13.42 LECTURE 16: FROUDE KRYLOV EXCITATION FORCE SPRING 2003
|
|
|
- Jesse Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13.42 LECURE 16: FROUDE KRYLOV EXCIAION FORCE SPRING 2003 c A. H. ECHE & M.S. RIANAFYLLOU 1. Radiation and Diffraction Potentials he total potential is a linear superposition of the incident, diffraction, and radiation potentials, φ = (φ I + φ D + φ R ) e iωt. he radiation potential is comprised of si components due to the motions in the si directions, φ j where j = 1,2,3,4,5,6. Each function φ j is the potential resulting from a unit motion in j th direction for a ody floating in a quiescent fluid. he resulting ody oundary condition follows from lecture 15: (1.1) (1.2) φ j n φ j n = iωn j ; (j = 1,2,3) = iω( r n) j 3 ; (j = 4,5,6) (1.3) r = (,y,) (1.4) n = n j (j = 1,2,3) = (n,n y,n ) In order to meet all the oundary conditions we must have waves that radiate away from the ody. hus φ j e ik as ±. For the diffraction prolem we know that the derivative of the total potential (here the incident potential plus the diffraction potential without consideration of the radiation potential) normal to the ody surface is ero on the ody: φ n = 0 on S B, where φ = φ I + φ D Spring
2 2 SPRING 2003 c A. H. ECHE & M.S. RIANAFYLLOU φ I n = φ D n ; on S B We have so far talked primarily aout the incident potential. he formulation of the incident potential is straight forward from the oundary value prolem (BVP) setup in lecture 15. here eist several viale forms of this potential function each are essentially a phase shifted version of another. he diffraction potential can also e found in the same fashion using the BVP for the diffraction potential with the appropriate oundary condition on the ody. his potential can e approimated for a long wave condition. his long wave approimation assumes that the incident wavelength is very long compared to the ody diameter and thus the induced velocity field from the incident waves on the structure can e assumed constant over the ody and approimated y the following equation: φ D i ω [ φi φ 1 + φ I y φ2 + φ ] I φ 3 Further eplanation of this approimation can e found in Newman (p. 301). Ultimately, if we assume the ody to e sufficiently small as not to affect the pressure field due to an incident wave, then we can diffraction effects can e completely ignored. his assumption comes from the Froude-Krylov hypothesis and assures a resulting ecitation force equivalent to the froude-krylov force: (t) = ρ φ t I n ds
3 FROUDE-KRYLOV FORCES 3 2. Vertical Froude-Krylov Force on a Single Hull Vessel B Deep water incident wave potential is: φ I = aω k ek Re {i e i(ωt k) he force in the vertical direction is found from the incident potential using eq. 1.5 along the ottom of the vessel. Here the normal in the -direction, n, is negative: n = 1, so the force per unit length in the -direction is (2.1) = Re { B/2 B/2 ρ i ω iaω k e k e i(ωt k) d (2.2) (2.3) { ρoω 2 = Re k 2 a e k e iωt ( e ikb/2 e ikb/2) = Re {2ρ ω2 k 2 a e k e iωt sin(kb/2) Recall that sin = ei e i 2i. Using the vertical velocity we can rewrite the force in terms of the velocity.
4 4 SPRING 2003 c A. H. ECHE & M.S. RIANAFYLLOU (2.4) (2.5) (2.6) w(t) = Re {aω e k i e i(ωt k) ẇ(t) = Re { aω 2 e k e i(ωt k) ẇ( = 0, = 0,t) = Re { a ω 2 e iωt Now we can write the force in the vertical direction as a function of the vertical (heave) acceleration, { 2ρ F = Re k 2 e k sin(kb/2) ẇ(0,0,t). Let s look at the case where ω 0 the wavenumer, k = ω 2 /g 0, also goes to ero and the following simplifications can e made: (2.7) e kt 1 k (2.8) sin(kb/2) kb/2 to yield a simplified heave force. (2.9) (2.10) F FK Re {2ρ ω2 { Re ρ g ab a (1 k) (kb/2) eiωt k2 ) e iωt (1 ω2 g If we look at the case where ω 0 and consider the heave restoring coefficient, C 33 = ρ g B, and the free surface elevation, η(,t) = Re { a e i(ωt k) we can rewrite this force as Re {C 33 η( = 0,t)
5 FROUDE-KRYLOV FORCES 5 3. Horiontal Froude-Krylov Force on a Single Hull Vessel he horiontal force on the vessel aove can e found in a similar fashion to the vertical force. (3.1) (3.2) (3.3) F = ρ φ S B t I n ds { = Re ρ i ω iωa 0 [ e k d e i(ωt kb/2) e i(ωt+kb/2)] k = Re {iρ aω2 ( 1 e k ) e iωt 2 sin(kb/2) k As frequency approaches ero similar simplifications can e made like aove for the vertical force: (3.4) (3.5) (3.6) F (t) Re {iρ aω2 k (K) eiωt 2 kb/2 u(t) = Re {aω e k e i(ωt k) u(t) = Re {i a ω 2 e k e i(ωt k) F (t) Re {ρb u( = 0, = 0,t) Where ρb = ρ, and is the vessel volume such that we are left with the surge force (3.7) F ρ u (3.8) F C 33 η + ρ ẇ
6 6 SPRING 2003 c A. H. ECHE & M.S. RIANAFYLLOU 4. Multi Hulled Vessel -B/2 B/2 Again, let s make a few asic assumptions: (/λ << 1), (B/λ 1), (a < ), and ( ). Let s look at the force in the -direction: ρ u( = B/2, = 0,t) + ρ u( = B/2, = 0,t) (4.1) η(,t) = acos(ωt k) (4.2) u(,,t) = a ω 2 e k sin(ωt k) (4.3) (4.4) ρ ( a ω 2 ) {sin(ωt + kb/2) + sin(ωt kb/2) (4.5) 2ρ (a ω 2 ) cos(kb/2) sin(ωt) Note that when kb/2 = π/2 (or B = λ/2) then (t) = 0.
