UNCLASSIFIED F/S 28/iS NI
|
|
|
- Gloria Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AD-R POSSIBLE he HRNISMS OF RTOM TRANSFER IN SCANNING / TUNNELING MICROSCOPY(U) CHICAGO UNIV IL JAMES FRANCK INST R GONER JUL 85 N@ C-88:18 UNCLASSIFIED F/S 28/iS NI
2 11111o IL25L 1386 MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART.4 - )ARDS 1963-A 9F
3 SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE r (Men_ Des Entered) REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE COMPLETING FORM. REPORT NUMBER s. GOVT ACCESSION NO. 3- RECIPIENT"S CATALOG NUMBER 4. TITLE (and Subtitle) S. TYPE OF REPORT & PERIOD COVERED Possible Mechanisms of Atom Transfer in Scanning Tunneling Microscopy 6. PERFORMING ORG. REPORT NUMBER 7. AUTHOR(sj S. CONTRACT OR GRANT NUMBER(*) Robert Gomer C /L. S. P[RF9.RI4NG OROANIZATI%4 t4ame AND ADDRESS 10. PROGRAM ELEMENT. PROJECT. TASK te unve y t, 1cago AREA & WORK UNIT NUMBERS The James Franck Institute 5640 South Ellis Avenue, Chicago, Illinois LO II. CONTROLLING OFFICE NAME AND ADDRESS 12. REPORT DATE Office of Naval Research July 1985 Physical Sciences Division (Code 421) is. NUMEROF PAGES 800 N. Quincy St., Arlington, VA MONITORING AGENCY NAME AOORESS(If different l rm Controllifnl Office) IS. SECURITY CLASS. (o1 tihle report) *unclassified I.. DECI. ASSIFICATION/OWNGRADING SCHEDULE >is IS. DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT (of this Report) This document has been approved for public release and sale; its distribution unlimited. 8 DTIC LJ 1. DISTRIBUTION ST, 71 : ENT (o. the abstract ente ed in Stoc.. It dffe., e-n Repet )..... SEP 5 5 F 16. SUPPLEMENTARY ictes Prepared for publication in IBM Journal of Research and Development 19. KEY WORDS (Continue on reverse side It neceee and Identify by block nmber) Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Tunneling Field Desorption Thermal Desorption 20. ABSTRACT (Continue an revere ie if nes) eeaey md identify by block number) Various mechanisms for the sudden transfer of an atom from or to the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope are considered. It is concluded that thermal desorption could be responsible and also that quasi-contact in which the adsorbed atom is in effect '.'touching" both surfaces, which would still be separated from each other by 2-4 A can also.lead to unactivated transfer via tunneling. For barrier widths as small as 0.5 A, however, tunneling becomes negligible. -" FORM unclassified SECURITY CLASSIFICATIO 1 latered) 85 ON1)PAje.
4 Possible Mechanisms of Atom Transfer in Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Robert Gomer Department of Chemistry and James Franck Institute University of Chicago Chicago, Illinois ABSTRACT Various mechanisms for the sudden transfer of an atom from or to the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope are considered. It is concluded that thermal desorption could be responsible and also that quasi-contact in which the adsorbed atom is in effect "touching' both surfaces, which would still be separated from each other by 2-4 A can also lead to unactivated transfer via tunneling. For barrier widths as small as 0.5 A, however, tunneling becomes negligible. Accession por DTIC TAB, Unarnotuneed [ Ju By stif... ica t ion - -' Dist ribution/ i Availability Codes. D'.t I special CO. INN
5 2 Introduction It is reported by various investigators [1] that there are occasional abrupt, usually irreversible, changes in tips and it has been speculated that these result from the transfer of an atom or group of atoms from substrate to tip or vice versa. This note examines various possibilities for such transfers. The mechanisms examined are atom tunneling, thermally activated desorption, and field ionization. 1. Atomic Tunneling When two surfaces are brought into close proximity, there is the possibility that a weakly bound atom on one surface may tunnel to the other. For simplicity we assume a parabolic barrier of height V and half-width 0 x 0. If we take the rate constant for tunneling to be with k t = v exp-2(2m1 2 ) _ v/v(x) - E dx (1) 0 V(x) = V (1-(x/Xo) 2 (2) we find easily that 2 v kt = v to00 exp-(2ma/ ) r V x (3) = v exp-69(mv ) x where M is the mass in a.m.u., V the barrier height in ev and x its half- 0 0 width in A. Let us assume that a jumping event occurs on average once a day so that k = 10 sec. We then find assuming v = sec, that M V = (0.57/x ) (a.m.u.) ev/a 2. If M = 28 a.m.u. corresponding to Si and x = 0.5, so that the actual barrier base width is 1 kv = 0.05 ev For such a small barrier thermally activated transfer would totally dominate and lead to a lifetime of sec. The situation changes dramatically, however, when x = 0.1 A. For such a distance and again for M = 28 a.m.u. o V = 1.1 ev. It should be noted that at such small separations i.e. with the 0 al
6 3 potential curves of the adsorbate on the two surfaces intersecting the barrier height can be much less than the heat of binding H a (Fig. 1). Other assumed barrier shapes, for instance rectangular or triangular do not alter the above conclusions materially. This calculation suggests that tunneling across gaps as small as 1 between the equilibrium atom positions corresponding to adsorption on the two substrates is prohibitively slow, but becomes quite probable when this distance is reduced to x 0.1 A. Since the equilibrium separation of an adsorbed atom from its substrate is 1-2 A the virtual overlap of positions corresponding to adsorption on the two substrates does not mean that the surfaces themselves are "touching", merely that they are both "in contact" with an adsorbed, or otherwise protruding atom. Such situations could arise for instance if the tip is moved over a local asperity. If the effective barrier width becomes < 0.1 A in this process transfer by tunneling can become much more probable than once a day. 2. Thermally _ Activated Desorption We assume that the appropriate rate constant, kd is given by kd = v exp-q/kt (4) -where v is an attempt frequency and Q, the activation energy of desorption is equal, in this case to the binding energy H. Again we assume k 10 - sec - 1 a d 12-1 and find H = I ev if T = 300 K and v = 10 sec. This makes thermal desorption at least a good possibility. There is also, in theory, the possibility of tunneling through a much reduced barrier combined with thermal activation. The considerations of the previous section indicate that this effect must be extremely small for massive adsorbates and can be neglected ** ~ ~ 0~~, ?,,... S. ;e,.,'- *9,,.o,.,.-. *., -. a...., - 4',,'. ---' *... ':.." 9.".% ".., '.' -''..''',''''., '' '.,*
7 4 3. Field Desorption In STM it may happen that the work functions of tip and substrate differ by 1-2 ev, particularly if the tip is dirty tungsten with *=5-6.5 ev while the substrate is a clean semiconductor with 4=4.5 ev. If tip and substrate are electrically connected a contact potential is thus created and if the separation is 1-2 A fields of the order of 1 volt/a can exist at or just in front of the surfaces. It has been shown previously [2) that the intersection of the field deformed ionic and undeformed neutral potential curves for a system M + A, where M is a conducting substrate and A and adsorbed atom is given by 2 Fexc =Ica *+H -Q-e /4x c (5) where F is the applied field, I the ionization potential of A,*the work function of M, H the zero field binding energy, Q the activation energy a 2 of field assisted but thermally activated desorption and e /4x = 3.6/x in ev-a units is an image correction (Fig. 2). Equation 5 holds for singly charged ions, and can of course be modified trivially for higher charges. Let us see if a field of 1 volt/a can decrease the activation energy of * thermal desorption appreciably. We assume I1 4 ev, F = 1 volt/a and a c H -Q a = 0.2 ev. on reaching the other electrode the positive ion A+ formed at xc is *desorption then neutralized so that the entire process is equivalent to transferring A from Mto M via a thermally activated process with an activation energy 1 2 Q < H1. a If A has a high electron affinity and M 1 a low work function, field of a negative ion from M could also occur if F had the opposite sign from that assumed here, i.e. if M Iwere negative with respect to M 2 In that case I -4in Eq. 5 must be replaced by *-Af where Af is the electron affinity of A, i.e. the energy gained in forming A,and the upper
8 W-II 5 curves in Fig. 2 must be relabeled M + A-. Conclusion The foregoing suggests that tunneling across distances < 0.1 A, can occur with reasonably high probability. This can happen for adsorbed or protruding atoms when the bulk of the tip and substrate surfaces are still separated by 2-4 A, depending on the details of the relevant atom-substrate potential curves. Tunneling across larger gaps than A, however, seems prohibitively slow. In addition, thermal desorption, possibly field assisted could also occur. The latter should show a strong temperature dependence, as indicated by Eq. 4 and it might therefore be possible to look for the frequency of atom transfers as function of temperature. Acknowledgments This work was supported in part by ONR Contract N C I have also profited from the Materials Research Laboratory of the National Science Foundation at the University of Chicago. This work was stimulated by the Workshop on Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, organized by H. Rohrer and G. Binning and supported by IBM Europe. It is a pleasure to thank them for the opportunity to attend. 0*. S * *~ A
