Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium
|
|
|
- Beatrice Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium Assist. Prof. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department
2 Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net eternal force must equal zero n Net eternal torque must equal zero q Center of gravity q Solving static equilibrium problems
3 Static and Dynamic Equilibrium q Equilibrium implies the object is at rest (static) or its center of mass moves with a constant velocity (dynamic) q We will consider only with the case in which linear and angular velocities are equal to zero, called static equilibrium : v CM 0 and w 0 q Eamples n n n n n Book on table Hanging sign Ceiling fan off Ceiling fan on Ladder leaning against wall
4 Conditions for Equilibrium q The first condition of equilibrium is a statement of translational equilibrium q The net eternal force on the object must equal zero! F net!! å F ma et 0 q It states that the translational acceleration of the object s center of mass must be zero
5 Conditions for Equilibrium q If the object is modeled as a particle, then this is the only condition that must be satisfied!! F net å Fet 0 q For an etended object to be in equilibrium, a second condition must be satisfied q This second condition involves the rotational motion of the etended object
6 Conditions for Equilibrium q The second condition of equilibrium is a statement of rotational equilibrium q The net eternal torque on the object must equal zero! t net!! åt Ia 0 et q It states the angular acceleration of the object to be zero q This must be true for any ais of rotation
7 Conditions for Equilibrium qthe net force equals zero åf! 0 n If the object is modeled as a particle, then this is the only condition that must be satisfied qthe net torque equals zero å! t 0 n This is needed if the object cannot be modeled as a particle qthese conditions describe the rigid objects in the equilibrium analysis model
8 Static Equilibrium q (A) (B) (C) (D) Consider a light rod subject to the two forces of equal magnitude as shown in figure. Choose the correct statement with regard to this situation: The object is in force equilibrium but not torque equilibrium. The object is in torque equilibrium but not force equilibrium The object is in both force equilibrium and torque equilibrium The object is in neither force equilibrium nor torque equilibrium
9 Equilibrium Equations q For simplicity, We will restrict the applications to situations in which all the forces lie in the y plane. q Equation 1: q Equation 2:! F! t net net! å Fet 0 : Fnet 0 Fnet, y 0 Fnet, z! åt : t 0 t 0 t, et 0 net, net, y net, z q There are three resulting equations F å F 0 F t net, net, y net, z å åt F et, et, y et, z
10 q EX: A seesaw consisting of a uniform board of mass m pl and length L supports at rest a father and daughter with masses M and m, respectively. The support is under the center of gravity of the board, the father is a distance d from the center, and the daughter is a distance 2.00 m from the center. q A) Find the magnitude of the upward force n eerted by the support on the board. q B) Find where the father should sit to balance the system at rest.
11 A) Find the magnitude of the upward force n eerted by the support on the board. B) Find where the father should sit to balance the system at rest. F n t net, y net, z mgd n - mg - Mg - m g 0 mg mgd æ ç è t m M + Mg + m d ö d ø + t 2m M pl + t g < + t pl - Mg Mg f pl n 2.00 m F F t net, net, y net, z å F å F åt et, et, y et, z 0 0 0
12 Ais of Rotation q The net torque is about an ais through any point in the y plane q Does it matter which ais you choose for calculating torques? q NO. The choice of an ais is arbitrary q If an object is in translational equilibrium and the net torque is zero about one ais, then the net torque must be zero about any other ais q We should be smart to choose a rotation ais to simplify problems
13 B) Find where the father should sit to balance the system at rest. Rotation ais O t mgd net, z m M d mgd - Mg æ ç è t + t + t + t Mg ö d ø f 2m M pl n Rotation ais P t 0 - Mg( d - Mgd - Mg - m mgd net, z æ ç è t + t + t + t m M d Mg ö d ø f 2m M pl + ) - m pl pl n gd + nd 0 gd + ( Mg + mg + m pl g) d 0 P O F F t net, net, y net, z å F å F åt et, et, y et, z 0 0 0
14 Center of Gravity q The torque due to the gravitational force on an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object q If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass q If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center
15 Where is the Center of Mass? q Assume m 1 1 kg, m 2 3 kg, and 1 1 m, 2 5 m, where is the center of mass of these two objects? m + m A) CM 1 m B) CM 2 m C) CM 3 m D) CM 4 m E) CM 5 m 1 1 CM m + 1 m 2 2 2
16 Center of Mass (CM) q An object can be divided into many small particles n Each particle will have a specific mass and specific coordinates q The coordinate of the center of mass will be CM å i å i m q Similar epressions can be found for the y coordinates i m i i
17 Center of Gravity (CG) q All the various gravitational forces acting on all the various mass elements are equivalent to a single gravitational force acting through a single point called the center of gravity (CG) Mg CG m g 1 1 CG 1 ( m1 + m2 + m3 +!) g + m g + m g +! CG CG q If g g2 3 1 g! q then CG m11 + m22 + m m + m + m ! +! 3 å mi å m i i
18 CG of a Ladder q A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall. When you calculate the torque due to the gravitational force, you have to find center of gravity of the ladder. The center of gravity should be located at A B D C E
19 Ladder Eample q A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall. The mass of the ladder is m, and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is µ s Find the minimum angle q at which the ladder does not slip.
