UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 28 APRIL 7, 2011
|
|
|
- Basil Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 28 APRIL 7, 20 Instructions. Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number. Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book. Each question is worth 0 points. For full credit, you must prove that your answers are correct even when the question doesn t say prove. There are lots of problems of widely varying difficulty. It is not expected that anyone will solve them all; look for ones that seem easy and fun. No calculators are allowed. Problem. There are some gas stations on a circular roadway. Together the stations contain just enough gas to make it all the way around. Show that it is possible to start at one of the stations with an empty tank (that is large enough to hold all the gas at all these stations) and make it all the way around. Suppose instead you have a large tank with enough gas to drive around and room for twice as much. Pick a station, and drive around, adding the available gas at each station. There will be a station where the gas you have is minimum. If you start there, even with an empty tank, you can make the trip. Problem 2. Four distinct points {P, P 2, P 3, P 4 } in the plane have the property that the set of six distances between the pairs of them, P i P j for i j, consists of precisely 2 real numbers. One example is the set of vertices of a square. Find, up to similarity, all configurations of four points with this property. Suppose that 3 of the four points, say A, B, C, form an equilateral triangle. Let x = AB = BC = AC. If D is the fourth point then either 0, or 2 of the distances AD, BD, CD are equal to x. If none of the distances AD, BD, CD are equal to x, then AD = BD = CD and D is the center of ABC (case ). If AD = x and BD = CD, then D lies on the perpendicular bisector of B and C, with distance x to A. There are two possibilities: Either AD lie on the same since of the line through B and C (case 2), or they lie on opposite sides (case 3). If AD = BD = x, then ABC and ABD are two equilateral triangles were A and D lie on opposite sides of BC (case 4). Suppose none of the 3 points form an equilateral triangle. There are two cases: either AB = BC = CD = DA and AC = BD. This is the square (case 5). The other case is where x = AB = BC = CD and y = BD = DA = AC where x < y. Then ABCD is a trapezium with base AD. Then A, B, C, D lie on a circle. Choose a point E with DE = EA = x such that A and E are of opposite sides of AD. The triangles ABC and DEA are congruent. It follows that E also lies on the circle through ABCD.
2 2 (UM) 2 C 28 Since x = AB = BC = CD = DE = EA, the points A, B, C, D, E form a regular pentagon. So A, B, C, D consist of 4 of the 5 vertices of a regular pentagon (case 6). Problem 3. Find all solutions for x 3 + y 3 = 3 z where x, y and z are integers. From (a + b)(a 2 ab + b 2 ) = 3 c and a 2 ab + b 2 0, follows that both a + b and a 2 ab + b 2 are powers of 3. We can write a = 3 k p and b = 3 k q such that 3 does not divide both p and q. It follows that p 2 pq +q 2 and p+q are powers of 3. If 3 (p+q), and 9 p 2 pq +q 2 = (p+q) 2 3pq, then 9 3pq and 3 pq. From 3 p + q and 3 pq follows that 3 p and 3 q. Contradiction. So p + q =, p 2 pq + q 2 = or p 2 pq + q 2 = 3. If p + q =, then p 2 pq + q 2 = 3p 2 3p + (mod3), hence 3p 2 3p + = and p = 0 or p =. If p 2 pq + q 2 =, then (q 2 p) p2 =. Hence 3 4 p2. If p 2 pq + q 2 = 3, then (q 2 p) p2 = 3, so p 2 4. In each of the cases, we have p 2 4 and similarly q 2 4. So we have p, q { 2,, 0,, 2}. We verify that the only solutions for (p, q) are {(0, ), (, 0), (, 2), (2, )}. Problem 4. What is the largest number of subsets you can choose from {,..., n} with each subset having an odd number of elements and the intersection of any two distinct subsets having an even number of elements? The largest number possible is n. The n one element sets do work. We shall sow there cannot be n +. Consider the ring F n where F = Z/2Z. Each subset of {,..., n} corresponds to an element, the sum of the corresponding standard basis elements. The elements with an even number of s form a vector subspace over F. Given n + elements they are dependent: one is a sum of others, say a = b + + b n. Then a = a a = ab ab n. Each term on the right sums to 0, while a sums to, a contradiction. Problem 5. Suppose that a, a 2,... is a sequence of real numbers such that n n a i = i= for all positive integers n. For every possible value of a, determine lim n a n. Let b n = i= n a i = i= a i n a i. Then we have a n+ = b n+ b n = b n+ /b n for all n. From this follows that b n+ = i= b2 n b n
3 (UM) 2 C 28 3 if a = b 0 then b b 2 b 3... and all b i s are negative. So lim n b n exists. Suppose that this limit is equal to b. Then we have b = b 2 /(b ) and b = 0. From lim n b n = b = 0 follows that lim n a n = lim n (b n b n ) = 0. Suppose that 0 < a <. Then a 2 < 0 and lim n a n = 0 as in the previous case. Suppose that a >, then we have b b 2 and lim n b n =. We have a n = b n b n = + b n So we get lim a n = lim + n n b n =. Problem 6. Let r > 0 be a fixed real number. Suppose that a differentiable function y = f(x) can be defined on the interval (0, B), B > 0, so that it is positive and satisfies the differential equation xy = y+y r+. Suppose that f() = a > 0. Find, as a function of r and a, the largest possible value of B for which there is such a function. We solve the differential equation: log(y r + ) r = y r dy y r + = so x(y r + ) /r is constant. For x = we have y = a, so and So B = (a r + ) /r. dy dx y + y = + C = log(x) + C, r+ x x(y r + ) /r = (a r + ) /r y = ((a r + )x r ) /r Problem 7. Suppose that G is a finite group containing elements x, y, z such that yx = x 2 y, zy = y 2 z and xz = z 2 x. Prove that x = y = z =. We prove the statement by induction on the group order G. Let d x, d y, d z be the orders of x, y and z. By cyclically permuting x, y and z, we may assume that d y d x. The group y = Z/d y Z generated by y acts on x = Z/d x Z by conjugation. Define a group homomorphism ψ : y Aut( x ) where Aut( x ) is the automorphism group of x and ψ(y) is conjugation by y. Then ψ has a nontrivial kernel, because Aut( x ) = φ(d x ) < d x d y where φ is Euler s phi function. So there exists a power y r of y with y r such that y r commutes with x. It follows that y is a normal subgroup of G. By induction, we may assume that the images of x, y, z are trivial in the group G/ y. So x, y, z all lie in y and x, y, z commute. From x 2 y = yx = xy follows that x = and similarly y = z =. Problem 8. Show that there is a 4 4 matrix M over the real numbers such that all the entries off the diagonal are nonzero, but all of the entries on the diagonal of M k are zero when k is an integer.
