On the anticrowding population dynamics taking into account a discrete set of offspring
|
|
|
- David Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 2015 DOI: /LMR.A pages On the anticrowding population dynamics taking into account a discrete set of offspring Šarūnas Repšys, Vladas Skakauskas Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University Naugarduko 4, LT Vilnius sarunas.repsys1@mif vu.lt, vladas.skakauskas@maf.vu.lt Abstract. A model of a population dynamics is solved numerically taking into account a discrete set of offsprings and the nonlinear (directed) diffusion. The model consists of a system of integro-partial differential equations subject to conditions of integral type. A spread of initially lokalized population is studied. Some numerical results are discussed. Keywords: population dynamics, anticrowding population, nonlinear diffusion, discrete set of offsprings. 1 Introduction Mammals and birds feed, warm, defend their youngs from enemies, and learn them to find a food and hide from enemies. If one of those duties is non realized young offsprings die. In recent years (see [3, 4, 2]) three models were proposed for populations taking care of their young offsprings. Two of them describe dynamics of two-sex population forming temporal and permanent pairs. In the third one a one-sex population dynamics model is studied taking into account the random spatial diffusion. In the present paper we consider a one-sex age-structured population deterministic model taking into account a discrete set of offsprings, their care, and nonlinear spatial diffusion of individuals. In case of linear diffusion initially localised population instantaneously spreads into all habitat. Nonlinear diffusion conditiones spread of population into a bounded domain. Goal of the paper is the numerical study of the population spread onto 1-dimensional habitat. Based on the paper [1] we proposed and approved a numerical algorithm. We assume that all individuals have prereproductive, reproductive, and postreproductive age intervals. The individuals of reproductive age are divided into groups of singles and those who take care of their young offsprings. All individuals of prereproductive age are divided into young (under maternal care) and juvenile classes. Juveniles can live without maternal care but cannot produce offsprings. The model consists of integro-partial differential equations. Number of these equations depends on a biologically possible maximal newborns number of the same generation produced by an individual. The paper is organised as follows. In Section 3 we introduce the model, in Section 4 we discuss numerical results. Concluding remarks are given in Section 5.
2 On the anticrowding population dynamics taking into account a discrete set 85 2 Notation R m : the Euclidean space of dimension m with x = (x 1,...,x m ); κ: the diffusion modulus; (0,T) and (T 1,T 3 ) (T < T 1 < T 3 ): the child care and reproductive age intervals, respectively; u(t,τ 1,x): the age-space-density of individuals aged τ 1 at time t at the position x who are of juvenile (τ 1 (T,T 1 )), single (τ 1 (T 1,T 3 )), or post-reproductive (τ 1 > T 3 ) age; u k (t,τ 1,τ 2,x): the age-space-density of individuals aged τ 1 at time t at the position x who take care of their k offsprings aged τ 2 at the same time; ν(t,τ 1,x): the natural death rate of individuals aged τ 1 at time t at the position x who are of juvenile or adult age; ν k (t,τ 1,τ 2,x): the natural death rate of individuals aged τ 1 at time t at the position x who take care of their k offsprings aged τ 2 ; ν ks (t,τ 1,τ 2,x): the natural death rate of k s young offsprings aged τ 2 at time t at the position x whose mother is aged τ 1 at the same time; ν k = ν k + k 1 s=0 ν ks; α k (t,τ 1,x)dt: the probability to producek offsprings in the time interval[t,t+dt] at the location x for an individual aged τ 1 ; N(t, x): sum of spatial densities of juvenile and adult individuals; u 0 (τ 1,x), u k0 (τ 1,τ 2,x): the initial age distributions; [u τ1=τ]: the jump discontinuity of u at the point τ 1 = τ; α = n α k, γ 1 (τ 1 ) = max(0,τ 1 T 3 ), γ 2 (τ 1 ) = min(τ 1 T 1,T); T 2 = T 1 +T : the minimal age of an individual finishing care of offsprings of the first generation; T 4 = T 3 +T: the maximal age of an individual finishing care of offsprings of the last generation; σ 1 = (T 1,T 3 ), σ 2 = (T 1,T 4 ), σ 3 = (T 2,T 4 ); σ 1 = (T, )\σ 1, σ 2 = (T, )\σ 2, σ 3 = (T, )\σ 3 ; Q = {(τ 1,τ 2 ) : τ 1 (T 1 +τ 2,T 3 +τ 2 ), τ 2 (0,T)}. 3 The anticrowding population model In this section, we give the population dynamics model in Ω with both the extremely inhospitable and impermeable boundary Ω which can be described by the system. Here t and τk denote partial derivatives, η is the operator of the outward normal derivative on the Ω, div(u k N) = u N + u N, while n is the biologically possible maximal number of newborns of the same generation produced by an individual. Liet. matem. rink. Proc. LMS, Ser. A, 56, 2015,
3 86 Š. Repšys, V. Skakauskas { 0, τ1 σ 1, t u+ τ1 u = νu+κdiv(u N) αu, τ 1 σ 1 0, τ 1 σ 2, γ2(τ + 1) ν k0 u k dτ 2, τ 1 σ 2 γ 1(τ 1) 0, τ 1 σ 3, + u τ2=t k, τ t > 0, x Ω, 1 σ 3, u τ1=t = ku k τ2=t dτ 1, σ 3 u t=0 = u 0, [u τ1=τ] = 0, τ = T 1,T 2,T 3,T 4, u Ω = 0 or η u Ω = 0, t u k + τ1 u k + τ2 u k +( ν k )u k κdiv(u k N) 0, k = n, = ν sk u s, 1 k n 1, (τ 1,τ 2 ) Q, t > 0, x Ω, s=k+1 u k τ2=0 = α k u, u k t=0 = u k0, u k Ω = 0 or η u k Ω = 0, (1) (2) N = T T udτ dτ 2 T3+τ 2 T 1+τ 2 u k dτ 1. (3) The first term on the right-hand side in Eq. (1) describes the fraction of individuals who produce offsprings, the second and third terms describe the fraction of individuals whose all young offsprings die and who finish child care, respectively. The transition term k 1 s=0 ν ksu k on the left-hand side in Eq. (2) describes the fraction of individuals aged τ 1 at time t who take care of k young offsprings and whose at least one young offspring dies. Similarly, the term on the right-hand side in this equation describes a fraction of individuals aged τ 1 at time t who take care of more than k, 1 k n 1, young offsprings aged τ 2 whose number after the death of offsprings becomes equal to k. The condition [u τ1=τ] = 0, τ = T 1,T 2,T 3,T 4, means that function u must be continuous at the point, τ 1 = τ, of the discontinuity of the right-hand side of Eq. (1). The integral term in the right-hand side of Eq. (1) 1 can be written as follows: τ2 T 1 ν k0 u k dτ 2, τ 1 (T 1,T 2 ), γ 2(τ 1) γ 1(τ 1) ν k0 u k dτ 2 = 0 T 0 T ν k0 u k dτ 2, τ 1 (T 2,T 3 ), τ 2 T 3 ν k0 u k dτ 2, τ 1 (T 3,T 4 ). The constant κ is the diffusion modulus. Given functions ν, ν k, ν ks,α k, u 0, and u k0 and the unknown ones u and u k are to be positive. The positive constants T and
