Algorithm. Executing the Max algorithm. Algorithm and Growth of Functions Benchaporn Jantarakongkul. (algorithm) ก ก. : ก {a i }=a 1,,a n a i N,
|
|
|
- Poppy Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Algorithm and Growth of Functions Benchaporn Jantarakongkul 1 Algorithm (algorithm) ก ก ก ก ก : ก {a i }=a 1,,a n a i N, ก ก : 1. ก v ( v ก ก ก ก ) ก ก a 1 2. ก a i 3. a i >v, ก v ก a i ก ก ก v ก ก 2 Executing the Max algorithm ก ก ก ก ก {a i }=7,12,3,15,8 ก ก v = a 1 = 7 ก : a 2 = 12 a 2 >v?, ก v 12 ก : a 3 = 3 3>12?, v. 15>12?, ก v=15 ก 3 1
2 Algorithm Characteristics Some important general features of algorithms: Input. Information or data that comes in. Output. Information or data that goes out. Definiteness. Algorithm is precisely defined. Correctness. Outputs correctly relate to inputs. Finiteness. Won t take forever to describe or run. Effectiveness. Individual steps are all do-able. Generality. Works for many possible inputs. Efficiency. Takes little time & memory to run. 4 Pseudocode Language procedure name(argument: type) variable:= expression {informal statement} begin statements end {comment} if condition then statement [else statement] for variable:= initial value to final value statement while condition statement return expression 5 Max procedure in pseudocode procedure max(a 1, a 2,, a n : integers) v:= a 1 {ก v ก ก } for i:= 2 to n { ก } if a i > v then v:= a i { กก v?} { ก v ก ก } return v 6 2
3 Example task ก ก (List) ก ก L ก n ก ก ก ก x ก x ก ก x ก (index) x ก ก ก 7 Search alg. #1: Linear Search procedure linear search (x: integer, a 1, a 2,, a n : distinct integers) i:= 1 { ก ก } while (i n x a i ) { } i:= i + 1 { } if i n then location:= i { ก } else location:= 0 { ก } return location { ก ก 0} 8 Search alg. #2: Binary Search : ก ก ก ก ก ก ก กก ( ก ก ) <x <x <x >x 9 3
4 Search alg. #2: Binary Search procedure binary search (x:integer, a 1, a 2,, a n : distinct integers) i:= 1 {ก ก } j:= n {ก ก } while i<j begin { ก ก >1 } m:= (i+j)/2 { ก } if x>a m then i := m+1 else j := m end if x = a i then location:= i else location:= 0 return location 10 Algorithm Examples ก ก k ก a c d f g h k l m o p r s u v x z ก ก ก 11 Algorithm Examples ก ก k ก a c d f g h k l m o p r s u v x z ก ก ก 12 4
5 Algorithm Examples ก ก k ก a c d f g h k l m o p r s u v x z ก ก ก 13 Algorithm Examples ก ก k ก a c d f g h k l m o p r s u v x z ก ก ก 14 Algorithm Examples ก ก k ก a c d f g h k l m o p r s u v x z ก ก ก k ก! 15 5
6 Time Complexity ก (Algorithm) ก: 1. (time) ก 2. (memory space) กก ก (Time complexity) 16 Time Complexity ก กก ก ก (number of operations) ก n ก ก ก ก Assignment(:=) Comparison(=,, <, >,, ) Arithmetic operation(+, -,, ) Logical operations (and, or, not) ก f(n) ก ก n ก f(n) ก (time complexity) 17 Orders of Growth ก กก (worst case) ก ก ก ก n ก ก ก ก ก ก กก ก ก ก ก ( ก ก ) ก ก ก ก ก f(n) ก g(n), f(n) กก g(n) ( n ก ) ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ( ก ก ก ) ก ก 18 6
7 Orders of Growth - Motivation ก A f A (n)=10n+12 ก n ก B f B (n)=n 2 +1 ก n ก ก ก ก A 19 Orders of Growth ก : time complexity ก A ก B n , ,000 ก A 10n ,012 10,012 1,000,012 ก B n ,001 1,000,001 10,000,000, Visualizing Orders of Growth กก n ก ก ก กก ก ก Value of function f B (n)=n 2 +1 f A (n)=10n+12 Increasing n 21 7
8 Big-O example, graphically ก 10n+12 ก n n>0 ก 11n ก n n ก ก 12 ก 11n cn =11n 10n+12 n n กก 12 n k=12 Value of function Increasing n 10n+12 O(n) 22 Concept of order of growth ก f A (n)=10n+ n+12 ก n (at most order n), n O(n) f B (n)=n 2 +1 ก n 2, O(n 2 ) ก O(n 2 ) ก ก ก O(n) ก ก n 2 ก กก 23 Example ก A B time complexities f g ก f(n) = 3 n 2-3n + 1 g(n)=n 2 ก ก Solution ก n f(n)=g(n) 3 n 2-3n + 1 = n 2 2 n 2-3n + 1 = 0 (2n - 1)(n - 1) = 0 n = 1/2 n =
9 Example n กก n > 1, n = 2 f(2) = 3(2) 2-3(2) + 1 = 7 g(2) = 2 2 = 4 g(n) < f(n) ก n > 1 g(n) ก ก ก B ก ( ก ) n 25 The Growth of Functions ก ก ก big-o O notation ก f g ก ก ก ก R R ก f(n) O(g(n g(n)) c k f(n) c g(n) ก n k ก ก f ก (at most order) g, f O(g), f = O(g) f O( O(g) big-o O notation ก ก ก ก f(n) n ก ก g(n) ก ก f(n) 2n+5 O(n) ก ก f(n) g(n) ก ก big-o f(n) c g(n) ก n k 26 The Growth of Functions ก f(n) O(g(n)), ก c k ก c, k กก c / k ก big-o ก Value of function c g (n) f (n) f(n) c*g(n), n k n k f (n) = O ( g ( n )) 27 9
10 n n O(n 2 ) c,k: n>k: n 2 +10n cn 2 n 2 +10n n 2 +n 2 n 10 n n 2n 2 ก n 10 c = 2, k = Value of function k =10 n n n 2 n 2 28 Does 5n+2 O(n)? Yes Proof: ก Big Oh, c>0 k>0 5n+2 cn ก n k ก ก c k ก k=1 5(1)+2 c = 7 ก c=6 5n+2 6n n 2 k=2 ก c>0 k>0 5n+2 cn ก n k Big Oh 5n+2 O(n) 29 Does n 2 O(n)? No (Prove by contradiction) n 2 O(n) ก Big Oh, c>0 k>0 0 n 2 cn ก n k n 2 cn n กก max{c, k}, ก ก ก c>0 n 2 cn ก n k, n 2 O(n) 30 10