7 FROUDE-KRYLOV FORCES 7 -B/2 B/2 c 4.1. Multi Hulled Vessel with additional pontoon. Use the same assumptions from aove to find the -force adjusted for the additional pontoon etween the two hulls. 2 ρ (a ω 2 ) cos(kb/2) sin(ωt) +c p( = B/2 + /2, = 0,t) c p( = B/2 /2, = 0,t) he last two terms are the adjustment to the force for the addition of the pontoon, δf FK (t). Pressure is found from the incident potential: p(,,t) = ρg a e k cos(ωt k). δ ( ) k = 2 ρ g a sin(ωt) sin (B ) 2 For B >> using g = ω 2 /k we get a force: F FK (t) 2 ρ a ω 2 sin(ωt) { cos(kb/2) + δ/2 sin(kb/2)
Froude Krylov Excitation Force
 13.4 Design Principles for Ocean Vehicles Prof. A.H. echet Spring 005 Froude Krylov Ecitation Force 1. Radiation and Diffraction Potentials he total potential is a linear superposition of the incident,
13.4 Design Principles for Ocean Vehicles Prof. A.H. echet Spring 005 Froude Krylov Ecitation Force 1. Radiation and Diffraction Potentials he total potential is a linear superposition of the incident,
Coupled Heave-Pitch Motions and Froude Krylov Excitation Forces
 Coupled Heave-Pitch Motions and Froude Krylov Excitation Forces 13.42 Lecture Notes; Spring 2004; c A.H. Techet 1. Coupled Equation of Motion in Heave and Pitch Once we have set up the simple equation
Coupled Heave-Pitch Motions and Froude Krylov Excitation Forces 13.42 Lecture Notes; Spring 2004; c A.H. Techet 1. Coupled Equation of Motion in Heave and Pitch Once we have set up the simple equation
1. Froude Krylov Excitation Force
 .016 Hydrodynamics eading #8.016 Hydrodynamics Prof. A.H. Techet 1. Froude Krylov Ecitation Force Ultimately, if we assume the body to be sufficiently small as not to affect the pressure field due to an
.016 Hydrodynamics eading #8.016 Hydrodynamics Prof. A.H. Techet 1. Froude Krylov Ecitation Force Ultimately, if we assume the body to be sufficiently small as not to affect the pressure field due to an
Hydrodynamic Forces on Floating Bodies
 Hydrodynamic Forces on Floating Bodies 13.42 Lecture Notes; c A.H. Techet 1. Forces on Large Structures For discussion in this section we will be considering bodies that are quite large compared to the
Hydrodynamic Forces on Floating Bodies 13.42 Lecture Notes; c A.H. Techet 1. Forces on Large Structures For discussion in this section we will be considering bodies that are quite large compared to the
Seakeeping Models in the Frequency Domain
 Seakeeping Models in the Frequency Domain (Module 6) Dr Tristan Perez Centre for Complex Dynamic Systems and Control (CDSC) Prof. Thor I Fossen Department of Engineering Cybernetics 18/09/2007 One-day
Seakeeping Models in the Frequency Domain (Module 6) Dr Tristan Perez Centre for Complex Dynamic Systems and Control (CDSC) Prof. Thor I Fossen Department of Engineering Cybernetics 18/09/2007 One-day
Theory of Ship Waves (Wave-Body Interaction Theory) Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018
 Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018 (1) viscous effects (2) shear stress (3) normal pressure (4) pursue (5) bear in mind (6) be denoted by (7) variation (8) adjacent surfaces (9) be composed of (10) integrand (11)
Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018 (1) viscous effects (2) shear stress (3) normal pressure (4) pursue (5) bear in mind (6) be denoted by (7) variation (8) adjacent surfaces (9) be composed of (10) integrand (11)
13.42 LECTURE 13: FLUID FORCES ON BODIES. Using a two dimensional cylinder within a two-dimensional flow we can demonstrate some of the principles
 13.42 LECTURE 13: FLUID FORCES ON BODIES SPRING 2003 c A. H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Morrison s Equation Using a two dimensional cylinder within a two-dimensional flow we can demonstrate some of
13.42 LECTURE 13: FLUID FORCES ON BODIES SPRING 2003 c A. H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Morrison s Equation Using a two dimensional cylinder within a two-dimensional flow we can demonstrate some of
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section 1.2 and 1.3
 Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem
 1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem Objective of the Chapter: Formulation of the potential flow around the hull of a ship advancing and oscillationg in waves Results of the Chapter:
1 POTENTIAL FLOW THEORY Formulation of the seakeeping problem Objective of the Chapter: Formulation of the potential flow around the hull of a ship advancing and oscillationg in waves Results of the Chapter:
If we assume that sustituting (4) into (3), we have d H y A()e ;j (4) d +! ; Letting! ;, (5) ecomes d d + where the independent solutions are Hence, H
 W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes. Innite Parallel Plate Waveguide. y σ σ 0 We have studied TEM (transverse electromagnetic) waves etween two pieces of parallel conductors in the transmission line theory.
W.C.Chew ECE 350 Lecture Notes. Innite Parallel Plate Waveguide. y σ σ 0 We have studied TEM (transverse electromagnetic) waves etween two pieces of parallel conductors in the transmission line theory.
kg meter ii) Note the dimensions of ρ τ are kg 2 velocity 2 meter = 1 sec 2 We will interpret this velocity in upcoming slides.