9 'i 6 _U References 7E] IBM Workshop on Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, Oberlech, Austria, July, [2] R. Gomer, L. W. Swanson, J. Chem. Phys. 38, 1613 (1963); R. Gomer, J. Chem. Phys. 31, 341 (1959). Figure Captions 1) Potential energy diagram for an atom A adsorbed on either of two substrates M and M 2 which are (a) moderately close, (b) so close that the potential curves overlap substantially. x(m 1 -A) separation of atom adsorbed on M from M 1 1 x(m 2 -A) separation of same atom when adsorbed on M42 from M2 surface; x(m 1 - M2) separation of M surface from M 2 surface; -x 0, x 0 end points of tunneling barrier, measured from position of barrier maximum, so that barrier e e width is 2 x. xl, x 2 equilibrium positions of A relative to M and M ' 2) Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism of field desorption of an adsorbed atom A.I, ionization potential of A, O,work function of substrate M, H, aheat of adsorption, Q,activation energy of desorption when a field is applied. (a) neutral (M+A) and ionic (M-+A + ) curves for F = 0. (b) same curves in the presence of an applied field, which deforms the ionic curve, but leaves the neutral curve unchanged, except for polarization effects which have been ignored here. For desorption of negative ions the sign of the field must be reversed and I-0 replaced by 0 - Af where Af is the electron affinity of A. x c is the transition point where A becomes ionized, and is given by solution of Eq. 5. -LA ".6... i;7:l
10 Vo= HV II I -xo ee X (MI -A) II(a) xoi XM -A) 'IV U :-x 0 XOe 1 2 Fig.1
11 M+A+ X (M-A) g \Fex M+A x X (M-A) Fig.2
12 FiLMED DTIC r
SaL1a. fa/ SLECTE '1~AIR FORCE GECOPNYSICS LABORATORY AIR FORCE SYSTEMS COMMAND AFGL-TH
 AD-Alla 950 BOSTON COLL CHESTNUT HILL MA DEPT OF PHYSICS FB2/ '5 PARTICLE TRAJECTORIES IN A MODEL ELECTRIC FIELD II.CU) DEC SI P CARINI. 6 KALMAN, Y SHIMA F19628-79-C-0031 UNCLASSIFIED SCIENTIFIC-2 AFGL-TR-B2-0149
AD-Alla 950 BOSTON COLL CHESTNUT HILL MA DEPT OF PHYSICS FB2/ '5 PARTICLE TRAJECTORIES IN A MODEL ELECTRIC FIELD II.CU) DEC SI P CARINI. 6 KALMAN, Y SHIMA F19628-79-C-0031 UNCLASSIFIED SCIENTIFIC-2 AFGL-TR-B2-0149
A STUDY OF SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES FOR ESTIMATING. J. Carroll* Md Robert Smith. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
 A STUDY OF SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES FOR ESTIMATING THE LARGEST OF THREE NORMAL t4eans Ra~nond by J. Carroll* Md Robert Smith University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill -e Abstract We study the problem of
A STUDY OF SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES FOR ESTIMATING THE LARGEST OF THREE NORMAL t4eans Ra~nond by J. Carroll* Md Robert Smith University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill -e Abstract We study the problem of
FINAL REPORT. Richard H. Clarke Department of Chemistry Boston University. February 25, U.S. Army Research Office DAAG K-0124
 9" f W.-F '..1. SPECTROSCOPIC INVESTIGATIONS OF ORGANIC MOLECULES ON GRAPHITE SURFACES FINAL REPORT CO I Richard H. Clarke Department of Chemistry Boston University February 25, 1986 V- - U.S. Army Research
9" f W.-F '..1. SPECTROSCOPIC INVESTIGATIONS OF ORGANIC MOLECULES ON GRAPHITE SURFACES FINAL REPORT CO I Richard H. Clarke Department of Chemistry Boston University February 25, 1986 V- - U.S. Army Research
, i, ~. '~~~* a F- WI W U V U S S S S S S It
 AD-A194 365 REACTION DYNAMICS ON SEMICONDUCTOR SURFACES(U) h RENSSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST TROY NY DEPT OF MATERIALS ENGINEERING J B HUDSON 29 FEB 86 NOB8e4-86-K-0259 UNCLASSIFIED F/G 7/4 NI @MonossonE ,
AD-A194 365 REACTION DYNAMICS ON SEMICONDUCTOR SURFACES(U) h RENSSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST TROY NY DEPT OF MATERIALS ENGINEERING J B HUDSON 29 FEB 86 NOB8e4-86-K-0259 UNCLASSIFIED F/G 7/4 NI @MonossonE ,
8kb IRT CORP SAN DIEGO CALIF F/S 20/8 MOLECLJt.AR BEAM STUDIES OF LOW ENERGY REACTIONS. (U) OCT 78 B H NEYNABER, S V TANG
 r AD A059 8kb IRT CORP SAN DIEGO CALIF F/S 20/8 MOLECLJt.AR BEAM STUDIES OF LOW ENERGY REACTIONS. (U) OCT 78 B H NEYNABER, S V TANG N0001U 7k C OO11 UNCLASSIFIED IRT 8105 008 NL I END! 9845 I DAtt A1 onc
r AD A059 8kb IRT CORP SAN DIEGO CALIF F/S 20/8 MOLECLJt.AR BEAM STUDIES OF LOW ENERGY REACTIONS. (U) OCT 78 B H NEYNABER, S V TANG N0001U 7k C OO11 UNCLASSIFIED IRT 8105 008 NL I END! 9845 I DAtt A1 onc
=6 RESOLUTION TEST CHART. hi..._ -i
 AD-A090 951 GEORGIA INST OF TECH ATLANTA SCHOOL OF PHYSICS F/G 1/4 THE DRIFT, DIFFUSION, AND REACTIONS OF SLOW IONS IN GASES.(U) FEUl 8G E W MCDANIEL. I R GATLAND NO00IN-76-C-0015 EEEEEE~r UNCLASSIFIED
AD-A090 951 GEORGIA INST OF TECH ATLANTA SCHOOL OF PHYSICS F/G 1/4 THE DRIFT, DIFFUSION, AND REACTIONS OF SLOW IONS IN GASES.(U) FEUl 8G E W MCDANIEL. I R GATLAND NO00IN-76-C-0015 EEEEEE~r UNCLASSIFIED
I I ! MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS-1963-A
 , D-Ri33 816 ENERGETIC ION BERM PLASMA INTERRCTIONS(U) PRINCETON / UNIV N J PLASMA PHYSICS LAB R MI KULSRUD 30 JUN 83 UNCLSSIFEDAFOSR-TR-83-0816 AFOSR-81-0106F/209 N EEEEONEE"_ I I 11111.!2 1.1. IL MICROCOPY
, D-Ri33 816 ENERGETIC ION BERM PLASMA INTERRCTIONS(U) PRINCETON / UNIV N J PLASMA PHYSICS LAB R MI KULSRUD 30 JUN 83 UNCLSSIFEDAFOSR-TR-83-0816 AFOSR-81-0106F/209 N EEEEONEE"_ I I 11111.!2 1.1. IL MICROCOPY
RD-R14i 390 A LIMIT THEOREM ON CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTIONS VIA RN ini EXTREMAL PRINCIPLE(U) TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN CENTER FOR CYBERNETIC STUDIES A BEN-TAL
 RD-R14i 390 A LIMIT THEOREM ON CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTIONS VIA RN ini EXTREMAL PRINCIPLE(U) TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN CENTER FOR CYBERNETIC STUDIES A BEN-TAL DEC 83 CCS-RR-477 UNCLASSIFIED N@884-i-C-236 F/0 2/1
RD-R14i 390 A LIMIT THEOREM ON CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTIONS VIA RN ini EXTREMAL PRINCIPLE(U) TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN CENTER FOR CYBERNETIC STUDIES A BEN-TAL DEC 83 CCS-RR-477 UNCLASSIFIED N@884-i-C-236 F/0 2/1
i of 6. PERFORMING ORG. REPORT NUMBER Approved for public Dtatibuft Unlimited
 SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE (When Data Entered) REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE COMPLETING FORM I. REPORT NUMBER 2. GOVT ACCESSION NO. 3. RECIPIENT'S CATALOG NUMBER WP-MDSGA-65-4
SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE (When Data Entered) REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE COMPLETING FORM I. REPORT NUMBER 2. GOVT ACCESSION NO. 3. RECIPIENT'S CATALOG NUMBER WP-MDSGA-65-4
A0A TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN DEPT OF CHEMISTRY F/G 7/5 PHOTOASSISTED WATER-GAS SHIFT REACTION ON PLATINIZED T7TANIAI T--ETCIUI
 AA113 878 TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN DEPT OF CHEMISTRY F/G 7/5 PHOTOASSISTED WATER-GAS SHIFT REACTION ON PLATINIZED T7TANIAI T--ETCIUI APR 82 S FANG. 8 CHEN..J M WHITE N14-75-C-922 UNCLASSIFIED NL OFFICE OF
AA113 878 TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN DEPT OF CHEMISTRY F/G 7/5 PHOTOASSISTED WATER-GAS SHIFT REACTION ON PLATINIZED T7TANIAI T--ETCIUI APR 82 S FANG. 8 CHEN..J M WHITE N14-75-C-922 UNCLASSIFIED NL OFFICE OF
lm1,1A1Hh"1i AD-A Bloomington, IN SEP Larry L. Kesmodel OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
 AD-A269 342 OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH END-OF-THE-YEAR REPORT PUBLICATIONS/PATENTS/PRESENTATIONS/HONORS/STUDENTS REPORTS for Grant or Contract N00014-89-J-1775 R & T Code 413n002 --- 01 Structure and Reactivity
AD-A269 342 OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH END-OF-THE-YEAR REPORT PUBLICATIONS/PATENTS/PRESENTATIONS/HONORS/STUDENTS REPORTS for Grant or Contract N00014-89-J-1775 R & T Code 413n002 --- 01 Structure and Reactivity
Peak Electric Field. Junction breakdown occurs when the peak electric field in the PN junction reaches a critical value. For the N + P junction,
 Peak Electric Field Junction breakdown occurs when the peak electric field in the P junction reaches a critical value. For the + P junction, qa E ( x) ( xp x), s W dep 2 s ( bi Vr ) 2 s potential barrier
Peak Electric Field Junction breakdown occurs when the peak electric field in the P junction reaches a critical value. For the + P junction, qa E ( x) ( xp x), s W dep 2 s ( bi Vr ) 2 s potential barrier
DISTRIBUTION A: Distribution approved for public release.
