Measure Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyharmonic Functions
|
|
|
- Horace Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chin. Ann. Math. Se. B 39(5), 08, DOI: 0.007/s Chinese Annals of Mathematics, Seies B c The Editoial Office of CAM and Spinge-Velag Belin Heidelbeg 08 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions Long TIAN Abstact This pape deals with the function u which satisfies k u = 0, whee k is an intege. Such a function u is called a polyhamonic function. The autho gives an uppe bound of the measue of the nodal set of u, and shows some gowth popety of u. Keywods Polyhamonic function, Nodal set, Fequency, Measue estimate, Gowth popety 000 MR Subject Classification 58E0, 53C50 Intoduction The nodal sets ae zeo level sets. We want to study the measue estimates of nodal sets of polyhamonic functions in this pape. In 979, Almgen [] intoduced the fequency concept of hamonic functions. Then in 986 and 987, Gaofalo and Lin[4 5] established the monotonicity fomula of the fequency and the doubling conditions fo solutions of the unifomly second ode elliptic equations, and showed the unique continuation of such solutions by using the doubling conditions. In 000, Han [6] studied the stuctue of the nodal sets of solutions of a class of unifomly high ode elliptic equations. In 003, Han, Hadt and Lin in [7] investigated stuctues and measue estimates of singula sets of solutions of high ode unifomly elliptic equations. In 04, the autho and Yang in [3] gave the measue estimates of nodal sets fo bi-hamonic functions. The classical fequency of a hamonic function is defined as follows. Definition. If u is a hamonic function in B, then fo any, one can define the fequency function of u centeed at the oigin with adius as follows: N() = D() H() = u dx u dσ, (.) whee dσ means the (n )-Hausdoff measue on the sphee. Similaly, one can define the fequency centeed at othe point. Based on this idea, we define the fequency of a polyhamonic function as follows. We fist show some notations in this pape as follows: u = u, u = u,, u k = k u, u k+ = k u = 0. Manuscipt eceived Apil 6, 05. Revised August, 06. Depatment of Applied Mathematics, Nanjing Univesity of Science and Technology, Nanjing 0094, China. tianlong98508@63.com This wok was suppoted by the National Natual Science Foundation of China (Nos.40307, 50 9).
2 98 L. Tian Definition. Suppose that u satisfies that k u = 0, whee k is a positive intege moe than o equal to. Such a function u is called a k-polyhamonic function in the est of this pape. Then we define whee D() = D i (), E() = N() = D()+E(), (.) H() E i (), H() = H i (), D i () = u i dx, E i () = u i u i+ dx, H i () = u i dσ. The function N() is called the fequency of u centeed at the oigin with adius. Similaly, we can define the fequency centeed at othe point. Remak. Noting that fo any j =,,,k, u j is a (k j+)-polyhamonic function, and u k is a hamonic function. Thus one can also define the fequency fo u j as above. We denote such fequency as N j (). It is easy to see that N () = N(), and N k () is just the classical fequency of a hamonic function as in Definition.. Remak. This fequency is in fact the following fom N() =. (.3) u i dσ Hee u iν is u ν and ν is the oute unit nomal on. Now we state the main esults of this pape. Theoem. Let u be a polyhamonic function in B R n, i.e., k u = 0 in B. Then H n ({x B : u(x) = 0}) C N 6 i ()+C, (.4) whee C is a positive constant depending only on n and k. Theoem. Let u be a k-polyhamonic function in the whole space R n. () If the fequency of u centeed at the oigin is bounded in R n, then u is a polynomial. Moeove, if N() < N 0 fo any > 0, then it holds that deg(u) CN 0 +C, (.5) whee deg(u) means the ode of degee of u and C is a positive constant depending only on n and k. In this case, fo any i =,,k, the functions u i ae also polynomials. () If u is a polynomial, then the fequency of u is bounded by the ode of degee of u in the whole space R n. The est of this pape is oganized as follows. In the second section we intoduce some inteesting popeties of the fequency and pove the monotonicity fomula of the fequency. In the thid section, the doubling conditions of the polyhamonic functions ae poved. The foth section gives the measue estimates of nodal sets of polyhamonic functions, i.e., the poof of Theoem.. The last section shows the gowth popety of polyhamonic functions.
3 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 99 Monotonicity Fomula of Fequency In this section, we will give some inteesting popeties fo the fequency of polyhamonic functions, and then pove the monotonicity fomula fo this fequency function. Lemma. If u satisfies k u = 0, whee k N and the vanishing ode of u at the oigin is l (k ), then lim N() l (k ). (.) 0 Poof Note that u is k-polyhamonic. So each u i is analytic nea the oigin, thus we may assume that fo each i =,,,k, u i (x) = P i (x) + R i (x), whee P i (x) is a homogeneous polynomial. Assume that the ode of degee of P i (x) is l i, and then R i (x) = o( x li ) as x 0. Because the vanishing ode of u at the oigin is l, it is known that l = l, and fo each i =,3,,k, l i l (i ). Let l 0 = inf{l,l,,l k }. Because each P i (x) is a homogeneous polynomial of degee l i, P i (x) can be witten as P i (x) = li φ i (θ), whee (,θ) is the pola coodinate system. Then u i dx+ k u i u i+ dσ N() = = u i dσ u i dσ = l i li φ i (θ)dσ + k o( li ) li φ i (θ)dσ + k o( li ) l 0 B l0 φ i (θ)dσ +o(l0 ) =, l0 φ i (θ)dσ ) +o(l0 whee dσ = n dω, dω is the (n )-Hausdoff measue on the unit sphee S n. Let 0 in the above fom, one can get lim 0 N() = l 0 l (k ). That is the desied esult. In ode to pove some popeties of the poposed fequency, we need the following two lemmas which can be seen in [9, 3]. Lemma. If u is a hamonic function in, then u dx n u dσ. (.) Lemma.3 Fo any u W, 0 ( ), it holds that u B dx 4 n u dx. (.3) Now we show some popeties of such fequency. Lemma.4 If n,, and u is a k-polyhamonic function as above, then the fequency of u satisfies that N() C, whee C is a positive constant depending only on n.
4 90 L. Tian Poof Fo any fixed i and, define the function u i and u i as follows: u i = u i+ in, u i = 0 on, u i = 0 in, u i = u i on. So u i = u i +u i. Note that fo any i =,,,k, u i ae hamonic functions, we have u i dσ n u i dσ = n which is pesented in [8, Chapte ]. On the othe hand, the functions u i so fom the Poincaé s inequality, we have B u i dσ 4 n u i dσ. u i dσ, (.4) ae all in W,p 0 ( ), Because and we have u i dσ = u i dσ + u i + u iu i B u i dσ 4 n u i u idσ = 0, u i dσ u i dσ. (.5) We wite the tem u i u i+ dσ as u i u i+ dσ = u i u i+, dσ + u i u i+, dσ + u i u i+, dσ + u i u i+, dσ = I+II+III+IV. Now we will give the estimates of I, II, III and IV sepaately. Fist conside the tem I. By using the fom (.5), we have I ( ) ( ) u i dσ + u i+, dσ 4 n u i dσ + u i+ dσ. Fo IV, by using (.4), we have IV ( ) u n idσ + u i+dσ. Now we focus on II. Also fom the foms (.4) (.5), we have fo any ǫ > 0, it holds that II ǫ u i dσ + ǫ B u i+, dσ ǫ n u i dσ + ǫn u i+ dσ.
