlled trial Two arms trial Test treatment
GRE 精确 完整 数学预测机经 发布适用 2015 年 10 月考试
 智课网 GRE 备考资料 GRE 精确 完整 数学预测机经 151015 发布适用 2015 年 10 月考试 20150920 1. n is an integer. : (-1)n(-1)n+2 : 1 A. is greater. B. is greater. C. The two quantities are equal D. The relationship cannot be determined
智课网 GRE 备考资料 GRE 精确 完整 数学预测机经 151015 发布适用 2015 年 10 月考试 20150920 1. n is an integer. : (-1)n(-1)n+2 : 1 A. is greater. B. is greater. C. The two quantities are equal D. The relationship cannot be determined
第五届控制科学与工程前沿论坛 高志强. Center for Advanced Control Technologies
 第五届控制科学与工程前沿论坛 自抗扰控制技术的理念 方法与应用 纪念韩京清先生逝世五周年 高志强 二零一三年四月十九日 Center for Advanced Control Technologies http://cact.csuohio.edu 概要 引言自抗扰控制的渊源自抗扰控制的应用自抗扰控制的论证抗扰技术研究小结 引言 君子务本, 本立而道生 韩京清 :1937-2008 六十年代 : 最优控制,
第五届控制科学与工程前沿论坛 自抗扰控制技术的理念 方法与应用 纪念韩京清先生逝世五周年 高志强 二零一三年四月十九日 Center for Advanced Control Technologies http://cact.csuohio.edu 概要 引言自抗扰控制的渊源自抗扰控制的应用自抗扰控制的论证抗扰技术研究小结 引言 君子务本, 本立而道生 韩京清 :1937-2008 六十年代 : 最优控制,
Zinc doped g C3N4/BiVO4 as a Z scheme photocatalyst system for water splitting under visible light
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (218) 472 478 催化学报 218 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article (Special Issue of Photocatalysis
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (218) 472 478 催化学报 218 年第 39 卷第 3 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article (Special Issue of Photocatalysis
Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1459 1464 Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip Ke ZHANG 1, Ping CAO 1, Rui BAO 1,2 1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1459 1464 Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip Ke ZHANG 1, Ping CAO 1, Rui BAO 1,2 1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering,
Single-atom catalysis: Bridging the homo- and heterogeneous catalysis
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 893 898 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Review Single-atom catalysis: Bridging
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 893 898 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Review Single-atom catalysis: Bridging
Easter Traditions 复活节习俗
 Easter Traditions 复活节习俗 1 Easter Traditions 复活节习俗 Why the big rabbit? 为什么有个大兔子? Read the text below and do the activity that follows 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : It s Easter in the UK and the shops are full of Easter
Easter Traditions 复活节习俗 1 Easter Traditions 复活节习俗 Why the big rabbit? 为什么有个大兔子? Read the text below and do the activity that follows 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : It s Easter in the UK and the shops are full of Easter
The Lagrange Mean Value Theorem Of Functions of n Variables
 陕西师范大学学士学位论文 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem Of Fuctios of Variables 作 者 单 位 数学与信息科学学院 指 导 老 师 曹怀 信 作 者 姓 名 李 碧 专 业 班 级数学与应用数学专业 4 级 班 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem of a Fuctio of Variables LI i lass, Grade
陕西师范大学学士学位论文 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem Of Fuctios of Variables 作 者 单 位 数学与信息科学学院 指 导 老 师 曹怀 信 作 者 姓 名 李 碧 专 业 班 级数学与应用数学专业 4 级 班 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem of a Fuctio of Variables LI i lass, Grade
Ni based catalysts derived from a metal organic framework for selective oxidation of alkanes
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (2016) 955 962 催化学报 2016 年第 37 卷第 6 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article (Special Issue on Environmental
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (2016) 955 962 催化学报 2016 年第 37 卷第 6 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article (Special Issue on Environmental
