ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS
|
|
|
- Conrad Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 613 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics, Mechanics, and Engineering Vol. 58, Issue IV, November, 2015 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF HUMAN BODY Sergiu Dan VESCAN, Mariana ARGHIR Abstract: Through the work aims to carry out an evaluation of quantitative mechanical characteristics of the human body. The study is part of a research activity, which analyses the action of mechanical vibration on the human body. This study constitutes part of scientific research, and makes in an own manner its mechanical profiling of human body segments. They will get the features: mass damper, and elasticity of the segments, which will be subsequently for subjected to theoretically and practically vibrations. Key words: mechanical characteristics, human body segments, vibrations. 1. GENERAL NOTIONS CONCERNING THE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE HUMAN BODY The movements of the human body stand factors resulting from the morpho-functional movement itself, between the bodies musculoskeletal system (bones, joints, muscles) and the organs of the nervous system [3]. The body must be regarded as a whole, in close interdependence with the environment in which it develops and moves. It is well known the importance of external factors on the human body, such as strength and elasticity, gravitational force, throttle, etc. It also may be considered low temperature environment upon obtaining good results through the phenomena of neuromuscular vasoconstrictie and exciting that they cause, influence of atmospheric pressure,and finally of movements made by pilots and cosmonauts as well as the influence of mechanical vibration present in various situations and strengths that can have a positive or negative effect on the body [3], [5]. Outside the outer mechanical forces which made entry into the tissue tension maximum mechanical forces are present and their own inner tissue (blood pressure, arterial pulses, metabolic processes, processes of development and restructuring of tissue, etc), that they remain continuously in a state of minimal tension. The state of tension created in tissues for the purposes of functional acts of their actions, as required. Functional structure thus appears as a result of adaptarilor, under the influence of mechanical factors. Tissue structures can be considered as mechano-structurs [5], [12] The relative density of the body segments The density, defined as the ratio between the mass and volume, may be considered for the whole body, for each body segment or for the various human tissues. Because the density varies with the type of tissue, and each body segment has a different combination of tissue, each segment has a single density. To calculate the density of the whole body can be used the expression [6]: ρ = IMC (1) Where: ρ segment density [kg/m 3 ] (in general, it is assumed that the average density of the entire body of 1.062x10-3 kg/cm 3 ); IMC - the index gain [m/kg], and has the expresion: IMC = h/m (2) h is the height (length) of the segment [m];
2 614 m segment mass [kg]. For segmental density can be made the following observations: individual segments grow in density with increasing density of the whole body; upper and lower limbs were much greater than the density of the whole body; the proximal segments are less dense than the distal segments. The distribution of masses of human body segments can be calculated using data from the literature, according to table 1. Table 1. Coefficient of mass segmentation Crt. Mass/ Density No. Total Body [kg/dm 3 ] Mass 1. Hand Forearm Arm Forarm and Hand Upper limb Leg Shank Thigh Leg and Shank Lower limb Head and neck Shoulder Thorax Abdomen Pelvis Thorax and Abdomen 17. Abdomen and Pelvis Torso Torso, head, neck BIOMECHANICAL MODEL OF HUMAN BODY, SUBJECTED TO VIBRATION Modeling human body presumes the following steps: 1. ation of the body; 2. Determine the values of the masses, rigidities and depreciation of individual segments. Thay are made in this paper ation of the body It proposes a biomechanical model of human body subjected to vibration produced by a vibrant platform. The figure 1 illustrates the human body posture sitting on the vibrating platform. Fig. 1. Human body posture sitting on the vibrating platform. It is considered that in this position, the area most exposed to vibration is the range of the legs up to his chest. Therefore, they are not taken into account the arms, neck and head. This part of the body is divided into six segments (Fig. 2). Fig. 2. ed biodynamic model of the human body. The segments masses are: m1 mass of the dorsal leg; m2 mass of the crurale of the previous leg (the calf of the leg); m3 mass of the femoral leg; m4 mass of the leg buttocks ; m5 mass of the abdomen; m6 mass of the thorax Initial conditions Vibrating Platform Vibrating Platform The initial conditions are: the masses of segmentation are concentrated in the centres of gravity; the system mass remains constant
3 615 during the vibratory movement; the forces of elasticity and damping acting on the gravity centre of each segment; elasticity characteristics are linear; depreciation is viscous; body segments are connected in series with each other; to calculate the dimensional properties of elasticity and damping, the segments of the body are considered geometrical bodies shaped ellipsoid (Fig.3), because this geometry most closely resemble the geometry of the human body segments [5]. Fig. 3. Ellipsoidal segment. a, b, c half-axes of ellipsoid [3]. 3. MODE OF WORK Half-axes corresponding to human body segments (Fig. 2), for a subject with 90kg weight and 1,79m high, are presented in table 2. Table 2. Dimensions of ellipsoids corresponding to segments of biodynamic model a b c [cm] [cm] [cm] Leg The femoral The gluteal Abdomen Torax Determination of segments masses Masses of human body segments (90kg) according to the indications in table 1 are given in table 3. Table 3. Masses of a human body segmentation of 90 kg Mass of [kg] Leg m 1= m 2= The femoral m 3= 9 The gluteal m 4= Abdomen m 5= Thorax m 6= Determination of segments ellasticities Elastic constants, vertical and horizontal, each segment individually, shall be calculated using the formulae [9]: π E a b sv = (3) c I π E a c sh = (4) b I The notations in the (3), and (4) relations are: sv vertical elastic constant [N/m]; sh horizontal elastic constant [N/m]; a, b, c half-axes of the ellipsoidal segment; I integrator factor, I = 3.66; E longitudinal ellasticity constant [N/m 2 ], which need to compute with relation [10]: E = EbVb + EtVt (5) Or, simplifing [5]: 3 2 = b t (6) E E E The symbols in the (5) and (6) relations are: Eb = 26 kn/m 2 the elasticity module of the bone; Et = 7.5 kn/m 2 the elasticity module of the muscle tissue; Vb the volum of the bone; Vt the volum of the muscle tissue. Elasticity compenents of the human body segments in vertical and horinzontal directions are given in the table 4. Table 4. Elasticity constants of a human body segmentation Elasticity constant [N/m] vertical horizontal Leg s 1v =1.777 x 10 5 s 1h =0.117 x 10 5 s 2v =0.403 x 10 5 s 2h = x 10 5 The femoral s 3v =0.473 x 10 5 s 3h = x 10 5 The gluteal s 4v =7.314 x 10 5 s 4h =0.343 x 10 5 Abdomen s 5v =2.125 x 10 5 s 5h =0.980 x 10 5 Thorax s 6v =1.751 x 10 5 s 6h =2.573 x 10 5 Elasticity constants of body segments through graphical representation leading to achievement of Figure 4.
