Inf2b Learning and Data
|
|
|
- Sheila Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inf2b Learning and Data Lecture : Single layer Neural Networks () (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murray and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR) School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Office hours: Wednesdays at 4:00-5:00 in IF-3.04 Jan-Mar 209 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks ()
2 Today s Schedule Discriminant functions (recap) 2 Decision boundary of linear discriminants (recap) 3 Discriminative training of linear discriminans (Perceptron) 4 Structures and decision boundaries of Perceptron 5 LSE Training of linear discriminants 6 Appendi - calculus, gradient descent, linear regression Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 2
3 Discriminant functions (recap) y k () = ln (P( C)P(C k )) = 2 ( µ k) T k ( µ k) 2 ln k + ln P(C k ) = 2 T k + µt k k 2 µt k k µ k 2 ln k + ln P(C k ) (a) (b) (c) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 3
4 Linear discriminants for a 2-class problem y () = w T + w 0 y 2 () = w T 2 + w 20 Combined discriminant function: y() = y () y 2 () = (w w 2 ) T + (w 0 w 20 ) = w T + w 0 Decision: {, if y() 0, C = 2, if y() < 0 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 4
5 Decision boundary of linear discriminants Decision boundary: y() = w T + w 0 = 0 Dimension Decision boundary 2 line w + w w 0 = 0 3 plane w + w w w 0 = 0 D hyperplane ( D i= w i i ) + w 0 = 0 NB: w is a normal vector to the hyperplane Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 5
6 Decision boundary of linear discriminant (2D) y() = w + w w 0 = 0 ( 2 = w w 2 w 0 w 2, when w 2 0) C T y( )= w +w0 =0 C w =( w, w2 ) slope = w /w T w 0 /w 2 slope = w /w 2 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 6
7 Decision boundary of linear discriminant (3D) y() = w + w w w 0 = 0 3 w=(w, w, w ) 2 3 T 2 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 7
8 Approach to linear discminant functions Generative models : p( C k ) Discriminant function based on Bayes decision rule y k () = ln p( C k ) + ln P(C k ) Gaussian pdf (model) y k () = 2 ( µ k) T k ( µ k) 2 ln k + ln P(C k ) Equal covariance assumption y k () = w T + w 0 Why not estimating the decision boundary or P(C k ) directly? Discriminative trainig / models (Logistic regression, Percepton / Neural network, SVM) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 8
9 Training linear discriminant functions directly A discriminant for a two-class problem: y() = y () y 2 () = (w w 2 ) T + (w 0 w 20 ) = w T + w 0 2 ( w,w) T 2 2 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 9
10 Perceptron error correction algorithm a(ẋ) = w T + w 0 = ẇ T ẋ where ẇ = (w 0, w T ) T, ẋ = (, T ) T Let s just use w and to denote ẇ and ẋ from now on! y() = g( a() ) = g( w T ) where g(a) = {, if a 0, 0, if a < 0 Training set : D = {(, t ),..., ( N, t N )} Modify w if i was misclassified g(a): activation / transfer function where t i {0, } : target value NB: w (new) w + η (t i y( i )) i (0 < η < ) learning rate (w (new) ) T i = w T i + η (t i y( i )) i 2 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 0
11 Geometry of Perceptron s error correction y( i ) = g(w T i ) w (new) w + η (t i y( i )) i (0 < η < ) y( i ) t i y( i ) t i 0 w T = w cos θ 2 C T w w C 0 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks ()
12 Geometry of Perceptron s error correction (cont.) y( i ) = g(w T i ) w (new) w + η (t i y( i )) i (0 < η < ) y( i ) t i y( i ) t i 0 2 C w w T = w cos θ C 0 T w Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 2
13 Geometry of Perceptron s error correction (cont.) y( i ) = g(w T i ) w (new) w + η (t i y( i )) i (0 < η < ) y( i ) t i y( i ) t i 0 η 2 (new) w η w C w T = w cos θ C 0 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 3
14 The Perceptron learning algorithm Incremental (online) Perceptron algorithm: for i =,..., N w w + η (t i y( i )) i Batch Perceptron algorithm: v sum = 0 for i =,..., N v sum = v sum + (t i y( i )) i w w + η v sum What about convergence? The Perceptron learning algorithm terminates if training samples are linearly separable. Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 4
15 Linearly separable vs linearly non-separable (a ) (a 2) Linearly separable (b) Linearly non separable Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 5
16 Background of Perceptron w w 2 w 3 y ( Hand-tuned.svg) (a) function unit 940s Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts : threshold logic Donald Hebb : Hebbian learning 957 Frank Rosenblatt : Perceptron Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 6
17 Character recognition by Perceptron (,) W j H i (W,H) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 7
18 Perceptron structures and decision boundaries y() = g(a()) = g( w T ) 2 w = (w 0, w,..., w D ) T = (,,..., D ) T {, if a 0, where g(a) = 0, if a < 0 w 0 w w 2 2 a() = + 2 = w 0 +w +w w 0 =, w =, w 2 = NB: A one node/neuron constructs a decision boundary, which splits the input space into two regions Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 8
19 Perceptron as a logical function NOT y 0 0 OR 2 y NAND 2 y OR 2 y Question: find the weights for each function Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 9
20 Perceptron structures and decision boundaries (cont.) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 20
21 Perceptron structures and decision boundaries (cont.) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 2
22 Perceptron structures and decision boundaries (cont.) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 22
23 Perceptron structures and decision boundaries (cont.) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 23