 II. Generalizing the 1-dimensional wave equation First generalize the notation. i) "q" has meant transverse deflection of the string. Replace q Ψ, where Ψ may indicate other properties of the medium that
II. Generalizing the 1-dimensional wave equation First generalize the notation. i) "q" has meant transverse deflection of the string. Replace q Ψ, where Ψ may indicate other properties of the medium that
/01/04: Morrison s Equation SPRING 2004 A. H. TECHET
 3.4 04/0/04: orrison s Equation SPRING 004 A.. TECET. General form of orrison s Equation Flow past a circular cylinder is a canonical problem in ocean engineering. For a purely inviscid, steady flow we
3.4 04/0/04: orrison s Equation SPRING 004 A.. TECET. General form of orrison s Equation Flow past a circular cylinder is a canonical problem in ocean engineering. For a purely inviscid, steady flow we
P = ρ{ g a } + µ 2 V II. FLUID STATICS
 II. FLUID STATICS From a force analysis on a triangular fluid element at rest, the following three concepts are easily developed: For a continuous, hydrostatic, shear free fluid: 1. Pressure is constant
II. FLUID STATICS From a force analysis on a triangular fluid element at rest, the following three concepts are easily developed: For a continuous, hydrostatic, shear free fluid: 1. Pressure is constant
13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES
 13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES SPRING 2003 c A.H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Basic Water Waves Laplace Equation 2 φ = 0 Free surface elevation: z = η(x, t) No vertical velocity at the bottom
13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES SPRING 2003 c A.H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Basic Water Waves Laplace Equation 2 φ = 0 Free surface elevation: z = η(x, t) No vertical velocity at the bottom
Physics 201, Lecture 27
 Physics 201, Lecture 27 Today s Topics n Oscillations (chapter 15) n Simple Harmonic Oscillation (SHM) n Mathematical Representations n Properties of SHM n Examples: Block-Spring Oscillator (More examples
Physics 201, Lecture 27 Today s Topics n Oscillations (chapter 15) n Simple Harmonic Oscillation (SHM) n Mathematical Representations n Properties of SHM n Examples: Block-Spring Oscillator (More examples
8.04 Spring 2013 March 12, 2013 Problem 1. (10 points) The Probability Current
 Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Seakeeping of Ships. { ζ + a } 3 ζ 3, ζ = ξ + i η (1)
 Seakeeping of Ships By Professor Masashi KASHIWAGI Problem Set: No. Date: 27 January 2010 Due: 28 February 2010 By using the computer program (iem2d.f) for the boundary-element (Green function) method
Seakeeping of Ships By Professor Masashi KASHIWAGI Problem Set: No. Date: 27 January 2010 Due: 28 February 2010 By using the computer program (iem2d.f) for the boundary-element (Green function) method
The electric field produced by oscillating charges contained in a slab
 The electric field produced by oscillating charges contained in a slab Ref: Feynman Lectures Vol-1, Chapter 31 1. An accelerated charge produces electromagnetic fields 2. Calculation of the field produced
The electric field produced by oscillating charges contained in a slab Ref: Feynman Lectures Vol-1, Chapter 31 1. An accelerated charge produces electromagnetic fields 2. Calculation of the field produced
(a) (x 2) dx (d) (x +1) 2 dx. (e) x 1/2 dx. (h) 1. (3/x) dx. Solution: (a) sin(x) dx. (b) 2 cos(x) dx =4sinx π/4. (c) (x 2) dx = ( x 2 /2 2x ) 3
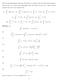 () Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to compute each of the following integrals. The last few are a little more challenging, and will require special care. Some of these integrals may not eist. Eplain
() Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to compute each of the following integrals. The last few are a little more challenging, and will require special care. Some of these integrals may not eist. Eplain
Physics 210: Worksheet 26 Name:
 (1) A all is floating in. If the density of the all is 0.95x10 kg/m, what percentage of the all is aove the? (2) An with a density of 19.x10 kg/m and a mass m50 kg is placed into a cylinder which contains
(1) A all is floating in. If the density of the all is 0.95x10 kg/m, what percentage of the all is aove the? (2) An with a density of 19.x10 kg/m and a mass m50 kg is placed into a cylinder which contains
Physics GRE Practice
 Physics GRE Practice Chapter 3: Harmonic Motion in 1-D Harmonic Motion occurs when the acceleration of a system is proportional to the negative of its displacement. or a x (1) ẍ x (2) Examples of Harmonic
Physics GRE Practice Chapter 3: Harmonic Motion in 1-D Harmonic Motion occurs when the acceleration of a system is proportional to the negative of its displacement. or a x (1) ẍ x (2) Examples of Harmonic
Resonance and response
 Chapter 2 Resonance and response Last updated September 20, 2008 In this section of the course we begin with a very simple system a mass hanging from a spring and see how some remarkable ideas emerge.
Chapter 2 Resonance and response Last updated September 20, 2008 In this section of the course we begin with a very simple system a mass hanging from a spring and see how some remarkable ideas emerge.
Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Prof. A.H. Techet Fall 2004
 13.01 ydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Prof. A.. Techet Fall 004 Morrison s Equation 1. General form of Morrison s Equation Flow past a circular cylinder is a canonical problem in ocean engineering. For
13.01 ydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Prof. A.. Techet Fall 004 Morrison s Equation 1. General form of Morrison s Equation Flow past a circular cylinder is a canonical problem in ocean engineering. For
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 17 EM Waves in Matter
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 17 EM Waves in Matter What We Did Last Time Reviewed reflection and refraction Total internal reflection is more subtle than it looks Imaginary waves extend a few beyond
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 17 EM Waves in Matter What We Did Last Time Reviewed reflection and refraction Total internal reflection is more subtle than it looks Imaginary waves extend a few beyond
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Review of Classical Mechanics
 Review of Classical Mechanics VBS/MRC Review of Classical Mechanics 0 Some Questions Why does a tennis racket wobble when flipped along a certain axis? What do hear when you pluck a Veena string? How do
Review of Classical Mechanics VBS/MRC Review of Classical Mechanics 0 Some Questions Why does a tennis racket wobble when flipped along a certain axis? What do hear when you pluck a Veena string? How do
OFFSHORE HYDROMECHANICS OE 4620-d
 Lecture OFFSHORE HYDROMECHANICS OE 4620-d MODULE 4 ch. 12 Wave Forces on Slender Cylinders ch. 13 Survival Loads on Tower Structures ch. 14 Sea Bed Boundary Effects Successive to Module 1. Morison Lab.
Lecture OFFSHORE HYDROMECHANICS OE 4620-d MODULE 4 ch. 12 Wave Forces on Slender Cylinders ch. 13 Survival Loads on Tower Structures ch. 14 Sea Bed Boundary Effects Successive to Module 1. Morison Lab.