4 On the anticrowding population dynamics taking into account a discrete set 87 T s are also to be given. We also assume that ν, ν k, α k, and ν sk do not depend on t and x and use the following compatibility conditions: u 0 τ1=t = ku k0 τ2=t dτ 1, u 0 x=0;1 = 0, σ 3 (4) [u 0 τ1=τ] = 0, τ = T 1,T 2,T 3,T 4, u k0 τ2=0 = (α k ) t=0 u 0, u k0 Ω = 0. 4 Initial and vital functions. Numerical results In this section using computer simulations, we study model (1) (4) in R 1. The conditions z Ω = 0 and η z = 0 now reduces to z x=0;1 = 0, η z x=0;1 = 0 where z = u,u k. The model was written on the characteristics lines and then solved numerically. For units of age and lenght we use T and L. We assume that integer n is equal to 3. This coresponds to species e.g., Felis yagouarundi (2 3 children), Pseudocheirus peregrinus (1 3 children), Tremarctos ornatus (1 3 children), and Artictis binturong (1 3 children). 4.1 Initial and vital functions In all calculations we use the vital rates ν(τ 1 ) = µ 1 τ q 1 +µ 2, q > 1, ν k (τ 1,τ 2 ) = µ k1 τ q k 1 +µ k2, q k > 1, ν ks (τ 1,τ 2 ) = µ ks1 τ 2 τ 0 q +µ ks2, τ 0 < T, α k (τ 1 ) = α k1 exp { ( τ 1 (T 3 +T 1 )/2 ) q 0/αk2 }, q0 > 1, and initial functions { u0 (τ 1,x) = F 0 (x)β 3 (τ 1 +β 2 )exp{ β 1 τ 1 }, u k0 (τ 1,τ 2,x) = α k (τ 1 τ 2 )u 0 (τ 1 τ 2,x)Ũk(τ 2 ) (5) (6) which are also used in [2]. Here Ũk(τ 2 ) = 1+ τ2 T (Ũk(T) 1). Using compatibility conditions (4) 1, we determine function T3 3 β 2 (x) = Ũk(T) kα k (τ 1 )(τ 1 T)exp{ β 1 τ 1 }dτ 1 T 1 { T3 3 } 1 exp{ β 1 T} Ũk(T) kα k (τ 1 )exp{ β 1 τ 1 }dτ 1 T. (7) T 1 The positive constants µ 1, µ 2, µ k1, µ k2, µ ks1, µ ks2, q > 1, q k > 1, β 1, β 3, Ũk(T), ξ 2 1, ξ 3 1, T < T 1 < T 3, α k1, α k2, τ 0 < T, and ρ 0 remain free. Liet. matem. rink. Proc. LMS, Ser. A, 56, 2015,
5 88 Š. Repšys, V. Skakauskas Fig. 1. Comparison of N(t, x) determined by the Dirichlet problem for κ = (1);0.005(2);0.001(3). Fig. 2. Behavior of N(t, x) determined by the Dirichlet problem for F 0 = F Numerical results Results of numerical calculations are displayed in Figs. 1 3 for the following constants and initial functions: β 1 = 0.55, β 2 = 5.7, κ = 0.01; T = 1, T 1 = 2, T 2 = 3, T 3 = 4, T 4 = 5, α 11 = 0.7, α 21 = 0.75, α 31 = 0.7, α 12 = α 22 = α 32 = 4, µ 1 = µ 2 = 0.01, µ 11 = µ 12 = µ 21 = µ 22 = µ 31 = µ 32 = 0.001, µ 321 = µ 322 = µ 211 = µ 212 = µ 101 = µ 102 = , µ 311 = µ 312 = µ 201 = µ 202 = 0.001, µ 301 = µ 302 = , Ũ 1 = 0.7, Ũ 2 = 0.6, Ũ 3 = 0.5, τ 0 = 0.2, ξ 3 = 1.5, q 0 = 1.5, q 1 = 2, q 2 = 2, q = 2, 0, x [0,0.375], F 0 = F 1 = (16(x 0.375)(x 0.625) 3/2, x [0.375,0.625), 0, x [0.625,1], { (16x(0.5 x)) 3/2, x [0,0.5], F 0 = F 2 = 0, x [0.5,1], Function N(t, x) determined by the solution to the Dirichlet problem is exhibited in Figs. 1 and 2. In Fig. 3 the comparison of N for Dirichlet and Neumann problems is given. All figures demonstrate a spread of N(t,x) over all interval [0,1] of initially localized functions. Fig. 1 demonstrates the influence of diffusivity κ while Fig. 2 illustrates N(t, x) detemined by the solution of the Dirichlet problem for initial function F 2. In Fig. 3 we compare the N(t,x) determined by the solution to the Dirichlet and Neumann problems for the initial function F 1.
6 On the anticrowding population dynamics taking into account a discrete set 89 Fig. 3. Comparison of N(t,x) for the Dirichlet (1) and Neumann (2) problems in the case F 0 = F 1. 5 Concluding remarks A one sex-age-structured population dynamics model is presented for Dirichlet and Neuman problems and solved numerically taking into acount a discrete set of offsprings, strong maternal care, and nonlinear spatial difusion. Acording to strong maternal care all offspring die if their mother dies. Because of the diffusion fluxes, u N and u k N, the model is nonlinear and describes an anticrowding population dynamics. A spread of initially localized population over all interval is studied. Our numerous simulations demonstrate a fast convergence of numerical algorithm used for calculations but it s mathematical justification is an open problem. References [1] C. Chiu. A numerical method for nonlinear age-dependent population models. Differ. Integral Eq., 3: , [2] Š. Repšys and V. Skakauskas. Modelling of a one-sex age-structured population dynamics with child care. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control, 12(1):77 94, [3] V. Skakauskas. A pair formation model with a discrete set of offspring and child care. Lith. Math. J., 47(1):78 111, [4] V. Skakauskas. A one-sex population dynamics model with discrete set of offsprings and child care. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control, 13(4): , REZIUMĖ Apie nesusispiečiančios populiacijos dinamiką atsižvelgiant į diskrečią palikuonių aibę Š. Repšys, V. Skakauskas Darbe pristatomas populiacijos dinamikos modelis, kuriame tariama, kad palikuonių aibė diskreti, o difuzija (migracija) netiesinė. Modelis sudarytas iš integro-diferencialinių lygčių. Modelis išsprendžiamas skaitiniais metodais, pateikiama ir aptariama keletas rezultatų. Raktiniai žodžiai: populiacijos dinamika, netiesinė difuzija, diskrečioji palikuonių aibė, nesusispiečianti populiacija. Liet. matem. rink. Proc. LMS, Ser. A, 56, 2015,
Nullity of the second order discrete problem with nonlocal multipoint boundary conditions
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 2015 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2015.13 pages 72 77 Nullity of the second order discrete problem with
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 2015 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2015.13 pages 72 77 Nullity of the second order discrete problem with
The Euler Mascheroni constant in school
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 032-288 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 55, 204 DOI: 0.5388/LMR.A.204.04 pages 7 2 The Euler Mascheroni constant in school Juozas Juvencijus
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 032-288 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 55, 204 DOI: 0.5388/LMR.A.204.04 pages 7 2 The Euler Mascheroni constant in school Juozas Juvencijus
A discrete limit theorem for the periodic Hurwitz zeta-function
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 032-288 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 205 DOI: 0.5388/LMR.A.205.6 pages 90 94 A discrete it theorem for the periodic Hurwitz zeta-function
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 032-288 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 205 DOI: 0.5388/LMR.A.205.6 pages 90 94 A discrete it theorem for the periodic Hurwitz zeta-function
The minimizer for the second order differential problem with one nonlocal condition
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 13-818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 58, 17 DOI: 1.15388/LMR.A.17.6 pages 8 33 The minimizer for the second order differential problem with
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 13-818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 58, 17 DOI: 1.15388/LMR.A.17.6 pages 8 33 The minimizer for the second order differential problem with
Hilbert Schmidt component analysis
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.02 pages 7 11 Hilbert Schmidt component analysis Povilas Daniušis,
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.02 pages 7 11 Hilbert Schmidt component analysis Povilas Daniušis,
Transformations of formulae of hybrid logic
 LMD2010log_norg 2010/10/1 18:30 page 1 #1 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys. LMD darbai ISSN 0132-2818 Volume 51, 2010, pages 1 14 www.mii.lt/lmr/ Transformations of formulae of hybrid logic Stanislovas Norgėla,
