Module #4. Fundamentals of strain The strain deviator Mohr s circle for strain READING LIST. DIETER: Ch. 2, Pages 38-46
|
|
|
- Bryce Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HOMEWORK From Dieter 2-7 Module #4 Fundamentals of strain The strain deviator Mohr s circle for strain READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 2, Pages Pages in Hosford Ch. 6 in Ne
2 Strain When a solid is subjected to a load, parts of the solid are displaced from their original positions. Think of it like this; the atoms making up the solid are displaced from their original positions. C Load B A B C A O O Load This displacement of points or particles under an applied stress is termed strain.
3 Total Displacement = -v u + + v v Translation Rotation Pure Shear
4 Where to begin Consider a point A in a solid located at position,,z. z w A (,,z) u u A A (+u,+v,z+w) v Appl force to the bod and point A (,,z) is displaced to A (+u,+v,z+w).
5 Displacement of points Displacement vector: u A = f(u,v,w) where u, v, and w are units of translation along the,, z aes. Solids are composed of man particles. If u A is constant for all particles, no deformation occurs (onl translation). If u A varies from particle to particle, i.e., u i = f( i ), the solid deforms. z A (,,z) u A A (+u,+v,z+w) Displacement = Translation + Rotation + Shear
6 1-D D Linear Strain A B d A B F Points A and B are displaced from their original positions The amount of displacement is a function of. Point B moves farther than Point A. Let distance A A = u. Thus, distance B B = u+(δu/δ)d = u+(u/)d.
7 1-D D Linear Strain cont d. A B d A B F Strain is defined b the following relationship: e u d d d L AB AB u u L AB d Integrating ields the displacement. u u e u o rigid bod translation, which we can subtract, ielding: u e o
8 Generalization to 3-D3 Displacement is related to the initial coordinates of the point. u ee ez z v ee ez zu w ezez ezzz i ij j Normal / Linear Strains: e u z w A (,,z) u A A (+u,+v,z+w) v u v w e, e, ezz z u v w e, e, ezz z If we orient the sstem such that the load is applied parallel to the -ais. The variables u, v, and w are displacements parallel to the,, and z aes.
9 Shear Strains in 2-D 2 D and 3-D3 Consider a square or cubic element that is distorted b shear. C D D C u A v B B Incremental displacement in -direction = u. Incremental displacement in -direction = v. Incremental displacement in z-direction = w.
10 2D Displacement of AD increases with distance along the -ais resulting in an angular distortion of -ais. C e DD u u or h DA shear distortion of the -ais in the -direction An analogous event occurs along the -ais. D A e D u v C B B BB v v or h AB shear distortion of the -ais in the -direction
11 Strain in 3-D3 The displacement strain is defined b nine strain components: e, e, e z, e, e, e z, e zz, e z, e z The strains on the negative faces are equal to satisf the requirements for equilibrium. z e z e z e zz e z e z e Notation is similar to stress; subscripts reversed: e ij : i = direction of displacement j = plane on which strain acts e e e Convention (+)ive when both i & j are (+)ive (+)ive when both i & j are (-)ive (-)ive when both i & j are opposite Tension: e ij = positive Compression: e ij = negative
12 3D Displacement Strain Matri u u u u u u z z e e ez v v v v v v eij e e ez z z ez ez ezz w w w w w w z z The displacement strain matri. Can produce pure shear strain and rigid-bod rotation.
13 u e = e u e = -e u e = u/ e = 0 v -v (1) Pure Shear w/o Rotation (2) Rotation (3) Simple Shear We need to break the displacement matri into strain and rotational components. We can decompose the total strain matri into smmetric and anti-smmetric components.
14 Decomposition of Strain e ij ij ij 1 1 ij ji ij 2 2 e e e e ji 1 2 u i j u j 1 u u i 2 Smmetric i j Anti-smmetric i j Shear Rotation
15 Displacement strain [matri] e e e e e e e e e z z z z zz = = Shear strain [tensor] + ε ij 1 1 e e e ez ez 2 2 z 1 1 z e e e ez ez 2 2 z z zz 1 1 ez ez ez ez e zz Rotation [tensor] e e ez ez 2 2 z 1 1 ij z e e 0 ez ez 2 2 z z zz 1 1 ez ez ez ez 0 2 2
16 Shear Strain Total angular change from a right angle. u e e 2 ( ij 0) e = e ij 2 (engineering shear strain) ij (1) Pure Shear w/o Rotation v z z u v w u z w v z
17 Transformation of Strains Equations for strain, analogous to those for stress, can be written b substituting for and /2 for. l m n 2lm 2mn 2nl normal zz z z l m n lm mn nl normal zz z z We can also define a coordinate sstem where there will be no shear strains. These will be principal aes
18 or zz zz zz z z zz z z - z z zz 0 -I I -I The directions in which the principal strains act are determined b substituting 1, 2, and 3, each for in: ( - )2l m zn 0 l ( - )2m zn 0 l m( - )2n 0 z z zz and then solving the resulting equations simultaneousl for l, m, and n (using the relationship l 2 + m 2 + n 2 = 1). (a) Substitute 1 for in & solve; (b) Substitute 2 for in & solve; (c) Substitute 3 for in & solve.
