Submitted to Acta Physica Polonica, Proceedings of the XXXI Zakopane School of Physics
|
|
|
- Theresa Kristina Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Submitted to Acta Physica Polonica, Proceedings of the XXXI Zakopane School of Physics Trends in Nuclear Physics, 3-11 September 1996, Zakopane, Poland GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN EXCITED 120 SN AND 208 PB NUCLEI POPULATED BY INELASTIC ALPHA SCATTERING T. BAUMANN a;b, E. RAMAKRISHNAN a;c, and M. THOENNESSEN a a National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics & Astronomy, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan , USA b Gesellschaft fur Schwerionenforschung, Planckstr. 1, D Darmstadt, Germany c Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX , USA The evolution of the giant dipole resonance in 120 Sn and 208 Pb nuclei at excitation energies in the range of 30{130 MeV was studied by comparing high energy ray measurements from the decay of the resonance at low angular momenta with theoretical model calculations. Both, a model of the adiabatic coupling of the GDR to the nuclear shape as well as a collisional model describe the increase of the width with temperature. However, while the collisional model is independent of angular momentum, the adiabatic model can describe the increase of the GDR width at high angular momenta. 1. Introduction The study of the giant dipole resonance (GDR) built on excited states reveals properties of nuclei at high temperatures. The GDR built on highly excited states has been studied since 1980 [1, 2] using fusion-evaporation reactions, and the most systematic data has been accumulated on Sn isotopes [3, 4]. In these measurements a broadening of the GDR width with increasing excitation energy was observed. In heavy-ion fusion reactions the compound nuclei are populated in high angular momentum states, due to the large angular momentum transfer in the entrance channel. High excitation energies are therefore inherently coupled with high spins, making an investigation of the temperature-related evolution of nuclear properties dicult. To decouple the eects of angular momentum and temperature is of high current interest [5]. This decoupling of temperature and spin eects in the study of excited state GDR is possible with small-angle light-ion scattering. Light-particle inelastic scattering has been
2 used extensively in the study of collective modes built on the ground state [6]. High energy excitations in the target nucleus show their signature in the continuum of the scatteredparticle spectra. Energy spectra of high energy rays measured in coincidence with the inelastically scattered projectiles show an enhancement in the GDR energy region, hence an examination of the GDR built on highly excited states is possible [7]. The angular momentum transferred to the target nuclei in light-ion inelastic scattering is very low compared to heavy-ion fusion reactions. Furthermore, a large range of excitation energies is populated, which oers the possibility to investigate the energy dependance of the evolution by gating on the energy loss of the scattered projectiles. A complementary approach to inelastic excitation is to employ fusion-evaporation reactions and gate on small ranges of the populated angular momenta via the measurement of -ray multiplicities with which the spin dependance of the GDR width at an approximately constant nuclear temperature is studied [8]. The measurements for the present analysis were performed with -particle beams from the K1200 cyclotron at the National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory. 40 MeV/nucleon -particles were scattered o 120 Sn and 208 Pb, and 50 MeV/nucleon o 120 Sn. The experimental details can be found elsewhere [9, ] and in the present paper the details of the statistical model and the comparison with theoretical models will be presented. 2. Statistical Model Calculations In order to extract the parameters of the GDR, the standard statistical model code cascade [11] was used. Two modications have been made to customize the standard code: (i) Incorporating the initial population distribution which is spread over a range of excitation energies and angular momenta and (ii) the level density description which is especially important for the decay of 208 Pb. The distribution of nuclei in the excitation versus angular momentum plane was obtained by taking -MeV-wide bins of the energy distribution measured in the inelastic spectra, and by using a simple model to calculate the angular momentum transfer through inelastic scattering at each energy. The angular momentum imparted to the target was computed by taking into account the dierence in the momenta of the incoming and outgoing particles, measured through the energy loss, and by choosing an impact parameter in the range of the nuclear interaction radius [12] up to the sum of the half-matter radii of projectile and target [9]. The level density description is a crucial point in the calculation of the statistical decay. The parameterization in the standard version of cascade was changed to describe the level densities of nuclei near closed shells correctly. Toachieve a smooth and uniform level density description over a large range of excitation energies, a formulation developed by W. Reisdorf et al. [13] was employed. In this parameterization the density parameter a depends on the excitation energy U via the expression, a =~a 1+ U 1, e,u (1) U and takes the ground state shell correction U into account. The quantity ~a is dened as ~a = A=da 0 with da 0 chosen to reproduce known level densities at low excitation energies.
3 A/a (MeV) 20 (a) (b) Figure 1: Level density parameters A=a for 120 Sn (a) and Pb isotopes (b). The level density for 120 Sn is parameterized as A=a = da +2:3(U=A) with da = 8 (solid line) and da =9 (dashed line). For the Pb isotopes the Reisdorf [13] approach for the level densities is used and A=a = da is plotted sequentially for 208 Pb (top) to 198 Pb (bottom). Figure 1 (right panel) shows the large dierences of the parameter da = A=a for neighboring Pb nuclei in Reisdorf's parameterization. At higher excitation energies and for nuclei farther away from the closed shell, these dierences smoothen out and the da-parameter converges to a value of about 9, which is consistent with systematics. In case of the Sn target, the shell inuence at low excitation energies is not signicant. In our measurement, the Sn target nuclei were populated to higher excitation energies compared to the Pb target. A level density with the parameter ~a was adopted according to reference [14], where ~a is given by: ~a = A da +2:3 U=A : (2) This description leads to a decrease of ~a from A=8 atlow excitation to A= at a nuclear temperature of 3 MeV (Figure 1, left panel). In the analysis of the lead target data this parameterization was not used because the nuclear temperatures were lower and the eect is smaller for heavier masses. To model the extracted -ray spectra, not only the statistically emitted rays, as calculated in the way described above, had to be taken into account, but also non-statistical contributions from nuclear bremsstrahlung processes. These were assumed to have an exponentially decreasing energy dependence of the form exp (,E =E 0 ). The inverse slope parameter E 0 was chosen according to bremsstrahlungs measurements at dierent projectile energies from Reference [15]. In the ts a value of 14 MeV was used for the beam energies of 40 and 50 MeV/nucleon. This value reproduced the observed slope in the -energy spectra at energies beyond the GDR. The exponential description for the non-statistical contribution was folded with the detector response and then normalized to the measured spectra in the high energy range of 25{30 MeV. The statistical calculations were normalized to the measured data in an energy region below the GDR energy, where the non-statistical contribution is negligible, and then folded with the response of the BaF 2 detectors. The scaled non-statistical contribution was added before comparison to the full measured spectra. Non-statistical contributions amounted to