11 Example f(n) ) = 7n7 2 O(n 3 ) n 7 : 7n 2 n 3 c = 1 k = 7: f(n) cn 3 n k f(n) O(n 3 ) ก : f(n) O(n 2 ) f(n) O(n 3 ) ก ก n 3 ก n 2, n 3 ก f(n) 31 Useful Rules for Big-O c>0, O(cf cf)=o( O(f+c)= )=O( O(f - c)=o( O(f) Example: 23*log n O(log n) f 1 (n) O(g 1 (n)) f 2 (n) O(g 2 (n)), (f 1 + f 2 )(n) O(max(g 1 (n), g 2 (n))) Example: (order) n 2 +n? n 2 O(n 2 ), n O(n) n 2 +n O(max(n 2,n)) n 2 +n O(n 2 ) ก ก (polynomial) f(n) ) = a k n k + a k-1 n k a 0, a 0, a 1,, a k, ก f(n) O(n k ) Example: (order) 4n 3 + 2n 2 + n + 5 O(n 3 ) 32 Useful Rules for Big-O f 1 (n) O(g(n)) f 2 (n) is O(g(n)), (f 1 + f 2 )(n) O(g(n)) Example: (order) n 2 + 3n 2 +1? n 2 O(n 2 ) 3n O(n 2 ) n 2 + 3n 2 +1 O(n 2 ) f 1 (n) O(g 1 (n)) f 2 (n) is O(g 2 (n)), (f 1 f 2 )(n) O(g 1 (n) g 2 (n)) Example: (order) (3n+1)*(2n+log n)? 3n+1 O(n) 2n+log n O(n) (3n+1)*(2n+log n) O(n*n)=O(n 2 ) 33 11
12 Complexity Examples ก : : 1. for i = 1 to n do 1.1 for j = 1 to n do A(i,j) := x 1.1 n ก 1. n ก Time Complexity f(n) = n 2 ก f(n) ก O(n 2 ) f(n) O(n 2 ) 34 Complexity Examples ก : 1. i := 1 2. p := 1 3. for j = 1 to n do 3.1 p := p i 3.2 i := i + 1 ก ก (assignment statements) ก 3. n ก ก 2 ก (arithmetic operations) Time complexity f(n) = 4n + 2 ก f(n) ก O(n) f(n) O(n) 35 Complexity Examples ก ก procedure max_diff1(a 1, a 2,,, a n : integers) m := 0 for i := 1 to n-1n for j := i + 1 to n if a i a j > m then m := a i a j {m ก } Time complexity f(n) : n n n = (n( 1)n/2 = 0.5n 2 0.5n ก f(n) ก O(n 2 ) f(n) O(n 2 ) 36 12
13 Complexity Examples ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก : procedure max_diff2(a 1, a 2,,, a n : integers) min := a1 max := a1 for i := 2 to n if a i < min then min := a i else if a i > max then max := a i m := max - min Time complexity f(n) : 2 +2( 2(n 1)+2 = 2n+22 ก f(n) ก O(n) f(n) O(n) 37 Efficiency of search algorithms Linear search: (sequential search) : Best case : First element is the required element: O(1) Worst case: Last element or element not present : O(n) Average case: N/2 : After dropping the multiplicative constant (1/2) : O(n) 38 Binary search algorithm Search requires the following steps: 1. Inspect the middle item of an array of size N. 2. Inspect the middle of an array of size N/2 3. Inspect the middle item of an array of size N/power(2,2) and so on until N/power(2,k) = 1. This implies k = log2n k is the number of partitions. Best case : O(1) Worst case : O(log2N) Average Case : O(log2N)/2 = O(log2N) 39 13
14 Growth-rate Functions ก g(n) ก ก n : O(1) constant time, the time is independent of n, e.g. array lookup O(log n) logarithmic time, usually the log is base 2, e.g. binary search O(n) linear time, Time requirement increases directly with the size of the problem. e.g. linear search O(n*log n) Algorithms that divide the problems into subproblems and solve them.e.g. efficient sorting algorithms e.g. merge sort O(n 2 ) quadratic time, Algorithms that use two nested loops are examples. e.g. selection sort, bubble sort O(n k ) polynomial (where k is some constant) O(2 n ) exponential time, very slow! Order of growth of some common functions O(1) < O(log n) < O(n) < O(n * log n) < O(n 2 ) < O(n 3 ) < O(2 n ) 40 A comparison of growth-rate functions 41 14
Fundamentals of Programming. Efficiency of algorithms November 5, 2017
 15-112 Fundamentals of Programming Efficiency of algorithms November 5, 2017 Complexity of sorting algorithms Selection Sort Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Efficiency of Algorithms A computer program should
15-112 Fundamentals of Programming Efficiency of algorithms November 5, 2017 Complexity of sorting algorithms Selection Sort Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Efficiency of Algorithms A computer program should
CSED233: Data Structures (2017F) Lecture4: Analysis of Algorithms
 (2017F) Lecture4: Analysis of Algorithms Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Running Time Most algorithms transform input objects into output objects. The running time of an algorithm typically
(2017F) Lecture4: Analysis of Algorithms Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Running Time Most algorithms transform input objects into output objects. The running time of an algorithm typically
Analysis of Algorithms
 October 1, 2015 Analysis of Algorithms CS 141, Fall 2015 1 Analysis of Algorithms: Issues Correctness/Optimality Running time ( time complexity ) Memory requirements ( space complexity ) Power I/O utilization
October 1, 2015 Analysis of Algorithms CS 141, Fall 2015 1 Analysis of Algorithms: Issues Correctness/Optimality Running time ( time complexity ) Memory requirements ( space complexity ) Power I/O utilization
What is Performance Analysis?