19 Equations for Principal Shearing Strains ma Deformation of a solid involves a combination of volume change and shape change. We can separate strain into hdrostatic (volume change) and deviatoric (shape change) components.
20 Hdrostatic Component Volume = dddz z d d dz Volume of strained element = zz dddz The volume strain is: dddz dddz zz dddz zz If we neglect the products of strains (i.e., ε ii ε jj ), this becomes: zz which is equal to the first invariant of the strain tensor
21 The hdrostatic component of strain, i.e., the mean strain, is: zz ii mean The mean strain does not induce shape change. It causes volume change. It is the hdrostatic component. The part that causes shape change is called the strain deviator. We get the strain deviator b subtracting the mean strain from the normal strain components. mean z ij mean z z z zz mean
22 The Strain Deviator mean z ij mean z z z zz mean 2 zz 3 z 2 zz 3 z z z 2 zz 3 ij ij m ij ij ij 3 3
23 Mohr s s Circle for Strain +γ/2 CW Allows us to determine the magnitude and directions of the principal strains. ma /2 H(, /2) Intersection with the -ais is min = 2 ( 2, ) C( average, 0) 2 ( 1, ) ε V(, - /2) CCW Intersection with the -ais is ma = 1
24 MAXIMUM & MINUMUM PRINCIPAL STRAINS IN 2-D STATE 2 2 ma 1 min ma 3 tan 2 normal tan 2 shear
25 Strain Measurement Strain can be measured using a strain gauge. When an object is deformed, the wires in the strain gate are strained which changes their electrical resistance, which is proportional to strain. Strain gauges make onl direct readings of linear strain. Shear strain must be determined indirectl Rectangular Delta
26 State of stress at a point: z z z z zz State of strain at a point: There are man different sstems of notation. BE WARY!
27 Matri Notation We often replace the indices with matri notation for simplicit zz 33 3 z 23 4 z This will be particularl important when we discuss higher order tensors and tensor relationships (i.e., elastic properties)
28 General forms for stress and strain in matri notation Special definitions NOTE ; ;
KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 Chapter 8 KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS Figure 8.1: 195 196 CHAPTER 8. KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 8.1 Motivation In Chapter 3, the conservation of linear momentum for a
Chapter 8 KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS Figure 8.1: 195 196 CHAPTER 8. KINEMATIC RELATIONS IN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 8.1 Motivation In Chapter 3, the conservation of linear momentum for a
σ = F/A. (1.2) σ xy σ yy σ zy , (1.3) σ xz σ yz σ zz The use of the opposite convention should cause no problem because σ ij = σ ji.
 Cambridge Universit Press 978-0-521-88121-0 - Metal Forming: Mechanics Metallurg, Third Edition Ecerpt 1 Stress Strain An understing of stress strain is essential for analzing metal forming operations.
Cambridge Universit Press 978-0-521-88121-0 - Metal Forming: Mechanics Metallurg, Third Edition Ecerpt 1 Stress Strain An understing of stress strain is essential for analzing metal forming operations.
σ = F/A. (1.2) σ xy σ yy σ zx σ xz σ yz σ, (1.3) The use of the opposite convention should cause no problem because σ ij = σ ji.
 Cambridge Universit Press 978-1-107-00452-8 - Metal Forming: Mechanics Metallurg, Fourth Edition Ecerpt 1 Stress Strain An understing of stress strain is essential for the analsis of metal forming operations.
Cambridge Universit Press 978-1-107-00452-8 - Metal Forming: Mechanics Metallurg, Fourth Edition Ecerpt 1 Stress Strain An understing of stress strain is essential for the analsis of metal forming operations.
x y plane is the plane in which the stresses act, yy xy xy Figure 3.5.1: non-zero stress components acting in the x y plane
 3.5 Plane Stress This section is concerned with a special two-dimensional state of stress called plane stress. It is important for two reasons: () it arises in real components (particularl in thin components
3.5 Plane Stress This section is concerned with a special two-dimensional state of stress called plane stress. It is important for two reasons: () it arises in real components (particularl in thin components
Strain Transformation equations
 Strain Transformation equations R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1. Stress transformation
Strain Transformation equations R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1. Stress transformation
4 Strain true strain engineering strain plane strain strain transformation formulae
 4 Strain The concept of strain is introduced in this Chapter. The approimation to the true strain of the engineering strain is discussed. The practical case of two dimensional plane strain is discussed,
4 Strain The concept of strain is introduced in this Chapter. The approimation to the true strain of the engineering strain is discussed. The practical case of two dimensional plane strain is discussed,
Lecture Triaxial Stress and Yield Criteria. When does yielding occurs in multi-axial stress states?
