Let s start by reviewing what we learned last time. Here is the basic line of reasoning for Einstein Solids
|
|
|
- Lenard Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5 In this chapter we want to review the concept of irreversibility in more detail and see how it comes from the multiplicity of states. In addition, we want to introduce the following new topics: Definition for Entropy Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy and disorder. Let s start by reviewing what we learned last time. Here is the basic line of reasoning for Einstein Solids (1) Define an Einstein Solid Atoms locked in lattice but individual atoms were free to oscillate as simple harmonic oscillators around an equilibrium position. o 3-D Problem 3 x 1-D Problem. (2) Define a Macrostate for a single solid using U : Internal Energy which is related to temperature by U = 3Nk N : Number of Atoms (3) The microstate of the solid is given by how much energy is stored in the 3N simple harmonic oscillators 3N integers required. Internal Energy (in terms of microstates) 3N i= 1 There are MANY microstates for each macrostate. Ω ( N, U ) = 5/20/2004 H133 Spring B T U = ε n i ε = { ω ( q + 3N ) 1! q!(3n 1)! q U ε
2 Irreversibility revisited (4) We can bring two Einstein Solids, A & B into thermal contact with one another and define the macrostate of the system by U A, N A U B, N B U sys =U A +U B (5) The two solids can share the total energy in different ways. We call each of the ways a macropartition. The number of microstates for the macropartition is given by We defined a Macropartition Table to summarize all this information (at least for small N and q) Macr o 0:4 1:3 Ω U A 0 1 AB = Ω U B 4 3 A Ω (6) ASSUMPTION: All microstates are equally likely in the long run (i.e. if we wait a long time) Consequence: Since macropartitions have a different number of microstates, macropartitions are NOT equally likely. o The macropartitions with the most microstates are the most likely macropartitions. (7) For large N, most microstates are concentrated in a tight band of macropartitions, near the macropartition which has roughly equal energy per solid. Ω A 1 3 B Ω B Ω AB More Rows 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
3 Implications Based on the line of reasoning that we just outlined there are two statements that we would like to show: A) If the combined system is not in the most probable macropartition to begin with, it will rapidly and inevitably move toward that macropartition. B) It will subsequently stay at that macropartition (or near to it), in spite of the random shuffling of energy back and forth between the two solids. These are basically statements of irreversibility. Let s be quantitative about seeing how these statements are true: Start with B Case #1: Two Solids with N A = N B = 4, U = 16ε Use StatMech to calculate a few quantities: Prob U A =U B =8ε Prob: Prob U A =16ε and U B =0 Prob: Prob U A =12ε and U B =4ε Prob: ~99% of microstates: Case #2: Two Solids with (2-atoms on a side): N A = N B = 8, U = 32ε Use StatMech to calculate a few quantities: Prob U A =U B =16ε Prob: Prob U A =32ε and U B =0 Prob: Prob U A =24ε and U B =8ε Prob: ~99% of microstates: 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
4 Implications Case #3: Two Solids with (5-atoms on a side): N A = N B = 125, U = 500ε Use StatMech to calculate a few quantities: Prob U A =U B =250ε Prob: Prob Prob U A =500ε and U B =0 Prob: U A =375ε and U B =125ε Prob: ~99% macropartitions Case #4: Two Solids with (10-atoms on a side): N A = N B = 1000, U = 4000ε ~99% macropartitions As N gets large (think ) the ~99% is going to get extremely narrow! Two Important Points: A) Although there is some probability of observing the system in the extreme macropartition (all the energy in one of the solids). For all practical purposes it is so unlikely as to be ~impossible. For N A = N B = 50, U = 200ε if you observed the system 1 billion times per second since the beginning of the universe, the probability you would have every seen it in the extreme macropartition is ~ B) We have been examining cases with N A =N B. Consider a case where they are very different. N A =5 and N B =20 Most probable partition is near U A /N A = U B /N B but this makes sense because we want T A =T B 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
5 Moving toward Equilibrium So far we calculated the overall probability of various macropartitions and showing that if we are in the region of the most microstates, we stay there. Now let s consider what happens when we start with two objects that are not in thermal equilibrium. There is a steady march toward equilibrium. Case Study: N A =N B =250 and U=1000ε Start a t=0 with U A =12ε and U B =988ε. Now we wait the characteristic amount of time four a transfer of a single unit, ε, of energy. As an approximation: The system could be in any microstate of macropartition with U A =13ε and U B =987ε. The system could be in any microstate of macropartition with U A =12ε and U B =988ε. The system could be in any microstate of macropartition with U A =11ε and U B =989ε. Since the system is randomly exploring these possible microstates, the probability of any of these should be the available microstates in each macropartition divided by the total microstates summed over the three. 13:987 12:988 11:989 Ω AB = Ω AB = Ω AB = Prob heat flows from cold to hot Prob. heat does not flow Prob. heat flows from hot to cold A gets hotter A,B stay same B gets hotter Total States: 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
6 Moving to Equilibrium Notice there are many more microstates in the macropartition that is one step closer to equilibrium than there are in the macropartition one step away from equilibrium or even the macropartition that the system started in. As we might expect, the numbers get even more daunting when N gets large. If we increase the study case above by a simple factor of 10, the probability that we go the wrong way is about Once again, think about what happens when we take N to be There is a rapid steady progression towards equilibrium simply because the number of microstates increases RAPIDLY in that direction. Although I have said it a few times now we see the source of irreversibility. However, we see this for an Einstein Solid. Can we extend what we learned to other macroscopic systems as well? YES! 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
