A New Static Var System Auxiliary Controller for Damping Torsional Oscillations in Series Compensated Power System
|
|
|
- Justin Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intrnational Journal of Elctrical Enginring. IN Volum, Numbr (00), pp Intrnational Rsarch Publication Hous A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr for Damping Torsional Oscillations in ris ompnsatd Powr ystm harma P.R. YA Univrsity of cinc and Tchnology, Faridabad, India prsharma966@gmail.com Abstract In this papr th application of an tatic Var ystm (V) auxiliary controllr for damping torsional oscillations in a sris compnsatd powr systm is prsntd. A nw auxiliary controllr, known as th combind drivativ of ractiv powr and drivativ of computd intrnal voltag auxiliary (DRPDIVA) controllr has bn dvlopd and incorporatd in th V control systm locatd at th middl of a sris compnsatd long transmission lin. Effctivnss of proposd controllr is tstd on a systm having a similar sprad of th torsional mods as th first IEEE bnchmark modl. Eign valu analysis study is conductd for various lvls of powr transfr and sris compnsation. Th rsults of ignvalu analysis ar validatd by carrying out tim domain analysis study basd on non linar modl. Th proposd V auxiliary controllr along with induction machin damping unit (IDU) stabilizs all th torsional mods for a wid oprating rang and thus nhancing th dynamic and transint prformanc of th systm. Kywords: tatic Var ystm, Induction machin damping unit (IDU), Auxiliary controllr, Torsional oscillations. Introduction ris compnsation is mployd in powr systms to rais th powr transfr capability. Howvr sris compnsation givs ris to dynamic instability and R problms. R occurs whn a natural frquncy of a sris compnsatd transmission systm matchs with th complmnt of on of th torsional mods of th turbingnrator shaft systm. Undr such conditions th turbin gnrator oscillats at a frquncy corrsponding to torsional mod frquncy of turbin gnrator shaft
2 5 harma P.R. During this condition th torsional oscillations can grow and may rsult in failur of turbin shaft. [-]. vral countrmasurs for damping of torsional oscillations such as Excitation control, [] tatic Var ompnsator( V), tatic ompnsator (TATO), tatic synchronous sris compnsator ( ) and unifid powr flow controllr(upf) hav bn rportd in litratur [-0]. Among ths th application of V controllr has gaind importanc in rcnt yars. In rcnt yars V has bn mployd to an incrasing xtnt in modrn powr systms [] du to its capability to work as Var gnration and absorption systms. Bsids, voltag control and improvmnt of transmission capability V in coordination with auxiliary controllrs [] can b usd for damping of torsional oscillations. Damping of powr systm oscillations plays an important rol not only in incrasing th transmission capability but also for stabilization of powr systm conditions aftr critical faults, particularly in wakly coupld ntworks. G. N. Pillai and A. Gosh t.al. [8] dsignd a powr flow controllr proposing an intgral stat fdback controllr that rducs th advrs ffct of powr flow controllr on torsional intractions and compard th torsional charactristics of compnsatd powr systm with that of fixd sris capacitor compnsatd systm. Ning Yang t.al. [9] dsignd a controllr that could modulat th impdanc of lin for nhancing th damping of torsional oscillations. But th rsults show that th controllr is not abl to damp out all th unstabl mods. In th rcnt yars thyristor controlld sris compnsators hav bn dvlopd to control powr flow on th ransmission lin and ar vry ffctiv for damping powr systm oscillations [0]. Noroozian, t. al. [6] proposd a robust control stratgy for thyristor controlld sris capacitor and static VAr systms to damp lctromchanical oscillations. haudhuri, B. Pal t al dsignd a multipl input ingl output (IO) controllr for T to improv damping of critical intr ara mods using global stabilizing signals[]. R.K.Vrma [5] t.al. hav dscribd th us of T for damping subsynchronous oscillations whn providd with clos loop currnt control. Albrto ota imos [6] t.al. hav proposd a powr oscillation damping controllr dsign implmntd in T to supprss low frquncy oscillations..k. Gupta, Narndra Kumar [] dvlopd a doubl ordr V auxiliary controllr in ombination with continuously controllabl sris compnsation and Induction machin damping unit (IDU) for damping torsional mods in a sris compnsatd powr systm. Th schm is abl to damp out th torsional mods at wid rang of sris compnsation. Howvr th control schm is complx and th difficult to implmnt. This papr xamins th ffctivnss of static var systm for damping torsional oscillations in sris compnsatd ac systm. Th V considrd is quippd with PI controllr that rgulats th gnrator trminal voltag. Auxiliary signals namly drivativ of computd intrnal voltag and drivativ of ractiv powr hav bn incorporatd in th V control loop.. Th proposd controllr along with IDU is abl to stabiliz all th torsional mods ovr a wid rang of sris compnsation lvls at various lvls of powr transfr and provids a cost ffctiv solution to R damping. Th proposd controllr is simpl and asy to implmnt bcaus th auxiliary signals ar drivd locally at th V bus.
3 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 5 ystm odl Th study systm consists of a stam turbin drivn synchronous gnrator (a sixmass modl) supplying bulk powr to an infinit bus ovr a long transmission lin (IEEE first bnchmark modl). An V of switchd capacitor and thyristor controlld ractor typ is considrd locatd at th middl of th transmission lin which provids continuously controllabl ractiv powr at its trminals in rspons to bus voltag and of drivativ of computd intrnal voltag and drivativ of ractiv powr auxiliary control signals. Th sris compnsation is applid at th snding nd of th lin. Figur. tudy ystm. Gnrator In th dtaild machin modl [8] usd hr, th stator is rprsntd by a dpndnt currnt sourc paralll with th inductanc. Th gnrator modl includs th fild winding f and a dampr winding h along d-axis and two dampr windings g and k along q-axis. Th IEEE typ- xcitation systm is usd for th gnrator. In th mchanical modl dtaild shaft torqu dynamics [] has bn considrd for th analysis of torsional mods du to R. Th rotor flux linkags ψ associatd with diffrnt windings ar dfind by: ψ f a ψ f + a ψ h + bvf + b id ψ h a ψ f + a ψ h + bid ψ g a 5ψ g + a 6ψ k + b5i () q ψ k a 7ψ g + a 8ψ k + b6iq Whr v f is th fild xcitation voltag. onstants a to a 8 and b to b 6 ar dfind in []. i d, i q ar d, and q axis componnts of th machin trminal currnt rspctivly which ar dfind with rspct to machin rfrnc fram. To hav a common axis of rprsntation with th ntwork and V, ths flux linkags ar
4 5 harma P.R. transformd to th synchronously rotating D-Q fram of rfrnc using th following transformation: i d cosδ sin δ i D i () q sin δ cosδ i Q Whr i D, i Q ar th rspctiv machin currnt componnts along D and Q axis. δ is th angl by which d-axis lads th D-axis. urrnts I d and I q, which ar th componnts of th dpndnt currnt sourc along d and q axis rspctivly, ar xprssd as: I c ψ + c ψ I d q f g h c ψ + c ψ () k Whr constants c - c ar dfind in []. ubstituting qn. () in qn. () and linarizing givs th stat and output quation of th rotor circuit as: X R A RX R + BRU R + BR U R + BRU R YR RX R + DRU R () X + D U + D U + D U YR R R R R R R R R Whr X R [ Δψ Δψ Δψ ψ ], f [ Δδ Δω] U R, U R ΔVf U R Y [ ΔI ΔI ] R h, [ Δi Δi ] D Q D g k Q chanical ystm Th mchanical systm (fig.) is dscribd by th six spring mass modl. Th govrning quations and th stat and output quations ar givn as follows: Fig.. ix-pring mass modl of mchanical systm