 Lecture 5.11 Triaial Stress and Yield Criteria When does ielding occurs in multi-aial stress states? Representing stress as a tensor operational stress sstem Compressive stress sstems Triaial stresses:
Lecture 5.11 Triaial Stress and Yield Criteria When does ielding occurs in multi-aial stress states? Representing stress as a tensor operational stress sstem Compressive stress sstems Triaial stresses:
And similarly in the other directions, so the overall result is expressed compactly as,
 SQEP Tutorial Session 5: T7S0 Relates to Knowledge & Skills.5,.8 Last Update: //3 Force on an element of area; Definition of principal stresses and strains; Definition of Tresca and Mises equivalent stresses;
SQEP Tutorial Session 5: T7S0 Relates to Knowledge & Skills.5,.8 Last Update: //3 Force on an element of area; Definition of principal stresses and strains; Definition of Tresca and Mises equivalent stresses;
Figure 1: General Plane Motion (Translation and Rotation)
 STRIN ND TH TRNSFORMTION OF STRIN INTRODUCTION - DFORMBL BODY MOTION ) Rigid Bod Motion T T Translation Rotation Figure : General Plane Motion (Translation and Rotation) Figure shows the general plane
STRIN ND TH TRNSFORMTION OF STRIN INTRODUCTION - DFORMBL BODY MOTION ) Rigid Bod Motion T T Translation Rotation Figure : General Plane Motion (Translation and Rotation) Figure shows the general plane
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT
Module #3. Transformation of stresses in 3-D READING LIST. DIETER: Ch. 2, pp Ch. 3 in Roesler Ch. 2 in McClintock and Argon Ch.
 HOMEWORK From Dieter -3, -4, 3-7 Module #3 Transformation of stresses in 3-D READING LIST DIETER: Ch., pp. 7-36 Ch. 3 in Roesler Ch. in McClintock and Argon Ch. 7 in Edelglass The Stress Tensor z z x O
HOMEWORK From Dieter -3, -4, 3-7 Module #3 Transformation of stresses in 3-D READING LIST DIETER: Ch., pp. 7-36 Ch. 3 in Roesler Ch. in McClintock and Argon Ch. 7 in Edelglass The Stress Tensor z z x O
THE GENERAL ELASTICITY PROBLEM IN SOLIDS
 Chapter 10 TH GNRAL LASTICITY PROBLM IN SOLIDS In Chapters 3-5 and 8-9, we have developed equilibrium, kinematic and constitutive equations for a general three-dimensional elastic deformable solid bod.
Chapter 10 TH GNRAL LASTICITY PROBLM IN SOLIDS In Chapters 3-5 and 8-9, we have developed equilibrium, kinematic and constitutive equations for a general three-dimensional elastic deformable solid bod.
Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Objectives
 Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid bod Concept of the free-bod diagram for a rigid bod Solve rigid-bod equilibrium problems using the equations
Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid bod Concept of the free-bod diagram for a rigid bod Solve rigid-bod equilibrium problems using the equations
Continuum mechanism: Stress and strain
 Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
1.1 The Equations of Motion
 1.1 The Equations of Motion In Book I, balance of forces and moments acting on an component was enforced in order to ensure that the component was in equilibrium. Here, allowance is made for stresses which
1.1 The Equations of Motion In Book I, balance of forces and moments acting on an component was enforced in order to ensure that the component was in equilibrium. Here, allowance is made for stresses which
Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies
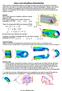 Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
Elements of Rock Mechanics
 Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aircraft Structures Structural & Loading Discontinuities
 Universit of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Aircraft Structures Structural & Loading Discontinuities Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/
Universit of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Aircraft Structures Structural & Loading Discontinuities Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/
Crystal Micro-Mechanics
 Crystal Micro-Mechanics Lectre Classical definition of stress and strain Heng Nam Han Associate Professor School of Materials Science & Engineering College of Engineering Seol National University Seol
Crystal Micro-Mechanics Lectre Classical definition of stress and strain Heng Nam Han Associate Professor School of Materials Science & Engineering College of Engineering Seol National University Seol
Consider a slender rod, fixed at one end and stretched, as illustrated in Fig ; the original position of the rod is shown dotted.
 4.1 Strain If an object is placed on a table and then the table is moved, each material particle moves in space. The particles undergo a displacement. The particles have moved in space as a rigid bod.
4.1 Strain If an object is placed on a table and then the table is moved, each material particle moves in space. The particles undergo a displacement. The particles have moved in space as a rigid bod.