24 Problems with the Perceptron learning algorithm No training algorithms for multi-layer Percepton Non-convergence for linearly non-separable data Weights w are adjusted for misclassified data only (correctly classified data are not considered at all) Consider not only mis-classification (on train data), but also the optimality of decision boundary Least squares error training Large margin classifiers (e.g. SVM) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 24
25 Training with least squares Squared error function: E(w) = N ( ) w T 2 n t n 2 n= Optimisation problem: min E(w) w One way to solve this is to apply gradient descent (steepest descent): w w η w E(w) where η : step size (a small positive const.) ( ) T E E w E(w) =,... w 0 w D Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 25
26 Training with least squares (cont.) E w i = = = w i 2 N n= N ( ) w T 2 n t n n= ( w T n t n ) w i w T n N ( ) w T n t n ni n= Trainable in linearly non-separable case Not robust (sensitive) against errornous data (outliers) far away from the boundary More or less a linear discriminant Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 26
27 Appendi derivatives Derivatives of functions of one variable df d = f f ( + ɛ) f () () = lim ɛ 0 ɛ e.g., f () = 4 3, f () = 2 2 Partial derivatives of functions of more than one variable f = lim f ( + ɛ, y) f (, y) ɛ 0 ɛ e.g., f (, y) = y 3 2, f = 2y 3 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 27
28 Derivative rules Function Derivative Constant c 0 Power n n n Eponential e e Logarithms ln() Sum rule f () + g() f () + g () Product rule f ()g() f ()g() + f ()g () Reciprocal rule f () f () g() f () f 2 () f ()g() f ()g () g 2 () Chain rule f (g()) f (g())g () z = f (y), y = g() dz d = dz dy dy d Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 28
29 Vectors of derivatives Consider f (), where = (,..., D ) T Notation: all partial derivatives put in a vector: ( f f () =, f,, f ) T 2 D Eample: f () = ( f () = ) Fact: f () changes most quickly in direction f () Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 29
30 Gradient descent (steepest descent) First order optimisation algorithm using f () Optimisation problem: min f () Useful when analytic solutions (closed forms) are not available or difficult to find Algorithm Set an initial value 0 and set t = 0 2 If f ( t ) 0, then stop. Otherwise, do the following. 3 t+ = t η f ( t ) for η > 0 4 t = t +, and go to step 2. Problem: stops at a local minimum (difficult to find a global maimum). Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 30
31 Linear regression (one variable) least squares line fitting Training set: D = {( n, t n )} N n= Linear regression: ˆt n = a n + b N Objective function: E = (t i (a i + b)) 2 n= n= Optimisation problem: min E a,b Partial derivatives: E N a = 2 ((t i (a i + b)) ( i ) n= N N N = 2a i 2 + 2b i 2 t i i n= E N b = 2 ((t i (a i + b)) n= N i + 2b N = 2a 2 t i n= n= n= Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 3 n= N
32 Linear regression (one variable) (cont.) Letting E E = 0 and a b = 0 ( N n= i 2 N ) ( n= i a N N n= i n= b ) = ( N n= t i i N n= t i ) Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 32
33 Linear regression (multiple variables) Y 2 E 3.. Linear least squares fitting with. We seek the linear function of that minie sum of squared residuals from Y. Training set: D = {( n, t n )} N n=, where n = (,,..., D ) T Linear regression: ˆt n = w T n Objective function: N ( ) E = tn w T 2 n n= Optimisation problem: min a,b E Elements of Statistical Learning (2nd Ed.) c Hastie, Tibshirani & Friedman 2009 Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 33
34 Linear regression (multiple variables) (cont.) E = N ( ) tn w T 2 n n= E N Partial derivatives: = 2 (t n w T n ) ni w i n= Vector/matri representation (NE) : T 0,..., d t =. =.., T =. N T N0,..., Nd t N E = (T w) T (T w) E w = 2 T (T W ) Letting E = 0 T (T W ) = 0 w T W = T T W = ( T ) T T analytic solution if the inverse eists Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 34
35 Summary Training discriminant functions directly (discriminative training) Perceptron training algorithm Perceptron error correction algorithm Least squares error + gradient descent algorithm Linearly separable vs linearly non-separable Perceptron structures and decision boundaries See Notes for a Perceptron with multiple output nodes Inf2b Learning and Data: Lecture Single layer Neural Networks () 35
Inf2b Learning and Data
 Inf2b Learning and Data Lecture 13: Review (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murray and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR) School of Informatics University of Edinburgh http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/inf2b/
Inf2b Learning and Data Lecture 13: Review (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murray and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR) School of Informatics University of Edinburgh http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/inf2b/
Inf2b Learning and Data
 Inf2b Learnin and Data Lecture 2 (Chapter 2): Multi-laer neural netorks (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murra and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technolo Research (CSTR) School of Informatics Universit
Inf2b Learnin and Data Lecture 2 (Chapter 2): Multi-laer neural netorks (Credit: Hiroshi Shimodaira Iain Murra and Steve Renals) Centre for Speech Technolo Research (CSTR) School of Informatics Universit
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F10 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers
 Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Multi-layer Neural Networks
 Multi-layer Neural Networks Steve Renals Informatics 2B Learning and Data Lecture 13 8 March 2011 Informatics 2B: Learning and Data Lecture 13 Multi-layer Neural Networks 1 Overview Multi-layer neural
