Glocal Control for Hierarchical Dynamical Systems
|
|
|
- Annice Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture Series, TU Munich October 22, 29 & November 5, 2013 Glocal Control for Hierarchical Dynamical Systems Theoretical Foundations with Applications in Energy Networks Shinji HARA The University of Tokyo, Japan
2 OUTLINE 1. Glocal Control & Energy Networks 2. A Unified Framework for Networked Dynamical Systems with Stability Analysis 3. From Homogeneous to Heterogeneous 4. From Frat to Hierarchical 5. Decentralized Hierarchical Control Synthesis 6. Applications in Energy Networks 2
3 Framework for Glocal Control Realization of Global Functions by Local Measurement and Control Real World Glocal Control System Local Control Meteorological Phenomena Power NWs Bio-Systems LR model Transportation MR model HR model Local Measurement 3
4 Messages : A New Framework 1 LTI system with generalized freq. variable a proper class of homogeneous multi-agent dynamical systems 2 Three types of stability tests, namely graphical, algebraic, and numeric (LMI) powerful tools for analysis Q3: from Homogeneous to Heterogeneous? Q4: from Flat Structure to Hierarchical Structure? 4
5 From Frat to Hierarchical Structures Larger Scale : Agent Layer 3 Layer 2 Layer 1 Subsystem n3 n2 n1 5
6 OUTLINE : Part 4 4. From Frat to Hierarchical Low-rank Interlayer Connections Hierarchical Consensus for Heterogeneous Networks Hierarchical Adaptive Consensus 6
7 OUTLINE : Part 4 4. From Frat to Hierarchical Low-rank Interlayer Connections Hierarchical Consensus for Heterogeneous Networks Hierarchical Adaptive Consensus (Shimizu, Hara: SICE2008) Q9: What are Key Properties in Hierarchical Systems? 7
8 Hierarchical NW Dynamical Systems Larger Scale : Agent Layer 3 Layer 2 Layer 1 Subsystem n3 n2 n1 # total agents : n1 n2 n3 8
9 Hierarchical Structure Homogeneous structure Upper-layer structure Property on Interactions Low Rank Interaction: Share an aggregated information Control uniformly weak interaction: Sparse Small gain 9
10 Eigenvalue Distributions : Rank = 1 T = I n1 = 25 > n2 = 4 Im :rank 1 :Identity Re 10
11 Time Responses (n1=25, n2=4) x-position : Rank 1 Rapid n1 > n2 Consensus Time x-position = I Time Distribution Aggregation Low-rank Interlayer Interactions Multiple resolution 11
12 General Case with h(s) = I Stability Boundary : Rank 1 : = I *: = Rank 1 12
13 OUTLINE : Part 4 4. From Frat to Hierarchical Low-rank Interlayer Connections Hierarchical Consensus for Heterogeneous Networks Hierarchical Adaptive Consensus (Fujimori et. al., CDC2011) Q10: What is a General Framework for Heterogeneous Network Synthesis? 13
14 Hierarchical Structure Design, and Local connection Distribution of information Aggregation of information 14
15 Hierarchical Structure Design, and Hierarchical structure is compressed into matrix 15
16 Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Homogeneous Heterogeneous can be written using Kronecker product. We need Khatori-Rao product. 16
17 Eigen-connection Matrix is right eigen-connection matrix of associated with eigenvalue Def ( is the right eigenvector associated with ) Analogously, left eigen-connection matrix can also be defined by using left eigenvector. 17
18 Assumption Theorem : Rank 1 Case has at least one simple eigenvalue is a right eigen-connection matrix of associated with eigenvalue Theorem: Rank 1 For any, the set of all the eigenvalues of is given by The eigenvalues of local interconnection The eigenvalues determined by hierarchical structure An analogous result is obtained for left eigen-connection matrices. 18
19 Numerical Examples (1/2) Without Control y Time[s] y^1 y^2 6 5 Rank 1 y y^1 y^ Time[s] : eigenvalue of 19
20 Numerical Examples (2/2) Without Control 8 6 y y^1 y^ Time[s] 8 6 Rank Rank 2 y 4 y y 1 y Time[s] y^1 y^ Time[s] 20
21 Assumption Theorem : Rank 2 Case has at least two simple eigenvalues is a right eigen-connection matrix of associated with eigenvalue Theorem: Rank 2 For any, the set of all the eigenvalues of is given by An analogous result is obtained for left eigen-connection matrices. 21
22 OUTLINE : Part 4 4. From Frat to Hierarchical Low-rank Interlayer Connections Hierarchical Consensus for Heterogeneous Networks Hierarchical Adaptive Consensus (Fujimori et.al., SICE2011) 22
23 Stability for Dissipative Agents Agent Dynamics Theorem (LMI) (Hirsch, Hara: IFAC2008) 23
24 Passive Systems : Non-hierarchical Case Nonlinear Dynamics Goal of Consensus Conformation of Outputs Assumption Passivity Graph -L is Strongly Connected with positive edges Theorem All agents achieve consensus robustly for unknown positive weights. 24
25 Passive Systems : Non-hierarchical Case Nonlinear Dynamics Goal of Consensus Conformation of Outputs Assumption Passivity Graph -L is Strongly Connected with positive edges Theorem All agents achieve consensus robustly for unknown positive weights. 25
26 Passive Systems : Hierarchical Case Regard S. C. multiple pendulums as a subsystem Subsystems exchange the weighted sum of information :input weight :output weight 26
27 An Example of Hierarchical Structure Whole Graph Laplacian aggregation There are Negative Edge! We need another criterion Q: How can we decide the weights so that the subsystem is passive? 27
28 Consensus of Hierarchical Structure Assumption Passivity subsystem: S. C. satisfy Proposition All the subsystems are Passive The positive left eigenvector of the graph Laplacian representing the connection inside the subsystem associated with the eigenvalue 0. Outputs of subsystems achieve consensus Agents in each subsystem achieve consensus When sums of output weights are coincident, all the agents achieve consensus. 28
29 Numerical Simulation (1/2) Case1) The Assumption is satisfied aggregation Sum of output weight is equivalent Angular velocity[rad/s]
30 Numerical Simulation (2/2) Case2) The Assumption is not satisfied aggregation Angular velocity[rad/s] Time[s] 30
31 Three Messages 1 Low rank interlayer connections are quite helpful for rapid consensus. aggregation 2 Heterogeneous agents: Khatri-Rao Product hierarchical network synthesis based on left eigenvectors 3 Nonlinear agents: left eigenvector strongly connected graph in the upper layer + subsystems which can be passive 31
32 Messages : A New Framework 1 LTI system with generalized freq. variable a proper class of homogeneous multi-agent systems 2 Three types of stability tests, namely graphical, algebraic, and numeric (LMI) powerful tools for analysis 3 From Homogeneous to Heterogeneous robust stability analysis (Hinf norm condition) 4 From Flat to Hierarchical Structure low-rank interlayer connection (aggregation & distribution) How to Design Decentralized Control Systems Systematically? 32
Lecture 02 Linear Algebra Basics
 Introduction to Computational Data Analysis CX4240, 2019 Spring Lecture 02 Linear Algebra Basics Chao Zhang College of Computing Georgia Tech These slides are based on slides from Le Song and Andres Mendez-Vazquez.
