EVALUATION OF THE BEHAVIOUR OF STEAM EXPANDED IN A SET OF NOZZLES, IN A GIVEN TEMPERATURE
|
|
|
- Harvey Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) 9-13 Journal Homepage: ISSN: EVALUATION OF THE BEHAVIOUR OF STEAM EXPANDED IN A SET OF NOZZLES, IN A GIVEN TEMPERATURE Kingsley Ejikeme Madu Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu University, Uli, Anambra, Nigeria Mobile Phone Number: +234(0) ; kingsleyblack2@gmail.com ABSTRACT Nozzles are essentially adiabatic devices and are used to accelerate a fluid; therefore, isentropic process serves as a suitable model for nozzles. The paper discussed the characteristics of an expanding steam passing through a duct of varying cross-section area. Based on the converging-diverging nozzle, the research investigated the condition of steam at the throat and exit, stating it to be superheated. With a critical temperature and critical velocity of o C and m/s respectively, the minimum area of the nozzle measured m 2. The expansion through the set of nozzles was largely isentropic, meaning that it is adiabatic and reversible. It was assumed that the fluid velocity and the fluid properties, change, only in the direction of flow. Nozzles are used, in practice, in steam and gas turbines, in jet engines, in rocket motors, in flow measurement, and in many other engineering applications. Keywords: Critical Conditions, Ambient Conditions, Expanded Steam, Converging-Diverging Nozzles How to cite this article: Madu, K. E. (2018). Evaluation of the Behaviour of Steam Expanded in a Set of Nozzles, in a Given Temperature. Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) INTRODUCTION A nozzle is a duct of smoothly varying cross-sectional area in which a steadily flowing fluid can be made to accelerate by a pressure drop along the duct. A steam nozzle is as passage of varying cross-section, which converts the heat energy of steam into kinetic energy (Ballaney, 2011). During the first part of the nozzle, the steam increases its velocity. But, in its later part, the steam gains more in volume than in velocity (Uppal and Rao, 2012). Since the mass of steam of steam passing through any section of the nozzle remains constant, the variation of steam pressure in the nozzle depends upon the velocity, specific volume, and dryness fraction of the steam. A well designed nozzle converts the heat energy of steam into kinetic energy, with a minimum loss. The main use of steam nozzle in steam turbines is to produce a jet of steam with a high velocity (Rajput, 2013). The smaller section of the nozzle is called throat. In practice, there are many applications which require a high-velocity stream of fluid; and the nozzle is the best means of obtaining this. For example, nozzles are used in steam and gas turbines, in jet engines, in rocket motors, in flow measurement, and in many other applications. When a fluid is decelerated in a duct, causing a rise in pressure along the stream, then the duct is called a diffuser; two applications, in practice, in which the diffuser is used, are the centrifugal compressor and the ramjet. The analysis presented in this paper, will be restricted to one-dimensional flow. In onedimensional flow, it is assumed that the fluid velocity and the fluid properties change, only in the direction of flow. This means that the fluid velocity is assumed to remain constant at a mean value across the crosssection of the duct. The effects of friction will not be analysed fundamentally, suitable efficiencies and coefficients being adopted to allow for the departure from the ideal frictionless case. The analysis of fluid Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) Page 9
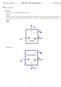
2 flow involving friction has become of increasing importance, due to the development of the turbojet, the ramjet, and the rocket, and the introduction of high-speed flight. According to Khurmi, and Gupta, (2008), the following three types of nozzle are important, from the subject point of view: Convergent Nozzle. When the cross-section of the nozzle decreases continuously from entrance to exit, it is called a convergent nozzle. Divergent Nozzle. When the cross-section of the nozzle increases continuously from entrance to exit, it is called a convergent nozzle. Convergent-Divergent Nozzle. When the cross section of the nozzle first decreases from its entrance to throat, and then increases from its throat to exit, it is called a convergent-divergent nozzle. This type of nozzle is widely used these days in various types of steam turbines. In a convergent-divergent