5 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 9 Similaly, fo III, we have III Cǫ u i+ dσ + ǫn u idσ. So E() ( 4 ǫ n + n ) D()+ ( n + ) H(). ǫn Choose ǫ = 4. Then fom Lemmas..3 and the fact that n,, we have So 4 ǫ n + n = 3 n <. E() CH() +D(). Thus N() = D()+E() H() D() E() C, H() which is the desied esult. Remak. It is obvious that the esult of the above lemmas also hold fo the fequency centeed at othe points. Remak. The fequency of a hamonic function is obviously nonnegative. Fo a polyhamonic function, the fequency may not be nonnegative, but fom Lemma.4, one knows that it also has a lowe bound. Next we will show the monotonicity fomula fo this fequency. Theoem. Let u be a k-polyhamonic function. Then thee exists two positive constants C 0 and C depending only on n and k such that if N() C 0, then it holds that Poof It is easy to check that N () N() C. (.6) N () N() = + D ()+E () D()+E() H () H(). (.7) We calculate D (), E () and H () sepaately. We wite H() as follows: H() = u (x)dσ x = n u (y)dσ y, x= whee dσ x and dσ y ae the (n )-Hausdoff measues on the coesponding sphees. This implies that H i() = (n ) n u i(y)dσ y + n u i (y)u iν (y)dσ y y = y = y =
6 9 L. Tian = n H i ()+. So H () = Now conside D () and E (). Fist note that whee and Fo D i (), it holds that D i () = + n D () = E () = D i (), E i (), D i() = u i dσ E i() = u i u i+ dσ. H(). (.8) u i x x dx = div( u i x)dx u i u i x l dx x j x j x l u i dx = = n u i dx+ = n D i()+ ( ui )( ui ) x l dx x j x l x j = n D i()+ u i u i x j x l x j x ldσ = n D i ()+ u iν dσ u i x l u i x u i+ dx. x j ( ui x j x l ) dx Fo E i (), we have E i() = u i u i+ dσ = u i u i+ x x dx = div(u i u i+ x)dx = n u i u i+ dx+ u i+ u i xdx+ u i u i+ xdx = n E i()+ u i+ u i xdx+ u i u i+ xdx. Thus D i()+e i() = n (D i ()+E i ())+ u iνdσ + u i+ x u i dx u i x u i+ dx
7 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 93 + u i u i+ dx. So D ()+E () D()+E() = n + + u iν dσ ( u i+ x u i dx u i x u i+ dx+ u i u i+ dx) = n + ( u i dx+ u i u i+ dx) u iν dσ + Then we will estimate R, R and R 3 sepaately. R R +R 3 D()+E(). R u i+ x u i dx ( u i+ dx+ ( ) C u i dx+ u i dσ. Fom the simila aguments, we have ) u i dx R u i x u i+ dx ( ) u i dx+ u i+ dx ( ) C u i dx+ u idσ and R 3 u i u i+ dx ( u idx+ ( ) C u i dx+ u i dσ. u i+dx ) Fom the assumption that N() C 0 and the poof of Lemma.4, we have E() CH()+ 3 4 D() C C 0 (D()+ E() )+ 3 4 D(), whee C is the constant in Lemma.4. Choose C 0 lage enough such that ( C C ) C0 C 0 C = 7 8.
8 94 L. Tian Then D()+E() 8 D(). So R R +R 3 D()+E() CD()+CH() D()+E() C. Thus Fom (.8), we have D ()+E () D()+E() C + n + n u iν dσ. H () H() = n +. u i dσ So we finally get This ends the poof. N () ( N() u iν dσ u i dσ ) C C. Remak.3 The above theoem also holds fo the fequency centeed at othe point, i.e., if u is a polyhamonic function and N(p,) is the fequency of u centeed at the point p with adius, then it holds that dn(p,) d C, (.9) N(p,) if N(p,) C 0, whee C 0 and C ae two positive constants depending only on n and k. Lemma.5 Fo any p B, we have 4 N (p, ) ( p ) C N()+C, (.0) whee C and C ae positive constants depending only on n and k. Poof We only povethe casethat p = 4. Othecasesaesimila. Note that (p) B B3 4 and B (p). Fom Theoem., we have 4 B B 34 (p) u idx 4 CN()+C B (p) u idσ. (.)
9 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 95 Now we claim that B5 8 (p) B 58 (p) u idσ 4 CN()+C B (p) B (p) In fact, fom (.3), (.8), Lemma.4 and some diect calculation, we know that d ( d log ) u (p) idσ = n + d (p) d log(h(p,)) Thus and B 34 (p) B (p) u i dx = u idx = C C = n = n + H (p,) H(p, ) + n + u idσ. (.) B u (p) iu iν dσ H(p, ) = N(p,) C. (.3) B 34 (p) B 58 (p) u i dσ n u i (p) dσ (p) B5 8 (p) B 58 (p) u i dσ, n u (p) idσ (p) B (p) B (p) u idσ. So the claim (.) holds. Integating (.3) fom to 5 8, we obtain ( log B5 8 (p) B 58 (p) Fom Theoem., we know that 5 8 So Then fom Theoem. again, we get ( u i ) log dσ fo any, and that is the desied esult. B (p) B (p) N(p,) ( d CN p, ) C. ( N p, ) CN()+C. N(p,) CN()+C u i dσ ) = 5 8 N(p,) d.
10 96 L. Tian 3 Doubling Conditions In this section, we will show the doubling condition of a polyhamonic function u. In fact, fom the poof of Lemma.5, it is easy to see that the following doubling condition holds. Lemma 3. Let u be a k-polyhamonic function, and assume that <. Then it holds that u idσ CN()+C B B u idσ (3.) and u B idx C N()+C u B B idx, (3.) whee C and C ae two positive constants depending only on n and k. Poof We only need to pove the fom (3.). Because one can simply integate (3.) fom 0 to to get (3.). Integating (.3) fom to, we know that and thus ( H() ) ( H() ) log () n log n = H() n H()e N(t) t dt. N(t) dt, t Fom Theoem., we know that N(t) max{cn(),c 0 } CN()+C fo any t (,). Hee C is some positive constant depending only on n and k, and C 0 is the same constant as in Theoem.. So which is the desied esult. H() n H()e CN()+C = CN()+C H(), It is known that the doubling condition fo hamonic functions and bi-hamonic functions as follows. Lemma 3. Let u be a hamonic function and <. Then u dx CN()+C u dx, (3.3) B B whee N() is the fequency of u and C is a positive constant depending only on n. Lemma 3.3 Let u be a bi-hamonic function and <. Then u dx B B 4C(N()+N())+C u dx, (3.4) whee N () is the fequency of u, N () is the fequency of u, and C is a positive constant depending only on n.
11 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 97 Lemmas can be seen in [9] and [3], espectively. Now we will show the doubling condition fo a polyhamonic function. Theoem 3. Let u be a k-polyhamonic function, i.e., u satisfies that k u = 0 in B R n and assume that <, n. Then it holds that u dx ( ) N i() +C B B CC u dx, (3.5) whee C is a positive constant depending only on n and k. Poof We pove this lemma by the inductions. Assume that we have aleady known that fo any j satisfies k j l, fom (3.5) and the following inequality u j+ dx N i()+c CC i=j+ B u jdx (3.6) holds fo u j. Fom the above two lemmas, we know that fo j = k and j = k, these two inequalities hold. Now we will pove that the inequalities (3.5) and (3.6) hold fo u eplaced by u l and thus the theoem is poved. Noting that u l = u l+, it holds that fo any text function ψ C0 (B ), u l ψdx = u l+ ψdx. (3.7) B B Choose ψ = u l φ, whee φ satisfies and φ = in, φ = 0 outside B, φ < C, φ < C. Put this Ψ into (3.7), we have u l+ u l φ dx = u l (u l φ )dx B B = u lφ dx+4 u l φ u l φdx+ u l u l ( φ +φ φ)dx B B B = u lφ dx 4 u l φ u l φdx u l u l ( φ +φ φ)dx. B B B Thus u lφ dx = u l u l+ φ dx+4 u l φ u l φdx+ u l u l ( φ +φ φ)dx B B B B ( ) ) ( ) ) u l+φ dx u l φ dx +4 u l φ dx u l φ dx B B B B
12 98 L. Tian ( ) ( ) + u l( φ + φ φ )dx u l ( φ + φ φ )dx. B B Now we conside the estimate of the tem B u l φ dx. u l φ dx B = u l u l+ φ dx u l φ u l φdx B B ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) u l φ dx u l+ φ dx + u l φ dx u l φ dx B B B B ( ) ( ) u l φ dx u l+ φ dx + u l φ dx+ u l φ dx. B B B B Thus we have ( u l φ dx u lφ dx B B Fom u l+ dx and the doubling condition fo u l, we have u l dx ) ( B N i()+c CC i=l+ B N i()+c CC i=l B ) u l+φ dx +4 u l φ dx. B u l dx u l dx. (3.8) This shows that (3.6) holds fo j = l. Then fom Lemma 3. and the induction assumptions, we have u l dx and thus the desied esult holds by inductions. 4 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets N i()+c CC i=l B u l dx, (3.9) In this section, we will show the uppe bound of the measue of the nodal set fo a polyhamonic function u, i.e., we will give the poof of Theoem.. To estimate the measue of the nodal set, we need an estimate fo the numbe of zeo points of analytic functions which was fist poved in []. Lemma 4. Suppose that f: B C C is analytic with f(0) = and sup B f N fo some positive constant N. Then fo any (0,), thee holds whee C is a positive constant depending only on. H 0 ({z : f(z) = 0}) CN, (4.)