20 Problem-Solving Strategy 1 q Draw sketch, decide what is in or out the system q Draw a free body diagram (FBD) q Show and label all eternal forces acting on the object q Indicate the locations of all the forces q Establish a convenient coordinate system q Find the components of the forces along the two aes q Apply the first condition for equilibrium q Be careful of signs F F net, net, y å F å F et, et, y 0 0
21 Which free-body diagram is correct? q A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall. The mass of the ladder is m, and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is µ s gravity: blue, friction: orange, normal: green A B C D
22 q A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall. The mass of the ladder is m, and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is µ s Find the minimum angle q at which the ladder does not slip. å å F F y P f n mg P f f - P 0 n - mg 0,ma µ n µ mg s s mg
23 Problem-Solving Strategy 2 q Choose a convenient ais for calculating the net torque on the object n Remember the choice of the ais is arbitrary q Choose an origin that simplifies the calculations as much as possible n A force that acts along a line passing through the origin produces a zero torque q Be careful of sign with respect to rotational ais n n n positive if force tends to rotate object in CCW negative if force tends to rotate object in CW zero if force is on the rotational ais q Apply the second condition for equilibrium t net, z åt et, z 0
24 Choose an origin O that simplifies the calculations as much as possible? q A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall. The mass of the ladder is m, and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is µ s Find the minimum angle. A) B) C) O D) O O mg mg mg mg O
25 q A uniform ladder of length l rests against a smooth, vertical wall. The mass of the ladder is m, and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is µ s Find the minimum angle q at which the ladder does not slip. åt sinq cosq q min O t min min n tan + t Pl sinq tanq -1 f + t min min 1 ( ) 2µ s g + t P l - mg cosq min 2 mg mg 2P 2µ mg tan -1 s 1 [ ] 2(0.4) 0 1 2µ! 51 s mg
26 Problem-Solving Strategy 3 q The two conditions of equilibrium will give a system of equations q Solve the equations simultaneously q Make sure your results are consistent with your free body diagram q If the solution gives a negative for a force, it is in the opposite direction to what you drew in the free body diagram q Check your results to confirm F F t net, net, y net, z å F å F åt et, et, y et, z 0 0 0
27 Horizontal Beam Eample q A uniform horizontal beam with a length of l 8.00 m and a weight of W b 200 N is attached to a wall by a pin connection. Its far end is supported by a cable that makes an angle of f 53 with the beam. A person of weight W p 600 N stands a distance d 2.00 m from the wall. Find the tension in the cable as well as the magnitude and direction of the force eerted by the wall on the beam.
28 Horizontal Beam Eample q The beam is uniform n So the center of gravity is at the geometric center of the beam q The person is standing on the beam q What are the tension in the cable and the force eerted by the wall on the beam?