nozzle, steam enters the nozzle with a high pressure, but with a negligible velocity. In the converging portion (i.e. from the inlet to the throat), there is a drop in steam pressure with a rise in its velocity. There is also a drop in the enthalpy or total heat of the steam. This drop of heat is not utilized in doing some external work, but is converted into kinetic energy. In the divergent portion (i.e. from the throat to the outlet), there is a further drop of steam pressure, with a further rise in its velocity. Again, there is a drop in the enthalpy or total heat of steam, which is converted into kinetic energy. It will be interesting to know that steam enters the nozzle with a high pressure and negligible velocity, but leaves the nozzle with a high velocity and small pressure. The pressure at which the steam leaves the nozzle, is known as back pressure (Yunus, and Michael, 2011). Moreover, no heat is supplied or rejected by the steam during flow through a nozzle. Therefore, it is considered as isentropic flow, and the corresponding expansion (i.e. decrease in pressure), is considered as an isentropic expansion. In the above analysis, it is assumed that no friction exists between the nozzle surface and the flowing steam. As regards nozzle shape, consider a stream of fluid at pressure, p 1 ; enthalpy, h ; and with a low velocity, C 1. It is required to find the shape of a duct which will cause the fluid to accelerate to a high velocity as the pressure falls along the duct. It can be assumed that the heat loss from the duct is negligibly small (i.e. adiabatic flow, Q = 0), and it is clear that no work is done on or by the fluid (i.e. W = 0). The steady-flow energy equation is given as: ṁ(h Z 1 g) + Q + W = ṁ(h Z 2 g) (1) In a steady flow, the rate of mass flow of fluid at any section is the same as at any other section. Applying the steady-flow energy equation, (Equation 1), between section 1 and any other section X X where the pressure is p, the enthalpy is h, and the velocity is C, we have; h 1 + = h + i.e. C 2 = 2(h 1 h) + or C = {2(h 1 h) + } (2) If the area at the section X X is A, and the specific volume is ν, then, using equation for mass flow rate; Mass flow, ṁ = The area per unit mass flow is given as: ṁ = (3) Then, substituting for the velocity C, from equation 2 Area per unit mass flow = (4) It can be seen from Equation 4 that in order to find the way in which the area of the duct varies, it is necessary to be able to evaluate the specific volume, v, and the enthalpy, h, at any section X X. To be able to do this, some information about the process undergone between section 1 and section X X, must be known. For the ideal frictionless case, since the flow is adiabatic and reversible, the process undergone is an isentropic process, and hence; s 1 = (entropy at any section X X) = s Now, using Equation 3, and the fact that s 1 = s, it is possible to plot the variation of the cross-sectional area of the duct against the pressure along the duct. For a vapour, this can be done using tables; for a perfect gas, the procedure is simpler, since we have Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) Page 10
3 pv y = constant, for an isentropic process. In either cases, choosing fixed inlet conditions, then the variation in the area, A, the specific volume, v, and the velocity, C, can be plotted against the pressure along the duct (Eastop, and McConkey, 1993). Typical curves are shown in Figure 1. isentropic expansion, and a flow of 300 Kg/min, we are to determine the following; Condition of steam at the throat Condition of steam at the exit Critical temperature Critical velocity Critical Enthalpy Minimum area of nozzles Exit velocity Exit area Quality of steam at the exit plane Diameter of the nozzles at the exit, for a set of 5 nozzles Type of Nozzle RESULTS AND DISCUSSION At a pressure of 10 bar, T s = o C (cf. Saturated water Pressure table) Figure 1: Cross- Sectional Area, Velocity, and Specific Volume Variations with Pressure through a Nozzle It can be seen that the area decreases initially, reaches a minimum, and then increases again. This can, also, be seen from Equation 3. When v increases less rapidly than C, then the area decreases; when v increases more rapidly than C, then the area increases. A nozzle, whose area varies as in Figure 1, is called a convergent-divergent nozzle. The section of minimum area is called the throat of the nozzle. The velocity at the throat of a nozzle operating at its designed pressure ratio, is the velocity of sound at the throat conditions. The flow up to the throat is subsonic; the flow after the throat is supersonic. It should be noted that a sonic or a supersonic flow requires a diverging duct to accelerate it. Worthy of note is the fact that the specific volume of a liquid is constant over a wide pressure range. Therefore, nozzles for liquids are always convergent, even at very high exit velocities (e.g. a fire-hose uses a convergent nozzle). 