EM waves: energy, resonators. Scalar wave equation Maxwell equations to the EM wave equation A simple linear resonator Energy in EM waves 3D waves
 EM waves: energy, resonators Scalar wave equation Maxwell equations to the EM wave equation A simple linear resonator Energy in EM waves 3D waves Simple scalar wave equation 2 nd order PDE 2 z 2 ψ (z,t)
EM waves: energy, resonators Scalar wave equation Maxwell equations to the EM wave equation A simple linear resonator Energy in EM waves 3D waves Simple scalar wave equation 2 nd order PDE 2 z 2 ψ (z,t)
Chapter 4 Water Waves
 2.20 Marine Hdrodnamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 15 Copright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved. Chapter 4 Water Waves 2.20 - Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 15 4.1 Exact (Nonlinear)
2.20 Marine Hdrodnamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 15 Copright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved. Chapter 4 Water Waves 2.20 - Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 15 4.1 Exact (Nonlinear)
Radiation Damping. 1 Introduction to the Abraham-Lorentz equation
 Radiation Damping Lecture 18 1 Introduction to the Abraham-Lorentz equation Classically, a charged particle radiates energy if it is accelerated. We have previously obtained the Larmor expression for the
Radiation Damping Lecture 18 1 Introduction to the Abraham-Lorentz equation Classically, a charged particle radiates energy if it is accelerated. We have previously obtained the Larmor expression for the
Lecture 11 March 1, 2010
 Physics 54, Spring 21 Lecture 11 March 1, 21 Last time we mentioned scattering removes power from beam. Today we treat this more generally, to find the optical theorem: the relationship of the index of
Physics 54, Spring 21 Lecture 11 March 1, 21 Last time we mentioned scattering removes power from beam. Today we treat this more generally, to find the optical theorem: the relationship of the index of
ragsdale (zdr82) HW7 ditmire (58335) 1 The magnetic force is
 ragsdale (zdr8) HW7 ditmire (585) This print-out should have 8 questions. Multiple-choice questions ma continue on the net column or page find all choices efore answering. 00 0.0 points A wire carring
ragsdale (zdr8) HW7 ditmire (585) This print-out should have 8 questions. Multiple-choice questions ma continue on the net column or page find all choices efore answering. 00 0.0 points A wire carring
Copyright (c) 2006 Warren Weckesser
 2.2. PLANAR LINEAR SYSTEMS 3 2.2. Planar Linear Systems We consider the linear system of two first order differential equations or equivalently, = ax + by (2.7) dy = cx + dy [ d x x = A x, where x =, and
2.2. PLANAR LINEAR SYSTEMS 3 2.2. Planar Linear Systems We consider the linear system of two first order differential equations or equivalently, = ax + by (2.7) dy = cx + dy [ d x x = A x, where x =, and
Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow
 OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
Min-Guk Seo, Dong-Min Park, Jae-Hoon Lee, Kyong-Hwan Kim, Yonghwan Kim
 International Research Exchange Meeting of Ship and Ocean Engineering in Osaka, December 1-, Osaka, Japan Comparative Study on Added Resistance Computation Min-Guk Seo, Dong-Min Park, Jae-Hoon Lee, Kyong-Hwan
International Research Exchange Meeting of Ship and Ocean Engineering in Osaka, December 1-, Osaka, Japan Comparative Study on Added Resistance Computation Min-Guk Seo, Dong-Min Park, Jae-Hoon Lee, Kyong-Hwan
Solutions a) The characteristic equation is r = 0 with roots ±2i, so the complementary solution is. y c = c 1 cos(2t)+c 2 sin(2t).
 Solutions 3.9. a) The characteristic equation is r + 4 = 0 with roots ±i, so the complementar solution is c = c cos(t)+c sin(t). b) We look for a particular solution in the form and obtain the equations
Solutions 3.9. a) The characteristic equation is r + 4 = 0 with roots ±i, so the complementar solution is c = c cos(t)+c sin(t). b) We look for a particular solution in the form and obtain the equations
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley)
 SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
MODELLING OF ACOUSTIC POWER RADIATION FROM MOBILE SCREW COMPRESSORS
 11 th International Conference on Viration Prolems Z. Dimitrovová et.al. (eds.) Lison, Portugal, 9 12 Septemer 213 MODELLING OF ACOUSTIC POWER RADIATION FROM MOBILE SCREW COMPRESSORS Jan Dupal* 1, Jan
11 th International Conference on Viration Prolems Z. Dimitrovová et.al. (eds.) Lison, Portugal, 9 12 Septemer 213 MODELLING OF ACOUSTIC POWER RADIATION FROM MOBILE SCREW COMPRESSORS Jan Dupal* 1, Jan
Partial Differential Equations for Engineering Math 312, Fall 2012
 Partial Differential Equations for Engineering Math 312, Fall 2012 Jens Lorenz July 17, 2012 Contents Department of Mathematics and Statistics, UNM, Albuquerque, NM 87131 1 Second Order ODEs with Constant
Partial Differential Equations for Engineering Math 312, Fall 2012 Jens Lorenz July 17, 2012 Contents Department of Mathematics and Statistics, UNM, Albuquerque, NM 87131 1 Second Order ODEs with Constant
Wave-Body Interaction Theory (Theory of Ship Waves) Lecture Notes for Graduate Course
 Wave-Body Interaction Theory (Theory of Ship Waves) Lecture Notes for Graduate Course ( April 018 ) Lab of Seakeeping & Floating-Body Dynamics in Waves Dept of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Osaka
Wave-Body Interaction Theory (Theory of Ship Waves) Lecture Notes for Graduate Course ( April 018 ) Lab of Seakeeping & Floating-Body Dynamics in Waves Dept of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Osaka
2 Law of conservation of energy
 1 Newtonian viscous Fluid 1 Newtonian fluid For a Newtonian we already have shown that σ ij = pδ ij + λd k,k δ ij + 2µD ij where λ and µ are called viscosity coefficient. For a fluid under rigid body motion
1 Newtonian viscous Fluid 1 Newtonian fluid For a Newtonian we already have shown that σ ij = pδ ij + λd k,k δ ij + 2µD ij where λ and µ are called viscosity coefficient. For a fluid under rigid body motion
Aalto University School of Engineering
 Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4140 Ship Dynamics (P) Lecture 9 Loads Where is this lecture on the course? Design Framework Lecture 5: Equations of Motion Environment Lecture 6: Strip Theory
Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4140 Ship Dynamics (P) Lecture 9 Loads Where is this lecture on the course? Design Framework Lecture 5: Equations of Motion Environment Lecture 6: Strip Theory
EECS 20N: Midterm 2 Solutions
 EECS 0N: Midterm Solutions (a) The LTI system is not causal because its impulse response isn t zero for all time less than zero. See Figure. Figure : The system s impulse response in (a). (b) Recall that
EECS 0N: Midterm Solutions (a) The LTI system is not causal because its impulse response isn t zero for all time less than zero. See Figure. Figure : The system s impulse response in (a). (b) Recall that
Final Exam December 20, 2011