29 Horizontal Beam Eample, 2 q Analyze n Draw a free body diagram n Use the pivot in the problem (at the wall) as the pivot n This will generally be easiest n Note there are three unknowns (T, R, q)
30 Horizontal Beam Eample, 3 q The forces can be resolved into components in the free body diagram q Apply the two conditions of equilibrium to obtain three equations q Solve for the unknowns
31 Horizontal Beam Eample, 3 0 sin sin 0 cos cos å - å b p y W W T R F T R F f q f q N m m N m N l l W W d T l W W d l T b p b p z 313 )sin53 (8 ) )(4 (200 ) )(2 (600 sin ) 2 ( 0 ) 2 ( ) )( sin ( å! f f t N N T R T T W W T T W W R R b p b p 581 cos 71.7 )cos53 (313 cos cos 71.7 sin sin tan sin sin tan cos sin 1 ø ö ç ç è æ !!! q f f f q f f q q q
32 P1:
33 P2: P3:
34 P4:
35 P5:
36 P7:
37 P8:
38 P9:
Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum
 Physics 101 Lecture 1 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net external
Physics 101 Lecture 1 Equilibrium and Angular Momentum Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net external
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium
 Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Physics 201, Lecture 21
 Physics 201, Lecture 21 Today s Topics q Static Equilibrium of Rigid Objects(Ch. 12.1-3) Review: Rotational and Translational Motion Conditions for Translational and Rotational Equilibrium Demos and Exercises
Physics 201, Lecture 21 Today s Topics q Static Equilibrium of Rigid Objects(Ch. 12.1-3) Review: Rotational and Translational Motion Conditions for Translational and Rotational Equilibrium Demos and Exercises
α = p = m v L = I ω Review: Torque Physics 201, Lecture 21 Review: Rotational Dynamics a = Στ = I α
 Physics 1, Lecture 1 Today s Topics q Static Equilibrium of Rigid Objects(Ch. 1.1-3) Review: Rotational and Translational Motion Conditions for Translational and Rotational Equilibrium Demos and Exercises
Physics 1, Lecture 1 Today s Topics q Static Equilibrium of Rigid Objects(Ch. 1.1-3) Review: Rotational and Translational Motion Conditions for Translational and Rotational Equilibrium Demos and Exercises
Announcements Oct 16, 2014
 Announcements Oct 16, 2014 1. Prayer 2. While waiting, see how many of these blanks you can fill out: Centripetal Accel.: Causes change in It points but not Magnitude: a c = How to use with N2: Always
Announcements Oct 16, 2014 1. Prayer 2. While waiting, see how many of these blanks you can fill out: Centripetal Accel.: Causes change in It points but not Magnitude: a c = How to use with N2: Always
Static Equilibrium. Lecture 24. Chapter 12. Physics I. Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 24 Chapter 12 Physics I Static Equilibrium Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will discuss static equilibrium of an object Today we are
Lecture 24 Chapter 12 Physics I Static Equilibrium Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will discuss static equilibrium of an object Today we are
Static Equilibrium; Torque
 Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74
 PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Physics 111. Lecture 22 (Walker: ) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009
 Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 13: ROTATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
!! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
Physics 211 Week 10. Statics: Walking the Plank (Solution)
 Statics: Walking the Plank (Solution) A uniform horizontal beam 8 m long is attached by a frictionless pivot to a wall. A cable making an angle of 37 o, attached to the beam 5 m from the pivot point, supports
Statics: Walking the Plank (Solution) A uniform horizontal beam 8 m long is attached by a frictionless pivot to a wall. A cable making an angle of 37 o, attached to the beam 5 m from the pivot point, supports
Static Equilibrium. Lecture 22. Chapter 12. Physics I Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 22 Chapter 12 Physics I 12.02.2013 Static Equilibrium Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov2013/physics1fall.html
Lecture 22 Chapter 12 Physics I 12.02.2013 Static Equilibrium Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov2013/physics1fall.html
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY. Conditions for static equilibrium Center of gravity (weight) Examples of static equilibrium
 CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
Definition. is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau)
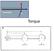 Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Unit 5 Forces I- Newton s First & Second Law
 Unit 5 Forces I- Newton s First & Second Law Unit is the NEWTON(N) Is by definition a push or a pull Does force need a Physical contact? Can exist during physical contact(tension, Friction, Applied Force)
Unit 5 Forces I- Newton s First & Second Law Unit is the NEWTON(N) Is by definition a push or a pull Does force need a Physical contact? Can exist during physical contact(tension, Friction, Applied Force)
Statics. Phys101 Lectures 19,20. Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain. Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5.
 Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium
 Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 9
 Solutions to Phsics: Principles with pplications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 9 CHPTER 9 6. We choose the coordinate sstem shown, with positive torques clockwise. We write τ = Iα about the point from the force
Solutions to Phsics: Principles with pplications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 9 CHPTER 9 6. We choose the coordinate sstem shown, with positive torques clockwise. We write τ = Iα about the point from the force
Announcements Oct 17, 2013
 Announcements Oct 17, 2013 1. No announcements! Colton - Lecture 14 - pg 1 Real satellites: http://science.nasa.gov/realtime/jtrack/3d/jtrack3d.html International space station, 340.5 km above surface
Announcements Oct 17, 2013 1. No announcements! Colton - Lecture 14 - pg 1 Real satellites: http://science.nasa.gov/realtime/jtrack/3d/jtrack3d.html International space station, 340.5 km above surface
Consider two students pushing with equal force on opposite sides of a desk. Looking top-down on the desk:
 1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques
 Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Equilibrium & Elasticity
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity Static equilibrium Elasticity 1. A uniform steel bar of length 3.0 m and weight 20 N rests on two supports (A and B) at its ends. A block
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity Static equilibrium Elasticity 1. A uniform steel bar of length 3.0 m and weight 20 N rests on two supports (A and B) at its ends. A block
Physics 185F2013 Lecture Eight
 Physics 185F2013 Lecture Eight Nov 19, 2013 Dr. Jones 1 1 Department of Physics Drexel University November 19, 2013 Dr. Jones (Drexel) Physics 185F2013 Lecture Eight November 19, 2013 1 / 18 Static Equilibrium
Physics 185F2013 Lecture Eight Nov 19, 2013 Dr. Jones 1 1 Department of Physics Drexel University November 19, 2013 Dr. Jones (Drexel) Physics 185F2013 Lecture Eight November 19, 2013 1 / 18 Static Equilibrium
Engineering Mechanics Statics
 Mechanical Systems Engineering _ 2016 Engineering Mechanics Statics 7. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Dr. Rami Zakaria Conditions for Rigid-Body Equilibrium Forces on a particle Forces on a rigid body The
Mechanical Systems Engineering _ 2016 Engineering Mechanics Statics 7. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Dr. Rami Zakaria Conditions for Rigid-Body Equilibrium Forces on a particle Forces on a rigid body The
Static Equilibrium and Torque
 10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
TEST REPORT. Question file: P Copyright:
 Date: February-12-16 Time: 2:00:28 PM TEST REPORT Question file: P12-2006 Copyright: Test Date: 21/10/2010 Test Name: EquilibriumPractice Test Form: 0 Test Version: 0 Test Points: 138.00 Test File: EquilibriumPractice
Date: February-12-16 Time: 2:00:28 PM TEST REPORT Question file: P12-2006 Copyright: Test Date: 21/10/2010 Test Name: EquilibriumPractice Test Form: 0 Test Version: 0 Test Points: 138.00 Test File: EquilibriumPractice
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics. 1. Torque. 2. Torque and Equilibrium. 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1. Torque 2. Torque and Equilibrium 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity 4. Torque and angular acceleration 5. Rotational Kinetic energy 6. Angular
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1. Torque 2. Torque and Equilibrium 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity 4. Torque and angular acceleration 5. Rotational Kinetic energy 6. Angular
Your Comments. That s the plan
 Your Comments I love physics as much as the next gal, but I was wondering. Why don't we get class off the day after an evening exam? What if the ladder has friction with the wall? Things were complicated
Your Comments I love physics as much as the next gal, but I was wondering. Why don't we get class off the day after an evening exam? What if the ladder has friction with the wall? Things were complicated
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 130) Lecture 0 Rotational dynamics equilibrium nd Newton s Law for rotational motion rolling Exam II review http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy130/ Lightning Review Last lecture:
General Physics (PHY 130) Lecture 0 Rotational dynamics equilibrium nd Newton s Law for rotational motion rolling Exam II review http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy130/ Lightning Review Last lecture:
Chapter 8. Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity
 Chapter 8 Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity Centripetal Acceleration An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration
Chapter 8 Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity Centripetal Acceleration An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Static Equilibrium. University of Arizona J. H. Burge
 Static Equilibrium Static Equilibrium Definition: When forces acting on an object which is at rest are balanced, then the object is in a state of static equilibrium. - No translations - No rotations In
Static Equilibrium Static Equilibrium Definition: When forces acting on an object which is at rest are balanced, then the object is in a state of static equilibrium. - No translations - No rotations In
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics
 Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium
 Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium Strike (Day 10) Prelectures, checkpoints, lectures continue with no change. Take-home quizzes this week. See Elaine Schulte s email. HW
Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium Strike (Day 10) Prelectures, checkpoints, lectures continue with no change. Take-home quizzes this week. See Elaine Schulte s email. HW
Static Equilibrium. Lana Sheridan. Dec 5, De Anza College
 tatic Equilibrium Lana heridan De Anza College Dec 5, 2016 Last time simple harmonic motion Overview Introducing static equilibrium center of gravity tatic Equilibrium: ystem in Equilibrium Knowing that
tatic Equilibrium Lana heridan De Anza College Dec 5, 2016 Last time simple harmonic motion Overview Introducing static equilibrium center of gravity tatic Equilibrium: ystem in Equilibrium Knowing that
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium; Elasticity and Fracture
 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination
2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination
Examples Newton's Laws and Friction
 Examples Newton's Laws and Friction 1. A 10.0 kg box is sitting on a table. (A) If a 49 N force is required to overcome friction and start the block moving, calculate the coefficient of static friction.
Examples Newton's Laws and Friction 1. A 10.0 kg box is sitting on a table. (A) If a 49 N force is required to overcome friction and start the block moving, calculate the coefficient of static friction.
Phys 1401: General Physics I
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
EQUILIBRIUM and ELASTICITY
 PH 221-1D Spring 2013 EQUILIBRIUM and ELASTICITY Lectures 30-32 Chapter 12 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity In this chapter we will
PH 221-1D Spring 2013 EQUILIBRIUM and ELASTICITY Lectures 30-32 Chapter 12 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity In this chapter we will
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Review for 3 rd Midterm
 Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Physics 2210 Fall smartphysics Rotational Statics 11/18/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 17-18 Rotational Statics 11/18/2015 τ TT = L T 1 sin 150 = 1 T 2 1L Poll 11-18-01 τ TT = L 2 T 2 sin 150 = 1 4 T 2L 150 150 τ gg = L 2 MM sin +90 = 1 2 MMM +90 MM τ
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 17-18 Rotational Statics 11/18/2015 τ TT = L T 1 sin 150 = 1 T 2 1L Poll 11-18-01 τ TT = L 2 T 2 sin 150 = 1 4 T 2L 150 150 τ gg = L 2 MM sin +90 = 1 2 MMM +90 MM τ
is the study of and. We study objects. is the study of and. We study objects.
 Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque Unit 4 Statics Dynamics vs Statics is the study of and. We study objects. is the study of and. We study objects. Recall Newton s First Law All objects remain
Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque Unit 4 Statics Dynamics vs Statics is the study of and. We study objects. is the study of and. We study objects. Recall Newton s First Law All objects remain
Phys 1401: General Physics I
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
Webreview practice test. Forces (again)
 Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview 4.3 - practice test. Forces (again) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 5.0-kg mass is suspended
Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview 4.3 - practice test. Forces (again) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 5.0-kg mass is suspended
Unit 4 Statics. Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque
 Unit 4 Statics Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque 1 Dynamics vs Statics Dynamics: is the study of forces and motion. We study why objects move. Statics: is the study of forces and NO motion.
Unit 4 Statics Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque 1 Dynamics vs Statics Dynamics: is the study of forces and motion. We study why objects move. Statics: is the study of forces and NO motion.
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015
 Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
Equilibrium. Lecture 8 Physics 106 Spring Equilibrium. Equilibrium. Equilibrium. Balance of Forces: Balance of Forces: Balance of Torques:
 Lecture 8 Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 1 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 2 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 3 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 4 3/8/2006 Andrei
Lecture 8 Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 1 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 2 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 3 3/8/2006 Andrei Sirenko, JIT 4 3/8/2006 Andrei
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
Application of Forces. Chapter Eight. Torque. Force vs. Torque. Torque, cont. Direction of Torque 4/7/2015
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Eight Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Application of Forces The point of application of a force is important This was ignored in treating objects as
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Eight Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Application of Forces The point of application of a force is important This was ignored in treating objects as
Test Corrections Use these concepts to explain corrected answers. Make sure you apply the concepts to the specific situation in each problem.