LMD2010log_norg 2010/10/1 18:30 page 1 #1 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys. LMD darbai ISSN 0132-2818 Volume 51, 2010, pages 1 14 www.mii.lt/lmr/ Transformations of formulae of hybrid logic Stanislovas Norgėla,
Algebraic and spectral analysis of local magnetic field intensity
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 6, DOI:.388/LMR.A.. pages 4 9 Algebraic and spectral analysis of local magnetic field intensity Mantas
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 6, DOI:.388/LMR.A.. pages 4 9 Algebraic and spectral analysis of local magnetic field intensity Mantas
Method of marks for propositional linear temporal logic
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A www.mii.lt/lmr/ Vol. 55, 2014, 46 50 Method of marks for propositional linear temporal logic Regimantas
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A www.mii.lt/lmr/ Vol. 55, 2014, 46 50 Method of marks for propositional linear temporal logic Regimantas
Analysis of genetic risk assessment methods
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 32-288 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 25 DOI:.5388/LMR.A.25.9 pages 7 2 Analysis of genetic risk assessment methods Vytautas Tiešis, Algirdas
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 32-288 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 25 DOI:.5388/LMR.A.25.9 pages 7 2 Analysis of genetic risk assessment methods Vytautas Tiešis, Algirdas
Discrete uniform limit law for additive functions on shifted primes
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vol. 2, No. 4, 437 447 ISSN 392-53 http://dx.doi.org/0.5388/na.206.4. Discrete uniform it law for additive functions on shifted primes Gediminas Stepanauskas,
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vol. 2, No. 4, 437 447 ISSN 392-53 http://dx.doi.org/0.5388/na.206.4. Discrete uniform it law for additive functions on shifted primes Gediminas Stepanauskas,
A general biochemical kinetics data fitting algorithm for quasi-steady-state detection
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.03 pages 12 17 A general biochemical kinetics data fitting algorithm
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.03 pages 12 17 A general biochemical kinetics data fitting algorithm
Radial basis function method modelling borehole heat transfer: the practical application
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.04 pages 18 23 Radial basis function method modelling borehole heat
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.04 pages 18 23 Radial basis function method modelling borehole heat
Populations Study Guide (KEY) All the members of a species living in the same place at the same time.
 Populations Study Guide (KEY) 1. Define Population. All the members of a species living in the same place at the same time. 2. List and explain the three terms that describe population. a. Size. How large
Populations Study Guide (KEY) 1. Define Population. All the members of a species living in the same place at the same time. 2. List and explain the three terms that describe population. a. Size. How large
Convergence of Finite Volumes schemes for an elliptic-hyperbolic system with boundary conditions
 Convergence of Finite Volumes schemes for an elliptic-hyperbolic system with boundary conditions Marie Hélène Vignal UMPA, E.N.S. Lyon 46 Allée d Italie 69364 Lyon, Cedex 07, France abstract. We are interested
Convergence of Finite Volumes schemes for an elliptic-hyperbolic system with boundary conditions Marie Hélène Vignal UMPA, E.N.S. Lyon 46 Allée d Italie 69364 Lyon, Cedex 07, France abstract. We are interested
Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations
 Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations Zhiping Li LMAM and School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University Introduction to Hyperbolic Equations The Hyperbolic Equations n-d 1st Order Linear
Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations Zhiping Li LMAM and School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University Introduction to Hyperbolic Equations The Hyperbolic Equations n-d 1st Order Linear
AN INEQUALITY FOR TAIL PROBABILITIES OF MARTINGALES WITH BOUNDED DIFFERENCES
 Lithuanian Mathematical Journal, Vol. 4, No. 3, 00 AN INEQUALITY FOR TAIL PROBABILITIES OF MARTINGALES WITH BOUNDED DIFFERENCES V. Bentkus Vilnius Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Akademijos 4,
Lithuanian Mathematical Journal, Vol. 4, No. 3, 00 AN INEQUALITY FOR TAIL PROBABILITIES OF MARTINGALES WITH BOUNDED DIFFERENCES V. Bentkus Vilnius Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Akademijos 4,
The investigation of physiological data using the theory of complex systems
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 2015 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2015.02 pages 7 11 The investigation of physiological data using the
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 56, 2015 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2015.02 pages 7 11 The investigation of physiological data using the
On Approximation of Analytic Functions by Periodic Hurwitz Zeta-Functions
 Mathematical Modelling and Analysis http://mma.vgtu.lt Volume 24, Issue, 2 33, 29 ISSN: 392-6292 https://doi.org/.3846/mma.29.2 eissn: 648-35 On Approximation of Analytic Functions by Periodic Hurwitz
Mathematical Modelling and Analysis http://mma.vgtu.lt Volume 24, Issue, 2 33, 29 ISSN: 392-6292 https://doi.org/.3846/mma.29.2 eissn: 648-35 On Approximation of Analytic Functions by Periodic Hurwitz
THE ANALYTICAL SOLUTIONS OF THE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS BY THE METHOD OF FACTORIZATION
 Materials Physics and Mechanics (5) 47-5 Received: March 7 5 THE ANALYTICAL SOLUTIONS OF THE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS BY THE METHOD OF FACTORIZATION VA Babeshko * OV Evdokimova OM Babeshko Kuban State University
Materials Physics and Mechanics (5) 47-5 Received: March 7 5 THE ANALYTICAL SOLUTIONS OF THE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS BY THE METHOD OF FACTORIZATION VA Babeshko * OV Evdokimova OM Babeshko Kuban State University
Random convolution of O-exponential distributions
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vol. 20, No. 3, 447 454 ISSN 1392-5113 http://dx.doi.org/10.15388/na.2015.3.9 Random convolution of O-exponential distributions Svetlana Danilenko a, Jonas Šiaulys
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vol. 20, No. 3, 447 454 ISSN 1392-5113 http://dx.doi.org/10.15388/na.2015.3.9 Random convolution of O-exponential distributions Svetlana Danilenko a, Jonas Šiaulys
ESTIMATION OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR QUANTILES IN A FINITE POPULATION
 Mathematical Modelling and Analysis Volume 13 Number 2, 2008, pages 195 202 c 2008 Technika ISSN 1392-6292 print, ISSN 1648-3510 online ESTIMATION OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR QUANTILES IN A FINITE POPULATION
Mathematical Modelling and Analysis Volume 13 Number 2, 2008, pages 195 202 c 2008 Technika ISSN 1392-6292 print, ISSN 1648-3510 online ESTIMATION OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR QUANTILES IN A FINITE POPULATION