1 Stress and Strain. Introduction
 1 Stress and Strain Introduction This book is concerned with the mechanical behavior of materials. The term mechanical behavior refers to the response of materials to forces. Under load, a material may
1 Stress and Strain Introduction This book is concerned with the mechanical behavior of materials. The term mechanical behavior refers to the response of materials to forces. Under load, a material may
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 4 Pure Bending
 EA 3702 echanics & aterials Science (echanics of aterials) Chapter 4 Pure Bending Pure Bending Ch 2 Aial Loading & Parallel Loading: uniform normal stress and shearing stress distribution Ch 3 Torsion:
EA 3702 echanics & aterials Science (echanics of aterials) Chapter 4 Pure Bending Pure Bending Ch 2 Aial Loading & Parallel Loading: uniform normal stress and shearing stress distribution Ch 3 Torsion:
MAE 322 Machine Design Lecture 2. Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University
 MAE 322 Machine Design Lecture 2 Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University Statics Load Failure Theories to Understand Maximum Normal Stress (MNS) Maximum Shear Stress (MSS) Distortion Energy (DE) Coulomb-Mohr
MAE 322 Machine Design Lecture 2 Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University Statics Load Failure Theories to Understand Maximum Normal Stress (MNS) Maximum Shear Stress (MSS) Distortion Energy (DE) Coulomb-Mohr
MATHEMATICAL FUNDAMENTALS I. Michele Fitzpatrick
 MTHEMTICL FUNDMENTLS I Michele Fitpatrick OVERVIEW Vectors and arras Matrices Linear algebra Del( operator Tensors DEFINITIONS vector is a single row or column of numbers. n arra is a collection of vectors
MTHEMTICL FUNDMENTLS I Michele Fitpatrick OVERVIEW Vectors and arras Matrices Linear algebra Del( operator Tensors DEFINITIONS vector is a single row or column of numbers. n arra is a collection of vectors
Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle
 Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle The fundamental quantities in solid mechanics are stresses and strains. In accordance with the continuum mechanics assumption, the molecular structure of materials is neglected
Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle The fundamental quantities in solid mechanics are stresses and strains. In accordance with the continuum mechanics assumption, the molecular structure of materials is neglected
1. Background. is usually significantly lower than it is in uniaxial tension
 NOTES ON QUANTIFYING MODES OF A SECOND- ORDER TENSOR. The mechanical behavior of rocks and rock-like materials (concrete, ceramics, etc.) strongly depends on the loading mode, defined by the values and
NOTES ON QUANTIFYING MODES OF A SECOND- ORDER TENSOR. The mechanical behavior of rocks and rock-like materials (concrete, ceramics, etc.) strongly depends on the loading mode, defined by the values and
Basic Equations of Elasticity
 A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
Symmetry and Properties of Crystals (MSE638) Stress and Strain Tensor
 Symmetry and Properties of Crystals (MSE638) Stress and Strain Tensor Somnath Bhowmick Materials Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur April 6, 2018 Tensile test and Hooke s Law Upto certain strain (0.75),
Symmetry and Properties of Crystals (MSE638) Stress and Strain Tensor Somnath Bhowmick Materials Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur April 6, 2018 Tensile test and Hooke s Law Upto certain strain (0.75),
By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in 2-D can be done graphically. + σ x σ y. cos 2θ + τ xy sin 2θ, (1) sin 2θ + τ xy cos 2θ.
 Mohr s Circle By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in -D can be done graphically. σ = σ x + σ y τ = σ x σ y + σ x σ y cos θ + τ xy sin θ, 1 sin θ + τ xy cos θ. Note that the angle of rotation,
Mohr s Circle By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in -D can be done graphically. σ = σ x + σ y τ = σ x σ y + σ x σ y cos θ + τ xy sin θ, 1 sin θ + τ xy cos θ. Note that the angle of rotation,
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. T Edition CHAPTER MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit
00 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. T Edition CHAPTER MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit
Stress and Strain ( , 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State University Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
 (3.8-3.1, 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State Universit Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering 1 Introduction MAE 316 is a continuation of MAE 314 (solid mechanics) Review
(3.8-3.1, 3.14) MAE 316 Strength of Mechanical Components NC State Universit Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering 1 Introduction MAE 316 is a continuation of MAE 314 (solid mechanics) Review
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies 1 2 Contents Introduction Free-Bod Diagram Reactions at Supports and Connections for a wo-dimensional Structure Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod in wo Dimensions Staticall Indeterminate
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies 1 2 Contents Introduction Free-Bod Diagram Reactions at Supports and Connections for a wo-dimensional Structure Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod in wo Dimensions Staticall Indeterminate
Lecture #6: 3D Rate-independent Plasticity (cont.) Pressure-dependent plasticity
 Lecture #6: 3D Rate-independent Plasticity (cont.) Pressure-dependent plasticity by Borja Erice and Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling
Lecture #6: 3D Rate-independent Plasticity (cont.) Pressure-dependent plasticity by Borja Erice and Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling
(MPa) compute (a) The traction vector acting on an internal material plane with normal n ( e1 e
 EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homework : Kinetics Due 1:00 noon Friday February 4th School of Engineering Brown University 1. For the Cauchy stress tensor with components 100 5 50 0 00 (MPa) compute (a) The
EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homework : Kinetics Due 1:00 noon Friday February 4th School of Engineering Brown University 1. For the Cauchy stress tensor with components 100 5 50 0 00 (MPa) compute (a) The
Tensor Transformations and the Maximum Shear Stress. (Draft 1, 1/28/07)
 Tensor Transformations and the Maximum Shear Stress (Draft 1, 1/28/07) Introduction The order of a tensor is the number of subscripts it has. For each subscript it is multiplied by a direction cosine array
Tensor Transformations and the Maximum Shear Stress (Draft 1, 1/28/07) Introduction The order of a tensor is the number of subscripts it has. For each subscript it is multiplied by a direction cosine array
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
APPLIED MECHANICS I Resultant of Concurrent Forces Consider a body acted upon by co-planar forces as shown in Fig 1.1(a).