 Test Corrections Use these concepts to explain corrected answers. Make sure you apply the concepts to the specific situation in each problem. Circular Motion Concepts When an object moves in a circle,
Test Corrections Use these concepts to explain corrected answers. Make sure you apply the concepts to the specific situation in each problem. Circular Motion Concepts When an object moves in a circle,
Chapter 18 Static Equilibrium
 Chapter 8 Static Equilibrium Chapter 8 Static Equilibrium... 8. Introduction Static Equilibrium... 8. Lever Law... 3 Example 8. Lever Law... 5 8.3 Generalized Lever Law... 6 8.4 Worked Examples... 8 Example
Chapter 8 Static Equilibrium Chapter 8 Static Equilibrium... 8. Introduction Static Equilibrium... 8. Lever Law... 3 Example 8. Lever Law... 5 8.3 Generalized Lever Law... 6 8.4 Worked Examples... 8 Example
Mechanics 1 Revision notes
 Mechanics 1 Revision notes 1. Kinematics in one and two dimensions EQUATIONS FOR CONSTANT ACCELERATION ARE NOT GIVEN Learn Them! v = u + at s = ut + 1 at s = vt 1 at s = 1 (u + v)t v = u + as s : displacement
Mechanics 1 Revision notes 1. Kinematics in one and two dimensions EQUATIONS FOR CONSTANT ACCELERATION ARE NOT GIVEN Learn Them! v = u + at s = ut + 1 at s = vt 1 at s = 1 (u + v)t v = u + as s : displacement
Lecture 5. Dynamics. Forces: Newton s First and Second
 Lecture 5 Dynamics. Forces: Newton s First and Second What is a force? It s a pull or a push: F F Force is a quantitative description of the interaction between two physical bodies that causes them to
Lecture 5 Dynamics. Forces: Newton s First and Second What is a force? It s a pull or a push: F F Force is a quantitative description of the interaction between two physical bodies that causes them to
Physics 101 Lecture 11 Torque
 Physics 101 Lecture 11 Torque Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Force vs. Torque q Forces cause accelerations q What cause angular accelerations? q A door is free to rotate about an axis
Physics 101 Lecture 11 Torque Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Force vs. Torque q Forces cause accelerations q What cause angular accelerations? q A door is free to rotate about an axis
τ net l = r p L = Iω = d L dt = I α ΔL Angular momentum (one) Angular momentum (system, fixed axis) Newton s second law (system)
 l = r p L = Iω = d L dt = I α ΔL = 0 Angular momentum (one) Angular momentum (system, fixed axis) Newton s second law (system) Conserva
l = r p L = Iω = d L dt = I α ΔL = 0 Angular momentum (one) Angular momentum (system, fixed axis) Newton s second law (system) Conserva
Unit 5 Forces I- Newtonʼ s First & Second Law
 Unit 5 orces I- Newtonʼ s irst & Second Law Unit is the NEWTON(N) Is by definition a push or a pull Does force need a Physical contact? Can exist during physical contact(tension, riction, Applied orce)
Unit 5 orces I- Newtonʼ s irst & Second Law Unit is the NEWTON(N) Is by definition a push or a pull Does force need a Physical contact? Can exist during physical contact(tension, riction, Applied orce)
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a velocity
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a velocity
1. An object is fired with an initial velocity of 23 m/s [R30 U]. What are the initial components of its velocity?
![1. An object is fired with an initial velocity of 23 m/s [R30 U]. What are the initial components of its velocity? 1. An object is fired with an initial velocity of 23 m/s [R30 U]. What are the initial components of its velocity?](/thumbs/89/100544541.jpg) Physics 304 Unit 1 - Total Review 1. An object is fired with an initial velocity of 3 m/s [R30U]. What are the initial components of its velocity?. An object rolls off the top of a horizontal table. a)
Physics 304 Unit 1 - Total Review 1. An object is fired with an initial velocity of 3 m/s [R30U]. What are the initial components of its velocity?. An object rolls off the top of a horizontal table. a)
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS
 EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and b) Recognize two-force members. In-Class
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and b) Recognize two-force members. In-Class
variable Formula S or v SI variable Formula S or v SI 4. How is a Newton defined? What does a Newton equal in pounds?