4 616 8 Constanta de elasticitate Elasticity Constant [N/m] *10 5 [N/m] Vertical Verticala Horizontal Orizontala 0 Leg Picior Lower leg Regiunea gambei Femoral Regiunea femurală Gluteal Regiunea fesieră Abdomen Thorax Torace Fig. 4. Chart of elasticity constants variation for the human body segments The graph in Figure 4 represent the variation of elasticity constants of biomechanical model segments proposed on the vertical and horizontal directions. It is noted that, in the direction of the horizontal, the most elastic area is that of the corresponding segment of the thorax, and is the most rigid of the foot. Vertical direction, the more elastic is the area of the segment corresponding to the pelvis, and it is the most rigid of the lower leg. In areas of the s of the lower leg, chest, and femoral constants of elasticity in the direction of horizontal upper values compared with the constants of elasticity on the vertical direction and vice versa, in the buttocks and abdominal s areas Determination of damping constants Damping constants, each segment individually, depends on the coefficient of viscosity of the blood and the size of the segment. Blood viscosity depends on the concentration of erythrocyte sedimentation, which increases resistance to blood flow. Blood viscosity decreases when flow velocity increases. This property defines the blood as pseudoplastic fluid and it is nenewtonian because blood is not a homogeneous fluid, is a suspension [12]. Coefficient of viscosity is measured in the Poiseuille (1 Poiseuille (1) = 1 Ns/m2). Unit commonly used is called poise (1 poise (p) = 10-1 Ns/m2). Blood viscosity varies most with temperature and with the number of red blood cells per unit volume. Blood viscosity values, at the normal temperature of the body shall be between 0.02 and 0.04 P [8]. Damping constants, segmental, is calculated using the expression [6]: 12µ A l β = (7) π 3 Dm e The notations are: β damping constant of a single segment [Ns/m]; µ the viscosity coefficient blood, µ=0.003 Ns/m 2 ; A segment aria [cm 2 ] (Table 5); Dm the average diameter of the segment [cm] (Tabel 6); l the average length of a segment [cm] (Tabel 6); e - eccentricity ellipse corresponding to a segment (Table 7). The area of an ellipsoid is determined with the formula's Knud Thomsen [7]: ( a b) + ( a c) + ( b c) A = 4π 3 The results are given in the Table (8)
5 617 Segm ent Aria [cm 2 ] Table 5. Surface areas biodynamic model segments Leg Lowe Femor Glute Abdo Thora r Leg al al men x Regio Regi Regio n on n Average lenghts and diametres of biodynamic model segments lv Table 6. Dv lh Dh [cm] [cm] [cm] [cm] Leg The femoral The gluteal Abdomen Thorax For a person of 1.79 m, lengths and diameters of the body segments, vertical and horizontal direction, are given in table 6. Table 7 contains the values of the corresponding ellipses prezentată de body segments taken into account for biomechanical model proposed. Table 7. The eccentricity ellipses of biodynamic model segments ev eh Leg 4%D v = % D h = % D v = % D h = The femoral 4% D v = % D h = The gluteal 1% D v = % D h = Abdomen 6% D v = % D h = Thorax 6% D v = % D h = Damping constants, components on the vertical and horizontal direction, the model proposed for the segments are given biodynamic in table 8. Table 8. Damping constants of biodynamic model segments Damping constants [Ns/m] vertical horizontal Leg β 1v = β 1h = 43.5 β 2v = β 2h =251.5 The femoral β 3v = β 3h = The gluteal β 4v = β 4h = 3.6 Abdomen β 5v = β 5h = 44.4 Thorax β 6v = β 6h = Constanta de amortizare [Ns/m] Verticala Orizontala Picior Regiunea gambei Regiunea femurală Regiunea fesieră Abdomen Torace Fig. 5. Graph of the damping constants variation of body segments The graph in Figure 5 represents the damping constants variation of component segments of biomechanical model proposed, on the vertical and horizontal directions.
6 618 It can be observed that, both in the direction of the horizontal and vertical direction, amorizarea has the maximum value in the corresponding segment femoral area and minimum in the area corresponding to the buttocks segment. In areas of the s of the abdomen and buttocks, feet, damping constants, the horizontal direction towards higher values of elastic constants on the vertical direction and vice versa, in areas of the s of the lower leg, thigh and chest. 4. CONCLUSIONS CONCERNING THE LOCATION OF THE MEASUREMENTS In this work it is proposed a new biomechanical model of human body in order to study the action of mechanical vibrations, if we consider the body on a vibrating platform. Body requested the vibrations is comprised of six distinct segments: foot, leg, femoral, of gluteal muscles, abdomen and thorax. As presented in Figure 2, the system has ten degrees of freedom. It is necessary to study the vibration setting mechanical properties: mass, damping and elasticity, which was done in this paper, for a subject of 90 kg and 1.79 m tall. 5. BIBLIOGRAPHY [1] Arghir Mariana, Mechanics. Statics & material point kinematics, 186 pag., Editura U.T.Press, ISBN , Cluj-Napoca, [2] Arghir Mariana, Mechanics. Rigid Body Kinematics & Dinamics, 240 pag., Editura U.T.Press, ISBN , Cluj-Napoca, [3] Budescu E., Biomecanica generală, 105 pag., Iasi, [4] Cochrane D. J., The Effect of Vibration Exercise on Aspects of Muscle Physiology and Muscular Performance, Doctoral thesis, Massey University, Palmerston N orth, Noua Zeelanda, [5] Griffin, M.J, Handbook of Human Vibration, Human Factors Research Unit, Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, The Univerity, Southampton, Academic Press, pag , 1990, U.K. [6] Griffin, M.J., The validation of biodynamic models, Clinical Biomechanics 16 Supplement Nr. 1, pag , Elsevier Science Ltd., 2001, U.K. [7] [8] [9] Mayank Mishra, Evaluation of Damping Coefficients of a Vibratory Model of Human Body, Master of Engineering in CAD/CAM & ROBOTICS, under the guidance of Dr. S. P. Nigam, Thapar University, India, [10] Rasmussen J., Andersen M. S., Musculoskeletal modelling of low-frequency whole-body vibrations, Joint Baltic-Nordic Acoustics Meeting, June 18th- 20th Odese, Danemarca, [11] SR ISO , Răspunsul uman la vibraţii. Aparatură de măsurare, [12] Truţa Aurica, Arghir Mariana, Noţiuni de biomecanica organismului uman în mediu vibraţional, Ed. Arcadia Media, Cluj - Napoca, 2010 ISBN [13] Urs Simona, Teza de doctorat Studiul privind influenţa vibraţiilor asupra organismului uman din punct de vedere fiziologic şi / sau funcţional, conducător ştiinţific Arghir Mariana, Cluj-Napoca, [14] Sergiu VESCAN, Mariana ARGHIR, The Biodynamic Model of Human Body, ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS; Series: Applied Mathematics, Mechanics, and Engineering, Vol. 57, Issue I, Pag , Ed. UT Pres, ISSN , Cluj-Napoca, March, Contribuţii la studiul caracteristicilor mecanice ale corpului uman Rezumat: Prin lucrarea prezentă se doreşte sǎ se realizeze o evaluare cantitativǎ a caracteristicilor mecanice ale corpului uman. Studiul face parte dintro activitate de cercetare, prin care se analizeazǎ acţiunea vibraţiilor mecanice asupra organismului uman. Acest studiu constituie partea de început a cercetǎrii ştiintifice, prin care se abordeazǎ întro manierǎ proprie determinarea caracteristicilor mecanice ale segmentelor corpului uman. Se vor obţine caracteristicile de: masǎ, amortizor şi elasticitate ale segmentelor, ce vor fi supuse ulterior la vibraţii, teoretic şi practic. Sergiu Dan VESCAN, PhD Student, Department of Engineering Mechanical Systems, UTCN, e- mail: sergiu_ro_2000@yahoo.com, Office Phone Mariana ARGHIR, Prof. Dr. Eng., Department of Engineering Mechanical Systems, UTCN, Mariana.Arghir@mep.utcluj.ro, Office Phone
ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS
 32 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics, Mechanics, and Engineering Vol. 9, Issue III, September, 2016 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY OF LOWER LIMB BIOMECHANICS
32 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics, Mechanics, and Engineering Vol. 9, Issue III, September, 2016 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY OF LOWER LIMB BIOMECHANICS
Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems
 Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems Lecture 6 Presented by Phillip Tran AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 The Musculoskeletal System The University of Sydney
Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems Lecture 6 Presented by Phillip Tran AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 The Musculoskeletal System The University of Sydney
ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS
 471 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics, Mechanics, and Engineering Vol. 57, Issue III, September, 2014 THEORETICAL DETERMINATION OF A VEHICLE VIBRATIONS
471 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics, Mechanics, and Engineering Vol. 57, Issue III, September, 2014 THEORETICAL DETERMINATION OF A VEHICLE VIBRATIONS
τ = F d Angular Kinetics Components of Torque (review from Systems FBD lecture Muscles Create Torques Torque is a Vector Work versus Torque
 Components of Torque (review from Systems FBD lecture Angular Kinetics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 11) Hay (Ch. 6), Hay & Ried (Ch. 12), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module I & J) or Hall (Ch. 13 & 14) axis of rotation
Components of Torque (review from Systems FBD lecture Angular Kinetics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 11) Hay (Ch. 6), Hay & Ried (Ch. 12), Kreighbaum & Barthels (Module I & J) or Hall (Ch. 13 & 14) axis of rotation
STUDY OF EFFECTS OF VIBRATIONS CAUSED BY RAILWAY TRAFFIC TO BUILDINGS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov CIBv 2014 Vol. 7 (56) Special Issue No. 1-2014 STUDY OF EFFECTS OF VIBRATIONS CAUSED BY RAILWAY TRAFFIC TO BUILDINGS R. NERIŞANU 1 D. DRĂGAN 1 M. SUCIU
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov CIBv 2014 Vol. 7 (56) Special Issue No. 1-2014 STUDY OF EFFECTS OF VIBRATIONS CAUSED BY RAILWAY TRAFFIC TO BUILDINGS R. NERIŞANU 1 D. DRĂGAN 1 M. SUCIU
A CONTINUOUS MODEL FOR THE VERTICAL VIBRATION OF THE HUMAN BODY IN A STANDING POSITION
 ABSTRACT A CONTINUOUS MODEL FOR THE VERTICAL VIBRATION OF THE HUMAN BODY IN A STANDING POSITION Tianjian Ji Building Research Establishment, Watford, UK This paper is concerned with modelling the vertical
ABSTRACT A CONTINUOUS MODEL FOR THE VERTICAL VIBRATION OF THE HUMAN BODY IN A STANDING POSITION Tianjian Ji Building Research Establishment, Watford, UK This paper is concerned with modelling the vertical
Mechanical energy transfer by internal force during the swing phase of running
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 772 777 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Mechanical energy transfer by internal force
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 34 (2012 ) 772 777 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Mechanical energy transfer by internal force
BIODYNAMICS: A LAGRANGIAN APPROACH
 Source: STANDARD HANDBOOK OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN CHAPTER 7 BIODYNAMICS: A LAGRANGIAN APPROACH Donald R. Peterson Biodynamics Laboratory at the Ergonomic Technology Center, University of Connecticut
Source: STANDARD HANDBOOK OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN CHAPTER 7 BIODYNAMICS: A LAGRANGIAN APPROACH Donald R. Peterson Biodynamics Laboratory at the Ergonomic Technology Center, University of Connecticut
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics, LTH, 2013 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2013 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back
Biomechanics, LTH, 2013 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2013 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back
The main force acting on the body is the gravitational force!
 The main force acting on the body is the gravitational force! (W= weight!) W = m g Stability of the body against the gravitational force is maintained by the bone structure of the skeleton! Gravitational
The main force acting on the body is the gravitational force! (W= weight!) W = m g Stability of the body against the gravitational force is maintained by the bone structure of the skeleton! Gravitational
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
ifly Post Field Trip Activity Teacher Instructions Grades 6-8
 ifly Post Field Trip Activity Teacher Instructions Grades 6-8 Learning Outcomes: Use measured data to predict results Understand the variables that affect terminal velocity Use algebraic reasoning to solve
ifly Post Field Trip Activity Teacher Instructions Grades 6-8 Learning Outcomes: Use measured data to predict results Understand the variables that affect terminal velocity Use algebraic reasoning to solve
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline
 Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
ANTHROPOMETRY (İnsan Vücudunu Ölçme Bilimi)
 ANTHROPOMETRY (İnsan Vücudunu Ölçme Bilimi) Dr. Kurtuluş Erinç Akdoğan kurtuluserinc@cankaya.edu.tr INTRODUCTION Anthropometry is the major branch of anthropology (insan bilimi) that studies the physical
ANTHROPOMETRY (İnsan Vücudunu Ölçme Bilimi) Dr. Kurtuluş Erinç Akdoğan kurtuluserinc@cankaya.edu.tr INTRODUCTION Anthropometry is the major branch of anthropology (insan bilimi) that studies the physical
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology. I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES OF THE INFLUENCE OF HUMAN STANDING POSITIONS ON THE FEET-TO-HEAD TRANSMISSION OF VIBRATIONS
 JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED MECHANICS 52, 4, pp. 1107-1114, Warsaw 2014 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES OF THE INFLUENCE OF HUMAN STANDING POSITIONS ON THE FEET-TO-HEAD TRANSMISSION OF VIBRATIONS Marek A.
JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED MECHANICS 52, 4, pp. 1107-1114, Warsaw 2014 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES OF THE INFLUENCE OF HUMAN STANDING POSITIONS ON THE FEET-TO-HEAD TRANSMISSION OF VIBRATIONS Marek A.