 AFRL-OSR-VA-TR-2013-0317 VACANCY TRANSPORT AND INTERACTIONS ON METAL SURFACES Gert Ehrlich UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS CHAMPAIGN 03/06/2014 Final Report DISTRIBUTION A: Distribution approved for public release.
AFRL-OSR-VA-TR-2013-0317 VACANCY TRANSPORT AND INTERACTIONS ON METAL SURFACES Gert Ehrlich UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS CHAMPAIGN 03/06/2014 Final Report DISTRIBUTION A: Distribution approved for public release.
1.0~ O. 1*1.8.2IIII II5 uuu11~ I 1 I6 MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS 1963-A
 6AD-Ai5@ 148 NUMERICAL ALGORITHMS AND SOFTWARE FOR MATRIX.RICCATI i/i EGUATIONS(U) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA LOS ANGELES A J LAUB 25 OCT 84 RlRO-i8289 15-MAl UNCLASSIFIED MEOMONEE OAAG29-i-K-8i3i
6AD-Ai5@ 148 NUMERICAL ALGORITHMS AND SOFTWARE FOR MATRIX.RICCATI i/i EGUATIONS(U) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA LOS ANGELES A J LAUB 25 OCT 84 RlRO-i8289 15-MAl UNCLASSIFIED MEOMONEE OAAG29-i-K-8i3i
.IEEEEEEIIEII. fflllffo. I ll, 7 AO-AO CALIFORNIA UN IV BERKELEY OPERATIONS RESEARCH CENTER FIG 12/1
 7 AO-AO95 140 CALIFORNIA UN IV BERKELEY OPERATIONS RESEARCH CENTER FIG 12/1.IEEEEEEIIEII AVAILABILITY OF SERIES SYSTEMS WITH COMPONENTS SUBJECT TO VARIO--ETC(U) JUN 80 Z S KHALIL AFOSR-77-3179 UNCLASSIFIED
7 AO-AO95 140 CALIFORNIA UN IV BERKELEY OPERATIONS RESEARCH CENTER FIG 12/1.IEEEEEEIIEII AVAILABILITY OF SERIES SYSTEMS WITH COMPONENTS SUBJECT TO VARIO--ETC(U) JUN 80 Z S KHALIL AFOSR-77-3179 UNCLASSIFIED
EEEJ AA CHICAGO UNIV ILL DEPT OF CHEMISTRY F/6 7/4 ION-ION NEUTRALIZATION PROCESSES AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES. (U)
 AA099 05 CHICAGO UNIV ILL DEPT OF CHEMISTRY F/6 7/4 ION-ION NEUTRALIZATION PROCESSES AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES. (U) EEEJ MA Y 81 R S BERRY DAAG29RO0-K-0016 UNCLASSIFIED 880 169451C NL UNCLASS!FIED, SECUI4ITY
AA099 05 CHICAGO UNIV ILL DEPT OF CHEMISTRY F/6 7/4 ION-ION NEUTRALIZATION PROCESSES AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES. (U) EEEJ MA Y 81 R S BERRY DAAG29RO0-K-0016 UNCLASSIFIED 880 169451C NL UNCLASS!FIED, SECUI4ITY
11111 I(25_L MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART NA11ONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS-1963 A
 AD-A130 564 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR SENSITV OF DIPOLAR MOLECULES U) UTAH UNIV SALTLAKE CITY DEPT OF BIOENGINEERING Il G FBLACKBURNET AL 30JUN 83 TR-2NUO4-8-K-066 UNCLASSIFED 0/G9/1 EhEEDhI 8H83 E 11111
AD-A130 564 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR SENSITV OF DIPOLAR MOLECULES U) UTAH UNIV SALTLAKE CITY DEPT OF BIOENGINEERING Il G FBLACKBURNET AL 30JUN 83 TR-2NUO4-8-K-066 UNCLASSIFED 0/G9/1 EhEEDhI 8H83 E 11111
AD-A ROCHESTER UNIV NY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT F/B 12/1. j FEB 82.J KEILSON F C-0003 UNCLASSIFIED AFGL-TR NL
 AD-A115 793 ROCHESTER UNIV NY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT F/B 12/1 F EFFORTS IN MARKOV MODELING OF WEATHER DURATIONS.(U) j FEB 82.J KEILSON F1962980-C-0003 UNCLASSIFIED AFGL-TR-82-0074 NL A'FGL -TR-82-0074
AD-A115 793 ROCHESTER UNIV NY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT F/B 12/1 F EFFORTS IN MARKOV MODELING OF WEATHER DURATIONS.(U) j FEB 82.J KEILSON F1962980-C-0003 UNCLASSIFIED AFGL-TR-82-0074 NL A'FGL -TR-82-0074
0') Chicago, Illinois 60637, K 0- J Office of Naval Research,...81
 AD-A096 910 CHICAGO UNIV IL JAMES FRANCK INST F A 7/4 ELECTRON IMPACT OESORPTION OF XE FROM THE TUNGSTEN 110) PLANE *U MAR A1 A ZHANG, R GOMER NOOO -077-C-ORIA UNC AiTAFTFn 6 W MEEhLEEElEE *ffll SICURITY
AD-A096 910 CHICAGO UNIV IL JAMES FRANCK INST F A 7/4 ELECTRON IMPACT OESORPTION OF XE FROM THE TUNGSTEN 110) PLANE *U MAR A1 A ZHANG, R GOMER NOOO -077-C-ORIA UNC AiTAFTFn 6 W MEEhLEEElEE *ffll SICURITY
REGENERATION OF SPENT ADSORBENTS USING ADVANCED OXIDATION (PREPRINT)
 AL/EQ-TP-1993-0307 REGENERATION OF SPENT ADSORBENTS USING ADVANCED OXIDATION (PREPRINT) John T. Mourand, John C. Crittenden, David W. Hand, David L. Perram, Sawang Notthakun Department of Chemical Engineering
AL/EQ-TP-1993-0307 REGENERATION OF SPENT ADSORBENTS USING ADVANCED OXIDATION (PREPRINT) John T. Mourand, John C. Crittenden, David W. Hand, David L. Perram, Sawang Notthakun Department of Chemical Engineering
Ln800 North Quincy Street IS. NUMBER11 OF PAGIES
 ISCURITY CL.ASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE (Whon Does An 084 REPOT DOUMENATIO PAG REPOT DCUMNTATON AGE39yolt READ ISTRUC'IOms COMPLEIMG FORM 1. RPOR NumaftL GOVT ACCESSION NO.3 RECIPIENT'S CATALOG NUMBERA C.