Service Bulletin-04 真空电容的外形尺寸
 Plasma Control Technologies Service Bulletin-04 真空电容的外形尺寸 在安装或者拆装真空电容时, 由于真空电容的电级片很容易移位, 所以要特别注意避免对电容的损伤, 这对于过去的玻璃电容来说非常明显, 但对于如今的陶瓷电容则不那么明显, 因为它们能够承载更高的机械的 电性能的负载及热负载 尽管从外表看来电容非常结实, 但是应当注意, 由于采用焊接工艺来封装铜和陶瓷,
Plasma Control Technologies Service Bulletin-04 真空电容的外形尺寸 在安装或者拆装真空电容时, 由于真空电容的电级片很容易移位, 所以要特别注意避免对电容的损伤, 这对于过去的玻璃电容来说非常明显, 但对于如今的陶瓷电容则不那么明显, 因为它们能够承载更高的机械的 电性能的负载及热负载 尽管从外表看来电容非常结实, 但是应当注意, 由于采用焊接工艺来封装铜和陶瓷,
Explainable Recommendation: Theory and Applications
 Explainable Recommendation: Theory and Applications Dissertation Submitted to Tsinghua University in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science and
Explainable Recommendation: Theory and Applications Dissertation Submitted to Tsinghua University in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science and
0 0 = 1 0 = 0 1 = = 1 1 = 0 0 = 1
 0 0 = 1 0 = 0 1 = 0 1 1 = 1 1 = 0 0 = 1 : = {0, 1} : 3 (,, ) = + (,, ) = + + (, ) = + (,,, ) = ( + )( + ) + ( + )( + ) + = + = = + + = + = ( + ) + = + ( + ) () = () ( + ) = + + = ( + )( + ) + = = + 0
0 0 = 1 0 = 0 1 = 0 1 1 = 1 1 = 0 0 = 1 : = {0, 1} : 3 (,, ) = + (,, ) = + + (, ) = + (,,, ) = ( + )( + ) + ( + )( + ) + = + = = + + = + = ( + ) + = + ( + ) () = () ( + ) = + + = ( + )( + ) + = = + 0
Lecture Note on Linear Algebra 16. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 Lecture Note on Linear Algebra 16. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Wei-Shi Zheng, wszheng@ieee.org, 2011 November 18, 2011 1 What Do You Learn from This Note In this lecture note, we are considering a very
Lecture Note on Linear Algebra 16. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors Wei-Shi Zheng, wszheng@ieee.org, 2011 November 18, 2011 1 What Do You Learn from This Note In this lecture note, we are considering a very
Alternative flat coil design for electromagnetic forming using FEM
 Alternative flat coil design for electromagnetic forming using FEM M. AHMED 1, S. K. PANTHI 1, N. RAMAKRISHNAN 2, A. K. JHA 1, A. H. YEGNESWARAN 1, R. DASGUPTA 1, S. AHMED 3 1. Advanced Materials and Processes
Alternative flat coil design for electromagnetic forming using FEM M. AHMED 1, S. K. PANTHI 1, N. RAMAKRISHNAN 2, A. K. JHA 1, A. H. YEGNESWARAN 1, R. DASGUPTA 1, S. AHMED 3 1. Advanced Materials and Processes
Molecular weights and Sizes
 Polymer Physcs 高分子物理 olecular weghts and Szes 高分子的分子量与尺寸 1 olecular weghts and molecular weght dstrbuton 分子量与分子量分布 Characterstcs of polymer molecular weghts 高分子的分子量的特点 The molecular weghts are very hgh,
Polymer Physcs 高分子物理 olecular weghts and Szes 高分子的分子量与尺寸 1 olecular weghts and molecular weght dstrbuton 分子量与分子量分布 Characterstcs of polymer molecular weghts 高分子的分子量的特点 The molecular weghts are very hgh,
Digital Image Processing. Point Processing( 点处理 )
 Digital Image Processing Point Processing( 点处理 ) Point Processing of Images In a digital image, point = pixel. Point processing transforms a pixel s value as function of its value alone; it it does not
Digital Image Processing Point Processing( 点处理 ) Point Processing of Images In a digital image, point = pixel. Point processing transforms a pixel s value as function of its value alone; it it does not
Anisotropic Dielectric Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Composites. FU Jin-Gang, ZHU Dong-Mei, ZHOU Wan-Cheng, LUO Fa
 第 27 卷第 11 期无机材料学报 Vol. 27 No. 11 2012 年 11 月 Journal of Inorganic Materials Nov., 2012 Article ID: 1000-324X(2012)11-1223-05 DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2012.12364 Anisotropic Dielectric Properties of Short