Multi-layer Neural Networks Steve Renals Informatics 2B Learning and Data Lecture 13 8 March 2011 Informatics 2B: Learning and Data Lecture 13 Multi-layer Neural Networks 1 Overview Multi-layer neural
Linear Models for Classification
 Linear Models for Classification Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 4 Classification: Hand-written Digit Recognition CHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 24, NO. 24, APRIL 2002 x i = t i = (0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
Linear Models for Classification Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 4 Classification: Hand-written Digit Recognition CHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 24, NO. 24, APRIL 2002 x i = t i = (0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Single layer NN. Neuron Model
 Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification
 Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
More about the Perceptron
 More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
SGN (4 cr) Chapter 5
 SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter 5 Linear Discriminant Analysis Jussi Tohka & Jari Niemi Department of Signal Processing Tampere University of Technology January 21, 2014 J. Tohka & J. Niemi (TUT-SGN) SGN-41006
SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter 5 Linear Discriminant Analysis Jussi Tohka & Jari Niemi Department of Signal Processing Tampere University of Technology January 21, 2014 J. Tohka & J. Niemi (TUT-SGN) SGN-41006
Chapter ML:VI. VI. Neural Networks. Perceptron Learning Gradient Descent Multilayer Perceptron Radial Basis Functions
 Chapter ML:VI VI. Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Gradient Descent Multilayer Perceptron Radial asis Functions ML:VI-1 Neural Networks STEIN 2005-2018 The iological Model Simplified model of a neuron:
Chapter ML:VI VI. Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Gradient Descent Multilayer Perceptron Radial asis Functions ML:VI-1 Neural Networks STEIN 2005-2018 The iological Model Simplified model of a neuron:
y(x n, w) t n 2. (1)
 Network training: Training a neural network involves determining the weight parameter vector w that minimizes a cost function. Given a training set comprising a set of input vector {x n }, n = 1,...N,
Network training: Training a neural network involves determining the weight parameter vector w that minimizes a cost function. Given a training set comprising a set of input vector {x n }, n = 1,...N,
Artificial Neural Networks The Introduction
 Artificial Neural Networks The Introduction 01001110 01100101 01110101 01110010 01101111 01101110 01101111 01110110 01100001 00100000 01110011 01101011 01110101 01110000 01101001 01101110 01100001 00100000
Artificial Neural Networks The Introduction 01001110 01100101 01110101 01110010 01101111 01101110 01101111 01110110 01100001 00100000 01110011 01101011 01110101 01110000 01101001 01101110 01100001 00100000
Neural Networks (Part 1) Goals for the lecture
 Neural Networks (Part ) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 208 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials developed
Neural Networks (Part ) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 208 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials developed
Machine Learning Lecture 5
 Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
In the Name of God. Lecture 11: Single Layer Perceptrons
 1 In the Name of God Lecture 11: Single Layer Perceptrons Perceptron: architecture We consider the architecture: feed-forward NN with one layer It is sufficient to study single layer perceptrons with just
1 In the Name of God Lecture 11: Single Layer Perceptrons Perceptron: architecture We consider the architecture: feed-forward NN with one layer It is sufficient to study single layer perceptrons with just
Machine Learning Lecture 7
 Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Informatics 2B: Learning and Data Lecture 10 Discriminant functions 2. Minimal misclassifications. Decision Boundaries
 Overview Gaussians estimated from training data Guido Sanguinetti Informatics B Learning and Data Lecture 1 9 March 1 Today s lecture Posterior probabilities, decision regions and minimising the probability
Overview Gaussians estimated from training data Guido Sanguinetti Informatics B Learning and Data Lecture 1 9 March 1 Today s lecture Posterior probabilities, decision regions and minimising the probability
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines
 Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Linear Classification. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Linear Classification CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Example of Linear Classification Red points: patterns belonging
Linear Classification CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Example of Linear Classification Red points: patterns belonging
Machine Learning 2017
 Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Artificial Neural Networks
 INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Utrecht University The Netherlands ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Artificial Neural Networks Lecturer: Silja Renooij These slides are part of the INFOB2KI Course Notes available from www.cs.uu.nl/docs/vakken/b2ki/schema.html
INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Utrecht University The Netherlands ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Artificial Neural Networks Lecturer: Silja Renooij These slides are part of the INFOB2KI Course Notes available from www.cs.uu.nl/docs/vakken/b2ki/schema.html
Linear Discrimination Functions
 Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Perceptrons and Support Vector machines
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
April 9, Depto. de Ing. de Sistemas e Industrial Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá. Linear Classification Models. Fabio A. González Ph.D.