 Newton s Laws 1 1. Define mass variable Formula S or v SI 2. Define inertia, how is inertia related to mass 3. What is a Force? variable Formula S or v SI 4. How is a Newton defined? What does a Newton
Newton s Laws 1 1. Define mass variable Formula S or v SI 2. Define inertia, how is inertia related to mass 3. What is a Force? variable Formula S or v SI 4. How is a Newton defined? What does a Newton
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1 Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related 2 Torque The door is free to rotate
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1 Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related 2 Torque The door is free to rotate
III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) Rotation. We repeat Chap. 2-8 with rotatiing objects. Eqs. of motion. Energy.
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
The case where there is no net effect of the forces acting on a rigid body
 The case where there is no net effect of the forces acting on a rigid body Outline: Introduction and Definition of Equilibrium Equilibrium in Two-Dimensions Special cases Equilibrium in Three-Dimensions
The case where there is no net effect of the forces acting on a rigid body Outline: Introduction and Definition of Equilibrium Equilibrium in Two-Dimensions Special cases Equilibrium in Three-Dimensions
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Force and Mass Units of Chapter 5 Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion The Vector Nature of Forces: Forces in Two Dimensions
Chapter 5 Newton s Laws of Motion Force and Mass Units of Chapter 5 Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion The Vector Nature of Forces: Forces in Two Dimensions
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 25, 2017
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 25, 2017 HW07 due Friday. It is mainly rotation, plus a couple of basic torque questions. And there are only 8 problems this week. For today, you read (in Perusall) Onouye/Kane
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 25, 2017 HW07 due Friday. It is mainly rotation, plus a couple of basic torque questions. And there are only 8 problems this week. For today, you read (in Perusall) Onouye/Kane
Physics 111. Tuesday, November 2, Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy
 ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
Chapter Objectives. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
 Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Lecture 2 - Force Analysis
 Lecture 2 - orce Analysis A Puzzle... Triangle or quadrilateral? 4 distinct points in a plane can either be arrange as a triangle with a point inside or as a quadrilateral. Extra Brownie Points: Use the
Lecture 2 - orce Analysis A Puzzle... Triangle or quadrilateral? 4 distinct points in a plane can either be arrange as a triangle with a point inside or as a quadrilateral. Extra Brownie Points: Use the
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body Concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body Concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body
Chapter 11. Today. Last Wednesday. Precession from Pre- lecture. Solving problems with torque
 Chapter 11 Last Wednesday Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum Conserva5on of angular momentum Today Precession from Pre- lecture Study the condi5ons for equilibrium
Chapter 11 Last Wednesday Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum Conserva5on of angular momentum Today Precession from Pre- lecture Study the condi5ons for equilibrium
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
The Laws of Motion. Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples
 The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
ΣF = 0 and Στ = 0 In 2-d: ΣF X = 0 and ΣF Y = 0 Goal: Write expression for Στ and ΣF
 Thur Sept 24 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email if conflict Today: Rotation and Torques Static Equilibrium Sign convention for torques: (-) CW torque (+) CCW torque Equilibrium
Thur Sept 24 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email if conflict Today: Rotation and Torques Static Equilibrium Sign convention for torques: (-) CW torque (+) CCW torque Equilibrium
Extension of Circular Motion & Newton s Laws. Chapter 6 Mrs. Warren Kings High School
 Extension of Circular Motion & Newton s Laws Chapter 6 Mrs. Warren Kings High chool Review from Chapter 4 Uniform Circular Motion Centripetal Acceleration Uniform Circular Motion, Force F r A force is
Extension of Circular Motion & Newton s Laws Chapter 6 Mrs. Warren Kings High chool Review from Chapter 4 Uniform Circular Motion Centripetal Acceleration Uniform Circular Motion, Force F r A force is
P12 Torque Notes.notebook. March 26, Torques
 Torques The size of a torque depends on two things: 1. The size of the force being applied (a larger force will have a greater effect) 2. The distance away from the pivot point (the further away from this
Torques The size of a torque depends on two things: 1. The size of the force being applied (a larger force will have a greater effect) 2. The distance away from the pivot point (the further away from this
Forces on an inclined plane Section 2.2
 Forces on an inclined plane Section 2.2 Examples of inclined planes Previous Knowledge Since some of the incline problems lets review friction (both kinetic and static) and normal force. Friction Friction
Forces on an inclined plane Section 2.2 Examples of inclined planes Previous Knowledge Since some of the incline problems lets review friction (both kinetic and static) and normal force. Friction Friction
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis. Lecture 13
 ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 13 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 13 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23
 PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23 Monday, April 29, 2013 Conditions for Equilibrium Elastic Properties of Solids Young s Modulus Bulk Modulus Density and Specific Gravity luid and Pressure Today s homework
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23 Monday, April 29, 2013 Conditions for Equilibrium Elastic Properties of Solids Young s Modulus Bulk Modulus Density and Specific Gravity luid and Pressure Today s homework
STATICS. Bodies. Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Design of a support
 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Mass & Weight. weight a force acting on a body due to the gravitational attraction pulling that body to another. NOT constant.