第 27 卷第 11 期无机材料学报 Vol. 27 No. 11 2012 年 11 月 Journal of Inorganic Materials Nov., 2012 Article ID: 1000-324X(2012)11-1223-05 DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2012.12364 Anisotropic Dielectric Properties of Short
Fabrication of ultrafine Pd nanoparticles on 3D ordered macroporous TiO2 for enhanced catalytic activity during diesel soot combustion
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 606 612 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 4 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue on
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 606 612 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 4 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue on
Chapter 2 the z-transform. 2.1 definition 2.2 properties of ROC 2.3 the inverse z-transform 2.4 z-transform properties
 Chapter 2 the -Transform 2.1 definition 2.2 properties of ROC 2.3 the inverse -transform 2.4 -transform properties 2.1 definition One motivation for introducing -transform is that the Fourier transform
Chapter 2 the -Transform 2.1 definition 2.2 properties of ROC 2.3 the inverse -transform 2.4 -transform properties 2.1 definition One motivation for introducing -transform is that the Fourier transform
Sichuan Earthquake 四川地震
 Sichuan Earthquake 四川地震 1 Sichuan Earthquake 四川地震 China Mourns Victims of the Sichuan Earthquake 中国为震灾遇难者哀悼 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : Flags are flying at half-mast
Sichuan Earthquake 四川地震 1 Sichuan Earthquake 四川地震 China Mourns Victims of the Sichuan Earthquake 中国为震灾遇难者哀悼 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : Flags are flying at half-mast
Avalanche Sizes of the Abelian Sandpile Model on Unicyclic Graphs
 第 46 卷第 4 期数学研究 Vol. 46 No. 4 2013 年 12 月 Journal of Mathematical Study Dec. 2013 Avalanche Sizes of the Abelian Sandpile Model on Unicyclic Graphs Wu Xiaoxia 1 Zhang Lianzhu 2 Qin Chengfu 3 Dong Hawei
第 46 卷第 4 期数学研究 Vol. 46 No. 4 2013 年 12 月 Journal of Mathematical Study Dec. 2013 Avalanche Sizes of the Abelian Sandpile Model on Unicyclic Graphs Wu Xiaoxia 1 Zhang Lianzhu 2 Qin Chengfu 3 Dong Hawei
Halloween 万圣节. Do you believe in ghosts? 你相信有鬼吗? Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 :
 Halloween 万圣节 1 Halloween 万圣节 Do you believe in ghosts? 你相信有鬼吗? Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : Though many people think it is an American festival, Halloween is
Halloween 万圣节 1 Halloween 万圣节 Do you believe in ghosts? 你相信有鬼吗? Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : Though many people think it is an American festival, Halloween is
Synthesis of anisole by vapor phase methylation of phenol with methanol over catalysts supported on activated alumina
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 72 726 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of anisole by vapor
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 72 726 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of anisole by vapor
THE INVERSE DERIVATIVE
 Phsics Disquisition THE INVERSE DERIVATIVE The new algorithm of the derivative GuagSan Yu ( Harbin Macro Dnamics Institute. 1566, P. R. China ) E-mail:1951669731@qq.com ( 15.1.1 16.1.6 ) Abstract: The
Phsics Disquisition THE INVERSE DERIVATIVE The new algorithm of the derivative GuagSan Yu ( Harbin Macro Dnamics Institute. 1566, P. R. China ) E-mail:1951669731@qq.com ( 15.1.1 16.1.6 ) Abstract: The
2NA. MAYFLOWER SECONDARY SCHOOL 2018 SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION Format Topics Comments. Exam Duration. Number. Conducted during lesson time
 Art NA T2 W3-W6 Project Work 1) Investigation and Interpretation of Theme 2) Control of Technical Processes 3) Reflection Conducted during lesson time Bahasa Melayu Express Stream SBB 1 2h Bahagian A E-mel