 Depto. de Ing. de Sistemas e Industrial Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá April 9, 2018 Content 1 2 3 4 Outline 1 2 3 4 problems { C 1, y(x) threshold predict(x) = C 2, y(x) < threshold, with threshold
Depto. de Ing. de Sistemas e Industrial Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá April 9, 2018 Content 1 2 3 4 Outline 1 2 3 4 problems { C 1, y(x) threshold predict(x) = C 2, y(x) < threshold, with threshold
PMR5406 Redes Neurais e Lógica Fuzzy Aula 3 Single Layer Percetron
 PMR5406 Redes Neurais e Aula 3 Single Layer Percetron Baseado em: Neural Networks, Simon Haykin, Prentice-Hall, 2 nd edition Slides do curso por Elena Marchiori, Vrije Unviersity Architecture We consider
PMR5406 Redes Neurais e Aula 3 Single Layer Percetron Baseado em: Neural Networks, Simon Haykin, Prentice-Hall, 2 nd edition Slides do curso por Elena Marchiori, Vrije Unviersity Architecture We consider
An Introduction to Statistical and Probabilistic Linear Models
 An Introduction to Statistical and Probabilistic Linear Models Maximilian Mozes Proseminar Data Mining Fakultät für Informatik Technische Universität München June 07, 2017 Introduction In statistical learning
An Introduction to Statistical and Probabilistic Linear Models Maximilian Mozes Proseminar Data Mining Fakultät für Informatik Technische Universität München June 07, 2017 Introduction In statistical learning
The Perceptron. Volker Tresp Summer 2016
 The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2016 1 Elements in Learning Tasks Collection, cleaning and preprocessing of training data Definition of a class of learning models. Often defined by the free model parameters
The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2016 1 Elements in Learning Tasks Collection, cleaning and preprocessing of training data Definition of a class of learning models. Often defined by the free model parameters
Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 2
 Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 2 RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Universität Mainz Klausurtagung des GK Eichtheorien exp. Tests... Bullay/Mosel 15 17 September, 2008 1 Outline
Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 2 RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Universität Mainz Klausurtagung des GK Eichtheorien exp. Tests... Bullay/Mosel 15 17 September, 2008 1 Outline
MACHINE LEARNING AND PATTERN RECOGNITION Fall 2004, Lecture 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts Yann LeCun
 Y. LeCun: Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition p. 1/2 MACHINE LEARNING AND PATTERN RECOGNITION Fall 2004, Lecture 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts Yann LeCun The Courant Institute, New York University
Y. LeCun: Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition p. 1/2 MACHINE LEARNING AND PATTERN RECOGNITION Fall 2004, Lecture 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts Yann LeCun The Courant Institute, New York University
Linear Models for Classification
 Linear Models for Classification Henrik I Christensen Robotics & Intelligent Machines @ GT Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332-0280 hic@cc.gatech.edu Henrik I Christensen (RIM@GT) Linear
Linear Models for Classification Henrik I Christensen Robotics & Intelligent Machines @ GT Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332-0280 hic@cc.gatech.edu Henrik I Christensen (RIM@GT) Linear
Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation
 Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation Informatics 1 CG: Lecture 7 Chris Lucas School of Informatics University of Edinburgh January 31, 2017 (Slides adapted from Mirella Lapata s.) 1 / 33 Reading:
Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation Informatics 1 CG: Lecture 7 Chris Lucas School of Informatics University of Edinburgh January 31, 2017 (Slides adapted from Mirella Lapata s.) 1 / 33 Reading:
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1
 Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Outline. Supervised Learning. Hong Chang. Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012)
 Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Linear Models for Regression Linear Regression Probabilistic Interpretation
Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Linear Models for Regression Linear Regression Probabilistic Interpretation
What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1
 What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1 Multi-layer networks Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 7 October 2015 MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 2 What Do Single
What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1 Multi-layer networks Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 7 October 2015 MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 2 What Do Single
NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION Nonlinear Classification and Regression: Outline 2 Multi-Layer Perceptrons The Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm Generalized Linear Models Radial Basis Function
NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION Nonlinear Classification and Regression: Outline 2 Multi-Layer Perceptrons The Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm Generalized Linear Models Radial Basis Function
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
The Perceptron. Volker Tresp Summer 2014
 The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2014 1 Introduction One of the first serious learning machines Most important elements in learning tasks Collection and preprocessing of training data Definition of a
The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2014 1 Introduction One of the first serious learning machines Most important elements in learning tasks Collection and preprocessing of training data Definition of a
Chapter 2 Single Layer Feedforward Networks
 Chapter 2 Single Layer Feedforward Networks By Rosenblatt (1962) Perceptrons For modeling visual perception (retina) A feedforward network of three layers of units: Sensory, Association, and Response Learning
Chapter 2 Single Layer Feedforward Networks By Rosenblatt (1962) Perceptrons For modeling visual perception (retina) A feedforward network of three layers of units: Sensory, Association, and Response Learning
Logistic Regression. COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala
 Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
3.4 Linear Least-Squares Filter
 X(n) = [x(1), x(2),..., x(n)] T 1 3.4 Linear Least-Squares Filter Two characteristics of linear least-squares filter: 1. The filter is built around a single linear neuron. 2. The cost function is the sum
X(n) = [x(1), x(2),..., x(n)] T 1 3.4 Linear Least-Squares Filter Two characteristics of linear least-squares filter: 1. The filter is built around a single linear neuron. 2. The cost function is the sum
The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt.