13 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 99 We also need the following pioi estimate. Lemma 4. Let u be a polyhamonic function. Then if <, we have u L () N i()+c k CC whee C is a positive constant depending only on n and k. ( u B R idx ), (4.) Poof Let w i, (x) = Γ(x y)u i+ (y)dy, i =,,,k, whee Γ(x y) = c x y n is the fundamental solution of the Laplace opeato. Then w i, (x) = Γ(x y)u i+ (y)dy C sup u i+ (y). It also holds that So w i, = u i+ in. (u i w i, ) = 0 in. Because u k is a hamonic function, it is known that fo any y, ( u k (y) = u k (z)dz (y) (y) ( C u k B (z)dz B (y) (y) ) CN k()+c ( ) u k(z)dz u k (z)dz ). Thus fo any x, w k, (x) CNk()+C ( ) u k(z)dz. On the othe hand, fom the fact that u k w k, is hamonic in B, we know that fo any x, u k (x) w k, (x) = (u k (z) w k, (z))dz (x) (x) ( ) ( u (x) k (z)dz + (x) (x) ( ) C u k B (z)dz +C sup u k (y) B y B ( k()+n k ())+C CC(N u k (z)dz (x) ) w k, (z) dz ) + CN k()+c ( u k(z)dz )
14 930 L. Tian (( ) k()+n k ())+C ( CC(N u )) k (z)dz + u k(z)dz. Then fo x, u k (x) u k (x) w k, (x) + w k, (x) (( ) k()+n k ())+C ( CC(N u k (z)dz ) ) + u k (z)dz. That is the desied esult fo u k. Repeat this agument k times, the desied esult can be poved. Now we show the measue estimate of the nodal set {x : u(x) = 0}. Poof of Theoem. Without loss of geneality, we may assume u dx =. B B Then fom Theoem 3. and Lemma.5, it holds that B (p) 6 B 6 (p) u dx 4 C N i() C fo any p B. Then thee exists a point x p B (p) such that 4 6 u(x p ) C N i() C. On the othe hand, fom Lemma 4. and (3.6), one knows that fo any x B 4, u(x) C N i()+c. Choosep j B tobethepointonthej-axisandtakef j(ω;t) = u(x pj +tω)fot ( 5 4 8, ) 5 8, whee ω S n. Then f j is an analytic function with espect to t. Extend it to a complex analytic function f j (ω;z), and keep the uppe bound. Then we have f j (ω;0) C N i() C (4.3) and f j (ω;z) C i()+c N. (4.4) Using Lemma 4., we have That means H 0({ t < 5 }) 8 : u(x p j +tω) = 0 C N i ()+C. H 0 ({t : u(x pj +tω) = 0,x pj +tω B }) C N 6 i ()+C.
15 Measue Estimates of Nodal Sets of Polyhamonic Functions 93 Then fom the integal geometic fomula, which can be seen in [3, 0], we have and this is the desied esult. H n ({x B : u(x) = 0}) C N 6 i ()+C, (4.5) 5 Gowth Popety of Polyhamonic Functions In this section, we will deive a gowth behavio of the polyhamonic functions in the whole space R n. The esult is witten in Theoem.. Poof of Theoem. Fist assume that N() is bounded, i.e., N() N 0 on R n. Then we need to show that u is a polynomial. Without loss of geneality, assume u B idσ =. (5.) B Fom the mean value fomula and the fact that u k is a hamonic function, we have that ( ) sup u k C u k B dσ B holds fo any >. Fo each i =,,,k, wite u i as u i = u i +u i as in the poof of Lemma.4, i.e., and u i = u i+ in B, u i = 0 on B Then fom the pioi estimate of u i Thus fo u k, it holds that u i = 0 in B, u i = u i on B. sup u i sup u i +sup u i and the mean value popety of u i, we have C sup B u i+ +C ( sup u k C sup u k +C B C (( B 4 Continue these aguments fo k times, we get sup u C k ( B u B idσ B ) ( u k dσ + B 4 B 4 B u i dσ ) ( u B idσ k B k ). B 4 u k dσ ) ) ).. (5.)
16 93 L. Tian Thus fom Lemma 3. and the assumption (5.), we have that sup u C CN0+C (5.3) holds fo any >. Thus u must be a polynomial and the ode of degee of u is less than o equal to CN 0 +C, whee C is a positive constant depending only on n and k. If a k-polyhamonic function u is a polynomial, then fom the fact that N() = u, i it is easy to check that N() is bounded by the odeof degeeof u. Of couse, fo any i =,,k, the functions u i ae all polynomials. Refeences [] Almgen, F. J., Diichlet s poblem fo muptiple valued functions and the egulaity of Mass minimizing integal cuents, Minimal Submanifolds and Geodesics, Obata, M. (ed.), Noth Holland, Amstedam, 979, 6. [] Donnelly, H. and Feffeman, C., Nodal sets of eigenfunctions on Riemannian manifolds, Invent. Math., 93, 988, [3] Fedee, H., Geometic Measue Theoy, Spinge-Velag, New Yok, 969. [4] Gaofalo, N. and Lin, F. H., Monotonicity popeties of vaiational integals, A p-weights and unique continuation, Indiana Univ. Math. J., 35, 986, [5] Gaofalo, N. and Lin, F. H., Unique continuation fo elliptic opeatos: a geometic-vaiational appoach, Comm. Pue. Appl. Math., 40, 987, [6] Han, Q., Schäude estimates fo elliptic opeatos with applications to nodal sets, The Jounal of Geometic Analysis, 0(3), 000, [7] Han, Q., Hadt, R. and Lin, F. H., Singula sets of highe ode elliptic equations, Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 8, 003, [8] Han, Q. and Lin, F. H., Nodal sets of solutions of elliptic diffeential equations, nodal.pdf. [9] Lin, F. H., Nodal sets of solutions of elliptic and paabolic equations, Comm. Pue. Appl. Math., 44, 99, [0] Lin, F. H. and Yang, X. P., Geometic Measue Theoy: An Intoduction, Advanced Mathematics,, Science Pess, Beijing; Intenational Pess, Boston, 00. [] Liu, H. R., Tian, L. and Yang, X. P., The gowth of H-hamonic functions on the Heisenbeg goup, Science China Mathematics, 54(4), 04, [] Schoen, R. M. and Yau, S. T., Lectues on Diffeential Geomety, Intenational Pess, Cambidge, MA, 994. [3] Tian, L. and Yang, X. P., Measue estimates of nodal sets of bi-hamonic functions, Jounal of Diffeential Equations, 56(), 04,
GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
Annales Academiæ Scientiaum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 32, 2007, 595 599 GROWTH ESTIMATES THROUGH SCALING FOR QUASILINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Teo Kilpeläinen, Henik Shahgholian and Xiao Zhong
Doubling property for the Laplacian and its applications (Course Chengdu 2007)
 Doubling popety fo the Laplacian and its applications Couse Chengdu 007) K.-D. PHUNG The oiginal appoach of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin Fo simplicity, we epoduce the poof of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin in the
Doubling popety fo the Laplacian and its applications Couse Chengdu 007) K.-D. PHUNG The oiginal appoach of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin Fo simplicity, we epoduce the poof of N. Gaofalo and F.H. Lin in the
SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF 2 2 OPERATOR MATRICES
 italian jounal of pue and applied mathematics n. 35 015 (433 44) 433 SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF OPERATOR MATRICES Watheq Bani-Domi Depatment of Mathematics
italian jounal of pue and applied mathematics n. 35 015 (433 44) 433 SOME GENERAL NUMERICAL RADIUS INEQUALITIES FOR THE OFF-DIAGONAL PARTS OF OPERATOR MATRICES Watheq Bani-Domi Depatment of Mathematics
On absence of solutions of a semi-linear elliptic equation with biharmonic operator in the exterior of a ball
 Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36, 63-69 016. Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. On absence of solutions of a semi-linea elliptic euation with bihamonic opeato
Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36, 63-69 016. Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. On absence of solutions of a semi-linea elliptic euation with bihamonic opeato
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
Jounal of Inequalities in Pue and Applied Mathematics COEFFICIENT INEQUALITY FOR A FUNCTION WHOSE DERIVATIVE HAS A POSITIVE REAL PART S. ABRAMOVICH, M. KLARIČIĆ BAKULA AND S. BANIĆ Depatment of Mathematics
A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol3 15 2007, 41 45 A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LI JULING AND GAO HONGYA Abstact We pove a new a pioi estimate fo vey weak
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol3 15 2007, 41 45 A NOTE ON VERY WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LI JULING AND GAO HONGYA Abstact We pove a new a pioi estimate fo vey weak
Integral operator defined by q-analogue of Liu-Srivastava operator