5 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 55 δ ω, i,,,,5,6 ω ω ω ω ω ω i 5 6 i [ ( D + D ) ω + D ω K ( δ δ ) + T ] [( D ω (D + D + D ) ω + D ω K ( δ δ ) K ( δ δ )) + T ] [( D ω (D + D + D ) ω + D ω K ( δ δ ) K ( δ δ )) + T ] [( D ω (D + D + D ) ω + D ω K ( δ δ ) K ( δ δ )) + T ] [( D ω (D + D + D ) ω + D ω K ( δ δ ) K ( δ δ )) + T ] [( D ω (D + D ) ω + D ω K ( δ δ )) + T ] m m m m as: Aftr linarzing th abov quations th stat and output quations can b writtn X A X + BU + BU (5) Y X (6) X Y U, [ Δδ ] t, Δδ, Δδ, Δδ, Δδ5, Δδ6, Δω, Δω, Δω, Δω, Δω5 Δω6 [ Δδ Δω ] t U ΔI, ΔI 5, [ ] t D Q [ Δi, Δi ] T 5, D Q Excitation ystm Th stat and output quations of th linarisd IEEE typ xcitation systm ar drivd asfollows: whr X A X + B U Y X E E E E E X E E E E [ ΔV f Vs Δ ΔV r ] t, YE [ ΔVf ], U E [ ΔVg ] (7) Ntwork Th transmission lin (fig.) is rprsntd by lumpd paramtr T- circuit. Th ntwork has bn rprsntd by its α axis quivalnt circuit, which is idntical with th positiv squnc ntwork. Th govrning quations of th α-axis, T-ntwork rprsntation ar drivd as follows:
6 56 harma P.R. Figur. α axis rprsntation of th ntwork whr di α ( L + L T ) Vα V α Ri α dt di α ( L + L ) A Vα (R + R A )i α L diα Vα dt dvα n i α i α i α dt dvα s i α (8) dt L L L + A T + d and n F imilarly, th quations can b drivd for th β- ntwork. Th α-β ntwork quations ar thn transformd to D-Q fram of rfrnc and subsquntly linarisd. Th stat and output quations for th ntwork modl ar finally obtaind as: X [A ]X + [B ]U + [B ]U + [B ] U (9) N N N N Y [ ]X + [D ]U + [D ]U + [D N N N N N N N N Y N [ N ] X N, Y N [ N] X N N N N N N ] U N Whr, X N [ i D U Δ Δ id Δ v D Δ v D Δ i Δ i Q Q Δ v Q Δ v Q N [ Δi D Δ i Q ] t, U N [ Δ İD Δ İQ ] t U N Y Y [ Δ I Δ I D Q ]t N [ ΔVgD VgQ N [ ΔVD Δ V Q ] t Δ ] t, YN [ Δi D Δ i ] t Q ] t
7 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 57 tatic Var ystm Fig. shows a small signal modl of a gnral V. Th trminal voltag prturbation V and th V incrmntal currnt wightd by th factor K D rprsnting currnt droop ar fd to th rfrnc junction. T rprsnts th masurmnt tim constant, which for simplicity is assumd to b qual for both voltag and currnt masurmnts. Th voltag rgulator is assumd to b a proportional- intgral (PI) controllr. Thyristor control action is rprsntd by an avrag dad tim T D and a firing dlay tim T s. B is th variation in TR suscptanc. V F rprsnts th incrmntal auxiliary control signal. Th α, β axis currnts ntring TR from th ntwork ar xprssd as: Fig.. V control systm with auxiliary fdback di α L V α R i α dt di β L Vβ R i β (0) dt Whr R, L rprsnt TR rsistanc and inductancs rspctivly. Th othr quations dscribing th V modl ar: z Vrf z + ΔVF ( ΔV K Δi ) z D z () T T z ( K (z ΔB I z D + K Pz z T ΔB) T s K ΔV P rf )
8 58 harma P.R. Whr ΔV, Δi ar incrmntal magnituds of V voltag and currnt, rspctivly, obtaind by linarising V (V V ), i (i i ) D + Q D + Th stat and output qns. of th V modl ar obtaind as: X [A ]X + [B ]U + [B ]U + [B ] U () Y [ ]X + [D ] U Q Whr X [ i D Q U U Y i Z Z Z [ ΔVD V Q ΔV F [ Δi D Δ i Q ] t Δ B] t, Δ ] t, U ΔVREF Dvlopmnt of V auxiliary controllr Th auxiliary signal U is implmntd through a first ordr auxiliary controllr transfr function G(s) as shown in fig.5, which is assumd to b: ΔVF K B ( + st ) G(s) U ( + st ) Figur 5. Gnral first-ordr auxiliary controllr G(s) B K BT T + () T K T ( + st )
9 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 59 Th stat and output quations ar givn by X A X + B U () [ ] [ ] [ ] X [ D ] U Y + Whr [ ] Z X, Y ΔVF B, [ A ], [ B ], [ ], [ ] T K T T T D K BT T ombind Drivativ of Ractiv Powr and Drivativ of omputd Intrnal Voltag (DRPDIV) Auxiliary ontrollr Th auxiliary controllr signal in this cas is th combination of drivativ of th lin ractiv powr and th drivativ of computd intrnal voltag with th objctiv of utilizing th bnficial contribution of both signals towards improving th dynamic prformanc of th systm. Th control schm for th composit controllr is illustratd in Fig.5. Th auxiliary control signals U and U corrspond, rspctivly, to th drivativ of lin ractiv powr and th drivativ of computd intrnal voltag dviations which ar drivd at th V bus. Fig. 5. ontrol schm for (DR.PDIV) auxiliary controllr Drivati of Ractiv Powr Auxiliary ignal Th auxiliary control signal in this cas is th dviation in th lin ractiv powr ntring th V bus. Th ractiv powr ntring th V bus can b xprssd as: Q V i V (5) D Q Q i D whr i D, i Q and V D, V Q ar th D-Q axis componnts of th lin currnt i and th V bus voltag V rspctivly. Linarizing qn. (5) givs th dviation in th ractiv powr as:
10 60 harma P.R. ΔQ V V Δi DO i Δi QO D DO Q [F6 ] X T Q + i ΔV QO Q ΔV D (6) Δ (7) whr F 6 (x) vctor having non zro lmnts as F 6 (,)V Qo, F 6 (,5)-V Do,F 6 (,)-i Qo,F 6 (,6)i Do Th drivativ of th ractiv powr is obtaind by diffrntiating q.(7) ΔQ F6 [AXT + BU ] [F7 ] X T (8) whr F 7 F 6 A and F 6 B0 Th quation (8) can b writtn as U [F R ]X R +[F ]X +[F E ]X E + [F N ]X N +[F ]X (9) whr U ΔQ c Drivativ of omputd Intrnal Voltag Auxiliary ignal Th drivativ of computd intrnal voltag signal has bn drivd by computation of intrnal voltag of th rmotly locatd gnrator utilizing locally masurabl V bus voltag and transmission lin currnts. Th DIV signal has a mor bnficial influnc on th high frquncy Torsional oscillations. As it is not fasibl to obtain this signal by masurmnt as th gnrating station and th V ar locatd far apart from ach othr, thrfor it is attmptd to driv th proposd signal in trms of paramtrs, which ar availabl at V bus. Th paramtrs utilizd for th signal ar bus voltag, transmission lin currnt at V bus and ractanc btwn th gnrator and V trminal. Th lin charging capacitanc and th rsistanc of th gnrator stator and th transmission lin ar nglctd. Th dpndnt currnt sourc rprsnt th gnrator and transformd to an quivalnt voltag sourc bhind th subtransint inductanc, From th quivalnt circuit, th total inductanc L E btwn th bus and quivalnt sourc is givn as: Fig 6: α-axis rprsntation of simplifid systm for DIV signal
11 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 6 L ( XL X ) ω0 " E Ld + LT + / Th αand β axis componnt of intrnal voltag ar xprssd as: diα α V α + LE V5 α dt (0) d iβ β Vβ + L E V5β dt () Th abov quations ar transformd to D-Q fram of rfrnc as: D VD + L E i D + ω0 L Ei Q V5D () V + L i + ω L i () Q Q E Q 0 E D V5Q whr D and Q ar D-Q axis componnt of th intrnal voltag rspctivly. Th computd intrnal voltag signal is obtaind as: + () q d Aftr linarising quation () Δ (5) D0Δ D + Q0 Δ Q 0 Putting th valu of Δ Q0 0 D0 0 Δ and Δ Q in quation (6): D [ ΔV + L Δi + ω L Δi ΔV ] [ ΔV + L Δi + ω L Δi ΔV ] Q D E E Q D 0 E 0 E D Q 5Q 5D + Whr [ F ] X T +.[ F ] T Δ (7) X X T [ X X X X X ] R E N F ( Χ5) Vctor having non-zro lmnt as follows: F Q0 D0 (,) ω0 E, F (,) F (,) L 0 F 0 D0 Q (,5) ω0 E, F (,6) 0, F (,7) L 0 D 0 Q F (,) E, F ( ) 0,5 L E L 0. X T AX T + BU in quation F [ X T ] + F [ AX T + BU ]. Δ [ F ] XT, whr F [ F + F A] 0 0 Δ (8) D0 0 Q 0 and (9) 0