A numerical method for the wave equation subject to a non-local conservation condition
 A numerical method for the wave equation subject to a non-local conservation condition Whye-Teong Ang Division of Engineering Mechanics School of Mechanical and Production Engineering Nanyang Technological
A numerical method for the wave equation subject to a non-local conservation condition Whye-Teong Ang Division of Engineering Mechanics School of Mechanical and Production Engineering Nanyang Technological
DYNAMICS IN 3-SPECIES PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH TIME DELAYS. Wei Feng
 DISCRETE AND CONTINUOUS Website: www.aimsciences.org DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS SUPPLEMENT 7 pp. 36 37 DYNAMICS IN 3-SPECIES PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH TIME DELAYS Wei Feng Mathematics and Statistics Department
DISCRETE AND CONTINUOUS Website: www.aimsciences.org DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS SUPPLEMENT 7 pp. 36 37 DYNAMICS IN 3-SPECIES PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH TIME DELAYS Wei Feng Mathematics and Statistics Department
b e i ga set s oane f dast heco mm on n va ns ing lo c u soft w section
 66 M M Eq: 66 - -I M - - - -- -- - - - - -- - S I T - I S W q - I S T q ] q T G S W q I ] T G ˆ Gα ˆ ˆ ] H Z ˆ T α 6H ; Z - S G W [6 S q W F G S W F S W S W T - I ] T ˆ T κ G Gα ±G κ α G ˆ + G > H O T
66 M M Eq: 66 - -I M - - - -- -- - - - - -- - S I T - I S W q - I S T q ] q T G S W q I ] T G ˆ Gα ˆ ˆ ] H Z ˆ T α 6H ; Z - S G W [6 S q W F G S W F S W S W T - I ] T ˆ T κ G Gα ±G κ α G ˆ + G > H O T
64 Garunk»stis and Laurin»cikas can not be satised for any polynomial P. S. M. Voronin [10], [12] obtained the functional independence of the Riemann
![64 Garunk»stis and Laurin»cikas can not be satised for any polynomial P. S. M. Voronin [10], [12] obtained the functional independence of the Riemann 64 Garunk»stis and Laurin»cikas can not be satised for any polynomial P. S. M. Voronin [10], [12] obtained the functional independence of the Riemann](/thumbs/92/110999423.jpg) PUBLICATIONS DE L'INSTITUT MATHÉMATIQUE Nouvelle série, tome 65 (79), 1999, 63 68 ON ONE HILBERT'S PROBLEM FOR THE LERCH ZETA-FUNCTION R. Garunk»stis and A. Laurin»cikas Communicated by Aleksandar Ivić
PUBLICATIONS DE L'INSTITUT MATHÉMATIQUE Nouvelle série, tome 65 (79), 1999, 63 68 ON ONE HILBERT'S PROBLEM FOR THE LERCH ZETA-FUNCTION R. Garunk»stis and A. Laurin»cikas Communicated by Aleksandar Ivić
Application of the Total Approximation Method for the Investigation of the Temperature Regime of a Polychromatic Solid-State Lamp
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control 2005 Vol. 10 No. 2 107 117 Application of the Total Approximation Method for the Investigation of the Temperature Regime of a Polychromatic Solid-State Lamp J.
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control 2005 Vol. 10 No. 2 107 117 Application of the Total Approximation Method for the Investigation of the Temperature Regime of a Polychromatic Solid-State Lamp J.
Modeling point processes by the stochastic differential equation
 Modeling point processes by the stochastic differential equation Vygintas Gontis, Bronislovas Kaulakys, Miglius Alaburda and Julius Ruseckas Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy of Vilnius University,
Modeling point processes by the stochastic differential equation Vygintas Gontis, Bronislovas Kaulakys, Miglius Alaburda and Julius Ruseckas Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy of Vilnius University,
4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]
![4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1] 4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]](/thumbs/84/91138454.jpg) Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Simultaneous vs. non simultaneous blow-up
 Simultaneous vs. non simultaneous blow-up Juan Pablo Pinasco and Julio D. Rossi Departamento de Matemática, F.C.E y N., UBA (428) Buenos Aires, Argentina. Abstract In this paper we study the possibility
Simultaneous vs. non simultaneous blow-up Juan Pablo Pinasco and Julio D. Rossi Departamento de Matemática, F.C.E y N., UBA (428) Buenos Aires, Argentina. Abstract In this paper we study the possibility
MACROSCOPIC VARIABLES, THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM. Contents AND BOLTZMANN ENTROPY. 1 Macroscopic Variables 3. 2 Local quantities and Hydrodynamics fields 4
 MACROSCOPIC VARIABLES, THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM AND BOLTZMANN ENTROPY Contents 1 Macroscopic Variables 3 2 Local quantities and Hydrodynamics fields 4 3 Coarse-graining 6 4 Thermal equilibrium 9 5 Two systems
MACROSCOPIC VARIABLES, THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM AND BOLTZMANN ENTROPY Contents 1 Macroscopic Variables 3 2 Local quantities and Hydrodynamics fields 4 3 Coarse-graining 6 4 Thermal equilibrium 9 5 Two systems
JOINT VALUE-DISTRIBUTION THEOREMS ON LERCH ZETA-FUNCTIONS. II
 Liet. Matem. Rink.,, No., 24, JOIN VALUE-DISRIBUION HEOREMS ON LERCH ZEA-FUNCIONS. II A. Laurinčikas Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University, Naugarduko 24, L-3225 Vilnius (e-mail: antanas.laurincikas@maf.vu.lt)
Liet. Matem. Rink.,, No., 24, JOIN VALUE-DISRIBUION HEOREMS ON LERCH ZEA-FUNCIONS. II A. Laurinčikas Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University, Naugarduko 24, L-3225 Vilnius (e-mail: antanas.laurincikas@maf.vu.lt)
Fibonacci Sequence. January 19, 2014
 Fibonacci Sequence January 19, 2014 Today we will learn about the Fibonacci sequence, one of the most famous sequences of numbers in mathematics. To construct it, we will look at the pattern of growth
Fibonacci Sequence January 19, 2014 Today we will learn about the Fibonacci sequence, one of the most famous sequences of numbers in mathematics. To construct it, we will look at the pattern of growth
On iterative methods for some elliptic equations with nonlocal conditions
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2014, Vol. 19, No. 3, 517 535 517 http://dx.doi.org/10.15388/na.2014.3.14 On iterative methods for some elliptic equations with nonlocal conditions Olga Štikonienė
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2014, Vol. 19, No. 3, 517 535 517 http://dx.doi.org/10.15388/na.2014.3.14 On iterative methods for some elliptic equations with nonlocal conditions Olga Štikonienė
Math 5587 Lecture 2. Jeff Calder. August 31, Initial/boundary conditions and well-posedness
 Math 5587 Lecture 2 Jeff Calder August 31, 2016 1 Initial/boundary conditions and well-posedness 1.1 ODE vs PDE Recall that the general solutions of ODEs involve a number of arbitrary constants. Example
Math 5587 Lecture 2 Jeff Calder August 31, 2016 1 Initial/boundary conditions and well-posedness 1.1 ODE vs PDE Recall that the general solutions of ODEs involve a number of arbitrary constants. Example
ON THE VORONIN'S UNIVERSALITY THEOREM FOR THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION
 Fizikos ir matematikos fakulteto Seminaro darbai, iauliu universitetas, 6, 2003, 2933 ON THE VORONIN'S UNIVERSALITY THEOREM FOR THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION Ram unas GARUNK TIS 1 Vilnius University, Naugarduko