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013, No. 4, 529 537 Integal opeato defined by q-analogue of Liu-Sivastava opeato Huda Aldweby and Maslina Daus Abstact. In this pape, we shall give an application of q-analogues
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013, No. 4, 529 537 Integal opeato defined by q-analogue of Liu-Sivastava opeato Huda Aldweby and Maslina Daus Abstact. In this pape, we shall give an application of q-analogues
Research Article On Alzer and Qiu s Conjecture for Complete Elliptic Integral and Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent Function
 Abstact and Applied Analysis Volume 011, Aticle ID 697547, 7 pages doi:10.1155/011/697547 Reseach Aticle On Alze and Qiu s Conjectue fo Complete Elliptic Integal and Invese Hypebolic Tangent Function Yu-Ming
Abstact and Applied Analysis Volume 011, Aticle ID 697547, 7 pages doi:10.1155/011/697547 Reseach Aticle On Alze and Qiu s Conjectue fo Complete Elliptic Integal and Invese Hypebolic Tangent Function Yu-Ming
arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013](/thumbs/96/127989960.jpg) A mixed method fo Diichlet poblems with adial basis functions axiv:1302.2079v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 Nobet Heue Thanh Tan Abstact We pesent a simple discetization by adial basis functions fo the Poisson
A mixed method fo Diichlet poblems with adial basis functions axiv:1302.2079v1 [math.na] 8 Feb 2013 Nobet Heue Thanh Tan Abstact We pesent a simple discetization by adial basis functions fo the Poisson
Numerical approximation to ζ(2n+1)
 Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Fom the SelectedWoks of Tian-Xiao He 6 Numeical appoximation to ζ(n+1) Tian-Xiao He, Illinois Wesleyan Univesity Michael J. Dancs Available at: https://woks.bepess.com/tian_xiao_he/6/
Vanishing lines in generalized Adams spectral sequences are generic
 ISSN 364-0380 (on line) 465-3060 (pinted) 55 Geomety & Topology Volume 3 (999) 55 65 Published: 2 July 999 G G G G T T T G T T T G T G T GG TT G G G G GG T T T TT Vanishing lines in genealized Adams spectal
ISSN 364-0380 (on line) 465-3060 (pinted) 55 Geomety & Topology Volume 3 (999) 55 65 Published: 2 July 999 G G G G T T T G T T T G T G T GG TT G G G G GG T T T TT Vanishing lines in genealized Adams spectal
On the Poisson Approximation to the Negative Hypergeometric Distribution
 BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://mathusmmy/bulletin Bull Malays Math Sci Soc (2) 34(2) (2011), 331 336 On the Poisson Appoximation to the Negative Hypegeometic Distibution
BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://mathusmmy/bulletin Bull Malays Math Sci Soc (2) 34(2) (2011), 331 336 On the Poisson Appoximation to the Negative Hypegeometic Distibution
STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS HAVING THE SAME LOGARITHMIC ORDER
 UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA doi: 104467/20843828AM170027078 542017, 15 32 STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS
UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA doi: 104467/20843828AM170027078 542017, 15 32 STUDY OF SOLUTIONS OF LOGARITHMIC ORDER TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL-DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH COEFFICIENTS
KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS
 Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
Jounal of Applied Analysis Vol. 14, No. 1 2008), pp. 43 52 KOEBE DOMAINS FOR THE CLASSES OF FUNCTIONS WITH RANGES INCLUDED IN GIVEN SETS L. KOCZAN and P. ZAPRAWA Received Mach 12, 2007 and, in evised fom,
Boundedness for Marcinkiewicz integrals associated with Schrödinger operators
 Poc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci. Vol. 24, No. 2, May 24, pp. 93 23. c Indian Academy of Sciences oundedness fo Macinkiewicz integals associated with Schödinge opeatos WENHUA GAO and LIN TANG 2 School
Poc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci. Vol. 24, No. 2, May 24, pp. 93 23. c Indian Academy of Sciences oundedness fo Macinkiewicz integals associated with Schödinge opeatos WENHUA GAO and LIN TANG 2 School
SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Fixed Point Theoy, Volume 5, No. 1, 2004, 71-80 http://www.math.ubbcluj.o/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm SOME SOLVABILITY THEOREMS FOR NONLINEAR EQUATIONS G. ISAC 1 AND C. AVRAMESCU 2 1 Depatment of Mathematics Royal
Perturbation to Symmetries and Adiabatic Invariants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of Relative Motion
 Commun. Theo. Phys. Beijing, China) 43 25) pp. 577 581 c Intenational Academic Publishes Vol. 43, No. 4, Apil 15, 25 Petubation to Symmeties and Adiabatic Invaiants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of
Commun. Theo. Phys. Beijing, China) 43 25) pp. 577 581 c Intenational Academic Publishes Vol. 43, No. 4, Apil 15, 25 Petubation to Symmeties and Adiabatic Invaiants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of
3.1 Random variables
 3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
3 Chapte III Random Vaiables 3 Random vaiables A sample space S may be difficult to descibe if the elements of S ae not numbes discuss how we can use a ule by which an element s of S may be associated
15 Solving the Laplace equation by Fourier method
 5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
5 Solving the Laplace equation by Fouie method I aleady intoduced two o thee dimensional heat equation, when I deived it, ecall that it taes the fom u t = α 2 u + F, (5.) whee u: [0, ) D R, D R is the
PINCHING THEOREM FOR THE VOLUME ENTROPY. 1. Introduction
 PINCHING THEOREM FOR THE VOLUME ENTROPY FRANÇOIS LEDRAPPIER AND XIAODONG WANG 1. Intoduction Fo a compact Riemannian manifold (M n ; g) with Ric (g) (n 1), we have the following shap geometic inequalities
PINCHING THEOREM FOR THE VOLUME ENTROPY FRANÇOIS LEDRAPPIER AND XIAODONG WANG 1. Intoduction Fo a compact Riemannian manifold (M n ; g) with Ric (g) (n 1), we have the following shap geometic inequalities
Mean Curvature and Shape Operator of Slant Immersions in a Sasakian Space Form
 Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
Mean Cuvatue and Shape Opeato of Slant Immesions in a Sasakian Space Fom Muck Main Tipathi, Jean-Sic Kim and Son-Be Kim Abstact Fo submanifolds, in a Sasakian space fom, which ae tangential to the stuctue
Exceptional regular singular points of second-order ODEs. 1. Solving second-order ODEs
 (May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
(May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
The first nontrivial curve in the fučĺk spectrum of the dirichlet laplacian on the ball consists of nonradial eigenvalues
 enedikt et al. ounday Value Poblems 2011, 2011:27 RESEARCH Open Access The fist nontivial cuve in the fučĺk spectum of the diichlet laplacian on the ball consists of nonadial eigenvalues Jiřĺ enedikt 1*,
enedikt et al. ounday Value Poblems 2011, 2011:27 RESEARCH Open Access The fist nontivial cuve in the fučĺk spectum of the diichlet laplacian on the ball consists of nonadial eigenvalues Jiřĺ enedikt 1*,
Math 124B February 02, 2012
 Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
Math 24B Febuay 02, 202 Vikto Gigoyan 8 Laplace s equation: popeties We have aleady encounteed Laplace s equation in the context of stationay heat conduction and wave phenomena. Recall that in two spatial
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
New problems in universal algebraic geometry illustrated by boolean equations
 New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
New poblems in univesal algebaic geomety illustated by boolean equations axiv:1611.00152v2 [math.ra] 25 Nov 2016 Atem N. Shevlyakov Novembe 28, 2016 Abstact We discuss new poblems in univesal algebaic