7 General Irreversibility What were the critical features of an Einstein Solid that lead us down this path? 1). 2) 3) Do most systems share these general features? YES! Let s consider each one of these questions: (1) TRUE: (2) TRUE : (3) TRUE: 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
8 Entropy Now that we have defined microstates and multiplicity we want to define Entropy. Without the microstate background defining entropy can be an obtuse one most intro text books define the entropy in terms of an integral of temperature. With multiplicity of microstates defined, the definition of entropy,s, is very easy S k B ln Ω Notice this provides a more useful way of talking about multiplicity since taking the ln turns very big numbers into small ones. Also, the factor of k B is not universal but it serves to reduce the scale even further. Consider the following example. o A mole of a solid has a multiplicity of o Ω ~ With our definition the Entropy is A much easier number to talk about. The other convenience is when we put two systems together (e.g. two Einstein Solids). We just ADD the entropies of the two systems! 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
9 Second Law of Thermodynamics Now that we have defined microstates and entropy we are ready to state the second law of thermodynamics The entropy of an isolated system never decreases. Given what we have learned we understand why this is true. A system moves from states where there are few microstates (low entropy) to states where there are many microstates (highest entropy). For systems with small N the 2 nd Law is one of probability. But N does not need to be very large and this statement turns into one of certainty for all practical purposes. Entropy and Disorder: Many people associate entropy and disorder. Be very careful about this. The correct definition is that entropy is high when the multiplicity of microstates is high. Often it is the case that the state of disorder is one where there are a lot of microstates. However, disorder is a subjective statement and so sometimes this association with entropy is false See Figure T5.7 (page 89) Ice in a glass and water. o Entropy of liquid water much higher than ice. Read Section 5.6 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
10 Example T5S.6: A certain macropartition of two Einstein Solids has an entropy of 305.2k B. The next macropartition closer to the most probable one 335.5k B. If the system is initially in the first macropartition and we check it later, how many times more likely is it to have moved to the other than to have stayed in the first? Remember a small difference in entropy corresponds to a large difference in microstates and the relative probability. 5/20/2004 H133 Spring
Lecture 8. The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange
 Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
Lecture 8. The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange
 Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
Physics 172H Modern Mechanics
 Physics 172H Modern Mechanics Instructor: Dr. Mark Haugan Office: PHYS 282 haugan@purdue.edu TAs: Alex Kryzwda John Lorenz akryzwda@purdue.edu jdlorenz@purdue.edu Lecture 22: Matter & Interactions, Ch.
Physics 172H Modern Mechanics Instructor: Dr. Mark Haugan Office: PHYS 282 haugan@purdue.edu TAs: Alex Kryzwda John Lorenz akryzwda@purdue.edu jdlorenz@purdue.edu Lecture 22: Matter & Interactions, Ch.
Lecture Notes Set 3a: Probabilities, Microstates and Entropy
 Lecture Notes Set 3a: Probabilities, Microstates and Entropy Thus far.. In Sections 1 and 2 of the module we ve covered a broad variety of topics at the heart of the thermal and statistical behaviour of
Lecture Notes Set 3a: Probabilities, Microstates and Entropy Thus far.. In Sections 1 and 2 of the module we ve covered a broad variety of topics at the heart of the thermal and statistical behaviour of
Guided Inquiry Worksheet 2: Interacting Einstein Solids & Entropy
 Guided Inquiry Worksheet 2: Interacting Einstein Solids & Entropy According to the fundamental assumption of statistical mechanics, AT EQUILIBRIUM, ALL ALLOWED MICROSTATES OF AN ISOLATED SYSTEM ARE EQUALLY
Guided Inquiry Worksheet 2: Interacting Einstein Solids & Entropy According to the fundamental assumption of statistical mechanics, AT EQUILIBRIUM, ALL ALLOWED MICROSTATES OF AN ISOLATED SYSTEM ARE EQUALLY
Lecture 9 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 9 Examples and Problems Counting microstates of combined systems Volume exchange between systems Definition of Entropy and its role in equilibrium The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of
Lecture 9 Examples and Problems Counting microstates of combined systems Volume exchange between systems Definition of Entropy and its role in equilibrium The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of
Lecture 15. Available Work and Free Energy. Lecture 15, p 1
 Lecture 15 Available Work and Free Energy U F F U -TS Lecture 15, p 1 Helpful Hints in Dealing with Engines and Fridges Sketch the process (see figures below). Define and Q c and W by (or W on ) as positive
Lecture 15 Available Work and Free Energy U F F U -TS Lecture 15, p 1 Helpful Hints in Dealing with Engines and Fridges Sketch the process (see figures below). Define and Q c and W by (or W on ) as positive
Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
213 Midterm coming up
 213 Midterm coming up Monday April 8 @ 7 pm (conflict exam @ 5:15pm) Covers: Lectures 1-12 (not including thermal radiation) HW 1-4 Discussion 1-4 Labs 1-2 Review Session Sunday April 7, 3-5 PM, 141 Loomis
213 Midterm coming up Monday April 8 @ 7 pm (conflict exam @ 5:15pm) Covers: Lectures 1-12 (not including thermal radiation) HW 1-4 Discussion 1-4 Labs 1-2 Review Session Sunday April 7, 3-5 PM, 141 Loomis
Thermodynamics: Entropy
 Thermodynamics: Entropy From Warmup I've heard people say that the Entropy Statement of the Second Law of Thermodynamics disproves God. Why is this? What are your thoughts? The second law of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics: Entropy From Warmup I've heard people say that the Entropy Statement of the Second Law of Thermodynamics disproves God. Why is this? What are your thoughts? The second law of thermodynamics
Chapter 4: Going from microcanonical to canonical ensemble, from energy to temperature.