12 6 harma P.R. F B 0 Th drivativ of computd intrnal voltag is givn as: Δ [ F ] T. X Aftr xpanding th quation (9) U [F R ]X R +[F ]X +[F E ]X E + [F N ]X N +[F ]X Whr U Δ ė Induction achin Damping Unit (IDU) Th proprty of induction machin to act as a gnrator or motor is utilizd to absorb th mchanical powr whn thr is xcss and to rlas it whn thr is a dficincy. inc th machin coms into opration during transints only, it is dsignd for vry high short- trm rating and vry small continuous rating. onsquntly th machin has low inrtia, low powr, and small siz and low cost. Bcaus of it small mass and tight coupling with th intrmdiat prssur turbin it has bn considrd as a singl mass unit with IP turbin. Elctrically it is connctd to th gnrator bus. Th pr unit torqu (T im ) is givn by: s T im (0) ( ) s.x ω + 0r. r and slip ( ω0 ω ) s ω 0 Hnc by considring qn. (0) th mchanical systm modl is modifid as blow: ( Dω (D + D + D ) ω + Dω K ( ) K ( )) δ δ δ δ + Tm + T im ω
13 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 6 s.x s.x + Δ s s r r ΔT im () ( ) s.x ω + 0r. r Δω As dviation in slip, Δ s ω0 At normal oprating point s 0, Δs Δω Hnc, Tim ω r ω r 0 D Δω (D + DΔω K Δω 0 + D + D + Δω ω0r ( δ δ ) K ( δ δ )) Th damping cofficint trm - (D + D + D ) of intrmdiat prssur turbin is thus modifid to -(D + D + D + /ω 0 r ) on application of IDU, similarly othr mchanical quations can b modifid to account th damping ffct of IDU for its diffrnt Locations on th TG shaft. Th stat and output quations of th diffrnt constitunt subsystms along with th auxiliary controllr stat and output quations ar combind to rsult in th linarisd stat quations of ovrall systm as: X T [A]X () Whr, X T [ X R X X E X N X X ] t Th dimnsion of th systm matrix is 5 A as tudy Th study systm consists of 0 VA synchronous gnrator supplying powr to an infinit bus ovr a 00 kv, 600 km. long sris compnsatd singl circuit transmission lin. Th systm data and torisonal spring mass systm data ar givn in Appndix. Th V rating for th lin has bn chosn to b 00 VAR inductiv to 00 VAR capacitiv. 5%,0% and 8% sris compnsation is usd at th snding nd of th transmission lin.
14 6 harma P.R. Torsional oscillations tudy Th ign valus hav bn computd for th systm with and without (DRPDIV) auxiliary controllr incorporatd in V control systm for wid rang of sris compnsation and powr transfr lvls. Tabl prsnts th ign valus for th systm at gnrator powr P G 800 W for compnsation lvls of 5%, 0% and 8% without any auxiliary controllr. Whn no auxiliary controllr is incorporatd. od and 5 ar unstabl for all lvls of sris compnsation usd. od is unstabl at 8% and mod is unstabl at 5%. od is unstabl at 5% and 8%. od is unstabl at 5%and od0 is unstabl at 5% and0% lvl of sris compnsation in th systm at P G 800 W. Tabl shows th systm ign valus whn combind drivativ of Ractiv powr and drivativ of omputd intrnal Voltag Auxiliary ontrollr is incorporatd in V control systm. It can b sn that all th mods ar stabl at P G 800 W for all lvls of sris compnsation. Tabl shows th systm ign valus without any auxiliary at P G 00,500and 800 W at 5% compnsation lvl. ods5,, and ar unstabl at all powr transfr lvls and ods and 0 ar unstabl at P G 800W. Tabl shows th systm ign valus whn combind drivativ of Ractiv powr and drivativ of omputd intrnal Voltag Auxiliary ontrollr is incorporatd in V control systm along with IDU. It can b sn that all th mods ar stabl at all lvls of powr transfr at 5% of sris compnsation Th auxiliary controllr paramtr ar slctd basd on an xtnsiv root locus study and ar listd in Tabl and. Tim domain simulation tudy A digital computr simulation study, using a nonlinar systm modl, has bn carrid out to dmonstrat th ffctivnss of th DRPDIV auxiliary controllr in coordination with IDU undr larg disturbanc conditions for damping torsional oscillations. Applying a pulsd torqu of 0% for 0.s simulats a disturbanc. Th simulation study has bn carrid out at P G 800W for 0% sris compnsation lvl. All th slf and mutual damping constants ar assumd to b zro. Fig. 6. and 6. show th rspons curvs of th trminal voltag, V bus voltag, V suscptanc, powr angl, variation in torsional torqus without and with th DRPDIV auxiliary controllr along with IDU aftr th disturbanc rspctivly. It can b sn that thr is tndncy towards instability as is xpctd from ignvalu study whn no auxiliary controllr is usd in th V control systm and th application of proposd DRPDIV auxiliary controllr in coordination with IDU damps out voltag,powr angl and torsional oscillations ffctivly and sttling tim is considrably rducd and a significant improvmnt in dynamic and transint prformanc is achivd. onclusion In this papr th ffctivnss of DRPDIV auxiliary controllr along with IDU
15 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 65 has bn valuatd for damping torsional mods for wid rang of sris compnsation at various lvls of powr transfr. Th following conclusions can b drawn from th ignvalu and tim domain simulation study prformd Th proposd auxiliary controllr is abl to stabiliz all th systm torsional mods for wid rang of oprating conditions and systm mod (mod0) is stabilizd with a good stability margin. DRPDIV auxiliary controllr dvlopd for V rapidly damps out th voltag, powr angl and torsional oscillations thus nhancing th dynamic transint prformanc of systm. Thus th proposd damping controllr provids an fficint and robust control of torsional oscillations damping ovr a wid oprating rang and undr larg disturbanc conditions Rfrncs [] Narndra Kumar,.P. Dav, Application of auxiliary controlld static var systm for damping sub synchronous rsonanc in powr systms. Elctric Powr ystm Rsarch 7 (996) [] A.Yan and Y.N.Yu, ulty mod stabilization of torsional oscillation using output fdback xcitation control, IEEE Trans. On PA, Vol.0, No.6,98, pp []. K. Gupta, Narndra Kumar t. al, ontrolld ris ompnsation in coordination with doubl Ordr V Auxiliary ontrollr and Inductiopn achin for rprssing th Torsional Oscillations in Powr systm. Elctric Powr ystm Rsarch 6(00) 9-0. [] O.Wasynczuk, Damping sub-synchronous rsonanc using ractiv powr control, IEEE Trans., PA, Vol.00, No., pp.096-0,98. [5] N.G.Hingorani, " nw schm for R damping of torsional oscillations and transint torqus-part, IEEE Trans., PA, Vol.00, No., pp ,08. [6] Noroozian,. Ghandhari,. Andrsson,G. Gronquist J. Hiskns, A robust control stratgy for shunt and sris ractiv compnsators to damp lctromchanical oscillations IEEE Trans. On Powr Dlivry, Vol.6, Oct (00) [7]. K. Gupta, N. Kumar, Damping ubsynchronous Rsonanc in Powr ystms, IEE Proc. Gnr. Trans. Distrib.Vol.9, No.6, 00, pp [8] G. N. Pillai, Arindam Gosh, A. Joshi, Torsional Oscillation tudis in an ompnsatd Powr ystm, Elctric Powr ystm rsarch 55(000) [9] Ning, Yang, Q. Liu, J. D. cally, T controllr Dsign for Damping Intr Ara Oscillations, IEEE Trans. On Powr ystm, () (998) 0-0. [0] R.. Ramshaw, K.R. Padiyar, Gnralizd systm odl for lip Ring achins, IEEE Proc.0 (6) 97.