Introduction to Computational Data Analysis CX4240, 2019 Spring Lecture 02 Linear Algebra Basics Chao Zhang College of Computing Georgia Tech These slides are based on slides from Le Song and Andres Mendez-Vazquez.
Graph and Controller Design for Disturbance Attenuation in Consensus Networks
 203 3th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 203) Oct. 20-23, 203 in Kimdaejung Convention Center, Gwangju, Korea Graph and Controller Design for Disturbance Attenuation in
203 3th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 203) Oct. 20-23, 203 in Kimdaejung Convention Center, Gwangju, Korea Graph and Controller Design for Disturbance Attenuation in
MTNS 06, Kyoto (July, 2006) Shinji Hara The University of Tokyo, Japan
 MTNS 06, Kyoto (July, 2006) Shinji Hara The University of Tokyo, Japan Outline Motivation & Background: H2 Tracking Performance Limits: new paradigm Explicit analytical solutions with examples H2 Regulation
MTNS 06, Kyoto (July, 2006) Shinji Hara The University of Tokyo, Japan Outline Motivation & Background: H2 Tracking Performance Limits: new paradigm Explicit analytical solutions with examples H2 Regulation
Glocal Control for Network Systems via Hierarchical State-Space Expansion
 Glocal Control for Network Systems via Hierarchical State-Space Expansion Hampei Sasahara, Takayuki Ishizaki, Tomonori Sadamoto, Jun-ichi Imura, Henrik Sandberg 2, and Karl Henrik Johansson 2 Abstract
Glocal Control for Network Systems via Hierarchical State-Space Expansion Hampei Sasahara, Takayuki Ishizaki, Tomonori Sadamoto, Jun-ichi Imura, Henrik Sandberg 2, and Karl Henrik Johansson 2 Abstract
LTI Systems with Generalized Frequency Variables: A Unified Framework for Homogeneous Multi-agent Dynamical Systems
 SICE Journal of Control, Measurement, and System Integration, Vol, No 5, pp 99 36, September 9 LTI Systems with Generalized Frequency Variables: A Unified Framework for Homogeneous Multi-agent Dynamical
SICE Journal of Control, Measurement, and System Integration, Vol, No 5, pp 99 36, September 9 LTI Systems with Generalized Frequency Variables: A Unified Framework for Homogeneous Multi-agent Dynamical
Digital Control Engineering Analysis and Design
 Digital Control Engineering Analysis and Design M. Sami Fadali Antonio Visioli AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic Press is
Digital Control Engineering Analysis and Design M. Sami Fadali Antonio Visioli AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic Press is
Linear vector spaces and subspaces.
 Math 2051 W2008 Margo Kondratieva Week 1 Linear vector spaces and subspaces. Section 1.1 The notion of a linear vector space. For the purpose of these notes we regard (m 1)-matrices as m-dimensional vectors,
Math 2051 W2008 Margo Kondratieva Week 1 Linear vector spaces and subspaces. Section 1.1 The notion of a linear vector space. For the purpose of these notes we regard (m 1)-matrices as m-dimensional vectors,
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Efficient Observation of Random Phenomena
 Lecture 9 Efficient Observation of Random Phenomena Tokyo Polytechnic University The 1st Century Center of Excellence Program Yukio Tamura POD Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Stochastic Representation
Lecture 9 Efficient Observation of Random Phenomena Tokyo Polytechnic University The 1st Century Center of Excellence Program Yukio Tamura POD Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Stochastic Representation
Fast Linear Iterations for Distributed Averaging 1
 Fast Linear Iterations for Distributed Averaging 1 Lin Xiao Stephen Boyd Information Systems Laboratory, Stanford University Stanford, CA 943-91 lxiao@stanford.edu, boyd@stanford.edu Abstract We consider
Fast Linear Iterations for Distributed Averaging 1 Lin Xiao Stephen Boyd Information Systems Laboratory, Stanford University Stanford, CA 943-91 lxiao@stanford.edu, boyd@stanford.edu Abstract We consider
Outline Python, Numpy, and Matplotlib Making Models with Polynomials Making Models with Monte Carlo Error, Accuracy and Convergence Floating Point Mod
 Outline Python, Numpy, and Matplotlib Making Models with Polynomials Making Models with Monte Carlo Error, Accuracy and Convergence Floating Point Modeling the World with Arrays The World in a Vector What
Outline Python, Numpy, and Matplotlib Making Models with Polynomials Making Models with Monte Carlo Error, Accuracy and Convergence Floating Point Modeling the World with Arrays The World in a Vector What
Linear Systems of ODE: Nullclines, Eigenvector lines and trajectories
 Linear Systems of ODE: Nullclines, Eigenvector lines and trajectories James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 6, 203 Outline
Linear Systems of ODE: Nullclines, Eigenvector lines and trajectories James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 6, 203 Outline
DECENTRALIZED CONTROL DESIGN USING LMI MODEL REDUCTION
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 58, NO. 6, 2007, 307 312 DECENTRALIZED CONTROL DESIGN USING LMI MODEL REDUCTION Szabolcs Dorák Danica Rosinová Decentralized control design approach based on partial
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 58, NO. 6, 2007, 307 312 DECENTRALIZED CONTROL DESIGN USING LMI MODEL REDUCTION Szabolcs Dorák Danica Rosinová Decentralized control design approach based on partial
Eigenvalue and Eigenvector Homework
 Eigenvalue and Eigenvector Homework Olena Bormashenko November 4, 2 For each of the matrices A below, do the following:. Find the characteristic polynomial of A, and use it to find all the eigenvalues
Eigenvalue and Eigenvector Homework Olena Bormashenko November 4, 2 For each of the matrices A below, do the following:. Find the characteristic polynomial of A, and use it to find all the eigenvalues
Linear Systems of ODE: Nullclines, Eigenvector lines and trajectories
 Linear Systems of ODE: Nullclines, Eigenvector lines and trajectories James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 6, 2013 Outline
Linear Systems of ODE: Nullclines, Eigenvector lines and trajectories James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University October 6, 2013 Outline
