Precision measurements of nuclear CR energy spectra and composition with the AMS-02 experiment
|
|
|
- Angelica McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Precision measurements of nuclear CR energy spectra and composition with the AMS-02 experiment To cite this article: E Fiandrini 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser Related content - AMS-02 in Space: Physics Results Nicola Tomassetti and AMS collaboration - AMS-02 antiprotons: implications for dark matter Mathieu Boudaud - Recent results of the AMS-02 experiment on the ISS Jorge Casaus and AMS Collaboration View the article online for updates and enhancements. This content was downloaded from IP address on 24/12/2018 at 21:19
2 Precision measurements of nuclear CR energy spectra and composition with the AMS-02 experiment E Fiandrini University and INFN Perugia, Via Pascoli snc, Perugia emanuele.fiandrini@pg.infn.it Abstract. The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer 02 (AMS-02) is a large acceptance highenergy physics experiment operating since May 2011 on board the International Space Station. More than 60 billion events have been collected by the instrument in the first four years of operation. AMS-02 offers a unique opportunity to study the Cosmic Rays (CRs) since it measures the spectra of all the species simultaneously. We report on the precision measurements of primary and secondary nuclear spectra, in the GeV-TeV energy interval. These measurements allow for the first time a detailed study of the spectral index variation with rigidity providing a new insight on the origin and propagation of CR. 1. Introduction The origin of the charged cosmic rays (CRs) is one of the major issues of modern astrophysics. The Nature gives us a very energetic beam, but does not provide the beam parameters, which are needed for a proper understanding of their origin. The observables are the CR energy spectra, chemical composition and arrival direction at the Earth s position. From these, the source spectra may be inferred, as well as the features of galactic medium. This implies that for a proper description of the CRs, the comprehension of the relation between observed data and source properties requires a consistent picture of cosmic ray transport in the galaxy. Propagation models take into account the acceleration at the sources, energy losses, nuclear interactions, diffusion and convective transport of CRs in the galactic environment [1,2,3]. The propagation of CR is modelled using the ratio of secondaries, created by fragmentation of heavier elements during the propagation in the interstellar medium (ISM), to primaries, produced and accelerated in the astrophysical sources. In particular, the ratios between light nuclei, such as Lithium, Boron, Beryllium, and their main progenitor, as Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen are used to constrain parameters such as the average amount of interstellar matter traversed by CRs between creation and observation, or their characteristic escape time from our galaxy in Leaky Box models. In diffusive models, the secondary to primary ratios are sensitive to the energy dependence of the diffusion coefficient D. An accurate knowledge of CR observables is important also for the search of exotic signals superimposed to the rare components of the cosmic rays. In fact, the flux from astrophysical sources is the background for any potential signal for new physics and must be estimated on the basis of the existing models of CR production and propagation. Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence. Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI. Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd 1
3 2. The AMS detector The AMS is a high energy magnetic spectrometer installed on the International Space Station since May The detailed description of the detector is presented in Ref. [4]. The relevant elements used in analyses that produced the results presented here are the permanent magnet [5], the silicon tracker, four planes of time of flight (TOF) scintillation counters, and an array of 8 anticoincidence counters (ACC). The AMS is equipped also with a transition radiation detector (TRD), a ring imaging Cherenkov detector (RICH), and an electromagnetic calorimeter (ECAL). The tracker [6] has nine layers, the first (L1) at the top of the detector, the second (L2) above the magnet, six (L3 to L8) within the bore of the magnet, and the last (L9) above the ECAL. L2 to L8 constitute the inner tracker. The tracker accurately determines the trajectory of cosmic rays by multiple measurements of the coordinates. The magnetic spectrometer measures the rigidity R of charged cosmic rays. For Z = 2 particles, the spatial resolution in the tracker layers is ~7 μm in the bending direction and the maximum detectable rigidity (MDR) is 3.2 TV over the 3 m lever arm from L1 to L9. Each layer of the tracker provides an independent measurement of the charge Z of the cosmic ray. The charge resolution of the combined inner tracker