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 28 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 28 Oct 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 28 Oct 2017](/thumbs/94/119001059.jpg) ON th COEFFICIENT OF DIVISORS OF x n axiv:70049v [mathnt] 28 Oct 207 SAI TEJA SOMU Abstact Let,n be two natual numbes and let H(,n denote the maximal absolute value of th coefficient of divisos of x n
ON th COEFFICIENT OF DIVISORS OF x n axiv:70049v [mathnt] 28 Oct 207 SAI TEJA SOMU Abstact Let,n be two natual numbes and let H(,n denote the maximal absolute value of th coefficient of divisos of x n
FREE TRANSVERSE VIBRATIONS OF NON-UNIFORM BEAMS
 Please cite this aticle as: Izabela Zamosa Fee tansvese vibations of non-unifom beams Scientific Reseach of the Institute of Mathematics and Compute Science Volume 9 Issue pages 3-9. The website: http://www.amcm.pcz.pl/
Please cite this aticle as: Izabela Zamosa Fee tansvese vibations of non-unifom beams Scientific Reseach of the Institute of Mathematics and Compute Science Volume 9 Issue pages 3-9. The website: http://www.amcm.pcz.pl/
A Multivariate Normal Law for Turing s Formulae
 A Multivaiate Nomal Law fo Tuing s Fomulae Zhiyi Zhang Depatment of Mathematics and Statistics Univesity of Noth Caolina at Chalotte Chalotte, NC 28223 Abstact This pape establishes a sufficient condition
A Multivaiate Nomal Law fo Tuing s Fomulae Zhiyi Zhang Depatment of Mathematics and Statistics Univesity of Noth Caolina at Chalotte Chalotte, NC 28223 Abstact This pape establishes a sufficient condition
Available online through ISSN
 Intenational eseach Jounal of Pue Algeba -() 01 98-0 Available online though wwwjpainfo ISSN 8 907 SOE ESULTS ON THE GOUP INVESE OF BLOCK ATIX OVE IGHT OE DOAINS Hanyu Zhang* Goup of athematical Jidong
Intenational eseach Jounal of Pue Algeba -() 01 98-0 Available online though wwwjpainfo ISSN 8 907 SOE ESULTS ON THE GOUP INVESE OF BLOCK ATIX OVE IGHT OE DOAINS Hanyu Zhang* Goup of athematical Jidong
 This aticle was oiginally published in a jounal published by Elsevie, the attached copy is povided by Elsevie fo the autho s benefit fo the benefit of the autho s institution, fo non-commecial eseach educational
This aticle was oiginally published in a jounal published by Elsevie, the attached copy is povided by Elsevie fo the autho s benefit fo the benefit of the autho s institution, fo non-commecial eseach educational
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theorem that relates to it
 Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
RADIALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS TO THE GRAPHIC WILLMORE SURFACE EQUATION
 RADIALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS TO THE GRAPHIC WILLMORE SURFACE EQUATION JINGYI CHEN AND YUXIANG LI Abstact. We show that a smooth adially symmetic solution u to the gaphic Willmoe suface equation is eithe
RADIALLY SYMMETRIC SOLUTIONS TO THE GRAPHIC WILLMORE SURFACE EQUATION JINGYI CHEN AND YUXIANG LI Abstact. We show that a smooth adially symmetic solution u to the gaphic Willmoe suface equation is eithe
Chaos and bifurcation of discontinuous dynamical systems with piecewise constant arguments
 Malaya Jounal of Matematik ()(22) 4 8 Chaos and bifucation of discontinuous dynamical systems with piecewise constant aguments A.M.A. El-Sayed, a, and S. M. Salman b a Faculty of Science, Aleandia Univesity,
Malaya Jounal of Matematik ()(22) 4 8 Chaos and bifucation of discontinuous dynamical systems with piecewise constant aguments A.M.A. El-Sayed, a, and S. M. Salman b a Faculty of Science, Aleandia Univesity,
ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS. D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi
 Opuscula Math. 37, no. 3 (017), 447 456 http://dx.doi.og/10.7494/opmath.017.37.3.447 Opuscula Mathematica ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi Communicated
Opuscula Math. 37, no. 3 (017), 447 456 http://dx.doi.og/10.7494/opmath.017.37.3.447 Opuscula Mathematica ON THE INVERSE SIGNED TOTAL DOMINATION NUMBER IN GRAPHS D.A. Mojdeh and B. Samadi Communicated
MATH 417 Homework 3 Instructor: D. Cabrera Due June 30. sin θ v x = v r cos θ v θ r. (b) Then use the Cauchy-Riemann equations in polar coordinates
 MATH 417 Homewok 3 Instucto: D. Cabea Due June 30 1. Let a function f(z) = u + iv be diffeentiable at z 0. (a) Use the Chain Rule and the fomulas x = cosθ and y = to show that u x = u cosθ u θ, v x = v
MATH 417 Homewok 3 Instucto: D. Cabea Due June 30 1. Let a function f(z) = u + iv be diffeentiable at z 0. (a) Use the Chain Rule and the fomulas x = cosθ and y = to show that u x = u cosθ u θ, v x = v
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II September 15, 2012 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.07: Electomagnetism II Septembe 5, 202 Pof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2 DUE DATE: Monday, Septembe 24, 202. Eithe hand it in at the lectue,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.07: Electomagnetism II Septembe 5, 202 Pof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 2 DUE DATE: Monday, Septembe 24, 202. Eithe hand it in at the lectue,
Lecture 23. Representation of the Dirac delta function in other coordinate systems
 Lectue 23 Repesentation of the Diac delta function in othe coodinate systems In a geneal sense, one can wite, ( ) = (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) = (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) J Whee J epesents the Jacobian of the tansfomation.
Lectue 23 Repesentation of the Diac delta function in othe coodinate systems In a geneal sense, one can wite, ( ) = (x x ) (y y ) (z z ) = (u u ) (v v ) (w w ) J Whee J epesents the Jacobian of the tansfomation.
Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn Tribonacci numbers with indices in arithmetic progression and their sums. Nurettin Irmak and Murat Alp
 Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 8- Vol. (0), No, pp. 5- DOI 0.85/MMN.0.5 Tibonacci numbes with indices in aithmetic pogession and thei sums Nuettin Imak and Muat Alp Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU
Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU e-issn 8- Vol. (0), No, pp. 5- DOI 0.85/MMN.0.5 Tibonacci numbes with indices in aithmetic pogession and thei sums Nuettin Imak and Muat Alp Miskolc Mathematical Notes HU
Enumerating permutation polynomials
 Enumeating pemutation polynomials Theodoulos Gaefalakis a,1, Giogos Kapetanakis a,, a Depatment of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics, Univesity of Cete, 70013 Heaklion, Geece Abstact We conside thoblem
Enumeating pemutation polynomials Theodoulos Gaefalakis a,1, Giogos Kapetanakis a,, a Depatment of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics, Univesity of Cete, 70013 Heaklion, Geece Abstact We conside thoblem
Chromatic number and spectral radius
 Linea Algeba and its Applications 426 2007) 810 814 www.elsevie.com/locate/laa Chomatic numbe and spectal adius Vladimi Nikifoov Depatment of Mathematical Sciences, Univesity of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152,
Linea Algeba and its Applications 426 2007) 810 814 www.elsevie.com/locate/laa Chomatic numbe and spectal adius Vladimi Nikifoov Depatment of Mathematical Sciences, Univesity of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152,
JANOWSKI STARLIKE LOG-HARMONIC UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS
 Hacettepe Jounal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 38 009, 45 49 JANOWSKI STARLIKE LOG-HARMONIC UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS Yaşa Polatoğlu and Ehan Deniz Received :0 :008 : Accepted 0 : :008 Abstact Let and
Hacettepe Jounal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 38 009, 45 49 JANOWSKI STARLIKE LOG-HARMONIC UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS Yaşa Polatoğlu and Ehan Deniz Received :0 :008 : Accepted 0 : :008 Abstact Let and
-Δ u = λ u. u(x,y) = u 1. (x) u 2. (y) u(r,θ) = R(r) Θ(θ) Δu = 2 u + 2 u. r = x 2 + y 2. tan(θ) = y/x. r cos(θ) = cos(θ) r.
