Completion of a Dislocated Metric Space
|
|
|
- Prudence Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 69 Chpter-3 Completio o Dislocte Metric Spce 3 Itrouctio: metric o X [] i We recll tht istce uctio o set X is si to be islocte i) y ) ii) 0 implies y iii) z) z or ll y z i X I is islocte metric o X the X ) is clle islocte metric spce is clle islocte qusimetric i symmetry coitio i) is roppe rom the bove eiitio We bbrevite islocte metric s metric islocte qusi metric s q metric I is q metric D is eie o the X D ) is islocte metric spce X X by D y )
2 By theorem 5 the topology 70 D iuce by D coicies with r li the ottio o chpter Further the clss B { V )/ X 0}is ope bse or D The presece o the trigle iequlity les Hussor property or some ice properties to X D) I prticulr X D) stisies properties C through C 5 Moreover iv) Cuchy sequeces i X D) Cuchy sequeces i X ) re ieticl v) Coverget sequeces i X D) re Cuchy sequeces hve uique limits X D) is complete i X ) is complete I the trigulr iequlity is elete rom the ioms o the it is iicult to eie the cocept o completio o the resultig istce spce I such morphous spce eve costt sequeces my il to coverge This relte iiculties compel us to reti the trigle iequlity i the iscussio o completeess We ormlly recor the eiitio o completeess: A metric spce X ) is complete i every Cuchy sequece i X ) coverges ' Deiitio: Let X ) Y ) be istce spces A mp : X Y is clle isoistce i or ll y X oe hs ) ) X Y re si to be isoistt i there eist isoistce : X Y oto
3 7 3 Completio: I wht ollows is islocte metric o oempty set X Lemm 3: is isolte poit o X i X {} or i 0 y Proo: Suppose is isolte poit o X The there eists r 0 such tht y r This implies X {} or i r 0 y Coversely suppose X {} or i 0 y I X {} the clerly is isolte poit o X I X {} the i r 0 y Hece is isolte poit o X which implies r r or ll y Corollry 3: I ) 0the is isolte poit o X Proo: I y the ) y ) so ) or ll y i X So { } X or i ) 0 y Lemm33: I R R re equivlece reltios o isjoit sets A A the R R R is equivlece reltio o A A A Proo: Routie hece omitte
4 7 Theorem 34: Let X ) be islocte metric spce The there eists complete islocte metric spce X ) isoistce T : X ) X ) such tht T X ) is ese i X Proo: Let I be the collectio o isolte poits o X J X I I be the collectio o sequeces i X which re ultimtely costt elemet lyig i I RI Let J eote the clss o Cuchy sequeces i J We eie reltios RJ respectively o I J s ollows: I ) y) re sequeces i I the ) RI y) i the ultimtely costt vlue o ) coicies with tht o y ) I ) y) re sequeces i J the ) RJ y) i lim y) 0 Veriictio tht J R I is equivlece reltio is esy Let us ow veriy tht R is equivlece reltio Suppose ) J 0 Sice ) is Cuchy sequece i J lim ) 0 hece ) RJ ) provig tht RJ is releive Suppose ) RJ y) or ) y) J The lim y) lim y ) 0 Hece RJ is symmetric I ) y ) z ) J ) R y ) y ) R z ) the there eist two J J itegers such tht y) i y z) i
5 73 Hece z) y) y z) i m{ } This proves ) RJ z) hece tht RJ is trsitive Let X I J The RRis equivlece reltio o X Let X eote X I X X cotiig the sequece ) eotes the equivlece clss i We eie : X X [0 ) s ollows: ) i y re respectively the y y y I ultimtely costt terms o ) y) lim ) i y y I y J evetully This limit eists sice y ) is Cuchy sequece is iepeet o the choice o the represettive sequece i the equivlece clss y I I ) J y) I the eie y y ) J y) J the eie y lim y) We ow check tht this limit eists is iepeet o the choice o represettive elemets rom the equivlece clsses y ote tht it ollows rom the trigle iequlity tht First we
6 y) m ym) m) y ym) Sice ) y ) re Cuchy sequeces give 0 there eists positive iteger 0 y y m ) or ll m 0 This implies tht m m such tht 74 m ) y ) y ) provig tht y is Cuchy sequece o rel umbers By the completeess o R this sequece coverges The eiitio o RJ mkes it obvious tht lim y) is iepeet o the choice o the represettive sequeces ) y) Veriictio tht respectively rom the clsses y is -metric o X : Clerly y ) 0 y ) y ) or y X Suppose y ) 0 Let ) y ) y We irst see tht either ) y) re both i I or both i J Suppose o the cotrry ) ) I y ) J Let be the ultimtely costt vlue o Now 0 y ) lim y) But 0 ) y ) Hece 0 ) lim y) 0 cotrry to the ct tht I
7 Suppose y I ) y ) y with b the ultimtely costt vlues o ) y) respectively 75 The y ) 0 b) 0 b ) y ) y Suppose y J ) y ) y y ) 0 lim y ) 0 ) y ) y Veriictio o the trigulr iequlity is routie Embeig o X i X : I X let ) be the costt sequece ) where the equivlece clss cotiig ) Deie T : X X by T ) It is cler tht T is isoistce We ow veriy tht T X ) is ese i Cse i): X Let X 0 ) I I this cse let be the ultimtely costt vlue o ) The by the eiitio o T T X ) The Thus TX) i this cse Cse ii): ) J Sice ) is Cuchy sequece there eists positive iteger 0 such tht