 1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
Introduction to Natural Computation. Lecture 9. Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation. Peter Lewis
 Introduction to Natural Computation Lecture 9 Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation Peter Lewis 1 / 25 Overview of the Lecture Why multilayer perceptrons? Some applications of multilayer perceptrons.
Introduction to Natural Computation Lecture 9 Multilayer Perceptrons and Backpropagation Peter Lewis 1 / 25 Overview of the Lecture Why multilayer perceptrons? Some applications of multilayer perceptrons.
The Perceptron Algorithm
 The Perceptron Algorithm Greg Grudic Greg Grudic Machine Learning Questions? Greg Grudic Machine Learning 2 Binary Classification A binary classifier is a mapping from a set of d inputs to a single output
The Perceptron Algorithm Greg Grudic Greg Grudic Machine Learning Questions? Greg Grudic Machine Learning 2 Binary Classification A binary classifier is a mapping from a set of d inputs to a single output
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions
 Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Introduction to Neural Networks
 Introduction to Neural Networks Steve Renals Automatic Speech Recognition ASR Lecture 10 24 February 2014 ASR Lecture 10 Introduction to Neural Networks 1 Neural networks for speech recognition Introduction
Introduction to Neural Networks Steve Renals Automatic Speech Recognition ASR Lecture 10 24 February 2014 ASR Lecture 10 Introduction to Neural Networks 1 Neural networks for speech recognition Introduction
Machine Learning Lecture 10
 Machine Learning Lecture 10 Neural Networks 26.11.2018 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Today s Topic Deep Learning 2 Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes
Machine Learning Lecture 10 Neural Networks 26.11.2018 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Today s Topic Deep Learning 2 Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes
CSC Neural Networks. Perceptron Learning Rule
 CSC 302 1.5 Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Rule 1 Objectives Determining the weight matrix and bias for perceptron networks with many inputs. Explaining what a learning rule is. Developing the perceptron
CSC 302 1.5 Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Rule 1 Objectives Determining the weight matrix and bias for perceptron networks with many inputs. Explaining what a learning rule is. Developing the perceptron
Neural networks. Chapter 20. Chapter 20 1
 Neural networks Chapter 20 Chapter 20 1 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer networks Applications of neural networks Chapter 20 2 Brains 10 11 neurons of > 20 types, 10 14 synapses, 1ms
Neural networks Chapter 20 Chapter 20 1 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer networks Applications of neural networks Chapter 20 2 Brains 10 11 neurons of > 20 types, 10 14 synapses, 1ms
Lecture 12. Neural Networks Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen
 Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 12 Neural Networks 10.12.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 12 Neural Networks 10.12.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Course 395: Machine Learning - Lectures
 Course 395: Machine Learning - Lectures Lecture 1-2: Concept Learning (M. Pantic) Lecture 3-4: Decision Trees & CBC Intro (M. Pantic & S. Petridis) Lecture 5-6: Evaluating Hypotheses (S. Petridis) Lecture
Course 395: Machine Learning - Lectures Lecture 1-2: Concept Learning (M. Pantic) Lecture 3-4: Decision Trees & CBC Intro (M. Pantic & S. Petridis) Lecture 5-6: Evaluating Hypotheses (S. Petridis) Lecture
Artificial Neural Network
 Artificial Neural Network Eung Je Woo Department of Biomedical Engineering Impedance Imaging Research Center (IIRC) Kyung Hee University Korea ejwoo@khu.ac.kr Neuron and Neuron Model McCulloch and Pitts
Artificial Neural Network Eung Je Woo Department of Biomedical Engineering Impedance Imaging Research Center (IIRC) Kyung Hee University Korea ejwoo@khu.ac.kr Neuron and Neuron Model McCulloch and Pitts
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9
 Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan Boulder 1 of 39 Recap Supervised learning Previously: KNN, naïve
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan Boulder 1 of 39 Recap Supervised learning Previously: KNN, naïve
Learning Linear Detectors
 Learning Linear Detectors Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Detection versus Classification Bayes Classifiers Linear Classifiers Examples of Detection 3 Learning: Detection
Learning Linear Detectors Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Detection versus Classification Bayes Classifiers Linear Classifiers Examples of Detection 3 Learning: Detection
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons
 Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 7 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Jordan Boyd-Graber Boulder Support Vector Machines 1 of
Support Vector Machines Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 7 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Jordan Boyd-Graber Boulder Support Vector Machines 1 of