Clustered Model Reduction of Interconnected Second-Order Systems and Its Applications to Power Systems
 Clustered Model Reduction of Interconnected Second-Order Systems and Its Applications to Power Systems Takayuki Ishizaki, Jun-ichi Imura (Tokyo Inst. of Tech.) Outline Introduction: Why clustered model
Clustered Model Reduction of Interconnected Second-Order Systems and Its Applications to Power Systems Takayuki Ishizaki, Jun-ichi Imura (Tokyo Inst. of Tech.) Outline Introduction: Why clustered model
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: The Gram-Schmidt process (continued). Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Orthogonal sets Let V be a vector space with an inner product. Definition. Nonzero vectors v 1,v
6545(Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 4, Issue 3, May - June (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL International Journal of JOURNAL Electrical Engineering OF ELECTRICAL and Technology (IJEET), ENGINEERING ISSN 976 & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 976 6545(Print) ISSN 976 6553(Online) Volume 4,
INTERNATIONAL International Journal of JOURNAL Electrical Engineering OF ELECTRICAL and Technology (IJEET), ENGINEERING ISSN 976 & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 976 6545(Print) ISSN 976 6553(Online) Volume 4,
Lyapunov functions on nonlinear spaces S 1 R R + V =(1 cos ) Constructing Lyapunov functions: a personal journey
 Constructing Lyapunov functions: a personal journey Lyapunov functions on nonlinear spaces R. Sepulchre -- University of Liege, Belgium Reykjavik - July 2013 Lyap functions in linear spaces (1994-1997)
Constructing Lyapunov functions: a personal journey Lyapunov functions on nonlinear spaces R. Sepulchre -- University of Liege, Belgium Reykjavik - July 2013 Lyap functions in linear spaces (1994-1997)
Copyrighted Material. 1.1 Large-Scale Interconnected Dynamical Systems
 Chapter One Introduction 1.1 Large-Scale Interconnected Dynamical Systems Modern complex dynamical systems 1 are highly interconnected and mutually interdependent, both physically and through a multitude
Chapter One Introduction 1.1 Large-Scale Interconnected Dynamical Systems Modern complex dynamical systems 1 are highly interconnected and mutually interdependent, both physically and through a multitude
V&V MURI Overview Caltech, October 2008
 V&V MURI Overview Caltech, October 2008 Pablo A. Parrilo Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems Massachusetts Institute of Technology Goals!! Specification, design, and certification!! Coherent
V&V MURI Overview Caltech, October 2008 Pablo A. Parrilo Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems Massachusetts Institute of Technology Goals!! Specification, design, and certification!! Coherent
Hierarchical Decentralized Observer Design for Linearly Coupled Network Systems
 Hierarchical Decentralized Observer Design for Linearly Coupled Network Systems Takayuki Ishizaki, Yukihiro Sakai, Kenji Kashima and Jun-ichi Imura* Abstract This paper proposes a novel type of decentralized
Hierarchical Decentralized Observer Design for Linearly Coupled Network Systems Takayuki Ishizaki, Yukihiro Sakai, Kenji Kashima and Jun-ichi Imura* Abstract This paper proposes a novel type of decentralized
Numerical Schemes from the Perspective of Consensus
 Numerical Schemes from the Perspective of Consensus Exploring Connections between Agreement Problems and PDEs Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Numerical Schemes from the Perspective of Consensus Exploring Connections between Agreement Problems and PDEs Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
Dissipativity. Outline. Motivation. Dissipative Systems. M. Sami Fadali EBME Dept., UNR
 Dissipativity M. Sami Fadali EBME Dept., UNR 1 Outline Differential storage functions. QSR Dissipativity. Algebraic conditions for dissipativity. Stability of dissipative systems. Feedback Interconnections
Dissipativity M. Sami Fadali EBME Dept., UNR 1 Outline Differential storage functions. QSR Dissipativity. Algebraic conditions for dissipativity. Stability of dissipative systems. Feedback Interconnections
Multivariate Statistical Analysis
 Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Decentralized control of complex systems: an overview
 Decentralized control of complex systems: an overview Madhu N. Belur (Course taught with Debraj Chakraborty) Control and Computing group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
Decentralized control of complex systems: an overview Madhu N. Belur (Course taught with Debraj Chakraborty) Control and Computing group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
A Scalable Robust Stability Criterion for Systems with Heterogeneous LTI Components
 9 merican ontrol onference Hyatt Regency Riverfront St. Louis MO US June - 9 ThB9. Scalable Robust Stability riterion for Systems with Heterogeneous LTI omponents U. T. Jönsson Royal Institute of Technology
9 merican ontrol onference Hyatt Regency Riverfront St. Louis MO US June - 9 ThB9. Scalable Robust Stability riterion for Systems with Heterogeneous LTI omponents U. T. Jönsson Royal Institute of Technology
Clustering-based State Aggregation of Dynamical Networks
 Clustering-based State Aggregation of Dynamical Networks Takayuki Ishizaki Ph.D. from Tokyo Institute of Technology (March 2012) Research Fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science More than
Clustering-based State Aggregation of Dynamical Networks Takayuki Ishizaki Ph.D. from Tokyo Institute of Technology (March 2012) Research Fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science More than
LECTURE NOTE #11 PROF. ALAN YUILLE
 LECTURE NOTE #11 PROF. ALAN YUILLE 1. NonLinear Dimension Reduction Spectral Methods. The basic idea is to assume that the data lies on a manifold/surface in D-dimensional space, see figure (1) Perform
LECTURE NOTE #11 PROF. ALAN YUILLE 1. NonLinear Dimension Reduction Spectral Methods. The basic idea is to assume that the data lies on a manifold/surface in D-dimensional space, see figure (1) Perform