8 76 ) i m Let The by virtue o the ct tht m J ) 0 ) ˆ lim Hece T X ) is ese i X ) is complete: Let ) 0 X be Cuchy sequece i m 0 implies m Sice T X ) is ese i tht z ) Hece 0 X 0 There eists 0 such tht There is o hrm i ssumig tht X or ech positive iteger there eists m m m m z z ) z ) ) z ) m 3 i m Hece z is Cuchy sequece i T X ) Sice T is isoistce z ) is Cuchy sequece i X Moreover z z ) z z ) i m 0 Let z eote z m m z ) z ) z z ) z i X such
9 77 lim z z m) m i lim z ) 0 provig tht X ) is complete This completes the proo o theorem 34 Deiitio 35: Let X ) X ) be metric spces X ) be completio o X ) i is si to i) X ) is complete ii) there is isoistce T : X ) X ) such tht T X ) is ese i X Note: I X ) is complete metric spce the its completio is X ) itsel Lemm 36: Let X ) be - metric spce X ) be completio o X ) Let T : X Xbe isoistce embeig X i X with T X ) ese i X The poit y o Xis isolte poit i oly i y T) or some isolte poit o X Proo: Suppose y is isolte poit o X Suppose i possible y TX ) the sice T X ) is ese i X there eists sequece { T )} i T X ) such tht lim T ) 0 By lemm 3 it ollows tht y is ot isolte poit o X cotrictio
10 Hece y T) or some i X Now T is isolte poit o X hece tht o T X ) Sice X T X ) re isoistt is isolte poit o X Coversely suppose is isolte poit o X Sice T is isoistce T ) is isolte poit o T X ) Suppose to obti cotrictio T ) is ot isolte poit o X The or ech positive iteger k there eists elemet k i X such tht k 0 k T Sice k X either k T X) or there eists yk i T X ) such tht y ) T 0 k k k 78 Now Also yk T yk k ) k T k k y k sice y ) T k k k k Hece 0 yk T which by lemm 3 cotricts the ct tht T ) k is isolte poit o T X ) Theorem 37: Let X ) be metric spce X ) X ) be completios o X ) Ti : X ) Xi i ) i ) be isoistces such tht Ti X ) is ese i X i The there eists isoistce o to T : X ) X ) such tht ollowig igrm is commuttive Proo:
11 79 T Deiitio o T : I X is isolte poit o Xthe ) isolte poit o X hece T T is isolte poit o X is Deie T ) T T I X is ot isolte poit there eists sequece z ) i X such tht { Tz } coverges to i X ) Sice T is isoistce { T z } is coverget hece ) Cuchy sequece so { z } is Cuchy sequece i X Sice T is isoistce { T z } is Cuchy sequece i X ) Sice X ) is complete there eists z X such tht lim T z z) 0 This z is iepeet o the choice o the sequece { z } i X Deie T ) z By eiitio T T T T is isoistce: I y X T T T ) T T ) T T T ) T T ) T ) T ) T ) T ) So I y X X limt y limt y where y X the
12 80 T T lim limt T lim y limt lim T T ) y ) lim T y y ) ) whe X X y X or whe X y Xthe rgumet is similr Hece T is isoistce T is bijectio : Iterchgig the plces o X X we get i similr wy isoistce S : X X such tht T ST Sice ST T TT T We hve TST TT T A STT ST T Sice T X ) is ese i X T X) i X We get TS ietity o X ST is ietity o X Hece S T re bijectios
13 8 33 Completio o the metric ssocite with - metric: Pscl Hitzler [] itrouce - metric ssocite with metric use this metric i provig some ie poit theorems tht re eee i progrmmig lguges I this sectio we estblish tht the metric ssocite with the completio o metric o spce is the completio o the metric ssocite with the metric Deiitio 33: Let ) X be metric spce Deie o X X by i 0 i y y is metric o X is clle the metric ssocite with Clerly 0 y ) wheever y I s{ } r 0 X write B s r r r ) { y / s r} The V ) B ) { } V ) B ) { } r The collectio { V ) / Xr 0} { V ) / Xr 0} geerte the sme topology o X However coverget sequeces i X re ot ecessrily the sme sice costt sequeces re coverget sequeces with respect to while this hols wrt or with ) 0 oly r s r s r
14 As metioe i 4 eistece o poits with positive sel istce les to uplestess i the etesio o the cocept o cotiuity i metric spces s well This is eviet rom the ollowig Emple: Let be metric o set X which is ot metric so tht the set A { / ) 0} is oempty I is the metric ssocite with the the ietity mp i : X ) X ) is cotiuous i the usul sese But i A the costt sequece ) coverges i X ) while it oes ot coverge i X ) Deiitio: I X ) be metric spce Y ) be the metric spce ssocite with We cll : X Y sequetilly cotiuous i lim ) 0 lim ) 0 Propositio 33: lim ) 0 i either i) evetully ie there eists N such tht or N or ii) ) c be split ito subsequeces y ) z ) where y or every z or y lim z ) 0 Proo: Assumelim ) 0 The or y subsequece u ) o ) lim ) 0 I there oes ot eist N such tht u or ll N let u y ) be the possibly iite) subsequece o ) such tht y or ll Let z ) be the subsequece o ) tht remis ter eletig ech y Clerly z or y lim ) 0 Further z or every so z lim z ) 0 Coversely ssume tht the coitio hols 8