 1.2 Basic Concepts What is Performance Analysis? Performance Analysis Space Complexity: - the amount of memory space used by the algorithm Time Complexity - the amount of computing time used by the algorithm
1.2 Basic Concepts What is Performance Analysis? Performance Analysis Space Complexity: - the amount of memory space used by the algorithm Time Complexity - the amount of computing time used by the algorithm
Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency. Dr. Yingwu Zhu
 Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency Dr. Yingwu Zhu Measure Algorithm Efficiency Time efficiency How fast the algorithm runs; amount of time required to accomplish the task Our focus! Space efficiency Amount
Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency Dr. Yingwu Zhu Measure Algorithm Efficiency Time efficiency How fast the algorithm runs; amount of time required to accomplish the task Our focus! Space efficiency Amount
Data Structures and Algorithms. Asymptotic notation
 Data Structures and Algorithms Asymptotic notation Estimating Running Time Algorithm arraymax executes 7n 1 primitive operations in the worst case. Define: a = Time taken by the fastest primitive operation
Data Structures and Algorithms Asymptotic notation Estimating Running Time Algorithm arraymax executes 7n 1 primitive operations in the worst case. Define: a = Time taken by the fastest primitive operation
Lecture 10: Big-Oh. Doina Precup With many thanks to Prakash Panagaden and Mathieu Blanchette. January 27, 2014
 Lecture 10: Big-Oh Doina Precup With many thanks to Prakash Panagaden and Mathieu Blanchette January 27, 2014 So far we have talked about O() informally, as a way of capturing the worst-case computation
Lecture 10: Big-Oh Doina Precup With many thanks to Prakash Panagaden and Mathieu Blanchette January 27, 2014 So far we have talked about O() informally, as a way of capturing the worst-case computation
Algorithms and Their Complexity
 CSCE 222 Discrete Structures for Computing David Kebo Houngninou Algorithms and Their Complexity Chapter 3 Algorithm An algorithm is a finite sequence of steps that solves a problem. Computational complexity
CSCE 222 Discrete Structures for Computing David Kebo Houngninou Algorithms and Their Complexity Chapter 3 Algorithm An algorithm is a finite sequence of steps that solves a problem. Computational complexity
Algorithms, Design and Analysis. Order of growth. Table 2.1. Big-oh. Asymptotic growth rate. Types of formulas for basic operation count
 Types of formulas for basic operation count Exact formula e.g., C(n) = n(n-1)/2 Algorithms, Design and Analysis Big-Oh analysis, Brute Force, Divide and conquer intro Formula indicating order of growth
Types of formulas for basic operation count Exact formula e.g., C(n) = n(n-1)/2 Algorithms, Design and Analysis Big-Oh analysis, Brute Force, Divide and conquer intro Formula indicating order of growth
Big O 2/14/13. Administrative. Does it terminate? David Kauchak cs302 Spring 2013
 /4/3 Administrative Big O David Kauchak cs3 Spring 3 l Assignment : how d it go? l Assignment : out soon l CLRS code? l Videos Insertion-sort Insertion-sort Does it terminate? /4/3 Insertion-sort Loop
/4/3 Administrative Big O David Kauchak cs3 Spring 3 l Assignment : how d it go? l Assignment : out soon l CLRS code? l Videos Insertion-sort Insertion-sort Does it terminate? /4/3 Insertion-sort Loop
Principles of Algorithm Analysis
 C H A P T E R 3 Principles of Algorithm Analysis 3.1 Computer Programs The design of computer programs requires:- 1. An algorithm that is easy to understand, code and debug. This is the concern of software
C H A P T E R 3 Principles of Algorithm Analysis 3.1 Computer Programs The design of computer programs requires:- 1. An algorithm that is easy to understand, code and debug. This is the concern of software
Analysis of Algorithms
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Analysis of Algorithms Input Algorithm Analysis
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Analysis of Algorithms Input Algorithm Analysis
Topic 17. Analysis of Algorithms
 Topic 17 Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithms- Review Efficiency of an algorithm can be measured in terms of : Time complexity: a measure of the amount of time required to execute an algorithm
Topic 17 Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithms- Review Efficiency of an algorithm can be measured in terms of : Time complexity: a measure of the amount of time required to execute an algorithm
Algorithms 2/6/2018. Algorithms. Enough Mathematical Appetizers! Algorithm Examples. Algorithms. Algorithm Examples. Algorithm Examples
 Enough Mathematical Appetizers! Algorithms What is an algorithm? Let us look at something more interesting: Algorithms An algorithm is a finite set of precise instructions for performing a computation
Enough Mathematical Appetizers! Algorithms What is an algorithm? Let us look at something more interesting: Algorithms An algorithm is a finite set of precise instructions for performing a computation
Lecture 2. Fundamentals of the Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency
 Lecture 2 Fundamentals of the Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency 1 Lecture Contents 1. Analysis Framework 2. Asymptotic Notations and Basic Efficiency Classes 3. Mathematical Analysis of Nonrecursive Algorithms
Lecture 2 Fundamentals of the Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency 1 Lecture Contents 1. Analysis Framework 2. Asymptotic Notations and Basic Efficiency Classes 3. Mathematical Analysis of Nonrecursive Algorithms
Algorithm Analysis, Asymptotic notations CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang
 Algorithm Analysis, Asymptotic notations CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Last class Introduction to algorithm analysis: fibonacci seq calculation counting number of computer steps recursive
Algorithm Analysis, Asymptotic notations CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Last class Introduction to algorithm analysis: fibonacci seq calculation counting number of computer steps recursive
Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms. Chapter 4
 Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 4 Overview Motivation Definition of Running Time Classifying Running Time Asymptotic Notation & Proving Bounds Algorithm Complexity vs Problem Complexity Overview
Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 4 Overview Motivation Definition of Running Time Classifying Running Time Asymptotic Notation & Proving Bounds Algorithm Complexity vs Problem Complexity Overview
Computer Algorithms CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Outline. Last class. Instructor: X. Zhang Lecture 2
 Computer Algorithms CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Lecture 2 Outline Introduction to algorithm analysis: fibonacci seq calculation counting number of computer steps recursive formula
Computer Algorithms CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Lecture 2 Outline Introduction to algorithm analysis: fibonacci seq calculation counting number of computer steps recursive formula
Computer Algorithms CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Lecture 2
 Computer Algorithms CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Lecture 2 Outline Introduction to algorithm analysis: fibonacci seq calculation counting number of computer steps recursive formula
Computer Algorithms CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Lecture 2 Outline Introduction to algorithm analysis: fibonacci seq calculation counting number of computer steps recursive formula
csci 210: Data Structures Program Analysis
 csci 210: Data Structures Program Analysis Summary Topics commonly used functions analysis of algorithms experimental asymptotic notation asymptotic analysis big-o big-omega big-theta READING: GT textbook
csci 210: Data Structures Program Analysis Summary Topics commonly used functions analysis of algorithms experimental asymptotic notation asymptotic analysis big-o big-omega big-theta READING: GT textbook
Measuring Goodness of an Algorithm. Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms. Measuring Efficiency of an Algorithm. Algorithm and Data Structure
 Measuring Goodness of an Algorithm Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1. Correctness : Does the algorithm produce the expected output?
Measuring Goodness of an Algorithm Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1. Correctness : Does the algorithm produce the expected output?
csci 210: Data Structures Program Analysis
 csci 210: Data Structures Program Analysis 1 Summary Summary analysis of algorithms asymptotic analysis big-o big-omega big-theta asymptotic notation commonly used functions discrete math refresher READING:
csci 210: Data Structures Program Analysis 1 Summary Summary analysis of algorithms asymptotic analysis big-o big-omega big-theta asymptotic notation commonly used functions discrete math refresher READING:
The Time Complexity of an Algorithm
 Analysis of Algorithms The Time Complexity of an Algorithm Specifies how the running time depends on the size of the input. Purpose To estimate how long a program will run. To estimate the largest input
Analysis of Algorithms The Time Complexity of an Algorithm Specifies how the running time depends on the size of the input. Purpose To estimate how long a program will run. To estimate the largest input
Time Analysis of Sorting and Searching Algorithms
 Time Analysis of Sorting and Searching Algorithms CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 5 (B00), Day 3 (A00) January 20, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Big-O : How to determine? Is f(n) big-o of g(n)?