4 Table 1: Results of the analysis of the 120 Sn and the 208 Pb data. The rst column list the excitation energy interval, and the following columns contain the nuclear temperature and the GDR width for both targets. 120 Sn 208 Pb Energy range T, GDR T, GDR (MeV) (MeV) (MeV) (MeV) (MeV) 30{ { { 40{ { { { { { { { { { 120{ { { about {15% in the GDR energy range. By applying the statistical model calculation and comparing to the measured -ray spectra from all energy cuts, the GDR parameters for the Sn and the Pb target were extracted as a function of excitation energy. A systematic increase of the resonance width with excitation energy was observed in both targets. The nuclear temperature reects the target excitation on which the dipole resonance is build on. The eective target excitation E e was calculated using the mean excitation of the input population of each energy cut and subtracting the mean value of rotational energy as well as the GDR energy. p To calculate the temperature with the eective target excitation the expression T = E e =a(e e )was employed. Here a(e e ) is the energy-dependent level density parameter used in the cascade calculation. Table 1 lists the extracted GDR width for the calculated temperature for the two targets 120 Sn and 208 Pb. The uncertainty of the extracted widths for the Sn and the Pb target were estimated to be 1 MeV and 0.5 MeV, respectively. This estimation was obtained by a variation of the width input parameter of the cascade calculation and comparison to the measured data with its statistical errors. The errors include the statistical uncertainty, the eect of the variation of GDR energy, and the uncertainty of the non-statistical contribution. They do not reect any systematic inuence of the level density description. 3. Comparison with Theoretical Models The increase of the GDR width with increasing excitation energy has been explained
5 Γ GDR (MeV) 120 Sn Pb Sn Pb Γ GDR (MeV) Figure 2: The extracted GDR widths for 120 Sn (left) and 208 Pb (right) as a function of nuclear temperature. The ground state value is included at zero temperature. The upper panel includes ts with a p T dependence (solid) and a T 2 dependence (dashed) and the lower panels compare the data with adiabatic coupling calculations (solid) and collisional damping calculations (dashed). by the adiabatic coupling of the resonance to shape variations of the nucleus induced by temperature and angular momentum [16], or by a convolution of Landau damping (one-body) with the damping due to two-body collisions [17]. Simple estimates of the adiabatic coupling model predict approximately a p T dependence of the width as a function of temperature [18], whereas the collisional model predicts a T 2 dependence [19], although this is still controversial because recently it was argued that the temperature dependence should be extremely weak [20]. Figure 2 show the measured width as a function of temperature for 120 Sn (left) and 208 Pb (right). As shown in the top panels the width increase is consistent with a quadratic dependence on temperature (dashed), which is expected from a two body collisional damping model. In contrast, a p T dependence, corresponding to the adiabatic coupling and shown as the solid line in the two top panels of Figure 2 describes only the 120 Sn data reasonably well whereas it fails to describe the observed increase in 208 Pb. However, these are only simple estimates and the full calculations were performed for both models [5, 21]. The results of the collisional model are shown as dashed lines in the lower panels of Figure 2. The calculated dependence is weaker than T 2 and although it can reproduce the 208 Pb data it fails to reproduce the 120 Sn data [17, 21]. The results of the adiabatic coupling model (solid lines in lower panels) are able to reproduce the trend of both data sets reasonable well. They both still show the general p T dependence. The upper solid line in the 120 Sn calculation includes the eect of the evaporation widths which increases rapidly with increasing excitation energy [22], and improves the agreement between the calculation and the highest temperature data points [5]. The important dierence between 120 Sn and 208 Pb is the strong shell eects present in the latter case, which shift the onset of the p T behavior to approximately 1 MeV, at which the shell eects are washed out.
6 <I>(h _ ) Γ GDR (MeV) (a) (b) Figure 3: Mean angular momentum (a) and GDR widths (b) from 50 MeV/nucleon scattering of 120 Sn 2 in comparison to fusion-evaporation measurements of 8,112 Sn nuclei from Ref.[3] (N) and Ref.[4] (). The direct comparison of these calculations with the data is however not straight forward. The determination of the temperature depends critically on the level density parameter. In order to get a more quantitative description of the data, it is necessary to incorporate the calculated GDR strength function in the statistical model code and compare the experimental spectra directly and not just the extracted GDR width. In case of the measurement of the GDR in excited 120 Sn nuclei a comparison with other experimental results is possible, as data from various fusion-evaporation experiments performed with Sn isotopes are available [3, 4, 8]. In Figure 3 the obtained results from the Sn measurement with 50 MeV/nucleon beam energy [9] is compared to fusion-evaporation measurements of Sn isotopes. The top panel shows the calculated mean angular momentum of the compound nuclei of the fusion reactions (lled symbols) and the inelastic scattering reaction (open squares) versus the nuclear temperature. The temperature for the data from Refs. [3] (triangles) and [4] (circles) was calculated using the same energy-dependent level density parameterization as for the inelastic scattering data. The angular momentum is about to 20~ lower in case of the inelastic scattering data. In the bottom panel the measured widths are plotted. In contrast to the angular momenta the values of the GDR width do not dier signicantly in their evolution with nuclear temperature, indicating that the eect of the spin on the resonance width is not large. Thus it seems that the observed width increase of the GDR in highly excited Sn isotopes is mainly a temperature related eect which is in apparent contrast to the recent observation of the increase of the GDR width due to angular momentum at a constant temperature [8]. However, both eects can be qualitatively described within the adiabatic coupling model as
7 Γ GDR (MeV) Spin (h) Figure 4: The GDR width as a function of spin at a constant temperature of 1.8 MeV. The data include inelastic scattering (diamond), inclusive fusion (circle) and multiplicity gated fusion (squares) experiments. The results of an adiabatic coupling and a collisional damping calculation are shown as solid and dashed lines, respectively. shown in gure 4. The gure includes experimental values of the GDR width for a constant temperature of 1.8 MeV for inelastic scattering (diamond) [9], inclusive fusion (circle) [4] and multiplicity gated fusion (squares) [8] experiments. At spins below 30~ the width is constant for a given temperature, consistent with gure 3 whereas at larger spins the width increases. The collisional damping model does not include spin eects and thus is constant (dashed) and underpredicts the experimental values of the GDR width. The adiabatic coupling model (solid) predicts an increase at larger spins, although it underpredicts the magnitude. 4. Conclusions and Outlook The study of the GDR as a function of temperature independent of the inuence of angular momenta is possible with small angle inelastic -scattering. The increase of the GDR width with temperature was compared with an adiabatic coupling model and with a collisional model. The adiabatic coupling of the GDR to the nuclear surface could explain the data and showed the inuence of shell eects up to a temperature of 1 MeV in 208 Pb. It also was able to predict the width increase for large angular momenta at a constant temperature. The collisional model agrees with the 208 Pb data, however, it underpredicts the width increase observed for 120 Sn and does not include any angular momentum eects. For the detailed comparison between the data and the calculations it will be necessary to include the strength functions explicitly into the statistical model code. These calculations are currently in progress and will potentially be able to distinguish between the two descriptions of the broadening of the GDR as a function of temperature.