15 83 The lim ) 0 Deiitio: I s { } ) is sequece i X we sy tht ) is s -Cuchy sequece or simply s - Cuchy i ) is Cuchy sequece i X s ) Propositio 333: I sequece ) i X is - Cuchy the ) is - Cuchy Coversely i ) is - Cuchy is ot evetully costt the ) is - Cuchy Proo: Sice 0 m) m) - Cuchy - Cuchy Coversely suppose tht ) is - Cuchy Give 0 N ) such tht ) i N) m N) So i m N) N) m the m ) m I ) is ot evetully costt N) there eists m N) such tht m The ) ) ) m m ) m ) m Thus i ) is ot evetully costt the or ll m N) N) ) m Hece ) is - Cuchy
16 84 Emple 334: Let X 0 ) y the y 0 i i y y I ) is y sequece i 0 ) the ) is - Cuchy i 0 there eists N ) such tht m This implies tht lim 0 Coversely i lim 0 the 0 N ) such tht or m N) N) Hece m or m N) N) Costt sequeces re ot - Cuchy but - Cuchy Theorem 335: Let X ) be metric spce be the metric ssocite with o X X ) be the completio o X ) be the metric ssocite with o X The X ) is the completio o X ) I prticulr i X ) is complete metric spce the X ) is complete metric spce We prove tht i) X is ese i X ) ii) Every - Cuchy sequece i X is coverget Proo o i) Let X X The there eists sequece ) i X such tht lim ) 0 Sice X so tht implies tht X is ese i X ) lim ) 0 This
17 85 Proo o ii) Let ) be - Cuchy i X I ) is evetully costt the there eists N X such tht or N I this cse lim ) 0 or N hece ) is coverget Suppose ) is ot evetully costt The by propositio 333 ) is - Cuchy sequece Sice X ) is complete there eists X such tht lim ) 0 Sice 0 ) ) 0 lim ) 0 Hece ) coverget to This completes the proo o ii) 34 Fie poit theorems: Let X ) be metric spce : X X be mppig Write V ) z ) { / V ) 0} Clerly every poit o z ) is ie poit o but the coverse is ot ecessrily true We cll poits o z ) s coiciece poits o The set z ) is close subset o X Mthew s theorem [8] sttes tht cotrctio o complete metric spce hs uique ie poit The sme theorem hs bee justiie by lterte proo by Pscl Hitzler[8] We preset etesio o this theorem or coiciece poits
18 Theorem 34[]: Let X ) be complete metric spce : X X be cotrctio The there is uique coiciece poit or Proo: For y Cosequetly i Hece { X the sequece o itertes stisies 86 where is y cotrctive costt m m m m = } is Cuchy sequece i X ) I the ) lim lim So lim ) Sice ) Sice 0 ; lim ) 0 Hece 0 Uiqueess : I 0 the ) ) so tht ) ) ) ) )
19 87 ) 0 Hece Theorem 34[] : Let ) sequetilly cotiuous Assume tht X be metric spce : X X be ) ) m{ y ) } wheever 0 The hs uique coiciece poit wheever Cl ) is oempty or some X Proo: Recll ) { ) / 0} write V ) Z { / V ) 0} Sice is sequetilly cotiuous so is V I Z the V ) m{ ) } m{ V ) V } V V ) Wheever V ) 0 i e Z ) k I ) Z= the V V k k Hece V ) is coverget ) Let be cluster poit o ) i ) i N = lim i ) k =lim i k k ) Cl )
20 88 Sice V is sequetilly cotiuous k V ) = lim V i k ) ) Let = lim V i = V ) Also = lim V i ) = V ; k V V ) ) From ) 3) it ollows tht V ) =0 ie 0 I ) V ) 0 V the = ) = ) I ) 0 ) = ) <m{v )V ) )}= ) which is cotrictio Hece )=0 BE Rhoes [3] presete list o eiitios o cotrctive type coitios or sel mp o metric spce X ) estblishe implictios oimplictios mog them there by cilittig to check i y ew cotrctive coitio implies y oe o the coitios metioe i [3] so s to erive ie poit theorem Amog the coitios i [3] Seghl s coitio is sigiict s goo umber o Cotrctive coitios imply Seghl s coitio We ow cosier vliity o islocte versios o these coitios
21 Let X ) be islocte metric spce : X X be mppig y be y elemets o X Cosier the ollowig coitios Bch) : There eists umber 0 such tht or ech y X ) Rkotch) : There eists mootoe ecresig uctio : 0 ) [0) such tht or ech y X y 3 Eelstei) : For ech y X y ) ) 4 K) :There eists umber 0 y X y ) y ) 89 such tht or ech 5 Bichii): There eists umber h 0 h such tht or ech ) hm y ) y X y 6 For ech y X y ) m y ) 7 Reich): There eist oegtive umbers b c stisyig b c such tht or ech y X y ) b y ) c 8 Reich) : There eist mootoiclly ecresig uctios b c rom 0 ) to [0 ) stisyig t) b t) c t) such tht or ech y X y ) b y ) c
22 90 9 There eist oegtive uctios b c stisyig sup y b y c y} such tht or ech y X y yx ) t bt y ) ct where t y 0 Sehgl): For ech y X y ) m y ) y Theorem 343[]: I is sel mp o islocte metric spce X ) stisies y o the coitios ) through 9) the hs uique ie poit provie Cl ) is oempty or some X Proo: I [3] BE Rhoes prove tht whe is metric ) ) 3) 0) 4) 5) 6) 0) 4) 7) 8) 0) 5) 7) 9) 0) whe 0 is replce by y these implictios hol goo i metric spce s well sice y 0 i metric spce It ow ollows tht hs ie poit which is uique whe ) hs cluster poit or some
23 9 Emple 344[]: Deie y For y i R is islocte metric o R I 0 0) ) B I 0 0 B ) = i i Also 0 B ) i < Emple 345[]: Deie : R R by ) Every oegtive rel umber is ie poit o but 0 is the oly coiciece poit ) )= + =0 0 Thus 0 is the oly coiciece poit while ll oegtive rel umbers re ie poits Theorem 346[4] : Let X ) be complete -metric spce sel mp o X 0h I is sequetilly cotiuous or ll y with 0 ) ) h m{ ) y y )}) the hs uique coiciece poit Proo: Assume tht stisies ) For X y positive iteger write m) { ) )} [ m )] =Sup{ u v) /{ u v} m)} We irst prove the ollowig Lemm: For every positive iteger m there eists positive iteger k m such tht [ m)] k m