 The Laplace opeato in pola coodinates We now conside the Laplace opeato with Diichlet bounday conditions on a cicula egion Ω {(x,y) x + y A }. Ou goal is to compute eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the
The Laplace opeato in pola coodinates We now conside the Laplace opeato with Diichlet bounday conditions on a cicula egion Ω {(x,y) x + y A }. Ou goal is to compute eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
A NEW VARIABLE STIFFNESS SPRING USING A PRESTRESSED MECHANISM
 Poceedings of the ASME 2010 Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences & Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE 2010 August 15-18, 2010, Monteal, Quebec, Canada DETC2010-28496
Poceedings of the ASME 2010 Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences & Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE 2010 August 15-18, 2010, Monteal, Quebec, Canada DETC2010-28496
Green s Identities and Green s Functions
 LECTURE 7 Geen s Identities and Geen s Functions Let us ecall The ivegence Theoem in n-dimensions Theoem 7 Let F : R n R n be a vecto field ove R n that is of class C on some closed, connected, simply
LECTURE 7 Geen s Identities and Geen s Functions Let us ecall The ivegence Theoem in n-dimensions Theoem 7 Let F : R n R n be a vecto field ove R n that is of class C on some closed, connected, simply
Regularity for Fully Nonlinear Elliptic Equations with Neumann Boundary Data
 Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 31: 1227 1252, 2006 Copyight Taylo & Fancis Goup, LLC ISSN 0360-5302 pint/1532-4133 online DOI: 10.1080/03605300600634999 Regulaity fo Fully Nonlinea Elliptic
Communications in Patial Diffeential Equations, 31: 1227 1252, 2006 Copyight Taylo & Fancis Goup, LLC ISSN 0360-5302 pint/1532-4133 online DOI: 10.1080/03605300600634999 Regulaity fo Fully Nonlinea Elliptic
Method for Approximating Irrational Numbers
 Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
Journal of Number Theory
 Jounal of umbe Theoy 3 2 2259 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDiect Jounal of umbe Theoy www.elsevie.com/locate/jnt Sums of poducts of hypegeometic Benoulli numbes Ken Kamano Depatment of Geneal
Jounal of umbe Theoy 3 2 2259 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDiect Jounal of umbe Theoy www.elsevie.com/locate/jnt Sums of poducts of hypegeometic Benoulli numbes Ken Kamano Depatment of Geneal
YUXIANG LI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES, TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY, BEIJING , P.R.CHINA.
 SOME REMARKS ON WILLMORE SURFACES EMBEDDED IN R 3 YUXIANG LI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES, TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY, BEIJING 100084, P.R.CHINA. EMAIL: YXLI@MATH.TSINGHUA.EDU.CN. Abstact. Let f : C R
SOME REMARKS ON WILLMORE SURFACES EMBEDDED IN R 3 YUXIANG LI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES, TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY, BEIJING 100084, P.R.CHINA. EMAIL: YXLI@MATH.TSINGHUA.EDU.CN. Abstact. Let f : C R
Energy Levels Of Hydrogen Atom Using Ladder Operators. Ava Khamseh Supervisor: Dr. Brian Pendleton The University of Edinburgh August 2011
 Enegy Levels Of Hydogen Atom Using Ladde Opeatos Ava Khamseh Supeviso: D. Bian Pendleton The Univesity of Edinbugh August 11 1 Abstact The aim of this pape is to fist use the Schödinge wavefunction methods
Enegy Levels Of Hydogen Atom Using Ladde Opeatos Ava Khamseh Supeviso: D. Bian Pendleton The Univesity of Edinbugh August 11 1 Abstact The aim of this pape is to fist use the Schödinge wavefunction methods
Analytical solutions to the Navier Stokes equations
 JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS 49, 113102 2008 Analytical solutions to the avie Stokes equations Yuen Manwai a Depatment of Applied Mathematics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univesity, Hung Hom, Kowloon,
JOURAL OF MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS 49, 113102 2008 Analytical solutions to the avie Stokes equations Yuen Manwai a Depatment of Applied Mathematics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univesity, Hung Hom, Kowloon,
TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS
 Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics: Advances and Applications Volume 4, Numbe, 200, Pages 97-4 TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS Dépatement de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences de
Jounal of Pue and Applied Mathematics: Advances and Applications Volume 4, Numbe, 200, Pages 97-4 TOPOLOGICAL DIVISOR OF ZERO PERTURBATION FUNCTIONS Dépatement de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences de
8 Separation of Variables in Other Coordinate Systems
 8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
A STABILITY RESULT FOR p-harmonic SYSTEMS WITH DISCONTINUOUS COEFFICIENTS. Bianca Stroffolini. 0. Introduction
 Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
Electonic Jounal of Diffeential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 02, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu o http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) A STABILITY RESULT
ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR ON THE UNIT BALL. Juntao Du and Xiangling Zhu
 Opuscula Math. 38, no. 6 (8), 89 839 https://doi.og/.7494/opmath.8.38.6.89 Opuscula Mathematica ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR FROM ω-bloch SPACES TO µ-zygmund SPACES ON THE UNIT BALL Juntao
Opuscula Math. 38, no. 6 (8), 89 839 https://doi.og/.7494/opmath.8.38.6.89 Opuscula Mathematica ESSENTIAL NORM OF AN INTEGRAL-TYPE OPERATOR FROM ω-bloch SPACES TO µ-zygmund SPACES ON THE UNIT BALL Juntao
Chapter 3: Theory of Modular Arithmetic 38
 Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Chapte 3: Theoy of Modula Aithmetic 38 Section D Chinese Remainde Theoem By the end of this section you will be able to pove the Chinese Remainde Theoem apply this theoem to solve simultaneous linea conguences
Mathematical Model of Magnetometric Resistivity. Sounding for a Conductive Host. with a Bulge Overburden
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 13, no. 7, 335-348 Mathematical Model of Magnetometic Resistivity Sounding fo a Conductive Host with a Bulge Ovebuden Teeasak Chaladgan Depatment of Mathematics Faculty
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 13, no. 7, 335-348 Mathematical Model of Magnetometic Resistivity Sounding fo a Conductive Host with a Bulge Ovebuden Teeasak Chaladgan Depatment of Mathematics Faculty
Absorption Rate into a Small Sphere for a Diffusing Particle Confined in a Large Sphere
 Applied Mathematics, 06, 7, 709-70 Published Online Apil 06 in SciRes. http://www.scip.og/jounal/am http://dx.doi.og/0.46/am.06.77065 Absoption Rate into a Small Sphee fo a Diffusing Paticle Confined in
Applied Mathematics, 06, 7, 709-70 Published Online Apil 06 in SciRes. http://www.scip.og/jounal/am http://dx.doi.og/0.46/am.06.77065 Absoption Rate into a Small Sphee fo a Diffusing Paticle Confined in
Nuclear size corrections to the energy levels of single-electron atoms
 Nuclea size coections to the enegy levels of single-electon atoms Babak Nadii Nii a eseach Institute fo Astonomy and Astophysics of Maagha (IAAM IAN P. O. Box: 554-44. Abstact A study is made of nuclea
Nuclea size coections to the enegy levels of single-electon atoms Babak Nadii Nii a eseach Institute fo Astonomy and Astophysics of Maagha (IAAM IAN P. O. Box: 554-44. Abstact A study is made of nuclea
ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS
 STUDIA UNIV BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume XLVIII, Numbe 4, Decembe 2003 ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS VATAN KARAKAYA AND NECIP SIMSEK Abstact The
STUDIA UNIV BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume XLVIII, Numbe 4, Decembe 2003 ON LACUNARY INVARIANT SEQUENCE SPACES DEFINED BY A SEQUENCE OF MODULUS FUNCTIONS VATAN KARAKAYA AND NECIP SIMSEK Abstact The
On the ratio of maximum and minimum degree in maximal intersecting families
 On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Septembe 5, 011 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Septembe 5, 011 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On the global uniform asymptotic stability of time-varying dynamical systems