 Chapter 4: Going from microcanonical to canonical ensemble, from energy to temperature. All calculations in statistical mechanics can be done in the microcanonical ensemble, where all copies of the system
Chapter 4: Going from microcanonical to canonical ensemble, from energy to temperature. All calculations in statistical mechanics can be done in the microcanonical ensemble, where all copies of the system
Lecture 6. Statistical Processes. Irreversibility. Counting and Probability. Microstates and Macrostates. The Meaning of Equilibrium Ω(m) 9 spins
 Lecture 6 Statistical Processes Irreversibility Counting and Probability Microstates and Macrostates The Meaning of Equilibrium Ω(m) 9 spins -9-7 -5-3 -1 1 3 5 7 m 9 Lecture 6, p. 1 Irreversibility Have
Lecture 6 Statistical Processes Irreversibility Counting and Probability Microstates and Macrostates The Meaning of Equilibrium Ω(m) 9 spins -9-7 -5-3 -1 1 3 5 7 m 9 Lecture 6, p. 1 Irreversibility Have
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Knight: Chapter 18. The Micro/Macro Connection. (Thermal Interactions and Heat & Irreversible Processes and the 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics)
 Knight: Chapter 18 The Micro/Macro Connection (Thermal Interactions and Heat & Irreversible Processes and the 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics) Last time p Thermal energy of a Monatomic gas.. E th = 3 2 NK BT
Knight: Chapter 18 The Micro/Macro Connection (Thermal Interactions and Heat & Irreversible Processes and the 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics) Last time p Thermal energy of a Monatomic gas.. E th = 3 2 NK BT
Chapter 12- The Law of Increasing Disorder
 Second Law of Thermodynamics Changes occurring in natural systems always proceed in such a way that the total amount of entropy in the universe is either unchanged or increased. If total disorder is increased,
Second Law of Thermodynamics Changes occurring in natural systems always proceed in such a way that the total amount of entropy in the universe is either unchanged or increased. If total disorder is increased,
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Worksheet for Exploration 21.1: Engine Efficiency W Q H U
 Worksheet for Exploration 21.1: Engine Efficiency In this animation, N = nr (i.e., k B = 1). This, then, gives the ideal gas law as PV = NT. Assume an ideal monatomic gas. The efficiency of an engine is
Worksheet for Exploration 21.1: Engine Efficiency In this animation, N = nr (i.e., k B = 1). This, then, gives the ideal gas law as PV = NT. Assume an ideal monatomic gas. The efficiency of an engine is
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The Molecular Interpretation of Entropy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Free
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The Molecular Interpretation of Entropy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Free
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THERMODYNAMICS SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS ENTROPY
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THERMODYNAMICS SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS ENTROPY The Second Law of Thermodynamics is one of the fundamental laws which describes the workings of our universe. Not like other laws
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THERMODYNAMICS SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS ENTROPY The Second Law of Thermodynamics is one of the fundamental laws which describes the workings of our universe. Not like other laws
Statistical thermodynamics for MD and MC simulations
 Statistical thermodynamics for MD and MC simulations knowing 2 atoms and wishing to know 10 23 of them Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař 22 June 2016 Introduction Thermodynamic properties of molecular systems
Statistical thermodynamics for MD and MC simulations knowing 2 atoms and wishing to know 10 23 of them Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař 22 June 2016 Introduction Thermodynamic properties of molecular systems
Physics 9 Wednesday, February 29, 2012
 Physics 9 Wednesday, February 29, 2012 learningcatalytics.com class session ID: 410176 Today: heat pumps, engines, etc. Aim to cover everything you need to know to do HW #8. Friday: start electricity (lots
Physics 9 Wednesday, February 29, 2012 learningcatalytics.com class session ID: 410176 Today: heat pumps, engines, etc. Aim to cover everything you need to know to do HW #8. Friday: start electricity (lots
Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat. Thursday 24th April, a.m p.m.