 PPLIED MECHNICS I 1. Introduction to Mechanics Mechanics is a science that describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. It is divided into three parts 1.
PPLIED MECHNICS I 1. Introduction to Mechanics Mechanics is a science that describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. It is divided into three parts 1.
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Course: US01CPHY01 UNIT 1 ELASTICITY I Introduction:
 Course: US0CPHY0 UNIT ELASTICITY I Introduction: If the distance between any two points in a body remains invariable, the body is said to be a rigid body. In practice it is not possible to have a perfectly
Course: US0CPHY0 UNIT ELASTICITY I Introduction: If the distance between any two points in a body remains invariable, the body is said to be a rigid body. In practice it is not possible to have a perfectly
University of Pretoria Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering MOW 227, 2 nd Semester 2014
 Universit of Pretoria Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering MOW 7, nd Semester 04 Semester Test Date: August, 04 Total: 00 Internal eaminer: Duration: hours Mr. Riaan Meeser Instructions:
Universit of Pretoria Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering MOW 7, nd Semester 04 Semester Test Date: August, 04 Total: 00 Internal eaminer: Duration: hours Mr. Riaan Meeser Instructions:
Tutorial #1 - CivE. 205 Name: I.D:
 Tutorial # - CivE. 0 Name: I.D: Eercise : For the Beam below: - Calculate the reactions at the supports and check the equilibrium of point a - Define the points at which there is change in load or beam
Tutorial # - CivE. 0 Name: I.D: Eercise : For the Beam below: - Calculate the reactions at the supports and check the equilibrium of point a - Define the points at which there is change in load or beam
With appropriate conditions from constitutive relations, the stress distribution can be found by fitting the boundary
 Lecture Note 3 Stress Functions First Semester, Academic Year Department of Mechanical ngineering Chulalongkorn Universit Objectives # Describe the equation of equilibrium using D/3D stress elements Set
Lecture Note 3 Stress Functions First Semester, Academic Year Department of Mechanical ngineering Chulalongkorn Universit Objectives # Describe the equation of equilibrium using D/3D stress elements Set
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Stress Functions. First Semester, Academic Year 2012 Department of Mechanical Engineering Chulalongkorn University
 Lecture Note 3 Stress Functions First Semester, Academic Year 01 Department of Mechanical Engineering Chulalongkorn Universit 1 Objectives #1 Describe the equation of equilibrium using D/3D stress elements
Lecture Note 3 Stress Functions First Semester, Academic Year 01 Department of Mechanical Engineering Chulalongkorn Universit 1 Objectives #1 Describe the equation of equilibrium using D/3D stress elements
3 Stress internal forces stress stress components Stress analysis stress transformation equations principal stresses stress invariants
 3 Stress orces acting at the surfaces of components were considered in the previous chapter. The task now is to eamine forces arising inside materials, internal forces. Internal forces are described using
3 Stress orces acting at the surfaces of components were considered in the previous chapter. The task now is to eamine forces arising inside materials, internal forces. Internal forces are described using
CH. 1 FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF MECHANICS
 446.201 (Solid echanics) Professor Youn, eng Dong CH. 1 FUNDENTL PRINCIPLES OF ECHNICS Ch. 1 Fundamental Principles of echanics 1 / 14 446.201 (Solid echanics) Professor Youn, eng Dong 1.2 Generalied Procedure
446.201 (Solid echanics) Professor Youn, eng Dong CH. 1 FUNDENTL PRINCIPLES OF ECHNICS Ch. 1 Fundamental Principles of echanics 1 / 14 446.201 (Solid echanics) Professor Youn, eng Dong 1.2 Generalied Procedure
A short review of continuum mechanics
 A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
ELASTICITY (MDM 10203)
 ELASTICITY () Lecture Module 3: Fundamental Stress and Strain University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Normal Stress inconstant stress distribution σ= dp da P = da A dimensional Area of σ and A σ A 3 dimensional
ELASTICITY () Lecture Module 3: Fundamental Stress and Strain University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Normal Stress inconstant stress distribution σ= dp da P = da A dimensional Area of σ and A σ A 3 dimensional
CH.7. PLANE LINEAR ELASTICITY. Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics
 CH.7. PLANE LINEAR ELASTICITY Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics Overview Plane Linear Elasticit Theor Plane Stress Simplifing Hpothesis Strain Field Constitutive Equation Displacement Field The
CH.7. PLANE LINEAR ELASTICITY Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics Overview Plane Linear Elasticit Theor Plane Stress Simplifing Hpothesis Strain Field Constitutive Equation Displacement Field The
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
ANALYSIS OF STRAINS CONCEPT OF STRAIN
 ANALYSIS OF STRAINS CONCEPT OF STRAIN Concept of strain : if a bar is subjected to a direct load, and hence a stress the bar will change in length. If the bar has an original length L and changes by an
ANALYSIS OF STRAINS CONCEPT OF STRAIN Concept of strain : if a bar is subjected to a direct load, and hence a stress the bar will change in length. If the bar has an original length L and changes by an
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
Stability Analysis of Laminated Composite Thin-Walled Beam Structures
 Paper 224 Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures echnolog, B.H.V. opping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, Scotland Stabilit nalsis
Paper 224 Civil-Comp Press, 2012 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures echnolog, B.H.V. opping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, Scotland Stabilit nalsis
16.20 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring Instructor: Raúl Radovitzky Aeronautics & Astronautics M.I.T
 16.20 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2013 Instructor: Raúl Radovitzky Aeronautics & Astronautics M.I.T February 15, 2013 2 Contents 1 Stress and equilibrium 5 1.1 Internal forces and
16.20 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2013 Instructor: Raúl Radovitzky Aeronautics & Astronautics M.I.T February 15, 2013 2 Contents 1 Stress and equilibrium 5 1.1 Internal forces and
Chapter 8 BIAXIAL BENDING
 Chapter 8 BAXAL BENDN 8.1 DEFNTON A cross section is subjected to biaial (oblique) bending if the normal (direct) stresses from section are reduced to two bending moments and. enerall oblique bending is
Chapter 8 BAXAL BENDN 8.1 DEFNTON A cross section is subjected to biaial (oblique) bending if the normal (direct) stresses from section are reduced to two bending moments and. enerall oblique bending is
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
1 Differential Equations for Solid Mechanics
 1 Differential Eqations for Solid Mechanics Simple problems involving homogeneos stress states have been considered so far, wherein the stress is the same throghot the component nder std. An eception to
1 Differential Eqations for Solid Mechanics Simple problems involving homogeneos stress states have been considered so far, wherein the stress is the same throghot the component nder std. An eception to
Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle. General Case of Combined Stresses. General Case of Combined Stresses con t. Two-dimensional stress condition
 Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Material in this lecture was taken from chapter 4 of General Case of Combined Stresses Two-dimensional stress condition General Case of Combined Stresses con t The normal
Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Material in this lecture was taken from chapter 4 of General Case of Combined Stresses Two-dimensional stress condition General Case of Combined Stresses con t The normal
Strain Transformation and Rosette Gage Theory
 Strain Transformation and Rosette Gage Theor It is often desired to measure the full state of strain on the surface of a part, that is to measure not onl the two etensional strains, and, but also the shear
Strain Transformation and Rosette Gage Theor It is often desired to measure the full state of strain on the surface of a part, that is to measure not onl the two etensional strains, and, but also the shear
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
VYSOKÁ ŠKOLA BÁŇSKÁ TECHNICKÁ UNIVERZITA OSTRAVA
 VYSOKÁ ŠKOLA BÁŇSKÁ TECHNICKÁ UNIVERZITA OSTRAVA FAKULTA METALURGIE A MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ APPLIED MECHANICS Study Support Leo Václavek Ostrava 2015 Title:Applied Mechanics Code: Author: doc. Ing.
VYSOKÁ ŠKOLA BÁŇSKÁ TECHNICKÁ UNIVERZITA OSTRAVA FAKULTA METALURGIE A MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ APPLIED MECHANICS Study Support Leo Václavek Ostrava 2015 Title:Applied Mechanics Code: Author: doc. Ing.
Surface force on a volume element.