4 4 (UM) 2 C 28 Let A be the matrix of a 45 rotation. All of the entries of A and A have absolute value equal to 2/2. Note that A 2 is the matrix of a 90 rotation and has diagonal entries 0 and nonzero entries off the diagonal. Also note that A 4 = I. The matrix whose block form is ( A 2 A A, A 2 ) has all entries off the diagonal nonzero, all entries on the diagonal equal to 0, and its square and, hence, all higher powers, are 0. Problem 9. How many of the binomial coefficients ( ) 20 r, r = 0,,..., 20 are even? We have 20 = (00) 2 in base 2. Computing modulo 2, we have ( + x) 2 = + x 2, and ( + x) 2n = + x 2n. So we have 20 ( 20 ) r x r = ( + x) 20 = r=0 = ( + x) 024 ( + x) 52 ( + x) 256 ( + x) 28 ( + x) 64 ( + x) 6 ( + x) 8 ( + x) 2 ( + x) = = ( + x 024 )( + x 52 )( + x 256 )( + x 28 )( + x 64 )( + x 6 )( + x 8 )( + x 2 )( + x) So ( + x) 20 has 2 9 = 52 odd coefficients, and = 500 even coefficients. Problem 0. One chooses 5 random points in the unit disc. Assume that we have a uniform distribution on the disc, and that the points are chosen independently. What is the probability that the convex hull of the 5 points is a triangle? If V = (x, y) = (r cos(ϕ), r sin(ϕ)) is a random vector in the unit disc, then the expected value of r 2 is (using change to polar coordinates polar coordinates) E(r 2 ) = x 2 + y 2 dx dy = 2π r 2 r dϕ dr = 2 r 3 dr = π x 2 +y 2 π Let V i = (r i cos(ϕ i ), r i sin(ϕ i )) be random vectors in the unit disc for i =, 2, 3, 4, 5. The area of V V 2 V 3 is ± 2 (r r 2 cos(β 3 ) + r 2 r 3 cos(β ) + r 3 r cos(β 2 )) where β 3 = ϕ 2 ϕ,β = ϕ 3 ϕ 2 and β 2 = α α 3. Then r, r 2, r 3, β, β 2, β 3 are independent random variables. The angles β, β 2, β 3 have a uniform distribution on [0, 2π], and for all i. We have E(cos 2 (β i )) = 2π 2π 0 cos 2 (θ) dθ = 2π 2π cos(2θ) dθ = 2 E(r 2 r 2 2 cos 2 (β 3 )) = E(r 2 )E(r 2 2)E(cos 2 (β 3 )) = = 8.
5 (UM) 2 C 28 5 and E(r r2r 2 3 cos(β ) cos(β 3 ) = E(r r2r 2 3 cos(β )E(cos(β 3 ) = 0 because E(cos(β 3 )) = 0. Let A be the area of V V 2 V 3. Then we have E(A 2 ) = E( 4 (a2 a 2 2 cos(β 3 ) + a 2 2a 2 3 cos 2 (β ) + a 2 3a 2 cos 2 (β 2 )+ + 2a a 2 2a 3 cos(β ) cos(β 3 ) + 2a 2 a 2 3a cos(β 2 ) cos(β ) + 2a 3 a 2 a 2 cos(β 3 ) cos(β 2 ))) = 4 ( ) = The probability that V 4 and V 5 lie in the convex hull of V, V 2, V 3 is A 2 /π 2. So for random V, V 2, V 3, this probability is E(A 2 /π 2 ) = 3 32π. 2 The probability that 2 of the vectors V, V 2,..., V 5 lie in the convex hull of the other 3 is ( 5 2 ) 3 32π 2 = 5 6π 2.
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 27 MARCH 28, 2010
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 27 MARCH 28, 200 Instructions. Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number. Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book. Each
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 27 MARCH 28, 200 Instructions. Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number. Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book. Each
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 31 MARCH 29, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 3 MARCH 9, 04 Instructions Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book Each question
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 3 MARCH 9, 04 Instructions Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book Each question
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
MATH HL OPTION - REVISION SETS, RELATIONS AND GROUPS Compiled by: Christos Nikolaidis
 MATH HL OPTION - REVISION SETS, RELATIONS AND GROUPS Compiled by: Christos Nikolaidis PART B: GROUPS GROUPS 1. ab The binary operation a * b is defined by a * b = a+ b +. (a) Prove that * is associative.
MATH HL OPTION - REVISION SETS, RELATIONS AND GROUPS Compiled by: Christos Nikolaidis PART B: GROUPS GROUPS 1. ab The binary operation a * b is defined by a * b = a+ b +. (a) Prove that * is associative.
This class will demonstrate the use of bijections to solve certain combinatorial problems simply and effectively.
 . Induction This class will demonstrate the fundamental problem solving technique of mathematical induction. Example Problem: Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible
. Induction This class will demonstrate the fundamental problem solving technique of mathematical induction. Example Problem: Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible
PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2012 MIDDLE SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS
 PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2012 MIDDLE SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS Copyright c Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem 1 Evaluate 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0. Answer: 549 The expression equals 625 64 9 2 1 = 549. Problem
PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2012 MIDDLE SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS Copyright c Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem 1 Evaluate 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0. Answer: 549 The expression equals 625 64 9 2 1 = 549. Problem
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 2010 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
= 10 such triples. If it is 5, there is = 1 such triple. Therefore, there are a total of = 46 such triples.
 . Two externally tangent unit circles are constructed inside square ABCD, one tangent to AB and AD, the other to BC and CD. Compute the length of AB. Answer: + Solution: Observe that the diagonal of the
. Two externally tangent unit circles are constructed inside square ABCD, one tangent to AB and AD, the other to BC and CD. Compute the length of AB. Answer: + Solution: Observe that the diagonal of the
The Alberta High School Mathematics Competition Solution to Part I, 2014.