 College of Science and Engineering School of Physics H T O F E E U D N I I N V E B R U S I R T Y H G Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat Thursday 24th April, 2008
College of Science and Engineering School of Physics H T O F E E U D N I I N V E B R U S I R T Y H G Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat Thursday 24th April, 2008
First Law Limitations
 First Law Limitations First Law: During any process, the energy of the universe is constant. du du du ZERO!!! universe sys surroundings Any energy transfer between system and surroundings is accomplished
First Law Limitations First Law: During any process, the energy of the universe is constant. du du du ZERO!!! universe sys surroundings Any energy transfer between system and surroundings is accomplished
Entropy A measure of molecular disorder
 Entropy A measure of molecular disorder Second Law uses Entropy, S, to identify spontaneous change. Restatement of Second Law: The entropy of the universe tends always towards a maximum (S universe > 0
Entropy A measure of molecular disorder Second Law uses Entropy, S, to identify spontaneous change. Restatement of Second Law: The entropy of the universe tends always towards a maximum (S universe > 0
Lecture 4: Classical Illustrations of Macroscopic Thermal Effects
 Lecture 4: Classical Illustrations of Macroscopic Thermal Effects Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal conductivity Irreversibility References for this Lecture: Elements Ch 3,4A-C Reference for Lecture
Lecture 4: Classical Illustrations of Macroscopic Thermal Effects Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal conductivity Irreversibility References for this Lecture: Elements Ch 3,4A-C Reference for Lecture
Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the Third Law
 Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the hird Law We have already noted that heat capacity and entropy have the same units. We will explore further the relationship between heat capacity and entropy. We
Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the hird Law We have already noted that heat capacity and entropy have the same units. We will explore further the relationship between heat capacity and entropy. We
PHYSICS. Chapter 20 Lecture 4/E FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 20 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 20 The Micro/Macro Connection IN THIS CHAPTER, you will see how macroscopic
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 20 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 20 The Micro/Macro Connection IN THIS CHAPTER, you will see how macroscopic
THERMODYNAMICS. Topic: 4 Spontaneous processes and criteria for spontaneity, entropy as a state function. VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
 THERMODYNAMICS Topic: 4 Spontaneous processes and criteria for spontaneity, entropy as a state function. VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. State Hess s law? Ans. Hess s law: The total heat change in a reaction
THERMODYNAMICS Topic: 4 Spontaneous processes and criteria for spontaneity, entropy as a state function. VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. State Hess s law? Ans. Hess s law: The total heat change in a reaction
Physics 111. Thursday, Dec. 9, 3-5pm and 7-9pm. Announcements. Thursday, December 9, 2004
 ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
Lecture 25 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas
 Lecture 5 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular collisions
Lecture 5 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular collisions
The Direction of Spontaneous Change: Entropy and Free Energy
 The Direction of Spontaneous Change: Entropy and Free Energy Reading: from Petrucci, Harwood and Herring (8th edition): Required for Part 1: Sections 20-1 through 20-4. Recommended for Part 1: Sections
The Direction of Spontaneous Change: Entropy and Free Energy Reading: from Petrucci, Harwood and Herring (8th edition): Required for Part 1: Sections 20-1 through 20-4. Recommended for Part 1: Sections
Lecture Notes Set 3b: Entropy and the 2 nd law
 Lecture Notes Set 3b: Entropy and the 2 nd law 3.5 Entropy and the 2 nd law of thermodynamics The st law of thermodynamics is simply a restatement of the conservation of energy principle and may be concisely
Lecture Notes Set 3b: Entropy and the 2 nd law 3.5 Entropy and the 2 nd law of thermodynamics The st law of thermodynamics is simply a restatement of the conservation of energy principle and may be concisely
Thermodynamics: More Entropy
 Thermodynamics: More Entropy From Warmup Yay for only having to read one section! I thought the entropy statement of the second law made a lot more sense than the other two. Just probability. I haven't
Thermodynamics: More Entropy From Warmup Yay for only having to read one section! I thought the entropy statement of the second law made a lot more sense than the other two. Just probability. I haven't
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
11/29/2017 IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES. UNIT 2 Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory
 11/9/017 AP PHYSICS UNIT Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory CHAPTER 13 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES The U G of the water-earth system at the
11/9/017 AP PHYSICS UNIT Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory CHAPTER 13 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES The U G of the water-earth system at the
Physics 207 Lecture 25. Lecture 25, Nov. 26 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas
 Lecture 25, Nov. 26 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular
Lecture 25, Nov. 26 Goals: Chapter 18 Understand the molecular basis for pressure and the idealgas law. redict the molar specific heats of gases and solids. Understand how heat is transferred via molecular
Before the Quiz. Make sure you have SIX pennies
 Before the Quiz Make sure you have SIX pennies If you have more than 6, please share with your neighbors There are some additional pennies in the baskets up front please be sure to return them after class!!!
Before the Quiz Make sure you have SIX pennies If you have more than 6, please share with your neighbors There are some additional pennies in the baskets up front please be sure to return them after class!!!
Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy
 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 1 Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy 1. Work 1 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 2 (c)
Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 1 Lecture Notes 2014March 13 on Thermodynamics A. First Law: based upon conservation of energy 1. Work 1 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Physics 8C, Spring 2014 Page 2 (c)
Chapter 17. Free Energy and Thermodynamics. Chapter 17 Lecture Lecture Presentation. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University
 Chapter 17 Lecture Lecture Presentation Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermodynamics Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University First Law of Thermodynamics You can t win! The first law of thermodynamics
Chapter 17 Lecture Lecture Presentation Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermodynamics Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University First Law of Thermodynamics You can t win! The first law of thermodynamics
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Matter is made of atoms and molecules
 Name Per Talking to the Text Atoms and Molecules pt.2 Author Says (important ideas, vocabulary) Matter is made of atoms and molecules We have already used the term atom and molecule a couple of times.