ISCURITY CL.ASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE (Whon Does An 084 REPOT DOUMENATIO PAG REPOT DCUMNTATON AGE39yolt READ ISTRUC'IOms COMPLEIMG FORM 1. RPOR NumaftL GOVT ACCESSION NO.3 RECIPIENT'S CATALOG NUMBERA C.
U-.-._ AD-A TWO STOCHASTIC MODE.ING PROBLEMS IN COMMUJNICATIONS AND NAVIG6ATON I/J U) VIRGINIA P0 TECHNIC INS A ND STE BLACKSBURG UNIV
 AD-A133 458 TWO STOCHASTIC MODE.ING PROBLEMS IN COMMUJNICATIONS AND NAVIG6ATON I/J U) VIRGINIA P0 TECHNIC INS A ND STE BLACKSBURG UNIV U-.-._ W E KO06 ER 12 SEP 83 ARO 16539.6-MA UNCLASSIFED DAAG2V V -C
AD-A133 458 TWO STOCHASTIC MODE.ING PROBLEMS IN COMMUJNICATIONS AND NAVIG6ATON I/J U) VIRGINIA P0 TECHNIC INS A ND STE BLACKSBURG UNIV U-.-._ W E KO06 ER 12 SEP 83 ARO 16539.6-MA UNCLASSIFED DAAG2V V -C
A7A INTERIMREPORT GRANT AFOSR AU)NORHCAROLNA / UNIV AT CHARLO0TE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS M ABDEL-HAMEED AN S DAUG 83 AFOSR-TN 83 AN N
 A7A35 620 INTERIMREPORT GRANT AFOSR80-0245AU)NORHCAROLNA / UNIV AT CHARLO0TE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS M ABDEL-HAMEED AN S DAUG 83 AFOSR-TN 83 AN N AFOSR-80-0245 1.0 12 III 12. 1 5III 1 11.4 il1.6 MICROCOPY
A7A35 620 INTERIMREPORT GRANT AFOSR80-0245AU)NORHCAROLNA / UNIV AT CHARLO0TE DEPT OF MATHEMATICS M ABDEL-HAMEED AN S DAUG 83 AFOSR-TN 83 AN N AFOSR-80-0245 1.0 12 III 12. 1 5III 1 11.4 il1.6 MICROCOPY
OF NAVAL RESEARCH. Technical Report No. 87. Prepared for Publication. in the.. v.. il and/or -- c Spocial Journal of Elactroanalytical Chemistry it
 ,~OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH Contract N00014-86-K-0556 Technical Report No. 87. Th., Combined Influence of Solution Resistance and Charge-Transfer Kinetics on Microelectrode Cyclic Voltammetry oo i Acee'ic
,~OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH Contract N00014-86-K-0556 Technical Report No. 87. Th., Combined Influence of Solution Resistance and Charge-Transfer Kinetics on Microelectrode Cyclic Voltammetry oo i Acee'ic
HIGH RESOLUTION ION KINETIC ENERGY ANALYSIS OF FIELD EMITTED IONS
 HIGH RESOLUTION ION KINETIC ENERGY ANALYSIS OF FIELD EMITTED IONS J. Liu, T. Tsong To cite this version: J. Liu, T. Tsong. HIGH RESOLUTION ION KINETIC ENERGY ANALYSIS OF FIELD EMITTED IONS. Journal de
HIGH RESOLUTION ION KINETIC ENERGY ANALYSIS OF FIELD EMITTED IONS J. Liu, T. Tsong To cite this version: J. Liu, T. Tsong. HIGH RESOLUTION ION KINETIC ENERGY ANALYSIS OF FIELD EMITTED IONS. Journal de
STM spectroscopy (STS)
 STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
1SEP 01 J S LANGER AFOSR
 AD-A113 871 CARNEGIE-MELLON UNIV PITTSBURGH PA DEPT OF PHYSICS PG2/ I PH4ASE TRANSFORMATIONS AND NONEQUILIBRIUM INTERFACES.CW) 1SEP 01 J S LANGER AFOSR-80-0034 UNCLASSIFIED AFOSR-TR-82-0307 NI. Unclassified
AD-A113 871 CARNEGIE-MELLON UNIV PITTSBURGH PA DEPT OF PHYSICS PG2/ I PH4ASE TRANSFORMATIONS AND NONEQUILIBRIUM INTERFACES.CW) 1SEP 01 J S LANGER AFOSR-80-0034 UNCLASSIFIED AFOSR-TR-82-0307 NI. Unclassified
IW IIIIL2 5-_6. -, ~IIIl IIII'nll MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART NAI IONAL BUIREAU O( STANDARDS 1963 A
 -R177 486 EXTREME VALUES OF QUEUES POINT PROCESSES AND STOCHASTIC I/i WETUORKSCU) GEORGIA INST OF TECH ATLANTA SCHOOL OF INDUSTRIAL AND SYSTEMS ENGINEERING R F SERFOZO 7UNCLASSIFIED 39 NOV 86 IEEE'.'.
-R177 486 EXTREME VALUES OF QUEUES POINT PROCESSES AND STOCHASTIC I/i WETUORKSCU) GEORGIA INST OF TECH ATLANTA SCHOOL OF INDUSTRIAL AND SYSTEMS ENGINEERING R F SERFOZO 7UNCLASSIFIED 39 NOV 86 IEEE'.'.
MICROCOPY RESOLUIION IESI CHARI. NAMfNA[ IC~ ANtn
 A0-A107 459 NEW YORK( UNIV NY COURANT INST OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE-S F/6 20/11 RESEARCH IN C ONTI NUUM MECANICS- C-30 SIIDNOV 81 F JOHN N5001V76C-130NL CHNCS( UNLASIIE 14"' '2."8 MICROCOPY RESOLUIION IESI
A0-A107 459 NEW YORK( UNIV NY COURANT INST OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE-S F/6 20/11 RESEARCH IN C ONTI NUUM MECANICS- C-30 SIIDNOV 81 F JOHN N5001V76C-130NL CHNCS( UNLASIIE 14"' '2."8 MICROCOPY RESOLUIION IESI
Bonds and Wavefunctions. Module α-1: Visualizing Electron Wavefunctions Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Instructor: Silvija Gradečak
 3.014 Materials Laboratory December 8 th 13 th, 2006 Lab week 4 Bonds and Wavefunctions Module α-1: Visualizing Electron Wavefunctions Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Instructor: Silvija Gradečak OBJECTIVES
3.014 Materials Laboratory December 8 th 13 th, 2006 Lab week 4 Bonds and Wavefunctions Module α-1: Visualizing Electron Wavefunctions Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Instructor: Silvija Gradečak OBJECTIVES
The ability of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM) to record real-space, atomicscale
 EXPERIMENTAL AND SIMULATED SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPY OF THE CLEAVED Rb 1 / 3 WO 3 (0001) SURFACE WEIER LU AND GREGORY S. ROHRER Carnegie Mellon University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
EXPERIMENTAL AND SIMULATED SCANNING TUNNELING MICROSCOPY OF THE CLEAVED Rb 1 / 3 WO 3 (0001) SURFACE WEIER LU AND GREGORY S. ROHRER Carnegie Mellon University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
APPLICATIONS OF QUANTUM FIELD THEORY TO ATOMIC COLLISIONS AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS(U) OREON UNIV EUGENE M D GIRARDEAU APR 83 QFT-2 NOOD 4-81-K 0759
 AD A129 236 APPLICATIONS OF QUANTUM FIELD THEORY TO ATOMIC COLLISIONS AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS(U) OREON UNIV EUGENE M D GIRARDEAU APR 83 QFT-2 NOOD 4-81-K 0759 *EEEEEEEIN UNCLASSIFIED F/G20/10 NL 1.0 W32
AD A129 236 APPLICATIONS OF QUANTUM FIELD THEORY TO ATOMIC COLLISIONS AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS(U) OREON UNIV EUGENE M D GIRARDEAU APR 83 QFT-2 NOOD 4-81-K 0759 *EEEEEEEIN UNCLASSIFIED F/G20/10 NL 1.0 W32
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 Public Reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 Public Reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
IUNCLSSIME N E F/G 11?2 NL
 AD-RI58 658 BORON-NITROGEN POLYNERS(U) ULTRASYSTENS INC IRVINE CA III 1 K L PACIOREK ET AL. 01 JUL 85 SN-2822-F NS9914-82-C-9482 IUNCLSSIME N E F/G 11?2 NL 1.0 16 2.: w1111342 1.8 11111125 1111.4 L MICROCOPY
AD-RI58 658 BORON-NITROGEN POLYNERS(U) ULTRASYSTENS INC IRVINE CA III 1 K L PACIOREK ET AL. 01 JUL 85 SN-2822-F NS9914-82-C-9482 IUNCLSSIME N E F/G 11?2 NL 1.0 16 2.: w1111342 1.8 11111125 1111.4 L MICROCOPY
;E (" DataEntered,) 1.GOVT ACCESSION NO.