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY
 The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
Identification of Joint Impedance
 Identification of Joint Impedance tools for understanding the human motion system, treatment selection and evaluation Lecture 12 SIPE 2010 Case Studies Erwin de Vlugt, PhD -Leiden Research Connection Laboratory
Identification of Joint Impedance tools for understanding the human motion system, treatment selection and evaluation Lecture 12 SIPE 2010 Case Studies Erwin de Vlugt, PhD -Leiden Research Connection Laboratory
II. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy is. B. Physiology is.
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING THE HD RADIAL BEARINGS IN THE CASE OF STATIC CHALLENGING WORKING
 7 th INTERNATIONAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY CONFERENCE Baia Mare, Romania, May 17-18, 2007 ISSN-1224-3264 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING THE HD RADIAL BEARINGS IN THE CASE OF STATIC CHALLENGING WORKING Marius
7 th INTERNATIONAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY CONFERENCE Baia Mare, Romania, May 17-18, 2007 ISSN-1224-3264 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING THE HD RADIAL BEARINGS IN THE CASE OF STATIC CHALLENGING WORKING Marius
BIOMECHANICS AND MOTOR CONTROL OF HUMAN MOVEMENT
 BIOMECHANICS AND MOTOR CONTROL OF HUMAN MOVEMENT Third Edition DAVID Α. WINTER University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. CONTENTS Preface to the Third Edition xv 1
BIOMECHANICS AND MOTOR CONTROL OF HUMAN MOVEMENT Third Edition DAVID Α. WINTER University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada WILEY JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. CONTENTS Preface to the Third Edition xv 1
VIBRATION TRANSMISSIBILITY BEHAVIOUR OF SIMPLE BIODYNAMIC MODELS USED IN VEHICLE SEAT DESIGN
 TECHNICAL TRANSACTIONS MECHANICS CZASOPISMO TECHNICZNE MECHANIKA DOI: 10.4467/2353737XCT.16.281.6113 5-M/2016 NIRESH BEHARI *, MARCIN NOGA ** VIBRATION TRANSMISSIBILITY BEHAVIOUR OF SIMPLE BIODYNAMIC MODELS
TECHNICAL TRANSACTIONS MECHANICS CZASOPISMO TECHNICZNE MECHANIKA DOI: 10.4467/2353737XCT.16.281.6113 5-M/2016 NIRESH BEHARI *, MARCIN NOGA ** VIBRATION TRANSMISSIBILITY BEHAVIOUR OF SIMPLE BIODYNAMIC MODELS
PART I ORTHOPAEDIC BIOMATERIALS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
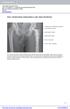 PT I OTHOPEDIC BIOMTEILS ND THEI POPETIES cetabular Cup: Polyethylene (polymer) emoral Head: Ceramic Bone Cement: Polymer emoral Stem: Metal emur: Composite emur + Stem: Composite Just as there are three
PT I OTHOPEDIC BIOMTEILS ND THEI POPETIES cetabular Cup: Polyethylene (polymer) emoral Head: Ceramic Bone Cement: Polymer emoral Stem: Metal emur: Composite emur + Stem: Composite Just as there are three
Angular Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed
 Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Biomechanical Model: Mo3on Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Sum of Joint Linear Speeds Principle
Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Biomechanical Model: Mo3on Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Sum of Joint Linear Speeds Principle
MODELING BIOMECHANICAL INTERACTION HUMAN - SMALL ARMS
 MODELING BIOMECHANICAL INTERACTION HUMAN - SMALL ARMS Ľubomír UHERÍK* Faculty of Special Technology, Alexander Dubček University of Trenčín, Pri Parku 19, 911 05, Trenčín, Slovakia *Corresponding author
MODELING BIOMECHANICAL INTERACTION HUMAN - SMALL ARMS Ľubomír UHERÍK* Faculty of Special Technology, Alexander Dubček University of Trenčín, Pri Parku 19, 911 05, Trenčín, Slovakia *Corresponding author
ME 176 Final Exam, Fall 1997
 Tuesday, December 16, 5:00 8:00 PM, 1997. Answer all questions for a maximum of 100 points. Please write all answers in the space provided. If you need additional space, write on the back sides. Indicate
Tuesday, December 16, 5:00 8:00 PM, 1997. Answer all questions for a maximum of 100 points. Please write all answers in the space provided. If you need additional space, write on the back sides. Indicate
Angular Kinetics. Learning Objectives: Learning Objectives: Properties of Torques (review from Models and Anthropometry) T = F d
 Angular Kinetics Readings: Chapter 11 [course text] Hay, Chapter 6 [on reserve] Hall, Chapter 13 & 14 [on reserve] Kreighbaum & Barthels, Modules I & J [on reserve] 1 Learning Objectives: By the end of
Angular Kinetics Readings: Chapter 11 [course text] Hay, Chapter 6 [on reserve] Hall, Chapter 13 & 14 [on reserve] Kreighbaum & Barthels, Modules I & J [on reserve] 1 Learning Objectives: By the end of
UNIT V : DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND MODEL STUDIES
 UNIT V : DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND MODEL STUDIES 1. Define dimensional analysis. Dimensional analysis is a mathematical technique which makes use of the study of dimensions as an aid to solution of several
UNIT V : DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND MODEL STUDIES 1. Define dimensional analysis. Dimensional analysis is a mathematical technique which makes use of the study of dimensions as an aid to solution of several
Section 6: 6: Kinematics Kinematics 6-1
 6-1 Section 6: Kinematics Biomechanics - angular kinematics Same as linear kinematics, but There is one vector along the moment arm. There is one vector perpendicular to the moment arm. MA F RMA F RD F
6-1 Section 6: Kinematics Biomechanics - angular kinematics Same as linear kinematics, but There is one vector along the moment arm. There is one vector perpendicular to the moment arm. MA F RMA F RD F
Received May 30, 2009 and accepted June 25, 2010
 Industrial 654 Health 2010, 48, 654 662 MGR Original TOWARD Article et al. A Variable Parameter Single Degree-of-freedom Model for Predicting the Effects of Sitting Posture and Vibration Magnitude on the
Industrial 654 Health 2010, 48, 654 662 MGR Original TOWARD Article et al. A Variable Parameter Single Degree-of-freedom Model for Predicting the Effects of Sitting Posture and Vibration Magnitude on the
An Indian Journal FULL PAPER ABSTRACT KEYWORDS. Trade Science Inc.