10 bar = 1000 kpa; and = Thus, P* = P 0 x = 10 x = 5.46 bar From the problem statement, S 0 = S* = S 1 = kj/kgk h 0 = kj/kg Task 1: Determination of Condition of Steam at the Throat P* = 5.46 bar S* = kj/kgk But S g at 500 kpa (5 bar) = kj/kgk Also S g at 600 kpa (6 bar) = kj/kgk Since S g at 5 bar and 6 bar < S*, then, the condition of steam at the throat is superheated. Task 2: Determination of Condition of Steam at the Exit P 1 = 3 bar S 1 = kj/kgk But S g at 300 kpa (3 bar) = kj/kgk Since S g at 3 bar < S*, then, the condition of steam at the exit is superheated. MATERIAL AND METHOD Steam is expanded in a set of nozzles from 10 bar, 350 o C to 3 bar as shown in Figure 2. Assuming an Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) Page 11
4 = o C For P 546 kpa, by interpolation, we get; Therefore, Specific Volume, = m 3 /Kg Enthalpy, Temperature, = kj/kg = o C Figure 2: h-s Graph of Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Task 3, and 4: Determination of Critical Temperature, and Critical Velocity The condition of steam at the throat, it must be reiterated, is superheated. At the throat, P* = 5.46 bar S* = kj/kgk For P 500 kpa, by interpolation, we have (cf. Superheated Water Table); Therefore, = kj/kg = m 3 /Kg = o C For P 600 kpa, by interpolation, we obtain Therefore; = kj/kg = m 3 /Kg But, Critical Temperature, T* = 350 x = o C Critical Velocity, V* = 44.72(h 0 - ) 1/2 = 44.72( ) 1/2 = m/s Task 5: Determination of the Minimum Area of Nozzle A* = ; where = Critical Specific Volume; and = Critical velocity A* = = m 2 Task 6: Determination of the Exit Velocity Recall that the condition at the exit is superheated and that; S 1 = kj/kgk, and P 1 = 3 bar (300 kpa) Interpolating, we obtain; Therefore, h I = 4011 kj/kgk v I = m 3 /Kg T I = o C Exit Velocity, V 1 = 44.72(h 0 h 1 ) 1/2 = 44.72( ) 1/2 = m/s Task 7: Determination of the Exit Area Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) Page 12
5 A 1 = = = m 2 Task 8: Determination of the Quality of Steam at the Exit Plane h 1 = + x 1 ( ) 4011 = x 1 (2163.5) x 1 = Task 9: Determination of the Diameter of the Nozzle at the Exit for a Set of 5 Nozzles The exit area was determined in Task 7. A correlation could be established between this function and the diameter of the nozzle, thus; A 1 = = d 1 = ( ) 1/2 d 1 = ( ) 1/2 = m 2 Task 10: Determination of the Type of the Nozzle The nozzle is typically convergent-divergent in nature; since there is a decrease in the value of pressure passing through the duct. The condition or quality of wet vapour is most frequently defined by its dryness fraction; this is known as well as the pressure or temperature, then the state of the wet vapour is fully defined. Dryness fraction x, equals the mass of dry vapour in 1 Kg of the mixture. Sometimes, a wetness fraction is define as the mass of liquid in 1 Kg of the mixture, i.e. wetness fraction = 1 x. Note that for a dry saturated vapour, x = 1, and that for a saturated liquid, x = 0. In our determination of quality of steam in Task 8, x 1, indicating the superheated state of the fluid. Moreover, in the above analysis, the minimum area of the nozzle is taken to be equal to the area of the throat. Besides, it was assumed that the cross-section of the nozzle at the exit is circular or cylindrical. task; but a combination of the two as we have in a converging-diverging nozzle, give a different result as we have in the analysis above. The cross-sectional area of a nozzle decreases in the flow direction for subsonic flows, and increases, for supersonic flow. The amount of mass flowing through a cross section per unit time is called the mass flow rate, and is denoted by ṁ. The dot over the symbol is used to indicate time rate of change. The volume of the fluid flowing through a cross section per unit time is called the volume flow rate. The mass flow rate is a function of density and volume flow rate. REFERENCES Ballaney, P. L. (2011). Thermal Engineering: Engineering Thermodynamics & Energy Conversion Techniques. Delhi: Khanna Publishers, p.789. Eastop, T. D. and McConkey, A. (1993). Applied Thermodynamics for Engineering Technologists. Delhi: Pearson, pp Khurmi, R. S. and Gupta J. K. (2008). A Textbook of Thermal Engineering. New Delhi: S.Chand, pp Rajput, R. K. (2013). Thermal Engineering. New Delhi: Laxmi Publications, pp Uppal, S. L. and Rao, S. (2012). Electrical Power Systems: Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Protection, and Utilization of Electrical Energy. Delhi: Khanna Publishers, pp Yunus, A. and Michael, A. B. (2011). Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach. New-York: McGraw Hills, p.856ff. CONCLUSION A nozzle is a device that increases the velocity of a fluid at the expense of pressure. A diffuser is a device that increases the pressure of a fluid by slowing it down. That is, nozzles and diffusers perform opposite Equatorial Journal of Engineering (2018) Page 13
Brown Hills College of Engineering & Technology
 UNIT 4 Flow Through Nozzles Velocity and heat drop, Mass discharge through a nozzle, Critical pressure ratio and its significance, Effect of friction, Nozzle efficiency, Supersaturated flow, Design pressure
UNIT 4 Flow Through Nozzles Velocity and heat drop, Mass discharge through a nozzle, Critical pressure ratio and its significance, Effect of friction, Nozzle efficiency, Supersaturated flow, Design pressure
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Please welcome for any correction or misprint in the entire manuscript and your valuable suggestions kindly mail us
 Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
Problems of Practices Of Fluid Mechanics Compressible Fluid Flow Prepared By Brij Bhooshan Asst. Professor B. S. A. College of Engg. And Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported By: Purvi Bhooshan
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 7. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Review of Fundamentals - Fluid Mechanics
 Review of Fundamentals - Fluid Mechanics Introduction Properties of Compressible Fluid Flow Basics of One-Dimensional Gas Dynamics Nozzle Operating Characteristics Characteristics of Shock Wave A gas turbine
Review of Fundamentals - Fluid Mechanics Introduction Properties of Compressible Fluid Flow Basics of One-Dimensional Gas Dynamics Nozzle Operating Characteristics Characteristics of Shock Wave A gas turbine
SPC 407 Sheet 2 - Solution Compressible Flow - Governing Equations
 SPC 407 Sheet 2 - Solution Compressible Flow - Governing Equations 1. Is it possible to accelerate a gas to a supersonic velocity in a converging nozzle? Explain. No, it is not possible. The only way to
SPC 407 Sheet 2 - Solution Compressible Flow - Governing Equations 1. Is it possible to accelerate a gas to a supersonic velocity in a converging nozzle? Explain. No, it is not possible. The only way to
Chapter 17. For the most part, we have limited our consideration so COMPRESSIBLE FLOW. Objectives
 Chapter 17 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW For the most part, we have limited our consideration so far to flows for which density variations and thus compressibility effects are negligible. In this chapter we lift this
Chapter 17 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW For the most part, we have limited our consideration so far to flows for which density variations and thus compressibility effects are negligible. In this chapter we lift this
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Applied Gas Dynamics Flow With Friction and Heat Transfer
 Applied Gas Dynamics Flow With Friction and Heat Transfer Ethirajan Rathakrishnan Applied Gas Dynamics, John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltd c 2010 Ethirajan Rathakrishnan 1 / 121 Introduction So far, we have
Applied Gas Dynamics Flow With Friction and Heat Transfer Ethirajan Rathakrishnan Applied Gas Dynamics, John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltd c 2010 Ethirajan Rathakrishnan 1 / 121 Introduction So far, we have
One-Dimensional Isentropic Flow
 Cairo University Second Year Faculty of Engineering Gas Dynamics AER 201B Aerospace Department Sheet (1) 2011-2012 One-Dimensional Isentropic Flow 1. Assuming the flow of a perfect gas in an adiabatic,
Cairo University Second Year Faculty of Engineering Gas Dynamics AER 201B Aerospace Department Sheet (1) 2011-2012 One-Dimensional Isentropic Flow 1. Assuming the flow of a perfect gas in an adiabatic,
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
SPC 407 Sheet 5 - Solution Compressible Flow Rayleigh Flow
 SPC 407 Sheet 5 - Solution Compressible Flow Rayleigh Flow 1. Consider subsonic Rayleigh flow of air with a Mach number of 0.92. Heat is now transferred to the fluid and the Mach number increases to 0.95.