Time Analysis of Sorting and Searching Algorithms CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 5 (B00), Day 3 (A00) January 20, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Big-O : How to determine? Is f(n) big-o of g(n)?
3. Algorithms. What matters? How fast do we solve the problem? How much computer resource do we need?
 3. Algorithms We will study algorithms to solve many different types of problems such as finding the largest of a sequence of numbers sorting a sequence of numbers finding the shortest path between two
3. Algorithms We will study algorithms to solve many different types of problems such as finding the largest of a sequence of numbers sorting a sequence of numbers finding the shortest path between two
CS173 Running Time and Big-O. Tandy Warnow
 CS173 Running Time and Big-O Tandy Warnow CS 173 Running Times and Big-O analysis Tandy Warnow Today s material We will cover: Running time analysis Review of running time analysis of Bubblesort Review
CS173 Running Time and Big-O Tandy Warnow CS 173 Running Times and Big-O analysis Tandy Warnow Today s material We will cover: Running time analysis Review of running time analysis of Bubblesort Review
Problem-Solving via Search Lecture 3
 Lecture 3 What is a search problem? How do search algorithms work and how do we evaluate their performance? 1 Agenda An example task Problem formulation Infrastructure for search algorithms Complexity
Lecture 3 What is a search problem? How do search algorithms work and how do we evaluate their performance? 1 Agenda An example task Problem formulation Infrastructure for search algorithms Complexity
Discrete Mathematics CS October 17, 2006
 Discrete Mathematics CS 2610 October 17, 2006 Uncountable sets Theorem: The set of real numbers is uncountable. If a subset of a set is uncountable, then the set is uncountable. The cardinality of a subset
Discrete Mathematics CS 2610 October 17, 2006 Uncountable sets Theorem: The set of real numbers is uncountable. If a subset of a set is uncountable, then the set is uncountable. The cardinality of a subset
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Runtime Analysis May 31, 2017 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 310 May 31, 2017 1 / 37 Topics Weiss chapter 5 What is algorithm analysis Big O, big, big notations
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Runtime Analysis May 31, 2017 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 310 May 31, 2017 1 / 37 Topics Weiss chapter 5 What is algorithm analysis Big O, big, big notations
Growth of Functions (CLRS 2.3,3)
 Growth of Functions (CLRS 2.3,3) 1 Review Last time we discussed running time of algorithms and introduced the RAM model of computation. Best-case running time: the shortest running time for any input
Growth of Functions (CLRS 2.3,3) 1 Review Last time we discussed running time of algorithms and introduced the RAM model of computation. Best-case running time: the shortest running time for any input
Analysis of Algorithms
 September 29, 2017 Analysis of Algorithms CS 141, Fall 2017 1 Analysis of Algorithms: Issues Correctness/Optimality Running time ( time complexity ) Memory requirements ( space complexity ) Power I/O utilization
September 29, 2017 Analysis of Algorithms CS 141, Fall 2017 1 Analysis of Algorithms: Issues Correctness/Optimality Running time ( time complexity ) Memory requirements ( space complexity ) Power I/O utilization
The Time Complexity of an Algorithm
 CSE 3101Z Design and Analysis of Algorithms The Time Complexity of an Algorithm Specifies how the running time depends on the size of the input. Purpose To estimate how long a program will run. To estimate
CSE 3101Z Design and Analysis of Algorithms The Time Complexity of an Algorithm Specifies how the running time depends on the size of the input. Purpose To estimate how long a program will run. To estimate
Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms
 Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Based
Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Based
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Autumn 2018-2019 Outline 1 Algorithm Analysis (contd.) Outline Algorithm Analysis (contd.) 1 Algorithm Analysis (contd.) Growth Rates of Some Commonly Occurring Functions
Data Structures and Algorithms Autumn 2018-2019 Outline 1 Algorithm Analysis (contd.) Outline Algorithm Analysis (contd.) 1 Algorithm Analysis (contd.) Growth Rates of Some Commonly Occurring Functions
Analysis of Algorithms Review
 COMP171 Fall 2005 Analysis of Algorithms Review Adapted from Notes of S. Sarkar of UPenn, Skiena of Stony Brook, etc. Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms / Slide 2 Outline Why Does Growth Rate Matter?
COMP171 Fall 2005 Analysis of Algorithms Review Adapted from Notes of S. Sarkar of UPenn, Skiena of Stony Brook, etc. Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms / Slide 2 Outline Why Does Growth Rate Matter?
Computational Complexity
 Computational Complexity S. V. N. Vishwanathan, Pinar Yanardag January 8, 016 1 Computational Complexity: What, Why, and How? Intuitively an algorithm is a well defined computational procedure that takes
Computational Complexity S. V. N. Vishwanathan, Pinar Yanardag January 8, 016 1 Computational Complexity: What, Why, and How? Intuitively an algorithm is a well defined computational procedure that takes
Runtime Complexity. CS 331: Data Structures and Algorithms
 Runtime Complexity CS 331: Data Structures and Algorithms So far, our runtime analysis has been based on empirical evidence i.e., runtimes obtained from actually running our algorithms But measured runtime
Runtime Complexity CS 331: Data Structures and Algorithms So far, our runtime analysis has been based on empirical evidence i.e., runtimes obtained from actually running our algorithms But measured runtime
Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science. Lecture 7: Introduction to Computational Complexity
 15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 7: Introduction to Computational Complexity September 20th, 2016 What have we done so far? What will we do next? What have we done so far? > Introduction
15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 7: Introduction to Computational Complexity September 20th, 2016 What have we done so far? What will we do next? What have we done so far? > Introduction
Enumerate all possible assignments and take the An algorithm is a well-defined computational
 EMIS 8374 [Algorithm Design and Analysis] 1 EMIS 8374 [Algorithm Design and Analysis] 2 Designing and Evaluating Algorithms A (Bad) Algorithm for the Assignment Problem Enumerate all possible assignments
EMIS 8374 [Algorithm Design and Analysis] 1 EMIS 8374 [Algorithm Design and Analysis] 2 Designing and Evaluating Algorithms A (Bad) Algorithm for the Assignment Problem Enumerate all possible assignments
COMPUTER ALGORITHMS. Athasit Surarerks.
 COMPUTER ALGORITHMS Athasit Surarerks. Introduction EUCLID s GAME Two players move in turn. On each move, a player has to write on the board a positive integer equal to the different from two numbers already
COMPUTER ALGORITHMS Athasit Surarerks. Introduction EUCLID s GAME Two players move in turn. On each move, a player has to write on the board a positive integer equal to the different from two numbers already
Ch01. Analysis of Algorithms
 Ch01. Analysis of Algorithms Input Algorithm Output Acknowledgement: Parts of slides in this presentation come from the materials accompanying the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich
Ch01. Analysis of Algorithms Input Algorithm Output Acknowledgement: Parts of slides in this presentation come from the materials accompanying the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich
Mat Week 6. Fall Mat Week 6. Algorithms. Properties. Examples. Searching. Sorting. Time Complexity. Example. Properties.