Distributed Randomized Algorithms for the PageRank Computation Hideaki Ishii, Member, IEEE, and Roberto Tempo, Fellow, IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 55, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2010 1987 Distributed Randomized Algorithms for the PageRank Computation Hideaki Ishii, Member, IEEE, and Roberto Tempo, Fellow, IEEE Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 55, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2010 1987 Distributed Randomized Algorithms for the PageRank Computation Hideaki Ishii, Member, IEEE, and Roberto Tempo, Fellow, IEEE Abstract
Mathematical Relationships Between Representations of Structure in Linear Interconnected Dynamical Systems
 American Control Conference on O'Farrell Street, San Francisco, CA, USA June 9 - July, Mathematical Relationships Between Representations of Structure in Linear Interconnected Dynamical Systems E. Yeung,
American Control Conference on O'Farrell Street, San Francisco, CA, USA June 9 - July, Mathematical Relationships Between Representations of Structure in Linear Interconnected Dynamical Systems E. Yeung,
Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control
 Bernard Brogliato, Rogelio Lozano, Bernhard Maschke and Olav Egeland Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control Theory and Applications 2nd Edition With 94 Figures 4y Sprin er 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example
Bernard Brogliato, Rogelio Lozano, Bernhard Maschke and Olav Egeland Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control Theory and Applications 2nd Edition With 94 Figures 4y Sprin er 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example
A State-Space Approach to Control of Interconnected Systems
 A State-Space Approach to Control of Interconnected Systems Part II: General Interconnections Cédric Langbort Center for the Mathematics of Information CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY clangbort@ist.caltech.edu
A State-Space Approach to Control of Interconnected Systems Part II: General Interconnections Cédric Langbort Center for the Mathematics of Information CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY clangbort@ist.caltech.edu
Patterned Linear Systems: Rings, Chains, and Trees
 Patterned Linear Systems: Rings Chains and Trees Sarah C Hamilton and Mireille E Broucke Abstract In a first paper we studied system theoretic properties of patterned systems and solved classical control
Patterned Linear Systems: Rings Chains and Trees Sarah C Hamilton and Mireille E Broucke Abstract In a first paper we studied system theoretic properties of patterned systems and solved classical control
Represent this system in terms of a block diagram consisting only of. g From Newton s law: 2 : θ sin θ 9 θ ` T
 Exercise (Block diagram decomposition). Consider a system P that maps each input to the solutions of 9 4 ` 3 9 Represent this system in terms of a block diagram consisting only of integrator systems, represented
Exercise (Block diagram decomposition). Consider a system P that maps each input to the solutions of 9 4 ` 3 9 Represent this system in terms of a block diagram consisting only of integrator systems, represented
Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control, Theory and Applications: Addendum/Erratum
 Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control, Theory and Applications: Addendum/Erratum Bernard Brogliato To cite this version: Bernard Brogliato. Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control, Theory and Applications:
Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control, Theory and Applications: Addendum/Erratum Bernard Brogliato To cite this version: Bernard Brogliato. Dissipative Systems Analysis and Control, Theory and Applications:
Feedback Control CONTROL THEORY FUNDAMENTALS. Feedback Control: A History. Feedback Control: A History (contd.) Anuradha Annaswamy
 Feedback Control CONTROL THEORY FUNDAMENTALS Actuator Sensor + Anuradha Annaswamy Active adaptive Control Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology must follow with» Speed» Accuracy Feeback: Measure
Feedback Control CONTROL THEORY FUNDAMENTALS Actuator Sensor + Anuradha Annaswamy Active adaptive Control Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology must follow with» Speed» Accuracy Feeback: Measure
Stability and Disturbance Propagation in Autonomous Vehicle Formations : A Graph Laplacian Approach
 Stability and Disturbance Propagation in Autonomous Vehicle Formations : A Graph Laplacian Approach Francesco Borrelli*, Kingsley Fregene, Datta Godbole, Gary Balas* *Department of Aerospace Engineering
Stability and Disturbance Propagation in Autonomous Vehicle Formations : A Graph Laplacian Approach Francesco Borrelli*, Kingsley Fregene, Datta Godbole, Gary Balas* *Department of Aerospace Engineering
Title unstable additive/multiplicative pe. works must be obtained from the IEE
 Title Robust stability of sampled-data sy unstable additive/multiplicative pe Author(s) Hagiwara, T; Araki, M Citation IEEE Transactions on Automatic Cont 346 Issue Date 998-09 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39968
Title Robust stability of sampled-data sy unstable additive/multiplicative pe Author(s) Hagiwara, T; Araki, M Citation IEEE Transactions on Automatic Cont 346 Issue Date 998-09 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/39968
Conceptual Questions for Review
 Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Conceptual Questions for Review Chapter 1 1.1 Which vectors are linear combinations of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3)? 1.2 Compare the dot product of v = (3, 1) and w = (4, 3) to the product of their lengths.
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
PENN STATE UNIVERSITY MATH 220: LINEAR ALGEBRA
 PENN STATE UNIVERSITY MATH 220: LINEAR ALGEBRA Penn State Bluebook: 1. Systems of Linear Equations 2. Matrix Algebra 3. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 4. Linear Systems of Differential Equations The above
PENN STATE UNIVERSITY MATH 220: LINEAR ALGEBRA Penn State Bluebook: 1. Systems of Linear Equations 2. Matrix Algebra 3. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 4. Linear Systems of Differential Equations The above
MATRICES. knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns.