SPC 407 Sheet 5 - Solution Compressible Flow Rayleigh Flow 1. Consider subsonic Rayleigh flow of air with a Mach number of 0.92. Heat is now transferred to the fluid and the Mach number increases to 0.95.
THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES
 Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Fluid Mechanics - Course 123 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
 Fluid Mechanics - Course 123 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW Flow of compressible fluids in a p~pe involves not only change of pressure in the downstream direction but also a change of both density of the fluid and
Fluid Mechanics - Course 123 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW Flow of compressible fluids in a p~pe involves not only change of pressure in the downstream direction but also a change of both density of the fluid and
GAS DYNAMICS AND JET PROPULSION
 GAS DYNAMICS AND JE PROPULSION 1. What is the basic difference between compressible and incompressible fluid flow? Compressible Incompressible 1. Fluid velocities are appreciable 1. Fluid velocities are
GAS DYNAMICS AND JE PROPULSION 1. What is the basic difference between compressible and incompressible fluid flow? Compressible Incompressible 1. Fluid velocities are appreciable 1. Fluid velocities are
Find: a) Mass of the air, in kg, b) final temperature of the air, in K, and c) amount of entropy produced, in kj/k.
 PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
1. For an ideal gas, internal energy is considered to be a function of only. YOUR ANSWER: Temperature
 CHAPTER 11 1. For an ideal gas, internal energy is considered to be a function of only. YOUR ANSWER: Temperature 2.In Equation 11.7 the subscript p on the partial derivative refers to differentiation at
CHAPTER 11 1. For an ideal gas, internal energy is considered to be a function of only. YOUR ANSWER: Temperature 2.In Equation 11.7 the subscript p on the partial derivative refers to differentiation at
Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual
 Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Download free books at Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual 2 2012 Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri & bookboon.com
Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Download free books at Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual 2 2012 Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri & bookboon.com
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics. Chapter 13 Compressible Flow. Fox, Pritchard, & McDonald
 Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Chapter 13 Compressible Flow Main Topics Basic Equations for One-Dimensional Compressible Flow Isentropic Flow of an Ideal Gas Area Variation Flow in a Constant Area Duct
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Chapter 13 Compressible Flow Main Topics Basic Equations for One-Dimensional Compressible Flow Isentropic Flow of an Ideal Gas Area Variation Flow in a Constant Area Duct
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
Richard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site
 Página 1 de 7 Richard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site Solid Rocket Motor Theory -- Nozzle Theory Nozzle Theory The rocket nozzle can surely be described as the epitome of elegant simplicity. The
Página 1 de 7 Richard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site Solid Rocket Motor Theory -- Nozzle Theory Nozzle Theory The rocket nozzle can surely be described as the epitome of elegant simplicity. The
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A.M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering
 Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A.M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, IIT Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 08 Cycle Components and Component
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A.M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, IIT Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 08 Cycle Components and Component
SATHYABAMA UNIVERISTY. Unit III
 Unit III UNIT III STEAM NOZZLES AND TURBINES Flow of steam through nozzles, shapes of nozzles, effect of friction, critical pressure ratio,supersaturated flow.impulse and reaction principles, compounding,
Unit III UNIT III STEAM NOZZLES AND TURBINES Flow of steam through nozzles, shapes of nozzles, effect of friction, critical pressure ratio,supersaturated flow.impulse and reaction principles, compounding,
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number:
 ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
IX. COMPRESSIBLE FLOW. ρ = P
 IX. COMPRESSIBLE FLOW Compressible flow is the study of fluids flowing at speeds comparable to the local speed of sound. This occurs when fluid speeds are about 30% or more of the local acoustic velocity.