Art NA T2 W3-W6 Project Work 1) Investigation and Interpretation of Theme 2) Control of Technical Processes 3) Reflection Conducted during lesson time Bahasa Melayu Express Stream SBB 1 2h Bahagian A E-mel
NiFe layered double hydroxide nanoparticles for efficiently enhancing performance of BiVO4 photoanode in
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (218) 613 618 催化学报 218 年第 39 卷第 4 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue on Environmental
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (218) 613 618 催化学报 218 年第 39 卷第 4 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication (Special Issue on Environmental
Species surface concentrations on a SAPO 34 catalyst exposed to a gas mixture
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 35 (214) 43 436 催化学报 214 年第 35 卷第 3 期 www.chxb.cn available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Species surface concentrations
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 35 (214) 43 436 催化学报 214 年第 35 卷第 3 期 www.chxb.cn available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Species surface concentrations
Influence of surface strain on activity and selectivity of Pd based catalysts for the hydrogenation of acetylene: A DFT study
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 1493 1499 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 9 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Influence of surface strain
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 1493 1499 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 9 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Influence of surface strain
多夸克态前沿简介 邹冰松 中国科学院理论物理研究所
 多夸克态前沿简介 邹冰松 中国科学院理论物理研究所 内容提要 一. 强子物理研究的意义二. 多夸克态研究的意义三. 多夸克态寻找的艰难历程四. Pc- 五夸克态五. 展望 一. 强子物理研究的意义 1) 强子结构 -- 物质微观结构研究的最前沿 引力相互作用宇宙 天体结构 > 10-2 m 电磁相互作用分子 原子结构 > 10-10 m 强相互作用原子核 强子结构 10-16 ~10-14 m
多夸克态前沿简介 邹冰松 中国科学院理论物理研究所 内容提要 一. 强子物理研究的意义二. 多夸克态研究的意义三. 多夸克态寻找的艰难历程四. Pc- 五夸克态五. 展望 一. 强子物理研究的意义 1) 强子结构 -- 物质微观结构研究的最前沿 引力相互作用宇宙 天体结构 > 10-2 m 电磁相互作用分子 原子结构 > 10-10 m 强相互作用原子核 强子结构 10-16 ~10-14 m
网叶马铃苣苔 ( 苦苣苔科 ) 的重新发现以及花的补充描述
 DOI:10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201808032 网叶马铃苣苔 ( 苦苣苔科 ) 的重新发现以及花的补充描述 张亚梅 1,2, 郭世伟 1,2, 陈文红 1, 税玉民 (1. 中国科学院昆明植物研究所东亚植物多样性和生物地理学重点实验室, 昆明 650201; 2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049) 摘要 : 花部形态是马铃苣苔属属下划分和种间界定的关键性状, 缺乏花器官的描述直接导致了一些存疑物种的存在
DOI:10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201808032 网叶马铃苣苔 ( 苦苣苔科 ) 的重新发现以及花的补充描述 张亚梅 1,2, 郭世伟 1,2, 陈文红 1, 税玉民 (1. 中国科学院昆明植物研究所东亚植物多样性和生物地理学重点实验室, 昆明 650201; 2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049) 摘要 : 花部形态是马铃苣苔属属下划分和种间界定的关键性状, 缺乏花器官的描述直接导致了一些存疑物种的存在
Proton gradient transfer acid complexes and their catalytic performance for the synthesis of geranyl acetate
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 2114 2121 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 12 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Proton gradient transfer
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 2114 2121 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 12 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Proton gradient transfer
Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2014, 51(2): DOI: /j.issn 信息物质的化学分析技术 黄翠虹 , ; 2.
 Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 204, 5(2): 586 590. DOI: 0.7679/j.issn.2095 353.204.069 信息物质的化学分析技术 * 李静静 雷彩燕 黄翠虹 2 周琳 闫凤鸣 **., 450002; 2., 528333 摘要 - GC-MS HPLC GC-MS 关键词 - Chemical analysis techniques
Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 204, 5(2): 586 590. DOI: 0.7679/j.issn.2095 353.204.069 信息物质的化学分析技术 * 李静静 雷彩燕 黄翠虹 2 周琳 闫凤鸣 **., 450002; 2., 528333 摘要 - GC-MS HPLC GC-MS 关键词 - Chemical analysis techniques