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 59014), No. 1, 57 67 On the global unifom asymptotic stability of time-vaying dynamical systems Zaineb HajSalem, Mohamed Ali Hammami and Mohamed Mabouk Abstact. The objective
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 59014), No. 1, 57 67 On the global unifom asymptotic stability of time-vaying dynamical systems Zaineb HajSalem, Mohamed Ali Hammami and Mohamed Mabouk Abstact. The objective
< 1. max x B(0,1) f. ν ds(y) Use Poisson s formula for the ball to prove. (r x ) x y n ds(y) (x B0 (0, r)). 1 nα(n)r n 1
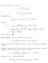 7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
7 On the othe hand, u x solves { u n in U u on U, so which implies that x G(x, y) x n ng(x, y) < n (x B(, )). Theefoe u(x) fo all x B(, ). G ν ds(y) + max g G x ν ds(y) + C( max g + max f ) f(y)g(x, y)
A Survey of Azimuthal Angle and Eigenvalues of the Laplace Equation
 Contempoay Engineeing Sciences, Vol., 08, no. 95, 4743-4749 HIKAI Ltd, www.m-hikai.com https://doi.og/0.988/ces.08.8950 A Suvey of Azimuthal Angle Eigenvalues of the Laplace Equation Luz aía ojas Duque
Contempoay Engineeing Sciences, Vol., 08, no. 95, 4743-4749 HIKAI Ltd, www.m-hikai.com https://doi.og/0.988/ces.08.8950 A Suvey of Azimuthal Angle Eigenvalues of the Laplace Equation Luz aía ojas Duque
A generalization of the Bernstein polynomials
 A genealization of the Benstein polynomials Halil Ouç and Geoge M Phillips Mathematical Institute, Univesity of St Andews, Noth Haugh, St Andews, Fife KY16 9SS, Scotland Dedicated to Philip J Davis This
A genealization of the Benstein polynomials Halil Ouç and Geoge M Phillips Mathematical Institute, Univesity of St Andews, Noth Haugh, St Andews, Fife KY16 9SS, Scotland Dedicated to Philip J Davis This
THE LAPLACE EQUATION. The Laplace (or potential) equation is the equation. u = 0. = 2 x 2. x y 2 in R 2
 THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR MAXIMALLY EDGE-CONNECTED AND SUPER-EDGE-CONNECTED GRAPHS DEPENDING ON THE CLIQUE NUMBER
 Discussiones Mathematicae Gaph Theoy 39 (019) 567 573 doi:10.7151/dmgt.096 SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR MAXIMALLY EDGE-CONNECTED AND SUPER-EDGE-CONNECTED GRAPHS DEPENDING ON THE CLIQUE NUMBER Lutz Volkmann
Discussiones Mathematicae Gaph Theoy 39 (019) 567 573 doi:10.7151/dmgt.096 SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR MAXIMALLY EDGE-CONNECTED AND SUPER-EDGE-CONNECTED GRAPHS DEPENDING ON THE CLIQUE NUMBER Lutz Volkmann
Results on the Commutative Neutrix Convolution Product Involving the Logarithmic Integral li(
 Intenational Jounal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Reseach (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2014, PP 736-741 ISSN 2347-307X (Pint) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) www.acjounals.og Results on the
Intenational Jounal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Reseach (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 8, August 2014, PP 736-741 ISSN 2347-307X (Pint) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) www.acjounals.og Results on the
Asymptotically Lacunary Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convergence and an Orlicz Function
 "Science Stays Tue Hee" Jounal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, 335-35 Science Signpost Publishing Asymptotically Lacunay Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convegence and an
"Science Stays Tue Hee" Jounal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, 335-35 Science Signpost Publishing Asymptotically Lacunay Statistical Equivalent Sequence Spaces Defined by Ideal Convegence and an
Lecture 7: Angular Momentum, Hydrogen Atom
 Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Solution to HW 3, Ma 1a Fall 2016
 Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Solution to HW 3, Ma a Fall 206 Section 2. Execise 2: Let C be a subset of the eal numbes consisting of those eal numbes x having the popety that evey digit in the decimal expansion of x is, 3, 5, o 7.
Moment-free numerical approximation of highly oscillatory integrals with stationary points
 Moment-fee numeical appoximation of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points Sheehan Olve Abstact We pesent a method fo the numeical quadatue of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points.
Moment-fee numeical appoximation of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points Sheehan Olve Abstact We pesent a method fo the numeical quadatue of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points.
Compactly Supported Radial Basis Functions
 Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Chapte 4 Compactly Suppoted Radial Basis Functions As we saw ealie, compactly suppoted functions Φ that ae tuly stictly conditionally positive definite of ode m > do not exist The compact suppot automatically
Fixed Point Results for Multivalued Maps
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 3, 119-1136 Fixed Point Results fo Multivalued Maps Abdul Latif Depatment of Mathematics King Abdulaziz Univesity P.O. Box 8003, Jeddah 1589 Saudi Aabia
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 3, 119-1136 Fixed Point Results fo Multivalued Maps Abdul Latif Depatment of Mathematics King Abdulaziz Univesity P.O. Box 8003, Jeddah 1589 Saudi Aabia
On a generalization of Eulerian numbers
 Notes on Numbe Theoy and Discete Mathematics Pint ISSN 1310 513, Online ISSN 367 875 Vol, 018, No 1, 16 DOI: 10756/nntdm018116- On a genealization of Euleian numbes Claudio Pita-Ruiz Facultad de Ingenieía,
Notes on Numbe Theoy and Discete Mathematics Pint ISSN 1310 513, Online ISSN 367 875 Vol, 018, No 1, 16 DOI: 10756/nntdm018116- On a genealization of Euleian numbes Claudio Pita-Ruiz Facultad de Ingenieía,
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Aug 2009
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Aug 2009 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Aug 2009](/thumbs/92/108818336.jpg) axiv:98.4578v [math.ca] 3 Aug 9 On L-convegence of tigonometic seies Bogdan Szal Univesity of Zielona Góa, Faculty of Mathematics, Compute Science and Econometics, 65-56 Zielona Góa, ul. Szafana 4a, Poland
axiv:98.4578v [math.ca] 3 Aug 9 On L-convegence of tigonometic seies Bogdan Szal Univesity of Zielona Góa, Faculty of Mathematics, Compute Science and Econometics, 65-56 Zielona Góa, ul. Szafana 4a, Poland
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE
 ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
ONE-POINT CODES USING PLACES OF HIGHER DEGREE GRETCHEN L. MATTHEWS AND TODD W. MICHEL DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES CLEMSON UNIVERSITY CLEMSON, SC 29634-0975 U.S.A. E-MAIL: GMATTHE@CLEMSON.EDU, TMICHEL@CLEMSON.EDU
COLLAPSING WALLS THEOREM
 COLLAPSING WALLS THEOREM IGOR PAK AND ROM PINCHASI Abstact. Let P R 3 be a pyamid with the base a convex polygon Q. We show that when othe faces ae collapsed (otated aound the edges onto the plane spanned
COLLAPSING WALLS THEOREM IGOR PAK AND ROM PINCHASI Abstact. Let P R 3 be a pyamid with the base a convex polygon Q. We show that when othe faces ae collapsed (otated aound the edges onto the plane spanned
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM
 A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
A THREE CRITICAL POINTS THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO THE ORDINARY DIRICHLET PROBLEM DIEGO AVERNA AND GABRIELE BONANNO Abstact. The aim of this pape is twofold. On one hand we establish a thee citical
A Lower Bound for the First Steklov Eigenvalue on a Domain
 Revista Colombiana de atemáticas Volumen 49(0151, páginas 95-104 A Lowe Bound fo the Fist Steklov Eigenvalue on a Domain na cota infeio paa el pime valo popio de Steklov en un dominio Gonzalo Gacía, Ósca
Revista Colombiana de atemáticas Volumen 49(0151, páginas 95-104 A Lowe Bound fo the Fist Steklov Eigenvalue on a Domain na cota infeio paa el pime valo popio de Steklov en un dominio Gonzalo Gacía, Ósca
CENTRAL INDEX BASED SOME COMPARATIVE GROWTH ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE ENTIRE FUNCTIONS FROM THE VIEW POINT OF L -ORDER. Tanmay Biswas