 Final Exam December 20, 2011 Math 420 - Ordinary Differential Equations No credit will be given for answers without mathematical or logical justification. Simplify answers as much as possible. Leave solutions
Final Exam December 20, 2011 Math 420 - Ordinary Differential Equations No credit will be given for answers without mathematical or logical justification. Simplify answers as much as possible. Leave solutions
Linear Differential Equations. Problems
 Chapter 1 Linear Differential Equations. Problems 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Show that the function ϕ : R R, given by the expression ϕ(t) = 2e 3t for all t R, is a solution of the Initial Value Problem x =
Chapter 1 Linear Differential Equations. Problems 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Show that the function ϕ : R R, given by the expression ϕ(t) = 2e 3t for all t R, is a solution of the Initial Value Problem x =
Assignment 8. [η j, η k ] = J jk
![Assignment 8. [η j, η k ] = J jk Assignment 8. [η j, η k ] = J jk](/thumbs/76/73228750.jpg) Assignment 8 Goldstein 9.8 Prove directly that the transformation is canonical and find a generating function. Q 1 = q 1, P 1 = p 1 p Q = p, P = q 1 q We can establish that the transformation is canonical
Assignment 8 Goldstein 9.8 Prove directly that the transformation is canonical and find a generating function. Q 1 = q 1, P 1 = p 1 p Q = p, P = q 1 q We can establish that the transformation is canonical
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 22
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 22 Chapter 11: Waves 11.1 Waves and Energy Transport 11.2 Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 11.3 Speed of Transverse Waves on a String 11.4 Periodic Waves Lecture 22 Purdue University,
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 22 Chapter 11: Waves 11.1 Waves and Energy Transport 11.2 Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 11.3 Speed of Transverse Waves on a String 11.4 Periodic Waves Lecture 22 Purdue University,
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
 Electromagnetic (EM) Waves Short review on calculus vector Outline A. Various formulations of the Maxwell equation: 1. In a vacuum 2. In a vacuum without source charge 3. In a medium 4. In a dielectric
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves Short review on calculus vector Outline A. Various formulations of the Maxwell equation: 1. In a vacuum 2. In a vacuum without source charge 3. In a medium 4. In a dielectric
In-plane free vibration analysis of combined ring-beam structural systems by wave propagation
 In-plane free viration analysis of comined ring-eam structural systems y wave propagation Benjamin Chouvion, Colin Fox, Stewart Mcwilliam, Atanas Popov To cite this version: Benjamin Chouvion, Colin Fox,
In-plane free viration analysis of comined ring-eam structural systems y wave propagation Benjamin Chouvion, Colin Fox, Stewart Mcwilliam, Atanas Popov To cite this version: Benjamin Chouvion, Colin Fox,
Damped harmonic motion
 Damped harmonic motion March 3, 016 Harmonic motion is studied in the presence of a damping force proportional to the velocity. The complex method is introduced, and the different cases of under-damping,
Damped harmonic motion March 3, 016 Harmonic motion is studied in the presence of a damping force proportional to the velocity. The complex method is introduced, and the different cases of under-damping,
Antiderivatives. Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if. F x f x for all x I.
 Antiderivatives Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if F x f x for all x I. Theorem If F is an antiderivative of f on I, then every function of
Antiderivatives Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if F x f x for all x I. Theorem If F is an antiderivative of f on I, then every function of
c. Better work with components of slowness vector s (or wave + k z 2 = k 2 = (ωs) 2 = ω 2 /c 2. k=(kx,k z )
 .50 Introduction to seismology /3/05 sophie michelet Today s class: ) Eikonal equation (basis of ray theory) ) Boundary conditions (Stein s book.3.0) 3) Snell s law Some remarks on what we discussed last
.50 Introduction to seismology /3/05 sophie michelet Today s class: ) Eikonal equation (basis of ray theory) ) Boundary conditions (Stein s book.3.0) 3) Snell s law Some remarks on what we discussed last
221B Lecture Notes on Resonances in Classical Mechanics
 1B Lecture Notes on Resonances in Classical Mechanics 1 Harmonic Oscillators Harmonic oscillators appear in many different contexts in classical mechanics. Examples include: spring, pendulum (with a small
1B Lecture Notes on Resonances in Classical Mechanics 1 Harmonic Oscillators Harmonic oscillators appear in many different contexts in classical mechanics. Examples include: spring, pendulum (with a small
Mathematical Tripos, Part IB : Electromagnetism
 Mathematical Tripos, Part IB : Electromagnetism Proof of the result G = m B Refer to Sec. 3.7, Force and couples, and supply the proof that the couple exerted by a uniform magnetic field B on a plane current
Mathematical Tripos, Part IB : Electromagnetism Proof of the result G = m B Refer to Sec. 3.7, Force and couples, and supply the proof that the couple exerted by a uniform magnetic field B on a plane current
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 2 Damped Oscillators Driven Oscillators
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture Damped Oscillators Driven Oscillators What We Did Last Time Analyzed a simple harmonic oscillator The equation of motion: The general solution: Studied the solution m
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture Damped Oscillators Driven Oscillators What We Did Last Time Analyzed a simple harmonic oscillator The equation of motion: The general solution: Studied the solution m
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Physics 101 Discussion Week 12 Explanation (2011)
 Physics 101 Discussion Week 12 Eplanation (2011) D12-1 Horizontal oscillation Q0. This is obviously about a harmonic oscillator. Can you write down Newton s second law in the (horizontal) direction? Let
Physics 101 Discussion Week 12 Eplanation (2011) D12-1 Horizontal oscillation Q0. This is obviously about a harmonic oscillator. Can you write down Newton s second law in the (horizontal) direction? Let
FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY MASTER'S THESIS. Open. Author: Thorgeir Anundsen (signature author)
 FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY MASTER'S THESIS Study program/specialization: Master Offshore systems, Marine and subsea technology. Spring semester, 2008 Open Author: Thorgeir Anundsen (signature author)
FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY MASTER'S THESIS Study program/specialization: Master Offshore systems, Marine and subsea technology. Spring semester, 2008 Open Author: Thorgeir Anundsen (signature author)
Appendix lecture 9: Extra terms.