 The Alberta High School Mathematics Competition Solution to Part I, 2014. Question 1. When the repeating decimal 0.6 is divided by the repeating decimal 0.3, the quotient is (a) 0.2 (b) 2 (c) 0.5 (d) 0.5
The Alberta High School Mathematics Competition Solution to Part I, 2014. Question 1. When the repeating decimal 0.6 is divided by the repeating decimal 0.3, the quotient is (a) 0.2 (b) 2 (c) 0.5 (d) 0.5
Homework 1/Solutions. Graded Exercises
 MTH 310-3 Abstract Algebra I and Number Theory S18 Homework 1/Solutions Graded Exercises Exercise 1. Below are parts of the addition table and parts of the multiplication table of a ring. Complete both
MTH 310-3 Abstract Algebra I and Number Theory S18 Homework 1/Solutions Graded Exercises Exercise 1. Below are parts of the addition table and parts of the multiplication table of a ring. Complete both
NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS. M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test. September 22, Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30
 NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS M A and MSc Scholarship Test September 22, 2018 Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30 Please read, carefully, the instructions that follow INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS M A and MSc Scholarship Test September 22, 2018 Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30 Please read, carefully, the instructions that follow INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
MATH 3030, Abstract Algebra FALL 2012 Toby Kenney Midyear Examination Friday 7th December: 7:00-10:00 PM
 MATH 3030, Abstract Algebra FALL 2012 Toby Kenney Midyear Examination Friday 7th December: 7:00-10:00 PM Basic Questions 1. Compute the factor group Z 3 Z 9 / (1, 6). The subgroup generated by (1, 6) is
MATH 3030, Abstract Algebra FALL 2012 Toby Kenney Midyear Examination Friday 7th December: 7:00-10:00 PM Basic Questions 1. Compute the factor group Z 3 Z 9 / (1, 6). The subgroup generated by (1, 6) is
1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why. (a b)(a c)(a d)(b c)(b d)(c d) a 2 + ab b = 2018.
 New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Wednesday, April 15, 2015
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
1. Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible by 5 n all of whose digits are odd.
 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
Definitions, Theorems and Exercises. Abstract Algebra Math 332. Ethan D. Bloch
 Definitions, Theorems and Exercises Abstract Algebra Math 332 Ethan D. Bloch December 26, 2013 ii Contents 1 Binary Operations 3 1.1 Binary Operations............................... 4 1.2 Isomorphic Binary
Definitions, Theorems and Exercises Abstract Algebra Math 332 Ethan D. Bloch December 26, 2013 ii Contents 1 Binary Operations 3 1.1 Binary Operations............................... 4 1.2 Isomorphic Binary
Georgia Tech High School Math Competition
 Georgia Tech High School Math Competition Multiple Choice Test February 28, 2015 Each correct answer is worth one point; there is no deduction for incorrect answers. Make sure to enter your ID number on
Georgia Tech High School Math Competition Multiple Choice Test February 28, 2015 Each correct answer is worth one point; there is no deduction for incorrect answers. Make sure to enter your ID number on
Problem Set Mash 1. a2 b 2 0 c 2. and. a1 a
 Problem Set Mash 1 Section 1.2 15. Find a set of generators and relations for Z/nZ. h 1 1 n 0i Z/nZ. Section 1.4 a b 10. Let G 0 c a, b, c 2 R,a6 0,c6 0. a1 b (a) Compute the product of 1 a2 b and 2 0
Problem Set Mash 1 Section 1.2 15. Find a set of generators and relations for Z/nZ. h 1 1 n 0i Z/nZ. Section 1.4 a b 10. Let G 0 c a, b, c 2 R,a6 0,c6 0. a1 b (a) Compute the product of 1 a2 b and 2 0
T-2 In the equation A B C + D E F = G H I, each letter denotes a distinct non-zero digit. Compute the greatest possible value of G H I.
 2016 ARML Local Problems and Solutions Team Round Solutions T-1 All the shelves in a library are the same length. When filled, two shelves side-by-side can hold exactly 12 algebra books and 10 geometry
2016 ARML Local Problems and Solutions Team Round Solutions T-1 All the shelves in a library are the same length. When filled, two shelves side-by-side can hold exactly 12 algebra books and 10 geometry
Math 121 Homework 5: Notes on Selected Problems
 Math 121 Homework 5: Notes on Selected Problems 12.1.2. Let M be a module over the integral domain R. (a) Assume that M has rank n and that x 1,..., x n is any maximal set of linearly independent elements
Math 121 Homework 5: Notes on Selected Problems 12.1.2. Let M be a module over the integral domain R. (a) Assume that M has rank n and that x 1,..., x n is any maximal set of linearly independent elements
Math 3140 Fall 2012 Assignment #3
 Math 3140 Fall 2012 Assignment #3 Due Fri., Sept. 21. Remember to cite your sources, including the people you talk to. My solutions will repeatedly use the following proposition from class: Proposition
Math 3140 Fall 2012 Assignment #3 Due Fri., Sept. 21. Remember to cite your sources, including the people you talk to. My solutions will repeatedly use the following proposition from class: Proposition
5 Group theory. 5.1 Binary operations
 5 Group theory This section is an introduction to abstract algebra. This is a very useful and important subject for those of you who will continue to study pure mathematics. 5.1 Binary operations 5.1.1
5 Group theory This section is an introduction to abstract algebra. This is a very useful and important subject for those of you who will continue to study pure mathematics. 5.1 Binary operations 5.1.1
SUMS PROBLEM COMPETITION, 2000
 SUMS ROBLEM COMETITION, 2000 SOLUTIONS 1 The result is well known, and called Morley s Theorem Many proofs are known See for example HSM Coxeter, Introduction to Geometry, page 23 2 If the number of vertices,
SUMS ROBLEM COMETITION, 2000 SOLUTIONS 1 The result is well known, and called Morley s Theorem Many proofs are known See for example HSM Coxeter, Introduction to Geometry, page 23 2 If the number of vertices,
Sydney University Mathematical Society Problems Competition Solutions.