 STRESS and STRAIN Reading: Section. of Stein and Wysession. In this section, we will see how Newton s second law and Generalized Hooke s law can be used to characterize the response of continuous medium
STRESS and STRAIN Reading: Section. of Stein and Wysession. In this section, we will see how Newton s second law and Generalized Hooke s law can be used to characterize the response of continuous medium
Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia
 Distributed Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction Moments of nertia of an Area Moments of nertia of an Area b ntegration Polar Moments of nertia Radius of Gration of an Area Sample Problems Parallel
Distributed Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction Moments of nertia of an Area Moments of nertia of an Area b ntegration Polar Moments of nertia Radius of Gration of an Area Sample Problems Parallel
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity
 Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
The Plane Stress Problem
 14 The Plane Stress Problem IFEM Ch 14 Slide 1 Plate in Plane Stress Thickness dimension or transverse dimension z Top surface Inplane dimensions: in, plane IFEM Ch 14 Slide 2 Mathematical Idealization
14 The Plane Stress Problem IFEM Ch 14 Slide 1 Plate in Plane Stress Thickness dimension or transverse dimension z Top surface Inplane dimensions: in, plane IFEM Ch 14 Slide 2 Mathematical Idealization
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by
 SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Stress and Strain
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Stress and Strain
Concept Question Comment on the general features of the stress-strain response under this loading condition for both types of materials
 Module 5 Material failure Learning Objectives review the basic characteristics of the uni-axial stress-strain curves of ductile and brittle materials understand the need to develop failure criteria for
Module 5 Material failure Learning Objectives review the basic characteristics of the uni-axial stress-strain curves of ductile and brittle materials understand the need to develop failure criteria for
Structural Analysis I Chapter 4 - Torsion TORSION
 ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the
 Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
ME 323 Examination #2 April 11, 2018
 ME 2 Eamination #2 April, 2 PROBLEM NO. 25 points ma. A thin-walled pressure vessel is fabricated b welding together two, open-ended stainless-steel vessels along a 6 weld line. The welded vessel has an
ME 2 Eamination #2 April, 2 PROBLEM NO. 25 points ma. A thin-walled pressure vessel is fabricated b welding together two, open-ended stainless-steel vessels along a 6 weld line. The welded vessel has an
Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions
 Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions State of stress in Three Dimensions References Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength
Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions State of stress in Three Dimensions References Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength
2. Supports which resist forces in two directions. Fig Hinge. Rough Surface. Fig Rocker. Roller. Frictionless Surface
 4. Structural Equilibrium 4.1 ntroduction n statics, it becomes convenient to ignore the small deformation and displacement. We pretend that the materials used are rigid, having the propert or infinite
4. Structural Equilibrium 4.1 ntroduction n statics, it becomes convenient to ignore the small deformation and displacement. We pretend that the materials used are rigid, having the propert or infinite
The. Consortium. Continuum Mechanics. Original notes by Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank University, London, UK Produced by the CRISP Consortium Ltd
 The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
Chapter 5 Elastic Strain, Deflection, and Stability 1. Elastic Stress-Strain Relationship
 Chapter 5 Elastic Strain, Deflection, and Stability Elastic Stress-Strain Relationship A stress in the x-direction causes a strain in the x-direction by σ x also causes a strain in the y-direction & z-direction
Chapter 5 Elastic Strain, Deflection, and Stability Elastic Stress-Strain Relationship A stress in the x-direction causes a strain in the x-direction by σ x also causes a strain in the y-direction & z-direction
Chapter 14 Truss Analysis Using the Stiffness Method
 Chapter 14 Truss Analsis Using the Stiffness Method Structural Mechanics 2 ept of Arch Eng, Ajou Univ Outline undamentals of the stiffness method Member stiffness matri isplacement and force transformation
Chapter 14 Truss Analsis Using the Stiffness Method Structural Mechanics 2 ept of Arch Eng, Ajou Univ Outline undamentals of the stiffness method Member stiffness matri isplacement and force transformation
Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, Virtual Power and Conservation Principles
 Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, irtual Power and Conservation Principles 1 Introduction Stress and strain are key concepts in the analytical characterization of the mechanical state of a solid body. While stress
Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, irtual Power and Conservation Principles 1 Introduction Stress and strain are key concepts in the analytical characterization of the mechanical state of a solid body. While stress
ME 7502 Lecture 2 Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites
 ME 75 Lecture Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites Concepts from Elasticit Theor Statistical Homogeneit, Representative Volume Element, Composite Material Effective Stress-
ME 75 Lecture Effective Properties of Particulate and Unidirectional Composites Concepts from Elasticit Theor Statistical Homogeneit, Representative Volume Element, Composite Material Effective Stress-
MMJ1153 COMPUTATIONAL METHOD IN SOLID MECHANICS PRELIMINARIES TO FEM
 B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
The Kinematic Equations
 The Kinematic Equations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0139 September 19, 000 Introduction The kinematic or strain-displacement
The Kinematic Equations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0139 September 19, 000 Introduction The kinematic or strain-displacement
Exercise solutions: concepts from chapter 5
 1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
Period #5: Strain. A. Context. Structural mechanics deals with the forces placed upon mechanical systems and the resulting deformations of the system.