Name Per Talking to the Text Atoms and Molecules pt.2 Author Says (important ideas, vocabulary) Matter is made of atoms and molecules We have already used the term atom and molecule a couple of times.
Heat What is heat? Work = 2. PdV 1
 eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
Chemistry 103 Spring Announcements 1. Ch. 16 OWL homework is active. 2. Next midterm exam on May 17 or 19.
 Today 1. More on entropy. Announcements 1. Ch. 16 OWL homework is active. 2. Next midterm exam on May 17 or 19. 3. CSULA closure on May 21 (furlough). 4. CSULA closure on May 31 (holiday). 5. Bring textbook
Today 1. More on entropy. Announcements 1. Ch. 16 OWL homework is active. 2. Next midterm exam on May 17 or 19. 3. CSULA closure on May 21 (furlough). 4. CSULA closure on May 31 (holiday). 5. Bring textbook
Active Learners Reflective Learners Use both ways equally frequently More Inclined to be Active More inclined to be Reflective
 Active Learners Reflective Learners Use both ways equally frequently More Inclined to be Active More inclined to be Reflective Sensory Leaners Intuitive Learners Use both ways equally frequently More inclined
Active Learners Reflective Learners Use both ways equally frequently More Inclined to be Active More inclined to be Reflective Sensory Leaners Intuitive Learners Use both ways equally frequently More inclined
So far changes in the state of systems that occur within the restrictions of the first law of thermodynamics were considered:
 Entropy So far changes in the state of systems that occur within the restrictions of the first law of thermodynamics were considered: Energy is transferred from one state to another by any possible forms,
Entropy So far changes in the state of systems that occur within the restrictions of the first law of thermodynamics were considered: Energy is transferred from one state to another by any possible forms,
Quiz 3 for Physics 176: Answers. Professor Greenside
 Quiz 3 for Physics 176: Answers Professor Greenside True or False Questions ( points each) For each of the following statements, please circle T or F to indicate respectively whether a given statement
Quiz 3 for Physics 176: Answers Professor Greenside True or False Questions ( points each) For each of the following statements, please circle T or F to indicate respectively whether a given statement
Imperial College London BSc/MSci EXAMINATION May 2008 THERMODYNAMICS & STATISTICAL PHYSICS
 Imperial College London BSc/MSci EXAMINATION May 2008 This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship THERMODYNAMICS & STATISTICAL PHYSICS For Second-Year Physics Students Wednesday,
Imperial College London BSc/MSci EXAMINATION May 2008 This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship THERMODYNAMICS & STATISTICAL PHYSICS For Second-Year Physics Students Wednesday,
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 9: Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 9: Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics Marc R. Roussel January 23, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Entropy and the second law January 23, 2018 1 / 29 States in thermodynamics The thermodynamic
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 9: Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics Marc R. Roussel January 23, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Entropy and the second law January 23, 2018 1 / 29 States in thermodynamics The thermodynamic
Thermodynamics: Entropy
 Thermodynamics: Entropy From Warmup I still do not understand the benefit of using a reversible process to calculate data when it is not possible to achieve. What makes a reversible process so useful?
Thermodynamics: Entropy From Warmup I still do not understand the benefit of using a reversible process to calculate data when it is not possible to achieve. What makes a reversible process so useful?
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics. Monday, January 6, 14
 Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Molecular Simulations Molecular dynamics: solve equations of motion Monte Carlo: importance sampling r 1 r 2 r n MD MC r 1 r 2 2 r n 2 3 3 4 4 Questions How can
Introduction Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Molecular Simulations Molecular dynamics: solve equations of motion Monte Carlo: importance sampling r 1 r 2 r n MD MC r 1 r 2 2 r n 2 3 3 4 4 Questions How can
Entropy, free energy and equilibrium. Spontaneity Entropy Free energy and equilibrium
 Entropy, free energy and equilibrium Spontaneity Entropy Free energy and equilibrium Learning objectives Discuss what is meant by spontaneity Discuss energy dispersal and its relevance to spontaneity Describe
Entropy, free energy and equilibrium Spontaneity Entropy Free energy and equilibrium Learning objectives Discuss what is meant by spontaneity Discuss energy dispersal and its relevance to spontaneity Describe
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy
 Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
Class 22 - Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy The second law of thermodynamics The first law relates heat energy, work and the internal thermal energy of a system, and is essentially a statement
Summary Part Thermodynamic laws Thermodynamic processes. Fys2160,
 ! Summary Part 2 21.11.2018 Thermodynamic laws Thermodynamic processes Fys2160, 2018 1 1 U is fixed ) *,,, -(/,,), *,, -(/,,) N, 3 *,, - /,,, 2(3) Summary Part 1 Equilibrium statistical systems CONTINUE...
! Summary Part 2 21.11.2018 Thermodynamic laws Thermodynamic processes Fys2160, 2018 1 1 U is fixed ) *,,, -(/,,), *,, -(/,,) N, 3 *,, - /,,, 2(3) Summary Part 1 Equilibrium statistical systems CONTINUE...