 [Type text] [Type text] [Type text] ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 10 Issue 12 BioTechnology 2014 An Indian Journal FULL PAPER BTAIJ, 10(12), 2014 [6844-6850] Man-gun model of shoulder supported firing and sensitivity
[Type text] [Type text] [Type text] ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 10 Issue 12 BioTechnology 2014 An Indian Journal FULL PAPER BTAIJ, 10(12), 2014 [6844-6850] Man-gun model of shoulder supported firing and sensitivity
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Class XI Physics Syllabus One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70
 Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
MODEL FOR FLEXIBLE PLATES SUPPORTED ON PILES
 BULETINUL INSTITUTULUI POLITEHNIC DIN IAŞI Publicat de Universitatea Tehnică,,Gheorghe Asachi din Iaşi Tomul LV (LIX), Fasc. 1, 2009 Secţia CONSTRUCŢII. ARHITECTURĂ MODEL FOR FLEXIBLE PLATES SUPPORTED
BULETINUL INSTITUTULUI POLITEHNIC DIN IAŞI Publicat de Universitatea Tehnică,,Gheorghe Asachi din Iaşi Tomul LV (LIX), Fasc. 1, 2009 Secţia CONSTRUCŢII. ARHITECTURĂ MODEL FOR FLEXIBLE PLATES SUPPORTED
of Rigid Segments Global or Laboratory Coordinate System 36 } Research Methods in Biomechanics
 36 } Research Methods in Biomechanics Camera 5 Camera 6 Camera 4 Direction of motion Calibrated 3-D space Camera 1 Camera 3 Computer Camera 2 Figure 2.1 Typical multicamera setup for a 3-D kinematic analysis.
36 } Research Methods in Biomechanics Camera 5 Camera 6 Camera 4 Direction of motion Calibrated 3-D space Camera 1 Camera 3 Computer Camera 2 Figure 2.1 Typical multicamera setup for a 3-D kinematic analysis.
Multi-body power analysis of kicking motion based on a double pendulum
 Available online at wwwsciencedirectcom Procedia Engineering 34 (22 ) 28 223 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Multi-body power analysis of kicking motion based
Available online at wwwsciencedirectcom Procedia Engineering 34 (22 ) 28 223 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Multi-body power analysis of kicking motion based
ATTENUATION OF THE ACOUSTIC SCREENS IN CLOSED SPACES
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 69, No. 3, 007 ISSN 15-358 ATTENUATION OF THE ACOUSTIC SCREENS IN CLOSED SPACES Ioan MAGHEŢI 1, Mariana SAVU Lucrarea prezintă calculul atenuării acustice a unui ecran
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 69, No. 3, 007 ISSN 15-358 ATTENUATION OF THE ACOUSTIC SCREENS IN CLOSED SPACES Ioan MAGHEŢI 1, Mariana SAVU Lucrarea prezintă calculul atenuării acustice a unui ecran
machine design, Vol.9(2017) No.3, ISSN pp
 machine design, Vol.9(2017) No.3, ISSN 1821-1259 pp. 81-86 DOI: 10.24867/MD.9.2017.3.81-86 Research paper GEOMETRY OF HUMAN BODY MODEL USED FOR SIMULATION OF THERMAL COMFORT IN AN AGRICULTURAL VEHICLE
machine design, Vol.9(2017) No.3, ISSN 1821-1259 pp. 81-86 DOI: 10.24867/MD.9.2017.3.81-86 Research paper GEOMETRY OF HUMAN BODY MODEL USED FOR SIMULATION OF THERMAL COMFORT IN AN AGRICULTURAL VEHICLE
U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014
 U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014 Epidemiology and Disease Surveillance Portfolio Injury Prevention Program Website: http://phc.amedd.army.mil/organization/hq/deds/pages/injurypreventionprogram.aspx
U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014 Epidemiology and Disease Surveillance Portfolio Injury Prevention Program Website: http://phc.amedd.army.mil/organization/hq/deds/pages/injurypreventionprogram.aspx
D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for
 D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for 2017-2018 UNIT NAME OF UNIT WEIGHTAGE 1. 2. 3. Physical World and Measurement Kinemetics Laws of Motion
D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for 2017-2018 UNIT NAME OF UNIT WEIGHTAGE 1. 2. 3. Physical World and Measurement Kinemetics Laws of Motion
A NEW HUMAN THERMAL MODEL
 A NEW HUMAN THERMAL MODEL Eugene H. Wissler The University of Texas at Austin Austin, Texas USA ehwissler@mail.utexas.edu INTRODUCTION Mathematical human thermal models serve important functions, both
A NEW HUMAN THERMAL MODEL Eugene H. Wissler The University of Texas at Austin Austin, Texas USA ehwissler@mail.utexas.edu INTRODUCTION Mathematical human thermal models serve important functions, both
Mitigations to Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) in Control Valve Piping System using Visco-Elastic Dampers & Neoprene Pads
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 07 January 2017 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Mitigations to Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) in Control Valve Piping System using
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 07 January 2017 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Mitigations to Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) in Control Valve Piping System using
The Biomechanics Behind Kicking a Soccer Ball
 VANIER COLLEGE The Biomechanics Behind Kicking a Soccer Ball The Energy Demands of the Body Raymond You Linear Algebra II Ivan T. Ivanov 5/19/2013 1 What is Inertia? Inertia is defined as an object s resistance
VANIER COLLEGE The Biomechanics Behind Kicking a Soccer Ball The Energy Demands of the Body Raymond You Linear Algebra II Ivan T. Ivanov 5/19/2013 1 What is Inertia? Inertia is defined as an object s resistance
HPER K530 Mechanical Analysis of Human Performance Fall, 2003 MID-TERM
 HPER K530 Mechanical Analysis of Human Performance Fall, 2003 Dapena MID-TERM Equations: S = S 0 + v t S = S 0 + v 0 t + 1/2 a t 2 v = v 0 + a t v 2 = v 2 0 + 2 a (S-S 0 ) e = h b /h d F CP = m v 2 / r
HPER K530 Mechanical Analysis of Human Performance Fall, 2003 Dapena MID-TERM Equations: S = S 0 + v t S = S 0 + v 0 t + 1/2 a t 2 v = v 0 + a t v 2 = v 2 0 + 2 a (S-S 0 ) e = h b /h d F CP = m v 2 / r
Forces on and in the Body
 Forces on and in the Body Physicists recognize four fundamental forces. In order of their relative strength from weakest to strongest. They are: 1- Gravitational force 2- Electrical force 3- Weak nuclear
Forces on and in the Body Physicists recognize four fundamental forces. In order of their relative strength from weakest to strongest. They are: 1- Gravitational force 2- Electrical force 3- Weak nuclear
Nonlinear Vibrations of Elastic Beams
 Acta Technica Napocensis: Civil Engineering & Architecture Vol. 56, No. 1, (2013) Journal homepage: http://constructii.utcluj.ro/actacivileng Nonlinear Vibrations of Elastic Beams Iacob Borş 1, Tudor Milchiş
Acta Technica Napocensis: Civil Engineering & Architecture Vol. 56, No. 1, (2013) Journal homepage: http://constructii.utcluj.ro/actacivileng Nonlinear Vibrations of Elastic Beams Iacob Borş 1, Tudor Milchiş
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 13: ROTATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
!! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
Simulation of Geometrical Cross-Section for Practical Purposes
 Simulation of Geometrical Cross-Section for Practical Purposes Bhasker R.S. 1, Prasad R. K. 2, Kumar V. 3, Prasad P. 4 123 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.D. Engineering College, Ghaziabad, UP,
Simulation of Geometrical Cross-Section for Practical Purposes Bhasker R.S. 1, Prasad R. K. 2, Kumar V. 3, Prasad P. 4 123 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.D. Engineering College, Ghaziabad, UP,