 Appendi lecture 9: Etra terms The Hyperolic method has een used to prove that d n = log + 2γ + O /2 n This can e used within the Convolution Method to prove Theorem There eists a constant C such that n
Appendi lecture 9: Etra terms The Hyperolic method has een used to prove that d n = log + 2γ + O /2 n This can e used within the Convolution Method to prove Theorem There eists a constant C such that n
Total energy in volume
 General Heat Transfer Equations (Set #3) ChE 1B Fundamental Energy Postulate time rate of change of internal +kinetic energy = rate of heat transfer + surface work transfer (viscous & other deformations)
General Heat Transfer Equations (Set #3) ChE 1B Fundamental Energy Postulate time rate of change of internal +kinetic energy = rate of heat transfer + surface work transfer (viscous & other deformations)
Lecture XXVI. Morris Swartz Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Johns Hopkins University November 5, 2003
 Lecture XXVI Morris Swartz Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Johns Hopins University morris@jhu.edu November 5, 2003 Lecture XXVI: Oscillations Oscillations are periodic motions. There are many examples of
Lecture XXVI Morris Swartz Dept. of Physics and Astronomy Johns Hopins University morris@jhu.edu November 5, 2003 Lecture XXVI: Oscillations Oscillations are periodic motions. There are many examples of
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Problem Set 4 Solutions AY 7b Spring 2012 Problem 1 For the very simple model of the MW where Θ() = 200 km s 1, we know that where Ω = Θ/. Since Θ const, we can rewrite this as v r (l) = (Ω Ω 0 ) sin l
Problem Set 4 Solutions AY 7b Spring 2012 Problem 1 For the very simple model of the MW where Θ() = 200 km s 1, we know that where Ω = Θ/. Since Θ const, we can rewrite this as v r (l) = (Ω Ω 0 ) sin l
PHY 396 K. Solutions for problems 1 and 2 of set #5.
 PHY 396 K. Solutions for problems 1 and of set #5. Problem 1a: The conjugacy relations  k,  k,, Ê k, Ê k, follow from hermiticity of the Âx and Êx quantum fields and from the third eq. 6 for the polarization
PHY 396 K. Solutions for problems 1 and of set #5. Problem 1a: The conjugacy relations  k,  k,, Ê k, Ê k, follow from hermiticity of the Âx and Êx quantum fields and from the third eq. 6 for the polarization
Physics 141, Lecture 7. Outline. Course Information. Course information: Homework set # 3 Exam # 1. Quiz. Continuation of the discussion of Chapter 4.
 Physics 141, Lecture 7. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 07, Page 1 Outline. Course information: Homework set # 3 Exam # 1 Quiz. Continuation of the
Physics 141, Lecture 7. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 07, Page 1 Outline. Course information: Homework set # 3 Exam # 1 Quiz. Continuation of the
1 Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Physics 1a Waves Lecture 3 Caltech, 10/09/18 1 Simple Harmonic Oscillator 1.4 General properties of Simple Harmonic Oscillator 1.4.4 Superposition of two independent SHO Suppose we have two SHOs described
Physics 1a Waves Lecture 3 Caltech, 10/09/18 1 Simple Harmonic Oscillator 1.4 General properties of Simple Harmonic Oscillator 1.4.4 Superposition of two independent SHO Suppose we have two SHOs described
Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2)
 Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2) January 25, 2016 7/441 Lecture outline A simple model of a linear oscillator lies in the foundation of many physical phenomena in accelerator dynamics. A typical
Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2) January 25, 2016 7/441 Lecture outline A simple model of a linear oscillator lies in the foundation of many physical phenomena in accelerator dynamics. A typical
Math 312 Lecture Notes Linear Two-dimensional Systems of Differential Equations
 Math 2 Lecture Notes Linear Two-dimensional Systems of Differential Equations Warren Weckesser Department of Mathematics Colgate University February 2005 In these notes, we consider the linear system of
Math 2 Lecture Notes Linear Two-dimensional Systems of Differential Equations Warren Weckesser Department of Mathematics Colgate University February 2005 In these notes, we consider the linear system of
Propagation of EM Waves in material media
 Propagation of EM Waves in material media S.M.Lea 09 Wave propagation As usual, we start with Maxwell s equations with no free charges: D =0 B =0 E = B t H = D t + j If we now assume that each field has
Propagation of EM Waves in material media S.M.Lea 09 Wave propagation As usual, we start with Maxwell s equations with no free charges: D =0 B =0 E = B t H = D t + j If we now assume that each field has
Exam in Fluid Mechanics 5C1214
 Eam in Fluid Mechanics 5C1214 Final eam in course 5C1214 13/01 2004 09-13 in Q24 Eaminer: Prof. Dan Henningson The point value of each question is given in parenthesis and you need more than 20 points
Eam in Fluid Mechanics 5C1214 Final eam in course 5C1214 13/01 2004 09-13 in Q24 Eaminer: Prof. Dan Henningson The point value of each question is given in parenthesis and you need more than 20 points
Peter Hertel. University of Osnabrück, Germany. Lecture presented at APS, Nankai University, China.