Homework 10: Do problem 6.2 in the text. Solution: Part (a)
 Homework 10: Do problem 6. in the text Solution: Part (a) The two boxes will come to the same temperature as each other when they are in thermal euilibrium. So, the final temperature is an average of the
Homework 10: Do problem 6. in the text Solution: Part (a) The two boxes will come to the same temperature as each other when they are in thermal euilibrium. So, the final temperature is an average of the
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Chapter 4 - Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 4 - The motive power of heat is independent of the agents employed to realize it. -Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton Fall 2013 An irreversible process is a process
Chapter 4 - The motive power of heat is independent of the agents employed to realize it. -Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton Fall 2013 An irreversible process is a process
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics 19.1 Spontaneous Processes Chemical thermodynamics is concerned with energy relationships in chemical reactions. We consider enthalpy and we also consider entropy in
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics 19.1 Spontaneous Processes Chemical thermodynamics is concerned with energy relationships in chemical reactions. We consider enthalpy and we also consider entropy in
Statistical Physics. The Second Law. Most macroscopic processes are irreversible in everyday life.
 Statistical Physics he Second Law ime s Arrow Most macroscopic processes are irreversible in everyday life. Glass breaks but does not reform. Coffee cools to room temperature but does not spontaneously
Statistical Physics he Second Law ime s Arrow Most macroscopic processes are irreversible in everyday life. Glass breaks but does not reform. Coffee cools to room temperature but does not spontaneously
Heat Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Heat Engines and the Second Law of hermodynamics here are three equivalent forms of the second law of thermodynamics; will state all three, discuss: I. (Kelvin-Planck) It is impossible to construct an
Thermodynamics: Chapter 02 The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Microscopic Foundation of Thermodynamics. September 10, 2013
 Thermodynamics: Chapter 02 The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Microscopic Foundation of Thermodynamics September 10, 2013 We have talked about some basic concepts in thermodynamics, T, W, Q, C,.... Some
Thermodynamics: Chapter 02 The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Microscopic Foundation of Thermodynamics September 10, 2013 We have talked about some basic concepts in thermodynamics, T, W, Q, C,.... Some
Chem rd law of thermodynamics., 2018 Uwe Burghaus, Fargo, ND, USA
 Chem 759 3 rd law of thermodynamics, 2018 Uwe Burghaus, Fargo, ND, USA Class 1-4 Class 5-8 Class 9 Class 10-16 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8, 12 tentative schedule 1 st law 2 nd law 3 rd law
Chem 759 3 rd law of thermodynamics, 2018 Uwe Burghaus, Fargo, ND, USA Class 1-4 Class 5-8 Class 9 Class 10-16 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8, 12 tentative schedule 1 st law 2 nd law 3 rd law
Irreversible Processes
 Irreversible Processes Examples: Block sliding on table comes to rest due to friction: KE converted to heat. Heat flows from hot object to cold object. Air flows into an evacuated chamber. Reverse process
Irreversible Processes Examples: Block sliding on table comes to rest due to friction: KE converted to heat. Heat flows from hot object to cold object. Air flows into an evacuated chamber. Reverse process
Concept: Thermodynamics
 1 Concept: Thermodynamics 2 Narayanan Komerath 3 Keywords: First law, Second law, Entropy, Work, Energy, Heat 4 5 6 1. Definition Thermodynamics relates heat to work and energy. In some ways it is a philosophical
1 Concept: Thermodynamics 2 Narayanan Komerath 3 Keywords: First law, Second law, Entropy, Work, Energy, Heat 4 5 6 1. Definition Thermodynamics relates heat to work and energy. In some ways it is a philosophical
Irreversibility. Have you ever seen this happen? (when you weren t asleep or on medication) Which stage never happens?
 Lecture 5: Statistical Processes Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates and Macrostates The meaning of equilibrium 0.10 0.08 Reading: Elements Ch. 5 Probability (N 1, N
Lecture 5: Statistical Processes Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates and Macrostates The meaning of equilibrium 0.10 0.08 Reading: Elements Ch. 5 Probability (N 1, N
Second Law of Thermodynamics -
 Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics - REVIEW ENTROPY EXAMPLE Dr. Garrick 1/19/09 First Law of Thermodynamics you can t win! First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be Created or Destroyed the total energy
Statistical mechanics of biological processes
 Statistical mechanics of biological processes 1 Modeling biological processes Describing biological processes requires models. If reaction occurs on timescales much faster than that of connected processes
Statistical mechanics of biological processes 1 Modeling biological processes Describing biological processes requires models. If reaction occurs on timescales much faster than that of connected processes
Thermodynamics: More Entropy
 Thermodynamics: More Entropy From Warmup On a kind of spiritual note, this could possibly explain how God works some miracles. Supposing He could precisely determine which microstate occurs, He could heat,
Thermodynamics: More Entropy From Warmup On a kind of spiritual note, this could possibly explain how God works some miracles. Supposing He could precisely determine which microstate occurs, He could heat,
Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
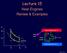 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Thermodynamic entropy
 1 1.1 Thermodynamics and entropy The existence of entropy follows inevitably from the first and second laws of thermodynamics. However, our purpose is not to reproduce this deduction, but rather to focus
1 1.1 Thermodynamics and entropy The existence of entropy follows inevitably from the first and second laws of thermodynamics. However, our purpose is not to reproduce this deduction, but rather to focus
Thermodynamics Second Law Entropy
 Thermodynamics Second Law Entropy Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 9, 2018 Last time entropy (macroscopic perspective) Overview entropy (microscopic perspective) Reminder of Example from Last Lecture
Thermodynamics Second Law Entropy Lana Sheridan De Anza College May 9, 2018 Last time entropy (macroscopic perspective) Overview entropy (microscopic perspective) Reminder of Example from Last Lecture
Sequences and infinite series
 Sequences and infinite series D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania March 29, 208 D. DeTurck Math 04 002 208A: Sequence and series / 54 Sequences The lists of numbers you generate using a numerical method
Sequences and infinite series D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania March 29, 208 D. DeTurck Math 04 002 208A: Sequence and series / 54 Sequences The lists of numbers you generate using a numerical method
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
The four laws of Thermodynamics. WOD are underlined.