Administration. Registration Hw3 is out. Lecture Captioning (Extra-Credit) Scribing lectures. Questions. Due on Thursday 10/6
 Administration Registration Hw3 is out Due on Thursday 10/6 Questions Lecture Captioning (Extra-Credit) Look at Piazza for details Scribing lectures With pay; come talk to me/send email. 1 Projects Projects
Administration Registration Hw3 is out Due on Thursday 10/6 Questions Lecture Captioning (Extra-Credit) Look at Piazza for details Scribing lectures With pay; come talk to me/send email. 1 Projects Projects
Lecture 12. Talk Announcement. Neural Networks. This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning. Recap: Generalized Linear Discriminants
 Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 2 Neural Networks 24..206 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Talk Announcement Yann LeCun (NYU & FaceBook AI) 28..
Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 2 Neural Networks 24..206 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Talk Announcement Yann LeCun (NYU & FaceBook AI) 28..
Artificial Neural Networks. Historical description
 Artificial Neural Networks Historical description Victor G. Lopez 1 / 23 Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) An artificial neural network is a computational model that attempts to emulate the functions of
Artificial Neural Networks Historical description Victor G. Lopez 1 / 23 Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) An artificial neural network is a computational model that attempts to emulate the functions of
Feed-forward Networks Network Training Error Backpropagation Applications. Neural Networks. Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726. Bishop PRML Ch.
 Neural Networks Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 5 Neural Networks Neural networks arise from attempts to model human/animal brains Many models, many claims of biological plausibility We will
Neural Networks Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 5 Neural Networks Neural networks arise from attempts to model human/animal brains Many models, many claims of biological plausibility We will
CMSC 421: Neural Computation. Applications of Neural Networks
 CMSC 42: Neural Computation definition synonyms neural networks artificial neural networks neural modeling connectionist models parallel distributed processing AI perspective Applications of Neural Networks
CMSC 42: Neural Computation definition synonyms neural networks artificial neural networks neural modeling connectionist models parallel distributed processing AI perspective Applications of Neural Networks
COMP9444 Neural Networks and Deep Learning 2. Perceptrons. COMP9444 c Alan Blair, 2017
 COMP9444 Neural Networks and Deep Learning 2. Perceptrons COMP9444 17s2 Perceptrons 1 Outline Neurons Biological and Artificial Perceptron Learning Linear Separability Multi-Layer Networks COMP9444 17s2
COMP9444 Neural Networks and Deep Learning 2. Perceptrons COMP9444 17s2 Perceptrons 1 Outline Neurons Biological and Artificial Perceptron Learning Linear Separability Multi-Layer Networks COMP9444 17s2
Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155. Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent
 Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155 Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent Announcements Homework 1 is out Due Tuesday Jan 12 th at 2pm Via Moodle Sign up for Moodle & Piazza if you haven
Machine Learning & Data Mining CMS/CS/CNS/EE 155 Lecture 2: Perceptron & Gradient Descent Announcements Homework 1 is out Due Tuesday Jan 12 th at 2pm Via Moodle Sign up for Moodle & Piazza if you haven
Learning from Data Logistic Regression
 Learning from Data Logistic Regression Copyright David Barber 2-24. Course lecturer: Amos Storkey a.storkey@ed.ac.uk Course page : http://www.anc.ed.ac.uk/ amos/lfd/ 2.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2...2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9
Learning from Data Logistic Regression Copyright David Barber 2-24. Course lecturer: Amos Storkey a.storkey@ed.ac.uk Course page : http://www.anc.ed.ac.uk/ amos/lfd/ 2.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2...2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Apprentissage, réseaux de neurones et modèles graphiques (RCP209) Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Apprentissage, réseaux de neurones et modèles graphiques (RCP209) Neural Networks and Deep Learning Nicolas Thome Prenom.Nom@cnam.fr http://cedric.cnam.fr/vertigo/cours/ml2/ Département Informatique Conservatoire
Apprentissage, réseaux de neurones et modèles graphiques (RCP209) Neural Networks and Deep Learning Nicolas Thome Prenom.Nom@cnam.fr http://cedric.cnam.fr/vertigo/cours/ml2/ Département Informatique Conservatoire
Linear Discriminant Functions
 Linear Discriminant Functions Linear discriminant functions and decision surfaces Definition It is a function that is a linear combination of the components of g() = t + 0 () here is the eight vector and
Linear Discriminant Functions Linear discriminant functions and decision surfaces Definition It is a function that is a linear combination of the components of g() = t + 0 () here is the eight vector and