 Sydney University Mathematical Society Problems Competition 005 Solutions 1 Suppose that we look at the set X n of strings of 0 s and 1 s of length n Given a string ɛ = (ɛ 1,, ɛ n ) X n, we are allowed
Sydney University Mathematical Society Problems Competition 005 Solutions 1 Suppose that we look at the set X n of strings of 0 s and 1 s of length n Given a string ɛ = (ɛ 1,, ɛ n ) X n, we are allowed
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, IX / Class IX
 I, 0 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 0 MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS CLASS CLASS - IX - IX IX / Class IX MA-0 90 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 (i) (ii) 8 6 0 0 (iii) 8 (iv) (v) General Instructions:
I, 0 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 0 MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS CLASS CLASS - IX - IX IX / Class IX MA-0 90 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 (i) (ii) 8 6 0 0 (iii) 8 (iv) (v) General Instructions:
UNC Charlotte 2005 Comprehensive March 7, 2005
 March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
2013 University of New South Wales School Mathematics Competition
 Parabola Volume 49, Issue (201) 201 University of New South Wales School Mathematics Competition Junior Division Problems and s Problem 1 Suppose that x, y, z are non-zero integers with no common factor
Parabola Volume 49, Issue (201) 201 University of New South Wales School Mathematics Competition Junior Division Problems and s Problem 1 Suppose that x, y, z are non-zero integers with no common factor
Gordon solutions. n=1 1. p n
 Gordon solutions 1. A positive integer is called a palindrome if its base-10 expansion is unchanged when it is reversed. For example, 121 and 7447 are palindromes. Show that if we denote by p n the nth
Gordon solutions 1. A positive integer is called a palindrome if its base-10 expansion is unchanged when it is reversed. For example, 121 and 7447 are palindromes. Show that if we denote by p n the nth
Organization Team Team ID#
 1. [4] A random number generator will always output 7. Sam uses this random number generator once. What is the expected value of the output? 2. [4] Let A, B, C, D, E, F be 6 points on a circle in that
1. [4] A random number generator will always output 7. Sam uses this random number generator once. What is the expected value of the output? 2. [4] Let A, B, C, D, E, F be 6 points on a circle in that
Non-standard MMC problems
 Non-standard MMC problems Carl Joshua Quines 1 Algebra 1. (15S/9B/E6) A quadratic function f(x) satisfies f(0) = 30 and f(2) = 0. Determine all the zeros of f(x). [2 and 15] 2. (15S/IVB/E6) What is the
Non-standard MMC problems Carl Joshua Quines 1 Algebra 1. (15S/9B/E6) A quadratic function f(x) satisfies f(0) = 30 and f(2) = 0. Determine all the zeros of f(x). [2 and 15] 2. (15S/IVB/E6) What is the
Mathematics. Exercise 6.4. (Chapter 6) (Triangles) (Class X) Question 1: Let and their areas be, respectively, 64 cm 2 and 121 cm 2.
 () Exercise 6.4 Question 1: Let and their areas be, respectively, 64 cm 2 and 121 cm 2. If EF = 15.4 cm, find BC. Answer 1: 1 () Question 2: Diagonals of a trapezium ABCD with AB DC intersect each other
() Exercise 6.4 Question 1: Let and their areas be, respectively, 64 cm 2 and 121 cm 2. If EF = 15.4 cm, find BC. Answer 1: 1 () Question 2: Diagonals of a trapezium ABCD with AB DC intersect each other
Math 114: Make-up Final Exam. Instructions:
 Math 114: Make-up Final Exam Instructions: 1. Please sign your name and indicate the name of your instructor and your teaching assistant: A. Your Name: B. Your Instructor: C. Your Teaching Assistant: 2.
Math 114: Make-up Final Exam Instructions: 1. Please sign your name and indicate the name of your instructor and your teaching assistant: A. Your Name: B. Your Instructor: C. Your Teaching Assistant: 2.
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Johns Hopkins University, Department of Mathematics Abstract Algebra - Spring 2009 Midterm
 Johns Hopkins University, Department of Mathematics 110.401 Abstract Algebra - Spring 2009 Midterm Instructions: This exam has 8 pages. No calculators, books or notes allowed. You must answer the first
Johns Hopkins University, Department of Mathematics 110.401 Abstract Algebra - Spring 2009 Midterm Instructions: This exam has 8 pages. No calculators, books or notes allowed. You must answer the first
Yale University Department of Mathematics Math 350 Introduction to Abstract Algebra Fall Midterm Exam Review Solutions
 Yale University Department of Mathematics Math 350 Introduction to Abstract Algebra Fall 2015 Midterm Exam Review Solutions Practice exam questions: 1. Let V 1 R 2 be the subset of all vectors whose slope
Yale University Department of Mathematics Math 350 Introduction to Abstract Algebra Fall 2015 Midterm Exam Review Solutions Practice exam questions: 1. Let V 1 R 2 be the subset of all vectors whose slope
Downloaded from
 Triangles 1.In ABC right angled at C, AD is median. Then AB 2 = AC 2 - AD 2 AD 2 - AC 2 3AC 2-4AD 2 (D) 4AD 2-3AC 2 2.Which of the following statement is true? Any two right triangles are similar
Triangles 1.In ABC right angled at C, AD is median. Then AB 2 = AC 2 - AD 2 AD 2 - AC 2 3AC 2-4AD 2 (D) 4AD 2-3AC 2 2.Which of the following statement is true? Any two right triangles are similar
81-E 2. Ans. : 2. Universal set U = { 2, 3, 5, 6, 10 }, subset A = { 5, 6 }. The diagram which represents A / is. Ans. : ( SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK )
 81-E 2 General Instructions : i) The question-cum-answer booklet contains two Parts, Part A & Part B. ii) iii) iv) Part A consists of 60 questions and Part B consists of 16 questions. Space has been provided
81-E 2 General Instructions : i) The question-cum-answer booklet contains two Parts, Part A & Part B. ii) iii) iv) Part A consists of 60 questions and Part B consists of 16 questions. Space has been provided
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 2003
 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 10.