16 66 harma P.R. [] K. R. Padiayar, R.K. Varma, Damping Torqu Analysis of tatic Var ontrollrs, IEEE Trans. on Powr ystms, 6() (99) [] Januszwski,. achowski, J Bialk J.W., Application of dirct Lyapunov mthod to improv damping of powr swings by control of UPF, IEE Proc. Gnr. Trans. Distrib. vol 5, (00), [] haudhuri, B. Pal, B.. Robust damping of multipl swing mods mploying global stabilizing signals with T, IEEE Trans. On Powr yst., Vol.9, pp , Fb.00. [] assimo Bongiorno, Jan vnsson, Lnnart Angquist, ingl Phas V Basd for ub synchronous Rsonanc Damping, IEEE Trans. On Powr Dlivry, Vol., July 008, [5] Rajiv K.Varma, oubhik Auddy and Ysni msdini, itigation of sub synchronous rsonanc in a sris-compnsatd wind farm using FAT controllrs, IEEE transactions on powr dlivry, vol., no., pp , 008. [6] Albrto ota imõs, Digo havs avlli, Paulo ésar Pllanda, Nlson artin and Pirr Apkarian, Robust Dsign of a T Oscillation Damping ontrollr in a Wak 500-kV Intrconnction onsidring ultipl Powr Flow cnarios and Extrnal Disturbancs, IEEE transactions on powr systms, vol., no., pp.6-6, 009 Appndix Gnrator Data: 0 VA, KV, R a 0.006, X L 0., Xo0.95 T do 6.66, Tqo 0., Tdo 0.0, Tqo 0.057s X d.9, X q.7, X d 0.67, Xq., Xd 0., Xq 0. p.u.. I Typ Excitation ystm T R 0, T A 0.0, T E.0, T F.0s, K A 00, K E.0; K F 0.06 put. V Fmax.9, V Fmin 0, V Rmax 7., V R min -7. Transformr Data R T 0, XT 0.5 p.u. (Gnrator Bas) Transmission Lin Data Voltag 00 KV, Lngth 600 km, Rsistanc R 0.0Ω / km, Ractanc X 0.5 Ω / km uscptanc B.7μ mho / km V Data ix-puls Opration
17 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 67 T.ms, T 5ms, T D.667ms, K 00, K P 0.5, K D 0.0 Torsional spring-mass systm data All slf and mutual damping constants ar assumd to zro Tabl. ystm Eign Valus Without Auxilliary ontrollr od P G 00 W P G 500 W P G 800 W od ±j ±j ±j od.059±j ±j ±j0.76 od.0±j ±j ±j60.5 od ±j ±j ±j6.969 od -.067±j ±j ±j98.77 od ±j ±j ±j.987 Elctrical od -9.56±j ±j ±j9.665 Tabl. ystm Eign Valus With ombind Drivativ Of omputd Intrnal Voltag& Drivativ Of Ractiv Powr With Imdu At 5 % ompnsation Lvl od PG00W K B , T 0.0, T K B , T 0.00 T 0.05 PG500W K B , T 0.0, T K B , T 0.00, T 0.07 PG800W K B -.006, T 0.0, T K B , T 0.00, T od ±j ±j ±j98.00 od -.060±j ±j ±j0.566 od -.075±j ±j ±j od -.005±j ±j ±j od -.05±j ±j ±j od ±j ±j ±j7.88
18 68 harma P.R. Elctrical mod -.86± j ± j ±j9.56 Tabl. ystm Eign Valus Without Auxilliary ontrollr PG800W od 5% 0% 8% od ±j ±j ±j od.±j ±j ±j0.709 od ±j ±j ±j60.66 od.00±j ±j ±j6.999 od.000±j ±j ±j98.69 od 0.05±j ±j ±j7.86 Elctrical od -0.68±j ± ± Tabl. ystm Eign Valus with Drivativ of Ractiv Powr and Drivativ of omputd Intrnal Voltag Auxiliary ontrollr at P G 800W od 5% K B T T 0.5 K B T 0.00T 0. 0% K B -.0, T 0.0, T K B , T 0.00, T0. 8% K B -.00, T.0, T 0. K B -.009, T 0.00, T 0. od ±j ±j ±j98.00 od -.65±j ±j ±j od -.069±j ±j ±j60.67 od -.087±j ±j ±j od -.00±j ±j ±j od ± ±j ±j Elctrical od ± ± ±7.9
19 A Nw tatic Var ystm Auxiliary ontrollr 69 Fig.6. (a-g) Rspons curvs without any auxiliary controllr at Pg 800 W du to 0% incras in T mch for 0. scs (T-circuit odl) Fig.6. (a-g) Rspons curvs with DRPDIV auxiliary controllr and IDU at Pg 800 W du to 0% incras in T mch for 0. sc (T-circuit odl)
20 70 harma P.R.
A New Scheme for Damping Torsional Modes in a Series Compensated Power System
 International Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering, Vol, o. 7, ovember 009 A ew Scheme for amping Torsional odes in a Series Compensated Power System Abstract In the present paper, a new scheme for
International Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering, Vol, o. 7, ovember 009 A ew Scheme for amping Torsional odes in a Series Compensated Power System Abstract In the present paper, a new scheme for
2/12/2013. Overview. 12-Power Transmission Text: Conservation of Complex Power. Introduction. Power Transmission-Short Line
 //03 Ovrviw -owr Transmission Txt: 4.6-4.0 ECEGR 45 owr ystms Consrvation of Complx owr hort in owr Transmission owr Transmission isualization Radial in Mdium and ong in owr Transmission oltag Collaps
//03 Ovrviw -owr Transmission Txt: 4.6-4.0 ECEGR 45 owr ystms Consrvation of Complx owr hort in owr Transmission owr Transmission isualization Radial in Mdium and ong in owr Transmission oltag Collaps
Design Guidelines for Quartz Crystal Oscillators. R 1 Motional Resistance L 1 Motional Inductance C 1 Motional Capacitance C 0 Shunt Capacitance
 TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Rotor Stationary Control Analysis Based on Coupling KdV Equation Finite Steady Analysis Liu Dalong1,a, Xu Lijuan2,a
 204 Intrnational Confrnc on Computr Scinc and Elctronic Tchnology (ICCSET 204) Rotor Stationary Control Analysis Basd on Coupling KdV Equation Finit Stady Analysis Liu Dalong,a, Xu Lijuan2,a Dpartmnt of
204 Intrnational Confrnc on Computr Scinc and Elctronic Tchnology (ICCSET 204) Rotor Stationary Control Analysis Basd on Coupling KdV Equation Finit Stady Analysis Liu Dalong,a, Xu Lijuan2,a Dpartmnt of
A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Decoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Codes
 Procdings of th 9th WSEAS Intrnational Confrnc on APPLICATIONS of COMPUTER ENGINEERING A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Dcoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Cods CHIRAG DADLANI and RANJAN BOSE Dpartmnt of Elctrical
Procdings of th 9th WSEAS Intrnational Confrnc on APPLICATIONS of COMPUTER ENGINEERING A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Dcoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Cods CHIRAG DADLANI and RANJAN BOSE Dpartmnt of Elctrical
IVE(TY) Department of Engineering E&T2520 Electrical Machines 1 Miscellaneous Exercises
 TRANSFORMER Q1 IE(TY) Dpartmnt of Enginring E&T50 Elctrical Machins 1 Miscllanous Exrciss Q Q3 A singl phas, 5 ka, 0/440, 60 Hz transformr gav th following tst rsults. Opn circuit tst (440 sid opn): 0
TRANSFORMER Q1 IE(TY) Dpartmnt of Enginring E&T50 Elctrical Machins 1 Miscllanous Exrciss Q Q3 A singl phas, 5 ka, 0/440, 60 Hz transformr gav th following tst rsults. Opn circuit tst (440 sid opn): 0
Sliding Mode Flow Rate Observer Design
 Sliding Mod Flow Rat Obsrvr Dsign Song Liu and Bin Yao School of Mchanical Enginring, Purdu Univrsity, Wst Lafaytt, IN797, USA liu(byao)@purdudu Abstract Dynamic flow rat information is ndd in a lot of
Sliding Mod Flow Rat Obsrvr Dsign Song Liu and Bin Yao School of Mchanical Enginring, Purdu Univrsity, Wst Lafaytt, IN797, USA liu(byao)@purdudu Abstract Dynamic flow rat information is ndd in a lot of
Dynamic Modelling of Hoisting Steel Wire Rope. Da-zhi CAO, Wen-zheng DU, Bao-zhu MA *
 17 nd Intrnational Confrnc on Mchanical Control and Automation (ICMCA 17) ISBN: 978-1-6595-46-8 Dynamic Modlling of Hoisting Stl Wir Rop Da-zhi CAO, Wn-zhng DU, Bao-zhu MA * and Su-bing LIU Xi an High
17 nd Intrnational Confrnc on Mchanical Control and Automation (ICMCA 17) ISBN: 978-1-6595-46-8 Dynamic Modlling of Hoisting Stl Wir Rop Da-zhi CAO, Wn-zhng DU, Bao-zhu MA * and Su-bing LIU Xi an High
10. The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Life Science Journal 2013;10(4) Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor (TCSC) for Power System Stabilization
 Thyristor Controlld Sris Capacitor () or or Systm Stabilization Mansour Babikr dris and Ali Juma Elzubia Dpt. o Elctrical Enginring, Faculty o Enginring, Misurata Univrsity Abstract: Th dynamic stability
Thyristor Controlld Sris Capacitor () or or Systm Stabilization Mansour Babikr dris and Ali Juma Elzubia Dpt. o Elctrical Enginring, Faculty o Enginring, Misurata Univrsity Abstract: Th dynamic stability
Torque Ripple Minimization in Switched Reluctance Motor Using Passivity-Based Robust Adaptive Control
 Intrnational Journal of Elctrical and Elctronics Enginring 5: orqu Rippl Minimization in Switchd Rluctanc Motor Using Passivity-Basd Control M.M. Namazi, S.M. Saghaiannjad, and A. Rashidi Abstract In this
Intrnational Journal of Elctrical and Elctronics Enginring 5: orqu Rippl Minimization in Switchd Rluctanc Motor Using Passivity-Basd Control M.M. Namazi, S.M. Saghaiannjad, and A. Rashidi Abstract In this
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
Linear-Phase FIR Transfer Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Let
 It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
Apparent Power and Power Factor Measurement by Using FPGA-based Chip Considering Nonsinusoidal and Unbalanced Conditions
 Procdings of t 8t WE Intrnational Confrnc on Instrumntation, Masurmnt, Circuits and ystms pparnt Powr and Powr Factor Masurmnt by Using FPG-basd Cip Considring Nonsinusoidal and Unbalancd Conditions HU-CHEN
Procdings of t 8t WE Intrnational Confrnc on Instrumntation, Masurmnt, Circuits and ystms pparnt Powr and Powr Factor Masurmnt by Using FPG-basd Cip Considring Nonsinusoidal and Unbalancd Conditions HU-CHEN
Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 2014/Dec./23 Neutrino frontier workshop 2014 Ryosuke Sasaki (Iwate U.)
 Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 214/Dc./23 Nutrino frontir workshop 214 Ryosuk Sasaki (Iwat U.) Tabl of Contnts Dvlopmnt of gnrating lctric fild in LAr TPC Introduction - Gnrating strong lctric fild is on of
Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 214/Dc./23 Nutrino frontir workshop 214 Ryosuk Sasaki (Iwat U.) Tabl of Contnts Dvlopmnt of gnrating lctric fild in LAr TPC Introduction - Gnrating strong lctric fild is on of
Synchronous machines
 Synchronous gnrator (altrnator): transorms mchanical nrgy into lctric nrgy; dsignd to gnrat sinusoidal oltags and currnts; usd in most powr plants, or car altrnators, tc. Synchronous motor: transorms lctric
Synchronous gnrator (altrnator): transorms mchanical nrgy into lctric nrgy; dsignd to gnrat sinusoidal oltags and currnts; usd in most powr plants, or car altrnators, tc. Synchronous motor: transorms lctric
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Preliminary Fundamentals
 1.0 Introduction Prliminary Fundamntals In all of our prvious work, w assumd a vry simpl modl of th lctromagntic torqu T (or powr) that is rquird in th swing quation to obtain th acclrating torqu. This
1.0 Introduction Prliminary Fundamntals In all of our prvious work, w assumd a vry simpl modl of th lctromagntic torqu T (or powr) that is rquird in th swing quation to obtain th acclrating torqu. This
Full Order Observer Controller Design for Two Interacting Tank System Based on State Space Approach
 Intrnational Journal of Application or Innovation in Enginring & Managmnt (IJAIEM) Wb Sit: www.ijaim.org Email: ditor@ijaim.org Volum 6, Issu 7, July 07 ISSN 39-4847 Full Ordr Obsrvr Controllr Dsign for
Intrnational Journal of Application or Innovation in Enginring & Managmnt (IJAIEM) Wb Sit: www.ijaim.org Email: ditor@ijaim.org Volum 6, Issu 7, July 07 ISSN 39-4847 Full Ordr Obsrvr Controllr Dsign for
2F1120 Spektrala transformer för Media Solutions to Steiglitz, Chapter 1
 F110 Spktrala transformr för Mdia Solutions to Stiglitz, Chaptr 1 Prfac This documnt contains solutions to slctd problms from Kn Stiglitz s book: A Digital Signal Procssing Primr publishd by Addison-Wsly.
F110 Spktrala transformr för Mdia Solutions to Stiglitz, Chaptr 1 Prfac This documnt contains solutions to slctd problms from Kn Stiglitz s book: A Digital Signal Procssing Primr publishd by Addison-Wsly.
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
System variables. Basic Modeling Concepts. Basic elements single and. Power = effort x flow. Power = F x v. Power = V x i. Power = T x w.
 Basic Modling Concpts Basic lmnts singl and multiport t dvics Systm variabls v m F V i Powr F x v T w Powr T x w Powr V x i P Q Powr P x Q Powr ort x low Eort & low ar powr variabls Eorts t... Flows...
Basic Modling Concpts Basic lmnts singl and multiport t dvics Systm variabls v m F V i Powr F x v T w Powr T x w Powr V x i P Q Powr P x Q Powr ort x low Eort & low ar powr variabls Eorts t... Flows...
Finite element discretization of Laplace and Poisson equations
 Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
CHAPTER 10. Consider the transmission lines for voltage and current as developed in Chapter 9 from the distributed equivalent circuit shown below.
 CHAPTER 1 1. Sinusoidal Stady Stat in Transmission ins 1.1 Phasor Rprsntation of olta and Currnt Wavs Considr th transmission lins for volta and currnt as dvlopd in Chaptr 9 from th distributd quivalnt
CHAPTER 1 1. Sinusoidal Stady Stat in Transmission ins 1.1 Phasor Rprsntation of olta and Currnt Wavs Considr th transmission lins for volta and currnt as dvlopd in Chaptr 9 from th distributd quivalnt
Impact of the Sampling Period on the Design of Digital PID Controllers
 Impact of th Sampling Priod on th Dsign of Digital PID Controllrs Dimitris Tsamatsoulis Halyps Building Matrials S.A. 17 th klm Nat. Road Athns Korinth, Aspropyrgos, Grc d.tsamatsoulis@halyps.gr Abstract
Impact of th Sampling Priod on th Dsign of Digital PID Controllrs Dimitris Tsamatsoulis Halyps Building Matrials S.A. 17 th klm Nat. Road Athns Korinth, Aspropyrgos, Grc d.tsamatsoulis@halyps.gr Abstract
Modified Direct Torque Control for Single-phase Induction Motor Drives
 Modifid Dirct Torqu Control for Singl-phas Induction Motor Drivs THANATCHAI KULWORAWANICHPONG and TAWAT CHUCHIT Powr Systm Rsarch Unit School of Elctrical Enginring Suranar Univrsity of Tchnology Univrsity
Modifid Dirct Torqu Control for Singl-phas Induction Motor Drivs THANATCHAI KULWORAWANICHPONG and TAWAT CHUCHIT Powr Systm Rsarch Unit School of Elctrical Enginring Suranar Univrsity of Tchnology Univrsity
Calculation of electromotive force induced by the slot harmonics and parameters of the linear generator
 Calculation of lctromotiv forc inducd by th lot harmonic and paramtr of th linar gnrator (*)Hui-juan IU (**)Yi-huang ZHANG (*)School of Elctrical Enginring, Bijing Jiaotong Univrity, Bijing,China 8++58483,
Calculation of lctromotiv forc inducd by th lot harmonic and paramtr of th linar gnrator (*)Hui-juan IU (**)Yi-huang ZHANG (*)School of Elctrical Enginring, Bijing Jiaotong Univrity, Bijing,China 8++58483,
Coupled Pendulums. Two normal modes.
 Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
INC 693, 481 Dynamics System and Modelling: Linear Graph Modeling II Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Professor
 INC 69, 48 Dynamics Systm and Modlling: Linar Graph Modling II Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Profssor Dpartmnt of Control Systm and Instrumntation Enginring King Mongkut s Unnivrsity of Tchnology Thonuri
INC 69, 48 Dynamics Systm and Modlling: Linar Graph Modling II Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Profssor Dpartmnt of Control Systm and Instrumntation Enginring King Mongkut s Unnivrsity of Tchnology Thonuri
2008 AP Calculus BC Multiple Choice Exam
 008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
ECE 344 Microwave Fundamentals
 ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
Lecture 2: Discrete-Time Signals & Systems. Reza Mohammadkhani, Digital Signal Processing, 2015 University of Kurdistan eng.uok.ac.