Intelligent Systems Discriminative Learning, Neural Networks
 Intelligent Systems Discriminative Learning, Neural Networks Carsten Rother, Dmitrij Schlesinger WS2014/2015, Outline 1. Discriminative learning 2. Neurons and linear classifiers: 1) Perceptron-Algorithm
Intelligent Systems Discriminative Learning, Neural Networks Carsten Rother, Dmitrij Schlesinger WS2014/2015, Outline 1. Discriminative learning 2. Neurons and linear classifiers: 1) Perceptron-Algorithm
Part 8: Neural Networks
 METU Informatics Institute Min720 Pattern Classification ith Bio-Medical Applications Part 8: Neural Netors - INTRODUCTION: BIOLOGICAL VS. ARTIFICIAL Biological Neural Netors A Neuron: - A nerve cell as
METU Informatics Institute Min720 Pattern Classification ith Bio-Medical Applications Part 8: Neural Netors - INTRODUCTION: BIOLOGICAL VS. ARTIFICIAL Biological Neural Netors A Neuron: - A nerve cell as
Deep Neural Networks (1) Hidden layers; Back-propagation
 Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 4 October 2017 / 9 October 2017 MLP Lecture 3 Deep Neural Networs (1) 1 Recap: Softmax single
Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 4 October 2017 / 9 October 2017 MLP Lecture 3 Deep Neural Networs (1) 1 Recap: Softmax single
Lecture 5 Multivariate Linear Regression
 Lecture 5 Multivariate Linear Regression Dan Sheldon September 23, 2014 Topics Multivariate linear regression Model Cost function Normal equations Gradient descent Features Book Data 10 8 Weight (lbs.)
Lecture 5 Multivariate Linear Regression Dan Sheldon September 23, 2014 Topics Multivariate linear regression Model Cost function Normal equations Gradient descent Features Book Data 10 8 Weight (lbs.)
Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification
 Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification Professor Ameet Talwalkar Slide Credit: Professor Fei Sha Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms October 13, 2015
Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification Professor Ameet Talwalkar Slide Credit: Professor Fei Sha Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms October 13, 2015
Mark Gales October y (x) x 1. x 2 y (x) Inputs. Outputs. x d. y (x) Second Output layer layer. layer.
 University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB & EIST Part II Paper I0: Advanced Pattern Processing Handouts 4 & 5: Multi-Layer Perceptron: Introduction and Training x y (x) Inputs x 2 y (x) 2 Outputs x
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB & EIST Part II Paper I0: Advanced Pattern Processing Handouts 4 & 5: Multi-Layer Perceptron: Introduction and Training x y (x) Inputs x 2 y (x) 2 Outputs x
Machine Learning Basics III
 Machine Learning Basics III Benjamin Roth CIS LMU München Benjamin Roth (CIS LMU München) Machine Learning Basics III 1 / 62 Outline 1 Classification Logistic Regression 2 Gradient Based Optimization Gradient
Machine Learning Basics III Benjamin Roth CIS LMU München Benjamin Roth (CIS LMU München) Machine Learning Basics III 1 / 62 Outline 1 Classification Logistic Regression 2 Gradient Based Optimization Gradient
Lecture 4: Feed Forward Neural Networks
 Lecture 4: Feed Forward Neural Networks Dr. Roman V Belavkin Middlesex University BIS4435 Biological neurons and the brain A Model of A Single Neuron Neurons as data-driven models Neural Networks Training
Lecture 4: Feed Forward Neural Networks Dr. Roman V Belavkin Middlesex University BIS4435 Biological neurons and the brain A Model of A Single Neuron Neurons as data-driven models Neural Networks Training
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
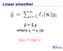 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Supervised Learning. George Konidaris
 Supervised Learning George Konidaris gdk@cs.brown.edu Fall 2017 Machine Learning Subfield of AI concerned with learning from data. Broadly, using: Experience To Improve Performance On Some Task (Tom Mitchell,
Supervised Learning George Konidaris gdk@cs.brown.edu Fall 2017 Machine Learning Subfield of AI concerned with learning from data. Broadly, using: Experience To Improve Performance On Some Task (Tom Mitchell,
Stochastic gradient descent; Classification
 Stochastic gradient descent; Classification Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 2 28 September 2016 MLP Lecture 2 Stochastic gradient descent; Classification 1 Single Layer Networks MLP
Stochastic gradient descent; Classification Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 2 28 September 2016 MLP Lecture 2 Stochastic gradient descent; Classification 1 Single Layer Networks MLP
Neural Networks. Bishop PRML Ch. 5. Alireza Ghane. Feed-forward Networks Network Training Error Backpropagation Applications
 Neural Networks Bishop PRML Ch. 5 Alireza Ghane Neural Networks Alireza Ghane / Greg Mori 1 Neural Networks Neural networks arise from attempts to model human/animal brains Many models, many claims of
Neural Networks Bishop PRML Ch. 5 Alireza Ghane Neural Networks Alireza Ghane / Greg Mori 1 Neural Networks Neural networks arise from attempts to model human/animal brains Many models, many claims of
Networks of McCulloch-Pitts Neurons