 ;E (" DataEntered,) AD-A 196 504:NTATION PAGE 1.GOVT ACCESSION NO. fitic f ILE GUM. BEFORCOMLETINFOR 3. RECIPIENT'S CATALOG NUMBER ALGO PUB 0120 4. TITLE (and Subtitle) S. TYPE OF REPORT & PERIOD COVERED
;E (" DataEntered,) AD-A 196 504:NTATION PAGE 1.GOVT ACCESSION NO. fitic f ILE GUM. BEFORCOMLETINFOR 3. RECIPIENT'S CATALOG NUMBER ALGO PUB 0120 4. TITLE (and Subtitle) S. TYPE OF REPORT & PERIOD COVERED
Report Documentation Page
 Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
A report (dated September 20, 2011) on. scientific research carried out under Grant: FA
 A report (dated September 20, 2011) on scientific research carried out under Grant: FA2386-10-1-4150 First-principles determination of thermal properties in nano-structured hexagonal solids with doping
A report (dated September 20, 2011) on scientific research carried out under Grant: FA2386-10-1-4150 First-principles determination of thermal properties in nano-structured hexagonal solids with doping
SYSTEMS OPTIMIZATION LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH STANFORD UNIVERSITY STANFORD, CALIFORNIA
 SYSTEMS OPTIMIZATION LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH STANFORD UNIVERSITY STANFORD, CALIFORNIA 94305-4022 00 0 NIN DTIC A Monotone Complementarity Problem in Hilbert Space by Jen-Chih Yao fl
SYSTEMS OPTIMIZATION LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH STANFORD UNIVERSITY STANFORD, CALIFORNIA 94305-4022 00 0 NIN DTIC A Monotone Complementarity Problem in Hilbert Space by Jen-Chih Yao fl
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. how does STM work? the quantum mechanical picture example of images how can we understand what we see?
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy how does STM work? the quantum mechanical picture example of images how can we understand what we see? Observation of adatom diffusion with a field ion microscope Scanning
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy how does STM work? the quantum mechanical picture example of images how can we understand what we see? Observation of adatom diffusion with a field ion microscope Scanning
Surface Physics Surface Diffusion. Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science
 Surface Physics 008 8. Surface Diffusion Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science Random-Walk Motion Thermal motion of an adatom on an ideal crystal surface: - Thermal excitation the adatom
Surface Physics 008 8. Surface Diffusion Assistant: Dr. Enrico Gnecco NCCR Nanoscale Science Random-Walk Motion Thermal motion of an adatom on an ideal crystal surface: - Thermal excitation the adatom
UNCLASSIFIED U. OF ZOWA81-2 ML.
 AD-AO9 626 IONA WNI IONA CITY DEPT OF PH4YSICS AND ASTRONOMY F/6 17/7 AN ANALYTICAL. SOLUTION OF THE TWO STAR SIGHT PROBLEM OF CELESTI-ETC(Ul FEB 81.J A VAN ALLEN N00014-76-C-OO16 UNCLASSIFIED U. OF ZOWA81-2
AD-AO9 626 IONA WNI IONA CITY DEPT OF PH4YSICS AND ASTRONOMY F/6 17/7 AN ANALYTICAL. SOLUTION OF THE TWO STAR SIGHT PROBLEM OF CELESTI-ETC(Ul FEB 81.J A VAN ALLEN N00014-76-C-OO16 UNCLASSIFIED U. OF ZOWA81-2
RATES(U) CALIFORNIA UNIV DAVIS W G HOOVER 91 MAR 85 =AD-RI53491 CONFORNTIONAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AT HIGH STRAIN II
 =AD-RI53491 CONFORNTIONAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AT HIGH STRAIN II RATES(U) CALIFORNIA UNIV DAVIS W G HOOVER 91 MAR 85 ASFEDM RO-i86iI. 7-EG DRR029-82-K-0022 UNCLASSIFE O O E FIG 28/4 NL 1.0 t--- --
=AD-RI53491 CONFORNTIONAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AT HIGH STRAIN II RATES(U) CALIFORNIA UNIV DAVIS W G HOOVER 91 MAR 85 ASFEDM RO-i86iI. 7-EG DRR029-82-K-0022 UNCLASSIFE O O E FIG 28/4 NL 1.0 t--- --
N _IC.25 N/PS. Bill~ 11 2 WA' ,' mm_
 AD-RIi 946 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH ON OPTOGALVANIC EFFECTS(U) 1/1 WISCONSIN UNIV-MADISON DEPT OF PHYSICS J E LAWLER 85 JUN 86 AFOSR-RR-86-8518 AFOSR-84-2298 UNCLASS IF [ED F/G 14/2 NL IEEEII. N-8 N/PS 11111_IC.25
AD-RIi 946 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH ON OPTOGALVANIC EFFECTS(U) 1/1 WISCONSIN UNIV-MADISON DEPT OF PHYSICS J E LAWLER 85 JUN 86 AFOSR-RR-86-8518 AFOSR-84-2298 UNCLASS IF [ED F/G 14/2 NL IEEEII. N-8 N/PS 11111_IC.25
Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid
 Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid Contents Density of states. DOS in a 3D uniform solid.................... 3.2 DOS for a 2D solid........................ 4.3 DOS for a D solid........................
Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid Contents Density of states. DOS in a 3D uniform solid.................... 3.2 DOS for a 2D solid........................ 4.3 DOS for a D solid........................
Mine Burial Studies with a Large Oscillating Water-Sediment Tunnel (LOWST)
 Mine Burial Studies with a Large Oscillating Water-Sediment Tunnel (LOWST) Marcelo H. Garcia Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 205 North Mathews
Mine Burial Studies with a Large Oscillating Water-Sediment Tunnel (LOWST) Marcelo H. Garcia Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 205 North Mathews
Design for Lifecycle Cost using Time-Dependent Reliability
 Design for Lifecycle Cost using Time-Dependent Reliability Amandeep Singh Zissimos P. Mourelatos Jing Li Mechanical Engineering Department Oakland University Rochester, MI 48309, USA : Distribution Statement
Design for Lifecycle Cost using Time-Dependent Reliability Amandeep Singh Zissimos P. Mourelatos Jing Li Mechanical Engineering Department Oakland University Rochester, MI 48309, USA : Distribution Statement
In order to determine the energy level alignment of the interface between cobalt and
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Energy level alignment of the CuPc/Co interface In order to determine the energy level alignment of the interface between cobalt and CuPc, we have performed one-photon photoemission
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Energy level alignment of the CuPc/Co interface In order to determine the energy level alignment of the interface between cobalt and CuPc, we have performed one-photon photoemission
M:FE. ULh N 90 M UV-LRSER REARCT IONS OF MOLECU.M ASSOATES(U) MRSNOIUTTS INST OF TECH LEX INGTON LINCOLN LAS ML 2? DEC 97 RAO-21?69.