 MATRICES After studying this chapter you will acquire the skills in knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns. List of
MATRICES After studying this chapter you will acquire the skills in knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns. List of
Estimation, Detection, and Identification CMU 18752
 Estimation, Detection, and Identification CMU 18752 Graduate Course on the CMU/Portugal ECE PhD Program Spring 2008/2009 Instructor: Prof. Paulo Jorge Oliveira pjcro @ isr.ist.utl.pt Phone: +351 21 8418053
Estimation, Detection, and Identification CMU 18752 Graduate Course on the CMU/Portugal ECE PhD Program Spring 2008/2009 Instructor: Prof. Paulo Jorge Oliveira pjcro @ isr.ist.utl.pt Phone: +351 21 8418053
OUTPUT CONSENSUS OF HETEROGENEOUS LINEAR MULTI-AGENT SYSTEMS BY EVENT-TRIGGERED CONTROL
 OUTPUT CONSENSUS OF HETEROGENEOUS LINEAR MULTI-AGENT SYSTEMS BY EVENT-TRIGGERED CONTROL Gang FENG Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering City University of Hong Kong July 25, 2014 Department
OUTPUT CONSENSUS OF HETEROGENEOUS LINEAR MULTI-AGENT SYSTEMS BY EVENT-TRIGGERED CONTROL Gang FENG Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering City University of Hong Kong July 25, 2014 Department
A MATRIX INEQUALITY BASED DESIGN METHOD FOR CONSENSUS PROBLEMS IN MULTI AGENT SYSTEMS
 Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci., 2009, Vol. 19, No. 4, 639 646 DOI: 10.2478/v10006-009-0051-1 A MATRIX INEQUALITY BASED DESIGN METHOD FOR CONSENSUS PROBLEMS IN MULTI AGENT SYSTEMS GUISHENG ZHAI, SHOHEI
Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci., 2009, Vol. 19, No. 4, 639 646 DOI: 10.2478/v10006-009-0051-1 A MATRIX INEQUALITY BASED DESIGN METHOD FOR CONSENSUS PROBLEMS IN MULTI AGENT SYSTEMS GUISHENG ZHAI, SHOHEI
Stabilization and Passivity-Based Control
 DISC Systems and Control Theory of Nonlinear Systems, 2010 1 Stabilization and Passivity-Based Control Lecture 8 Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems, Chapter 10, plus handout from R. Sepulchre, Constructive
DISC Systems and Control Theory of Nonlinear Systems, 2010 1 Stabilization and Passivity-Based Control Lecture 8 Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems, Chapter 10, plus handout from R. Sepulchre, Constructive
Decentralized Stabilization of Heterogeneous Linear Multi-Agent Systems
 1 Decentralized Stabilization of Heterogeneous Linear Multi-Agent Systems Mauro Franceschelli, Andrea Gasparri, Alessandro Giua, and Giovanni Ulivi Abstract In this paper the formation stabilization problem
1 Decentralized Stabilization of Heterogeneous Linear Multi-Agent Systems Mauro Franceschelli, Andrea Gasparri, Alessandro Giua, and Giovanni Ulivi Abstract In this paper the formation stabilization problem
Clustering-Based Model Order Reduction for Multi-Agent Systems with General Linear Time-Invariant Agents
 Max Planck Institute Magdeburg Preprints Petar Mlinarić Sara Grundel Peter Benner Clustering-Based Model Order Reduction for Multi-Agent Systems with General Linear Time-Invariant Agents MAX PLANCK INSTITUT
Max Planck Institute Magdeburg Preprints Petar Mlinarić Sara Grundel Peter Benner Clustering-Based Model Order Reduction for Multi-Agent Systems with General Linear Time-Invariant Agents MAX PLANCK INSTITUT
Consensus Protocols for Networks of Dynamic Agents
 Consensus Protocols for Networks of Dynamic Agents Reza Olfati Saber Richard M. Murray Control and Dynamical Systems California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91125 e-mail: {olfati,murray}@cds.caltech.edu
Consensus Protocols for Networks of Dynamic Agents Reza Olfati Saber Richard M. Murray Control and Dynamical Systems California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91125 e-mail: {olfati,murray}@cds.caltech.edu
Robust Synchronization in Networks of Compartmental Systems. Milad Alekajbaf
 Robust Synchronization in Networks of Compartmental Systems by Milad Alekajbaf A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Applied Science Graduate Department of
Robust Synchronization in Networks of Compartmental Systems by Milad Alekajbaf A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Applied Science Graduate Department of
Active Passive Networked Multiagent Systems
 Active Passive Networked Multiagent Systems Tansel Yucelen and John Daniel Peterson Abstract This paper introduces an active passive networked multiagent system framework, which consists of agents subject
Active Passive Networked Multiagent Systems Tansel Yucelen and John Daniel Peterson Abstract This paper introduces an active passive networked multiagent system framework, which consists of agents subject
Linear Algebra II Lecture 13
 Linear Algebra II Lecture 13 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta November 14, 2014 Outline 1 2 If v is an eigenvector of T : V V corresponding to λ, then v is an eigenvector of T m corresponding to λ m since
Linear Algebra II Lecture 13 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta November 14, 2014 Outline 1 2 If v is an eigenvector of T : V V corresponding to λ, then v is an eigenvector of T m corresponding to λ m since
Recent Advances in Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems
 Int. Workshop on Complex Eng. Systems and Design, Hong Kong, 22 May 2009 Recent Advances in Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems Jinhu Lü Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science Chinese Academy of Sciences
Int. Workshop on Complex Eng. Systems and Design, Hong Kong, 22 May 2009 Recent Advances in Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems Jinhu Lü Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science Chinese Academy of Sciences
A Graph-Theoretic Characterization of Structural Controllability for Multi-Agent System with Switching Topology
 Joint 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference Shanghai, P.R. China, December 16-18, 29 FrAIn2.3 A Graph-Theoretic Characterization of Structural Controllability
Joint 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference Shanghai, P.R. China, December 16-18, 29 FrAIn2.3 A Graph-Theoretic Characterization of Structural Controllability
Constant coefficients systems
 5.3. 2 2 Constant coefficients systems Section Objective(s): Diagonalizable systems. Real Distinct Eigenvalues. Complex Eigenvalues. Non-Diagonalizable systems. 5.3.. Diagonalizable Systems. Remark: We
5.3. 2 2 Constant coefficients systems Section Objective(s): Diagonalizable systems. Real Distinct Eigenvalues. Complex Eigenvalues. Non-Diagonalizable systems. 5.3.. Diagonalizable Systems. Remark: We
Model-based Fault Diagnosis Techniques Design Schemes, Algorithms, and Tools
 Steven X. Ding Model-based Fault Diagnosis Techniques Design Schemes, Algorithms, and Tools Springer Notation XIX Part I Introduction, basic concepts and preliminaries 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Basic concepts
Steven X. Ding Model-based Fault Diagnosis Techniques Design Schemes, Algorithms, and Tools Springer Notation XIX Part I Introduction, basic concepts and preliminaries 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Basic concepts
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
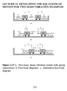 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Spectral clustering. Two ideal clusters, with two points each. Spectral clustering algorithms
 A simple example Two ideal clusters, with two points each Spectral clustering Lecture 2 Spectral clustering algorithms 4 2 3 A = Ideally permuted Ideal affinities 2 Indicator vectors Each cluster has an