8 5. References [1] K. A. Snover, Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 36, 545 (1986). [2] J. J. Gaardhje, Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 42, 483 (1992). [3] J. J. Gaardhje, C. Ellegaard, B. Herskind, and S. G. Steadman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 148 (1984); J. J. Gaardhje, C. Ellegaard, B. Herskind, R. M. Diamond, M. A. Deleplanque, G. Dines, A. O. Macchiavelli, and F. S. Stephens, ibid. 56, 1783 (1986). [4] D. R. Chakrabarty, S. Sen, M. Thoennessen, N. Alamanos, P. Paul, R. Schicker, J. Stachel, and J. J. Gaardhje, Phys. Rev. C 36, 1886 (1987). [5] W. E. Ormand, P. F. Bortignon, and R. A. Broglia, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 607 (1996). [6] Proc. of the Gull Lake Nuclear Physics Conf. on Giant Resonances, Nucl. Phys. A569 (1994), Proc. of the Groningen Conf. on Giant Resonances, Nucl. Phys. A599 (1996). [7] M. Thoennessen et al., Phys. Rev. C 43, R12 (1991). [8] A. Bracco, F. Camera, M. Mattiuzzi, B. Million, M. Pignanelli, J. J. Gaardhje, A. Maj, T. Ramsy, T.Tveter, and Z. Zelazny, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3748 (1995). [9] E. Ramakrishnan et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 2025 (1996). [] E. Ramakrishnan et al., Phys. Lett. B 383, 252 (1996). [11] F. Puhlhofer, Nucl. Phys. A280, 267 (1977). [12] W. W. Wilcke, J. R. Birkelund, H. J. Wollersheim, A. D. Hoover, J. R. Huizenga, W. U. Schroder, and L. E. Tubbs, At. Nucl. Data Tables 25, 389 (1980). [13] W. Reisdorf, Z. Phys. A 300, 227 (1981). [14] S. Shlomo and J. B. Natowitz, Phys. Rev. C 44, 2878 (1991). [15] H. Nifenecker and J. A. Pinston, Annu. Rev. Nuc. Part. Sci. 40, 113 (1990). [16] M. Gallardo, M. Diebel, T. Dssing, and R. A. Broglia, Nucl. Phys. A443, 415 (1985); Y. Alhassid, B. Bush, and S. Levit, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 1926 (1988); J. M. Pacheco, C. Yannouleas, and R. A. Broglia, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 294 (1988); Y. Alhassid and B. Bush, Nucl. Phys. A509, 461 (1990). [17] V. Baran, M. Colonna, M. DiToro, A. Guarnera, V.N. Kondratyev, and A. Smerzi, Nucl. Phys. A599, 29c (1996). [18] R. A. Broglia, P. F. Bortignon, and A. Bracco, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 28, 517 (1992). [19] A. Smerzi, A. Bonasera, and M. DiToro, Phys. Rev. C 44, 1713 (1991). [20] P. Donati, N. Giovanardi, P. F. Bortignon, and R. A. Broglia, Phys. Lett. B 383, 15 (1996). [21] M. DiToro, private communication. [22] Ph. Chomaz, Phys. Lett. B 347, 1 (1995).
Temperature dependence of the giant dipole resonance in 120 Sn
 Temperature dependence of the giant dipole resonance in 120 Sn G. Gervais, 1,* M. Thoennessen, 1 and W. E. Ormand 2 1 National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Temperature dependence of the giant dipole resonance in 120 Sn G. Gervais, 1,* M. Thoennessen, 1 and W. E. Ormand 2 1 National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Evidence for the inuence of reaction dynamics on the population of compound nuclei
 1 Submitted to the Proceedings of the First Latin-American Workshop on: On and O Line Beam Gamma Spectroscopy for the Study of Heavy Ion Reactions and Pre-Equilibrium Processes, September 4-8, 1995, Universidad
1 Submitted to the Proceedings of the First Latin-American Workshop on: On and O Line Beam Gamma Spectroscopy for the Study of Heavy Ion Reactions and Pre-Equilibrium Processes, September 4-8, 1995, Universidad
Submitted to the Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Dynamical Aspects of Nuclear Fission
 Submitted to the Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Dynamical Aspects of Nuclear Fission August 30 - September 4, 1996, Casta-Papiernicka, Slovak Republic Dynamical Fission Timescales
Submitted to the Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Dynamical Aspects of Nuclear Fission August 30 - September 4, 1996, Casta-Papiernicka, Slovak Republic Dynamical Fission Timescales
GDR FEEDING OF THE HIGHLY-DEFORMED BAND IN 42 Ca
 Vol. 36 (2005) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 4 GDR FEEDING OF THE HIGHLY-DEFORMED BAND IN 42 Ca M. Kmiecik a, A. Maj a, J. Styczeń a, P. Bednarczyk a,d,e M. Brekiesz a, J. Grębosz a, M. Lach a, W. Męczyński
Vol. 36 (2005) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 4 GDR FEEDING OF THE HIGHLY-DEFORMED BAND IN 42 Ca M. Kmiecik a, A. Maj a, J. Styczeń a, P. Bednarczyk a,d,e M. Brekiesz a, J. Grębosz a, M. Lach a, W. Męczyński
Giant Dipole Resonance - New Experimental Perspectives
 Proceedings of the DAE Symp. on Nucl. Phys. 7 (0) 4 Giant Dipole Resonance - New Experimental Perspectives Sudhee R. Banerjee Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, /AF, Bidhan Nagar, Kolkata - 700 064, INDIA
Proceedings of the DAE Symp. on Nucl. Phys. 7 (0) 4 Giant Dipole Resonance - New Experimental Perspectives Sudhee R. Banerjee Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, /AF, Bidhan Nagar, Kolkata - 700 064, INDIA
S. YOKOYAMA 1;2. Abstract. Light particle-unstable nuclei were studied along the neutron. B is a possible candidate for neutron
 Submitted to the Proceedings of Hirschegg Workshop XXIV on \Extremes of Nuclear Structure", January -20, 1996. NUCLEAR STRUCTURE OF PARTICLE UNSTALE NUCLEI M. THOENNESSEN, 1;2 A. AZHARI, 1;2 T. AUMANN,
Submitted to the Proceedings of Hirschegg Workshop XXIV on \Extremes of Nuclear Structure", January -20, 1996. NUCLEAR STRUCTURE OF PARTICLE UNSTALE NUCLEI M. THOENNESSEN, 1;2 A. AZHARI, 1;2 T. AUMANN,
R.L. VARNER, N. GAN, J.R. BEENE, M.L. HALBERT, D.W. STRACENER. Physics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA
 GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN EXOTIC NUCLEI: BE R.L. VARNER, N. GAN, J.R. BEENE, M.L. HALBERT, D.W. STRACENER Physics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA A. AZHARI, E. RAMAKRISHNAN,
GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN EXOTIC NUCLEI: BE R.L. VARNER, N. GAN, J.R. BEENE, M.L. HALBERT, D.W. STRACENER Physics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA A. AZHARI, E. RAMAKRISHNAN,
II. GAMMA-DECAY STRENGTH FUNCTION IN HEATED NUCLEI The gamma- decay strength function f E1 ( ) determines the -emission from heated nuclei [8]. It is
![II. GAMMA-DECAY STRENGTH FUNCTION IN HEATED NUCLEI The gamma- decay strength function f E1 ( ) determines the -emission from heated nuclei [8]. It is II. GAMMA-DECAY STRENGTH FUNCTION IN HEATED NUCLEI The gamma- decay strength function f E1 ( ) determines the -emission from heated nuclei [8]. It is](/thumbs/88/115278293.jpg) An investigation of interplay between dissipation mechanisms in heated Fermi systems by means of radiative strength functions V.A. Plujko (Plyuyko) Abstract A simple analytical expression for the -decay
An investigation of interplay between dissipation mechanisms in heated Fermi systems by means of radiative strength functions V.A. Plujko (Plyuyko) Abstract A simple analytical expression for the -decay
arxiv: v2 [nucl-th] 27 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v2 [nucl-th] 27 Nov 2012 arxiv: v2 [nucl-th] 27 Nov 2012](/thumbs/91/106352024.jpg) DAMPING OF GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN HIGHLY EXCITED NUCLEI arxiv:19.58v [nucl-th] 7 Nov 1 Nguyen Dinh Dang Theoretical Nuclear Physics Laboratory, Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, RIKEN, -1
DAMPING OF GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN HIGHLY EXCITED NUCLEI arxiv:19.58v [nucl-th] 7 Nov 1 Nguyen Dinh Dang Theoretical Nuclear Physics Laboratory, Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, RIKEN, -1
Evolution of the Giant Dipole Resonance Properties with Excitation Energy
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Evolution of the Giant Dipole Resonance Properties with Excitation Energy D.Santonocito 1 and Y.Blumenfeld 2 1 INFN - Laboratorio Nazionale del Sud,
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Evolution of the Giant Dipole Resonance Properties with Excitation Energy D.Santonocito 1 and Y.Blumenfeld 2 1 INFN - Laboratorio Nazionale del Sud,
Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei. S. Leoni and A. Bracco
 Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei S. Leoni and A. Bracco 4. Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei * 4.1. Introduction The study of the nucleus at the limits of excitation energy and
Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei S. Leoni and A. Bracco 4. Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei * 4.1. Introduction The study of the nucleus at the limits of excitation energy and
4. Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei *
 4. Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei * 4.1. Introduction The study of the nucleus at the limits of excitation energy and angular momentum is one of the central topics addressed with EUROBALL
4. Rotational motion in thermally excited nuclei * 4.1. Introduction The study of the nucleus at the limits of excitation energy and angular momentum is one of the central topics addressed with EUROBALL
Open problems in formation and decay of composite systems in heavy ion reactions
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 57, Nos 2 & 3 journal of Aug. & Sept. 200 physics pp. 469 479 Open problems in formation and decay of composite systems in heavy ion reactions G VIESTI, V RIZZI,
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 57, Nos 2 & 3 journal of Aug. & Sept. 200 physics pp. 469 479 Open problems in formation and decay of composite systems in heavy ion reactions G VIESTI, V RIZZI,
A DISSERTATION. Michigan State University. in partial fulllment of the requirements. Department of Physics and Astronomy
 GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN HIGHLY EXCITED 208 Pb NUCLEI by EASWAR RAMAKRISHNAN A DISSERTATION Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulllment of the requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF
GIANT DIPOLE RESONANCE IN HIGHLY EXCITED 208 Pb NUCLEI by EASWAR RAMAKRISHNAN A DISSERTATION Submitted to Michigan State University in partial fulllment of the requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF
Montecarlo simulation of the decay of warm superdeformed nuclei
 Montecarlo simulation of the decay of warm superdeformed nuclei E. Vigezzi INFN Milano Understanding the dynamics in the SD well: probing γ strength functions, energy barriers, level densities, residual
Montecarlo simulation of the decay of warm superdeformed nuclei E. Vigezzi INFN Milano Understanding the dynamics in the SD well: probing γ strength functions, energy barriers, level densities, residual
Damping of hot giant dipole resonance due to complex configuration mixing
 3 December 998 Physics Letters B 445 998 7 Damping of hot giant dipole resonance due to complex configuration mixing Nguyen Dinh Dang a,b,,, Kosai Tanabe a, Akito Arima b,c a Department of Physics, Saitama
3 December 998 Physics Letters B 445 998 7 Damping of hot giant dipole resonance due to complex configuration mixing Nguyen Dinh Dang a,b,,, Kosai Tanabe a, Akito Arima b,c a Department of Physics, Saitama
New T=1 effective interactions for the f 5/2 p 3/2 p 1/2 g 9/2 model space: Implications for valence-mirror symmetry and seniority isomers
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 044314 (2004) New T=1 effective interactions for the f 5/2 p 3/2 p 1/2 g 9/2 model space: Implications for valence-mirror symmetry and seniority isomers A. F. Lisetskiy, 1 B. A. Brown,
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 044314 (2004) New T=1 effective interactions for the f 5/2 p 3/2 p 1/2 g 9/2 model space: Implications for valence-mirror symmetry and seniority isomers A. F. Lisetskiy, 1 B. A. Brown,
Surrogate reactions: the Weisskopf-Ewing approximation and its limitations
 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07537 Invited Surrogate reactions: the Weisskopf-Ewing approximation and its limitations J. Escher 1,a, L.A.
International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology 2007 DOI: 10.1051/ndata:07537 Invited Surrogate reactions: the Weisskopf-Ewing approximation and its limitations J. Escher 1,a, L.A.
OPAL =0.08) (%) (y cut R 3. N events T ρ. L3 Data PYTHIA ARIADNE HERWIG. L3 Data PYTHIA ARIADNE HERWIG
 CR-244 15 May 1996 QCD-RESULTS AND STUDIES OF FOUR FERMION PROCESSES AT THE INTERMEDIATE LEP ENERGY SCALE p s = 130{136 GEV Hans-Christian Schultz-Coulon Universitat Freiburg, Fakultat fur Physik Hermann-Herder-Strae
CR-244 15 May 1996 QCD-RESULTS AND STUDIES OF FOUR FERMION PROCESSES AT THE INTERMEDIATE LEP ENERGY SCALE p s = 130{136 GEV Hans-Christian Schultz-Coulon Universitat Freiburg, Fakultat fur Physik Hermann-Herder-Strae
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, (2004)
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 014307 (2004) Giant resonances in 112 Sn and 124 Sn: Isotopic dependence of monopole resonance energies Y.-W. Lui, D. H. Youngblood, Y. Tokimoto, H. L. Clark, and B. John* Cyclotron
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 70, 014307 (2004) Giant resonances in 112 Sn and 124 Sn: Isotopic dependence of monopole resonance energies Y.-W. Lui, D. H. Youngblood, Y. Tokimoto, H. L. Clark, and B. John* Cyclotron
Dependence on neutron energy of neutron induced peaks in Ge detectors. E. Gete, D.F. Measday B.A. Moftah, M.A. Saliba, T.J. Stocki
 TRI{PP{96{10 Apr 1996 Dependence on neutron energy of neutron induced peaks in Ge detectors E. Gete, D.F. Measday B.A. Moftah, M.A. Saliba, T.J. Stocki TRIUMF, 4004 Wesbrook Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
TRI{PP{96{10 Apr 1996 Dependence on neutron energy of neutron induced peaks in Ge detectors E. Gete, D.F. Measday B.A. Moftah, M.A. Saliba, T.J. Stocki TRIUMF, 4004 Wesbrook Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, no. 1, March, 2009 55 A Comparison between Channel Selections in Heavy Ion Reactions S. Mohammadi Physics Department, Payame Noor University, Mashad 91735, IRAN (Received
Exploring contributions from incomplete fusion in 6,7 Li+ 209 Bi and 6,7 Li+ 198 Pt reactions
 Exploring contributions from incomplete fusion in 6,7 Li+ 209 Bi and 6,7 Li+ 98 Pt reactions V. V. Parkar, V. Jha, and S. Kailas,2 Nuclear Physics Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai - 400085,
Exploring contributions from incomplete fusion in 6,7 Li+ 209 Bi and 6,7 Li+ 98 Pt reactions V. V. Parkar, V. Jha, and S. Kailas,2 Nuclear Physics Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai - 400085,
SOME ASPECTS OF TRANSFER REACTIONS IN LIGHT AND HEAVY ION COLLISIONS
 Vol. 44 (2013) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 3 SOME ASPECTS OF TRANSFER REACTIONS IN LIGHT AND HEAVY ION COLLISIONS Giovanni Pollarolo Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Torino and INFN, Sez. di Torino
Vol. 44 (2013) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 3 SOME ASPECTS OF TRANSFER REACTIONS IN LIGHT AND HEAVY ION COLLISIONS Giovanni Pollarolo Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Torino and INFN, Sez. di Torino
Coupling of giant resonances to soft E1 and E2 modes in 8 B
 Physics Letters B 547 (2002) 205 209 www.elsevier.com/locate/npe Coupling of giant resonances to soft E1 and E2 modes in 8 B C.A. Bertulani National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan State
Physics Letters B 547 (2002) 205 209 www.elsevier.com/locate/npe Coupling of giant resonances to soft E1 and E2 modes in 8 B C.A. Bertulani National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan State
Evidence for K mixing in 178 Hf
 Hyperfine Interactions 107 (1997) 141^147 141 Evidence for K mixing in 178 Hf C.B. Collins The University of Texas at Dallas, Center for Quantum Electronics, PO Box 830688, Richardson, TX 75083-0688, USA
Hyperfine Interactions 107 (1997) 141^147 141 Evidence for K mixing in 178 Hf C.B. Collins The University of Texas at Dallas, Center for Quantum Electronics, PO Box 830688, Richardson, TX 75083-0688, USA
Sub-barrier fusion enhancement due to neutron transfer
 Sub-barrier fusion enhancement due to neutron transfer V. I. Zagrebaev Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reaction, JINR, Dubna, Moscow Region, Russia Received 6 March 2003; published 25 June 2003 From the analysis
Sub-barrier fusion enhancement due to neutron transfer V. I. Zagrebaev Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reaction, JINR, Dubna, Moscow Region, Russia Received 6 March 2003; published 25 June 2003 From the analysis