Fizikos ir matematikos fakulteto Seminaro darbai, iauliu universitetas, 6, 2003, 2933 ON THE VORONIN'S UNIVERSALITY THEOREM FOR THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION Ram unas GARUNK TIS 1 Vilnius University, Naugarduko
ANALYSIS OF THE LAW OF THE ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR THE IDLE TIME OF A CUSTOMER IN MULTIPHASE QUEUES
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 66 No. 2 2011, 183-190 ANALYSIS OF THE LAW OF THE ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR THE IDLE TIME OF A CUSTOMER IN MULTIPHASE QUEUES Saulius Minkevičius
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 66 No. 2 2011, 183-190 ANALYSIS OF THE LAW OF THE ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR THE IDLE TIME OF A CUSTOMER IN MULTIPHASE QUEUES Saulius Minkevičius
A Method for Measuring the Specific Electrical Conductivity of an Anisotropically Conductive Medium
 Vol. 113 2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 A Method for Measuring the Specific Electrical Conductivity of an Anisotropically Conductive Medium S. Ašmontas a,, J. Kleiza b and V. Kleiza a a Kaunas Technology
Vol. 113 2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 A Method for Measuring the Specific Electrical Conductivity of an Anisotropically Conductive Medium S. Ašmontas a,, J. Kleiza b and V. Kleiza a a Kaunas Technology
ON WEAK SOLUTION OF A HYPERBOLIC DIFFERENTIAL INCLUSION WITH NONMONOTONE DISCONTINUOUS NONLINEAR TERM
 Internat. J. Math. & Math. Sci. Vol. 22, No. 3 (999 587 595 S 6-72 9922587-2 Electronic Publishing House ON WEAK SOLUTION OF A HYPERBOLIC DIFFERENTIAL INCLUSION WITH NONMONOTONE DISCONTINUOUS NONLINEAR
Internat. J. Math. & Math. Sci. Vol. 22, No. 3 (999 587 595 S 6-72 9922587-2 Electronic Publishing House ON WEAK SOLUTION OF A HYPERBOLIC DIFFERENTIAL INCLUSION WITH NONMONOTONE DISCONTINUOUS NONLINEAR
Asymptotics for posterior hazards
 Asymptotics for posterior hazards Pierpaolo De Blasi University of Turin 10th August 2007, BNR Workshop, Isaac Newton Intitute, Cambridge, UK Joint work with Giovanni Peccati (Université Paris VI) and
Asymptotics for posterior hazards Pierpaolo De Blasi University of Turin 10th August 2007, BNR Workshop, Isaac Newton Intitute, Cambridge, UK Joint work with Giovanni Peccati (Université Paris VI) and
Modified Serre Green Naghdi equations with improved or without dispersion
 Modified Serre Green Naghdi equations with improved or without dispersion DIDIER CLAMOND Université Côte d Azur Laboratoire J. A. Dieudonné Parc Valrose, 06108 Nice cedex 2, France didier.clamond@gmail.com
Modified Serre Green Naghdi equations with improved or without dispersion DIDIER CLAMOND Université Côte d Azur Laboratoire J. A. Dieudonné Parc Valrose, 06108 Nice cedex 2, France didier.clamond@gmail.com
A new regularity criterion for weak solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations
 A new regularity criterion for weak solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations Yong Zhou Department of Mathematics, East China Normal University Shanghai 6, CHINA yzhou@math.ecnu.edu.cn Proposed running
A new regularity criterion for weak solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations Yong Zhou Department of Mathematics, East China Normal University Shanghai 6, CHINA yzhou@math.ecnu.edu.cn Proposed running
TIME PERIODIC PROBLEMS FOR NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN DOMAINS WITH CYLINDRICAL OUTLETS TO INFINITY
 thesis 28/6/13 22:48 page 1 #1 VILNIUS GEDIMINAS TECHNINICAL UNIVERSITETY INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS AND INFORMATICS Vaidas KEBLIKAS TIME PERIODIC PROBLEMS FOR NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN DOMAINS WITH CYLINDRICAL
thesis 28/6/13 22:48 page 1 #1 VILNIUS GEDIMINAS TECHNINICAL UNIVERSITETY INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS AND INFORMATICS Vaidas KEBLIKAS TIME PERIODIC PROBLEMS FOR NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN DOMAINS WITH CYLINDRICAL
Insect Success. Insects are one of the most successful groups of living organisms on earth
 Insect Success Insects are one of the most successful groups of living organisms on earth Why Insects are so successful Insects comprise about 95% of all known animal species. Actually it is insects instead
Insect Success Insects are one of the most successful groups of living organisms on earth Why Insects are so successful Insects comprise about 95% of all known animal species. Actually it is insects instead
On the convergence rate of a difference solution of the Poisson equation with fully nonlocal constraints
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 04, Vol. 9, No. 3, 367 38 367 http://dx.doi.org/0.5388/na.04.3.4 On the convergence rate of a difference solution of the Poisson equation with fully nonlocal
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 04, Vol. 9, No. 3, 367 38 367 http://dx.doi.org/0.5388/na.04.3.4 On the convergence rate of a difference solution of the Poisson equation with fully nonlocal
WXML Final Report: Chinese Restaurant Process
 WXML Final Report: Chinese Restaurant Process Dr. Noah Forman, Gerandy Brito, Alex Forney, Yiruey Chou, Chengning Li Spring 2017 1 Introduction The Chinese Restaurant Process (CRP) generates random partitions
WXML Final Report: Chinese Restaurant Process Dr. Noah Forman, Gerandy Brito, Alex Forney, Yiruey Chou, Chengning Li Spring 2017 1 Introduction The Chinese Restaurant Process (CRP) generates random partitions
The derivation of the Liouville equation
 Chapter 5 The derivation of the Liouville equation The probability density ρ in phase space can be defined as the relative number density of the phase points associated with an infinite statistical ensemble.
Chapter 5 The derivation of the Liouville equation The probability density ρ in phase space can be defined as the relative number density of the phase points associated with an infinite statistical ensemble.
Asynchronous Training in Wireless Sensor Networks
 u t... t. tt. tt. u.. tt tt -t t t - t, t u u t t. t tut t t t t t tt t u t ut. t u, t tt t u t t t t, t tt t t t, t t t t t. t t tt u t t t., t- t ut t t, tt t t tt. 1 tut t t tu ut- tt - t t t tu tt-t
u t... t. tt. tt. u.. tt tt -t t t - t, t u u t t. t tut t t t t t tt t u t ut. t u, t tt t u t t t t, t tt t t t, t t t t t. t t tt u t t t., t- t ut t t, tt t t tt. 1 tut t t tu ut- tt - t t t tu tt-t
Splitting methods with boundary corrections
 Splitting methods with boundary corrections Alexander Ostermann University of Innsbruck, Austria Joint work with Lukas Einkemmer Verona, April/May 2017 Strang s paper, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 1968 S (5)
Splitting methods with boundary corrections Alexander Ostermann University of Innsbruck, Austria Joint work with Lukas Einkemmer Verona, April/May 2017 Strang s paper, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 1968 S (5)
Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations
 Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations Zhiping Li LMAM and School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University Modified Equation of a Difference Scheme What is a Modified Equation of a Difference
Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations Zhiping Li LMAM and School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University Modified Equation of a Difference Scheme What is a Modified Equation of a Difference
EXTREME OF RANDOM FIELD OVER RECTANGLE WITH APPLICATION TO CONCRETE RUPTURE STRESSES
 8 th ASCE Specialty Conference on Probabilistic Mechanics and Structural Reliability PMC2- EXTREME OF RANDOM FIELD OVER RECTANGLE WITH APPLICATION TO CONCRETE RUPTURE STRESSES Ove Ditlevsen, M. ASCE Technical
8 th ASCE Specialty Conference on Probabilistic Mechanics and Structural Reliability PMC2- EXTREME OF RANDOM FIELD OVER RECTANGLE WITH APPLICATION TO CONCRETE RUPTURE STRESSES Ove Ditlevsen, M. ASCE Technical
Convergence and Error Bound Analysis for the Space-Time CESE Method
 Convergence and Error Bound Analysis for the Space-Time CESE Method Daoqi Yang, 1 Shengtao Yu, Jennifer Zhao 3 1 Department of Mathematics Wayne State University Detroit, MI 480 Department of Mechanics
Convergence and Error Bound Analysis for the Space-Time CESE Method Daoqi Yang, 1 Shengtao Yu, Jennifer Zhao 3 1 Department of Mathematics Wayne State University Detroit, MI 480 Department of Mechanics
Two Concerns for Managers of Polar Bear Populations in the Near Future
 Two Concerns for Managers of Polar Bear Populations in the Near Future Presentation to the Polar Bear Range States Meeting 24-26 October, 2011 Ian Stirling, PhD, FRSC on behalf of the IUCN Polar Bear Specialist
Two Concerns for Managers of Polar Bear Populations in the Near Future Presentation to the Polar Bear Range States Meeting 24-26 October, 2011 Ian Stirling, PhD, FRSC on behalf of the IUCN Polar Bear Specialist
3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity
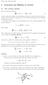 Version date: March 22, 21 1 3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity 3.1 The vorticity equation We start from Navier Stokes: u t + u u = 1 ρ p + ν 2 u 1) where we have not included a term describing a
Version date: March 22, 21 1 3 Generation and diffusion of vorticity 3.1 The vorticity equation We start from Navier Stokes: u t + u u = 1 ρ p + ν 2 u 1) where we have not included a term describing a
On one system of the Burgers equations arising in the two-velocity hydrodynamics
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS On one system of the Burgers equations arising in the two-velocity hydrodynamics To cite this article: Kholmatzhon Imomnazarov et al 216 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS On one system of the Burgers equations arising in the two-velocity hydrodynamics To cite this article: Kholmatzhon Imomnazarov et al 216 J. Phys.:
Analysis of an S-I-R Model of Epidemics with Directed Spatial Diffusion
 Analysis of an S-I-R Model of Epidemics with Directed Spatial Diffusion F.A.Milner R.Zhao Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 797-7 Abstract An S-I-R epidemic model is described
Analysis of an S-I-R Model of Epidemics with Directed Spatial Diffusion F.A.Milner R.Zhao Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 797-7 Abstract An S-I-R epidemic model is described
First Order Initial Value Problems
 First Order Initial Value Problems A first order initial value problem is the problem of finding a function xt) which satisfies the conditions x = x,t) x ) = ξ 1) where the initial time,, is a given real
First Order Initial Value Problems A first order initial value problem is the problem of finding a function xt) which satisfies the conditions x = x,t) x ) = ξ 1) where the initial time,, is a given real
SNC2D BIOLOGY 3/17/2013. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L The Importance of Cell Division (P.26-27) The Importance of Cell Division
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L The Importance of Cell Division (P.26-27) The Importance of Cell Division You began life as a single fertilized cell. Now your body is made up of trillions
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L The Importance of Cell Division (P.26-27) The Importance of Cell Division You began life as a single fertilized cell. Now your body is made up of trillions
A Low-Dimensional Model for the Maximal Amplification Factor of Bichromatic Wave Groups
 PROC. ITB Eng. Science Vol. 35 B, No., 3, 39-53 39 A Low-Dimensional Model for the Maximal Amplification Factor of Bichromatic Wave Groups W. N. Tan,* & Andonowati Fakulti Sains, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
PROC. ITB Eng. Science Vol. 35 B, No., 3, 39-53 39 A Low-Dimensional Model for the Maximal Amplification Factor of Bichromatic Wave Groups W. N. Tan,* & Andonowati Fakulti Sains, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Hydrodynamic Limit with Geometric Correction in Kinetic Equations
 Hydrodynamic Limit with Geometric Correction in Kinetic Equations Lei Wu and Yan Guo KI-Net Workshop, CSCAMM University of Maryland, College Park 2015-11-10 1 Simple Model - Neutron Transport Equation
Hydrodynamic Limit with Geometric Correction in Kinetic Equations Lei Wu and Yan Guo KI-Net Workshop, CSCAMM University of Maryland, College Park 2015-11-10 1 Simple Model - Neutron Transport Equation
An Approximate Solution for Volterra Integral Equations of the Second Kind in Space with Weight Function
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11 17 no. 18 849-861 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ijma.17.771 An Approximate Solution for Volterra Integral Equations of the Second
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11 17 no. 18 849-861 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ijma.17.771 An Approximate Solution for Volterra Integral Equations of the Second
Positive solutions for a class of fractional boundary value problems
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vol. 21, No. 1, 1 17 ISSN 1392-5113 http://dx.doi.org/1.15388/na.216.1.1 Positive solutions for a class of fractional boundary value problems Jiafa Xu a, Zhongli
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vol. 21, No. 1, 1 17 ISSN 1392-5113 http://dx.doi.org/1.15388/na.216.1.1 Positive solutions for a class of fractional boundary value problems Jiafa Xu a, Zhongli
On uniqueness of weak solutions to transport equation with non-smooth velocity field
 On uniqueness of weak solutions to transport equation with non-smooth velocity field Paolo Bonicatto Abstract Given a bounded, autonomous vector field b: R d R d, we study the uniqueness of bounded solutions
On uniqueness of weak solutions to transport equation with non-smooth velocity field Paolo Bonicatto Abstract Given a bounded, autonomous vector field b: R d R d, we study the uniqueness of bounded solutions
Nonlinear Filtering Revisited: a Spectral Approach, II
 Nonlinear Filtering Revisited: a Spectral Approach, II Sergey V. Lototsky Center for Applied Mathematical Sciences University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-3 sergey@cams-00.usc.edu Remijigus
Nonlinear Filtering Revisited: a Spectral Approach, II Sergey V. Lototsky Center for Applied Mathematical Sciences University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-3 sergey@cams-00.usc.edu Remijigus
L n = l n (π n ) = length of a longest increasing subsequence of π n.