IX. COMPRESSIBLE FLOW Compressible flow is the study of fluids flowing at speeds comparable to the local speed of sound. This occurs when fluid speeds are about 30% or more of the local acoustic velocity.
Week 8. Steady Flow Engineering Devices. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 8. Steady Flow Engineering Devices Objectives 1. Solve energy balance problems for common steady-flow devices such as nozzles, compressors, turbines, throttling valves, mixers, heaters, and heat exchangers
Week 8. Steady Flow Engineering Devices Objectives 1. Solve energy balance problems for common steady-flow devices such as nozzles, compressors, turbines, throttling valves, mixers, heaters, and heat exchangers
To receive full credit all work must be clearly provided. Please use units in all answers.
 Exam is Open Textbook, Open Class Notes, Computers can be used (Computer limited to class notes, lectures, homework, book material, calculator, conversion utilities, etc. No searching for similar problems
Exam is Open Textbook, Open Class Notes, Computers can be used (Computer limited to class notes, lectures, homework, book material, calculator, conversion utilities, etc. No searching for similar problems
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Contents. Preface... xvii
 Contents Preface... xvii CHAPTER 1 Idealized Flow Machines...1 1.1 Conservation Equations... 1 1.1.1 Conservation of mass... 2 1.1.2 Conservation of momentum... 3 1.1.3 Conservation of energy... 3 1.2
Contents Preface... xvii CHAPTER 1 Idealized Flow Machines...1 1.1 Conservation Equations... 1 1.1.1 Conservation of mass... 2 1.1.2 Conservation of momentum... 3 1.1.3 Conservation of energy... 3 1.2
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
Section 4.1: Introduction to Jet Propulsion. MAE Propulsion Systems II
 Section 4.1: Introduction to Jet Propulsion Jet Propulsion Basics Squeeze Bang Blow Suck Credit: USAF Test Pilot School 2 Basic Types of Jet Engines Ramjet High Speed, Supersonic Propulsion, Passive Compression/Expansion
Section 4.1: Introduction to Jet Propulsion Jet Propulsion Basics Squeeze Bang Blow Suck Credit: USAF Test Pilot School 2 Basic Types of Jet Engines Ramjet High Speed, Supersonic Propulsion, Passive Compression/Expansion
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Lecture-2. One-dimensional Compressible Fluid Flow in Variable Area
 Lecture-2 One-dimensional Compressible Fluid Flow in Variable Area Summary of Results(Cont..) In isoenergetic-isentropic flow, an increase in velocity always corresponds to a Mach number increase and vice
Lecture-2 One-dimensional Compressible Fluid Flow in Variable Area Summary of Results(Cont..) In isoenergetic-isentropic flow, an increase in velocity always corresponds to a Mach number increase and vice
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
P 1 P * 1 T P * 1 T 1 T * 1. s 1 P 1
 ME 131B Fluid Mechanics Solutions to Week Three Problem Session: Isentropic Flow II (1/26/98) 1. From an energy view point, (a) a nozzle is a device that converts static enthalpy into kinetic energy. (b)
ME 131B Fluid Mechanics Solutions to Week Three Problem Session: Isentropic Flow II (1/26/98) 1. From an energy view point, (a) a nozzle is a device that converts static enthalpy into kinetic energy. (b)
1 st Law Analysis of Control Volume (open system) Chapter 6
 1 st Law Analysis of Control Volume (open system) Chapter 6 In chapter 5, we did 1st law analysis for a control mass (closed system). In this chapter the analysis of the 1st law will be on a control volume
1 st Law Analysis of Control Volume (open system) Chapter 6 In chapter 5, we did 1st law analysis for a control mass (closed system). In this chapter the analysis of the 1st law will be on a control volume
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
ENT 254: Applied Thermodynamics
 ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics
 June 21, 2010 Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics Introduction This article is a summary of selected parts of chapters 4, 5 and 6 in the textbook by Moran and Shapiro (2008. The intent
June 21, 2010 Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics Introduction This article is a summary of selected parts of chapters 4, 5 and 6 in the textbook by Moran and Shapiro (2008. The intent
Introduction. In general, gases are highly compressible and liquids have a very low compressibility. COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
 COMRESSIBLE FLOW COMRESSIBLE FLOW Introduction he compressibility of a fluid is, basically, a measure of the change in density that will be produced in the fluid by a specific change in pressure and temperature.
