Bacillus spores as building blocks for stimuliresponsive materials and nanogenerators
|
|
|
- Della Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bacillus spores as building blocks for stimuliresponsive materials and nanogenerators Xi Chen, L Mahadevan, Adam Driks & Ozgur Sahin 1- Estimation of energy densities from the AFM based measurements Supplementary Figure S1. Estimation of energy density from indentation force measurements. (a) Illustration of the contact between an AFM tip and a bacterial spore. (b) A simple geometric model of the experiment in (a). Energy density is determined for the case where the spore is uniformly indented along the cylindrical axis (c). Energy density is defined as the amount of work that a unit volume of spores can do in one hydrationdehydration cycle. This value can be determined by measuring the work done in a cycle and dividing it to the volume contributing to the work. Due to the finite size of the tip, the AFM based experiment does not allow uniform compression of the spores even with the large tip radii (~ 850 nm) employed in our experiments (a). The stresses and strains distribute non-uniformly along the long axis of the spore and the maximum pressure appears at the center of the contact region. To account for this non-uniformity, we approximate the spore with a cylinder that is being indented by a rigid sphere (b). We then compare this configuration with the case where the cylinder is uniformly compressed as illustrated in (c) for the same depth of indentation. Material properties are kept constant in (b) and (c). The energy density is determined by first applying the spherical-tip model in (b) to the experimental data to determine an effective elastic modulus value for the hydrated spore and then using this value to calculate the amount of work for the case in (c) when the spore is compressed uniformly with a flat tip. We relied on the experimentally determined values of indentation depths, spore diameters, and work done in a single hydration-dehydration cycle for each individual spore. Supplementary Figure S2. (a) Illustration of the sphere-cylinderplane contact and (b) the planecylinder-plane contact showing variables used in calculations. Figure S2 introduces the parameters used in our calculations. We denote the forces acting on the cylinder in (a) and (b) as and, respectively. Due to symmetry can be written as, where is force at a unit length along the cylinder. The displacements and NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY 1
2 correspond to the total deformation of the cylindrical sample in (a) and (b), which include deformations at the top and bottom. With these definitions the energy density will be given by the equation: S1.1 The force-distance relationship can be approximated by treating the contacts at the top and bottom sides of the cylinder with the Hertz model for plane-cylinder contact 1 : S1.. Here is the indentation modulus and is the indentation depth at the top side of the cylinder. Because we keep the indentation depths in (a) and (b) the same:. Substituting and into (S1), we get 4 S1. To evaluate this equation, we determine the values of and from the experimentally measured work and deformation. Separating the work done by the deformations at the top and bottom sides of the cylinder in (a) simplifies calculations: S1.4 The work due to deformations at the top side can be estimated using the Hertz model for spherecylinder contact 1-3, which gives force-distance relationship of the form: S1.5 Here is a geometric constant that depends on and. The value of is determined numerically and it is approximately 1.0 for 5 and 5. (Note that goes to infinity, Eq. (S1.5) converges the expression for the contact between sphere and plane 4). The force-distance relationship of the deformations at the bottom side of the cylinder in (a) is more difficult to represent analytically, because stresses are not distributed uniformly as in (b). However, considering that the diameter of the cylinder (~700 nm) is larger than the contact length at the spherecylinder interface (~400 nm), the impact of assuming a uniform stress profile within an interaction region of (See Supp. Fig. S2(a)) to the overall energy density is likely to be small. (To ensure the safety of this assumption, we repeated the calculations for the two extremes where is equal to the contact length and to the length of the spore 1.5 µm. The resulting estimates of energy density were within 10%). With this assumption, the force-distance relationship for the bottom contact is given by (S1.2) evaluated for a total length of L: 4. S1.6 Note that equating (S1.5) and (S1.6) and using the definition allow relating bot and to the experimentally determined using only geometrical parameters, and L. With these substitutions, the work in (S1.4) can be determined by integrating (S1.5) and (S1.6). Equating W to the experimentally determined values gives. (Measurements from all three spore types ranged from 6.0 to 8.0 GPa). Substituting the value of in (S1.3) gives the estimated energy density for uniformly compressed spores (Fig. 1f). 2 NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY
3 We note that our calculations assumed uniform material properties for spores. Although spores consist of layers, the elastic moduli of these layers are largely similar. For example, previously reported AFM based elastic modulus measurements of the coat and cortex layers provided similar values (13.6 GPa vs. 6.9 GPa) 4. Note that our estimates based on total work in a hydration-dehydration cycle gave similar results (~ 7GPa). Furthermore, measurements with the mutant spore that lacks most of its coat still resulted in similar estimates for elastic modulus, suggesting that the layers have little influence over our estimates of energy density. Other potential sources of uncertainty in energy density estimates are wrinkled coat morphology of spores and measurement uncertainties in spore heights and indentation depths. Standard deviations in the energy densities obtained from 5 spores for each spore type (Fig. 1f) suggest that the effects are relatively small. 2- Design principles for maximum energy transfer to an elastic substrate The contracting spore layer exerts a plane stress at the interface between spores and the substrate. As a result, the substrate shape deforms into a curved surface (Supp. Fig. S3). The relationship between the radius of curvature r and plane stress σ is given with the following formula 5 : (S2.1) Here E is the Young s modulus, ν is the Poisson s coefficient, and t is the thickness of the elastic substrate. In the resulting curved geometry, the strain within the elastic substrate varies linearly with distance. The neutral plane with zero strain is located 2t/3 away from the spore-substrate interface 5. Therefore, the strain s at the interface is given by (S2.2) Supplementary Figure S3. Schematic of an elastic substrate coated with a layer of bacterial spores deformed by the stress generated by the spores. Using s, we can rewrite Eq. (S2.1) as: (S2.3) Eq. S2.3 provides the plain stress-strain relationship dictated by the elastic substrate. Strain within the spore layer provides a second relationship. Precise modeling of this relationship is complicated by the complex geometries of spores and their arrangements on the surface. For simplicity, we assume the following linear relationship: (S2.4) Here M is the modulus of stretching, s dry is the strain induced in unconstrained spores upon drying, and s is given by Eq. (S2.2). Note that s dry has a negative value and for s dry < s < 0, plane stress σ is also negative. Solving (S2.3) and (S2.4) for equilibriumσ and s, and maximizing the work done by the spore layer give. Substituting, where h is the effective thickness and E h is the effective elastic modulus of spore layer, we obtain the condition of maximum energy transfer as: NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY 3
4 (S2.5) To estimate the value of the left hand side of Eq. (S2.5), we use E h ~ 7 GPa, as estimated from AFM experiments on individual spores. The bacterial spore layer has an approximate thickness of 700 nm. However due to their round shaped cross sections, spores do not make physical contact in the entirety of the 700 nm. To account for this geometrical effect, we assumed h ~ 350 nm. According to Eq. (S2.5), for a given substrate material with elastic modulus E s, maximal energy transfer to the substrate takes place at some specific thickness. In this work we used natural latex rubber sheets, which have E s ~ 1.3 GPa and v ~ 0.5. Then, the thickness of the rubber sheet should be 3.15 mm. We observed cracks in spore layers, likely because of insufficiently strong spore-spore adhesion. Therefore, we reduced the thickness of the rubber sheet to 0.5 mm (Fig. 2) and 0.75 mm (Fig. 3). 3- Typical values reported for materials frequently used or studied in the context of actuators, and stimuli responsive materials Table S1. Typical or demonstrated values of strain and energy density of various actuator materials and water-responsive materials (Values are plotted in Fig. 1g) Materials Strain (%) Energy density (kj/m 3 ) Mammalian skeletal muscle 20 8 Bio-inspired polymer composite (water responsive) Carbon nanotube actuators Piezoceramics Magnetostrictors Dielectric elastomers Thermal expansion (Al, dt = 500 K) Spider silk (water responsive) Shape memory alloys (TiNi) Ref , , References 1 Johnson, K. L. Contact mechanics. (Cambridge University Press, 1985). 2 Puttock, M. J. & Thwaite, E. G. Elastic compression of spheres and cylinders at point and line contact. (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, 1969). 3 Hrouz, J., Vojta, V. & Ilavsky, M. Penetration Behavior of the System Sphere-Cylinder. Polym Eng Sci 20, , doi:doi /pen (1980). 4 Sahin, O., Yong, E. H., Driks, A. & Mahadevan, L. Physical basis for the adaptive flexibility of Bacillus spore coats. J. R. Soc. Interface 9, , doi: /rsif (2012). 4 NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY
5 5 Stoney, G. G. The tension of metallic films deposited by electrolysis. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 82, (1909). 6 Madden, J. D. W. et al. Artificial muscle technology: Physical principles and naval prospects. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 29, , doi: /joe (2004). 7 Ma, M., Guo, L., Anderson, D. G. & Langer, R. Bio-inspired polymer composite actuator and generator driven by water gradients. Science 339, , doi: /science (2013). 8 Aliev, A. E. et al. Giant-Stroke, Superelastic Carbon Nanotube Aerogel Muscles. Science 323, , doi:doi /science (2009). 9 Zhang, Q. M., Bharti, V. V. & Zhao, X. Giant electrostriction and relaxor ferroelectric behavior in electron-irradiated poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) copolymer. Science 280, (1998). 10 Madden, J. D. Mobile robots: Motor challenges and materials solutions. Science 318, , doi:doi /science (2007). 11 Brochu, P. & Pei, Q. B. Advances in Dielectric Elastomers for Actuators and Artificial Muscles. Macromol Rapid Comm 31, 10-36, doi:doi /marc (2010). 12 Agnarsson, I., Dhinojwala, A., Sahni, V. & Blackledge, T. A. Spider silk as a novel high performance biomimetic muscle driven by humidity. Journal of Experimental Biology 212, (2009). NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY 5
Supplementary Material
 Mangili et al. Supplementary Material 2 A. Evaluation of substrate Young modulus from AFM measurements 3 4 5 6 7 8 Using the experimental correlations between force and deformation from AFM measurements,
Mangili et al. Supplementary Material 2 A. Evaluation of substrate Young modulus from AFM measurements 3 4 5 6 7 8 Using the experimental correlations between force and deformation from AFM measurements,
UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT
 2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
Determination of Mechanical Properties of Elastomers Using Instrumented Indentation
 Determination of Mechanical Properties of Elastomers Using Instrumented Indentation, Antonios E. Giannakopoulos and Dimitrios Bourntenas University of Thessaly, Department of Civil Engineering, Volos 38334,
Determination of Mechanical Properties of Elastomers Using Instrumented Indentation, Antonios E. Giannakopoulos and Dimitrios Bourntenas University of Thessaly, Department of Civil Engineering, Volos 38334,
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films
 Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Performance of a bio-inspired spider web
 Performance of a bio-inspired spider web Lingyue Zheng 1, Majid Behrooz 1, Rui Li 2, Xiaojie Wang 1 and Faramarz Gordaninejad 1 1 Composite and Intelligent Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical
Performance of a bio-inspired spider web Lingyue Zheng 1, Majid Behrooz 1, Rui Li 2, Xiaojie Wang 1 and Faramarz Gordaninejad 1 1 Composite and Intelligent Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical
Curvature of a Cantilever Beam Subjected to an Equi-Biaxial Bending Moment. P. Krulevitch G. C. Johnson
 UCRL-JC-30440 PREPRINT Curvature of a Cantilever Beam Subjected to an Equi-Biaxial Bending Moment P. Krulevitch G. C. Johnson This paper was prepared for submittal to the Materials Research Society Spring
UCRL-JC-30440 PREPRINT Curvature of a Cantilever Beam Subjected to an Equi-Biaxial Bending Moment P. Krulevitch G. C. Johnson This paper was prepared for submittal to the Materials Research Society Spring
ADHESION OF AN AXISYMMETRIC ELASTIC BODY: RANGES OF VALIDITY OF MONOMIAL APPROXIMATIONS AND A TRANSITION MODEL
 ADHESION OF AN AXISYMMETRIC ELASTIC BODY: RANGES OF VALIDITY OF MONOMIAL APPROXIMATIONS AND A TRANSITION MODEL A Thesis Presented By Fouad Oweiss to The Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
ADHESION OF AN AXISYMMETRIC ELASTIC BODY: RANGES OF VALIDITY OF MONOMIAL APPROXIMATIONS AND A TRANSITION MODEL A Thesis Presented By Fouad Oweiss to The Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field
 Lecture 7-1 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field - Electrostriction The electrostrictive effect is a quadratic dependence of strain or stress on the polarization P
Lecture 7-1 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field - Electrostriction The electrostrictive effect is a quadratic dependence of strain or stress on the polarization P
Nonlinear Finite Element Modeling of Nano- Indentation Group Members: Shuaifang Zhang, Kangning Su. ME 563: Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis.
 ME 563: Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis Spring 2016 Nonlinear Finite Element Modeling of Nano- Indentation Group Members: Shuaifang Zhang, Kangning Su Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering,
ME 563: Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis Spring 2016 Nonlinear Finite Element Modeling of Nano- Indentation Group Members: Shuaifang Zhang, Kangning Su Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering,
! Importance of Particle Adhesion! History of Particle Adhesion! Method of measurement of Adhesion! Adhesion Induced Deformation
 ! Importance of Particle Adhesion! History of Particle Adhesion! Method of measurement of Adhesion! Adhesion Induced Deformation! JKR and non-jkr Theory! Role of Electrostatic Forces! Conclusions Books:
! Importance of Particle Adhesion! History of Particle Adhesion! Method of measurement of Adhesion! Adhesion Induced Deformation! JKR and non-jkr Theory! Role of Electrostatic Forces! Conclusions Books:
Figure 43. Some common mechanical systems involving contact.
 33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
AFM Studies of Pristine PCBM Changes Under Light Exposure. Erin Chambers
 AFM Studies of Pristine PCBM Changes Under Light Exposure Erin Chambers Faculty of health, science, and technology Department of engineering and physics 15 cr Krister Svensson Lars Johansson 28 March 2013
AFM Studies of Pristine PCBM Changes Under Light Exposure Erin Chambers Faculty of health, science, and technology Department of engineering and physics 15 cr Krister Svensson Lars Johansson 28 March 2013
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 MASSACHUSTTS INSTITUT OF TCHNOLOGY DPARTMNT OF MATRIALS SCINC AND NGINRING CAMBRIDG, MASSACHUSTTS 0239 322 MCHANICAL PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS PROBLM ST 4 SOLUTIONS Consider a 500 nm thick aluminum ilm on a
MASSACHUSTTS INSTITUT OF TCHNOLOGY DPARTMNT OF MATRIALS SCINC AND NGINRING CAMBRIDG, MASSACHUSTTS 0239 322 MCHANICAL PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS PROBLM ST 4 SOLUTIONS Consider a 500 nm thick aluminum ilm on a
Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application
 Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Smart Polymer Material as Artificial Muscle Actuator
 Smart Polymer Material as Artificial Muscle Actuator Yusuf Wibisono Advanced Materials Science and Engineering Actuator Motion-generating device A mechanical device for moving or controlling a mechanism
Smart Polymer Material as Artificial Muscle Actuator Yusuf Wibisono Advanced Materials Science and Engineering Actuator Motion-generating device A mechanical device for moving or controlling a mechanism
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. a, the cross-sectional and b, top view SEM images of a PC/SWNT bilayer (SWNT film thickness of ~ 1µm). S1 Supplementary Figure S2. The obtained SWNT film
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. a, the cross-sectional and b, top view SEM images of a PC/SWNT bilayer (SWNT film thickness of ~ 1µm). S1 Supplementary Figure S2. The obtained SWNT film