 Fall 2013 Student Responsibilities Reading: Textbook, Section 3.1 3.2 Assignments: 1. for sections 3.1 and 3.2 2. Worksheet #4 on Execution s 3. Worksheet #5 on Growth Rates Attendance: Strongly Encouraged
Fall 2013 Student Responsibilities Reading: Textbook, Section 3.1 3.2 Assignments: 1. for sections 3.1 and 3.2 2. Worksheet #4 on Execution s 3. Worksheet #5 on Growth Rates Attendance: Strongly Encouraged
Algorithms Design & Analysis. Analysis of Algorithm
 Algorithms Design & Analysis Analysis of Algorithm Review Internship Stable Matching Algorithm 2 Outline Time complexity Computation model Asymptotic notions Recurrence Master theorem 3 The problem of
Algorithms Design & Analysis Analysis of Algorithm Review Internship Stable Matching Algorithm 2 Outline Time complexity Computation model Asymptotic notions Recurrence Master theorem 3 The problem of
Student Responsibilities Week 6. Mat Properties of Algorithms. 3.1 Algorithms. Finding the Maximum Value in a Finite Sequence Pseudocode
 Student Responsibilities Week 6 Mat 345 Week 6 Reading: Textbook, Section 3.1 3. Assignments: 1. for sections 3.1 and 3.. Worksheet #4 on Execution Times 3. Worksheet #5 on Growth Rates Attendance: Strongly
Student Responsibilities Week 6 Mat 345 Week 6 Reading: Textbook, Section 3.1 3. Assignments: 1. for sections 3.1 and 3.. Worksheet #4 on Execution Times 3. Worksheet #5 on Growth Rates Attendance: Strongly
Math 3012 Applied Combinatorics Lecture 5
 September 1, 2015 Math 3012 Applied Combinatorics Lecture 5 William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Test 1 and Homework Due Date Reminder Test 1, Thursday September 17, 2015. Taken here in MRDC 2404.
September 1, 2015 Math 3012 Applied Combinatorics Lecture 5 William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Test 1 and Homework Due Date Reminder Test 1, Thursday September 17, 2015. Taken here in MRDC 2404.
Ch 01. Analysis of Algorithms
 Ch 01. Analysis of Algorithms Input Algorithm Output Acknowledgement: Parts of slides in this presentation come from the materials accompanying the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T.
Ch 01. Analysis of Algorithms Input Algorithm Output Acknowledgement: Parts of slides in this presentation come from the materials accompanying the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T.
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Section 4.3 Prof. Nathan Wodarz Math 209 - Fall 2008 Contents 1 Analysis of Algorithms 2 1.1 Analysis of Algorithms....................... 2 2 Complexity Analysis 4 2.1 Notation
Analysis of Algorithms Section 4.3 Prof. Nathan Wodarz Math 209 - Fall 2008 Contents 1 Analysis of Algorithms 2 1.1 Analysis of Algorithms....................... 2 2 Complexity Analysis 4 2.1 Notation
Data Structures and Algorithms Running time and growth functions January 18, 2018
 Data Structures and Algorithms Running time and growth functions January 18, 2018 Measuring Running Time of Algorithms One way to measure the running time of an algorithm is to implement it and then study
Data Structures and Algorithms Running time and growth functions January 18, 2018 Measuring Running Time of Algorithms One way to measure the running time of an algorithm is to implement it and then study
CSE 421: Intro Algorithms. 2: Analysis. Winter 2012 Larry Ruzzo
 CSE 421: Intro Algorithms 2: Analysis Winter 2012 Larry Ruzzo 1 Efficiency Our correct TSP algorithm was incredibly slow Basically slow no matter what computer you have We want a general theory of efficiency
CSE 421: Intro Algorithms 2: Analysis Winter 2012 Larry Ruzzo 1 Efficiency Our correct TSP algorithm was incredibly slow Basically slow no matter what computer you have We want a general theory of efficiency
3.1 Asymptotic notation
 3.1 Asymptotic notation The notations we use to describe the asymptotic running time of an algorithm are defined in terms of functions whose domains are the set of natural numbers N = {0, 1, 2,... Such
3.1 Asymptotic notation The notations we use to describe the asymptotic running time of an algorithm are defined in terms of functions whose domains are the set of natural numbers N = {0, 1, 2,... Such
Defining Efficiency. 2: Analysis. Efficiency. Measuring efficiency. CSE 421: Intro Algorithms. Summer 2007 Larry Ruzzo
 CSE 421: Intro Algorithms 2: Analysis Summer 2007 Larry Ruzzo Defining Efficiency Runs fast on typical real problem instances Pro: sensible, bottom-line-oriented Con: moving target (diff computers, compilers,
CSE 421: Intro Algorithms 2: Analysis Summer 2007 Larry Ruzzo Defining Efficiency Runs fast on typical real problem instances Pro: sensible, bottom-line-oriented Con: moving target (diff computers, compilers,
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 2: Iterative and Divide and Conquer Algorithms
 CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 2: Iterative and Divide and Conquer Algorithms Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Lecture Outline CS 4407, Algorithms Growth Functions
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 2: Iterative and Divide and Conquer Algorithms Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Lecture Outline CS 4407, Algorithms Growth Functions
Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science. Lecture 9: Introduction to Computational Complexity
 15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 9: Introduction to Computational Complexity February 14th, 2017 Poll What is the running time of this algorithm? Choose the tightest bound. def
15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 9: Introduction to Computational Complexity February 14th, 2017 Poll What is the running time of this algorithm? Choose the tightest bound. def
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 4 - Jan. 10, 2018 CLRS 1.1, 1.2, 2.2, 3.1, 4.3, 4.5 University of Manitoba Picture is from the cover of the textbook CLRS. 1 /
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 4 - Jan. 10, 2018 CLRS 1.1, 1.2, 2.2, 3.1, 4.3, 4.5 University of Manitoba Picture is from the cover of the textbook CLRS. 1 /
COMP 9024, Class notes, 11s2, Class 1
 COMP 90, Class notes, 11s, Class 1 John Plaice Sun Jul 31 1::5 EST 011 In this course, you will need to know a bit of mathematics. We cover in today s lecture the basics. Some of this material is covered
COMP 90, Class notes, 11s, Class 1 John Plaice Sun Jul 31 1::5 EST 011 In this course, you will need to know a bit of mathematics. We cover in today s lecture the basics. Some of this material is covered
CSCI 3110 Assignment 6 Solutions
 CSCI 3110 Assignment 6 Solutions December 5, 2012 2.4 (4 pts) Suppose you are choosing between the following three algorithms: 1. Algorithm A solves problems by dividing them into five subproblems of half
CSCI 3110 Assignment 6 Solutions December 5, 2012 2.4 (4 pts) Suppose you are choosing between the following three algorithms: 1. Algorithm A solves problems by dividing them into five subproblems of half
Lecture 2. More Algorithm Analysis, Math and MCSS By: Sarah Buchanan
 Lecture 2 More Algorithm Analysis, Math and MCSS By: Sarah Buchanan Announcements Assignment #1 is posted online It is directly related to MCSS which we will be talking about today or Monday. There are
Lecture 2 More Algorithm Analysis, Math and MCSS By: Sarah Buchanan Announcements Assignment #1 is posted online It is directly related to MCSS which we will be talking about today or Monday. There are
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 1
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 1 Introduction Analysis framework and asymptotic notations What is an algorithm? An algorithm is a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions for solving
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 1 Introduction Analysis framework and asymptotic notations What is an algorithm? An algorithm is a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions for solving
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 4 - Jan. 14, 2019 CLRS 1.1, 1.2, 2.2, 3.1, 4.3, 4.5 University of Manitoba Picture is from the cover of the textbook CLRS. COMP
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 4 - Jan. 14, 2019 CLRS 1.1, 1.2, 2.2, 3.1, 4.3, 4.5 University of Manitoba Picture is from the cover of the textbook CLRS. COMP
Solving Recurrences. 1. Express the running time (or use of some other resource) as a recurrence.