 The four laws of Thermodynamics WOD are underlined. The four laws of Thermodynamics The 0 th Law (discovered 4 th ) The 1 st Law (discovered 2 nd ) The 2 nd Law (discovered 1 st ) The 3 rd Law (discovered
The four laws of Thermodynamics WOD are underlined. The four laws of Thermodynamics The 0 th Law (discovered 4 th ) The 1 st Law (discovered 2 nd ) The 2 nd Law (discovered 1 st ) The 3 rd Law (discovered
Irreversible Processes
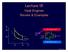 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Thermodynamics: Reversibility and Carnot
 Thermodynamics: Reversibility and Carnot From Warmup It seems like this reading (for Friday) explained the homework assigned for Wednesday's lecture. Is homework based on the previous lecture, or the current
Thermodynamics: Reversibility and Carnot From Warmup It seems like this reading (for Friday) explained the homework assigned for Wednesday's lecture. Is homework based on the previous lecture, or the current
Lecture 13. The Second Law
 MIT 3.00 Fall 2002 c W.C Carter 88 Lecture 13 The Second Law Last Time Consequences of an Ideal Gas Internal Energy a Function of T Only A New State Function for Any System: Enthalpy H = U + PV A New State
MIT 3.00 Fall 2002 c W.C Carter 88 Lecture 13 The Second Law Last Time Consequences of an Ideal Gas Internal Energy a Function of T Only A New State Function for Any System: Enthalpy H = U + PV A New State
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Lecture 6 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 6 Examples and Problems Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal diffusion Thermal conductivity Irreversibility Hot Cold Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates
Lecture 6 Examples and Problems Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal diffusion Thermal conductivity Irreversibility Hot Cold Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates
5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.60 Spring 2008 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.60 Spring 2008 Lecture
Chapter 17.3 Entropy and Spontaneity Objectives Define entropy and examine its statistical nature Predict the sign of entropy changes for phase
 Chapter 17.3 Entropy and Spontaneity Objectives Define entropy and examine its statistical nature Predict the sign of entropy changes for phase changes Apply the second law of thermodynamics to chemical
Chapter 17.3 Entropy and Spontaneity Objectives Define entropy and examine its statistical nature Predict the sign of entropy changes for phase changes Apply the second law of thermodynamics to chemical
Basics of Statistical Mechanics
 Basics of Statistical Mechanics Review of ensembles Microcanonical, canonical, Maxwell-Boltzmann Constant pressure, temperature, volume, Thermodynamic limit Ergodicity (see online notes also) Reading assignment:
Basics of Statistical Mechanics Review of ensembles Microcanonical, canonical, Maxwell-Boltzmann Constant pressure, temperature, volume, Thermodynamic limit Ergodicity (see online notes also) Reading assignment:
Heat Machines (Chapters 18.6, 19)
 eat Machines (hapters 8.6, 9) eat machines eat engines eat pumps The Second Law of thermodynamics Entropy Ideal heat engines arnot cycle Other cycles: Brayton, Otto, Diesel eat Machines Description The
eat Machines (hapters 8.6, 9) eat machines eat engines eat pumps The Second Law of thermodynamics Entropy Ideal heat engines arnot cycle Other cycles: Brayton, Otto, Diesel eat Machines Description The
The goal of equilibrium statistical mechanics is to calculate the diagonal elements of ˆρ eq so we can evaluate average observables < A >= Tr{Â ˆρ eq
 Chapter. The microcanonical ensemble The goal of equilibrium statistical mechanics is to calculate the diagonal elements of ˆρ eq so we can evaluate average observables < A >= Tr{Â ˆρ eq } = A that give
Chapter. The microcanonical ensemble The goal of equilibrium statistical mechanics is to calculate the diagonal elements of ˆρ eq so we can evaluate average observables < A >= Tr{Â ˆρ eq } = A that give
Entropy. Physics 1425 Lecture 36. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Entropy Physics 1425 Lecture 36 Michael Fowler, UVa First and Second Laws of A quick review. Thermodynamics First Law: total energy conserved in any process: joules in = joules out Second Law: heat only
Entropy Physics 1425 Lecture 36 Michael Fowler, UVa First and Second Laws of A quick review. Thermodynamics First Law: total energy conserved in any process: joules in = joules out Second Law: heat only
Math 138: Introduction to solving systems of equations with matrices. The Concept of Balance for Systems of Equations
 Math 138: Introduction to solving systems of equations with matrices. Pedagogy focus: Concept of equation balance, integer arithmetic, quadratic equations. The Concept of Balance for Systems of Equations
Math 138: Introduction to solving systems of equations with matrices. Pedagogy focus: Concept of equation balance, integer arithmetic, quadratic equations. The Concept of Balance for Systems of Equations