 N 90 M UV-LRSER REARCT IONS OF MOLECU.M ASSOATES(U) v M:FE MRSNOIUTTS INST OF TECH LEX INGTON LINCOLN LAS M I 0JE.INET LhH ML 2? DEC 97 RAO-21?69. 6-PH ULh IU~lMSjIEO KPR-mRO-l31-G6 F/O?/5 M 1-0 1 1*18
N 90 M UV-LRSER REARCT IONS OF MOLECU.M ASSOATES(U) v M:FE MRSNOIUTTS INST OF TECH LEX INGTON LINCOLN LAS M I 0JE.INET LhH ML 2? DEC 97 RAO-21?69. 6-PH ULh IU~lMSjIEO KPR-mRO-l31-G6 F/O?/5 M 1-0 1 1*18
Concepts in Surface Physics
 M.-C. Desjonqueres D. Spanjaard Concepts in Surface Physics Second Edition With 257 Figures Springer 1. Introduction................................. 1 2. Thermodynamical and Statistical Properties of
M.-C. Desjonqueres D. Spanjaard Concepts in Surface Physics Second Edition With 257 Figures Springer 1. Introduction................................. 1 2. Thermodynamical and Statistical Properties of
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates
 Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
MODELING SOLAR UV/EUV IRRADIANCE AND IONOSPHERE VARIATIONS WITH MT. WILSON MAGNETIC INDICIES
 1 MODELING SOLAR UV/EUV IRRADIANCE AND IONOSPHERE VARIATIONS WITH MT. WILSON MAGNETIC INDICIES Roger K. Ulrich Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California at Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA
1 MODELING SOLAR UV/EUV IRRADIANCE AND IONOSPHERE VARIATIONS WITH MT. WILSON MAGNETIC INDICIES Roger K. Ulrich Department of Physics and Astronomy University of California at Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA
Spectroscopy at nanometer scale
 Spectroscopy at nanometer scale 1. Physics of the spectroscopies 2. Spectroscopies for the bulk materials 3. Experimental setups for the spectroscopies 4. Physics and Chemistry of nanomaterials Various
Spectroscopy at nanometer scale 1. Physics of the spectroscopies 2. Spectroscopies for the bulk materials 3. Experimental setups for the spectroscopies 4. Physics and Chemistry of nanomaterials Various
Knü. ADOAOll 835 ON PACKING SQUARES WITH EQUAL SQUARES. P. Erdos, et al. Stanford University. Prepared for:
 ADOAOll 835 ON PACKING SQUARES WITH EQUAL SQUARES P. Erdos, et al Stanford University Prepared for: National Science Foundation Office of Naval Research March 1975 DISTRIBUTED BY: Knü National Technical
ADOAOll 835 ON PACKING SQUARES WITH EQUAL SQUARES P. Erdos, et al Stanford University Prepared for: National Science Foundation Office of Naval Research March 1975 DISTRIBUTED BY: Knü National Technical
I 6. *1 C1.mI~e c ~...y'.~oe ~oai uliu~a W t ý. DTE 1994OR Technical 6/93-5/ University of Oregon ONR Technical Report Eugene, OR #12
 AD-A279 445 I 6 *1 C1.mI~e c ~...y'.~oe ~oai uliu~a W t ý l s Iw see~em b~utn.cup e ftm.a of~~ ea'hioflw aft to 4ovsq4too.wauvam.h-d ckk~mw. swi Wei Ilebl* O 0 I t. Q I A. 600~e to. 011"o-ol 0 ia.qa eag
AD-A279 445 I 6 *1 C1.mI~e c ~...y'.~oe ~oai uliu~a W t ý l s Iw see~em b~utn.cup e ftm.a of~~ ea'hioflw aft to 4ovsq4too.wauvam.h-d ckk~mw. swi Wei Ilebl* O 0 I t. Q I A. 600~e to. 011"o-ol 0 ia.qa eag
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 Public Reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 Public Reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Eu... p UNCLASSIFIED ARO-i72672-EG DAAO2-8-C-i42 F/G 21/2 NL. D-A INVESTIGATION OF THE KINETICS OF CATALYZED COMBUSTION i/i
 I D-A142 153 INVESTIGATION OF THE KINETICS OF CATALYZED COMBUSTION i/i OF FUEL(U) UNITED TECHNOLOGIES RESEARCH CENTER EAST I HARTFORD CT P J IARTENEY 04 MAY 84 UTRC/955279-i p UNCLASSIFIED ARO-i72672-EG
I D-A142 153 INVESTIGATION OF THE KINETICS OF CATALYZED COMBUSTION i/i OF FUEL(U) UNITED TECHNOLOGIES RESEARCH CENTER EAST I HARTFORD CT P J IARTENEY 04 MAY 84 UTRC/955279-i p UNCLASSIFIED ARO-i72672-EG
Volume 6 Water Surface Profiles
 A United States Contribution to the International Hydrological Decade HEC-IHD-0600 Hydrologic Engineering Methods For Water Resources Development Volume 6 Water Surface Profiles July 1975 Approved for
A United States Contribution to the International Hydrological Decade HEC-IHD-0600 Hydrologic Engineering Methods For Water Resources Development Volume 6 Water Surface Profiles July 1975 Approved for
Reverse Ion Acceleration by Laser-Matter Interaction
 Reverse Ion Acceleration by Laser-Matter Interaction Peter Messmer*, Peter H. Stoltz, Chet Nieter Tech-X Corporation, Boulder, CO 80303 Jean-Luc Cambier AFRL/PRSA, Edwards AFB, CA 93524 * messmer@txcorp.com
Reverse Ion Acceleration by Laser-Matter Interaction Peter Messmer*, Peter H. Stoltz, Chet Nieter Tech-X Corporation, Boulder, CO 80303 Jean-Luc Cambier AFRL/PRSA, Edwards AFB, CA 93524 * messmer@txcorp.com
2) Atom manipulation. Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment:
 2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
A -.GO63 CHICAGO UNIV IL JAMES FRANCK INST F/G 7/4 ADSORPTIONOOF OXYEN ON THE TUNGSTEN (110) PLANE AT LOW TEMPERA ETC(U) OCT G0 R OPILA, R GOMER
 A -.GO63 CHICAGO UNIV IL JAMES FRANCK INST F/G 7/4 ADSORPTIONOOF OXYEN ON THE TUNGSTEN (110) PLANE AT LOW TEMPERA ETC(U) OCT G0 R OPILA, R GOMER NOGO001477- C Ole UNCLSSIFIEDEOR-4 NL SMWPRITY CLASSIFICATION
A -.GO63 CHICAGO UNIV IL JAMES FRANCK INST F/G 7/4 ADSORPTIONOOF OXYEN ON THE TUNGSTEN (110) PLANE AT LOW TEMPERA ETC(U) OCT G0 R OPILA, R GOMER NOGO001477- C Ole UNCLSSIFIEDEOR-4 NL SMWPRITY CLASSIFICATION
UNCLASSIFIED F/G 9/2 NL
 AfD-fli44 356 REHOSTING THE THEOREM PROVER(U) TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN i/i INST FOR COMPUTING SCIENCE AND COMPUTER APPLICATIONS R S BOYER ET AL. 13 JUL 84 N00014-8i-K-0634 UNCLASSIFIED F/G 9/2 NL lm J& 6 I
AfD-fli44 356 REHOSTING THE THEOREM PROVER(U) TEXAS UNIV AT AUSTIN i/i INST FOR COMPUTING SCIENCE AND COMPUTER APPLICATIONS R S BOYER ET AL. 13 JUL 84 N00014-8i-K-0634 UNCLASSIFIED F/G 9/2 NL lm J& 6 I
Quantitation and Ratio Determination of Uranium Isotopes in Water and Soil Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
 Quantitation and Ratio Determination of Uranium Isotopes in Water and Soil Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) D.N. Kurk, T.E. Beegle, S.C. Spence and R.J. Swatski Report Documentation
Quantitation and Ratio Determination of Uranium Isotopes in Water and Soil Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) D.N. Kurk, T.E. Beegle, S.C. Spence and R.J. Swatski Report Documentation
Dynamics of Transport and Variability in the Denmark Strait Overflow
 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Dynamics of Transport and Variability in the Denmark Strait Overflow by James B. Girton Technical Report APL-UW TR 0103 August 2001 Applied Physics
Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Dynamics of Transport and Variability in the Denmark Strait Overflow by James B. Girton Technical Report APL-UW TR 0103 August 2001 Applied Physics
Catalytic Oxidation of CW Agents Using H O in 2 2 Ionic Liquids
 Catalytic Oxidation of CW Agents Using H O in 2 2 Ionic Liquids William M. Nelson,, PhD IL Waste Management & Research Center 2003 Joint Service Scientific Conference on Chemical & Biological Defense Research
Catalytic Oxidation of CW Agents Using H O in 2 2 Ionic Liquids William M. Nelson,, PhD IL Waste Management & Research Center 2003 Joint Service Scientific Conference on Chemical & Biological Defense Research
V BI. H. Föll: kiel.de/matwis/amat/semi_en/kap_2/backbone/r2_2_4.html. different electrochemical potentials (i.e.