强子谱和强子结构研究前沿简介 邹冰松 中国科学院高能物理研究所 中国科学院大科学装置理论物理研究中心
 强子谱和强子结构研究前沿简介 邹冰松 中国科学院高能物理研究所 中国科学院大科学装置理论物理研究中心 内容提要 一. 背景知识简介 二. 强子谱和强子结构研究前沿热点 三. 北京正负电子对撞机 BEPC 强子谱研究 一. 背景知识简介 1) 物质的基本相互作用和结构 2) 强子物理研究的基本问题 3) 探索强子内部结构的基本途径 1) 物质的基本相互作用和结构 引力相互作用宇宙 天体结构 > 10-2
强子谱和强子结构研究前沿简介 邹冰松 中国科学院高能物理研究所 中国科学院大科学装置理论物理研究中心 内容提要 一. 背景知识简介 二. 强子谱和强子结构研究前沿热点 三. 北京正负电子对撞机 BEPC 强子谱研究 一. 背景知识简介 1) 物质的基本相互作用和结构 2) 强子物理研究的基本问题 3) 探索强子内部结构的基本途径 1) 物质的基本相互作用和结构 引力相互作用宇宙 天体结构 > 10-2
Fuzzy Description Logics
 Fuzzy Description Logics 1. Introduction to Description Logics Rafael Peñaloza Rende, January 2016 Literature Description Logics Baader, Calvanese, McGuinness, Nardi, Patel-Schneider (eds.) The Description
Fuzzy Description Logics 1. Introduction to Description Logics Rafael Peñaloza Rende, January 2016 Literature Description Logics Baader, Calvanese, McGuinness, Nardi, Patel-Schneider (eds.) The Description
Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 /
 Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 / 王金兰 Email: jlwang@seu.edu.cn Department of Physics Southeast University What is nanometer? Nano is Small (10-7 --10-9 m; 1-100 nm) 10 0 m 10-1 m 10-2 m 10-3 m 10-4
Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 / 王金兰 Email: jlwang@seu.edu.cn Department of Physics Southeast University What is nanometer? Nano is Small (10-7 --10-9 m; 1-100 nm) 10 0 m 10-1 m 10-2 m 10-3 m 10-4
澳作生态仪器有限公司 叶绿素荧光测量中的 PAR 测量 植物逆境生理生态研究方法专题系列 8 野外进行荧光测量时, 光照和温度条件变异性非常大 如果不进行光照和温度条件的控制或者精确测量, 那么荧光的测量结果将无法科学解释
 叶绿素荧光测量中的 PAR 测量 植物逆境生理生态研究方法专题系列 8 野外进行荧光测量时, 光照和温度条件变异性非常大 如果不进行光照和温度条件的控制或者精确测量, 那么荧光的测量结果将无法科学解释 Yield can vary significantly with light level and with temperature. Without controlling irradiation
叶绿素荧光测量中的 PAR 测量 植物逆境生理生态研究方法专题系列 8 野外进行荧光测量时, 光照和温度条件变异性非常大 如果不进行光照和温度条件的控制或者精确测量, 那么荧光的测量结果将无法科学解释 Yield can vary significantly with light level and with temperature. Without controlling irradiation
國立中正大學八十一學年度應用數學研究所 碩士班研究生招生考試試題
 國立中正大學八十一學年度應用數學研究所 碩士班研究生招生考試試題 基礎數學 I.(2%) Test for convergence or divergence of the following infinite series cos( π (a) ) sin( π n (b) ) n n=1 n n=1 n 1 1 (c) (p > 1) (d) n=2 n(log n) p n,m=1 n 2 +
國立中正大學八十一學年度應用數學研究所 碩士班研究生招生考試試題 基礎數學 I.(2%) Test for convergence or divergence of the following infinite series cos( π (a) ) sin( π n (b) ) n n=1 n n=1 n 1 1 (c) (p > 1) (d) n=2 n(log n) p n,m=1 n 2 +
Lecture 13 Metabolic Diversity 微生物代谢的多样性
 Lecture 13 Metabolic Diversity 微生物代谢的多样性 Chapter 17 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS School of Life Science and Biotechnology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn I. The Phototrophic
Lecture 13 Metabolic Diversity 微生物代谢的多样性 Chapter 17 in BROCK BIOLOGY OF MICROORGANISMS School of Life Science and Biotechnology Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://micro.sjtu.edu.cn I. The Phototrophic
available at journal homepage:
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 40 (2019) 141 146 催化学报 2019 年第 40 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication The origin of the
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 40 (2019) 141 146 催化学报 2019 年第 40 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication The origin of the
The preload analysis of screw bolt joints on the first wall graphite tiles in East
 The preload analysis of screw bolt joints on the first wall graphite tiles in East AO ei( 曹磊 ), SONG Yuntao( 宋云涛 ) Institute of plasma physics, hinese academy of sciences, Hefei 230031, hina Abstract The
The preload analysis of screw bolt joints on the first wall graphite tiles in East AO ei( 曹磊 ), SONG Yuntao( 宋云涛 ) Institute of plasma physics, hinese academy of sciences, Hefei 230031, hina Abstract The