 MTH 234 Solutions to Exam 2 April 11th 216 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through
MTH 234 Solutions to Exam 2 April 11th 216 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through
40th International Mathematical Olympiad
 40th International Mathematical Olympiad Bucharest, Romania, July 999 Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition: for any two distinct points
40th International Mathematical Olympiad Bucharest, Romania, July 999 Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition: for any two distinct points
(3) Let Y be a totally bounded subset of a metric space X. Then the closure Y of Y
 () Consider A = { q Q : q 2 2} as a subset of the metric space (Q, d), where d(x, y) = x y. Then A is A) closed but not open in Q B) open but not closed in Q C) neither open nor closed in Q D) both open
() Consider A = { q Q : q 2 2} as a subset of the metric space (Q, d), where d(x, y) = x y. Then A is A) closed but not open in Q B) open but not closed in Q C) neither open nor closed in Q D) both open
IIT Mumbai 2015 MA 419, Basic Algebra Tutorial Sheet-1
 IIT Mumbai 2015 MA 419, Basic Algebra Tutorial Sheet-1 Let Σ be the set of all symmetries of the plane Π. 1. Give examples of s, t Σ such that st ts. 2. If s, t Σ agree on three non-collinear points, then
IIT Mumbai 2015 MA 419, Basic Algebra Tutorial Sheet-1 Let Σ be the set of all symmetries of the plane Π. 1. Give examples of s, t Σ such that st ts. 2. If s, t Σ agree on three non-collinear points, then
13 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 20 February 2010
 13 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 0 February 010 1. [3] Suppose that x and y are positive reals such that Find x. x y = 3, x + y = 13. 3+ Answer: 17 Squaring both sides of x y =
13 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 0 February 010 1. [3] Suppose that x and y are positive reals such that Find x. x y = 3, x + y = 13. 3+ Answer: 17 Squaring both sides of x y =
School of Mathematics and Statistics MT5824 Topics in Groups Problem Sheet V: Direct and semidirect products (Solutions)
 CMRD 2010 School of Mathematics and Statistics MT5824 Topics in Groups Problem Sheet V: Direct and semidirect products (Solutions) 1. Give an example of two groups G and H and a subgroup of the direct
CMRD 2010 School of Mathematics and Statistics MT5824 Topics in Groups Problem Sheet V: Direct and semidirect products (Solutions) 1. Give an example of two groups G and H and a subgroup of the direct
ANALYSIS OF SMALL GROUPS
 ANALYSIS OF SMALL GROUPS 1. Big Enough Subgroups are Normal Proposition 1.1. Let G be a finite group, and let q be the smallest prime divisor of G. Let N G be a subgroup of index q. Then N is a normal
ANALYSIS OF SMALL GROUPS 1. Big Enough Subgroups are Normal Proposition 1.1. Let G be a finite group, and let q be the smallest prime divisor of G. Let N G be a subgroup of index q. Then N is a normal
GROUPS. Chapter-1 EXAMPLES 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. BINARY OPERATION
 Chapter-1 GROUPS 1.1. INTRODUCTION The theory of groups arose from the theory of equations, during the nineteenth century. Originally, groups consisted only of transformations. The group of transformations
Chapter-1 GROUPS 1.1. INTRODUCTION The theory of groups arose from the theory of equations, during the nineteenth century. Originally, groups consisted only of transformations. The group of transformations
GALOIS GROUPS OF CUBICS AND QUARTICS (NOT IN CHARACTERISTIC 2)
 GALOIS GROUPS OF CUBICS AND QUARTICS (NOT IN CHARACTERISTIC 2) KEITH CONRAD We will describe a procedure for figuring out the Galois groups of separable irreducible polynomials in degrees 3 and 4 over
GALOIS GROUPS OF CUBICS AND QUARTICS (NOT IN CHARACTERISTIC 2) KEITH CONRAD We will describe a procedure for figuring out the Galois groups of separable irreducible polynomials in degrees 3 and 4 over
Math 430 Final Exam, Fall 2008
 IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, December 9, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Final Exam, Fall 2008 Grades should be posted Friday 12/12. Have a good break, and don t forget
IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, December 9, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Final Exam, Fall 2008 Grades should be posted Friday 12/12. Have a good break, and don t forget
2011 Olympiad Solutions
 011 Olympiad Problem 1 Let A 0, A 1, A,..., A n be nonnegative numbers such that Prove that A 0 A 1 A A n. A i 1 n A n. Note: x means the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x.) Solution: We
011 Olympiad Problem 1 Let A 0, A 1, A,..., A n be nonnegative numbers such that Prove that A 0 A 1 A A n. A i 1 n A n. Note: x means the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x.) Solution: We
Singapore Mathematical Society
 Singapore Mathematical Society Interschool Mathematical Competition 1990 Part A Saturday, 23 June 1990 100Q-1100 Attempt as many questions as you can. No calculators are allowed. Circle your answers on
Singapore Mathematical Society Interschool Mathematical Competition 1990 Part A Saturday, 23 June 1990 100Q-1100 Attempt as many questions as you can. No calculators are allowed. Circle your answers on
GRE Subject test preparation Spring 2016 Topic: Abstract Algebra, Linear Algebra, Number Theory.
 GRE Subject test preparation Spring 2016 Topic: Abstract Algebra, Linear Algebra, Number Theory. Linear Algebra Standard matrix manipulation to compute the kernel, intersection of subspaces, column spaces,
GRE Subject test preparation Spring 2016 Topic: Abstract Algebra, Linear Algebra, Number Theory. Linear Algebra Standard matrix manipulation to compute the kernel, intersection of subspaces, column spaces,
right angle an angle whose measure is exactly 90ᴼ
 right angle an angle whose measure is exactly 90ᴼ m B = 90ᴼ B two angles that share a common ray A D C B Vertical Angles A D C B E two angles that are opposite of each other and share a common vertex two
right angle an angle whose measure is exactly 90ᴼ m B = 90ᴼ B two angles that share a common ray A D C B Vertical Angles A D C B E two angles that are opposite of each other and share a common vertex two
NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS. M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test. September 22, Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30
 NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test September 22, 2012 Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30 Please read, carefully, the instructions on the following page 1 INSTRUCTIONS
NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test September 22, 2012 Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30 Please read, carefully, the instructions on the following page 1 INSTRUCTIONS
Name: Solutions Final Exam
 Instructions. Answer each of the questions on your own paper. Be sure to show your work so that partial credit can be adequately assessed. Put your name on each page of your paper. 1. [10 Points] All of
Instructions. Answer each of the questions on your own paper. Be sure to show your work so that partial credit can be adequately assessed. Put your name on each page of your paper. 1. [10 Points] All of
NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS. M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test. September 25, Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30
 NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test September 25, 2010 Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30 Please read, carefully, the instructions on the following page 1 INSTRUCTIONS
NATIONAL BOARD FOR HIGHER MATHEMATICS M. A. and M.Sc. Scholarship Test September 25, 2010 Time Allowed: 150 Minutes Maximum Marks: 30 Please read, carefully, the instructions on the following page 1 INSTRUCTIONS
INMO-2001 Problems and Solutions
 INMO-2001 Problems and Solutions 1. Let ABC be a triangle in which no angle is 90. For any point P in the plane of the triangle, let A 1,B 1,C 1 denote the reflections of P in the sides BC,CA,AB respectively.
INMO-2001 Problems and Solutions 1. Let ABC be a triangle in which no angle is 90. For any point P in the plane of the triangle, let A 1,B 1,C 1 denote the reflections of P in the sides BC,CA,AB respectively.