A simple example Two ideal clusters, with two points each Spectral clustering Lecture 2 Spectral clustering algorithms 4 2 3 A = Ideally permuted Ideal affinities 2 Indicator vectors Each cluster has an
Convergence Speed in Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems - A Robust Control Approach
 nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control December -,. Florence, Italy Convergence Speed in Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems - A Robust Control Approach Ulf Pilz and Herbert Werner Abstract In
nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control December -,. Florence, Italy Convergence Speed in Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems - A Robust Control Approach Ulf Pilz and Herbert Werner Abstract In
STATE ESTIMATION IN COORDINATED CONTROL WITH A NON-STANDARD INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE. Jun Yan, Keunmo Kang, and Robert Bitmead
 STATE ESTIMATION IN COORDINATED CONTROL WITH A NON-STANDARD INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE Jun Yan, Keunmo Kang, and Robert Bitmead Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering University of California San
STATE ESTIMATION IN COORDINATED CONTROL WITH A NON-STANDARD INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE Jun Yan, Keunmo Kang, and Robert Bitmead Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering University of California San
Structured State Space Realizations for SLS Distributed Controllers
 Structured State Space Realizations for SLS Distributed Controllers James Anderson and Nikolai Matni Abstract In recent work the system level synthesis (SLS) paradigm has been shown to provide a truly
Structured State Space Realizations for SLS Distributed Controllers James Anderson and Nikolai Matni Abstract In recent work the system level synthesis (SLS) paradigm has been shown to provide a truly
A Decentralized Consensus Algorithm for Distributed State Observers with Robustness Guarantees
 A Decentralized Consensus Algorithm for Distributed State Observers with Robustness Guarantees Yuchun Li and Ricardo G. Sanfelice Abstract Motivated by the design of distributed observers with good performance
A Decentralized Consensus Algorithm for Distributed State Observers with Robustness Guarantees Yuchun Li and Ricardo G. Sanfelice Abstract Motivated by the design of distributed observers with good performance
Linear transformations
 Linear transformations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T. Linear transformations
Linear transformations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T. Linear transformations
Multi-Robotic Systems
 CHAPTER 9 Multi-Robotic Systems The topic of multi-robotic systems is quite popular now. It is believed that such systems can have the following benefits: Improved performance ( winning by numbers ) Distributed
CHAPTER 9 Multi-Robotic Systems The topic of multi-robotic systems is quite popular now. It is believed that such systems can have the following benefits: Improved performance ( winning by numbers ) Distributed
On the Scalability in Cooperative Control. Zhongkui Li. Peking University
 On the Scalability in Cooperative Control Zhongkui Li Email: zhongkli@pku.edu.cn Peking University June 25, 2016 Zhongkui Li (PKU) Scalability June 25, 2016 1 / 28 Background Cooperative control is to
On the Scalability in Cooperative Control Zhongkui Li Email: zhongkli@pku.edu.cn Peking University June 25, 2016 Zhongkui Li (PKU) Scalability June 25, 2016 1 / 28 Background Cooperative control is to
Spectral Graph Theory
 Spectral Graph Theory Aaron Mishtal April 27, 2016 1 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra Primer History Theory Applications Open Problems Homework Problems References 2 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra
Spectral Graph Theory Aaron Mishtal April 27, 2016 1 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra Primer History Theory Applications Open Problems Homework Problems References 2 / 36 Outline Overview Linear Algebra
Approximate Distributed Kalman Filtering in Sensor Networks with Quantifiable Performance
 25 International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN) http://www.cds.caltech.edu/~murray/papers/25h_som5-ipsn.html Approximate Distributed Kalman Filtering in Sensor Networks
25 International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN) http://www.cds.caltech.edu/~murray/papers/25h_som5-ipsn.html Approximate Distributed Kalman Filtering in Sensor Networks
Lecture 10. Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis
 CS-621 Theory Gems October 18, 2012 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will see how one can use random walks to
CS-621 Theory Gems October 18, 2012 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will see how one can use random walks to
Data Mining Lecture 4: Covariance, EVD, PCA & SVD
 Data Mining Lecture 4: Covariance, EVD, PCA & SVD Jo Houghton ECS Southampton February 25, 2019 1 / 28 Variance and Covariance - Expectation A random variable takes on different values due to chance The
Data Mining Lecture 4: Covariance, EVD, PCA & SVD Jo Houghton ECS Southampton February 25, 2019 1 / 28 Variance and Covariance - Expectation A random variable takes on different values due to chance The
When Gradient Systems and Hamiltonian Systems Meet
 When Gradient Systems and Hamiltonian Systems Meet Arjan van der Schaft Johann Bernoulli Institute for Mathematics and Computer Science University of Groningen, the Netherlands December 11, 2011 on the
When Gradient Systems and Hamiltonian Systems Meet Arjan van der Schaft Johann Bernoulli Institute for Mathematics and Computer Science University of Groningen, the Netherlands December 11, 2011 on the
Contents. 1 State-Space Linear Systems 5. 2 Linearization Causality, Time Invariance, and Linearity 31
 Contents Preamble xiii Linear Systems I Basic Concepts 1 I System Representation 3 1 State-Space Linear Systems 5 1.1 State-Space Linear Systems 5 1.2 Block Diagrams 7 1.3 Exercises 11 2 Linearization
Contents Preamble xiii Linear Systems I Basic Concepts 1 I System Representation 3 1 State-Space Linear Systems 5 1.1 State-Space Linear Systems 5 1.2 Block Diagrams 7 1.3 Exercises 11 2 Linearization
Consensus of Information Under Dynamically Changing Interaction Topologies
 Consensus of Information Under Dynamically Changing Interaction Topologies Wei Ren and Randal W. Beard Abstract This paper considers the problem of information consensus among multiple agents in the presence
Consensus of Information Under Dynamically Changing Interaction Topologies Wei Ren and Randal W. Beard Abstract This paper considers the problem of information consensus among multiple agents in the presence
Graph Theoretic Methods in the Stability of Vehicle Formations
 Graph Theoretic Methods in the Stability of Vehicle Formations G. Lafferriere, J. Caughman, A. Williams gerardol@pd.edu, caughman@pd.edu, ancaw@pd.edu Abstract This paper investigates the stabilization
Graph Theoretic Methods in the Stability of Vehicle Formations G. Lafferriere, J. Caughman, A. Williams gerardol@pd.edu, caughman@pd.edu, ancaw@pd.edu Abstract This paper investigates the stabilization
SESSION 2 MULTI-AGENT NETWORKS. Magnus Egerstedt - Aug. 2013
 SESSION 2 MULTI-AGENT NETWORKS Variations on the Theme: Directed Graphs Instead of connectivity, we need directed notions: Strong connectivity = there exists a directed path between any two nodes Weak
SESSION 2 MULTI-AGENT NETWORKS Variations on the Theme: Directed Graphs Instead of connectivity, we need directed notions: Strong connectivity = there exists a directed path between any two nodes Weak
Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C.
 Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C 1 Upper Triangular Representation Proposition: Let T L(V ) There exists an orthonormal
Math 342 - Linear Algebra II Notes Throughout these notes we assume V, W are finite dimensional inner product spaces over C 1 Upper Triangular Representation Proposition: Let T L(V ) There exists an orthonormal
Linear Control Systems Lecture #3 - Frequency Domain Analysis. Guillaume Drion Academic year
 Linear Control Systems Lecture #3 - Frequency Domain Analysis Guillaume Drion Academic year 2018-2019 1 Goal and Outline Goal: To be able to analyze the stability and robustness of a closed-loop system
Linear Control Systems Lecture #3 - Frequency Domain Analysis Guillaume Drion Academic year 2018-2019 1 Goal and Outline Goal: To be able to analyze the stability and robustness of a closed-loop system
Numerical Methods I Singular Value Decomposition
 Numerical Methods I Singular Value Decomposition Aleksandar Donev Courant Institute, NYU 1 donev@courant.nyu.edu 1 MATH-GA 2011.003 / CSCI-GA 2945.003, Fall 2014 October 9th, 2014 A. Donev (Courant Institute)
Numerical Methods I Singular Value Decomposition Aleksandar Donev Courant Institute, NYU 1 donev@courant.nyu.edu 1 MATH-GA 2011.003 / CSCI-GA 2945.003, Fall 2014 October 9th, 2014 A. Donev (Courant Institute)
On the Controllability of Nearest Neighbor Interconnections
 On the Controllability of Nearest Neighbor Interconnections Herbert G. Tanner Mechanical Engineering Department University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM 87 Abstract In this paper we derive necessary and
On the Controllability of Nearest Neighbor Interconnections Herbert G. Tanner Mechanical Engineering Department University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM 87 Abstract In this paper we derive necessary and
Non-linear Dimensionality Reduction
 Non-linear Dimensionality Reduction CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Introduction Laplacian Eigenmaps Locally Linear Embedding (LLE)
Non-linear Dimensionality Reduction CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Introduction Laplacian Eigenmaps Locally Linear Embedding (LLE)
LOW ORDER H CONTROLLER DESIGN: AN LMI APPROACH
 LOW ORDER H CONROLLER DESIGN: AN LMI APPROACH Guisheng Zhai, Shinichi Murao, Naoki Koyama, Masaharu Yoshida Faculty of Systems Engineering, Wakayama University, Wakayama 640-8510, Japan Email: zhai@sys.wakayama-u.ac.jp
LOW ORDER H CONROLLER DESIGN: AN LMI APPROACH Guisheng Zhai, Shinichi Murao, Naoki Koyama, Masaharu Yoshida Faculty of Systems Engineering, Wakayama University, Wakayama 640-8510, Japan Email: zhai@sys.wakayama-u.ac.jp
ANALYSIS OF CONSENSUS AND COLLISION AVOIDANCE USING THE COLLISION CONE APPROACH IN THE PRESENCE OF TIME DELAYS. A Thesis by. Dipendra Khatiwada
 ANALYSIS OF CONSENSUS AND COLLISION AVOIDANCE USING THE COLLISION CONE APPROACH IN THE PRESENCE OF TIME DELAYS A Thesis by Dipendra Khatiwada Bachelor of Science, Wichita State University, 2013 Submitted
ANALYSIS OF CONSENSUS AND COLLISION AVOIDANCE USING THE COLLISION CONE APPROACH IN THE PRESENCE OF TIME DELAYS A Thesis by Dipendra Khatiwada Bachelor of Science, Wichita State University, 2013 Submitted
Family Feud Review. Linear Algebra. October 22, 2013
 Review Linear Algebra October 22, 2013 Question 1 Let A and B be matrices. If AB is a 4 7 matrix, then determine the dimensions of A and B if A has 19 columns. Answer 1 Answer A is a 4 19 matrix, while
Review Linear Algebra October 22, 2013 Question 1 Let A and B be matrices. If AB is a 4 7 matrix, then determine the dimensions of A and B if A has 19 columns. Answer 1 Answer A is a 4 19 matrix, while
Example Linear Algebra Competency Test
 Example Linear Algebra Competency Test The 4 questions below are a combination of True or False, multiple choice, fill in the blank, and computations involving matrices and vectors. In the latter case,
Example Linear Algebra Competency Test The 4 questions below are a combination of True or False, multiple choice, fill in the blank, and computations involving matrices and vectors. In the latter case,
Hierarchical Decentralized Observers for Networked Linear Systems
 Hierarchical Decentralized Observers for Networked Linear Systems Takayuki Ishizaki 1,2, Masakazu Koike 1,2, Tomonori Sadamoto 1, Jun-ichi Imura 1,2 Abstract In this paper, we propose a design method of
Hierarchical Decentralized Observers for Networked Linear Systems Takayuki Ishizaki 1,2, Masakazu Koike 1,2, Tomonori Sadamoto 1, Jun-ichi Imura 1,2 Abstract In this paper, we propose a design method of
Stability of Hybrid Control Systems Based on Time-State Control Forms
 Stability of Hybrid Control Systems Based on Time-State Control Forms Yoshikatsu HOSHI, Mitsuji SAMPEI, Shigeki NAKAURA Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering Tokyo Institute of Technology 2
Stability of Hybrid Control Systems Based on Time-State Control Forms Yoshikatsu HOSHI, Mitsuji SAMPEI, Shigeki NAKAURA Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering Tokyo Institute of Technology 2
A Group Analytic Network Process (ANP) for Incomplete Information
 A Group Analytic Network Process (ANP) for Incomplete Information Kouichi TAJI Yousuke Sagayama August 5, 2004 Abstract In this paper, we propose an ANP framework for group decision-making problem with
A Group Analytic Network Process (ANP) for Incomplete Information Kouichi TAJI Yousuke Sagayama August 5, 2004 Abstract In this paper, we propose an ANP framework for group decision-making problem with
Distributed motion constraints for algebraic connectivity of robotic networks
 Distributed motion constraints for algebraic connectivity of robotic networks IEEE Conference on Decision and Control December, 2008 Michael Schuresko Jorge Cortés Applied Mathematics and Statistics University