 Consider the the band diagram for a homojunction, formed when two bits of the same type of semicondutor (e.g. Si) are doped p and ntype and then brought into contact. Electrons in the two bits have different
Consider the the band diagram for a homojunction, formed when two bits of the same type of semicondutor (e.g. Si) are doped p and ntype and then brought into contact. Electrons in the two bits have different
EEEE~hEEI ISEP 78 E L REISS NO0O14-76.C-0010 AO-A NEW YORK UNIV NYTECOURANT INST OF NATNENATICAI. SCIENCES F/6 20/1
 k I AO-A092 062 NEW YORK UNIV NYTECOURANT INST OF NATNENATICAI. SCIENCES F/6 20/1 PROPAGATION, SCTTERING, AND REFLECTION OF WAVES IN CONTINUOUS -- ETCCU) ISEP 78 E L REISS NO0O14-76.C-0010 UNCLASSIFIlED
k I AO-A092 062 NEW YORK UNIV NYTECOURANT INST OF NATNENATICAI. SCIENCES F/6 20/1 PROPAGATION, SCTTERING, AND REFLECTION OF WAVES IN CONTINUOUS -- ETCCU) ISEP 78 E L REISS NO0O14-76.C-0010 UNCLASSIFIlED
AD-A FATION PAGE cmb No SUPPLEMENTARY NOTESlIII lllll II ili JUN PRICE CODE
 Form Approved AD-A252 270 FATION PAGE cmb No. 0704-0188 ge I~ uour oer resorse. including tile time for reviewing instructions. searchng existing cata sourcf-.. 'r, P 'llecicon o0 of information Send Commintsr
Form Approved AD-A252 270 FATION PAGE cmb No. 0704-0188 ge I~ uour oer resorse. including tile time for reviewing instructions. searchng existing cata sourcf-.. 'r, P 'llecicon o0 of information Send Commintsr
THE CLOSENES S OFYUNIFORM4 RANDOM POINTS IN A SQUAREDAND A CIRCE E ETC U) FEB Al 0 J DALEY
 ADA095 697 NORTH CAROLINA UNIV AT CHAPEL HILL INST OF STATISTICS F/S 12/1 THE CLOSENES S OFYUNIFORM4 RANDOM POINTS IN A SQUAREDAND A CIRCE E ETC U) FEB Al 0 J DALEY NOO N 75-C-0809 UNCLASSIFIED MIRED SER-1327
ADA095 697 NORTH CAROLINA UNIV AT CHAPEL HILL INST OF STATISTICS F/S 12/1 THE CLOSENES S OFYUNIFORM4 RANDOM POINTS IN A SQUAREDAND A CIRCE E ETC U) FEB Al 0 J DALEY NOO N 75-C-0809 UNCLASSIFIED MIRED SER-1327
Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Quantum Theory: Techniques and Applications (Part II)
 Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Quantum Theory: Techniques and Applications (Part II) The Particle in the Box and the Real World, Phys. Chem. nd Ed. T. Engel, P. Reid (Ch.16) Objectives Importance of the concept for
Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Quantum Theory: Techniques and Applications (Part II) The Particle in the Box and the Real World, Phys. Chem. nd Ed. T. Engel, P. Reid (Ch.16) Objectives Importance of the concept for
Hurricane Wave Topography and Directional Wave Spectra in Near Real-Time
 Hurricane Wave Topography and Directional Wave Spectra in Near Real-Time Edward J. Walsh NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Code 972 Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, VA 23337 phone: (303) 497-6357
Hurricane Wave Topography and Directional Wave Spectra in Near Real-Time Edward J. Walsh NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Code 972 Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, VA 23337 phone: (303) 497-6357
PIPS 3.0. Pamela G. Posey NRL Code 7322 Stennis Space Center, MS Phone: Fax:
 PIPS 3.0 Ruth H. Preller Naval Research Laboratory, Code 7322 Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 phone: (228) 688-5444 fax: (228)688-4759 email: preller@nrlssc.navy.mil Pamela G. Posey NRL Code 7322 Stennis
PIPS 3.0 Ruth H. Preller Naval Research Laboratory, Code 7322 Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 phone: (228) 688-5444 fax: (228)688-4759 email: preller@nrlssc.navy.mil Pamela G. Posey NRL Code 7322 Stennis
STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope
 STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Basic idea STM working principle Schematic representation of the sample-tip tunnel barrier Assume tip and sample described by two infinite plate electrodes Φ t +Φ s =
STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope Basic idea STM working principle Schematic representation of the sample-tip tunnel barrier Assume tip and sample described by two infinite plate electrodes Φ t +Φ s =
THE OBSERVED HAZARD AND MULTICONPONENT SYSTEMS. (U) JAN 80 M BROWN- S M R OSS N0001R77-C I~OREE80-1 he UNCLASSIFIED CA-
 THE OBSERVED HAZARD AND MULTICONPONENT SYSTEMS. (U) JAN 80 M BROWN- S M R OSS N0001R77-C-0299 I~OREE80-1 he UNCLASSIFIED CA- Hf - 3I 2~? IRO.25 1UONT. 11111.8 MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART (Q ORC 80-1
THE OBSERVED HAZARD AND MULTICONPONENT SYSTEMS. (U) JAN 80 M BROWN- S M R OSS N0001R77-C-0299 I~OREE80-1 he UNCLASSIFIED CA- Hf - 3I 2~? IRO.25 1UONT. 11111.8 MICROCOPY RESOLUTION TEST CHART (Q ORC 80-1
collisions of electrons. In semiconductor, in certain temperature ranges the conductivity increases rapidly by increasing temperature
 1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
1.9. Temperature Dependence of Semiconductor Conductivity Such dependence is one most important in semiconductor. In metals, Conductivity decreases by increasing temperature due to greater frequency of
AD-A a-- -" I o 1" oo-
 - *111E11'D~ih&; om A~woved :UMENTAT N PAGE 0"9 No. 0704-0185 AD-A254 914 a-- -" I o 1" oo- "w"mi " ft,. fwn ".momunm $Cv",ex. Dstwooate for inlom/ou" o...atr,oo., m o' 2l mtuhuu R % I R. ORTdfmf n,ajw
- *111E11'D~ih&; om A~woved :UMENTAT N PAGE 0"9 No. 0704-0185 AD-A254 914 a-- -" I o 1" oo- "w"mi " ft,. fwn ".momunm $Cv",ex. Dstwooate for inlom/ou" o...atr,oo., m o' 2l mtuhuu R % I R. ORTdfmf n,ajw
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling
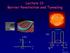 Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Electronic Structure of Surfaces
 Electronic Structure of Surfaces When solids made of an infinite number of atoms are formed, it is a common misconception to consider each atom individually. Rather, we must consider the structure of the
Electronic Structure of Surfaces When solids made of an infinite number of atoms are formed, it is a common misconception to consider each atom individually. Rather, we must consider the structure of the
System Reliability Simulation and Optimization by Component Reliability Allocation
 System Reliability Simulation and Optimization by Component Reliability Allocation Zissimos P. Mourelatos Professor and Head Mechanical Engineering Department Oakland University Rochester MI 48309 Report
System Reliability Simulation and Optimization by Component Reliability Allocation Zissimos P. Mourelatos Professor and Head Mechanical Engineering Department Oakland University Rochester MI 48309 Report
SW06 Shallow Water Acoustics Experiment Data Analysis
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SW06 Shallow Water Acoustics Experiment Data Analysis James F. Lynch MS #12, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SW06 Shallow Water Acoustics Experiment Data Analysis James F. Lynch MS #12, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods
December 1999 FINAL TECHNICAL REPORT 1 Mar Mar 98
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE AFRL-SR- BL_TR " Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instruct the collection
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE AFRL-SR- BL_TR " Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instruct the collection
AD-A MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH LEXINGTON LINCOLN LAB FIG 20/6 ZERN IKE ABERRATIONS AND THEIR FAR FIELDS INTENSITIES.(U) SEP So J HERRMANN
 AD-A093 175 MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH LEXINGTON LINCOLN LAB FIG 20/6 ZERN IKE ABERRATIONS AND THEIR FAR FIELDS INTENSITIES.(U) SEP So J HERRMANN F19628-80-C-0002 UNCLAS I TN-1980-422ESD-TR-8-88 L iiii'.,!ii
AD-A093 175 MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH LEXINGTON LINCOLN LAB FIG 20/6 ZERN IKE ABERRATIONS AND THEIR FAR FIELDS INTENSITIES.(U) SEP So J HERRMANN F19628-80-C-0002 UNCLAS I TN-1980-422ESD-TR-8-88 L iiii'.,!ii
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE. Theoretical Study on Nano-Catalyst Burn Rate. Yoshiyuki Kawazoe (Tohoku Univ) N/A AOARD UNIT APO AP
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Marcus Theory for Electron Transfer a short introduction
 Marcus Theory for Electron Transfer a short introduction Minoia Andrea MPIP - Journal Club -Mainz - January 29, 2008 1 Contents 1 Intro 1 2 History and Concepts 2 2.1 Frank-Condon principle applied to