The 3rd Olympiad of Metropolises
 The 3rd Olympiad of Metropolises Day 1. Solutions Problem 1. Solve the system of equations in real numbers: (x 1)(y 1)(z 1) xyz 1, Answer: x 1, y 1, z 1. (x )(y )(z ) xyz. (Vladimir Bragin) Solution 1.
The 3rd Olympiad of Metropolises Day 1. Solutions Problem 1. Solve the system of equations in real numbers: (x 1)(y 1)(z 1) xyz 1, Answer: x 1, y 1, z 1. (x )(y )(z ) xyz. (Vladimir Bragin) Solution 1.
SOUTH AFRICAN TERTIARY MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD
 SOUTH AFRICAN TERTIARY MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD. Determine the following value: 7 August 6 Solutions π + π. Solution: Since π
SOUTH AFRICAN TERTIARY MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD. Determine the following value: 7 August 6 Solutions π + π. Solution: Since π
1. Matrices and Determinants
 Important Questions 1. Matrices and Determinants Ex.1.1 (2) x 3x y Find the values of x, y, z if 2x + z 3y w = 0 7 3 2a Ex 1.1 (3) 2x 3x y If 2x + z 3y w = 3 2 find x, y, z, w 4 7 Ex 1.1 (13) 3 7 3 2 Find
Important Questions 1. Matrices and Determinants Ex.1.1 (2) x 3x y Find the values of x, y, z if 2x + z 3y w = 0 7 3 2a Ex 1.1 (3) 2x 3x y If 2x + z 3y w = 3 2 find x, y, z, w 4 7 Ex 1.1 (13) 3 7 3 2 Find
GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions.
 GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions. 1. E (Calculus) Apply L Hôpital s Rule two times: cos(3x) 1 3 sin(3x) 9 cos(3x) lim x 0 = lim x 2 x 0 = lim 2x x 0 = 9. 2 2 2. C (Geometry) Note that a line segment
GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions. 1. E (Calculus) Apply L Hôpital s Rule two times: cos(3x) 1 3 sin(3x) 9 cos(3x) lim x 0 = lim x 2 x 0 = lim 2x x 0 = 9. 2 2 2. C (Geometry) Note that a line segment
Groups and Symmetries
 Groups and Symmetries Definition: Symmetry A symmetry of a shape is a rigid motion that takes vertices to vertices, edges to edges. Note: A rigid motion preserves angles and distances. Definition: Group
Groups and Symmetries Definition: Symmetry A symmetry of a shape is a rigid motion that takes vertices to vertices, edges to edges. Note: A rigid motion preserves angles and distances. Definition: Group
Definition List Modern Algebra, Fall 2011 Anders O.F. Hendrickson
 Definition List Modern Algebra, Fall 2011 Anders O.F. Hendrickson On almost every Friday of the semester, we will have a brief quiz to make sure you have memorized the definitions encountered in our studies.
Definition List Modern Algebra, Fall 2011 Anders O.F. Hendrickson On almost every Friday of the semester, we will have a brief quiz to make sure you have memorized the definitions encountered in our studies.
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS
 International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2008. 1. A standard 8 8 chessboard is modified by varying the distances between parallel grid lines, so that the cells are rectangles
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2008. 1. A standard 8 8 chessboard is modified by varying the distances between parallel grid lines, so that the cells are rectangles
CBSE Sample Paper-03 (Unsolved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MATHEMATICS Class IX. Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
 CBSE Sample Paper-3 (Unsolved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MATHEMATICS Class IX Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 9 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists
CBSE Sample Paper-3 (Unsolved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MATHEMATICS Class IX Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 9 General Instructions: a) All questions are compulsory. b) The question paper consists
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS
 International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2011 1 Pete has marked at least 3 points in the plane such that all distances between them are different A pair of marked points
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2011 1 Pete has marked at least 3 points in the plane such that all distances between them are different A pair of marked points
CAREER POINT. PRMO EXAM-2017 (Paper & Solution) Sum of number should be 21
 PRMO EXAM-07 (Paper & Solution) Q. How many positive integers less than 000 have the property that the sum of the digits of each such number is divisible by 7 and the number itself is divisible by 3? Sum
PRMO EXAM-07 (Paper & Solution) Q. How many positive integers less than 000 have the property that the sum of the digits of each such number is divisible by 7 and the number itself is divisible by 3? Sum
Homework Assignments Math /02 Fall 2017
 Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2017 Assignment 1 Due date : Wednesday, August 30 Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22,
Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2017 Assignment 1 Due date : Wednesday, August 30 Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22,
HMMT November 2013 Saturday 9 November 2013
 . [5] Evaluate + 5 + 8 + + 0. 75 There are 0 HMMT November 0 Saturday 9 November 0 Guts Round = 4 terms with average +0, so their sum is 7 0 = 75.. [5] Two fair six-sided dice are rolled. What is the probability
. [5] Evaluate + 5 + 8 + + 0. 75 There are 0 HMMT November 0 Saturday 9 November 0 Guts Round = 4 terms with average +0, so their sum is 7 0 = 75.. [5] Two fair six-sided dice are rolled. What is the probability
1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2017
 1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 017 1.1 Junior Section Question 1. Suppose x 1, x, x 3 are the roots of polynomial P (x) = x 3 6x + 5x + 1. The sum x 1 + x + x 3 is (A): 4 (B): 6 (C): 8 (D): 14 (E):
1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 017 1.1 Junior Section Question 1. Suppose x 1, x, x 3 are the roots of polynomial P (x) = x 3 6x + 5x + 1. The sum x 1 + x + x 3 is (A): 4 (B): 6 (C): 8 (D): 14 (E):
1. (A) Factor to get (2x+3)(2x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/2 and 5, which sum to 7/2.