Nuclear structure at high excitation energies
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 57, Nos 2 & 3 journal of Aug. & Sept. 2001 physics pp. 459 467 Nuclear structure at high excitation energies A ANSARI Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar 751 005,
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 57, Nos 2 & 3 journal of Aug. & Sept. 2001 physics pp. 459 467 Nuclear structure at high excitation energies A ANSARI Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar 751 005,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in. G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration
 Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Isospin influence on Fragments production in 78 Kr + 40 Ca and 86 Kr + 48 Ca collisions at 10 MeV/nucleon G. Politi for NEWCHIM/ISODEC collaboration Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Sezione INFN - Catania,
Author(s) Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki. Citation Physics Procedia (2015), 64:
 Title Fission Study of Actinide Nuclei Us Reactions Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Author(s) Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orland James; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Chiba, Sat Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki
Title Fission Study of Actinide Nuclei Us Reactions Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Author(s) Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orland James; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Chiba, Sat Tatsuzawa, Ryotaro; Takaki, Naoyuki
High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model
 High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model Hua Zheng, 1,2 Gianluca Giuliani, 1 Matteo Barbarino, 1 and Aldo Bonasera 1,3 1 Cyclotron
High order corrections to density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations and the CoMD-α Model Hua Zheng, 1,2 Gianluca Giuliani, 1 Matteo Barbarino, 1 and Aldo Bonasera 1,3 1 Cyclotron
Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 3 journal of September 2015 physics pp. 379 384 Fission fragment mass distributions via prompt γ -ray spectroscopy L S DANU, D C BISWAS, B K NAYAK and
The rotational γ -continuum in the mass region A 110
 Nuclear Physics A 673 (2000) 64 84 www.elsevier.nl/locate/npe The rotational γ -continuum in the mass region A 110 A. Bracco a, S. Frattini a,s.leoni a, F. Camera a, B. Million a,n.blasi a, G. Falconi
Nuclear Physics A 673 (2000) 64 84 www.elsevier.nl/locate/npe The rotational γ -continuum in the mass region A 110 A. Bracco a, S. Frattini a,s.leoni a, F. Camera a, B. Million a,n.blasi a, G. Falconi
Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B
 investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
investigated at relativistic energies at R 3 B for the R 3 B collaboration Technische Universität Darmstadt E-mail: fa.schindler@gsi.de Reactions of neutron-rich Sn isotopes have been measured in inverse
Probing surface diffuseness of nucleus-nucleus potential with quasielastic scattering at deep sub-barrier energies
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C 73, 034607 (2006) Probing surface diffuseness of nucleus-nucleus potential with quasielastic scattering at deep sub-barrier energies K. Washiyama, K. Hagino, and M. Dasgupta 2 Department
PHYSICAL REVIEW C 73, 034607 (2006) Probing surface diffuseness of nucleus-nucleus potential with quasielastic scattering at deep sub-barrier energies K. Washiyama, K. Hagino, and M. Dasgupta 2 Department
Warm superdeformed nuclei:
 S. Leoni University of Milano and INFN Warm superdeformed nuclei: Probes of Nuclear Structure and Tunneling Processes At the Onset of Chaos Oslo WS May 29 Outline: 1- INTRO: Warm Superdeformed Nuclei 2-
S. Leoni University of Milano and INFN Warm superdeformed nuclei: Probes of Nuclear Structure and Tunneling Processes At the Onset of Chaos Oslo WS May 29 Outline: 1- INTRO: Warm Superdeformed Nuclei 2-
DIFFUSENESS OF WOODS SAXON POTENTIAL AND SUB-BARRIER FUSION
 Modern Physics Letters A Vol. 26, No. 28 (20) 229 234 c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 0.42/S0277303654 DIFFUSENESS OF WOODS SAXON POTENTIAL AND SUB-BARRIER FUSION MANJEET SINGH, SUKHVINDER S.
Modern Physics Letters A Vol. 26, No. 28 (20) 229 234 c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 0.42/S0277303654 DIFFUSENESS OF WOODS SAXON POTENTIAL AND SUB-BARRIER FUSION MANJEET SINGH, SUKHVINDER S.
Annax-I. Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in
 Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
Annax-I Investigation of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in 40 Ca on 68,70 Zn at and near the Coulomb barrier. Abstract We will study the multi-nucleon transfer between two medium-heavy nuclei to find
At low excitation, the compound nucleus de-excites by statistical emission of light particles (n,p,α)
 Does the α cluster structure in light nuclei persist through the fusion process? Justin Vadas, T.K. Steinbach, J. Schmidt, V. Singh, S. Hudan, R.T. de Souza; Indiana University L. Baby, S. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover;
Does the α cluster structure in light nuclei persist through the fusion process? Justin Vadas, T.K. Steinbach, J. Schmidt, V. Singh, S. Hudan, R.T. de Souza; Indiana University L. Baby, S. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover;
Michigan State University, East Lansing MI48824, USA INTRODUCTION
 Two-Proton Decay of the First Excited State of 17 Ne M.J. Chromik 1;2,P.G. Thirolf 1;2, M. Thoennessen 1, M. Fauerbach 1, T. Glasmacher 1, R. Ibbotson 1, R.A. Kryger 1, H. Scheit 1, and P.J. Woods 3 1
Two-Proton Decay of the First Excited State of 17 Ne M.J. Chromik 1;2,P.G. Thirolf 1;2, M. Thoennessen 1, M. Fauerbach 1, T. Glasmacher 1, R. Ibbotson 1, R.A. Kryger 1, H. Scheit 1, and P.J. Woods 3 1
ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS
 Vol. 29 (1998) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS M. Andersson a, Chr. Bargholtz a, E. Fumero a, K. Fransson a L. Holmberg a, K. Lindh a, L. Mårtensson a,
Vol. 29 (1998) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 11 ISOSPIN RESOLVED DOUBLE PION PRODUCTION AT CELSIUS M. Andersson a, Chr. Bargholtz a, E. Fumero a, K. Fransson a L. Holmberg a, K. Lindh a, L. Mårtensson a,
Charged-particle evaporation from hot 164 Yb compound nuclei and the role of 5 He emission
 PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 56, NUMBER 2 AUGUST 1997 Charged-particle evaporation from hot 164 Yb compound nuclei and the role of 5 He emission R. J. Charity, M. Korolija,* D. G. Sarantites, and L. G. Sobotka
PHYSICAL REVIEW C VOLUME 56, NUMBER 2 AUGUST 1997 Charged-particle evaporation from hot 164 Yb compound nuclei and the role of 5 He emission R. J. Charity, M. Korolija,* D. G. Sarantites, and L. G. Sobotka
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations
 Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
Density and temperature of fermions and bosons from quantum fluctuations Hua Zheng and Aldo Bonasera 1 1 Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, INFN, via Santa Sofia, 6, 951 Catania, Italy In recent years, the
The many facets of breakup reactions with exotic beams
 Angela Bonaccorso The many facets of breakup reactions with exotic beams G Blanchon, DM Brink, F Carstoiu, A Garcia-Camacho, R Kumar, JMargueron, N Vinh Mau JAPAN-ITALY EFES Workshop on Correlations in
Angela Bonaccorso The many facets of breakup reactions with exotic beams G Blanchon, DM Brink, F Carstoiu, A Garcia-Camacho, R Kumar, JMargueron, N Vinh Mau JAPAN-ITALY EFES Workshop on Correlations in
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 27 May 2002
 1 MEASUREMENTS OF NUCLEAR LEVEL DENSITIES AND γ-ray STRENGTH FUNCTIONS AND THEIR INTERPRETATIONS M. Guttormsen, M. Hjorth-Jensen, J. Rekstad and S. Siem Department of Physics, University of Oslo, Box 1048
1 MEASUREMENTS OF NUCLEAR LEVEL DENSITIES AND γ-ray STRENGTH FUNCTIONS AND THEIR INTERPRETATIONS M. Guttormsen, M. Hjorth-Jensen, J. Rekstad and S. Siem Department of Physics, University of Oslo, Box 1048
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei
 Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
What is Spallation???