 J Koean Soc Math Educ Se B: Pue Appl Math ISSNPint 16-0657 https://doiog/107468/jksmeb01853193 ISSNOnline 87-6081 Volume 5, Numbe 3 August 018, Pages 193 01 CENTRAL INDEX BASED SOME COMPARATIVE GROWTH
J Koean Soc Math Educ Se B: Pue Appl Math ISSNPint 16-0657 https://doiog/107468/jksmeb01853193 ISSNOnline 87-6081 Volume 5, Numbe 3 August 018, Pages 193 01 CENTRAL INDEX BASED SOME COMPARATIVE GROWTH
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT Link to: phsicspages home page. To leave a comment o epot an eo, please use the auilia blog. Refeence: d Inveno, Ra, Intoducing Einstein s Relativit
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT Link to: phsicspages home page. To leave a comment o epot an eo, please use the auilia blog. Refeence: d Inveno, Ra, Intoducing Einstein s Relativit
The Derivative of the Sine and Cosine. A New Derivation Approach
 The Deivative of the Sine and Cosine. A New Deivation Appoach By John T. Katsikadelis Scool of Civil Engineeing, National Technical Univesity of Athens, Athens 15773, Geece. e-mail: jkats@cental.ntua.g
The Deivative of the Sine and Cosine. A New Deivation Appoach By John T. Katsikadelis Scool of Civil Engineeing, National Technical Univesity of Athens, Athens 15773, Geece. e-mail: jkats@cental.ntua.g
A Backward Identification Problem for an Axis-Symmetric Fractional Diffusion Equation
 Mathematical Modelling and Analysis Publishe: Taylo&Fancis and VGTU Volume 22 Numbe 3, May 27, 3 32 http://www.tandfonline.com/tmma https://doi.og/.3846/3926292.27.39329 ISSN: 392-6292 c Vilnius Gediminas
Mathematical Modelling and Analysis Publishe: Taylo&Fancis and VGTU Volume 22 Numbe 3, May 27, 3 32 http://www.tandfonline.com/tmma https://doi.og/.3846/3926292.27.39329 ISSN: 392-6292 c Vilnius Gediminas
12th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Cairo, Egypt, December 29-31,
 th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Caio, Egypt, Decembe 9-3, 7 5 Magnetostatic Field calculations associated with thick Solenoids in the Pesence of Ion using a Powe Seies expansion and the Complete
th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED MATHEMATICS, Caio, Egypt, Decembe 9-3, 7 5 Magnetostatic Field calculations associated with thick Solenoids in the Pesence of Ion using a Powe Seies expansion and the Complete
Multiple Criteria Secretary Problem: A New Approach
 J. Stat. Appl. Po. 3, o., 9-38 (04 9 Jounal of Statistics Applications & Pobability An Intenational Jounal http://dx.doi.og/0.785/jsap/0303 Multiple Citeia Secetay Poblem: A ew Appoach Alaka Padhye, and
J. Stat. Appl. Po. 3, o., 9-38 (04 9 Jounal of Statistics Applications & Pobability An Intenational Jounal http://dx.doi.og/0.785/jsap/0303 Multiple Citeia Secetay Poblem: A ew Appoach Alaka Padhye, and
FRACTIONAL HERMITE-HADAMARD TYPE INEQUALITIES FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVE ARE
 Kagujevac Jounal of Mathematics Volume 4) 6) Pages 7 9. FRACTIONAL HERMITE-HADAMARD TYPE INEQUALITIES FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVE ARE s )-CONVEX IN THE SECOND SENSE K. BOUKERRIOUA T. CHIHEB AND
Kagujevac Jounal of Mathematics Volume 4) 6) Pages 7 9. FRACTIONAL HERMITE-HADAMARD TYPE INEQUALITIES FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVE ARE s )-CONVEX IN THE SECOND SENSE K. BOUKERRIOUA T. CHIHEB AND
On Polynomials Construction
 Intenational Jounal of Mathematical Analysis Vol., 08, no. 6, 5-57 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikai.com https://doi.og/0.988/ima.08.843 On Polynomials Constuction E. O. Adeyefa Depatment of Mathematics, Fedeal
Intenational Jounal of Mathematical Analysis Vol., 08, no. 6, 5-57 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikai.com https://doi.og/0.988/ima.08.843 On Polynomials Constuction E. O. Adeyefa Depatment of Mathematics, Fedeal
Localization of Eigenvalues in Small Specified Regions of Complex Plane by State Feedback Matrix
 Jounal of Sciences, Islamic Republic of Ian (): - () Univesity of Tehan, ISSN - http://sciencesutaci Localization of Eigenvalues in Small Specified Regions of Complex Plane by State Feedback Matix H Ahsani
Jounal of Sciences, Islamic Republic of Ian (): - () Univesity of Tehan, ISSN - http://sciencesutaci Localization of Eigenvalues in Small Specified Regions of Complex Plane by State Feedback Matix H Ahsani
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 May 2017](/thumbs/88/114976486.jpg) On The Numbe Of Unlabeled Bipatite Gaphs Abdullah Atmaca and A Yavuz Ouç axiv:7050800v [mathco] 4 May 207 Abstact This pape solves a poblem that was stated by M A Haison in 973 [] This poblem, that has
On The Numbe Of Unlabeled Bipatite Gaphs Abdullah Atmaca and A Yavuz Ouç axiv:7050800v [mathco] 4 May 207 Abstact This pape solves a poblem that was stated by M A Haison in 973 [] This poblem, that has
HE DI ELMONSER. 1. Introduction In 1964 H. Mink and L. Sathre [15] proved the following inequality. n, n N. ((n + 1)!) n+1
![HE DI ELMONSER. 1. Introduction In 1964 H. Mink and L. Sathre [15] proved the following inequality. n, n N. ((n + 1)!) n+1 HE DI ELMONSER. 1. Introduction In 1964 H. Mink and L. Sathre [15] proved the following inequality. n, n N. ((n + 1)!) n+1](/thumbs/95/122572903.jpg) -ANALOGUE OF THE ALZER S INEQUALITY HE DI ELMONSER Abstact In this aticle, we ae inteested in giving a -analogue of the Alze s ineuality Mathematics Subject Classification (200): 26D5 Keywods: Alze s ineuality;
-ANALOGUE OF THE ALZER S INEQUALITY HE DI ELMONSER Abstact In this aticle, we ae inteested in giving a -analogue of the Alze s ineuality Mathematics Subject Classification (200): 26D5 Keywods: Alze s ineuality;
The inviscid limit of incompressible fluid flow in an annulus
 The inviscid limit of incompessible fluid flow in an annulus Saa Fietze, Robet Geity, and Tiago Picon ugust 8, 2006 bstact Incompessible, ciculaly symmetic fluid flow in a two-dimensional annulus = {x
The inviscid limit of incompessible fluid flow in an annulus Saa Fietze, Robet Geity, and Tiago Picon ugust 8, 2006 bstact Incompessible, ciculaly symmetic fluid flow in a two-dimensional annulus = {x
On the ratio of maximum and minimum degree in maximal intersecting families
 On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Mach 6, 013 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
On the atio of maximum and minimum degee in maximal intesecting families Zoltán Lóánt Nagy Lale Özkahya Balázs Patkós Máté Vize Mach 6, 013 Abstact To study how balanced o unbalanced a maximal intesecting
A PROOF OF THE INF-SUP CONDITION FOR THE STOKES EQUATIONS ON LIPSCHITZ DOMAINS
 A PROOF OF THE INF-SUP CONDITION FOR THE STOKES EQUATIONS ON LIPSCHITZ DOMAINS JAMES H. BRAMBLE Abstact. The pupose of this pape is to pesent a athe simple poof of an inequality of Nečas [9] which is equivalent
A PROOF OF THE INF-SUP CONDITION FOR THE STOKES EQUATIONS ON LIPSCHITZ DOMAINS JAMES H. BRAMBLE Abstact. The pupose of this pape is to pesent a athe simple poof of an inequality of Nečas [9] which is equivalent
On the Quasi-inverse of a Non-square Matrix: An Infinite Solution
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 11, 2017, no 27, 1337-1351 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaicom https://doiog/1012988/ams20177273 On the Quasi-invese of a Non-squae Matix: An Infinite Solution Ruben D Codeo J
Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Radial Solutions for a Class of Quasilinear Elliptic Systems
 JOURAL OF PARTIAL DIFFERETIAL EQUATIOS J Pat Diff Eq, Vol 8, o 4, pp 37-38 doi: 48/jpdev8n46 Decembe 5 Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Radial Solutions fo a Class of Quasilinea Elliptic Systems LI
JOURAL OF PARTIAL DIFFERETIAL EQUATIOS J Pat Diff Eq, Vol 8, o 4, pp 37-38 doi: 48/jpdev8n46 Decembe 5 Existence and Uniqueness of Positive Radial Solutions fo a Class of Quasilinea Elliptic Systems LI
What Form of Gravitation Ensures Weakened Kepler s Third Law?
 Bulletin of Aichi Univ. of Education, 6(Natual Sciences, pp. - 6, Mach, 03 What Fom of Gavitation Ensues Weakened Keple s Thid Law? Kenzi ODANI Depatment of Mathematics Education, Aichi Univesity of Education,
Bulletin of Aichi Univ. of Education, 6(Natual Sciences, pp. - 6, Mach, 03 What Fom of Gavitation Ensues Weakened Keple s Thid Law? Kenzi ODANI Depatment of Mathematics Education, Aichi Univesity of Education,