 Longest increasing subsequences π n : permutation of 1,2,...,n. L n = l n (π n ) = length of a longest increasing subsequence of π n. Example: π n = (π n (1),..., π n (n)) = (7, 2, 8, 1, 3, 4, 10, 6, 9,
Longest increasing subsequences π n : permutation of 1,2,...,n. L n = l n (π n ) = length of a longest increasing subsequence of π n. Example: π n = (π n (1),..., π n (n)) = (7, 2, 8, 1, 3, 4, 10, 6, 9,
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Engineering Acoustics Session 1aEA: Thermoacoustics I 1aEA7. On discontinuity
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Engineering Acoustics Session 1aEA: Thermoacoustics I 1aEA7. On discontinuity
Simultaneous vs. non simultaneous blow-up
 Simultaneous vs. non simultaneous blow-up Juan Pablo Pinasco and Julio D. Rossi Departamento de Matemática, F..E y N., UBA (428) Buenos Aires, Argentina. Abstract In this paper we study the possibility
Simultaneous vs. non simultaneous blow-up Juan Pablo Pinasco and Julio D. Rossi Departamento de Matemática, F..E y N., UBA (428) Buenos Aires, Argentina. Abstract In this paper we study the possibility
Some Properties of NSFDEs
 Chenggui Yuan (Swansea University) Some Properties of NSFDEs 1 / 41 Some Properties of NSFDEs Chenggui Yuan Swansea University Chenggui Yuan (Swansea University) Some Properties of NSFDEs 2 / 41 Outline
Chenggui Yuan (Swansea University) Some Properties of NSFDEs 1 / 41 Some Properties of NSFDEs Chenggui Yuan Swansea University Chenggui Yuan (Swansea University) Some Properties of NSFDEs 2 / 41 Outline
The 2D Magnetohydrodynamic Equations with Partial Dissipation. Oklahoma State University
 The 2D Magnetohydrodynamic Equations with Partial Dissipation Jiahong Wu Oklahoma State University IPAM Workshop Mathematical Analysis of Turbulence IPAM, UCLA, September 29-October 3, 2014 1 / 112 Outline
The 2D Magnetohydrodynamic Equations with Partial Dissipation Jiahong Wu Oklahoma State University IPAM Workshop Mathematical Analysis of Turbulence IPAM, UCLA, September 29-October 3, 2014 1 / 112 Outline
On the Biological Foundation of Risk Preferences
 On the Biological Foundation of Risk Preferences Roberto Robatto and Balázs Szentes April 8, 014 Abstract This paper considers a continuous-time biological model in which the growth rate of a population
On the Biological Foundation of Risk Preferences Roberto Robatto and Balázs Szentes April 8, 014 Abstract This paper considers a continuous-time biological model in which the growth rate of a population
NON-EXTINCTION OF SOLUTIONS TO A FAST DIFFUSION SYSTEM WITH NONLOCAL SOURCES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016, No. 45, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu NON-EXTINCTION OF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016, No. 45, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu NON-EXTINCTION OF
Branching Random Walks with Immigration
 UDC 519.21 Branching Random Walks with Immigration D. Han, Yu. Makarova, S. Molchanov, E. Yarovaya Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of North Carolina at Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 28223,
UDC 519.21 Branching Random Walks with Immigration D. Han, Yu. Makarova, S. Molchanov, E. Yarovaya Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of North Carolina at Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 28223,
Twists of Lerch zeta-functions
 Twists of Lerch zeta-functions Ramūnas Garunkštis, Jörn Steuding April 2000 Abstract We study twists Lλ, α, s, χ, Q) χn+q)eλn) n+α) of Lerch zeta-functions with s Dirichlet characters χ mod and parameters
Twists of Lerch zeta-functions Ramūnas Garunkštis, Jörn Steuding April 2000 Abstract We study twists Lλ, α, s, χ, Q) χn+q)eλn) n+α) of Lerch zeta-functions with s Dirichlet characters χ mod and parameters
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models
 Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
Numerical Approximation of Phase Field Models Lecture 2: Allen Cahn and Cahn Hilliard Equations with Smooth Potentials Robert Nürnberg Department of Mathematics Imperial College London TUM Summer School
On the Spread of Epidemics in a Closed Heterogeneous Population
 On the Spread of Epidemics in a Closed Heterogeneous Population Artem Novozhilov Applied Mathematics 1 Moscow State University of Railway Engineering (MIIT) the 3d Workshop on Mathematical Models and Numerical
On the Spread of Epidemics in a Closed Heterogeneous Population Artem Novozhilov Applied Mathematics 1 Moscow State University of Railway Engineering (MIIT) the 3d Workshop on Mathematical Models and Numerical
Self-Organization and Collective Decision Making in Animal and Human Societies
 Self-Organization and Collective Decision Making... Frank Schweitzer SYSS Dresden 31 March 26 1 / 23 Self-Organization and Collective Decision Making in Animal and Human Societies Frank Schweitzer fschweitzer@ethz.ch
Self-Organization and Collective Decision Making... Frank Schweitzer SYSS Dresden 31 March 26 1 / 23 Self-Organization and Collective Decision Making in Animal and Human Societies Frank Schweitzer fschweitzer@ethz.ch
THE CONFERENCE THEORY OF THE RIEMANN ZETA AND ALLIED FUNCTIONS AT OBERWOLFACH
 39 Proc. Sci. Seminar Faculty of Physics and Mathematics, Šiauliai University, 5, 22, 39 44 THE CONFERENCE THEORY OF THE RIEMANN ZETA AND ALLIED FUNCTIONS AT OBERWOLFACH Antanas LAURINČIKAS Faculty of
39 Proc. Sci. Seminar Faculty of Physics and Mathematics, Šiauliai University, 5, 22, 39 44 THE CONFERENCE THEORY OF THE RIEMANN ZETA AND ALLIED FUNCTIONS AT OBERWOLFACH Antanas LAURINČIKAS Faculty of
strengthened. In 1971, M. M. Dodson [5] showed that fl(k; p) <c 1 if p>k 2 (here and below c 1 ;c 2 ;::: are some positive constants). Various improve
![strengthened. In 1971, M. M. Dodson [5] showed that fl(k; p) <c 1 if p>k 2 (here and below c 1 ;c 2 ;::: are some positive constants). Various improve strengthened. In 1971, M. M. Dodson [5] showed that fl(k; p) <c 1 if p>k 2 (here and below c 1 ;c 2 ;::: are some positive constants). Various improve](/thumbs/83/87461611.jpg) Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vilnius, IMI, 1999, No 4, pp. 23-30 ON WARING'S PROBLEM FOR A PRIME MODULUS A. Dubickas Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University, Naugarduko
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, Vilnius, IMI, 1999, No 4, pp. 23-30 ON WARING'S PROBLEM FOR A PRIME MODULUS A. Dubickas Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius University, Naugarduko
Operations Research Letters. On a time consistency concept in risk averse multistage stochastic programming
 Operations Research Letters 37 2009 143 147 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Operations Research Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/orl On a time consistency concept in risk averse
Operations Research Letters 37 2009 143 147 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Operations Research Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/orl On a time consistency concept in risk averse
Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind with Jump Discontinuous Kernels
 Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind with Jump Discontinuous Kernels Denis Sidorov Energy Systems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences e-mail: contact.dns@gmail.com INV Follow-up Meeting Isaac
Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind with Jump Discontinuous Kernels Denis Sidorov Energy Systems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences e-mail: contact.dns@gmail.com INV Follow-up Meeting Isaac
Modeling using conservation laws. Let u(x, t) = density (heat, momentum, probability,...) so that. u dx = amount in region R Ω. R
 Modeling using conservation laws Let u(x, t) = density (heat, momentum, probability,...) so that u dx = amount in region R Ω. R Modeling using conservation laws Let u(x, t) = density (heat, momentum, probability,...)
Modeling using conservation laws Let u(x, t) = density (heat, momentum, probability,...) so that u dx = amount in region R Ω. R Modeling using conservation laws Let u(x, t) = density (heat, momentum, probability,...)
Diffusion Processes. Lectures INF2320 p. 1/72
 Diffusion Processes Lectures INF2320 p. 1/72 Lectures INF2320 p. 2/72 Diffusion processes Examples of diffusion processes Heat conduction Heat moves from hot to cold places Diffusive (molecular) transport
Diffusion Processes Lectures INF2320 p. 1/72 Lectures INF2320 p. 2/72 Diffusion processes Examples of diffusion processes Heat conduction Heat moves from hot to cold places Diffusive (molecular) transport
Mathematical modelling and controlling the dynamics of infectious diseases
 Mathematical modelling and controlling the dynamics of infectious diseases Musa Mammadov Centre for Informatics and Applied Optimisation Federation University Australia 25 August 2017, School of Science,
Mathematical modelling and controlling the dynamics of infectious diseases Musa Mammadov Centre for Informatics and Applied Optimisation Federation University Australia 25 August 2017, School of Science,
1 Comparison of Kansa s method versus Method of Fundamental Solution (MFS) and Dual Reciprocity Method of Fundamental Solution (MFS- DRM)
 1 Comparison of Kansa s method versus Method of Fundamental Solution (MFS) and Dual Reciprocity Method of Fundamental Solution (MFS- DRM) 1.1 Introduction In this work, performances of two most widely
1 Comparison of Kansa s method versus Method of Fundamental Solution (MFS) and Dual Reciprocity Method of Fundamental Solution (MFS- DRM) 1.1 Introduction In this work, performances of two most widely
CRANK-NICOLSON FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD FOR SOLVING TIME-FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION EQUATION
 Journal of Fractional Calculus and Applications, Vol. 2. Jan. 2012, No. 2, pp. 1-9. ISSN: 2090-5858. http://www.fcaj.webs.com/ CRANK-NICOLSON FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD FOR SOLVING TIME-FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION
Journal of Fractional Calculus and Applications, Vol. 2. Jan. 2012, No. 2, pp. 1-9. ISSN: 2090-5858. http://www.fcaj.webs.com/ CRANK-NICOLSON FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD FOR SOLVING TIME-FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION
Some Semi-Markov Processes
 Some Semi-Markov Processes and the Navier-Stokes equations NW Probability Seminar, October 22, 2006 Mina Ossiander Department of Mathematics Oregon State University 1 Abstract Semi-Markov processes were
Some Semi-Markov Processes and the Navier-Stokes equations NW Probability Seminar, October 22, 2006 Mina Ossiander Department of Mathematics Oregon State University 1 Abstract Semi-Markov processes were
Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations
 Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations Zhiping Li LMAM and School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University A Model Problem and Its Difference Approximations 1-D Initial Boundary Value
Numerical Solutions to Partial Differential Equations Zhiping Li LMAM and School of Mathematical Sciences Peking University A Model Problem and Its Difference Approximations 1-D Initial Boundary Value
THE EXISTENCE OF GLOBAL ATTRACTOR FOR A SIXTH-ORDER PHASE-FIELD EQUATION IN H k SPACE
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 8, Iss. 2, 218 ISSN 1223-727 THE EXISTENCE OF GLOBAL ATTRACTOR FOR A SIXTH-ORDER PHASE-FIELD EQUATION IN H k SPACE Xi Bao 1, Ning Duan 2, Xiaopeng Zhao 3 In this paper,
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 8, Iss. 2, 218 ISSN 1223-727 THE EXISTENCE OF GLOBAL ATTRACTOR FOR A SIXTH-ORDER PHASE-FIELD EQUATION IN H k SPACE Xi Bao 1, Ning Duan 2, Xiaopeng Zhao 3 In this paper,
Propagation and quenching in a reactive Burgers-Boussinesq system.