24 9 Proo: To prove this it is eough i we prove tht [ m )] m m where m m { ) } ) We prove this by usig iuctio Assume tht ) is true or m ie [ m )] m We hve to prove or m ie [ m )] m ) We hve [ ) m)] Also i m m{ ) m m } } i ) m m i m m { ) ) } 3) Hece [ m )] =Sup { ) / 0 i j m } i j =Sup {{ ) m m } i j { ) / 0 i j m }} m{ ) m m [ ) m]} m rom ) 3) Hece [ m )] Proo o the Theorem: I m This proves the lemm i m j m
25 93 i j i j ) ) [ m )] m i j i i h m{ ) ) ) i j j i j j ) ) ) ) } h[ m)] Also j j m { ) ) } I m re positive itegers such tht m the by ) m m ) ) h ) k h k ; k m - - ) or some 0 h h [ m )] ) m - +) by bove lemm) By the lemm k 0 k m [ m )] k Assume k ) h [ m)] h k k k k h
26 94 I k =0 [ m )] ) + ) ) +h ) h m Hece ) h m h h This is true or every m > Sice 0 h < lim Hece { m )} is Cuchy sequece i X ) h = 0 Sice X is complete z X so tht lim ) z We prove tht z z 0 0 z z z z z) z By sequetil cotiuity o lim z) z 0 Hece z z 0 hece z is coiciece poit o Suppose z z re coiciece poits o The z z )= z z 0 similrly z z)=0 I z z) 0 the by ) z z)= z ) z h m{ z z ) z z z z z z z z }
27 95 h z z) cotrictio Hece z z)=0hece z zthis completes the proo We ow prove ie poit theorem or sel mp o metric spce stisyig the logue o 9) i [3] Theorem 347[4]: Let X ) be complete metric spce : X X be sequetilly cotiuous mppig such tht there eist rel umbers 0 0 mi{ } stisyig 4 t lest oe o the ollowig or ech i ) ) ii iii y X ) ) [ + y ) ] ) ) [ ) + y ] The hs uique coiciece poit Proo: Puttig ) y i the bove = m { } we get Agi puttig y = ) i the bove i) ii) iii) yiels ) ) )
28 96 I h=m { } the 0 h ) h I m re positive itegers such tht m ) h h sice 0 h ; lim h 0 m the Hece { )} is Cuchy s sequece i X ) Sice X is complete z i X lim ) = z Sice is sequetilly cotiuous lim ) = z) i X ) Sice 0 z z z ) z It ollows tht z z =0 Hece z is coiciece poit Uiqueess : I z zre coiciece poits o the by hypothesis Either z z) z z) or 0 or z z) Sice 0 Hece z z 0 we must hve z z)=0 4 The metric versio or the cotrctive iequlity 0) i the moiie orm ) give below yiels the ollowig Theorem 348[4] : Let X ) be complete metric spce : X X be sequetilly cotiuous mppig Assume tht there eist o-egtive costts i stisyig < such tht or ech y X with y
29 97 ) ) ) y y y y y The hs uique coiciece poit Proo:Cosier ) ) ) = ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) where I m the
30 98 m m ) ) m = ) Hece { )} is Cuchy s sequece i X ) hece coverget Let lim the ) lim sice is sequetilly cotiuous ) So = lim ) lim Sice 0 =0 Hece ) = Hece is coiciece poit or Uiqueess: I 0 ) = )
31 99 Cosier ) ) ) ) where 4 5 ) 0 Hece It is ot out o plce to preset here ew ie poit theorems or sel mps o complete metric spces erive by the uthor re publishe i vrious jourls A ew o theorems re liste without proo here uer Theorem 349[5]: Let X ) be complete -metric spce Let A B S T : X X be cotiuous mppigs stisyig I T X ) A X ) S X ) B X ) II The pirs S A) T B) re wekly comptible III S T m{ A B A S) By T} For ll y X where0 the A B S T hve uique commo ie poit Theorem 340[5]: Let X ) be complete metric spce Let A B S T : X X be cotiuous mppig stisyig I T X ) A X ) S X ) B X ) II The pirs S A) T B) re wekly comptible
32 III For ll A S) By T S T { } A B A B o yo X where 0 0 the A B S 4 T hve uique commo ie poit Theorem 34[6]: Let X ) A B S T : X X be cotiuous mppigs stisyig I T X ) A X ) S X ) B X ) be complete metric spce Let II The pirs S A) T B) re wekly comptible III 00 5 S T A B A S) 3 By T 4 A T By S) For ll y X where the A B S T hve uique 0 5 commo ie poit Theorem:34[6]: Let X ) be complete metric spce Let S T : X X be cotiuous mppigs stisyig S T T S T S) 3 Sy T 4 T T 5 Sy S) or ll y X where the S T hve uique ie poit
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
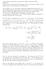 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
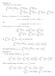 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
Some Results on the Variation of Composite Function of Functions of Bounded d Variation
 AMRICAN JOURNAL OF UNDRGRADUAT RSARCH OL. 6 NO. 4 Some Results o the ritio o Composite Fuctio o Fuctios o Boue ritio Mohse Soltir Deprtmet o Mthemtics Fculty o Sciece K.N. Toosi Uiversity o Techology P.O.
AMRICAN JOURNAL OF UNDRGRADUAT RSARCH OL. 6 NO. 4 Some Results o the ritio o Composite Fuctio o Fuctios o Boue ritio Mohse Soltir Deprtmet o Mthemtics Fculty o Sciece K.N. Toosi Uiversity o Techology P.O.
is infinite. The converse is proved similarly, and the last statement of the theorem is clear too.