ILC Group Annual Report 2017
 ILC Group Annual Report 2017 D. SHEN 2017.12.31 报告摘要 Letter 本报告主要汇总了迭代学习控制研究组在 2017 年的研究内容 报告的主要内容包括研究组在本年度的相关数据 会议交流等学术活动 讨论组报告列表 研究生信息表 研究方向概述以及本年度发表论文集 本研究小组的主要研究方向为迭代学习控制 围绕这一方向, 研究组在本年度开展了一系列的研究,
ILC Group Annual Report 2017 D. SHEN 2017.12.31 报告摘要 Letter 本报告主要汇总了迭代学习控制研究组在 2017 年的研究内容 报告的主要内容包括研究组在本年度的相关数据 会议交流等学术活动 讨论组报告列表 研究生信息表 研究方向概述以及本年度发表论文集 本研究小组的主要研究方向为迭代学习控制 围绕这一方向, 研究组在本年度开展了一系列的研究,
MASTER S DEGREE THESIS. Electrochemical Stability of Pt-Au alloy Nanoparticles and the Effect of Alloying Element (Au) on the Stability of Pt
 Electrochemical Stability of P-Au Nanoparticles and the Name: Amsalu Efrem Yemene Supervisor: Prof.Chen,Bing Hui Effect of alloying Element (Au) on the stability of Pt Xiamen University, China University
Electrochemical Stability of P-Au Nanoparticles and the Name: Amsalu Efrem Yemene Supervisor: Prof.Chen,Bing Hui Effect of alloying Element (Au) on the stability of Pt Xiamen University, China University
Firms and People in Place
 Firms and People in Place Driving Forces for Regional Growth Wenjuan Li Doctoral Thesis Department of Social and Economic Geography Umeå University, Sweden GERUM 2007:1 GERUM Kulturgeografi 2007:1 This
Firms and People in Place Driving Forces for Regional Growth Wenjuan Li Doctoral Thesis Department of Social and Economic Geography Umeå University, Sweden GERUM 2007:1 GERUM Kulturgeografi 2007:1 This
Growth of Cu/SSZ 13 on SiC for selective catalytic reduction of NO
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 71 78 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 1 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Growth of Cu/SSZ 13 on SiC
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 71 78 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 1 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Growth of Cu/SSZ 13 on SiC
= lim(x + 1) lim x 1 x 1 (x 2 + 1) 2 (for the latter let y = x2 + 1) lim
 1061 微乙 01-05 班期中考解答和評分標準 1. (10%) (x + 1)( (a) 求 x+1 9). x 1 x 1 tan (π(x )) (b) 求. x (x ) x (a) (5 points) Method without L Hospital rule: (x + 1)( x+1 9) = (x + 1) x+1 x 1 x 1 x 1 x 1 (x + 1) (for the
1061 微乙 01-05 班期中考解答和評分標準 1. (10%) (x + 1)( (a) 求 x+1 9). x 1 x 1 tan (π(x )) (b) 求. x (x ) x (a) (5 points) Method without L Hospital rule: (x + 1)( x+1 9) = (x + 1) x+1 x 1 x 1 x 1 x 1 (x + 1) (for the
ILC Group Annual Report 2018
 ILC Group Annual Report 28 D. SHEN 28.2.3 报告摘要 Letter 本报告主要汇总了智能与学习系统中心 (Center of Intelligent and Learning Systems) 在 28 年的研究内容 报告的主要内容包括研究组在本年度的相关数据 会议交流等学术活动 讨论组报告列表 研究生信息表 研究方向概述以及本年度发表论文集 本研究小组的主要研究方向为迭代学习控制
ILC Group Annual Report 28 D. SHEN 28.2.3 报告摘要 Letter 本报告主要汇总了智能与学习系统中心 (Center of Intelligent and Learning Systems) 在 28 年的研究内容 报告的主要内容包括研究组在本年度的相关数据 会议交流等学术活动 讨论组报告列表 研究生信息表 研究方向概述以及本年度发表论文集 本研究小组的主要研究方向为迭代学习控制
Basic& ClinicalMedicine March2017 Vol.37 No.3 : (2017) 研究论文,-./ )89:;/Ⅱ,,,,,,!,"#$,%&' ("# <= 9>? B,"# 400
 2017 3 37 3 Basic& ClinicalMedicine March2017 Vol.37 No.3 :1001 6325(2017)03 0341 05 研究论文,-./01 2343567)89:;/Ⅱ,,,,,,!,"#$,%&' ("# ? =@=A B,"# 400016)!": # CD,E -./ 2343567)89 89:;/Ⅱ(Ang Ⅱ) F $% GHIJ-./KL,E
2017 3 37 3 Basic& ClinicalMedicine March2017 Vol.37 No.3 :1001 6325(2017)03 0341 05 研究论文,-./01 2343567)89:;/Ⅱ,,,,,,!,"#$,%&' ("# ? =@=A B,"# 400016)!": # CD,E -./ 2343567)89 89:;/Ⅱ(Ang Ⅱ) F $% GHIJ-./KL,E
Brainwashed Tom Burrell Pdf Download >>> DOWNLOAD
 Brainwashed Tom Burrell Pdf Download >>> DOWNLOAD 1 / 5 2 / 5 ,...TomBurr... WPanorama's...download...includes...both...the...image...viewer...program...and...a...scr eensaverbrainwashed:.challenging.the.myth.of.black.inferiority.tom.burrell.2017-11...