 Mass & Weight mass how much stuff a body has. Doesn t change. Is responsible for the inertial properties of a body. The greater the mass, the greater the force required to achieve some acceleration: Fnet
Mass & Weight mass how much stuff a body has. Doesn t change. Is responsible for the inertial properties of a body. The greater the mass, the greater the force required to achieve some acceleration: Fnet
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Engineering Mechanics: Statics. Chapter 7: Virtual Work
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 7: Virtual Work Introduction Previous chapters-- FBD & zero-force and zero-moment equations -- Suitable when equilibrium position is known For bodies composed of
Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 7: Virtual Work Introduction Previous chapters-- FBD & zero-force and zero-moment equations -- Suitable when equilibrium position is known For bodies composed of
Torque rotational force which causes a change in rotational motion. This force is defined by linear force multiplied by a radius.
 Warm up A remote-controlled car's wheel accelerates at 22.4 rad/s 2. If the wheel begins with an angular speed of 10.8 rad/s, what is the wheel's angular speed after exactly three full turns? AP Physics
Warm up A remote-controlled car's wheel accelerates at 22.4 rad/s 2. If the wheel begins with an angular speed of 10.8 rad/s, what is the wheel's angular speed after exactly three full turns? AP Physics
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 28, 2015
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 8, 015 HW7 (due this Friday will be quite easy in comparison with HW6, to make up for your having a lot to read this week. For today, you read Chapter 3 (analyzes cables, trusses,
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 8, 015 HW7 (due this Friday will be quite easy in comparison with HW6, to make up for your having a lot to read this week. For today, you read Chapter 3 (analyzes cables, trusses,
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
Recap I. Angular position: Angular displacement: s. Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration:
 Recap I Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Recap II Circular
Recap I Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Recap II Circular
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 19. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 36.
 Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
4.1 Forces. Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion
 4.1 Forces Chapter 4 he Laws of Motion 4.2 Newton s First Law it s not the nature of an object to stop, once set in motion, but rather to continue in its original state of motion. An object moves with
4.1 Forces Chapter 4 he Laws of Motion 4.2 Newton s First Law it s not the nature of an object to stop, once set in motion, but rather to continue in its original state of motion. An object moves with
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 4
 1 Which of ewton's Three Laws of Motion is best expressed by the equation F=ma? a ewton's First Law b ewton's Second Law c ewton's Third Law d one of the above 4.1 2 A person is running on a track. Which
1 Which of ewton's Three Laws of Motion is best expressed by the equation F=ma? a ewton's First Law b ewton's Second Law c ewton's Third Law d one of the above 4.1 2 A person is running on a track. Which
Mechanics 2. Revision Notes
 Mechanics 2 Revision Notes October 2016 2 M2 OCTOER 2016 SD Mechanics 2 1 Kinematics 3 Constant acceleration in a vertical plane... 3 Variable acceleration... 5 Using vectors... 6 2 Centres of mass 7 Centre
Mechanics 2 Revision Notes October 2016 2 M2 OCTOER 2016 SD Mechanics 2 1 Kinematics 3 Constant acceleration in a vertical plane... 3 Variable acceleration... 5 Using vectors... 6 2 Centres of mass 7 Centre