is ΔZ 0.07 for Z=2 particles. Two planes of TOF counters [12] are located above L2 and two planes are located below the magnet. The overall velocity (β=v/c) resolution has been measured to be Δβ/β 2 =0.02 for Z=2 particles. The signals from the two upper layers are combined to get an independent measurement of the charge with an accuracy ΔZ 0.08 for Z=2. The signals from the two lower planes provide another independent charge measurement with the same accuracy. This allows for multiple independent charge measurements along the particle trajectory in the detector, which is crucial for the nuclei specie identification. AMS can measure the particle charge up to iron (Z=26) and it provides a very good charge separation for light nuclei up to Oxygen, as shown in Fig 1. Figure 1. Tracker charge distribution of the light nuclei, as measured by the energy deposits in the tracker planes. For a given charge, the contamination due to other charges is well below % level up to Oxygen. Actually, the major background for such kind of species is the production of light nuclei inside the detector material from heavier elements crossing it, due to inelastic interactions. Thanks to the multiple charge measurements capability in the upper and lower detectors of the instrument, inelastic interactions in the detector material can be rejected with high efficiency (>96%) and low contamination (<3%). TheAMS nuclear fluxes The isotropic flux Φ for the in the rigidity bin (R, R+ΔR) is: 2
4 Φ = N AεTΔR where N is the number of events corrected with the rigidity resolution function, A is the effective acceptance, ε is the trigger efficiency, and T is the exposure time. Extensive studies of the systematic errors were made. These errors include the uncertainties in the trigger efficiency, the geomagnetic cutoff factor, the acceptance taking into account the event selection and reconstruction and also accounting for particle interactions in the detector, the unfolding, the rigidity resolution function, the absolute rigidity scale, and the background contamination discussed above. Statistical errors are negligible for protons and Helium which are dominated by systematic errors over the whole range of energies studied, while light nuclei such as Li, B, C are dominated by the statistical errors at high energies. The proton flux is shown in Fig. 2, as a function of the kinetic energy in the the range 1-2 TeV/n, together with some data from previous experiments. The details of proton flux analysis can be found in Ref.[7]. Total error (statistical + systematic) is ~6% at 1.8 TeV/n. The flux is well fitted with a double power law, with a continuous change in the protons flux slope observed at ~336 GeV, where the slope changes from γ= to Figure 2. Proton flux multiplied by E 2.7 as a function of kinetic energy. Figure 3. Helium flux multiplied by E 2.7 as a function of the kinetic energy per nucleon. 3
5 Helium flux is shown in Fig. 3 as a function of kinetic energy up to 2 TeV/n. The details of the analysis can be found in Ref. [8]. Total error (statistical + systematic) is ~8% at 2 TeV/n. As for the protons, the He flux is well fitted by a double power law, with a continuous change in the helium flux slope observed at ~245 GV, where the slope changes from γ=-2.78 to Boron-to-Carbon Ratio AMS-02 PAMELA (2014) TRACER (2006) CREAM-I (2004) ATIC-02 (2003) AMS-01 (1998) Buckley et al. (1991) CRN-Spacelab2 (1985) Webber et al. (1981) HEAO3-C2 (1980) Simon et al. ( ) Dwyer & Meyer ( ) Orth et al. (1972) Kinetic Energy (GeV/n) Figure 4. Boron over Carbon ratio as a function of kinetic energy per nucleon In Fig.4 the current status of the Boron to Carbon (B/C) flux ratio measurement with AMS is shown up to ~1 TeV/n, together with some previous experimental results [9]. The error is ~10% at 1 Tev/n. The experimental uncertainties at high energy are dominated by the limited statistics, which is 10% of the expected total data sample that AMS will be able to collect during its long term operation on ISS. It's clear the capability of AMS to provide the first precise measurement of the B/C ratio at very high energy and it will help in solving the model parameters degeneracy. It's clear the capability of AMS to provide the first precise measurement. AMS Orth et al (1978) Juliusson et al (1974) Figure 5. Lithium flux as a function of the rigidity R. 4