Brainwashed Tom Burrell Pdf Download >>> DOWNLOAD 1 / 5 2 / 5 ,...TomBurr... WPanorama's...download...includes...both...the...image...viewer...program...and...a...scr eensaverbrainwashed:.challenging.the.myth.of.black.inferiority.tom.burrell.2017-11...
Chapter 7 Propositional and Predicate Logic
 Chapter 7 Propositional and Predicate Logic 1 What is Artificial Intelligence? A more difficult question is: What is intelligence? This question has puzzled philosophers, biologists and psychologists for
Chapter 7 Propositional and Predicate Logic 1 What is Artificial Intelligence? A more difficult question is: What is intelligence? This question has puzzled philosophers, biologists and psychologists for
International Workshop on Advances in Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computation
 International Workshop on Advances in umerical Analysis and Scientific Computation Shanghai ormal University, Shanghai, China June 30-July 3, 2018 Contents Themes and Objectives...3 Sponsors...3 Organizing
International Workshop on Advances in umerical Analysis and Scientific Computation Shanghai ormal University, Shanghai, China June 30-July 3, 2018 Contents Themes and Objectives...3 Sponsors...3 Organizing
Nature 2018 A. Banino, Caswell Barry et.al 唐姝炅 _
 Nature 2018 A. Banino, Caswell Barry et.al 201711060109 唐姝炅201711060109_595014505 1 Nature, 557:429-433, 2018 Andrea Banino, Caswell Barry, Benigno Uria, Charles Blundell, Timothy Lillicrap, Piotr Mirowski,
Nature 2018 A. Banino, Caswell Barry et.al 201711060109 唐姝炅201711060109_595014505 1 Nature, 557:429-433, 2018 Andrea Banino, Caswell Barry, Benigno Uria, Charles Blundell, Timothy Lillicrap, Piotr Mirowski,
Increasing the range of non noble metal single atom catalysts
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 38 (2017) 1489 1497 催化学报 2017 年第 38 卷第 9 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Perspective (Special Issue of
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 38 (2017) 1489 1497 催化学报 2017 年第 38 卷第 9 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Perspective (Special Issue of
Recent progress in Ag3PO4 based all solid state Z scheme photocatalytic systems
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 38 (2017) 1794 1803 催化学报 2017 年第 38 卷第 11 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Minireview Recent progress in
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 38 (2017) 1794 1803 催化学报 2017 年第 38 卷第 11 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Minireview Recent progress in
Silver catalyzed three component reaction of phenyldiazoacetate with arylamine and imine
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 1594 1598 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 10 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication Silver catalyzed
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 39 (2018) 1594 1598 催化学报 2018 年第 39 卷第 10 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Communication Silver catalyzed
目錄 Contents. Copyright 2008, FengShui BaZi Centre < 2
 目錄 Contents 1. 子平八字命理学简介 Introduction of [Zi Ping Ba Zi] Destiny, Fate & Luck Analysis 1.1 日历种类 Type of Calendar 1.2 年, 月, 日, 时, 的关系 The Relationships between Year, Month, Day & Hour 1.3 命运的原理 The Principle
目錄 Contents 1. 子平八字命理学简介 Introduction of [Zi Ping Ba Zi] Destiny, Fate & Luck Analysis 1.1 日历种类 Type of Calendar 1.2 年, 月, 日, 时, 的关系 The Relationships between Year, Month, Day & Hour 1.3 命运的原理 The Principle
Synthesis of Ag/AgCl/Fe S plasmonic catalyst for bisphenol A degradation in heterogeneous photo Fenton system under visible light irradiation
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 38 (217) 1726 1735 催化学报 217 年第 38 卷第 1 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of Ag/AgCl/Fe
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 38 (217) 1726 1735 催化学报 217 年第 38 卷第 1 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of Ag/AgCl/Fe
tan θ(t) = 5 [3 points] And, we are given that d [1 points] Therefore, the velocity of the plane is dx [4 points] (km/min.) [2 points] (The other way)