 Lctur 2: Discrt-Tim Signals & Systms Rza Mohammadkhani, Digital Signal Procssing, 2015 Univrsity of Kurdistan ng.uok.ac.ir/mohammadkhani 1 Signal Dfinition and Exampls 2 Signal: any physical quantity that
Lctur 2: Discrt-Tim Signals & Systms Rza Mohammadkhani, Digital Signal Procssing, 2015 Univrsity of Kurdistan ng.uok.ac.ir/mohammadkhani 1 Signal Dfinition and Exampls 2 Signal: any physical quantity that
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis
 Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 5 Two-Dimnsional Formulation Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 5 Two-Dimnsional Formulation Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
TOPOLOGY DESIGN OF STRUCTURE LOADED BY EARTHQUAKE. Vienna University of Technology
 Bluchr Mchanical Enginring Procdings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.procdings.bluchr.com.br/vnto/10wccm TOPOLOGY DESIG OF STRUCTURE LOADED BY EARTHQUAKE P. Rosko 1 1 Cntr of Mchanics and Structural Dynamics,
Bluchr Mchanical Enginring Procdings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.procdings.bluchr.com.br/vnto/10wccm TOPOLOGY DESIG OF STRUCTURE LOADED BY EARTHQUAKE P. Rosko 1 1 Cntr of Mchanics and Structural Dynamics,
Two Products Manufacturer s Production Decisions with Carbon Constraint
 Managmnt Scinc and Enginring Vol 7 No 3 pp 3-34 DOI:3968/jms9335X374 ISSN 93-34 [Print] ISSN 93-35X [Onlin] wwwcscanadant wwwcscanadaorg Two Products Manufacturr s Production Dcisions with Carbon Constraint
Managmnt Scinc and Enginring Vol 7 No 3 pp 3-34 DOI:3968/jms9335X374 ISSN 93-34 [Print] ISSN 93-35X [Onlin] wwwcscanadant wwwcscanadaorg Two Products Manufacturr s Production Dcisions with Carbon Constraint
SAFE HANDS & IIT-ian's PACE EDT-15 (JEE) SOLUTIONS
 It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
Homotopy perturbation technique
 Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB
 MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB INTRODUCTION Elctronic circuit boards consist of componnts which gnrats substantial amounts of hat during thir opration. A clar knowldg of th lvl of hat dissipation
MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB INTRODUCTION Elctronic circuit boards consist of componnts which gnrats substantial amounts of hat during thir opration. A clar knowldg of th lvl of hat dissipation
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
Types of Transfer Functions. Types of Transfer Functions. Types of Transfer Functions. Ideal Filters. Ideal Filters
 Typs of Transfr Typs of Transfr x[n] X( LTI h[n] H( y[n] Y( y [ n] h[ k] x[ n k] k Y ( H ( X ( Th tim-domain classification of an LTI digital transfr function is basd on th lngth of its impuls rspons h[n]:
Typs of Transfr Typs of Transfr x[n] X( LTI h[n] H( y[n] Y( y [ n] h[ k] x[ n k] k Y ( H ( X ( Th tim-domain classification of an LTI digital transfr function is basd on th lngth of its impuls rspons h[n]:
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Vibration Control of an Electromechanical Model with Time-Dependent Magnetic Field
 Journal of Mchanical Dsign and Vibration, 06, Vol. 4, No., -9 Availabl onlin at http://pubs.scipub.com/jmdv/4// Scinc and Education Publishing DOI:0.69/jmdv-4-- Vibration Control of an Elctromchanical
Journal of Mchanical Dsign and Vibration, 06, Vol. 4, No., -9 Availabl onlin at http://pubs.scipub.com/jmdv/4// Scinc and Education Publishing DOI:0.69/jmdv-4-- Vibration Control of an Elctromchanical
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
NEW APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA
 NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
What are those βs anyway? Understanding Design Matrix & Odds ratios
 Ral paramtr stimat WILD 750 - Wildlif Population Analysis of 6 What ar thos βs anyway? Undrsting Dsign Matrix & Odds ratios Rfrncs Hosmr D.W.. Lmshow. 000. Applid logistic rgrssion. John Wily & ons Inc.
Ral paramtr stimat WILD 750 - Wildlif Population Analysis of 6 What ar thos βs anyway? Undrsting Dsign Matrix & Odds ratios Rfrncs Hosmr D.W.. Lmshow. 000. Applid logistic rgrssion. John Wily & ons Inc.
Evaluating Reliability Systems by Using Weibull & New Weibull Extension Distributions Mushtak A.K. Shiker
 Evaluating Rliability Systms by Using Wibull & Nw Wibull Extnsion Distributions Mushtak A.K. Shikr مشتاق عبذ الغني شخير Univrsity of Babylon, Collg of Education (Ibn Hayan), Dpt. of Mathmatics Abstract
Evaluating Rliability Systms by Using Wibull & Nw Wibull Extnsion Distributions Mushtak A.K. Shikr مشتاق عبذ الغني شخير Univrsity of Babylon, Collg of Education (Ibn Hayan), Dpt. of Mathmatics Abstract
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS
 CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
INC 693, 481 Dynamics System and Modelling: The Language of Bound Graphs Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Professor
 INC 693, 48 Dynamics Systm and Modlling: Th Languag o Bound Graphs Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Prossor Dpartmnt o Control Systm and Instrumntation Enginring King Mongkut s Unnivrsity o Tchnology
INC 693, 48 Dynamics Systm and Modlling: Th Languag o Bound Graphs Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Prossor Dpartmnt o Control Systm and Instrumntation Enginring King Mongkut s Unnivrsity o Tchnology
Thermodynamical insight on the role of additives in shifting the equilibrium between white and grey tin
 hrmodynamical insight on th rol of additivs in shifting th quilibrium btwn whit and gry tin Nikolay Dmntv Dpartmnt of Chmistry, mpl Univrsity, Philadlphia, PA 19122 Abstract In this study mthods of statistical
hrmodynamical insight on th rol of additivs in shifting th quilibrium btwn whit and gry tin Nikolay Dmntv Dpartmnt of Chmistry, mpl Univrsity, Philadlphia, PA 19122 Abstract In this study mthods of statistical
Supplementary Materials
 6 Supplmntary Matrials APPENDIX A PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION OF FUEL-RATE-SPEED FUNCTION A truck running on a road with grad/slop θ positiv if moving up and ngativ if moving down facs thr rsistancs: arodynamic
6 Supplmntary Matrials APPENDIX A PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION OF FUEL-RATE-SPEED FUNCTION A truck running on a road with grad/slop θ positiv if moving up and ngativ if moving down facs thr rsistancs: arodynamic
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
Vector Control Using Series Iron Loss Model of Induction, Motors and Power Loss Minimization
 World Acadmy of Scinc, Enginring and Tchnology 52 29 Vctor Control Using Sris Iron Loss Modl of Induction, Motors and Powr Loss Minimization Khldoun Aissa, and Khodja Djalal Eddin Abstract Th iron loss
World Acadmy of Scinc, Enginring and Tchnology 52 29 Vctor Control Using Sris Iron Loss Modl of Induction, Motors and Powr Loss Minimization Khldoun Aissa, and Khodja Djalal Eddin Abstract Th iron loss
Finite Element Model of a Ferroelectric
 Excrpt from th Procdings of th COMSOL Confrnc 200 Paris Finit Elmnt Modl of a Frrolctric A. Lópz, A. D Andrés and P. Ramos * GRIFO. Dpartamnto d Elctrónica, Univrsidad d Alcalá. Alcalá d Hnars. Madrid,
Excrpt from th Procdings of th COMSOL Confrnc 200 Paris Finit Elmnt Modl of a Frrolctric A. Lópz, A. D Andrés and P. Ramos * GRIFO. Dpartamnto d Elctrónica, Univrsidad d Alcalá. Alcalá d Hnars. Madrid,
As the matrix of operator B is Hermitian so its eigenvalues must be real. It only remains to diagonalize the minor M 11 of matrix B.