 s Lecture 4 Netorks of McCulloch-Pitts Neurons The McCulloch and Pitts (M_P) Neuron x x sgn x n Netorks of M-P Neurons One neuron can t do much on its on, but a net of these neurons x i x i i sgn i ij
s Lecture 4 Netorks of McCulloch-Pitts Neurons The McCulloch and Pitts (M_P) Neuron x x sgn x n Netorks of M-P Neurons One neuron can t do much on its on, but a net of these neurons x i x i i sgn i ij
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771
 Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Neural Networks: Introduction
 Neural Networks: Introduction Machine Learning Fall 2017 Based on slides and material from Geoffrey Hinton, Richard Socher, Dan Roth, Yoav Goldberg, Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Shai Ben-David, and others 1
Neural Networks: Introduction Machine Learning Fall 2017 Based on slides and material from Geoffrey Hinton, Richard Socher, Dan Roth, Yoav Goldberg, Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Shai Ben-David, and others 1
Neural networks. Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 1
 Neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 1 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer perceptrons Applications of neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 2 Brains 10
Neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 1 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer perceptrons Applications of neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 2 Brains 10
Introduction To Artificial Neural Networks
 Introduction To Artificial Neural Networks Machine Learning Supervised circle square circle square Unsupervised group these into two categories Supervised Machine Learning Supervised Machine Learning Supervised
Introduction To Artificial Neural Networks Machine Learning Supervised circle square circle square Unsupervised group these into two categories Supervised Machine Learning Supervised Machine Learning Supervised
The Perceptron. Volker Tresp Summer 2018
 The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2018 1 Elements in Learning Tasks Collection, cleaning and preprocessing of training data Definition of a class of learning models. Often defined by the free model parameters
The Perceptron Volker Tresp Summer 2018 1 Elements in Learning Tasks Collection, cleaning and preprocessing of training data Definition of a class of learning models. Often defined by the free model parameters
Lecture 3: Pattern Classification. Pattern classification
 EE E68: Speech & Audio Processing & Recognition Lecture 3: Pattern Classification 3 4 5 The problem of classification Linear and nonlinear classifiers Probabilistic classification Gaussians, mitures and
EE E68: Speech & Audio Processing & Recognition Lecture 3: Pattern Classification 3 4 5 The problem of classification Linear and nonlinear classifiers Probabilistic classification Gaussians, mitures and
Multilayer Neural Networks
 Multilayer Neural Networks Multilayer Neural Networks Discriminant function flexibility NON-Linear But with sets of linear parameters at each layer Provably general function approximators for sufficient
Multilayer Neural Networks Multilayer Neural Networks Discriminant function flexibility NON-Linear But with sets of linear parameters at each layer Provably general function approximators for sufficient
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Neural Networks
 Machine Learning (CSE 446): Neural Networks Noah Smith c 2017 University of Washington nasmith@cs.washington.edu November 6, 2017 1 / 22 Admin No Wednesday office hours for Noah; no lecture Friday. 2 /
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Neural Networks Noah Smith c 2017 University of Washington nasmith@cs.washington.edu November 6, 2017 1 / 22 Admin No Wednesday office hours for Noah; no lecture Friday. 2 /
Artificial Neuron (Perceptron)
 9/6/208 Gradient Descent (GD) Hantao Zhang Deep Learning with Python Reading: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gradient_descent Artificial Neuron (Perceptron) = w T = w 0 0 + + w 2 2 + + w d d where
9/6/208 Gradient Descent (GD) Hantao Zhang Deep Learning with Python Reading: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gradient_descent Artificial Neuron (Perceptron) = w T = w 0 0 + + w 2 2 + + w d d where
Neural Networks Lecture 2:Single Layer Classifiers
 Neural Networks Lecture 2:Single Layer Classifiers H.A Talebi Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Winter 2011. A. Talebi, Farzaneh Abdollahi Neural
Neural Networks Lecture 2:Single Layer Classifiers H.A Talebi Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Winter 2011. A. Talebi, Farzaneh Abdollahi Neural
Multilayer Neural Networks. (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs)
 Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w x + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature x 2 = w w 2 x w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron can separate
Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w x + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature x 2 = w w 2 x w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron can separate
Introduction to Machine Learning
 1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