T s change via collisions at boundary (not mechanical interaction)
 Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermodynamics Overview Everything in the world is a balance of energy, in various forms from biological processes to the rusting of a nail. Two of the most important questions chemists ask are:
Chemical Thermodynamics Overview Everything in the world is a balance of energy, in various forms from biological processes to the rusting of a nail. Two of the most important questions chemists ask are:
Agenda. Chapter 10, Problem 26. All matter is made of atoms. Atomic Structure 4/8/14. What is the structure of matter? Atomic Terminology
 Agenda Today: HW Quiz, Thermal physics (i.e., heat) Thursday: Finish thermal physics, atomic structure (lots of review from chemistry!) Chapter 10, Problem 26 A boy reaches out of a window and tosses a
Agenda Today: HW Quiz, Thermal physics (i.e., heat) Thursday: Finish thermal physics, atomic structure (lots of review from chemistry!) Chapter 10, Problem 26 A boy reaches out of a window and tosses a
Entropy and Free Energy. The Basis for Thermodynamics
 Entropy and Free Energy The Basis for Thermodynamics First law of thermodynamics: The change in the energy of a system U = q+ w is the sum of the heat and the work done by or on the system. the first law
Entropy and Free Energy The Basis for Thermodynamics First law of thermodynamics: The change in the energy of a system U = q+ w is the sum of the heat and the work done by or on the system. the first law
8 A Microscopic Approach to Entropy
 8 A Microscopic Approach to Entropy The thermodynamic approach www.xtremepapers.com Internal energy and enthalpy When energy is added to a body, its internal energy U increases by an amount ΔU. The energy
8 A Microscopic Approach to Entropy The thermodynamic approach www.xtremepapers.com Internal energy and enthalpy When energy is added to a body, its internal energy U increases by an amount ΔU. The energy
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Lecture 6 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 6 Examples and Problems Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal diffusion Thermal conductivity Irreversibility Hot Cold Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates
Lecture 6 Examples and Problems Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal diffusion Thermal conductivity Irreversibility Hot Cold Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates
Lecture 8: Chemical Equilibrium for the Autodissociation of Pure Water
 Lecture 8: Chemical Equilibrium for the Autodissociation of Pure Water One of the great things about college courses is that they tend to shake the foundation for the stuff you learned to be true in grade
Lecture 8: Chemical Equilibrium for the Autodissociation of Pure Water One of the great things about college courses is that they tend to shake the foundation for the stuff you learned to be true in grade
to satisfy the large number approximations, W W sys can be small.
 Chapter 12. The canonical ensemble To discuss systems at constant T, we need to embed them with a diathermal wall in a heat bath. Note that only the system and bath need to be large for W tot and W bath
Chapter 12. The canonical ensemble To discuss systems at constant T, we need to embed them with a diathermal wall in a heat bath. Note that only the system and bath need to be large for W tot and W bath
12 The Laws of Thermodynamics
 June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
[ ( )] + exp 2α / ( k B T) [ ] + exp 3α / k B T
![[ ( )] + exp 2α / ( k B T) [ ] + exp 3α / k B T [ ( )] + exp 2α / ( k B T) [ ] + exp 3α / k B T](/thumbs/81/84416061.jpg) hermal Physics Homework #10 (optional) (19 points) 1 Your work on this homework set will not be accepted after 3 p.m. on December 4 (W) 1. (3 points) A common mistake people make when they try to calculate
hermal Physics Homework #10 (optional) (19 points) 1 Your work on this homework set will not be accepted after 3 p.m. on December 4 (W) 1. (3 points) A common mistake people make when they try to calculate
UNIT 5 Readiness Assessment Quiz
 UNIT 5 Readiness Assessment Quiz Name: Vanden Bout/LaBrake UTEID: Spring 2013 CH302 I. MYTH BUSTERS: Soda Freezing Demonstration. Sometimes when you purchase a bottle of soda from a vending machine, the
UNIT 5 Readiness Assessment Quiz Name: Vanden Bout/LaBrake UTEID: Spring 2013 CH302 I. MYTH BUSTERS: Soda Freezing Demonstration. Sometimes when you purchase a bottle of soda from a vending machine, the
Conduction. Heat Transfer Methods. Conduction. Conduction
 Heat Transfer Methods Conduction: Thermal kinetic energy passed from particle-to-particle along a length of material. Convection: Thermal energy carried by moving fluid. Radiation: Thermal energy carried
Heat Transfer Methods Conduction: Thermal kinetic energy passed from particle-to-particle along a length of material. Convection: Thermal energy carried by moving fluid. Radiation: Thermal energy carried
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas
 P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