ASSISTED RESEARCH OF THE FOURIER SPECTRUM OF THE ROBOTS WITH MAGNETORHEOLOGICAL DAMPER
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 72, Iss. 3, 2010 ISSN 1454-2358 ASSISTED RESEARCH OF THE FOURIER SPECTRUM OF THE ROBOTS WITH MAGNETORHEOLOGICAL DAMPER Şerban OLARU 1, Aurel OPREAN 2, Adrian OLARU 3 În
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 72, Iss. 3, 2010 ISSN 1454-2358 ASSISTED RESEARCH OF THE FOURIER SPECTRUM OF THE ROBOTS WITH MAGNETORHEOLOGICAL DAMPER Şerban OLARU 1, Aurel OPREAN 2, Adrian OLARU 3 În
Dynamic Response of Beams on Elastic Foundation with Axial Load
 Acta Technica Napocensis: Civil Engineering & Architecture Vol. 56, No. 1, (2013) Journal homepage: http://constructii.utcluj.ro/actacivileng Dynamic Response of Beams on Elastic Foundation with Axial
Acta Technica Napocensis: Civil Engineering & Architecture Vol. 56, No. 1, (2013) Journal homepage: http://constructii.utcluj.ro/actacivileng Dynamic Response of Beams on Elastic Foundation with Axial
ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS
 101 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Vol. 54, Issue I, 2011 MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND PROGRAM FOR ANALYZING THE THERMOREFRACTORY INSULATION
101 TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CLUJ-NAPOCA ACTA TECHNICA NAPOCENSIS Series: Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Vol. 54, Issue I, 2011 MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND PROGRAM FOR ANALYZING THE THERMOREFRACTORY INSULATION
Anthropometry Formulas
 Anthropometry Formulas W. Rose KAAP47/67 Segment Dimensions FF = mmmm, dddd dddd = FF mm ττ = IIII, dddd dddd = ττ II Length of body segments is often obtainable by direct measurement. If not, the segment
Anthropometry Formulas W. Rose KAAP47/67 Segment Dimensions FF = mmmm, dddd dddd = FF mm ττ = IIII, dddd dddd = ττ II Length of body segments is often obtainable by direct measurement. If not, the segment
Lab #7 - Joint Kinetics and Internal Forces
 Purpose: Lab #7 - Joint Kinetics and Internal Forces The objective of this lab is to understand how to calculate net joint forces (NJFs) and net joint moments (NJMs) from force data. Upon completion of
Purpose: Lab #7 - Joint Kinetics and Internal Forces The objective of this lab is to understand how to calculate net joint forces (NJFs) and net joint moments (NJMs) from force data. Upon completion of
Jurong Junior College 2014 J1 H1 Physics (8866) Tutorial 3: Forces (Solutions)
 Jurong Junior College 2014 J1 H1 Physics (8866) Tutorial 3: Forces (Solutions) Take g = 9.81 m s -2, P atm = 1.0 x 10 5 Pa unless otherwise stated Learning Outcomes (a) Sub-Topic recall and apply Hooke
Jurong Junior College 2014 J1 H1 Physics (8866) Tutorial 3: Forces (Solutions) Take g = 9.81 m s -2, P atm = 1.0 x 10 5 Pa unless otherwise stated Learning Outcomes (a) Sub-Topic recall and apply Hooke
Models and Anthropometry
 Learning Objectives Models and Anthropometry Readings: some of Chapter 8 [in text] some of Chapter 11 [in text] By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: Describe common anthropometric measurements
Learning Objectives Models and Anthropometry Readings: some of Chapter 8 [in text] some of Chapter 11 [in text] By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: Describe common anthropometric measurements
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
What is a Skeleton? SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Lesson Curriculum K 5 th Grade 55 Minute Program
 Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
DIVIDED SYLLABUS ( ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL
 DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
EXPERIMENTAL ASSESSMENT CONCERNING THE HD RADIAL BEARINGS IN THE CASE OF DYNAMIC CHALLENGING WORKING
 THE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF THE CARPATHIAN EURO-REGION SPECIALIST IN INDUSTRIAL SYSTEMS 6 th edition EXPERIMENTAL ASSESSMENT CONCERNING THE HD RADIAL BEARINGS IN THE CASE OF DYNAMIC CHALLENGING WORKING
THE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF THE CARPATHIAN EURO-REGION SPECIALIST IN INDUSTRIAL SYSTEMS 6 th edition EXPERIMENTAL ASSESSMENT CONCERNING THE HD RADIAL BEARINGS IN THE CASE OF DYNAMIC CHALLENGING WORKING
Simple Biomechanical Models. Introduction to Static Equilibrium F F. Components of Torque. Muscles Create Torques. Torque is a Vector
 Simple Biomechanical Models Introduction to Static Equilibrium Components of Torque axis of rotation (fulcrum) force (not directed through axis of rotation) force (moment) arm T = F x d force arm Muscles
Simple Biomechanical Models Introduction to Static Equilibrium Components of Torque axis of rotation (fulcrum) force (not directed through axis of rotation) force (moment) arm T = F x d force arm Muscles
Skeletal 2 - joints. Puzzle 1 bones
 Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
POLAR CHARACTERISTIC OF ENERGETIC INTENSITY EMITTED BY AN ANISOTROPIC THERMAL SOURCE IRREGULARLY SHAPED
 Annals of the Academ of Romanian Scientists Series on Science and Technolog of nformation SSN 066-856 Volume 1, Number 1/008 43 POLAR CHARACTERSTC OF ENERGETC NTENSTY EMTTED BY AN ANSOTROPC THERMAL SOURCE
Annals of the Academ of Romanian Scientists Series on Science and Technolog of nformation SSN 066-856 Volume 1, Number 1/008 43 POLAR CHARACTERSTC OF ENERGETC NTENSTY EMTTED BY AN ANSOTROPC THERMAL SOURCE
Center of Mass of Human s Body Segments
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 21, No. 3 2017 485 497 c Lodz University of Technology Center of Mass of Human s Body Segments Melvin Adolphe Joseph Clerval Zbyszko Kirchof Robin Lacombe Delpech
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 21, No. 3 2017 485 497 c Lodz University of Technology Center of Mass of Human s Body Segments Melvin Adolphe Joseph Clerval Zbyszko Kirchof Robin Lacombe Delpech
Lecturer, Department t of Mechanical Engineering, SVMIT, Bharuch
 Fluid Mechanics By Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Department t of Mechanical Engineering, i SVMIT, Bharuch Review of fundamentals Properties of Fluids Introduction Any characteristic of a system is called a
Fluid Mechanics By Ashish J. Modi Lecturer, Department t of Mechanical Engineering, i SVMIT, Bharuch Review of fundamentals Properties of Fluids Introduction Any characteristic of a system is called a
1817. Research of sound absorption characteristics for the periodically porous structure and its application in automobile
 1817. Research of sound absorption characteristics for the periodically porous structure and its application in automobile Xian-lin Ren School of Mechatronics Engineering, University of Electronic Science
1817. Research of sound absorption characteristics for the periodically porous structure and its application in automobile Xian-lin Ren School of Mechatronics Engineering, University of Electronic Science
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
Human response of vertical and pitch motion to vertical vibration on whole body according to sitting posture
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 26 (8) (2012) 2477~2484 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-012-0626-x Human response of vertical and pitch motion to vertical vibration
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 26 (8) (2012) 2477~2484 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-012-0626-x Human response of vertical and pitch motion to vertical vibration