 crystal The Hopping University of Osnabrück, Germany Lecture presented at APS, Nankai University, China http://www.home.uni-osnabrueck.de/phertel Spring 2011 States and amplitudes crystal The system has
crystal The Hopping University of Osnabrück, Germany Lecture presented at APS, Nankai University, China http://www.home.uni-osnabrueck.de/phertel Spring 2011 States and amplitudes crystal The system has
93 Analytical solution of differential equations
 1 93 Analytical solution of differential equations 1. Nonlinear differential equation The only kind of nonlinear differential equations that we solve analytically is the so-called separable differential
1 93 Analytical solution of differential equations 1. Nonlinear differential equation The only kind of nonlinear differential equations that we solve analytically is the so-called separable differential
Computational Analysis of Added Resistance in Short Waves
 13 International Research Exchange Meeting of Ship and Ocean Engineering in Osaka -1 December, Osaka, Japan Computational Analysis of Added Resistance in Short Waves Yonghwan Kim, Kyung-Kyu Yang and Min-Guk
13 International Research Exchange Meeting of Ship and Ocean Engineering in Osaka -1 December, Osaka, Japan Computational Analysis of Added Resistance in Short Waves Yonghwan Kim, Kyung-Kyu Yang and Min-Guk
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture 25 Oscillations simple harmonic motion pendulum driven and damped oscillations http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Oscillations
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture 25 Oscillations simple harmonic motion pendulum driven and damped oscillations http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Oscillations
Exercises Lecture 15
 AM1 Mathematical Analysis 1 Oct. 011 Feb. 01 Date: January 7 Exercises Lecture 15 Harmonic Oscillators In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium
AM1 Mathematical Analysis 1 Oct. 011 Feb. 01 Date: January 7 Exercises Lecture 15 Harmonic Oscillators In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium
Physics 7Em Midterm Exam 1
 Physics 7Em Midterm Exam 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS. There are 10 multiple choice problems. Each is worth 2 points. There is no penalty for wrong answers. In each, choose the best answer; only one answer
Physics 7Em Midterm Exam 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS. There are 10 multiple choice problems. Each is worth 2 points. There is no penalty for wrong answers. In each, choose the best answer; only one answer
A sufficient condition for the existence of the Fourier transform of f : R C is. f(t) dt <. f(t) = 0 otherwise. dt =
 Fourier transform Definition.. Let f : R C. F [ft)] = ˆf : R C defined by The Fourier transform of f is the function F [ft)]ω) = ˆfω) := ft)e iωt dt. The inverse Fourier transform of f is the function
Fourier transform Definition.. Let f : R C. F [ft)] = ˆf : R C defined by The Fourier transform of f is the function F [ft)]ω) = ˆfω) := ft)e iωt dt. The inverse Fourier transform of f is the function
Chapter 13. Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition. Next Week!
 Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
On Vertical Variations of Wave-Induced Radiation Stress Tensor
 Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 55 (2008), No. 3 4, pp. 83 93 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 On Vertical Variations of Wave-Induced Radiation Stress Tensor Włodzimierz Chybicki
Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 55 (2008), No. 3 4, pp. 83 93 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 On Vertical Variations of Wave-Induced Radiation Stress Tensor Włodzimierz Chybicki
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
Continuous-Time Frequency Response (II) Lecture 28: EECS 20 N April 2, Laurent El Ghaoui
 EECS 20 N April 2, 2001 Lecture 28: Continuous-Time Frequency Response (II) Laurent El Ghaoui 1 annoucements homework due on Wednesday 4/4 at 11 AM midterm: Friday, 4/6 includes all chapters until chapter
EECS 20 N April 2, 2001 Lecture 28: Continuous-Time Frequency Response (II) Laurent El Ghaoui 1 annoucements homework due on Wednesday 4/4 at 11 AM midterm: Friday, 4/6 includes all chapters until chapter
Phys 4322 Final Exam - Solution May 12, 2015
 Phys 4322 Final Exam - Solution May 12, 2015 You may NOT use any book or notes other than that supplied with this test. You will have 3 hours to finish. DO YOUR OWN WORK. Express your answers clearly and
Phys 4322 Final Exam - Solution May 12, 2015 You may NOT use any book or notes other than that supplied with this test. You will have 3 hours to finish. DO YOUR OWN WORK. Express your answers clearly and
The Performance of Heaving Bodies
 The Performance of Heaving Bodies P. Persad 1 & The Caribbean region has been identified as a favourable A. Singh 2 area for the exploitation of wave energy. A cost effective approach to the development
The Performance of Heaving Bodies P. Persad 1 & The Caribbean region has been identified as a favourable A. Singh 2 area for the exploitation of wave energy. A cost effective approach to the development
Fourier series. Complex Fourier series. Positive and negative frequencies. Fourier series demonstration. Notes. Notes. Notes.
 Fourier series Fourier series of a periodic function f (t) with period T and corresponding angular frequency ω /T : f (t) a 0 + (a n cos(nωt) + b n sin(nωt)), n1 Fourier series is a linear sum of cosine
Fourier series Fourier series of a periodic function f (t) with period T and corresponding angular frequency ω /T : f (t) a 0 + (a n cos(nωt) + b n sin(nωt)), n1 Fourier series is a linear sum of cosine
C) 2 D) 4 E) 6. ? A) 0 B) 1 C) 1 D) The limit does not exist.