 Propagation and quenching in a reactive system., University of New Meico, Los Alamos National Laboratory, University of Chicago October 28 Between Math and Astrophysics Motivation The model Reaction Compression
Propagation and quenching in a reactive system., University of New Meico, Los Alamos National Laboratory, University of Chicago October 28 Between Math and Astrophysics Motivation The model Reaction Compression
Author(s) Huang, Feimin; Matsumura, Akitaka; Citation Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 41(1)
 Title On the stability of contact Navier-Stokes equations with discont free b Authors Huang, Feimin; Matsumura, Akitaka; Citation Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 4 Issue 4-3 Date Text Version publisher URL
Title On the stability of contact Navier-Stokes equations with discont free b Authors Huang, Feimin; Matsumura, Akitaka; Citation Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 4 Issue 4-3 Date Text Version publisher URL
Conservative Control Systems Described by the Schrödinger Equation
 Conservative Control Systems Described by the Schrödinger Equation Salah E. Rebiai Abstract An important subclass of well-posed linear systems is formed by the conservative systems. A conservative system
Conservative Control Systems Described by the Schrödinger Equation Salah E. Rebiai Abstract An important subclass of well-posed linear systems is formed by the conservative systems. A conservative system
6. Age structure. for a, t IR +, subject to the boundary condition. (6.3) p(0; t) = and to the initial condition
 6. Age structure In this section we introduce a dependence of the force of infection upon the chronological age of individuals participating in the epidemic. Age has been recognized as an important factor
6. Age structure In this section we introduce a dependence of the force of infection upon the chronological age of individuals participating in the epidemic. Age has been recognized as an important factor
Poisson INAR processes with serial and seasonal correlation
 Poisson INAR processes with serial and seasonal correlation Márton Ispány University of Debrecen, Faculty of Informatics Joint result with Marcelo Bourguignon, Klaus L. P. Vasconcellos, and Valdério A.
Poisson INAR processes with serial and seasonal correlation Márton Ispány University of Debrecen, Faculty of Informatics Joint result with Marcelo Bourguignon, Klaus L. P. Vasconcellos, and Valdério A.
Application of finite difference method to estimation of diffusion coefficient in a one dimensional nonlinear inverse diffusion problem
 International Mathematical Forum, 1, 2006, no. 30, 1465-1472 Application of finite difference method to estimation of diffusion coefficient in a one dimensional nonlinear inverse diffusion problem N. Azizi
International Mathematical Forum, 1, 2006, no. 30, 1465-1472 Application of finite difference method to estimation of diffusion coefficient in a one dimensional nonlinear inverse diffusion problem N. Azizi
CONSTRUCTING SOLUTIONS TO THE ULTRA-DISCRETE PAINLEVE EQUATIONS
 CONSTRUCTING SOLUTIONS TO THE ULTRA-DISCRETE PAINLEVE EQUATIONS D. Takahashi Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics Ryukoku University Seta, Ohtsu 50-1, Japan T. Tokihiro Department of Mathematical
CONSTRUCTING SOLUTIONS TO THE ULTRA-DISCRETE PAINLEVE EQUATIONS D. Takahashi Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics Ryukoku University Seta, Ohtsu 50-1, Japan T. Tokihiro Department of Mathematical
Α Dispersion Relation for Open Spiral Galaxies
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1980) 1, 79 95 Α Dispersion Relation for Open Spiral Galaxies G. Contopoulos Astronomy Department, University of Athens, Athens, Greece Received 1980 March 20; accepted 1980 April
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1980) 1, 79 95 Α Dispersion Relation for Open Spiral Galaxies G. Contopoulos Astronomy Department, University of Athens, Athens, Greece Received 1980 March 20; accepted 1980 April
Chapter 2 Boundary and Initial Data
 Chapter 2 Boundary and Initial Data Abstract This chapter introduces the notions of boundary and initial value problems. Some operator notation is developed in order to represent boundary and initial value
Chapter 2 Boundary and Initial Data Abstract This chapter introduces the notions of boundary and initial value problems. Some operator notation is developed in order to represent boundary and initial value
Models for dynamic fracture based on Griffith s criterion
 Models for dynamic fracture based on Griffith s criterion Christopher J. Larsen Abstract There has been much recent progress in extending Griffith s criterion for crack growth into mathematical models
Models for dynamic fracture based on Griffith s criterion Christopher J. Larsen Abstract There has been much recent progress in extending Griffith s criterion for crack growth into mathematical models
Doubly Inhomogeneous Cluster Point Processes
 Doubly Inhomogeneous Cluster Point Processes Tomáš Mrkvička, Samuel Soubeyrand May 2016 Abscissa Motivation - Group dispersal model It is dispersal model, where particles are released in groups by a single
Doubly Inhomogeneous Cluster Point Processes Tomáš Mrkvička, Samuel Soubeyrand May 2016 Abscissa Motivation - Group dispersal model It is dispersal model, where particles are released in groups by a single
A short story about FRAP (fluourescence recovery after photobleaching)
 1 A short story about FRAP (fluourescence recovery after photobleaching) Bob Pego (Carnegie Mellon) work involving team leader: James McNally (NCI Lab of Receptor Biology & Gene Expression) Biophysicists:
1 A short story about FRAP (fluourescence recovery after photobleaching) Bob Pego (Carnegie Mellon) work involving team leader: James McNally (NCI Lab of Receptor Biology & Gene Expression) Biophysicists:
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 24 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 24 Oct 2013 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 24 Oct 2013](/thumbs/95/123545959.jpg) arxiv:137.2446v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 24 Oct 213 Extinction transition in stochastic population dynamics in a random, convective environment Róbert Juhász Institute for Solid State Physics and Optics, Wigner
arxiv:137.2446v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 24 Oct 213 Extinction transition in stochastic population dynamics in a random, convective environment Róbert Juhász Institute for Solid State Physics and Optics, Wigner