 1 Recurrences and Recursive Code Solving Recurrences Many (perhaps most) recursive algorithms fall into one of two categories: tail recursion and divide-andconquer recursion. We would like to develop some
1 Recurrences and Recursive Code Solving Recurrences Many (perhaps most) recursive algorithms fall into one of two categories: tail recursion and divide-andconquer recursion. We would like to develop some
Running Time Evaluation
 Running Time Evaluation Quadratic Vs. Linear Time Lecturer: Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 220 Algorithms and Data Structures 1 / 19 1 Running time 2 Examples 3 Big-Oh, Big-Omega, and Big-Theta Tools 4 Time
Running Time Evaluation Quadratic Vs. Linear Time Lecturer: Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 220 Algorithms and Data Structures 1 / 19 1 Running time 2 Examples 3 Big-Oh, Big-Omega, and Big-Theta Tools 4 Time
Omega notation. Transitivity etc.
 Omega notation Big-Omega: Lecture 2, Sept. 25, 2014 f () n (()) g n const cn, s.t. n n : cg() n f () n Small-omega: 0 0 0 f () n (()) g n const c, n s.t. n n : cg() n f () n 0 0 0 Intuition (works most
Omega notation Big-Omega: Lecture 2, Sept. 25, 2014 f () n (()) g n const cn, s.t. n n : cg() n f () n Small-omega: 0 0 0 f () n (()) g n const c, n s.t. n n : cg() n f () n 0 0 0 Intuition (works most
Cpt S 223. School of EECS, WSU
 Algorithm Analysis 1 Purpose Why bother analyzing code; isn t getting it to work enough? Estimate time and memory in the average case and worst case Identify bottlenecks, i.e., where to reduce time Compare
Algorithm Analysis 1 Purpose Why bother analyzing code; isn t getting it to work enough? Estimate time and memory in the average case and worst case Identify bottlenecks, i.e., where to reduce time Compare
Big , and Definition Definition
 Big O, Ω, and Θ Big-O gives us only a one-way comparison; if f is O(g) then g eventually is bigger than f from that point on, but in fact f could be very small in comparison. Example; 3n is O(2 2n ). We
Big O, Ω, and Θ Big-O gives us only a one-way comparison; if f is O(g) then g eventually is bigger than f from that point on, but in fact f could be very small in comparison. Example; 3n is O(2 2n ). We
Asymptotic Analysis. Thomas A. Anastasio. January 7, 2004
 Asymptotic Analysis Thomas A. Anastasio January 7, 004 1 Introduction As a programmer, you often have a choice of data structures and algorithms. Choosing the best one for a particular job involves, among
Asymptotic Analysis Thomas A. Anastasio January 7, 004 1 Introduction As a programmer, you often have a choice of data structures and algorithms. Choosing the best one for a particular job involves, among
Asymptotic Running Time of Algorithms
 Asymptotic Complexity: leading term analysis Asymptotic Running Time of Algorithms Comparing searching and sorting algorithms so far: Count worst-case of comparisons as function of array size. Drop lower-order
Asymptotic Complexity: leading term analysis Asymptotic Running Time of Algorithms Comparing searching and sorting algorithms so far: Count worst-case of comparisons as function of array size. Drop lower-order
Growth of Functions. As an example for an estimate of computation time, let us consider the sequential search algorithm.
 Function Growth of Functions Subjects to be Learned Contents big oh max function big omega big theta little oh little omega Introduction One of the important criteria in evaluating algorithms is the time
Function Growth of Functions Subjects to be Learned Contents big oh max function big omega big theta little oh little omega Introduction One of the important criteria in evaluating algorithms is the time
Algorithm efficiency can be measured in terms of: Time Space Other resources such as processors, network packets, etc.
 Algorithms Analysis Algorithm efficiency can be measured in terms of: Time Space Other resources such as processors, network packets, etc. Algorithms analysis tends to focus on time: Techniques for measuring
Algorithms Analysis Algorithm efficiency can be measured in terms of: Time Space Other resources such as processors, network packets, etc. Algorithms analysis tends to focus on time: Techniques for measuring
Lecture 12: Algorithm Analysis
 Lecture 12: Algorithm Analysis CS6507 Python Programming and Data Science Applications Dr Kieran T. Herley Department of Computer Science University College Cork 2017-2018 KH (26/02/18) Lecture 12: Algorithm
Lecture 12: Algorithm Analysis CS6507 Python Programming and Data Science Applications Dr Kieran T. Herley Department of Computer Science University College Cork 2017-2018 KH (26/02/18) Lecture 12: Algorithm
Reminder of Asymptotic Notation. Inf 2B: Asymptotic notation and Algorithms. Asymptotic notation for Running-time
 1 / 18 Reminder of Asymptotic Notation / 18 Inf B: Asymptotic notation and Algorithms Lecture B of ADS thread Let f, g : N! R be functions. We say that: I f is O(g) if there is some n 0 N and some c >
1 / 18 Reminder of Asymptotic Notation / 18 Inf B: Asymptotic notation and Algorithms Lecture B of ADS thread Let f, g : N! R be functions. We say that: I f is O(g) if there is some n 0 N and some c >
Introduction. An Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures
 Introduction An Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Overview Aims This course is an introduction to the design, analysis and wide variety of algorithms (a topic often called Algorithmics ).