6 Like Boron and Berillium, Lithium is produced by the spallation of heavier nuclei during the propagation in the galaxy with the ISM (C, N, O,, Fe + ISM --> Li, Be, B) [10] and is sensitive to CR propagation parameters as diffusion, convection, reacceleration. Fig. 5 shows the current status of the Li flux measurement as a function of rigidity R up to 300 GV[10]. A change of spectral index as a function of rigidity is observed in the Li spectrum as for the lighter primary CR species, however - due to the faintness of the Li flux - further investigation of possible systematics effects and a larger collected statistics are needed to accurately evaluate this effect. Conclusions AMS provides the most accurate measurements of H and He in the rigidity range between 1 GV and 2 TV, and 1 GV and 3 TV, respectively. A continuous spectral change is observed for both H and He at about the same energy, a possible indication of a feature at the sources or a propagation effect. The proton to He flux ratio is well described by a single power law above 45 GV [9], which is unexpected if the two species have a common origin. The new precise measurement that AMS will provide on other primary CR nuclear flux ratios, as C/He or C/O, will add valuable information to better understand the origin of this behaviour. At the same time, the simultaneous measurement of secondary components as B/C or Li, whose current status has been reported, will represent a crucial input for any reliable propagation model of CR in the galactic environment. Acknowledgments This work has been supported by acknowledged persons and institutions in the published papers about the AMS-02 proton and He measurements [8,9]. References [1] Strong A et al 2007 Annual Rev. of Nucl. and Part. Sci [2] Maurin D et al 2001 Astrophys J [3] de Nolfo G et al 2006 Adv. Space Res [4] Kounine A 2012 Int. J. Mod. Phys. E ; Rosier-Lees S 2015 in Proceedings of Astroparticle Physics TEVPA/IDM, Amsterdam (to be published); Ting S 2013 Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) ; Bertucci B 2011 Proc. Sci. EPS-HEP 67; Incagli M 2010 AIP Conf. Proc ; Battiston R 2008 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A [5] Lübelsmeyer K et al 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A [6] Alpat B et al. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A [7] AMS collaboration 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett [8] Aguilar M et al (AMS Collaboration) 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 [9] Oliva A th ICRC The Hague 265 [10] Derome L th ICRC The Hague 303 5
The Latest Results from AMS on the International Space Station
 The on the International Space Station Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge MA 02139, US E-mail: Samuel.Ting@cern.ch In four years on the International Space Station,
The on the International Space Station Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge MA 02139, US E-mail: Samuel.Ting@cern.ch In four years on the International Space Station,
Dark Matter Searches with AMS-02. AMS: Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
 Dark Matter Searches with AMS-02 AMS: Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer 2007/2008 Wim de Boer on behalf of the AMS collaboration University of Karlsruhe July, 20. 2004 COSPAR, Paris, W. de Boer, Univ. Karlsruhe
Dark Matter Searches with AMS-02 AMS: Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer 2007/2008 Wim de Boer on behalf of the AMS collaboration University of Karlsruhe July, 20. 2004 COSPAR, Paris, W. de Boer, Univ. Karlsruhe
The PAMELA Satellite Experiment: An Observatory in Space for Particles, Antiparticles and Nuclei in the Cosmic Rays
 : An Observatory in Space for Particles, Antiparticles and Nuclei in the Cosmic Rays M. Ricci 1 on behalf of the PAMELA Collaboration INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Via Enrico Fermi 40, I-00044
: An Observatory in Space for Particles, Antiparticles and Nuclei in the Cosmic Rays M. Ricci 1 on behalf of the PAMELA Collaboration INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Via Enrico Fermi 40, I-00044
Current and Future balloon and space experiments L. Derome (LPSC Grenoble) Tango, May 4-6th, 2009
 Current and Future balloon and space experiments L. Derome (LPSC Grenoble) Tango, May 4-6th, 2009 L. Derome, Tango, May 4-6th 2009 1 Plan I will focus on: Future experiments which are going to measure
Current and Future balloon and space experiments L. Derome (LPSC Grenoble) Tango, May 4-6th, 2009 L. Derome, Tango, May 4-6th 2009 1 Plan I will focus on: Future experiments which are going to measure
Cosmic Ray Physics with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
 Cosmic Ray Physics with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Università di Roma La Sapienza, INFN on behalf of AMS Collaboration Outline Introduction AMS02 Spectrometer Cosmic Rays: origin & propagations: Dominant
Cosmic Ray Physics with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Università di Roma La Sapienza, INFN on behalf of AMS Collaboration Outline Introduction AMS02 Spectrometer Cosmic Rays: origin & propagations: Dominant
New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station. Henning Gast RWTH Aachen
 New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station Henning Gast RWTH Aachen 1 Questions to AMS-02: Are there galaxies made of anti-matter in the Universe? What is the nature of Dark
New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station Henning Gast RWTH Aachen 1 Questions to AMS-02: Are there galaxies made of anti-matter in the Universe? What is the nature of Dark
Measurements of Heavy Nuclei with the CALET Experiment