 What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT. Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF
 98 7 HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT J. J. VAN HUNEN (for the HERMES collaboration) Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF Postbus 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
98 7 HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT J. J. VAN HUNEN (for the HERMES collaboration) Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF Postbus 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation
 July 2007 EPL, 79 (2007) 12001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/79/12001 www.epljournal.org Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation M. Mocko 1,M.B.Tsang 1(a),Z.Y.Sun 1,2,
July 2007 EPL, 79 (2007) 12001 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/79/12001 www.epljournal.org Extrapolation of neutron-rich isotope cross-sections from projectile fragmentation M. Mocko 1,M.B.Tsang 1(a),Z.Y.Sun 1,2,
SURROGATE REACTIONS. An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL
 SURROGATE REACTIONS An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL Compound Nuclear Reaction cross sections Cross sections for compound-nuclear reactions are required input for astrophysical models and
SURROGATE REACTIONS An overview of papers by Jason Burke from LLNL Compound Nuclear Reaction cross sections Cross sections for compound-nuclear reactions are required input for astrophysical models and
Measurement of the g-factors of 2 + states in stable A=112,114,116 Sn isotopes using the transient field technique
 Measurement of the g-factors of 2 + states in stable A=112,114,116 Sn isotopes using the transient field technique A. Jungclaus 1, J. Leske 2, K.-H. Speidel 3, V. Modamio 1, J. Walker 1, P. Doornenbal
Measurement of the g-factors of 2 + states in stable A=112,114,116 Sn isotopes using the transient field technique A. Jungclaus 1, J. Leske 2, K.-H. Speidel 3, V. Modamio 1, J. Walker 1, P. Doornenbal
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure
 Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Introduction: heavy-ion fusion reactions 2. Fusion and Quasi-elastic
Heavy-ion sub-barrier fusion reactions: a sensitive tool to probe nuclear structure Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Introduction: heavy-ion fusion reactions 2. Fusion and Quasi-elastic
Investigation of the Giant Monopole Resonance in the Cd and Pb Isotopes: The Asymmetry Term in Nuclear Incompressibility and the MEM Effect
 460 Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement No. 196, 2012 Investigation of the Giant Monopole Resonance in the Cd and Pb Isotopes: The Asymmetry Term in Nuclear Incompressibility and the MEM Effect
460 Progress of Theoretical Physics Supplement No. 196, 2012 Investigation of the Giant Monopole Resonance in the Cd and Pb Isotopes: The Asymmetry Term in Nuclear Incompressibility and the MEM Effect
Citation for published version (APA): van Pol, J. H. G. (1996). Dissipation mechanisms studied with nuclear bremsstrahlung Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Dissipation mechanisms studied with nuclear bremsstrahlung van Pol, Johannes Hubertus Gerardus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Dissipation mechanisms studied with nuclear bremsstrahlung van Pol, Johannes Hubertus Gerardus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
MESON PRODUCTION IN NN COLLISIONS
 MENU 07 11th International Conference on Meson-Nucleon Physics and the Structure of the Nucleon September10-14, 07 IKP, Forschungzentrum Jülich, Germany MESON PRODUCTION IN NN COLLISIONS K. Nakayama a,b,1,
MENU 07 11th International Conference on Meson-Nucleon Physics and the Structure of the Nucleon September10-14, 07 IKP, Forschungzentrum Jülich, Germany MESON PRODUCTION IN NN COLLISIONS K. Nakayama a,b,1,
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup
 Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Dipole Response of Exotic Nuclei and Symmetry Energy Experiments at the LAND R 3 B Setup Dominic Rossi for the LAND collaboration GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH D 64291 Darmstadt, Germany
Electromagnetic Dipole Strength distribution in 124,128,134 Xe below the neutron separation energy
 Electromagnetic Dipole Strength distribution in 124,128,134 Xe below the neutron separation energy Ralph Massarczyk Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf 29.05.2013 R.Massarczyk (HZDR) dipole strength in
Electromagnetic Dipole Strength distribution in 124,128,134 Xe below the neutron separation energy Ralph Massarczyk Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf 29.05.2013 R.Massarczyk (HZDR) dipole strength in
Microscopic Fusion Dynamics Based on TDHF
 Dynamical Approach Microscopic Fusion Dynamics Based on TDHF FISSION FUSION Calculate PES as a function of nuclear shape Microscopic HF, HFB, RMF + constraints e.g. Q20, Q30, Q40 as H + lql0 Macroscopic-Microscopic
Dynamical Approach Microscopic Fusion Dynamics Based on TDHF FISSION FUSION Calculate PES as a function of nuclear shape Microscopic HF, HFB, RMF + constraints e.g. Q20, Q30, Q40 as H + lql0 Macroscopic-Microscopic
COLLECTIVITY IN LIGHT NUCLEI AND THE GDR
 COLLECTIVITY IN LIGHT NUCLEI AND THE GDR A. MAJ, J. STYCZEŃ, M. KMIECIK, P. BEDNARCZYK, M. BREKIESZ, J. GRȨBOSZ, M. LACH, W. MȨCZYŃSKI, M. ZIȨBLIŃSKI AND K. ZUBER The Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear
COLLECTIVITY IN LIGHT NUCLEI AND THE GDR A. MAJ, J. STYCZEŃ, M. KMIECIK, P. BEDNARCZYK, M. BREKIESZ, J. GRȨBOSZ, M. LACH, W. MȨCZYŃSKI, M. ZIȨBLIŃSKI AND K. ZUBER The Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 29 Apr 1999
 Observation of Thermodynamical Properties in the 162 Dy, 166 Er and 172 Yb Nuclei E. Melby, L. Bergholt, M. Guttormsen, M. Hjorth-Jensen, F. Ingebretsen, S. Messelt, J. Rekstad, A. Schiller, S. Siem, and
Observation of Thermodynamical Properties in the 162 Dy, 166 Er and 172 Yb Nuclei E. Melby, L. Bergholt, M. Guttormsen, M. Hjorth-Jensen, F. Ingebretsen, S. Messelt, J. Rekstad, A. Schiller, S. Siem, and
Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department. Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas Abstract
 Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
Subthreshold kaon production and the nuclear equation of state G. Q. Li and C. M. Ko Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 77843 Abstract We reexamine
X. Chen, Y. -W. Lui, H. L. Clark, Y. Tokimoto, and D. H. Youngblood
 Folding model analysis for 240MeV 6 Li elastic scattering on 28 Si and 24 Mg X. Chen, Y. -W. Lui, H. L. Clark, Y. Tokimoto, and D. H. Youngblood In order to study giant resonance induced by 6 Li scattering,
Folding model analysis for 240MeV 6 Li elastic scattering on 28 Si and 24 Mg X. Chen, Y. -W. Lui, H. L. Clark, Y. Tokimoto, and D. H. Youngblood In order to study giant resonance induced by 6 Li scattering,
Improving neutron detection efficiency by using passive converters
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 192 (2002) 339 344 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Improving neutron detection efficiency by using passive converters T. Baumann a, *, H. Ikeda b,c, M.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 192 (2002) 339 344 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Improving neutron detection efficiency by using passive converters T. Baumann a, *, H. Ikeda b,c, M.