 . The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric equations = t, y = t t + are A) =, y = B) = only C) =, y = D) = only E) =, y =. What are the coordinates of the inflection point on the graph of y = ( +
. The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric equations = t, y = t t + are A) =, y = B) = only C) =, y = D) = only E) =, y =. What are the coordinates of the inflection point on the graph of y = ( +
7.8 Improper Integrals
 CHAPTER 7. TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION 67 7.8 Improper Integrals Eample. Find Solution. Z e d. Z e d = = e e!! e = (e ) = Z Eample. Find d. Solution. We do this prolem twice: once the WRONG way, and once
CHAPTER 7. TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION 67 7.8 Improper Integrals Eample. Find Solution. Z e d. Z e d = = e e!! e = (e ) = Z Eample. Find d. Solution. We do this prolem twice: once the WRONG way, and once
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 32th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10124 APPLYING STRIP THEORY BASED LINEAR SEAKEEPING
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 32th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2013 June 9-14, 2013, Nantes, France OMAE2013-10124 APPLYING STRIP THEORY BASED LINEAR SEAKEEPING
Time-Dependent Statistical Mechanics A1. The Fourier transform
 Time-Dependent Statistical Mechanics A1. The Fourier transform c Hans C. Andersen November 5, 2009 1 Definition of the Fourier transform and its inverse. Suppose F (t) is some function of time. Then its
Time-Dependent Statistical Mechanics A1. The Fourier transform c Hans C. Andersen November 5, 2009 1 Definition of the Fourier transform and its inverse. Suppose F (t) is some function of time. Then its
Laminar Boundary Layers. Answers to problem sheet 1: Navier-Stokes equations
 Laminar Boundary Layers Answers to problem sheet 1: Navier-Stokes equations The Navier Stokes equations for d, incompressible flow are + v ρ t + u + v v ρ t + u v + v v = 1 = p + µ u + u = p ρg + µ v +
Laminar Boundary Layers Answers to problem sheet 1: Navier-Stokes equations The Navier Stokes equations for d, incompressible flow are + v ρ t + u + v v ρ t + u v + v v = 1 = p + µ u + u = p ρg + µ v +
Physics 214 Final Exam Solutions Winter 2017
 Physics 14 Final Exam Solutions Winter 017 1 An electron of charge e and mass m moves in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B If the energy loss by radiation is neglected, the orbit is a
Physics 14 Final Exam Solutions Winter 017 1 An electron of charge e and mass m moves in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B If the energy loss by radiation is neglected, the orbit is a
Theory of Linear Systems Exercises. Luigi Palopoli and Daniele Fontanelli
 Theory of Linear Systems Exercises Luigi Palopoli and Daniele Fontanelli Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Scienza dell Informazione Università di Trento Contents Chapter. Exercises on the Laplace Transform
Theory of Linear Systems Exercises Luigi Palopoli and Daniele Fontanelli Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Scienza dell Informazione Università di Trento Contents Chapter. Exercises on the Laplace Transform
PH575 Spring Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5
 PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5 PH575 POP QUIZ Phonons are: A. Fermions B. Bosons C. Lattice vibrations D. Light/matter interactions PH575 POP QUIZ Phonon dispersion relation:
PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5 PH575 POP QUIZ Phonons are: A. Fermions B. Bosons C. Lattice vibrations D. Light/matter interactions PH575 POP QUIZ Phonon dispersion relation:
Vibrations and Waves Physics Year 1. Handout 1: Course Details
 Vibrations and Waves Jan-Feb 2011 Handout 1: Course Details Office Hours Vibrations and Waves Physics Year 1 Handout 1: Course Details Dr Carl Paterson (Blackett 621, carl.paterson@imperial.ac.uk Office
Vibrations and Waves Jan-Feb 2011 Handout 1: Course Details Office Hours Vibrations and Waves Physics Year 1 Handout 1: Course Details Dr Carl Paterson (Blackett 621, carl.paterson@imperial.ac.uk Office
ECE 659, PRACTICE EXAM II Actual Exam Friday, Feb.21, 2014, FNY B124, PM CLOSED BOOK. = H nm. Actual Exam will have five questions.
 1 ECE 659, PRACTICE EXAM II Actual Exam Friday, Feb.1, 014, FNY B14, 330-40PM CLOSED BOOK Useful relation h( k ) = H nm [ ] e +i k.( r m r n ) Actual Exam will have five questions. The following questions
1 ECE 659, PRACTICE EXAM II Actual Exam Friday, Feb.1, 014, FNY B14, 330-40PM CLOSED BOOK Useful relation h( k ) = H nm [ ] e +i k.( r m r n ) Actual Exam will have five questions. The following questions
Figure 1: Surface waves
 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 1 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 4.1 Introduction We consider waves on the surface of liquids, e.g. waves on the sea or a lake or a river. These can be generated by the wind, by
4 Surface Waves on Liquids 1 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 4.1 Introduction We consider waves on the surface of liquids, e.g. waves on the sea or a lake or a river. These can be generated by the wind, by
JWKB QUANTIZATION CONDITION. exp ± i x. wiggly-variable k(x) Logical Structure of pages 6-11 to 6-14 (not covered in lecture):
 7-1 JWKB QUANTIZATION CONDITION Last time: ( ) i 3 1. V ( ) = α φ( p) = Nep Ep p 6m hα ψ( ) = Ai( z) zeroes of Ai, Ai tales of Ai (and Bi) asymptotic forms far from turning points 2. Semi-Classical Approimation
7-1 JWKB QUANTIZATION CONDITION Last time: ( ) i 3 1. V ( ) = α φ( p) = Nep Ep p 6m hα ψ( ) = Ai( z) zeroes of Ai, Ai tales of Ai (and Bi) asymptotic forms far from turning points 2. Semi-Classical Approimation
Name:... Section:... Physics 208 Quiz 8. April 11, 2008; due April 18, 2008
 Name:... Section:... Problem 1 (6 Points) Physics 8 Quiz 8 April 11, 8; due April 18, 8 Consider the AC circuit consisting of an AC voltage in series with a coil of self-inductance,, and a capacitor of
Name:... Section:... Problem 1 (6 Points) Physics 8 Quiz 8 April 11, 8; due April 18, 8 Consider the AC circuit consisting of an AC voltage in series with a coil of self-inductance,, and a capacitor of
Representation theory of SU(2), density operators, purification Michael Walter, University of Amsterdam
 Symmetry and Quantum Information Feruary 6, 018 Representation theory of S(), density operators, purification Lecture 7 Michael Walter, niversity of Amsterdam Last week, we learned the asic concepts of
Symmetry and Quantum Information Feruary 6, 018 Representation theory of S(), density operators, purification Lecture 7 Michael Walter, niversity of Amsterdam Last week, we learned the asic concepts of
B2.III Revision notes: quantum physics
 B.III Revision notes: quantum physics Dr D.M.Lucas, TT 0 These notes give a summary of most of the Quantum part of this course, to complement Prof. Ewart s notes on Atomic Structure, and Prof. Hooker s
B.III Revision notes: quantum physics Dr D.M.Lucas, TT 0 These notes give a summary of most of the Quantum part of this course, to complement Prof. Ewart s notes on Atomic Structure, and Prof. Hooker s
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 2, February ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue, February-8 48 Structural Response of a Standalone FPSO by Swell Wave in Offshore Nigeria Abam Tamunopekere Joshua*, Akaawase
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue, February-8 48 Structural Response of a Standalone FPSO by Swell Wave in Offshore Nigeria Abam Tamunopekere Joshua*, Akaawase