 7636S ADVANCED QUANTUM MECHANICS Solutions Spring. Considr a thr dimnsional kt spac. If a crtain st of orthonormal kts, say, and 3 ar usd as th bas kts, thn th oprators A and B ar rprsntd by a b A a and
7636S ADVANCED QUANTUM MECHANICS Solutions Spring. Considr a thr dimnsional kt spac. If a crtain st of orthonormal kts, say, and 3 ar usd as th bas kts, thn th oprators A and B ar rprsntd by a b A a and
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Performance Prediction of the Single-Sided Linear. Induction Motors for Transportation Considers. Longitudinal End Effect by Using Analytic Method
 Contmporary Enginring Scincs, Vol., 9, no., 95-14 Prformanc Prdiction of th Singl-Sidd Linar Induction Motors for Transportation Considrs Longitudinal End Effct by Using Analytic Mthod Ali Suat Grçk Univrsity
Contmporary Enginring Scincs, Vol., 9, no., 95-14 Prformanc Prdiction of th Singl-Sidd Linar Induction Motors for Transportation Considrs Longitudinal End Effct by Using Analytic Mthod Ali Suat Grçk Univrsity
Types of Transfer Functions. Types of Transfer Functions. Ideal Filters. Ideal Filters. Ideal Filters
 Typs of Transfr Typs of Transfr Th tim-domain classification of an LTI digital transfr function squnc is basd on th lngth of its impuls rspons: - Finit impuls rspons (FIR) transfr function - Infinit impuls
Typs of Transfr Typs of Transfr Th tim-domain classification of an LTI digital transfr function squnc is basd on th lngth of its impuls rspons: - Finit impuls rspons (FIR) transfr function - Infinit impuls
SYSTEM stability is the most important issue for power
 Global Transint Stability and Voltag Rgulation for Multimachin Powr Systms Mark Gordon Mmbr IEEE David J. Hill Fllow IEEE Abstract This papr addrsss simultanously th major fundamntal and difficult issus
Global Transint Stability and Voltag Rgulation for Multimachin Powr Systms Mark Gordon Mmbr IEEE David J. Hill Fllow IEEE Abstract This papr addrsss simultanously th major fundamntal and difficult issus
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
1 Isoparametric Concept
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
α I I R α N I F I F i C i E R Cx R Ex C Cx i B R Bx
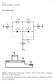 Bipolar transistor, continud - 1 - Ebrs-Moll modl α I I R α N I F E i E i C C R Ex I F I R R Cx C Cx i B R Bx B E B C Figur 1: Dashd lin indicats th "intrinsic" portion of th dvic, xcluding "parasitic"
Bipolar transistor, continud - 1 - Ebrs-Moll modl α I I R α N I F E i E i C C R Ex I F I R R Cx C Cx i B R Bx B E B C Figur 1: Dashd lin indicats th "intrinsic" portion of th dvic, xcluding "parasitic"
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
A Combination of STATCOM and Distribution Transformer With Passivity-based Control for Reactive Power Compensation
 Intrnational Confrnc on Enrgy and Environmntal Protction (ICEEP 216) A Combination of SACOM and Distribution ransformr With Passivity-basd Control for Ractiv Powr Compnsation Jinmu Lai1, a, Xianggn Yin
Intrnational Confrnc on Enrgy and Environmntal Protction (ICEEP 216) A Combination of SACOM and Distribution ransformr With Passivity-basd Control for Ractiv Powr Compnsation Jinmu Lai1, a, Xianggn Yin
One Dimensional State Space Approach to Thermoelastic Interactions with Viscosity
 7 IJSRST Volum 3 Issu 8 Print ISSN: 395-6 Onlin ISSN: 395-6X Thmd Sction: Scincand Tchnology On Dimnsional Stat Spac Approach to Thrmolastic Intractions with Viscosity Kavita Jain Rnu Yadav Dpartmnt of
7 IJSRST Volum 3 Issu 8 Print ISSN: 395-6 Onlin ISSN: 395-6X Thmd Sction: Scincand Tchnology On Dimnsional Stat Spac Approach to Thrmolastic Intractions with Viscosity Kavita Jain Rnu Yadav Dpartmnt of
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
The Relativistic Stern-Gerlach Force C. Tschalär 1. Introduction
 Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Topology Optimization of Suction Muffler for Noise Attenuation
 Purdu Univrsity Purdu -Pubs Intrnational Comprssor Enginring Confrnc School of Mchanical Enginring 2012 Topology Optimization of Suction Mufflr for Nois Attnuation Jin Woo L jinwool@ajou.ac.kr Dong Wook
Purdu Univrsity Purdu -Pubs Intrnational Comprssor Enginring Confrnc School of Mchanical Enginring 2012 Topology Optimization of Suction Mufflr for Nois Attnuation Jin Woo L jinwool@ajou.ac.kr Dong Wook
A Recent Approach to Repetitive Control Strategy for Induced Draft Fan
 Europan Journal of Applid Scincs 9 (5): 258-264, 217 ISSN 279-277 IDOSI Publications, 217 DOI: 1.5829/idosi.jas.217.258.264 A Rcnt Approach to Rptitiv Control Stratgy for Inducd Draft Fan 1 1 1 2 G. Thanigaivl,
Europan Journal of Applid Scincs 9 (5): 258-264, 217 ISSN 279-277 IDOSI Publications, 217 DOI: 1.5829/idosi.jas.217.258.264 A Rcnt Approach to Rptitiv Control Stratgy for Inducd Draft Fan 1 1 1 2 G. Thanigaivl,
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Numerical considerations regarding the simulation of an aircraft in the approaching phase for landing
 INCAS BULLETIN, Volum, Numbr 1/ 1 Numrical considrations rgarding th simulation of an aircraft in th approaching phas for landing Ionl Cristinl IORGA ionliorga@yahoo.com Univrsity of Craiova, Alxandru
INCAS BULLETIN, Volum, Numbr 1/ 1 Numrical considrations rgarding th simulation of an aircraft in th approaching phas for landing Ionl Cristinl IORGA ionliorga@yahoo.com Univrsity of Craiova, Alxandru
B. water content (WC) = 0.4 WC CSF WC GM WC WM, or WC = = mol/l.
 9.. A. Rlvant quation: M (TR, TE) = M ( TR /T ) TE / T M (NAA) = 38. M (cratin) = 9.6 M (cholin) = 98.4 M (watr) = 7,4 B. watr contnt (WC) =.4 WC CSF +.5 WC GM +. WC WM, or WC =.4. 55.6 +.5.87 55.6 +..83
9.. A. Rlvant quation: M (TR, TE) = M ( TR /T ) TE / T M (NAA) = 38. M (cratin) = 9.6 M (cholin) = 98.4 M (watr) = 7,4 B. watr contnt (WC) =.4 WC CSF +.5 WC GM +. WC WM, or WC =.4. 55.6 +.5.87 55.6 +..83
Transitional Probability Model for a Serial Phases in Production
 Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Vol. 3 No. 2 (2010) pag 49-54. Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Transitional Probability Modl for a Srial Phass in Production Adam Baharum School of Mathmatical
Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Vol. 3 No. 2 (2010) pag 49-54. Jurnal Karya Asli Lorkan Ahli Matmatik Transitional Probability Modl for a Srial Phass in Production Adam Baharum School of Mathmatical
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Predictive Controller for Pitch Controller Missile. Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Khorasan University, Mashhad, Iran
 Prdictiv Controllr for Pitch Controllr issil Amir Torabi (Corrsponding author), Sobhan Salhi, Ali Karsaz, Ebrahim Tarsayi. Faculty of Elctrical Enginring, Khorasan Univrsity, ashhad, Iran. Faculty of Elctrical
Prdictiv Controllr for Pitch Controllr issil Amir Torabi (Corrsponding author), Sobhan Salhi, Ali Karsaz, Ebrahim Tarsayi. Faculty of Elctrical Enginring, Khorasan Univrsity, ashhad, Iran. Faculty of Elctrical
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis
 Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 43 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 3 Computr Implmntation of D FEM Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 43 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 3 Computr Implmntation of D FEM Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Anti-Synchronization of Tigan and Li Systems with Unknown Parameters via Adaptive Control
 An Intrnational Journal of Optimization and Control: Thoris & Applications Vol., No.1, pp.17-8 (01) IJOCTA ISSN: 146-0957 ISSN: 146-570 http://www.ijocta.com Anti-Synchronization of Tigan and Li Systms
An Intrnational Journal of Optimization and Control: Thoris & Applications Vol., No.1, pp.17-8 (01) IJOCTA ISSN: 146-0957 ISSN: 146-570 http://www.ijocta.com Anti-Synchronization of Tigan and Li Systms
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Rational Approximation for the one-dimensional Bratu Equation
 Intrnational Journal of Enginring & Tchnology IJET-IJES Vol:3 o:05 5 Rational Approximation for th on-dimnsional Bratu Equation Moustafa Aly Soliman Chmical Enginring Dpartmnt, Th British Univrsity in
Intrnational Journal of Enginring & Tchnology IJET-IJES Vol:3 o:05 5 Rational Approximation for th on-dimnsional Bratu Equation Moustafa Aly Soliman Chmical Enginring Dpartmnt, Th British Univrsity in
On the Hamiltonian of a Multi-Electron Atom
 On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
Abstract Interpretation: concrete and abstract semantics
 Abstract Intrprtation: concrt and abstract smantics Concrt smantics W considr a vry tiny languag that manags arithmtic oprations on intgrs valus. Th (concrt) smantics of th languags cab b dfind by th funzcion
Abstract Intrprtation: concrt and abstract smantics Concrt smantics W considr a vry tiny languag that manags arithmtic oprations on intgrs valus. Th (concrt) smantics of th languags cab b dfind by th funzcion
A New Approach to the Fatigue Life Prediction for Notched Components Under Multiaxial Cyclic Loading. Zhi-qiang TAO and De-guang SHANG *
 2017 2nd Intrnational Conrnc on Applid Mchanics, Elctronics and Mchatronics Enginring (AMEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-497-4 A Nw Approach to th Fatigu Li Prdiction or Notchd Componnts Undr Multiaxial Cyclic
2017 2nd Intrnational Conrnc on Applid Mchanics, Elctronics and Mchatronics Enginring (AMEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-497-4 A Nw Approach to th Fatigu Li Prdiction or Notchd Componnts Undr Multiaxial Cyclic
Chapter 6. The Discrete Fourier Transform and The Fast Fourier Transform
 Pusan ational Univrsity Chaptr 6. Th Discrt Fourir Transform and Th Fast Fourir Transform 6. Introduction Frquncy rsponss of discrt linar tim invariant systms ar rprsntd by Fourir transform or z-transforms.