 Solutions 00 53 rd AMC 1 A 1. (A) Factor to get (x+3)(x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/ and 5, which sum to 7/.. (A) Let x be the number she was given. Her calculations produce so x 9 3 = 43, x 9 = 19
Solutions 00 53 rd AMC 1 A 1. (A) Factor to get (x+3)(x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/ and 5, which sum to 7/.. (A) Let x be the number she was given. Her calculations produce so x 9 3 = 43, x 9 = 19
1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that
 1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that g(x)(x 2 3x + 2) = h(x)(x 2 + 3x + 2) and f(x) = g(x)h(x) + (x 4 5x 2 + 4). Prove that f(x) has at least four real roots. 2. Let M be
1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that g(x)(x 2 3x + 2) = h(x)(x 2 + 3x + 2) and f(x) = g(x)h(x) + (x 4 5x 2 + 4). Prove that f(x) has at least four real roots. 2. Let M be
UNM - PNM STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST XLVI - SOLUTIONS. February 1, 2014 Second Round Three Hours
 UNM - PNM STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST XLVI - SOLUTIONS February 1, 2014 Second Round Three Hours 1. Four siblings BRYAN, BARRY, SARAH and SHANA are having their names monogrammed on their towels. Different
UNM - PNM STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST XLVI - SOLUTIONS February 1, 2014 Second Round Three Hours 1. Four siblings BRYAN, BARRY, SARAH and SHANA are having their names monogrammed on their towels. Different
Homework Assignments Math /02 Fall 2014
 Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2014 Assignment 1 Due date : Friday, September 5 6th Edition Problem Set Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14,
Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2014 Assignment 1 Due date : Friday, September 5 6th Edition Problem Set Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14,
Problem 1. Problem 2. Problem 3. Problem 4. PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 2009 MIDDLE SCHOOL - PROBLEMS. c Copyright Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane
 PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 009 MIDDLE SCHOOL - PROBLEMS c Copyright Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem The pentagon below has three right angles. Find its area. 4 Problem Let p =, p =, p = 5,...
PURPLE COMET MATH MEET April 009 MIDDLE SCHOOL - PROBLEMS c Copyright Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem The pentagon below has three right angles. Find its area. 4 Problem Let p =, p =, p = 5,...
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
The Advantage Testing Foundation Olympiad Solutions
 The Advantage Testing Foundation 014 Olympiad Problem 1 Say that a convex quadrilateral is tasty if its two diagonals divide the quadrilateral into four nonoverlapping similar triangles. Find all tasty
The Advantage Testing Foundation 014 Olympiad Problem 1 Say that a convex quadrilateral is tasty if its two diagonals divide the quadrilateral into four nonoverlapping similar triangles. Find all tasty
Year 9 Term 3 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 9 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 5 Year 9 Term 3 Week 5 Homework 1 5.1 Geometry (Review)................................... 1 5.1.1 Angle sum
Yimin Math Centre Year 9 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 5 Year 9 Term 3 Week 5 Homework 1 5.1 Geometry (Review)................................... 1 5.1.1 Angle sum
MIDDLE SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS. is 1. = 3. Multiplying by 20n yields 35n + 24n + 20 = 60n, and, therefore, n = 20.
 PURPLE COMET! MATH MEET April 208 MIDDLE SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS Copyright c Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem Find n such that the mean of 7 4, 6 5, and n is. Answer: 20 For the mean of three numbers
PURPLE COMET! MATH MEET April 208 MIDDLE SCHOOL - SOLUTIONS Copyright c Titu Andreescu and Jonathan Kane Problem Find n such that the mean of 7 4, 6 5, and n is. Answer: 20 For the mean of three numbers
Some notes on Coxeter groups
 Some notes on Coxeter groups Brooks Roberts November 28, 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Sources 2 2 Reflections 3 3 The orthogonal group 7 4 Finite subgroups in two dimensions 9 5 Finite subgroups in three
Some notes on Coxeter groups Brooks Roberts November 28, 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Sources 2 2 Reflections 3 3 The orthogonal group 7 4 Finite subgroups in two dimensions 9 5 Finite subgroups in three
SOLUTIONS OF 2012 MATH OLYMPICS LEVEL II T 3 T 3 1 T 4 T 4 1
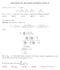 SOLUTIONS OF 0 MATH OLYMPICS LEVEL II. If T n = + + 3 +... + n and P n = T T T 3 T 3 T 4 T 4 T n T n for n =, 3, 4,..., then P 0 is the closest to which of the following numbers? (a).9 (b).3 (c) 3. (d).6
SOLUTIONS OF 0 MATH OLYMPICS LEVEL II. If T n = + + 3 +... + n and P n = T T T 3 T 3 T 4 T 4 T n T n for n =, 3, 4,..., then P 0 is the closest to which of the following numbers? (a).9 (b).3 (c) 3. (d).6
Math 581 Problem Set 7 Solutions
 Math 581 Problem Set 7 Solutions 1. Let f(x) Q[x] be a polynomial. A ring isomorphism φ : R R is called an automorphism. (a) Let φ : C C be a ring homomorphism so that φ(a) = a for all a Q. Prove that
Math 581 Problem Set 7 Solutions 1. Let f(x) Q[x] be a polynomial. A ring isomorphism φ : R R is called an automorphism. (a) Let φ : C C be a ring homomorphism so that φ(a) = a for all a Q. Prove that
CCSU Regional Math Competition, 2012 Part I
 CCSU Regional Math Competition, Part I Each problem is worth ten points. Please be sure to use separate pages to write your solution for every problem.. Find all real numbers r, with r, such that a -by-r
CCSU Regional Math Competition, Part I Each problem is worth ten points. Please be sure to use separate pages to write your solution for every problem.. Find all real numbers r, with r, such that a -by-r
Physics 251 Solution Set 1 Spring 2017
 Physics 5 Solution Set Spring 07. Consider the set R consisting of pairs of real numbers. For (x,y) R, define scalar multiplication by: c(x,y) (cx,cy) for any real number c, and define vector addition
Physics 5 Solution Set Spring 07. Consider the set R consisting of pairs of real numbers. For (x,y) R, define scalar multiplication by: c(x,y) (cx,cy) for any real number c, and define vector addition
Some practice problems for midterm 2
 Some practice problems for midterm 2 Kiumars Kaveh November 14, 2011 Problem: Let Z = {a G ax = xa, x G} be the center of a group G. Prove that Z is a normal subgroup of G. Solution: First we prove Z is
Some practice problems for midterm 2 Kiumars Kaveh November 14, 2011 Problem: Let Z = {a G ax = xa, x G} be the center of a group G. Prove that Z is a normal subgroup of G. Solution: First we prove Z is
Definitions. Notations. Injective, Surjective and Bijective. Divides. Cartesian Product. Relations. Equivalence Relations
 Page 1 Definitions Tuesday, May 8, 2018 12:23 AM Notations " " means "equals, by definition" the set of all real numbers the set of integers Denote a function from a set to a set by Denote the image of
Page 1 Definitions Tuesday, May 8, 2018 12:23 AM Notations " " means "equals, by definition" the set of all real numbers the set of integers Denote a function from a set to a set by Denote the image of
THE UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO UNDERGRADUATE MATHEMATICS COMPETITION. Sunday, March 14, 2004 Time: hours No aids or calculators permitted.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO UNDERGRADUATE MATHEMATICS COMPETITION Sunday, March 1, Time: 3 1 hours No aids or calculators permitted. 1. Prove that, for any complex numbers z and w, ( z + w z z + w w z +
THE UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO UNDERGRADUATE MATHEMATICS COMPETITION Sunday, March 1, Time: 3 1 hours No aids or calculators permitted. 1. Prove that, for any complex numbers z and w, ( z + w z z + w w z +
ENTRY GROUP THEORY. [ENTRY GROUP THEORY] Authors: started Mark Lezama: October 2003 Literature: Algebra by Michael Artin, Mathworld.