![tan θ(t) = 5 [3 points] And, we are given that d [1 points] Therefore, the velocity of the plane is dx [4 points] (km/min.) [2 points] (The other way) tan θ(t) = 5 [3 points] And, we are given that d [1 points] Therefore, the velocity of the plane is dx [4 points] (km/min.) [2 points] (The other way)](/thumbs/74/69694342.jpg) 1051 微甲 06-10 班期中考解答和評分標準 1. (10%) A plane flies horizontally at an altitude of 5 km and passes directly over a tracking telescope on the ground. When the angle of elevation is π/3, this angle is decreasing
1051 微甲 06-10 班期中考解答和評分標準 1. (10%) A plane flies horizontally at an altitude of 5 km and passes directly over a tracking telescope on the ground. When the angle of elevation is π/3, this angle is decreasing
5. Polymorphism, Selection. and Phylogenetics. 5.1 Population genetics. 5.2 Phylogenetics
 5. Polymorphism, Selection 5.1 Population genetics and Phylogenetics Polymorphism in the genomes Types of polymorphism Measure of polymorphism Natural and artificial selection: the force shaping the genomes
5. Polymorphism, Selection 5.1 Population genetics and Phylogenetics Polymorphism in the genomes Types of polymorphism Measure of polymorphism Natural and artificial selection: the force shaping the genomes
2 Results and Discussion
 第 5 卷第 10 期无机材料学报 Vol. 5 No. 10 010 年 10 月 ournal of Inorganic Materials Oct., 010 Article ID: 1000-3X(010)10-1110-05 DOI: 10.37/SP..1077.010.10188 Optical Parameters of Nd 3+ Ion in Sr 3 Gd (BO 3 ) Crystal
第 5 卷第 10 期无机材料学报 Vol. 5 No. 10 010 年 10 月 ournal of Inorganic Materials Oct., 010 Article ID: 1000-3X(010)10-1110-05 DOI: 10.37/SP..1077.010.10188 Optical Parameters of Nd 3+ Ion in Sr 3 Gd (BO 3 ) Crystal
Lecture 7 Basics for Machine Learning and A Special Emphasis on CNN. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2018
 Lecture 7 Basics for Machine Learning and A Special Emphasis on CNN Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2018 10 Breakthrough Technologies 2017 (MIT Tech Review) Reversing
Lecture 7 Basics for Machine Learning and A Special Emphasis on CNN Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2018 10 Breakthrough Technologies 2017 (MIT Tech Review) Reversing
New Newtonian Mechanics and New Laws of Motion
 New Newtonian Mechanics and New Laws of Motion GuagSan Yu ( Harbin Macro Dynamics Institute. 150066, P. R. China ) E-mail:sxzyu35@hotmail.com ( 015.5.10 015.5.0 ) Abstract: The Newton third law by the
New Newtonian Mechanics and New Laws of Motion GuagSan Yu ( Harbin Macro Dynamics Institute. 150066, P. R. China ) E-mail:sxzyu35@hotmail.com ( 015.5.10 015.5.0 ) Abstract: The Newton third law by the
偏微分方程及其应用国际会议在数学科学学院举行
 1 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议在数学科学学院举行 2007 年 5 月 28 日至 31 日, 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议 (International Conference on PDEs and Applications) 在北京师范大学数学科学学院举行 国际著名数学家, 世界数学家大会一小时报告人, 美国科学院院士,University of Texas at Austin 教授 Luis Caffarelli
1 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议在数学科学学院举行 2007 年 5 月 28 日至 31 日, 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议 (International Conference on PDEs and Applications) 在北京师范大学数学科学学院举行 国际著名数学家, 世界数学家大会一小时报告人, 美国科学院院士,University of Texas at Austin 教授 Luis Caffarelli
Happy Niu Year 牛年快乐 1
 Happy Niu Year 牛年快乐 1 Celebrating in Style 庆新年 Happy Niu Year 牛年快乐 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : 2008 is now finally in the past as millions of Chinese people
Happy Niu Year 牛年快乐 1 Celebrating in Style 庆新年 Happy Niu Year 牛年快乐 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 : 2008 is now finally in the past as millions of Chinese people
A timed communication behaviour model for distributed systems
 A timed communication behaviour model for distributed systems Yanwen Chen To cite this version: Yanwen Chen. A timed communication behaviour model for distributed systems. Other [cs.oh]. Université Nice
A timed communication behaviour model for distributed systems Yanwen Chen To cite this version: Yanwen Chen. A timed communication behaviour model for distributed systems. Other [cs.oh]. Université Nice
SnO2 based solid solutions for CH4 deep oxidation: Quantifying the lattice capacity of SnO2 using an X ray diffraction extrapolation method
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (2016) 1293 1302 催化学报 2016 年第 37 卷第 8 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article SnO2 based solid solutions
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (2016) 1293 1302 催化学报 2016 年第 37 卷第 8 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article SnO2 based solid solutions