 12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
b a 2 ((g(x))2 (f(x)) 2 dx
 Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
Reversing the Arithmetic mean Geometric mean inequality
 Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Basic Limit Theorems
 Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER Ifiite Series.5 Altertig Series d Absolute Covergece Next, let us cosider series with both positive d egtive terms. The simplest d most useful is ltertig
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER Ifiite Series.5 Altertig Series d Absolute Covergece Next, let us cosider series with both positive d egtive terms. The simplest d most useful is ltertig
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Mathematical Notation Math Calculus & Analytic Geometry I
 Mthemticl Nottio Mth - Clculus & Alytic Geometry I Nme : Use Wor or WorPerect to recrete the ollowig ocumets. Ech rticle is worth poits c e prite give to the istructor or emile to the istructor t jmes@richl.eu.
Mthemticl Nottio Mth - Clculus & Alytic Geometry I Nme : Use Wor or WorPerect to recrete the ollowig ocumets. Ech rticle is worth poits c e prite give to the istructor or emile to the istructor t jmes@richl.eu.
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
Advanced Calculus Test File Spring Test 1
 Advced Clculus Test File Sprig 009 Test Defiitios - Defie the followig terms.) Crtesi product of A d B.) The set, A, is coutble.) The set, A, is ucoutble 4.) The set, A, is ifiite 5.) The sets A d B re
Advced Clculus Test File Sprig 009 Test Defiitios - Defie the followig terms.) Crtesi product of A d B.) The set, A, is coutble.) The set, A, is ucoutble 4.) The set, A, is ifiite 5.) The sets A d B re
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS
 M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
Publications of Problems & Applications in Engineering Research-PAPER ISSN: ; e-issn:
 137 http://techicljourls.org Publictios of Problems & Applictios i Egieerig Reserch-PAPER ISSN: 2230-8547; e-issn: 2230-8555 SOME RESULTS ON FIXED POINTS OF CONTROL FUNCTION IN A SETTING OF 2-METRIC SPACE
137 http://techicljourls.org Publictios of Problems & Applictios i Egieerig Reserch-PAPER ISSN: 2230-8547; e-issn: 2230-8555 SOME RESULTS ON FIXED POINTS OF CONTROL FUNCTION IN A SETTING OF 2-METRIC SPACE
Mathematical Notation Math Calculus & Analytic Geometry I
 Mthemticl Nottio Mth - Clculus & Alytic Geometry I Use Wor or WorPerect to recrete the ollowig ocumets. Ech rticle is worth poits shoul e emile to the istructor t jmes@richl.eu. Type your me t the top
Mthemticl Nottio Mth - Clculus & Alytic Geometry I Use Wor or WorPerect to recrete the ollowig ocumets. Ech rticle is worth poits shoul e emile to the istructor t jmes@richl.eu. Type your me t the top
Orthogonal functions - Function Approximation
 Orthogol uctios - Fuctio Approimtio - he Problem - Fourier Series - Chebyshev Polyomils he Problem we re tryig to pproimte uctio by other uctio g which cosists o sum over orthogol uctios Φ weighted by
Orthogol uctios - Fuctio Approimtio - he Problem - Fourier Series - Chebyshev Polyomils he Problem we re tryig to pproimte uctio by other uctio g which cosists o sum over orthogol uctios Φ weighted by
Homework 2 solutions
 Sectio 2.1: Ex 1,3,6,11; AP 1 Sectio 2.2: Ex 3,4,9,12,14 Homework 2 solutios 1. Determie i ech uctio hs uique ixed poit o the speciied itervl. gx = 1 x 2 /4 o [0,1]. g x = -x/2, so g is cotiuous d decresig
Sectio 2.1: Ex 1,3,6,11; AP 1 Sectio 2.2: Ex 3,4,9,12,14 Homework 2 solutios 1. Determie i ech uctio hs uique ixed poit o the speciied itervl. gx = 1 x 2 /4 o [0,1]. g x = -x/2, so g is cotiuous d decresig
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
Chapter 25 Sturm-Liouville problem (II)
 Chpter 5 Sturm-Liouville problem (II Speer: Lug-Sheg Chie Reerece: [] Veerle Ledou, Study o Specil Algorithms or solvig Sturm-Liouville d Schrodiger Equtios. [] 王信華教授, chpter 8, lecture ote o Ordiry Dieretil
Chpter 5 Sturm-Liouville problem (II Speer: Lug-Sheg Chie Reerece: [] Veerle Ledou, Study o Specil Algorithms or solvig Sturm-Liouville d Schrodiger Equtios. [] 王信華教授, chpter 8, lecture ote o Ordiry Dieretil
Multiplication and Translation Operators on the Fock Spaces for the q-modified Bessel Function *
 Advces i Pure Mthemtics 0-7 doi:0436/pm04039 Pulished Olie July 0 (http://wwwscirporg/jourl/pm) Multiplictio d Trsltio Opertors o the Fock Spces or the -Modiied Bessel Fuctio * Astrct Fethi Solti Higher
Advces i Pure Mthemtics 0-7 doi:0436/pm04039 Pulished Olie July 0 (http://wwwscirporg/jourl/pm) Multiplictio d Trsltio Opertors o the Fock Spces or the -Modiied Bessel Fuctio * Astrct Fethi Solti Higher
Interpolation. 1. What is interpolation?