Distributed motion constraints for algebraic connectivity of robotic networks IEEE Conference on Decision and Control December, 2008 Michael Schuresko Jorge Cortés Applied Mathematics and Statistics University
Control Systems. Laplace domain analysis
 Control Systems Laplace domain analysis L. Lanari outline introduce the Laplace unilateral transform define its properties show its advantages in turning ODEs to algebraic equations define an Input/Output
Control Systems Laplace domain analysis L. Lanari outline introduce the Laplace unilateral transform define its properties show its advantages in turning ODEs to algebraic equations define an Input/Output
Fisher s Linear Discriminant Analysis
 Fisher s Linear Discriminant Analysis Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Fisher s Linear Discriminant Analysis Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Zero controllability in discrete-time structured systems
 1 Zero controllability in discrete-time structured systems Jacob van der Woude arxiv:173.8394v1 [math.oc] 24 Mar 217 Abstract In this paper we consider complex dynamical networks modeled by means of state
1 Zero controllability in discrete-time structured systems Jacob van der Woude arxiv:173.8394v1 [math.oc] 24 Mar 217 Abstract In this paper we consider complex dynamical networks modeled by means of state
Robust Stabilization of the Uncertain Linear Systems. Based on Descriptor Form Representation t. Toru ASAI* and Shinji HARA**
 Robust Stabilization of the Uncertain Linear Systems Based on Descriptor Form Representation t Toru ASAI* and Shinji HARA** This paper proposes a necessary and sufficient condition for the quadratic stabilization
Robust Stabilization of the Uncertain Linear Systems Based on Descriptor Form Representation t Toru ASAI* and Shinji HARA** This paper proposes a necessary and sufficient condition for the quadratic stabilization
Reliability Theory of Dynamically Loaded Structures (cont.)
 Outline of Reliability Theory of Dynamically Loaded Structures (cont.) Probability Density Function of Local Maxima in a Stationary Gaussian Process. Distribution of Extreme Values. Monte Carlo Simulation
Outline of Reliability Theory of Dynamically Loaded Structures (cont.) Probability Density Function of Local Maxima in a Stationary Gaussian Process. Distribution of Extreme Values. Monte Carlo Simulation
1. Structured representation of high-order tensors revisited. 2. Multi-linear algebra (MLA) with Kronecker-product data.
 Lect. 4. Toward MLA in tensor-product formats B. Khoromskij, Leipzig 2007(L4) 1 Contents of Lecture 4 1. Structured representation of high-order tensors revisited. - Tucker model. - Canonical (PARAFAC)
Lect. 4. Toward MLA in tensor-product formats B. Khoromskij, Leipzig 2007(L4) 1 Contents of Lecture 4 1. Structured representation of high-order tensors revisited. - Tucker model. - Canonical (PARAFAC)
A fast algorithm to compute the controllability, decentralized fixed-mode, and minimum-phase radius of LTI systems
 Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Conference on Decision Control Cancun, Mexico, Dec. 9-, 8 TuA6. A fast algorithm to compute the controllability, decentralized fixed-mode, minimum-phase radius of LTI systems
Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Conference on Decision Control Cancun, Mexico, Dec. 9-, 8 TuA6. A fast algorithm to compute the controllability, decentralized fixed-mode, minimum-phase radius of LTI systems
RECENTLY, there has been renewed research interest
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL 49, NO 12, DECEMBER 2004 2113 Distributed Control of Heterogeneous Systems Geir E Dullerud Raffaello D Andrea Abstract This paper considers control design for
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL 49, NO 12, DECEMBER 2004 2113 Distributed Control of Heterogeneous Systems Geir E Dullerud Raffaello D Andrea Abstract This paper considers control design for
Stability Analysis of Stochastically Varying Formations of Dynamic Agents
 Stability Analysis of Stochastically Varying Formations of Dynamic Agents Vijay Gupta, Babak Hassibi and Richard M. Murray Division of Engineering and Applied Science California Institute of Technology
Stability Analysis of Stochastically Varying Formations of Dynamic Agents Vijay Gupta, Babak Hassibi and Richard M. Murray Division of Engineering and Applied Science California Institute of Technology
Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems
 THIRD EDITION Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems Gene F. Franklin Stanford University J. David Powell Stanford University Abbas Emami-Naeini Integrated Systems, Inc. TT Addison-Wesley Publishing Company
THIRD EDITION Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems Gene F. Franklin Stanford University J. David Powell Stanford University Abbas Emami-Naeini Integrated Systems, Inc. TT Addison-Wesley Publishing Company
Iterative solvers for linear equations
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 23 Iterative solvers for linear equations Daniel A. Spielman November 26, 2018 23.1 Overview In this and the next lecture, I will discuss iterative algorithms for solving
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 23 Iterative solvers for linear equations Daniel A. Spielman November 26, 2018 23.1 Overview In this and the next lecture, I will discuss iterative algorithms for solving
LAKELAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE FORM
 LAKELAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE FORM ORIGINATION DATE: 8/2/99 APPROVAL DATE: 3/22/12 LAST MODIFICATION DATE: 3/28/12 EFFECTIVE TERM/YEAR: FALL/ 12 COURSE ID: COURSE TITLE: MATH2800 Linear Algebra
LAKELAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE FORM ORIGINATION DATE: 8/2/99 APPROVAL DATE: 3/22/12 LAST MODIFICATION DATE: 3/28/12 EFFECTIVE TERM/YEAR: FALL/ 12 COURSE ID: COURSE TITLE: MATH2800 Linear Algebra