Homework of chapter (1) (Solution)
 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم The Islamic University of Gaza, Civil Engineering Department, Fluid mechanics-discussion, Instructor: Dr. Khalil M. Al Astal T.A: Eng. Mohammed H El Nazli Eng. Sarah R Rostom First
بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم The Islamic University of Gaza, Civil Engineering Department, Fluid mechanics-discussion, Instructor: Dr. Khalil M. Al Astal T.A: Eng. Mohammed H El Nazli Eng. Sarah R Rostom First
Various vehicle speeds and road profiles effects on transmitted accelerations analysis to human body segments using vehicle and biomechanical models
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Various vehicle speeds and road profiles effects on transmitted accelerations analysis to human body segments using vehicle and biomechanical models Somaye Jamali
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Various vehicle speeds and road profiles effects on transmitted accelerations analysis to human body segments using vehicle and biomechanical models Somaye Jamali
Kinesiology 201 Solutions Kinematics
 Kinesiology 201 Solutions Kinematics Tony Leyland School of Kinesiology Simon Fraser University 1. a) Vertical ocity = 10 sin20 = 3.42 m/s Horizontal ocity = 10 cos20 = 9.4 m/s B Vertical A-B (start to
Kinesiology 201 Solutions Kinematics Tony Leyland School of Kinesiology Simon Fraser University 1. a) Vertical ocity = 10 sin20 = 3.42 m/s Horizontal ocity = 10 cos20 = 9.4 m/s B Vertical A-B (start to
Fluid Properties and Units
 Fluid Properties and Units CVEN 311 Continuum Continuum All materials, solid or fluid, are composed of molecules discretely spread and in continuous motion. However, in dealing with fluid-flow flow relations
Fluid Properties and Units CVEN 311 Continuum Continuum All materials, solid or fluid, are composed of molecules discretely spread and in continuous motion. However, in dealing with fluid-flow flow relations
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Mathematical Model of Blood Flow in Carotid Bifurcation
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Mathematical Model of Blood Flow in Carotid Bifurcation E. Muraca *,1, V. Gramigna 1, and G. Fragomeni 1 1 Department of Experimental Medicine
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Mathematical Model of Blood Flow in Carotid Bifurcation E. Muraca *,1, V. Gramigna 1, and G. Fragomeni 1 1 Department of Experimental Medicine
Available online at ScienceDirect. The 2014 conference of the International Sports Engineering Association
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 72 ( 2014 ) 97 102 The 2014 conference of the International Sports Engineering Association Dynamic contribution analysis of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 72 ( 2014 ) 97 102 The 2014 conference of the International Sports Engineering Association Dynamic contribution analysis of
Physics 153 Introductory Physics II. Week One: FLUIDS. Dr. Joseph J. Trout
 Physics 153 Introductory Physics II Week One: FLUIDS Dr. Joseph J. Trout joseph.trout@drexel.edu 610-348-6495 States (Phases) of Matter: Solid: Fixed shape. Fixed size. Even a large force will not readily
Physics 153 Introductory Physics II Week One: FLUIDS Dr. Joseph J. Trout joseph.trout@drexel.edu 610-348-6495 States (Phases) of Matter: Solid: Fixed shape. Fixed size. Even a large force will not readily
STRUCTURAL INTENSITY METHOD APPLIED TO STUDY OF VIBRATIONS DAMPING / METODA INTENSIMETRIEI STUCTURALE APLICATĂ LA STUDIUL AMORTIZĂRII VIBRAŢIILOR
 Vol.48, No. / 06 STRUCTURAL INTENSITY METHOD APPLIED TO STUDY OF VIBRATIONS DAMPING / METODA INTENSIMETRIEI STUCTURALE APLICATĂ LA STUDIUL AMORTIZĂRII VIBRAŢIILOR Assoc. Prof. Ph.D. Eng. Carp-Ciocârdia
Vol.48, No. / 06 STRUCTURAL INTENSITY METHOD APPLIED TO STUDY OF VIBRATIONS DAMPING / METODA INTENSIMETRIEI STUCTURALE APLICATĂ LA STUDIUL AMORTIZĂRII VIBRAŢIILOR Assoc. Prof. Ph.D. Eng. Carp-Ciocârdia
Fluid Mechanics Introduction
 Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Mathematical Models and Numerical Simulations for the Blood Flow in Large Vessels
 Mathematical Models and Numerical Simulations for the Blood Flow in Large Vessels Balazs ALBERT 1 Titus PETRILA 2a Corresponding author 1 Babes-Bolyai University M. Kogalniceanu nr. 1 400084 Cluj-Napoca
Mathematical Models and Numerical Simulations for the Blood Flow in Large Vessels Balazs ALBERT 1 Titus PETRILA 2a Corresponding author 1 Babes-Bolyai University M. Kogalniceanu nr. 1 400084 Cluj-Napoca
The simulation of aerial. determination of the angular momentum of the human body. Loughborough University Institutional Repository
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository The simulation of aerial movementiii. The determination of the angular momentum of the human body This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository The simulation of aerial movementiii. The determination of the angular momentum of the human body This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
C 2 Continuous Gait-Pattern Generation for Biped Robots
 C Continuous Gait-Pattern Generation for Biped Robots Shunsuke Kudoh 1 Taku Komura 1 The University of Tokyo, JAPAN, kudoh@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp City University of ong Kong, ong Kong, taku@ieee.org Abstract
C Continuous Gait-Pattern Generation for Biped Robots Shunsuke Kudoh 1 Taku Komura 1 The University of Tokyo, JAPAN, kudoh@cvl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp City University of ong Kong, ong Kong, taku@ieee.org Abstract
Electrical Engineering 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials
 Electrical Engineering 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December, 2004 This examination
Electrical Engineering 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December, 2004 This examination
Considerations Concerning the Dynamics of Vibratory Mills Used in Powders Mechanical Milling Process
 ANALELE UNIVERSITĂłII EFTIMIE MURGU REŞIłA ANUL XVII, NR. 1, 21, ISSN 1453-7397 Radu Panaitescu-Liess, Amelitta Legendi, Cristian Pavel Considerations Concerning the Dynamics of Vibratory Mills Used in
ANALELE UNIVERSITĂłII EFTIMIE MURGU REŞIłA ANUL XVII, NR. 1, 21, ISSN 1453-7397 Radu Panaitescu-Liess, Amelitta Legendi, Cristian Pavel Considerations Concerning the Dynamics of Vibratory Mills Used in
Soil Dynamics Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Soil Dynamics Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 5 Machine Foundations Lecture - 31 EHS Theory, Vibrational Control Let us start our
Soil Dynamics Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 5 Machine Foundations Lecture - 31 EHS Theory, Vibrational Control Let us start our
PhD Thesis RESEARCH ON CAPACITIVE MEASUREMENT PRINCIPLES FOR LIQUID LEVELS. Abstract
 Investeşte în oameni! FONDUL SOCIAL EUROPEAN Programul Operaţional Sectorial Dezvoltarea Resurselor Umane 2007 2013 Axa prioritară: 1 Educaţia şi formarea profesională în sprijinul creşterii economice
Investeşte în oameni! FONDUL SOCIAL EUROPEAN Programul Operaţional Sectorial Dezvoltarea Resurselor Umane 2007 2013 Axa prioritară: 1 Educaţia şi formarea profesională în sprijinul creşterii economice
Statics. Phys101 Lectures 19,20. Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain. Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5.
 Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Problem Set x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Problem Set 10 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer (a) A thin uniform disc of mass M and radius R is mounted on an axis passing
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Problem Set 10 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer (a) A thin uniform disc of mass M and radius R is mounted on an axis passing
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Effect on the Flow of Bile Due to Radially Varying Viscosity in the Cystic Duct
 International Journal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical esearch (IJSIM) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 24, PP 8-85 ISSN 2347-37X (Print) & ISSN 2347-342 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Effect on the
International Journal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical esearch (IJSIM) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 24, PP 8-85 ISSN 2347-37X (Print) & ISSN 2347-342 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Effect on the
Low-level Fall Simulation: Toddler Falling From Chair
 Low-level Fall Simulation: Toddler Falling From Chair R. J. Reimann Professor Emeritus of Physics Boise State University 11 June 2012 (rev. 7/9/2013) This simulation was generated using Working Model software
Low-level Fall Simulation: Toddler Falling From Chair R. J. Reimann Professor Emeritus of Physics Boise State University 11 June 2012 (rev. 7/9/2013) This simulation was generated using Working Model software
Modeling of Lumber Vertebrae of Spine Using Bondgraphs
 Indian Journal of Biomechanics: Special Issue (NCBM 7-8 March 009) Modeling of Lumber Vertebrae of Spine Using Bondgraphs Pratibha Tyagi 1, Vikas Rastogi, Ajat Shatru Arora 3 1 Sant Longowal Institute
Indian Journal of Biomechanics: Special Issue (NCBM 7-8 March 009) Modeling of Lumber Vertebrae of Spine Using Bondgraphs Pratibha Tyagi 1, Vikas Rastogi, Ajat Shatru Arora 3 1 Sant Longowal Institute
Table of Contents. Preface... 13
 Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.1 Composite Functions and Inverse Functions
 Intermediate Algebra Section 9. Composite Functions and Inverse Functions We have added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided functions in previous chapters. Another way to combine functions is called composite
Intermediate Algebra Section 9. Composite Functions and Inverse Functions We have added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided functions in previous chapters. Another way to combine functions is called composite
FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE Av. de la Gare Lausanne Suisse Tél. (41-32) Fax (41-32)
 FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE Av. de la Gare 12 1003 Lausanne Suisse Tél. (41-32) 494 64 10 Fax (41-32) 494 64 19 e-mail: info@fig-gymnastics.org www. fig-gymnastics.com FIG ACADEMY BIOMECHANICS
FÉDÉRATION INTERNATIONALE DE GYMNASTIQUE Av. de la Gare 12 1003 Lausanne Suisse Tél. (41-32) 494 64 10 Fax (41-32) 494 64 19 e-mail: info@fig-gymnastics.org www. fig-gymnastics.com FIG ACADEMY BIOMECHANICS
Vibration Analysis of a Two Wheeler (Analytically)
 Vibration Analysis of a Two Wheeler (Analytically) Mukesh Hadpe 1, Dr.D.S.Deshmukh 2, P.M.Solanki 3 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, SSBT S COET, Bambhori, Jalgaon, Maharashtra, India
Vibration Analysis of a Two Wheeler (Analytically) Mukesh Hadpe 1, Dr.D.S.Deshmukh 2, P.M.Solanki 3 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, SSBT S COET, Bambhori, Jalgaon, Maharashtra, India
Basic Biomechanics II DEA 325/651 Professor Alan Hedge
 Basic Biomechanics II DEA 325/651 Professor Alan Hedge Definitions! Scalar quantity quantity with magnitude only (e.g. length, weight)! Vector quantity quantity with magnitude + direction (e.g. lifting
Basic Biomechanics II DEA 325/651 Professor Alan Hedge Definitions! Scalar quantity quantity with magnitude only (e.g. length, weight)! Vector quantity quantity with magnitude + direction (e.g. lifting
681. Design of elastomeric shock absorbers with a soft stiffness characteristics of type force-settlement
 681. Design of elastomeric shock absorbers with a soft stiffness characteristics of type force-settlement V. Gonca 1, J. Shvab Riga Technical University, Ezermalas 6 d, LV-1006, Riga, Latvia E-mail: 1
681. Design of elastomeric shock absorbers with a soft stiffness characteristics of type force-settlement V. Gonca 1, J. Shvab Riga Technical University, Ezermalas 6 d, LV-1006, Riga, Latvia E-mail: 1
Numerical simulation of human thermal comfort in indoor environment
 Numerical simulation of human thermal comfort in indoor environment TIBERIU SPIRCU 1, IULIA MARIA CÂRSTEA 2, ION CARSTEA 3 1, 2 University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Carol Davila, Bucharest ROMANIA E_mail:spircut@yahoo.com
Numerical simulation of human thermal comfort in indoor environment TIBERIU SPIRCU 1, IULIA MARIA CÂRSTEA 2, ION CARSTEA 3 1, 2 University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Carol Davila, Bucharest ROMANIA E_mail:spircut@yahoo.com