Supplementary Figures
 Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Experimental Investigation of Fully Plastic Contact of a Sphere Against a Hard Flat
 J. Jamari e-mail: j.jamari@ctw.utwente.nl D. J. Schipper University of Twente, Surface Technology and Tribology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Drienerloolaan 5, Postbus 17, 7500 AE, Enschede, The
J. Jamari e-mail: j.jamari@ctw.utwente.nl D. J. Schipper University of Twente, Surface Technology and Tribology, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Drienerloolaan 5, Postbus 17, 7500 AE, Enschede, The
A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY OF ELASTIC-PLASTIC HEMISPHERICAL CONTACT BEHAVIOR AGAINST A RIGID FLAT UNDER VARYING MODULUS OF ELASTICITY AND SPHERE RADIUS
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY OF ELASTIC-PLASTIC HEMISPHERICAL CONTACT BEHAVIOR
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY OF ELASTIC-PLASTIC HEMISPHERICAL CONTACT BEHAVIOR
A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal
 Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
MONTE CARLO STUDIES ON ELONGATION OF LIQUID CRYSTAL ELASTOMERS UNDER EXTERNAL ELECTRIC FIELD E. V. Proutorov 1, H. Koibuchi 2
 MONTE CARLO STUDIES ON ELONGATION OF LIQUID CRYSTAL ELASTOMERS UNDER EXTERNAL ELECTRIC FIELD E. V. Proutorov 1, H. Koibuchi 2 1 Department of Physics, Cherepovets State University, Lunacharsky Prospect
MONTE CARLO STUDIES ON ELONGATION OF LIQUID CRYSTAL ELASTOMERS UNDER EXTERNAL ELECTRIC FIELD E. V. Proutorov 1, H. Koibuchi 2 1 Department of Physics, Cherepovets State University, Lunacharsky Prospect
Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages
 Supplementary Information for Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages Qiming Wang 1, Zhigang Suo 2 and Xuanhe Zhao 1 * 1 Soft Active Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Supplementary Information for Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages Qiming Wang 1, Zhigang Suo 2 and Xuanhe Zhao 1 * 1 Soft Active Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Influence of friction in material characterization in microindentation measurement
 Influence of friction in material characterization in microindentation measurement W.C. Guo a,b,, G. Rauchs c, W.H. Zhang b, J.P. Ponthot a a LTAS. Department of Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering, University
Influence of friction in material characterization in microindentation measurement W.C. Guo a,b,, G. Rauchs c, W.H. Zhang b, J.P. Ponthot a a LTAS. Department of Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering, University
Frontiers of Fracture Mechanics. Adhesion and Interfacial Fracture Contact Damage
 Frontiers of Fracture Mechanics Adhesion and Interfacial Fracture Contact Damage Biology, Medicine & Dentistry The Next Frontiers For Mechanics One of the current challenges in materials & mechanics is
Frontiers of Fracture Mechanics Adhesion and Interfacial Fracture Contact Damage Biology, Medicine & Dentistry The Next Frontiers For Mechanics One of the current challenges in materials & mechanics is
EE C247B / ME C218 INTRODUCTION TO MEMS DESIGN SPRING 2016 C. NGUYEN PROBLEM SET #4
 Issued: Wednesday, March 4, 2016 PROBLEM SET #4 Due: Monday, March 14, 2016, 8:00 a.m. in the EE C247B homework box near 125 Cory. 1. This problem considers bending of a simple cantilever and several methods
Issued: Wednesday, March 4, 2016 PROBLEM SET #4 Due: Monday, March 14, 2016, 8:00 a.m. in the EE C247B homework box near 125 Cory. 1. This problem considers bending of a simple cantilever and several methods
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
A Transparent Perovskite Light Emitting Touch-
 Supporting Information for A Transparent Perovskite Light Emitting Touch- Responsive Device Shu-Yu Chou, Rujun Ma, Yunfei Li,, Fangchao Zhao, Kwing Tong, Zhibin Yu, and Qibing Pei*, Department of Materials
Supporting Information for A Transparent Perovskite Light Emitting Touch- Responsive Device Shu-Yu Chou, Rujun Ma, Yunfei Li,, Fangchao Zhao, Kwing Tong, Zhibin Yu, and Qibing Pei*, Department of Materials
STANDARD SAMPLE. Reduced section " Diameter. Diameter. 2" Gauge length. Radius
 MATERIAL PROPERTIES TENSILE MEASUREMENT F l l 0 A 0 F STANDARD SAMPLE Reduced section 2 " 1 4 0.505" Diameter 3 4 " Diameter 2" Gauge length 3 8 " Radius TYPICAL APPARATUS Load cell Extensometer Specimen
MATERIAL PROPERTIES TENSILE MEASUREMENT F l l 0 A 0 F STANDARD SAMPLE Reduced section 2 " 1 4 0.505" Diameter 3 4 " Diameter 2" Gauge length 3 8 " Radius TYPICAL APPARATUS Load cell Extensometer Specimen
Electrostriction of lead zirconate titanate/polyurethane composites
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 97, 104112 2005 Electrostriction of lead zirconate titanate/polyurethane composites K. S. Lam, Y. Zhou, Y. W. Wong, a and F. G. Shin Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 97, 104112 2005 Electrostriction of lead zirconate titanate/polyurethane composites K. S. Lam, Y. Zhou, Y. W. Wong, a and F. G. Shin Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong
Please do not adjust margins. Graphene oxide based moisture-responsive biomimetic film actuators with nacrelike layered structures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Journal Name ARTICLE Supporting information
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Journal Name ARTICLE Supporting information
Large scale growth and characterization of atomic hexagonal boron. nitride layers
 Supporting on-line material Large scale growth and characterization of atomic hexagonal boron nitride layers Li Song, Lijie Ci, Hao Lu, Pavel B. Sorokin, Chuanhong Jin, Jie Ni, Alexander G. Kvashnin, Dmitry
Supporting on-line material Large scale growth and characterization of atomic hexagonal boron nitride layers Li Song, Lijie Ci, Hao Lu, Pavel B. Sorokin, Chuanhong Jin, Jie Ni, Alexander G. Kvashnin, Dmitry
ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES: STATE OF THE ART AND A NEW TECHNOLOGY
 ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES: STATE OF THE ART AND A NEW TECHNOLOGY PETR KOCIS, RADEK KNOFLICEK Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Producing Machines, Systems and Robotics,
ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES: STATE OF THE ART AND A NEW TECHNOLOGY PETR KOCIS, RADEK KNOFLICEK Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Producing Machines, Systems and Robotics,
Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation
 Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation M Shakeri, S Salehghaffari and R. Mirzaeifar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amirkabir
Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation M Shakeri, S Salehghaffari and R. Mirzaeifar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amirkabir
A CONTACT-MECHANICS BASED MODEL FOR DISHING AND EROSION IN
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 671 001 Materials Research Society A CONTACT-MECHANICS BASED MODEL FOR DISHING AND EROSION IN CHEMICAL-MECHANICAL POLISHING Joost J. Vlassak Division of Engineering and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 671 001 Materials Research Society A CONTACT-MECHANICS BASED MODEL FOR DISHING AND EROSION IN CHEMICAL-MECHANICAL POLISHING Joost J. Vlassak Division of Engineering and
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Dynamic surface deformation of silicone elastomers for management of marine biofouling: laboratory and field studies using pneumatic actuation Phanindhar Shivapooja, a Qiming
Supplementary information Dynamic surface deformation of silicone elastomers for management of marine biofouling: laboratory and field studies using pneumatic actuation Phanindhar Shivapooja, a Qiming
Supporting Information. Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films
 Supporting Information Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films Matthew Daly a,1, Changhong Cao b,1, Hao Sun b, Yu Sun b, *, Tobin Filleter b, *, and Chandra Veer Singh a, * a Department
Supporting Information Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films Matthew Daly a,1, Changhong Cao b,1, Hao Sun b, Yu Sun b, *, Tobin Filleter b, *, and Chandra Veer Singh a, * a Department
1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor.
 Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary figure 1: The fang model (longitudinal section) used for the stiffness analysis. The base of the fang is considered fixed (i.e. zero displacement constraint) and the
Supplementary figures Supplementary figure 1: The fang model (longitudinal section) used for the stiffness analysis. The base of the fang is considered fixed (i.e. zero displacement constraint) and the
Revealing bending and force in a soft body through a plant root inspired. approach. Lucia Beccai 1* Piaggio 34, Pontedera (Italy)
 Revealing bending and force in a soft body through a plant root inspired approach Chiara Lucarotti 1,2, Massimo Totaro 1, Ali Sadeghi 1, Barbara Mazzolai 1, Lucia Beccai 1* 1 Center for Micro-BioRobotics
Revealing bending and force in a soft body through a plant root inspired approach Chiara Lucarotti 1,2, Massimo Totaro 1, Ali Sadeghi 1, Barbara Mazzolai 1, Lucia Beccai 1* 1 Center for Micro-BioRobotics
XI. NANOMECHANICS OF GRAPHENE
 XI. NANOMECHANICS OF GRAPHENE Carbon is an element of extraordinary properties. The carbon-carbon bond possesses large magnitude cohesive strength through its covalent bonds. Elemental carbon appears in
XI. NANOMECHANICS OF GRAPHENE Carbon is an element of extraordinary properties. The carbon-carbon bond possesses large magnitude cohesive strength through its covalent bonds. Elemental carbon appears in
Intensity (a.u.) Intensity (a.u.) Raman Shift (cm -1 ) Oxygen plasma. 6 cm. 9 cm. 1mm. Single-layer graphene sheet. 10mm. 14 cm
 Intensity (a.u.) Intensity (a.u.) a Oxygen plasma b 6 cm 1mm 10mm Single-layer graphene sheet 14 cm 9 cm Flipped Si/SiO 2 Patterned chip Plasma-cleaned glass slides c d After 1 sec normal Oxygen plasma
Intensity (a.u.) Intensity (a.u.) a Oxygen plasma b 6 cm 1mm 10mm Single-layer graphene sheet 14 cm 9 cm Flipped Si/SiO 2 Patterned chip Plasma-cleaned glass slides c d After 1 sec normal Oxygen plasma
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry
Effect of Strain Hardening on Unloading of a Deformable Sphere Loaded against a Rigid Flat A Finite Element Study
 Effect of Strain Hardening on Unloading of a Deformable Sphere Loaded against a Rigid Flat A Finite Element Study Biplab Chatterjee, Prasanta Sahoo 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jadavpur University
Effect of Strain Hardening on Unloading of a Deformable Sphere Loaded against a Rigid Flat A Finite Element Study Biplab Chatterjee, Prasanta Sahoo 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jadavpur University
3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture,
 3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture, 09.21.07 1. In the beam considered in PS1, steel beams carried the distributed weight of the rooms above. To reduce stress on the beam, it
3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture, 09.21.07 1. In the beam considered in PS1, steel beams carried the distributed weight of the rooms above. To reduce stress on the beam, it
Modeling Contact between Rigid Sphere and Elastic Layer Bonded to Rigid Substrate
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPONENTS AND PACKAGING TECHNOLOGIES, VOL. 24, NO. 2, JUNE 2001 207 Modeling Contact between Rigid Sphere and Elastic Layer Bonded to Rigid Substrate Mirko Stevanović, M. Michael
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPONENTS AND PACKAGING TECHNOLOGIES, VOL. 24, NO. 2, JUNE 2001 207 Modeling Contact between Rigid Sphere and Elastic Layer Bonded to Rigid Substrate Mirko Stevanović, M. Michael