COMRESSIBLE FLOW COMRESSIBLE FLOW Introduction he compressibility of a fluid is, basically, a measure of the change in density that will be produced in the fluid by a specific change in pressure and temperature.
Lecture with Numerical Examples of Ramjet, Pulsejet and Scramjet
 Lecture 41 1 Lecture with Numerical Examples of Ramjet, Pulsejet and Scramjet 2 Problem-1 Ramjet A ramjet is flying at Mach 1.818 at an altitude 16.750 km altitude (Pa = 9.122 kpa, Ta= - 56.5 0 C = 216.5
Lecture 41 1 Lecture with Numerical Examples of Ramjet, Pulsejet and Scramjet 2 Problem-1 Ramjet A ramjet is flying at Mach 1.818 at an altitude 16.750 km altitude (Pa = 9.122 kpa, Ta= - 56.5 0 C = 216.5
Energy and Energy Balances
 Energy and Energy Balances help us account for the total energy required for a process to run Minimizing wasted energy is crucial in Energy, like mass, is. This is the Components of Total Energy energy
Energy and Energy Balances help us account for the total energy required for a process to run Minimizing wasted energy is crucial in Energy, like mass, is. This is the Components of Total Energy energy
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP112 LECTURE 7
 Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP11 LECTURE 7 Thermodynamics ENGR360/MEP11 Objectives: 1. Conservation of mass principle.. Conservation of energy principle applied to control volumes (first law of thermodynamics).
Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP11 LECTURE 7 Thermodynamics ENGR360/MEP11 Objectives: 1. Conservation of mass principle.. Conservation of energy principle applied to control volumes (first law of thermodynamics).
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
Flow Characteristic Through Convergent-Divergent Nozzle
 2018 IJSRST Volume 4 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Flow Characteristic Through Convergent-Divergent Nozzle S. Sathyapriya 1, R. Swathi 2, P.
2018 IJSRST Volume 4 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Flow Characteristic Through Convergent-Divergent Nozzle S. Sathyapriya 1, R. Swathi 2, P.
UNIT 1 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW FUNDAMENTALS
 UNIT 1 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW FUNDAMENTALS 1) State the difference between compressible fluid and incompressible fluid? 2) Define stagnation pressure? 3) Express the stagnation enthalpy in terms of static enthalpy
UNIT 1 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW FUNDAMENTALS 1) State the difference between compressible fluid and incompressible fluid? 2) Define stagnation pressure? 3) Express the stagnation enthalpy in terms of static enthalpy
First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
Chapter Two. Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter Two Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency Laith Batarseh The equation of continuity Most analyses in this book are limited to one-dimensional steady flows where the velocity
Chapter Two Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency Laith Batarseh The equation of continuity Most analyses in this book are limited to one-dimensional steady flows where the velocity
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 13 June 2007
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
As Per New GTU Syllabus
 As Per New GTU Syllabus Prepared by: Mr. Bhavin J. Vegada (M.Tech Thermal Engg.) Mr. Ketan C. Agola (M.Tech. Thermal Engg.) Darshan Institute of Engineering &Technology BRIEF CONTENTS Chapter No. Title
As Per New GTU Syllabus Prepared by: Mr. Bhavin J. Vegada (M.Tech Thermal Engg.) Mr. Ketan C. Agola (M.Tech. Thermal Engg.) Darshan Institute of Engineering &Technology BRIEF CONTENTS Chapter No. Title
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion
 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion (For B.E. Mechanical Engineering Students) (As per Anna University and Leading Universities New Revised Syllabus) Prof. K. Pandian Dr. A.Anderson, M.E., Ph.D., Professor
Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion (For B.E. Mechanical Engineering Students) (As per Anna University and Leading Universities New Revised Syllabus) Prof. K. Pandian Dr. A.Anderson, M.E., Ph.D., Professor
1. (20 pts total 2pts each) - Circle the most correct answer for the following questions.