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM
 Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Isoscaling, isobaric yield ratio and the symmetry energy: interpretation of the results with SMM P. Marini, A. Botvina, A. Bonasera, Z. Kohley, L. W. May, R. Tripathi, S. Wuenschel, and S. J. Yennello
Theoretical Analysis of Neutron Double-Differential Cross Section of n + 19 F at 14.2 MeV
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 47 (2007) pp. 102 106 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 47, No. 1, January 15, 2007 Theoretical Analysis of Neutron Double-Differential Cross Section of n +
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 47 (2007) pp. 102 106 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 47, No. 1, January 15, 2007 Theoretical Analysis of Neutron Double-Differential Cross Section of n +
Order-to-Chaos Transition in Rotational Nuclei
 Order-to-Chaos Transition in Rotational Nuclei I.Y. Lee, F.S. Stephens, M.A. Deleplanque, A.O. Macchiavelli, D. Ward, P. Fallon, M. Cormaz, R.M. Clark, M. Descovich, R.M. Diamond, and E. Rodriguez-Vieitez
Order-to-Chaos Transition in Rotational Nuclei I.Y. Lee, F.S. Stephens, M.A. Deleplanque, A.O. Macchiavelli, D. Ward, P. Fallon, M. Cormaz, R.M. Clark, M. Descovich, R.M. Diamond, and E. Rodriguez-Vieitez
Isospin Character of Low-Lying Pygmy Dipole States via Inelastic Scattering of 17 O ions
 14 th International Conference on Nuclear Reaction Mechanisms Varenna, June 15-19, 2015 Isospin Character of Low-Lying Pygmy Dipole States via Inelastic Scattering of 17 O ions Fabio Crespi Università
14 th International Conference on Nuclear Reaction Mechanisms Varenna, June 15-19, 2015 Isospin Character of Low-Lying Pygmy Dipole States via Inelastic Scattering of 17 O ions Fabio Crespi Università
Lecture 14 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Nuclear Reactions Ch 11 Ch 13 Ch /2 7.5 Reaction dynamics /4 Reaction cross sections 11.
 Lecture 14 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Nuclear Reactions Ch 11 Ch 13 Ch 13 7.1/2 7.5 Reaction dynamics 11.2 13.2 7.3/4 Reaction cross sections 11.4 2.10 Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3
Lecture 14 Krane Enge Cohen Williams Nuclear Reactions Ch 11 Ch 13 Ch 13 7.1/2 7.5 Reaction dynamics 11.2 13.2 7.3/4 Reaction cross sections 11.4 2.10 Reaction theories compound nucleus 11.10 13.7 13.1-3
Fusion of light halo nuclei
 Fusion of light halo nuclei Alinka Lépine-Szily Instituto de Física-Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil 1111118th 118th Intn Few-Body Problems in PhysIcs 8th International IUPAP Conference on
Fusion of light halo nuclei Alinka Lépine-Szily Instituto de Física-Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil 1111118th 118th Intn Few-Body Problems in PhysIcs 8th International IUPAP Conference on
Investigation of the Pygmy Dipole Resonance in particle- coincidence experiments
 Investigation of the Pygmy Dipole Resonance in particle- coincidence experiments V. Derya 1*, J. Endres 1, M. N. Harakeh 2,3, D. Savran 4,5, M. Spieker 1*, H. J. Wörtche 2, and A. Zilges 1 1 Institute
Investigation of the Pygmy Dipole Resonance in particle- coincidence experiments V. Derya 1*, J. Endres 1, M. N. Harakeh 2,3, D. Savran 4,5, M. Spieker 1*, H. J. Wörtche 2, and A. Zilges 1 1 Institute
(Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S Pb
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content (Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S + 208 Pb To cite this article: M Evers et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012129 - Quantum
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Related content (Multi-)nucleon transfer in the reactions 16 O, 3 32 S + 208 Pb To cite this article: M Evers et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 420 012129 - Quantum
DSAM lifetime measurements for the chiral bands in 194 Tl
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS DSAM lifetime measurements for the chiral bands in 194 Tl To cite this article: P L Masiteng et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 724 012028 Related content
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS DSAM lifetime measurements for the chiral bands in 194 Tl To cite this article: P L Masiteng et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 724 012028 Related content
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008](/thumbs/82/87023836.jpg) Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Elie: an event generator for nuclear reactions Dominique Durand arxiv:0803.2159v1 [nucl-th] 14 Mar 2008 LPC Caen-ENSICAEN-Université de Caen-Basse-Normandie durand@lpccaen.in2p3.fr Abstract An event generator
Renormalization Group Methods for the Nuclear Many-Body Problem
 Renormalization Group Methods for the Nuclear Many-Body Problem A. Schwenk a,b.friman b and G.E. Brown c a Department of Physics, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 41 b Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung,
Renormalization Group Methods for the Nuclear Many-Body Problem A. Schwenk a,b.friman b and G.E. Brown c a Department of Physics, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 41 b Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung,
1 Introduction The structure of the proton is a matter of universal interest in nuclear and particle physics. Charge and current distributions are obt
 New Measurement of (GE/GM) for the Proton R. E. Segel (Spokesperson) Northwestern University, Evanstan, IL J. Arrington (Spokesperson), F. Dohrmann, D. Gaskell, D. F. Geesaman, K. Hadi, R. J. Holt, H.
New Measurement of (GE/GM) for the Proton R. E. Segel (Spokesperson) Northwestern University, Evanstan, IL J. Arrington (Spokesperson), F. Dohrmann, D. Gaskell, D. F. Geesaman, K. Hadi, R. J. Holt, H.