![ENTRY GROUP THEORY. [ENTRY GROUP THEORY] Authors: started Mark Lezama: October 2003 Literature: Algebra by Michael Artin, Mathworld. ENTRY GROUP THEORY. [ENTRY GROUP THEORY] Authors: started Mark Lezama: October 2003 Literature: Algebra by Michael Artin, Mathworld.](/thumbs/90/104374286.jpg) ENTRY GROUP THEORY [ENTRY GROUP THEORY] Authors: started Mark Lezama: October 2003 Literature: Algebra by Michael Artin, Mathworld Group theory [Group theory] is studies algebraic objects called groups.
ENTRY GROUP THEORY [ENTRY GROUP THEORY] Authors: started Mark Lezama: October 2003 Literature: Algebra by Michael Artin, Mathworld Group theory [Group theory] is studies algebraic objects called groups.
EASY PUTNAM PROBLEMS
 EASY PUTNAM PROBLEMS (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. The problems in the Putnam Competition are usually very hard, but practically every session contains at least one problem very easy to solve
EASY PUTNAM PROBLEMS (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. The problems in the Putnam Competition are usually very hard, but practically every session contains at least one problem very easy to solve
2. In ABC, the measure of angle B is twice the measure of angle A. Angle C measures three times the measure of angle A. If AC = 26, find AB.
 2009 FGCU Mathematics Competition. Geometry Individual Test 1. You want to prove that the perpendicular bisector of the base of an isosceles triangle is also the angle bisector of the vertex. Which postulate/theorem
2009 FGCU Mathematics Competition. Geometry Individual Test 1. You want to prove that the perpendicular bisector of the base of an isosceles triangle is also the angle bisector of the vertex. Which postulate/theorem
Problems (F/M): Part 2 - Solutions (16 pages; 29/4/17)
 Problems (F/M): Part 2 - Solutions (16 pages; 29/4/17) (11) Show that n ( n r=0 r ) = 2n Solution Method 1: Consider (1 + 1) n Method 2: Pascal's triangle The sum of each row is twice the sum of the previous
Problems (F/M): Part 2 - Solutions (16 pages; 29/4/17) (11) Show that n ( n r=0 r ) = 2n Solution Method 1: Consider (1 + 1) n Method 2: Pascal's triangle The sum of each row is twice the sum of the previous
SMT 2018 Geometry Test Solutions February 17, 2018
 SMT 018 Geometry Test Solutions February 17, 018 1. Consider a semi-circle with diameter AB. Let points C and D be on diameter AB such that CD forms the base of a square inscribed in the semicircle. Given
SMT 018 Geometry Test Solutions February 17, 018 1. Consider a semi-circle with diameter AB. Let points C and D be on diameter AB such that CD forms the base of a square inscribed in the semicircle. Given
2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time is
 . If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
. If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions
 Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions Quiz #1. Tuesday, 17 January, 2012. [10 minutes] 1. Given a line segment AB, use (some of) Postulates I V,
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions Quiz #1. Tuesday, 17 January, 2012. [10 minutes] 1. Given a line segment AB, use (some of) Postulates I V,
Math 370 Homework 2, Fall 2009
 Math 370 Homework 2, Fall 2009 (1a) Prove that every natural number N is congurent to the sum of its decimal digits mod 9. PROOF: Let the decimal representation of N be n d n d 1... n 1 n 0 so that N =
Math 370 Homework 2, Fall 2009 (1a) Prove that every natural number N is congurent to the sum of its decimal digits mod 9. PROOF: Let the decimal representation of N be n d n d 1... n 1 n 0 so that N =
PRACTICE FINAL MATH , MIT, SPRING 13. You have three hours. This test is closed book, closed notes, no calculators.
 PRACTICE FINAL MATH 18.703, MIT, SPRING 13 You have three hours. This test is closed book, closed notes, no calculators. There are 11 problems, and the total number of points is 180. Show all your work.
PRACTICE FINAL MATH 18.703, MIT, SPRING 13 You have three hours. This test is closed book, closed notes, no calculators. There are 11 problems, and the total number of points is 180. Show all your work.
Comprehensive Mathematics Contest
 Comprehensive Mathematics Contest Elon University Mathematics and Statistics Department Saturday, March 17, 2018 Multiple Choice 1. Let a and b be lengths of the major and minor axis of the ellipse given
Comprehensive Mathematics Contest Elon University Mathematics and Statistics Department Saturday, March 17, 2018 Multiple Choice 1. Let a and b be lengths of the major and minor axis of the ellipse given
Chapter SSM: Linear Algebra. 5. Find all x such that A x = , so that x 1 = x 2 = 0.
 Chapter Find all x such that A x : Chapter, so that x x ker(a) { } Find all x such that A x ; note that all x in R satisfy the equation, so that ker(a) R span( e, e ) 5 Find all x such that A x 5 ; x x
Chapter Find all x such that A x : Chapter, so that x x ker(a) { } Find all x such that A x ; note that all x in R satisfy the equation, so that ker(a) R span( e, e ) 5 Find all x such that A x 5 ; x x
MAY THE FORCE BE WITH YOU, YOUNG JEDIS!!!
 Final Exam Math 222 Spring 2011 May 11, 2011 Name: Recitation Instructor s Initials: You may not use any type of calculator whatsoever. (Cell phones off and away!) You are not allowed to have any other
Final Exam Math 222 Spring 2011 May 11, 2011 Name: Recitation Instructor s Initials: You may not use any type of calculator whatsoever. (Cell phones off and away!) You are not allowed to have any other
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