 Iterpoltio. Wht is iterpoltio? A uctio is ote give ol t discrete poits such s:.... How does oe id the vlue o t other vlue o? Well cotiuous uctio m e used to represet the + dt vlues with pssig through the
Iterpoltio. Wht is iterpoltio? A uctio is ote give ol t discrete poits such s:.... How does oe id the vlue o t other vlue o? Well cotiuous uctio m e used to represet the + dt vlues with pssig through the
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES
 Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
Uiv. Beogrd. Publ. Elektroteh. Fk. Ser. Mt. 8 006 4. Avilble electroiclly t http: //pefmth.etf.bg.c.yu SOME SHARP OSTROWSKI-GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITIES Zheg Liu Usig vrit of Grüss iequlity to give ew proof
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Relation of BSTs to Quicksort, Analysis of Random BST. Lecture 9
 Reltio o BSTs to Quicsort, Alysis o Rdom BST Lecture 9 Biry-serch-tree sort T Crete empty BST or i = to do TREE-INSERT(T, A[i]) Perorm iorder tree wl o T. Emple: 3 A = [3 8 2 6 7 5] 8 Tree-wl time = O(),
Reltio o BSTs to Quicsort, Alysis o Rdom BST Lecture 9 Biry-serch-tree sort T Crete empty BST or i = to do TREE-INSERT(T, A[i]) Perorm iorder tree wl o T. Emple: 3 A = [3 8 2 6 7 5] 8 Tree-wl time = O(),
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Math 140B - Notes. Neil Donaldson. September 2, 2009
 Mth 40B - Notes Neil Doldso September 2, 2009 Itroductio This clss cotiues from 40A. The mi purpose of the clss is to mke bsic clculus rigorous.. Nottio We will observe the followig ottio throughout this
Mth 40B - Notes Neil Doldso September 2, 2009 Itroductio This clss cotiues from 40A. The mi purpose of the clss is to mke bsic clculus rigorous.. Nottio We will observe the followig ottio throughout this
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The limit comparison test
 Roerto s Notes o Ifiite Series Chpter : Covergece tests Sectio 4 The limit compriso test Wht you eed to kow lredy: Bsics of series d direct compriso test. Wht you c ler here: Aother compriso test tht does
Roerto s Notes o Ifiite Series Chpter : Covergece tests Sectio 4 The limit compriso test Wht you eed to kow lredy: Bsics of series d direct compriso test. Wht you c ler here: Aother compriso test tht does
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Principles of Mathematical Analysis
 Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Topic 9 - Taylor and MacLaurin Series
 Topic 9 - Taylor ad MacLauri Series A. Taylors Theorem. The use o power series is very commo i uctioal aalysis i act may useul ad commoly used uctios ca be writte as a power series ad this remarkable result
Topic 9 - Taylor ad MacLauri Series A. Taylors Theorem. The use o power series is very commo i uctioal aalysis i act may useul ad commoly used uctios ca be writte as a power series ad this remarkable result
Fourier Series. Topic 4 Fourier Series. sin. sin. Fourier Series. Fourier Series. Fourier Series. sin. b n. a n. sin
 Topic Fourier Series si Fourier Series Music is more th just pitch mplitue it s lso out timre. The richess o sou or ote prouce y musicl istrumet is escrie i terms o sum o umer o istict requecies clle hrmoics.
Topic Fourier Series si Fourier Series Music is more th just pitch mplitue it s lso out timre. The richess o sou or ote prouce y musicl istrumet is escrie i terms o sum o umer o istict requecies clle hrmoics.
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Integral Operator Defined by k th Hadamard Product
 ITB Sci Vol 4 A No 35-5 35 Itegrl Opertor Deied by th Hdmrd Product Msli Drus & Rbh W Ibrhim School o Mthemticl Scieces Fculty o sciece d Techology Uiversiti Kebgs Mlysi Bgi 436 Selgor Drul Ehs Mlysi Emil:
ITB Sci Vol 4 A No 35-5 35 Itegrl Opertor Deied by th Hdmrd Product Msli Drus & Rbh W Ibrhim School o Mthemticl Scieces Fculty o sciece d Techology Uiversiti Kebgs Mlysi Bgi 436 Selgor Drul Ehs Mlysi Emil:
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS. Linear Equations. x l ( 3,1 ) _x-axis. Origin ( 0, 0 ) Slope = change in y change in x. Equation for l 1.
 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
Numbers (Part I) -- Solutions
 Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
Chapter 2 Infinite Series Page 1 of 9
 Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Topic 4 Fourier Series. Today
 Topic 4 Fourier Series Toy Wves with repetig uctios Sigl geertor Clssicl guitr Pio Ech istrumet is plyig sigle ote mile C 6Hz) st hrmoic hrmoic 3 r hrmoic 4 th hrmoic 6Hz 5Hz 783Hz 44Hz A sigle ote will
Topic 4 Fourier Series Toy Wves with repetig uctios Sigl geertor Clssicl guitr Pio Ech istrumet is plyig sigle ote mile C 6Hz) st hrmoic hrmoic 3 r hrmoic 4 th hrmoic 6Hz 5Hz 783Hz 44Hz A sigle ote will
Infinite Sequences and Series. Sequences. Sequences { } { } A sequence is a list of number in a definite order: a 1, a 2, a 3,, a n, or {a n } or
 Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series -- Chpter Ifiite Sequeces d Series Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces -- Chpter. Sequeces Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces
Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series -- Chpter Ifiite Sequeces d Series Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces -- Chpter. Sequeces Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces
Theorem 3. A subset S of a topological space X is compact if and only if every open cover of S by open sets in X has a finite subcover.
 Compactess Defiitio 1. A cover or a coverig of a topological space X is a family C of subsets of X whose uio is X. A subcover of a cover C is a subfamily of C which is a cover of X. A ope cover of X is
Compactess Defiitio 1. A cover or a coverig of a topological space X is a family C of subsets of X whose uio is X. A subcover of a cover C is a subfamily of C which is a cover of X. A ope cover of X is
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Definition 4.2. (a) A sequence {x n } in a Banach space X is a basis for X if. unique scalars a n (x) such that x = n. a n (x) x n. (4.