Introduction An Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Overview Aims This course is an introduction to the design, analysis and wide variety of algorithms (a topic often called Algorithmics ).
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity
 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Lecture 2: Analysis Larry Ruzzo 1 Why big-o: measuring algorithm efficiency outline What s big-o: definition and related concepts Reasoning with big-o:
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Lecture 2: Analysis Larry Ruzzo 1 Why big-o: measuring algorithm efficiency outline What s big-o: definition and related concepts Reasoning with big-o:
Asymptotic Notation. such that t(n) cf(n) for all n n 0. for some positive real constant c and integer threshold n 0
 Asymptotic Notation Asymptotic notation deals with the behaviour of a function in the limit, that is, for sufficiently large values of its parameter. Often, when analysing the run time of an algorithm,
Asymptotic Notation Asymptotic notation deals with the behaviour of a function in the limit, that is, for sufficiently large values of its parameter. Often, when analysing the run time of an algorithm,
Define Efficiency. 2: Analysis. Efficiency. Measuring efficiency. CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity. Winter 2007 Larry Ruzzo
 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational 2: Analysis Winter 2007 Larry Ruzzo Define Efficiency Runs fast on typical real problem instances Pro: sensible, bottom-line-oriented Con: moving target (diff computers,
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational 2: Analysis Winter 2007 Larry Ruzzo Define Efficiency Runs fast on typical real problem instances Pro: sensible, bottom-line-oriented Con: moving target (diff computers,
Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 465
 Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 465 LECTURE 3 Asymptotic Notation O-, Ω-, Θ-, o-, ω-notation Divide and Conquer Merge Sort Binary Search Sofya Raskhodnikova and Adam Smith /5/0 Review Questions If input
Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 465 LECTURE 3 Asymptotic Notation O-, Ω-, Θ-, o-, ω-notation Divide and Conquer Merge Sort Binary Search Sofya Raskhodnikova and Adam Smith /5/0 Review Questions If input
CSC2100B Data Structures Analysis
 CSC2100B Data Structures Analysis Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Algorithm An algorithm
CSC2100B Data Structures Analysis Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Algorithm An algorithm
Analysis of Algorithms [Reading: CLRS 2.2, 3] Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College
![Analysis of Algorithms [Reading: CLRS 2.2, 3] Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College Analysis of Algorithms [Reading: CLRS 2.2, 3] Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College](/thumbs/79/78926994.jpg) Analysis of Algorithms [Reading: CLRS 2.2, 3] Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College Why analysis? We want to predict how the algorithm will behave (e.g. running time) on arbitrary inputs, and how it will
Analysis of Algorithms [Reading: CLRS 2.2, 3] Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College Why analysis? We want to predict how the algorithm will behave (e.g. running time) on arbitrary inputs, and how it will
Analysis of Algorithms I: Asymptotic Notation, Induction, and MergeSort
 Analysis of Algorithms I: Asymptotic Notation, Induction, and MergeSort Xi Chen Columbia University We continue with two more asymptotic notation: o( ) and ω( ). Let f (n) and g(n) are functions that map
Analysis of Algorithms I: Asymptotic Notation, Induction, and MergeSort Xi Chen Columbia University We continue with two more asymptotic notation: o( ) and ω( ). Let f (n) and g(n) are functions that map
CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis. Ruth Anderson Winter 2019
 CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis Ruth Anderson Winter 2019 Today Algorithm Analysis What do we care about? How to compare two algorithms Analyzing Code Asymptotic Analysis
CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis Ruth Anderson Winter 2019 Today Algorithm Analysis What do we care about? How to compare two algorithms Analyzing Code Asymptotic Analysis
Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms
 Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu What is an Algorithm?
Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu What is an Algorithm?
Announcements. CompSci 102 Discrete Math for Computer Science. Chap. 3.1 Algorithms. Specifying Algorithms
 CompSci 102 Discrete Math for Computer Science Announcements Read for next time Chap. 3.1-3.3 Homework 3 due Tuesday We ll finish Chapter 2 first today February 7, 2012 Prof. Rodger Chap. 3.1 Algorithms
CompSci 102 Discrete Math for Computer Science Announcements Read for next time Chap. 3.1-3.3 Homework 3 due Tuesday We ll finish Chapter 2 first today February 7, 2012 Prof. Rodger Chap. 3.1 Algorithms
Lecture 1: Asymptotics, Recurrences, Elementary Sorting
 Lecture 1: Asymptotics, Recurrences, Elementary Sorting Instructor: Outline 1 Introduction to Asymptotic Analysis Rate of growth of functions Comparing and bounding functions: O, Θ, Ω Specifying running
Lecture 1: Asymptotics, Recurrences, Elementary Sorting Instructor: Outline 1 Introduction to Asymptotic Analysis Rate of growth of functions Comparing and bounding functions: O, Θ, Ω Specifying running
Advanced Algorithmics (6EAP)
 Advanced Algorithmics (6EAP) MTAT.03.238 Order of growth maths Jaak Vilo 2017 fall Jaak Vilo 1 Program execution on input of size n How many steps/cycles a processor would need to do How to relate algorithm
Advanced Algorithmics (6EAP) MTAT.03.238 Order of growth maths Jaak Vilo 2017 fall Jaak Vilo 1 Program execution on input of size n How many steps/cycles a processor would need to do How to relate algorithm
data structures and algorithms lecture 2
 data structures and algorithms 2018 09 06 lecture 2 recall: insertion sort Algorithm insertionsort(a, n): for j := 2 to n do key := A[j] i := j 1 while i 1 and A[i] > key do A[i + 1] := A[i] i := i 1 A[i
data structures and algorithms 2018 09 06 lecture 2 recall: insertion sort Algorithm insertionsort(a, n): for j := 2 to n do key := A[j] i := j 1 while i 1 and A[i] > key do A[i + 1] := A[i] i := i 1 A[i
In-Class Soln 1. CS 361, Lecture 4. Today s Outline. In-Class Soln 2
 In-Class Soln 1 Let f(n) be an always positive function and let g(n) = f(n) log n. Show that f(n) = o(g(n)) CS 361, Lecture 4 Jared Saia University of New Mexico For any positive constant c, we want to
In-Class Soln 1 Let f(n) be an always positive function and let g(n) = f(n) log n. Show that f(n) = o(g(n)) CS 361, Lecture 4 Jared Saia University of New Mexico For any positive constant c, we want to
Data Structures. Outline. Introduction. Andres Mendez-Vazquez. December 3, Data Manipulation Examples
 Data Structures Introduction Andres Mendez-Vazquez December 3, 2015 1 / 53 Outline 1 What the Course is About? Data Manipulation Examples 2 What is a Good Algorithm? Sorting Example A Naive Algorithm Counting
Data Structures Introduction Andres Mendez-Vazquez December 3, 2015 1 / 53 Outline 1 What the Course is About? Data Manipulation Examples 2 What is a Good Algorithm? Sorting Example A Naive Algorithm Counting
LECTURE NOTES ON DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 G.PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY LECTURE NOTES ON DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 UNIT 1 Basic Concepts Algorithm An Algorithm is a finite
G.PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY LECTURE NOTES ON DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 UNIT 1 Basic Concepts Algorithm An Algorithm is a finite
Solving Recurrences. 1. Express the running time (or use of some other resource) as a recurrence.