STUDIES ON NANO-INDENTATION OF POLYMERIC THIN FILMS USING FINITE ELEMENT METHODS
 STUDIES ON NANO-INDENTATION OF POLYMERIC THIN FILMS USING FINITE ELEMENT METHODS Shen Xiaojun, Yi Sung, Lallit Anand Singapore-MIT Alliance E4-04-0, 4 Engineering Drive 3, Singapore 7576 Zeng Kaiyang Institute
STUDIES ON NANO-INDENTATION OF POLYMERIC THIN FILMS USING FINITE ELEMENT METHODS Shen Xiaojun, Yi Sung, Lallit Anand Singapore-MIT Alliance E4-04-0, 4 Engineering Drive 3, Singapore 7576 Zeng Kaiyang Institute
Electrostriction in elastic dielectrics undergoing large deformation
 Electrostriction in elastic dielectrics undergoing large deformation Xuanhe Zhao and Zhigang Suo* School of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University MA 08 USA Abstract We develop a thermodynamic
Electrostriction in elastic dielectrics undergoing large deformation Xuanhe Zhao and Zhigang Suo* School of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University MA 08 USA Abstract We develop a thermodynamic
Mathematical Model for Pressure-Deformation Relationship of Miniaturized McKibben Actuators. {ashwinkp,
 Mathematical Model for Pressure-Deformation Relationship of Miniaturized McKibben Actuators Ashwin K.P 1 and Ashitava Ghosal 1 1 Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Email: {ashwinkp, asitava}@iisc.ac.in
Mathematical Model for Pressure-Deformation Relationship of Miniaturized McKibben Actuators Ashwin K.P 1 and Ashitava Ghosal 1 1 Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Email: {ashwinkp, asitava}@iisc.ac.in
Unloading of an elastic plastic loaded spherical contact
 International Journal of Solids and Structures 42 (2005) 3716 3729 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijsolstr Unloading of an elastic plastic loaded spherical contact I. Etsion *, Y. Kligerman, Y. Kadin Department
International Journal of Solids and Structures 42 (2005) 3716 3729 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijsolstr Unloading of an elastic plastic loaded spherical contact I. Etsion *, Y. Kligerman, Y. Kadin Department
EAP - ElectroActive Polymers
 A Short Introduction to Robotics Applications AIRLab - Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Lab Politecnico di Milano http://www.airlab.elet.polimi.it/ February 2007 Introduction to EAP Focus: Emulate
A Short Introduction to Robotics Applications AIRLab - Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Lab Politecnico di Milano http://www.airlab.elet.polimi.it/ February 2007 Introduction to EAP Focus: Emulate
Class XI Physics. Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids. NCERT Solutions
 Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Instrumented Indentation Testing
 Instrumented Indentation Testing J.L. Hay, MTS Systems Corporation G.M. Pharr, The University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory INSTRUMENTED INDENTATION TESTING (IIT), also known as depth-sensing
Instrumented Indentation Testing J.L. Hay, MTS Systems Corporation G.M. Pharr, The University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory INSTRUMENTED INDENTATION TESTING (IIT), also known as depth-sensing
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERFACIAL CRACK BETWEEN THE TWO LAYERS
 Djoković, J. M., et.al.: Influence of Temperature on Behavior of the Interfacial THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 010, Vol. 14, Suppl., pp. S59-S68 S59 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERFACIAL CRACK
Djoković, J. M., et.al.: Influence of Temperature on Behavior of the Interfacial THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 010, Vol. 14, Suppl., pp. S59-S68 S59 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERFACIAL CRACK
A General Equation for Fitting Contact Area and Friction vs Load Measurements
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 211, 395 400 (1999) Article ID jcis.1998.6027, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on A General Equation for Fitting Contact Area and Friction vs Load
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 211, 395 400 (1999) Article ID jcis.1998.6027, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on A General Equation for Fitting Contact Area and Friction vs Load
Supplementary Figure 1 shows overall fabrication process and detailed illustrations are given
 Supplementary Figure 1. Pressure sensor fabrication schematics. Supplementary Figure 1 shows overall fabrication process and detailed illustrations are given in Methods section. (a) Firstly, the sacrificial
Supplementary Figure 1. Pressure sensor fabrication schematics. Supplementary Figure 1 shows overall fabrication process and detailed illustrations are given in Methods section. (a) Firstly, the sacrificial
Application of Discrete Element Method to Study Mechanical Behaviors of Ceramic Breeder Pebble Beds. Zhiyong An, Alice Ying, and Mohamed Abdou UCLA
 Application of Discrete Element Method to Study Mechanical Behaviors of Ceramic Breeder Pebble Beds Zhiyong An, Alice Ying, and Mohamed Abdou UCLA Presented at CBBI-4 Petten, The Netherlands September
Application of Discrete Element Method to Study Mechanical Behaviors of Ceramic Breeder Pebble Beds Zhiyong An, Alice Ying, and Mohamed Abdou UCLA Presented at CBBI-4 Petten, The Netherlands September
Nano-mechatronics. Presented by: György BudaváriSzabó (X0LY4M)
 Nano-mechatronics Presented by: György BudaváriSzabó (X0LY4M) Nano-mechatronics Nano-mechatronics is currently used in broader spectra, ranging from basic applications in robotics, actuators, sensors,
Nano-mechatronics Presented by: György BudaváriSzabó (X0LY4M) Nano-mechatronics Nano-mechatronics is currently used in broader spectra, ranging from basic applications in robotics, actuators, sensors,
Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 146 (2004) 28 34 Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process Hariharasudhan Palaniswamy, Gracious Ngaile, Taylan Altan ERC
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 146 (2004) 28 34 Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process Hariharasudhan Palaniswamy, Gracious Ngaile, Taylan Altan ERC
From wrinkly elastomers to Janus particles to Janus fibres
 From wrinkly elastomers to Janus particles to Janus fibres Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa and Centro de Física Teórica e Computacional, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Work done in collaboration
From wrinkly elastomers to Janus particles to Janus fibres Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa and Centro de Física Teórica e Computacional, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Work done in collaboration
INTRODUCTION TO STRAIN
 SIMPLE STRAIN INTRODUCTION TO STRAIN In general terms, Strain is a geometric quantity that measures the deformation of a body. There are two types of strain: normal strain: characterizes dimensional changes,
SIMPLE STRAIN INTRODUCTION TO STRAIN In general terms, Strain is a geometric quantity that measures the deformation of a body. There are two types of strain: normal strain: characterizes dimensional changes,
Determining the Elastic Modulus and Hardness of an Ultrathin Film on a Substrate Using Nanoindentation
 Determining the Elastic Modulus and Hardness of an Ultrathin Film on a Substrate Using Nanoindentation The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Determining the Elastic Modulus and Hardness of an Ultrathin Film on a Substrate Using Nanoindentation The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
August 27, International ANSYS Conference Nick Reynolds, Ph.D. Director, Materials Pre-Sales, US, Accelrys
 Multiscale modeling and simulation developing solutions which link the atomistic, mesoscale, and engineering scales August 27, 2008 2008 International ANSYS Conference Nick Reynolds, Ph.D. Director, Materials
Multiscale modeling and simulation developing solutions which link the atomistic, mesoscale, and engineering scales August 27, 2008 2008 International ANSYS Conference Nick Reynolds, Ph.D. Director, Materials
CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES
 CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES * Governing equations in beam and plate bending ** Solution by superposition 1.1 From Beam Bending to Plate Bending 1.2 Governing Equations For Symmetric
CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES * Governing equations in beam and plate bending ** Solution by superposition 1.1 From Beam Bending to Plate Bending 1.2 Governing Equations For Symmetric
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians. An Introduction to Solid Mechanics. Is that supposed to bend there?
 High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus. Case study
 Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
TOUGHNESS OF PLASTICALLY-DEFORMING ASYMMETRIC JOINTS. Ford Research Laboratory, Ford Motor Company, Dearborn, MI 48121, U.S.A. 1.
 TOUGHNESS OF PLASTICALLY-DEFORMING ASYMMETRIC JOINTS M. D. Thouless, M. S. Kafkalidis, S. M. Ward and Y. Bankowski Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Michigan, Ann
TOUGHNESS OF PLASTICALLY-DEFORMING ASYMMETRIC JOINTS M. D. Thouless, M. S. Kafkalidis, S. M. Ward and Y. Bankowski Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Michigan, Ann
Lab Exercise #5: Tension and Bending with Strain Gages
 Lab Exercise #5: Tension and Bending with Strain Gages Pre-lab assignment: Yes No Goals: 1. To evaluate tension and bending stress models and Hooke s Law. a. σ = Mc/I and σ = P/A 2. To determine material
Lab Exercise #5: Tension and Bending with Strain Gages Pre-lab assignment: Yes No Goals: 1. To evaluate tension and bending stress models and Hooke s Law. a. σ = Mc/I and σ = P/A 2. To determine material
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
Question Figure shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?
 Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Elastic Properties of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Balloons
 Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 364 305 (2001) Elastic Properties of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Balloons R. STANNARIUS A, H. SCHÜRING A, C. TLKSDRF B and R. ZENTEL B A Universität Leipzig, Institut für Experimentalphysik
Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 364 305 (2001) Elastic Properties of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Balloons R. STANNARIUS A, H. SCHÜRING A, C. TLKSDRF B and R. ZENTEL B A Universität Leipzig, Institut für Experimentalphysik
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
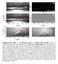 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Final Project: Indentation Simulation Mohak Patel ENGN-2340 Fall 13
 Final Project: Indentation Simulation Mohak Patel ENGN-2340 Fall 13 Aim The project requires a simulation of rigid spherical indenter indenting into a flat block of viscoelastic material. The results from
Final Project: Indentation Simulation Mohak Patel ENGN-2340 Fall 13 Aim The project requires a simulation of rigid spherical indenter indenting into a flat block of viscoelastic material. The results from
Class XI Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
 Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Stress-Strain Behavior
 Stress-Strain Behavior 6.3 A specimen of aluminum having a rectangular cross section 10 mm 1.7 mm (0.4 in. 0.5 in.) is pulled in tension with 35,500 N (8000 lb f ) force, producing only elastic deformation.
Stress-Strain Behavior 6.3 A specimen of aluminum having a rectangular cross section 10 mm 1.7 mm (0.4 in. 0.5 in.) is pulled in tension with 35,500 N (8000 lb f ) force, producing only elastic deformation.