 4. BASES I BAACH SPACES 39 4. BASES I BAACH SPACES Sice a Baach space X is a vector space, it must possess a Hamel, or vector space, basis, i.e., a subset {x γ } γ Γ whose fiite liear spa is all of X ad
4. BASES I BAACH SPACES 39 4. BASES I BAACH SPACES Sice a Baach space X is a vector space, it must possess a Hamel, or vector space, basis, i.e., a subset {x γ } γ Γ whose fiite liear spa is all of X ad
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
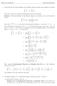 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Content: Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, James Stewart, 2007 Chapter 1: Functions and Limits., in a set B.
 Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Multiplicative Versions of Infinitesimal Calculus
 Multiplictive Versios o Iiitesiml Clculus Wht hppes whe you replce the summtio o stdrd itegrl clculus with multiplictio? Compre the revited deiitio o stdrd itegrl D å ( ) lim ( ) D i With ( ) lim ( ) D
Multiplictive Versios o Iiitesiml Clculus Wht hppes whe you replce the summtio o stdrd itegrl clculus with multiplictio? Compre the revited deiitio o stdrd itegrl D å ( ) lim ( ) D i With ( ) lim ( ) D
Certain sufficient conditions on N, p n, q n k summability of orthogonal series
 Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
LEVEL I. ,... if it is known that a 1
 LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
3.7 The Lebesgue integral
 3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Product measures, Tonelli s and Fubini s theorems For use in MAT3400/4400, autumn 2014 Nadia S. Larsen. Version of 13 October 2014.
 Product measures, Toelli s ad Fubii s theorems For use i MAT3400/4400, autum 2014 Nadia S. Larse Versio of 13 October 2014. 1. Costructio of the product measure The purpose of these otes is to preset the
Product measures, Toelli s ad Fubii s theorems For use i MAT3400/4400, autum 2014 Nadia S. Larse Versio of 13 October 2014. 1. Costructio of the product measure The purpose of these otes is to preset the
Course 121, , Test III (JF Hilary Term)
 Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Limit of a function:
 - Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
- Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
Toeplitz and Translation Operators on the q-fock Spaces *
 Advces i Pure Mthemtics 35-333 doi:436/pm659 Published Olie November (http://wwwscirporg/jourl/pm) Toeplit d Trsltio Opertors o the -Foc Spces * Abstrct Fethi Solti Higher College o Techology d Iormtics
Advces i Pure Mthemtics 35-333 doi:436/pm659 Published Olie November (http://wwwscirporg/jourl/pm) Toeplit d Trsltio Opertors o the -Foc Spces * Abstrct Fethi Solti Higher College o Techology d Iormtics
f(tx + (1 t)y) h(t)f(x) + h(1 t)f(y) (1.1)
 MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 68, 206, 45 57 Mrch 206 origili uqi rd reserch pper INTEGRAL INEQUALITIES OF JENSEN TYPE FOR λ-convex FUNCTIONS S. S. Drgomir Abstrct. Some itegrl iequlities o Jese type or λ-covex uctios
MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 68, 206, 45 57 Mrch 206 origili uqi rd reserch pper INTEGRAL INEQUALITIES OF JENSEN TYPE FOR λ-convex FUNCTIONS S. S. Drgomir Abstrct. Some itegrl iequlities o Jese type or λ-covex uctios
Merge Sort. Outline and Reading. Divide-and-Conquer. Divide-and-conquer paradigm ( 4.1.1) Merge-sort ( 4.1.1)
 Merge Sort 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Merge Sort versio 1.3 1 Outlie d Redig Divide-d-coquer prdigm ( 4.1.1 Merge-sort ( 4.1.1 Algorithm Mergig two sorted sequeces Merge-sort tree
Merge Sort 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Merge Sort versio 1.3 1 Outlie d Redig Divide-d-coquer prdigm ( 4.1.1 Merge-sort ( 4.1.1 Algorithm Mergig two sorted sequeces Merge-sort tree
 n. A Very Interesting Example + + = d. + x3. + 5x4. math 131 power series, part ii 7. One of the first power series we examined was. 2!
 mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
Chapter Real Numbers
 Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
Important Facts You Need To Know/Review:
 Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
MA541 : Real Analysis. Tutorial and Practice Problems - 1 Hints and Solutions
 MA54 : Real Aalysis Tutorial ad Practice Problems - Hits ad Solutios. Suppose that S is a oempty subset of real umbers that is bouded (i.e. bouded above as well as below). Prove that if S sup S. What ca
MA54 : Real Aalysis Tutorial ad Practice Problems - Hits ad Solutios. Suppose that S is a oempty subset of real umbers that is bouded (i.e. bouded above as well as below). Prove that if S sup S. What ca
Basic Maths. Fiorella Sgallari University of Bologna, Italy Faculty of Engineering Department of Mathematics - CIRAM
 Bsic Mths Fiorell Sgllri Uiversity of Bolog, Itly Fculty of Egieerig Deprtmet of Mthemtics - CIRM Mtrices Specil mtrices Lier mps Trce Determits Rk Rge Null spce Sclr products Norms Mtri orms Positive
Bsic Mths Fiorell Sgllri Uiversity of Bolog, Itly Fculty of Egieerig Deprtmet of Mthemtics - CIRM Mtrices Specil mtrices Lier mps Trce Determits Rk Rge Null spce Sclr products Norms Mtri orms Positive
Module 4. Signal Representation and Baseband Processing. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Sigl Represettio d Bsed Processig Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Lesso 5 Orthogolity Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Ater redig this lesso, you will ler out Bsic cocept o orthogolity d orthoormlity; Strum -
Module 4 Sigl Represettio d Bsed Processig Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Lesso 5 Orthogolity Versio ECE IIT, Khrgpur Ater redig this lesso, you will ler out Bsic cocept o orthogolity d orthoormlity; Strum -
On a New Subclass of Multivalant Functions Defined by Al-Oboudi Differential Operator
 Glol Jourl o Pure d Alied Mthetics. ISSN 973-768 Volue 4 Nuer 5 28. 733-74 Reserch Idi Pulictios htt://www.riulictio.co O New Suclss o Multivlt Fuctios eied y Al-Ooudi ieretil Oertor r.m.thirucher 2 T.Stli
Glol Jourl o Pure d Alied Mthetics. ISSN 973-768 Volue 4 Nuer 5 28. 733-74 Reserch Idi Pulictios htt://www.riulictio.co O New Suclss o Multivlt Fuctios eied y Al-Ooudi ieretil Oertor r.m.thirucher 2 T.Stli
2 Banach spaces and Hilbert spaces
 2 Baach spaces ad Hilbert spaces Tryig to do aalysis i the ratioal umbers is difficult for example cosider the set {x Q : x 2 2}. This set is o-empty ad bouded above but does ot have a least upper boud
2 Baach spaces ad Hilbert spaces Tryig to do aalysis i the ratioal umbers is difficult for example cosider the set {x Q : x 2 2}. This set is o-empty ad bouded above but does ot have a least upper boud
Integration. Table of contents
 Itegrtio Tle of cotets. Defiitio of Riem Itegrtio.................................. Prtitio of itervls........................................... Upper/lower Riem sum......................................3.
Itegrtio Tle of cotets. Defiitio of Riem Itegrtio.................................. Prtitio of itervls........................................... Upper/lower Riem sum......................................3.
f(x) is a function of x and it is defined on the set R of real numbers. If then f(x) is continuous at x=x 0, where x 0 R.
 MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES Limit Cotiuity Coverget squece Series Dieretible uctios Itegrble uctios Summtio deiitio o itegrl Me vlue theorem Me vlue theorem or itegrls Tylor's theorem Computer represettio
MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES Limit Cotiuity Coverget squece Series Dieretible uctios Itegrble uctios Summtio deiitio o itegrl Me vlue theorem Me vlue theorem or itegrls Tylor's theorem Computer represettio
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
(II.G) PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES
 II.G PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES I II.C, we used the Chiese Remider Theorem to reduce cogrueces modulo m r i i to cogrueces modulo r i i. For exmles d roblems, we stuck with r i 1 becuse we hd
II.G PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES I II.C, we used the Chiese Remider Theorem to reduce cogrueces modulo m r i i to cogrueces modulo r i i. For exmles d roblems, we stuck with r i 1 becuse we hd
Properties of Fuzzy Length on Fuzzy Set
 Ope Access Library Joural 206, Volume 3, e3068 ISSN Olie: 2333-972 ISSN Prit: 2333-9705 Properties of Fuzzy Legth o Fuzzy Set Jehad R Kider, Jaafar Imra Mousa Departmet of Mathematics ad Computer Applicatios,
Ope Access Library Joural 206, Volume 3, e3068 ISSN Olie: 2333-972 ISSN Prit: 2333-9705 Properties of Fuzzy Legth o Fuzzy Set Jehad R Kider, Jaafar Imra Mousa Departmet of Mathematics ad Computer Applicatios,
Section 6.3: Geometric Sequences
 40 Chpter 6 Sectio 6.: Geometric Sequeces My jobs offer ul cost-of-livig icrese to keep slries cosistet with ifltio. Suppose, for exmple, recet college grdute fids positio s sles mger erig ul slry of $6,000.
40 Chpter 6 Sectio 6.: Geometric Sequeces My jobs offer ul cost-of-livig icrese to keep slries cosistet with ifltio. Suppose, for exmple, recet college grdute fids positio s sles mger erig ul slry of $6,000.
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
2. Infinite Series 3. Power Series 4. Taylor Series 5. Review Questions and Exercises 6. Sequences and Series with Maple
 Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
COMMON FIXED POINT THEOREMS IN FUZZY METRIC SPACES FOR SEMI-COMPATIBLE MAPPINGS
 PK ISSN 0022-2941; CODEN JNSMAC Vol. 49, No.1 & 2 (April & October 2009) PP 33-47 COMMON FIXED POINT THEOREMS IN FUZZY METRIC SPACES FOR SEMI-COMPATIBLE MAPPINGS *M. A. KHAN, *SUMITRA AND ** R. CHUGH *Departmet
PK ISSN 0022-2941; CODEN JNSMAC Vol. 49, No.1 & 2 (April & October 2009) PP 33-47 COMMON FIXED POINT THEOREMS IN FUZZY METRIC SPACES FOR SEMI-COMPATIBLE MAPPINGS *M. A. KHAN, *SUMITRA AND ** R. CHUGH *Departmet
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Journl o Inequlities in Pure nd Applied Mthemtics http://jipm.vu.edu.u/ Volume 6, Issue 4, Article 6, 2005 MROMORPHIC UNCTION THAT SHARS ON SMALL UNCTION WITH ITS DRIVATIV QINCAI ZHAN SCHOOL O INORMATION
Journl o Inequlities in Pure nd Applied Mthemtics http://jipm.vu.edu.u/ Volume 6, Issue 4, Article 6, 2005 MROMORPHIC UNCTION THAT SHARS ON SMALL UNCTION WITH ITS DRIVATIV QINCAI ZHAN SCHOOL O INORMATION
Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
 Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