 ME 50 Gas Dynamics Spring 009 Final Exam NME:. (0 pts total pts each) - Circle the most correct answer for the following questions. i. normal shock propagated into still air travels with a speed (a) equal
ME 50 Gas Dynamics Spring 009 Final Exam NME:. (0 pts total pts each) - Circle the most correct answer for the following questions. i. normal shock propagated into still air travels with a speed (a) equal
CLASS Fourth Units (Second part)
 CLASS Fourth Units (Second part) Energy analysis of closed systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. MOVING BOUNDARY WORK Moving boundary work (P
CLASS Fourth Units (Second part) Energy analysis of closed systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. MOVING BOUNDARY WORK Moving boundary work (P
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a 1.6-cm-diameter pipe.
 4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
Figure 1. Mach cone that arises upon supersonic flow around an object
 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND ISENTROPIC FLOWS Introduction The purpose of this applet is to simulate the operation of a converging-diverging nozzle, perhaps the most important and basic piece of engineering
UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND ISENTROPIC FLOWS Introduction The purpose of this applet is to simulate the operation of a converging-diverging nozzle, perhaps the most important and basic piece of engineering
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 6. Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6.1 Introduction
 Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
3. Write a detailed note on the following thrust vector control methods:
 Code No: R05322103 Set No. 1 1. Starting from the first principles and with the help of neatly drawn velocity triangles obtain the following relationship: Ψ = 2 Φ (tan β 2 + tan β 3 ) where Ψ is the blade
Code No: R05322103 Set No. 1 1. Starting from the first principles and with the help of neatly drawn velocity triangles obtain the following relationship: Ψ = 2 Φ (tan β 2 + tan β 3 ) where Ψ is the blade
ESO201A: Thermodynamics
 ESO201A: Thermodynamics First Semester 2015-2016 Mid-Semester Examination Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Time: 120 mins Marks: 250 Solve sub-parts of a question serially. Question #1 (60 marks): One kmol
ESO201A: Thermodynamics First Semester 2015-2016 Mid-Semester Examination Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Time: 120 mins Marks: 250 Solve sub-parts of a question serially. Question #1 (60 marks): One kmol
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
Refrigeration. 05/04/2011 T.Al-Shemmeri 1
 Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
Refrigeration is a process of controlled removal of heat from a substance to keep it at a temperature below the ambient condition, often below the freezing point of water (0 O C) 05/04/0 T.Al-Shemmeri
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, Chapter 7 ENTROPY
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter Four fluid flow mass, energy, Bernoulli and momentum
 4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
ENTROPY. Chapter 7. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. #01 Lecture No. # 07 Jet Engine Cycles For Aircraft propulsion
Jet Aircraft Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof A M Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. #01 Lecture No. # 07 Jet Engine Cycles For Aircraft propulsion
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 17 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good morning to all of you. We were discussing
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 17 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good morning to all of you. We were discussing
Fanno Flow. Gas Dynamics
 Fanno Flow Simple frictional flow ( Fanno Flow Adiabatic frictional flow in a constant-area duct * he Flow of a compressible fluid in a duct is Always accompanied by :- ariation in the cross sectional
Fanno Flow Simple frictional flow ( Fanno Flow Adiabatic frictional flow in a constant-area duct * he Flow of a compressible fluid in a duct is Always accompanied by :- ariation in the cross sectional
2013/5/22. ( + ) ( ) = = momentum outflow rate. ( x) FPressure. 9.3 Nozzles. δ q= heat added into the fluid per unit mass
 9.3 Nozzles (b) omentum conservation : (i) Governing Equations Consider: nonadiabatic ternal (body) force ists variable flow area continuously varying flows δq f ternal force per unit volume +d δffdx dx
9.3 Nozzles (b) omentum conservation : (i) Governing Equations Consider: nonadiabatic ternal (body) force ists variable flow area continuously varying flows δq f ternal force per unit volume +d δffdx dx
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams
 Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 20 June 2005
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