Failure modes of glass panels subjected to soft missile impact
 Failure modes of glass panels subjected to soft missile impact L. R. Dharani & J. Yu Dept. of Mech. and Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, University of Missouri-Rolla, U.S.A. Abstract Damage
Failure modes of glass panels subjected to soft missile impact L. R. Dharani & J. Yu Dept. of Mech. and Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, University of Missouri-Rolla, U.S.A. Abstract Damage
Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Surface Electric Potential of P(VDF-TrFE) Films
 Ferroelectrics, 446:102 106, 2013 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2013.821017 Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Surface Electric
Ferroelectrics, 446:102 106, 2013 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2013.821017 Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Surface Electric
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
3-D Finite Element Analysis of Instrumented Indentation of Transversely Isotropic Materials
 3-D Finite Element Analysis of Instrumented Indentation of Transversely Isotropic Materials Abstract: Talapady S. Bhat and T. A. Venkatesh Department of Material Science and Engineering Stony Brook University,
3-D Finite Element Analysis of Instrumented Indentation of Transversely Isotropic Materials Abstract: Talapady S. Bhat and T. A. Venkatesh Department of Material Science and Engineering Stony Brook University,
Mechanics of wafer bonding: Effect of clamping
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 95, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 2004 Mechanics of wafer bonding: Effect of clamping K. T. Turner a) Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 0219 M. D. Thouless
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 95, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 2004 Mechanics of wafer bonding: Effect of clamping K. T. Turner a) Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 0219 M. D. Thouless
EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A SPHERE AGAINST A RIGID FLAT A FINITE ELEMENT STUDY
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- EFFECT OF STRAIN HARDENING ON ELASTIC-PLASTIC CONTACT BEHAVIOUR OF A
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF SLIDING CONTACT BETWEEN A CIRCULAR ASPERITY AND AN ELASTIC URFACE IN PLANE STRAIN CONDITION
 7 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (1) FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF SLIDING CONTACT BETWEEN A CIRCULAR ASPERITY AND AN ELASTIC URFACE IN PLANE STRAIN CONDITION S. Subutay Akarca,
7 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (1) FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF SLIDING CONTACT BETWEEN A CIRCULAR ASPERITY AND AN ELASTIC URFACE IN PLANE STRAIN CONDITION S. Subutay Akarca,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Tunable Shape Memory Polymer Mold
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Tunable Shape Memory Polymer Mold
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading
 MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018) 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading Statics
MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018) 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading Statics
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 4, No 1, 2013
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 4, No 1, 2013 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Nanoindentation
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 4, No 1, 2013 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Nanoindentation
Chapter 7. Highlights:
 Chapter 7 Highlights: 1. Understand the basic concepts of engineering stress and strain, yield strength, tensile strength, Young's(elastic) modulus, ductility, toughness, resilience, true stress and true
Chapter 7 Highlights: 1. Understand the basic concepts of engineering stress and strain, yield strength, tensile strength, Young's(elastic) modulus, ductility, toughness, resilience, true stress and true
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers by Oscillatory Indentation
 Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers by Oscillatory Indentation By Jennifer Hay, Nanomechanics, Inc. Abstract This application note teaches the theory and practice of measuring the complex modulus
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers by Oscillatory Indentation By Jennifer Hay, Nanomechanics, Inc. Abstract This application note teaches the theory and practice of measuring the complex modulus
AME COMPUTATIONAL MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Friction and Contact-Impact
 1 Friction AME553 -- COMPUTATIONAL MULTIBODY DYNAMICS Friction and Contact-Impact Friction force may be imposed between contacting bodies to oppose their relative motion. Friction force can be a function
1 Friction AME553 -- COMPUTATIONAL MULTIBODY DYNAMICS Friction and Contact-Impact Friction force may be imposed between contacting bodies to oppose their relative motion. Friction force can be a function
Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to:
 Chapter 12 Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to: Demonstrate your understanding of elasticity, elastic limit, stress, strain, and ultimate strength. Write and apply formulas
Chapter 12 Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to: Demonstrate your understanding of elasticity, elastic limit, stress, strain, and ultimate strength. Write and apply formulas
I. INTRODUCTION II. SAMPLE PREPARATION JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER 2002 Longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients of lead zirconate titanateõvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene composites with different
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER 2002 Longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients of lead zirconate titanateõvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene composites with different
Notes on Rubber Friction
 Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
Notes on Rubber Friction 2011 A G Plint Laws of Friction: In dry sliding between a given pair of materials under steady conditions, the coefficient of friction may be almost constant. This is the basis
A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface
 A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface *Leiming Gao 1), Gregory de Boer 2) and Rob Hewson 3) 1), 3) Aeronautics Department, Imperial College London, London, SW7
A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface *Leiming Gao 1), Gregory de Boer 2) and Rob Hewson 3) 1), 3) Aeronautics Department, Imperial College London, London, SW7
Equilibrium Piezoelectric Potential Distribution in a Deformed ZnO Nanowire
 DOI 10.1007/s12274-009-9063-2 Research Article 00624 Equilibrium Piezoelectric Potential Distribution in a Deformed ZnO Nanowire Giulia Mantini 1,2, Yifan Gao 1, A. DʼAmico 2, C. Falconi 2, and Zhong Lin
DOI 10.1007/s12274-009-9063-2 Research Article 00624 Equilibrium Piezoelectric Potential Distribution in a Deformed ZnO Nanowire Giulia Mantini 1,2, Yifan Gao 1, A. DʼAmico 2, C. Falconi 2, and Zhong Lin
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
EE C247B / ME C218 INTRODUCTION TO MEMS DESIGN SPRING 2014 C. Nguyen PROBLEM SET #4
 Issued: Wednesday, Mar. 5, 2014 PROBLEM SET #4 Due (at 9 a.m.): Tuesday Mar. 18, 2014, in the EE C247B HW box near 125 Cory. 1. Suppose you would like to fabricate the suspended cross beam structure below
Issued: Wednesday, Mar. 5, 2014 PROBLEM SET #4 Due (at 9 a.m.): Tuesday Mar. 18, 2014, in the EE C247B HW box near 125 Cory. 1. Suppose you would like to fabricate the suspended cross beam structure below