 Period #5: Strain A. Contet Strctral mechanics deals with the forces placed pon mechanical sstems and the reslting deformations of the sstem. Solid mechanics on the smaller scale relates stresses in the
Period #5: Strain A. Contet Strctral mechanics deals with the forces placed pon mechanical sstems and the reslting deformations of the sstem. Solid mechanics on the smaller scale relates stresses in the
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Survey of Wave Types and Characteristics
 Seminar: Vibrations and Structure-Borne Sound in Civil Engineering Theor and Applications Surve of Wave Tpes and Characteristics Xiuu Gao April 1 st, 2006 Abstract Mechanical waves are waves which propagate
Seminar: Vibrations and Structure-Borne Sound in Civil Engineering Theor and Applications Surve of Wave Tpes and Characteristics Xiuu Gao April 1 st, 2006 Abstract Mechanical waves are waves which propagate
Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
STATICS. Equivalent Systems of Forces. Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Contents & Objectives.
 3 Rigid CHATER VECTOR ECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit Bodies: Equivalent Sstems of Forces Contents & Objectives
3 Rigid CHATER VECTOR ECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit Bodies: Equivalent Sstems of Forces Contents & Objectives
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
Calculus of the Elastic Properties of a Beam Cross-Section
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Calculus of the Elastic Properties of a Beam Cross-Section Dipartimento di Modellistica per l Ingegneria Università degli Studi della Calabria (Ital) COMSOL
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Calculus of the Elastic Properties of a Beam Cross-Section Dipartimento di Modellistica per l Ingegneria Università degli Studi della Calabria (Ital) COMSOL
MAE 322 Machine Design. Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University
 MAE 322 Machine Design Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University What is this Machine Design course really about? What you will learn: How to design machine elements 1) Design so they won t break under varying
MAE 322 Machine Design Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University What is this Machine Design course really about? What you will learn: How to design machine elements 1) Design so they won t break under varying
STATICS. Moments of Inertia VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Ninth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 N E 9 Distributed CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANCS FOR ENGNEERS: STATCS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction
N E 9 Distributed CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANCS FOR ENGNEERS: STATCS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Teas Tech Universit Forces: Moments of nertia Contents ntroduction
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 CHATR Stress MCHANICS OF MATRIALS and Strain Axial Loading Stress & Strain: Axial Loading Suitability of a structure or machine may depend on the deformations in the structure as well as the stresses induced
CHATR Stress MCHANICS OF MATRIALS and Strain Axial Loading Stress & Strain: Axial Loading Suitability of a structure or machine may depend on the deformations in the structure as well as the stresses induced
Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture
 Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing
Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing
ME 243. Lecture 10: Combined stresses
 ME 243 Mechanics of Solids Lecture 10: Combined stresses Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
ME 243 Mechanics of Solids Lecture 10: Combined stresses Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
Ádx 1 + Áu 1 + u 1 ˆ
 Muddy Card Responses Lecture M16. The mud marked * is from the equivalent lecture (also M16) in 2000. I seem to have done a better job of explaining some of the derivations, as there were fewer questions
Muddy Card Responses Lecture M16. The mud marked * is from the equivalent lecture (also M16) in 2000. I seem to have done a better job of explaining some of the derivations, as there were fewer questions
Aircraft Structures Beams Torsion & Section Idealization
 Universit of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Aircraft Structures Beams Torsion & Section Idealiation Ludovic Noels omputational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials M3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/
Universit of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Aircraft Structures Beams Torsion & Section Idealiation Ludovic Noels omputational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials M3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/
Stress-strain relations
 SICLLY INDRMIN SRSS SYSMS staticall determinate stress sstem simple eample of this is a bar loaded b a weight, hanging in tension. he solution for the stress is simpl W/ where is the cross sectional area.
SICLLY INDRMIN SRSS SYSMS staticall determinate stress sstem simple eample of this is a bar loaded b a weight, hanging in tension. he solution for the stress is simpl W/ where is the cross sectional area.
Examination in Damage Mechanics and Life Analysis (TMHL61) LiTH Part 1
 Part 1 1. (1p) Define the Kronecker delta and explain its use. The Kronecker delta δ ij is defined as δ ij = 0 if i j 1 if i = j and it is used in tensor equations to include (δ ij = 1) or "sort out" (δ
Part 1 1. (1p) Define the Kronecker delta and explain its use. The Kronecker delta δ ij is defined as δ ij = 0 if i j 1 if i = j and it is used in tensor equations to include (δ ij = 1) or "sort out" (δ