Double giant resonances in deformed nuclei
 Double giant resonances in deformed nuclei V.Yu. Ponomarev 1,2, C.A. Bertulani 1, and A.V. Sushkov 2 1 Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, 21945-970 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
Double giant resonances in deformed nuclei V.Yu. Ponomarev 1,2, C.A. Bertulani 1, and A.V. Sushkov 2 1 Instituto de Física, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, 21945-970 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 27 Feb 2003
 Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
Measuring Neutron Separation Energies Far from Stability W.A. Friedman a and M.B. Tsang b a Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706, USA arxiv:nucl-ex/0302030v1 27 Feb 2003 b
Collective Excitations in Exotic Nuclei
 Collective Excitations in Exotic Nuclei David Radford (ORNL) RIA Summer School, August 2002 I Nuclear Excitations: Single particle motion vs. Collective motion Collective Modes: Rotations and Vibrations
Collective Excitations in Exotic Nuclei David Radford (ORNL) RIA Summer School, August 2002 I Nuclear Excitations: Single particle motion vs. Collective motion Collective Modes: Rotations and Vibrations
N=Z Z=20 N=20. Dripline. Stable nucleus. Studied nucleus. Compound nucleus. 1p2n 0.090% 1p1n 0.015% 2p1n. 2a1p1n 2a1p
 Excited States in the 39 K and 39 Ca Mirror Pair by Thomas Andersson February 1999 Supervisors: Prof. Claes Fahlander Dr. Dirk Rudolph Department of Physics Division of Cosmic and Subatomic Physics Lund
Excited States in the 39 K and 39 Ca Mirror Pair by Thomas Andersson February 1999 Supervisors: Prof. Claes Fahlander Dr. Dirk Rudolph Department of Physics Division of Cosmic and Subatomic Physics Lund
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes. Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2
 Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
Photonuclear Reaction Cross Sections for Gallium Isotopes Serkan Akkoyun 1, Tuncay Bayram 2 1 Cumhuriyet University, Vocational School of Healt, Sivas, Turkey 2 Sinop University, Department of Physics,
hep-ph/ Oct
 DMR-THEP-94-6/W March 1994 Energy dependence of source geometry and chaoticity in hadronic collisions from Bose-Einstein correlations I.V. Andreev 1;2, M. Plumer 1y, B.R. Schlei 1z and R.M. Weiner 1x 1
DMR-THEP-94-6/W March 1994 Energy dependence of source geometry and chaoticity in hadronic collisions from Bose-Einstein correlations I.V. Andreev 1;2, M. Plumer 1y, B.R. Schlei 1z and R.M. Weiner 1x 1
Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 401 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16401-0 Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions J. Benlliure( 1 ),J.L.Rodriguez-Sanchez( 1 ),J.Vargas(
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 401 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16401-0 Colloquia: IWM-EC 2016 Exciting baryon resonances in isobar charge-exchange reactions J. Benlliure( 1 ),J.L.Rodriguez-Sanchez( 1 ),J.Vargas(
In this paper the uncertainties in the NLO QCD inclusive jet calculations are explored using two available programs: Jetrad [4] a complete O( S3 ) eve
![In this paper the uncertainties in the NLO QCD inclusive jet calculations are explored using two available programs: Jetrad [4] a complete O( S3 ) eve In this paper the uncertainties in the NLO QCD inclusive jet calculations are explored using two available programs: Jetrad [4] a complete O( S3 ) eve](/thumbs/72/66472712.jpg) An Investigation of Uncertainties in the QCD NLO Predictions of the Inclusive Jet Cross Section in pp Collisions at p s =.8 TeV and 630 GeV B. Abbott, 5 I.A. Bertram, 6 M. Bhattacharjee, 7 G. Di Loreto,
An Investigation of Uncertainties in the QCD NLO Predictions of the Inclusive Jet Cross Section in pp Collisions at p s =.8 TeV and 630 GeV B. Abbott, 5 I.A. Bertram, 6 M. Bhattacharjee, 7 G. Di Loreto,
Effect of Barrier Height on Nuclear Fusion
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 78-4861.Volume 9, Issue 1 Ver. I (Jan. Feb. 17), PP 8-16 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Barrier Height on Nuclear Fusion G. S. Hassan 1, A. Abd-EL-Daiem,
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 78-4861.Volume 9, Issue 1 Ver. I (Jan. Feb. 17), PP 8-16 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Barrier Height on Nuclear Fusion G. S. Hassan 1, A. Abd-EL-Daiem,
Introduction to Nuclear Science
 Introduction to Nuclear Science PIXIE-PAN Summer Science Program University of Notre Dame 2006 Tony Hyder, Professor of Physics Topics we will discuss Ground-state properties of the nucleus Radioactivity
Introduction to Nuclear Science PIXIE-PAN Summer Science Program University of Notre Dame 2006 Tony Hyder, Professor of Physics Topics we will discuss Ground-state properties of the nucleus Radioactivity
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION. A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal. and. the Kr Collaboration
 AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
On unitarity of the particle-hole dispersive optical model
 On unitarity of the particle-hole dispersive optical model M.L. Gorelik 1), S. Shlomo 2,3), B.A. Tulupov 4), M.H. Urin 5) 1) Moscow Economic School, Moscow 123022, Russia 2) Cyclotron Institute, Texas
On unitarity of the particle-hole dispersive optical model M.L. Gorelik 1), S. Shlomo 2,3), B.A. Tulupov 4), M.H. Urin 5) 1) Moscow Economic School, Moscow 123022, Russia 2) Cyclotron Institute, Texas
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca n
 Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
Study of Isospin simmetry using the PARIS detector. Alice Mentana
 Study of Isospin simmetry using the PARIS detector Alice Mentana The Isospin simmetry Isospin Mixing (breaking of Isospin simmetry) Experimental technique: γ-decay of GDR Experimental apparatus: the PARIS
Study of Isospin simmetry using the PARIS detector Alice Mentana The Isospin simmetry Isospin Mixing (breaking of Isospin simmetry) Experimental technique: γ-decay of GDR Experimental apparatus: the PARIS
CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions
 CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 10; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 4 Notation Energetics of Nuclear Reactions Reaction Types and Mechanisms
CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 10; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 4 Notation Energetics of Nuclear Reactions Reaction Types and Mechanisms
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program
 Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Partonic transport simulations of jet quenching
 Partonic transport simulations of jet quenching Z. Xu, C. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik J. W. Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt Outline motivation introduction to the model simulations of Au+Au
Partonic transport simulations of jet quenching Z. Xu, C. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik J. W. Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt Outline motivation introduction to the model simulations of Au+Au
Probing the shell model using nucleon knockout reactions
 Probing the shell model using nucleon knockout reactions J A Tostevin Department of Physics, School of Electronics and Physical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, United Kingdom, and Graduate
Probing the shell model using nucleon knockout reactions J A Tostevin Department of Physics, School of Electronics and Physical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, United Kingdom, and Graduate
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast
 Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
Experimental Indications for the Response of the Spectators to the Participant Blast M. V. Ricciardi a, T. Enqvist a,*, J. Pereira b, J. Benlliure b, M. Bernas c, E. Casarejos b, V. Henzl a,, A. Kelić
FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds
 9 FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds LIU ZU-HUA 1 and BAO JING-DONG 2,3 1 China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, People s Republic of China 2 Department
9 FAVORABLE HOT FUSION REACTION FOR SYNTHESIS OF NEW SUPERHEAVY NUCLIDE 272 Ds LIU ZU-HUA 1 and BAO JING-DONG 2,3 1 China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing 102413, People s Republic of China 2 Department
1. Nuclear Size. A typical atom radius is a few!10 "10 m (Angstroms). The nuclear radius is a few!10 "15 m (Fermi).
 1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
Noncentral collisions
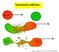 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