 Solving Recurrences Recurrences and Recursive Code Many (perhaps most) recursive algorithms fall into one of two categories: tail recursion and divide-andconquer recursion. We would like to develop some
Solving Recurrences Recurrences and Recursive Code Many (perhaps most) recursive algorithms fall into one of two categories: tail recursion and divide-andconquer recursion. We would like to develop some
Computational complexity and some Graph Theory
 Graph Theory Lars Hellström January 22, 2014 Contents of todays lecture An important concern when choosing the algorithm to use for something (after basic requirements such as correctness and stability)
Graph Theory Lars Hellström January 22, 2014 Contents of todays lecture An important concern when choosing the algorithm to use for something (after basic requirements such as correctness and stability)
Time Complexity (1) CSCI Spring Original Slides were written by Dr. Frederick W Maier. CSCI 2670 Time Complexity (1)
 Time Complexity (1) CSCI 2670 Original Slides were written by Dr. Frederick W Maier Spring 2014 Time Complexity So far we ve dealt with determining whether or not a problem is decidable. But even if it
Time Complexity (1) CSCI 2670 Original Slides were written by Dr. Frederick W Maier Spring 2014 Time Complexity So far we ve dealt with determining whether or not a problem is decidable. But even if it
Mathematical Background. Unsigned binary numbers. Powers of 2. Logs and exponents. Mathematical Background. Today, we will review:
 Mathematical Background Mathematical Background CSE 373 Data Structures Today, we will review: Logs and eponents Series Recursion Motivation for Algorithm Analysis 5 January 007 CSE 373 - Math Background
Mathematical Background Mathematical Background CSE 373 Data Structures Today, we will review: Logs and eponents Series Recursion Motivation for Algorithm Analysis 5 January 007 CSE 373 - Math Background
CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis. Ruth Anderson Winter 2018
 CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis Ruth Anderson Winter 2018 Today Algorithm Analysis What do we care about? How to compare two algorithms Analyzing Code Asymptotic Analysis
CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis Ruth Anderson Winter 2018 Today Algorithm Analysis What do we care about? How to compare two algorithms Analyzing Code Asymptotic Analysis
CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis. Ruth Anderson Winter 2018
 CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis Ruth Anderson Winter 2018 Today Algorithm Analysis What do we care about? How to compare two algorithms Analyzing Code Asymptotic Analysis
CSE332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 2: Algorithm Analysis Ruth Anderson Winter 2018 Today Algorithm Analysis What do we care about? How to compare two algorithms Analyzing Code Asymptotic Analysis
Data structures Exercise 1 solution. Question 1. Let s start by writing all the functions in big O notation:
 Data structures Exercise 1 solution Question 1 Let s start by writing all the functions in big O notation: f 1 (n) = 2017 = O(1), f 2 (n) = 2 log 2 n = O(n 2 ), f 3 (n) = 2 n = O(2 n ), f 4 (n) = 1 = O
Data structures Exercise 1 solution Question 1 Let s start by writing all the functions in big O notation: f 1 (n) = 2017 = O(1), f 2 (n) = 2 log 2 n = O(n 2 ), f 3 (n) = 2 n = O(2 n ), f 4 (n) = 1 = O
Fall 2016 Test 1 with Solutions
 CS3510 Design & Analysis of Algorithms Fall 16 Section B Fall 2016 Test 1 with Solutions Instructor: Richard Peng In class, Friday, Sep 9, 2016 Do not open this quiz booklet until you are directed to do
CS3510 Design & Analysis of Algorithms Fall 16 Section B Fall 2016 Test 1 with Solutions Instructor: Richard Peng In class, Friday, Sep 9, 2016 Do not open this quiz booklet until you are directed to do
Answer the following questions: Q1: ( 15 points) : A) Choose the correct answer of the following questions: نموذج اإلجابة
 Benha University Final Exam Class: 3 rd Year Students Subject: Design and analysis of Algorithms Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: 10/1/2017 Time: 3 hours Examiner: Dr. El-Sayed Badr Answer the
Benha University Final Exam Class: 3 rd Year Students Subject: Design and analysis of Algorithms Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: 10/1/2017 Time: 3 hours Examiner: Dr. El-Sayed Badr Answer the
Announcements. CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 2: Math Review; Algorithm Analysis. Today. Mathematical induction. Dan Grossman Spring 2010
 Announcements CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 2: Math Review; Algorithm Analysis Dan Grossman Spring 2010 Project 1 posted Section materials on using Eclipse will be very useful if you have never used
Announcements CSE332: Data Abstractions Lecture 2: Math Review; Algorithm Analysis Dan Grossman Spring 2010 Project 1 posted Section materials on using Eclipse will be very useful if you have never used
ASYMPTOTIC COMPLEXITY SEARCHING/SORTING
 Quotes about loops O! Thou hast damnable iteration and art, indeed, able to corrupt a saint. Shakespeare, Henry IV, Pt I, 1 ii Use not vain repetition, as the heathen do. Matthew V, 48 Your if is the only
Quotes about loops O! Thou hast damnable iteration and art, indeed, able to corrupt a saint. Shakespeare, Henry IV, Pt I, 1 ii Use not vain repetition, as the heathen do. Matthew V, 48 Your if is the only
Exercise Sheet #1 Solutions, Computer Science, A M. Hallett, K. Smith a k n b k = n b + k. a k n b k c 1 n b k. a k n b.
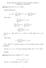 Exercise Sheet #1 Solutions, Computer Science, 308-251A M. Hallett, K. Smith 2002 Question 1.1: Prove (n + a) b = Θ(n b ). Binomial Expansion: Show O(n b ): (n + a) b = For any c 1 > b = O(n b ). Show
Exercise Sheet #1 Solutions, Computer Science, 308-251A M. Hallett, K. Smith 2002 Question 1.1: Prove (n + a) b = Θ(n b ). Binomial Expansion: Show O(n b ): (n + a) b = For any c 1 > b = O(n b ). Show
A New Paradigm for the Computational Complexity Analysis of Algorithms and Functions
 Issue 1, Volume 1, 2007 5 A New Paradigm for the Computational Complexity Analysis of Algorithms and Functions Ahmed Tare Abstract There exists a variety of techniques for the computational complexity
Issue 1, Volume 1, 2007 5 A New Paradigm for the Computational Complexity Analysis of Algorithms and Functions Ahmed Tare Abstract There exists a variety of techniques for the computational complexity