Marcus Theory for Electron Transfer a short introduction Minoia Andrea MPIP - Journal Club -Mainz - January 29, 2008 1 Contents 1 Intro 1 2 History and Concepts 2 2.1 Frank-Condon principle applied to
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/e1602726/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Selective control of electron and hole tunneling in 2D assembly This PDF file includes: Dongil Chu, Young Hee Lee,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/e1602726/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Selective control of electron and hole tunneling in 2D assembly This PDF file includes: Dongil Chu, Young Hee Lee,
Scattering of Internal Gravity Waves at Finite Topography
 Scattering of Internal Gravity Waves at Finite Topography Peter Muller University of Hawaii Department of Oceanography 1000 Pope Road, MSB 429 Honolulu, HI 96822 phone: (808)956-8081 fax: (808)956-9164
Scattering of Internal Gravity Waves at Finite Topography Peter Muller University of Hawaii Department of Oceanography 1000 Pope Road, MSB 429 Honolulu, HI 96822 phone: (808)956-8081 fax: (808)956-9164
Charge fluctuators, their temperature and their response to sudden electrical fields
 Charge fluctuators, their temperature and their response to sudden electrical fields Outline Charge two-level fluctuators Measuing noise with an SET Temperature and bias dependence of the noise TLF temperature
Charge fluctuators, their temperature and their response to sudden electrical fields Outline Charge two-level fluctuators Measuing noise with an SET Temperature and bias dependence of the noise TLF temperature
Microscopical and Microanalytical Methods (NANO3)
 Microscopical and Microanalytical Methods (NANO3) 06.11.15 10:15-12:00 Introduction - SPM methods 13.11.15 10:15-12:00 STM 20.11.15 10:15-12:00 STS Erik Zupanič erik.zupanic@ijs.si stm.ijs.si 27.11.15
Microscopical and Microanalytical Methods (NANO3) 06.11.15 10:15-12:00 Introduction - SPM methods 13.11.15 10:15-12:00 STM 20.11.15 10:15-12:00 STS Erik Zupanič erik.zupanic@ijs.si stm.ijs.si 27.11.15
,AD-R A MEASURE OF VARIABILITY BASED ON THE HARMONIC MEAN AND i/i ITS USE IN APPROXIMATIONS(U) CITY COIL NEW YORK DEPT OF MATHEMATICS M BROWN
 ,AD-R127 397 A MEASURE OF VARIABILITY BASED ON THE HARMONIC MEAN AND i/i ITS USE IN APPROXIMATIONS(U) CITY COIL NEW YORK DEPT OF MATHEMATICS M BROWN MAR 03 CUNY-MB3 AFOSR-TR-83-8298 UNCLASSIFIED RFOSR-82-824
,AD-R127 397 A MEASURE OF VARIABILITY BASED ON THE HARMONIC MEAN AND i/i ITS USE IN APPROXIMATIONS(U) CITY COIL NEW YORK DEPT OF MATHEMATICS M BROWN MAR 03 CUNY-MB3 AFOSR-TR-83-8298 UNCLASSIFIED RFOSR-82-824
Development and Application of Acoustic Metamaterials with Locally Resonant Microstructures
 Development and Application of Acoustic Metamaterials with Locally Resonant Microstructures AFOSR grant #FA9550-10-1-0061 Program manager: Dr. Les Lee PI: C.T. Sun Purdue University West Lafayette, Indiana
Development and Application of Acoustic Metamaterials with Locally Resonant Microstructures AFOSR grant #FA9550-10-1-0061 Program manager: Dr. Les Lee PI: C.T. Sun Purdue University West Lafayette, Indiana
Fleet Maintenance Simulation With Insufficient Data
 Fleet Maintenance Simulation With Insufficient Data Zissimos P. Mourelatos Mechanical Engineering Department Oakland University mourelat@oakland.edu Ground Robotics Reliability Center (GRRC) Seminar 17
Fleet Maintenance Simulation With Insufficient Data Zissimos P. Mourelatos Mechanical Engineering Department Oakland University mourelat@oakland.edu Ground Robotics Reliability Center (GRRC) Seminar 17
Modulation Instability of Spatially-Incoherent Light Beams and Pattern Formation in Incoherent Wave Systems
 Modulation Instability of Spatially-Incoherent Light Beams and Pattern Formation in Incoherent Wave Systems Detlef Kip, (1,2) Marin Soljacic, (1,3) Mordechai Segev, (1,4) Evgenia Eugenieva, (5) and Demetrios
Modulation Instability of Spatially-Incoherent Light Beams and Pattern Formation in Incoherent Wave Systems Detlef Kip, (1,2) Marin Soljacic, (1,3) Mordechai Segev, (1,4) Evgenia Eugenieva, (5) and Demetrios
Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction
 Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction Contents 1 Optical absorption 1 1.1 Absorption coefficient....................... 2 2 Optical recombination 5 3 Recombination and carrier lifetime 6 3.1
Lecture 15: Optoelectronic devices: Introduction Contents 1 Optical absorption 1 1.1 Absorption coefficient....................... 2 2 Optical recombination 5 3 Recombination and carrier lifetime 6 3.1
AD-At AN OUTPUT MATCHING APPROACH TO MULTIVARIABLE LINEAR Il 0001 UNCLASSIFIED AFOSR-TR AFOSR U/ 14/2 NL 1
 AD-At28 662 AN OUTPUT MATCHING APPROACH TO MULTIVARIABLE LINEAR Il DIGITAL MATHEMATICS CONTROL(U) ANDSTATISTIC. WRIGHT STATE D FMLLER30DNOV82 UNIV DAYTON OH DEPT 0001 OF UNCLASSIFIED AFOSR-TR-83-0400 AFOSR-82-0208
AD-At28 662 AN OUTPUT MATCHING APPROACH TO MULTIVARIABLE LINEAR Il DIGITAL MATHEMATICS CONTROL(U) ANDSTATISTIC. WRIGHT STATE D FMLLER30DNOV82 UNIV DAYTON OH DEPT 0001 OF UNCLASSIFIED AFOSR-TR-83-0400 AFOSR-82-0208
Semiconductor Junctions
 8 Semiconductor Junctions Almost all solar cells contain junctions between different materials of different doping. Since these junctions are crucial to the operation of the solar cell, we will discuss
8 Semiconductor Junctions Almost all solar cells contain junctions between different materials of different doping. Since these junctions are crucial to the operation of the solar cell, we will discuss
VLBA IMAGING OF SOURCES AT 24 AND 43 GHZ
 VLBA IMAGING OF SOURCES AT 24 AND 43 GHZ D.A. BOBOLTZ 1, A.L. FEY 1, P. CHARLOT 2,3 & THE K-Q VLBI SURVEY COLLABORATION 1 U.S. Naval Observatory 3450 Massachusetts Ave., NW, Washington, DC, 20392-5420,
VLBA IMAGING OF SOURCES AT 24 AND 43 GHZ D.A. BOBOLTZ 1, A.L. FEY 1, P. CHARLOT 2,3 & THE K-Q VLBI SURVEY COLLABORATION 1 U.S. Naval Observatory 3450 Massachusetts Ave., NW, Washington, DC, 20392-5420,
From manipulation of the charge state to imaging of individual molecular orbitals and bond formation
 Scanning Probe Microscopy of Adsorbates on Insulating Films: From manipulation of the charge state to imaging of individual molecular orbitals and bond formation Gerhard Meyer, Jascha Repp, Peter Liljeroth
Scanning Probe Microscopy of Adsorbates on Insulating Films: From manipulation of the charge state to imaging of individual molecular orbitals and bond formation Gerhard Meyer, Jascha Repp, Peter Liljeroth
Scanning Probe Microscopy
 1 Scanning Probe Microscopy Dr. Benjamin Dwir Laboratory of Physics of Nanostructures (LPN) Benjamin.dwir@epfl.ch PH.D3.344 Outline: Introduction: What is SPM, history STM AFM Image treatment Advanced
1 Scanning Probe Microscopy Dr. Benjamin Dwir Laboratory of Physics of Nanostructures (LPN) Benjamin.dwir@epfl.ch PH.D3.344 Outline: Introduction: What is SPM, history STM AFM Image treatment Advanced
Probing into the Electrical Double Layer Using a Potential Nano-Probe
 A3 Foresight Program, 2. 27-3. 1, 26 Probing into the Electrical Double Layer Using a Potential Nano-Probe Heon Kang ( 姜憲 ) Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Republic of Korea (E-mail:
A3 Foresight Program, 2. 27-3. 1, 26 Probing into the Electrical Double Layer Using a Potential Nano-Probe Heon Kang ( 姜憲 ) Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Republic of Korea (E-mail:
Supporting Information for PbTiO 3
 Supporting Information for PbTiO 3 (001) Capped with ZnO(11 20): An Ab-Initio Study of Effect of Substrate Polarization on Interface Composition and CO 2 Dissociation Babatunde O. Alawode and Alexie M.
Supporting Information for PbTiO 3 (001) Capped with ZnO(11 20): An Ab-Initio Study of Effect of Substrate Polarization on Interface Composition and CO 2 Dissociation Babatunde O. Alawode and Alexie M.
EE 130 Intro to MS Junctions Week 6 Notes. What is the work function? Energy to excite electron from Fermi level to the vacuum level
 EE 13 Intro to S Junctions eek 6 Notes Problem 1 hat is the work function? Energy to ecite electron from Fermi level to the vacuum level Electron affinity of 4.5eV Electron affinity of Ge 4.eV orkfunction
EE 13 Intro to S Junctions eek 6 Notes Problem 1 hat is the work function? Energy to ecite electron from Fermi level to the vacuum level Electron affinity of 4.5eV Electron affinity of Ge 4.eV orkfunction