Pusan ational Univrsity Chaptr 6. Th Discrt Fourir Transform and Th Fast Fourir Transform 6. Introduction Frquncy rsponss of discrt linar tim invariant systms ar rprsntd by Fourir transform or z-transforms.
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
Function Spaces. a x 3. (Letting x = 1 =)) a(0) + b + c (1) = 0. Row reducing the matrix. b 1. e 4 3. e 9. >: (x = 1 =)) a(0) + b + c (1) = 0
 unction Spacs Prrquisit: Sction 4.7, Coordinatization n this sction, w apply th tchniqus of Chaptr 4 to vctor spacs whos lmnts ar functions. Th vctor spacs P n and P ar familiar xampls of such spacs. Othr
unction Spacs Prrquisit: Sction 4.7, Coordinatization n this sction, w apply th tchniqus of Chaptr 4 to vctor spacs whos lmnts ar functions. Th vctor spacs P n and P ar familiar xampls of such spacs. Othr
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALS
 Slid DIGITAL SIGAL PROCESSIG UIT I DISCRETE TIME SIGALS AD SYSTEM Slid Rviw of discrt-tim signals & systms Signal:- A signal is dfind as any physical quantity that varis with tim, spac or any othr indpndnt
Slid DIGITAL SIGAL PROCESSIG UIT I DISCRETE TIME SIGALS AD SYSTEM Slid Rviw of discrt-tim signals & systms Signal:- A signal is dfind as any physical quantity that varis with tim, spac or any othr indpndnt
Full Waveform Inversion Using an Energy-Based Objective Function with Efficient Calculation of the Gradient
 Full Wavform Invrsion Using an Enrgy-Basd Objctiv Function with Efficint Calculation of th Gradint Itm yp Confrnc Papr Authors Choi, Yun Sok; Alkhalifah, ariq Ali Citation Choi Y, Alkhalifah (217) Full
Full Wavform Invrsion Using an Enrgy-Basd Objctiv Function with Efficint Calculation of th Gradint Itm yp Confrnc Papr Authors Choi, Yun Sok; Alkhalifah, ariq Ali Citation Choi Y, Alkhalifah (217) Full
Analysis of potential flow around two-dimensional body by finite element method
 Vol. 7(2), pp. 9-22, May, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JMER2014.0342 rticl Numbr: 20E80053033 ISSN 2141 2383 Copyright 2015 uthor(s) rtain th copyright of this articl http://www.acadmicjournals.org/jmer Journal of
Vol. 7(2), pp. 9-22, May, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JMER2014.0342 rticl Numbr: 20E80053033 ISSN 2141 2383 Copyright 2015 uthor(s) rtain th copyright of this articl http://www.acadmicjournals.org/jmer Journal of
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Iterative learning control with initial rectifying action for nonlinear continuous systems X.-D. Li 1 T.W.S. Chow 2 J.K.L. Ho 3 J.
 Publishd in IET Control Thory and Applications Rcivd on 24th Dcmbr 27 Rvisd on 21st May 28 doi: 1.149/it-cta:27486 ISSN 1751-8644 Itrativ larning control with initial rctifying action for nonlinar continuous
Publishd in IET Control Thory and Applications Rcivd on 24th Dcmbr 27 Rvisd on 21st May 28 doi: 1.149/it-cta:27486 ISSN 1751-8644 Itrativ larning control with initial rctifying action for nonlinar continuous
Exercise 1. Sketch the graph of the following function. (x 2
 Writtn tst: Fbruary 9th, 06 Exrcis. Sktch th graph of th following function fx = x + x, spcifying: domain, possibl asymptots, monotonicity, continuity, local and global maxima or minima, and non-drivability
Writtn tst: Fbruary 9th, 06 Exrcis. Sktch th graph of th following function fx = x + x, spcifying: domain, possibl asymptots, monotonicity, continuity, local and global maxima or minima, and non-drivability
Overcoming the shrink-and-swell effect in water level control strategy on industrial boiler-drum
 Standard Scintific Rsarch and Essays Vol1 (1): 019-024, Fbruary 2013 http://www.standrsjournals.org/journals/ssre Rsarch Articl Ovrcoming th shrink-and-swll ffct in watr lvl control stratgy on industrial
Standard Scintific Rsarch and Essays Vol1 (1): 019-024, Fbruary 2013 http://www.standrsjournals.org/journals/ssre Rsarch Articl Ovrcoming th shrink-and-swll ffct in watr lvl control stratgy on industrial
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Volterra Kernel Estimation for Nonlinear Communication Channels Using Deterministic Sequences
 1 Voltrra Krnl Estimation for Nonlinar Communication Channls Using Dtrministic Squncs Endr M. Ekşioğlu and Ahmt H. Kayran Dpartmnt of Elctrical and Elctronics Enginring, Istanbul Tchnical Univrsity, Istanbul,
1 Voltrra Krnl Estimation for Nonlinar Communication Channls Using Dtrministic Squncs Endr M. Ekşioğlu and Ahmt H. Kayran Dpartmnt of Elctrical and Elctronics Enginring, Istanbul Tchnical Univrsity, Istanbul,
At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to understand:
 Instructional Objctivs: At th nd of this lsson, th studnts should b abl to undrstand: Dsign thod for variabl load Equivalnt strss on shaft Dsign basd on stiffnss and torsional rigidit Critical spd of shaft
Instructional Objctivs: At th nd of this lsson, th studnts should b abl to undrstand: Dsign thod for variabl load Equivalnt strss on shaft Dsign basd on stiffnss and torsional rigidit Critical spd of shaft
2. Background Material
 S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
Gradient-based step response identification of low-order model for time delay systems Rui Yan, Fengwei Chen, Shijian Dong, Tao Liu*
 Gradint-basd stp rspons idntification of low-ordr modl for tim dlay systms Rui Yan, Fngwi Chn, Shijian Dong, ao Liu* Institut of Advancd Control chnology, Dalian Univrsity of chnology, Dalian, 64, P R
Gradint-basd stp rspons idntification of low-ordr modl for tim dlay systms Rui Yan, Fngwi Chn, Shijian Dong, ao Liu* Institut of Advancd Control chnology, Dalian Univrsity of chnology, Dalian, 64, P R
Forces. Quantum ElectroDynamics. α = = We have now:
 W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