 Measurements of Heavy Nuclei with the CALET Experiment for the CALET Collaboration University of Maryland, Baltimore County and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 8 Greenbelt Rd. Greenbelt, MD 771, USA E-mail:
Measurements of Heavy Nuclei with the CALET Experiment for the CALET Collaboration University of Maryland, Baltimore County and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 8 Greenbelt Rd. Greenbelt, MD 771, USA E-mail:
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 3 Feb 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 3 Feb 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 3 Feb 2014](/thumbs/74/70088395.jpg) The cosmic ray electron and positron spectra measured by AMS-0 Claudio Corti, on behalf of the AMS-0 collaboration Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu - HI (US) arxiv:40.047v
The cosmic ray electron and positron spectra measured by AMS-0 Claudio Corti, on behalf of the AMS-0 collaboration Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu - HI (US) arxiv:40.047v
GeV to Multi-TeV Cosmic Rays: AMS-02 Status and Future Prospects
 : AMS-02 Status and Future Prospects DPNC and Center for Astroparticle Physics (CAP Genève) Université de Genève E-mail: martin.pohl@cern.ch Due to recent observations, there is a renewed interest in GeV
: AMS-02 Status and Future Prospects DPNC and Center for Astroparticle Physics (CAP Genève) Université de Genève E-mail: martin.pohl@cern.ch Due to recent observations, there is a renewed interest in GeV
Cosmic Ray panorama. Pamela.roma2.infn.it PAMELA (2012) Experimental challenges : e + /p ~ 10-3 e + /e - ~ 10-1
 1912 1932 Cosmic Ray panorama http::// Pamela.roma2.infn.it PAMELA (2012) Experimental challenges : e + /p ~ 10-3 e + /e - ~ 10-1 Pamela : < 0.1 evt year/gev Flux E α α 2.7 / 3.3 Statistical precision
1912 1932 Cosmic Ray panorama http::// Pamela.roma2.infn.it PAMELA (2012) Experimental challenges : e + /p ~ 10-3 e + /e - ~ 10-1 Pamela : < 0.1 evt year/gev Flux E α α 2.7 / 3.3 Statistical precision
Indirect Search for Dark Matter with AMS-02
 Indirect Search for Dark Matter with AMS-02 A. Malinin, UMD For the AMS Collaboration SUSY06, UC Irvine, June 14, 2006 Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer science The AMS is a particle physics experiment in space.
Indirect Search for Dark Matter with AMS-02 A. Malinin, UMD For the AMS Collaboration SUSY06, UC Irvine, June 14, 2006 Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer science The AMS is a particle physics experiment in space.
AMS-02 Antiprotons Reloaded
 AMS-02 Antiprotons Reloaded Martin W. Winkler in collaboration with R. Kappl and A. Reinert based on JCAP 09/2014 and arxiv:1506.04145 TAUP 2015 Torino September 9 2015 Martin W. Winkler (Bonn University)
AMS-02 Antiprotons Reloaded Martin W. Winkler in collaboration with R. Kappl and A. Reinert based on JCAP 09/2014 and arxiv:1506.04145 TAUP 2015 Torino September 9 2015 Martin W. Winkler (Bonn University)
Primary Cosmic Rays : what are we learning from AMS
 Primary Cosmic Rays : what are we learning from AMS Roberto Battiston University and INFN-TIFPA of Trento HERD Workshop IHEP-Beijing December 2-3 2013 1 Agile Fermi PAMELA AMS Direct study of the HESS
Primary Cosmic Rays : what are we learning from AMS Roberto Battiston University and INFN-TIFPA of Trento HERD Workshop IHEP-Beijing December 2-3 2013 1 Agile Fermi PAMELA AMS Direct study of the HESS
Chapter 6.2: space based cosmic ray experiments. A. Zech, Instrumentation in High Energy Astrophysics
 Chapter 6.2: space based cosmic ray experiments 1 A bit of history... space based experiments 1912-1950: first observations of the cosmic ray flux with detectors onboard balloons and air-planes. 1950s/60s:
Chapter 6.2: space based cosmic ray experiments 1 A bit of history... space based experiments 1912-1950: first observations of the cosmic ray flux with detectors onboard balloons and air-planes. 1950s/60s:
Antiproton Flux and Antiproton-to-Proton Flux Ratio in Primary Cosmic Rays Measured with AMS on the Space Station
 Antiroton Flux and Antiroton-to-Proton Flux Ratio in Primary Cosmic Rays Measured with AMS on the Sace Station Andreas Bachlechner on behalf of the AMS collaboration 3 07.08.017 von TeVPA 017, Columbus
Antiroton Flux and Antiroton-to-Proton Flux Ratio in Primary Cosmic Rays Measured with AMS on the Sace Station Andreas Bachlechner on behalf of the AMS collaboration 3 07.08.017 von TeVPA 017, Columbus
Operation and Performance of the AMS-02 Silicon Tracker
 Operation and Performance of the AMS-02 Silicon Tracker Saouter, P. Université de Genève, 24 Quai Ernest-Ansermet, Genève, Switzerland. E-mail: Pierre.Erwan.Saouter@cern.ch The AMS-02 magnetic spectrometer
Operation and Performance of the AMS-02 Silicon Tracker Saouter, P. Université de Genève, 24 Quai Ernest-Ansermet, Genève, Switzerland. E-mail: Pierre.Erwan.Saouter@cern.ch The AMS-02 magnetic spectrometer
Antimatter and DM search in space with AMS Introduction. 2 Cosmology with Cosmic Rays
 Antimatter and DM search in space with AMS-02 Francesca R. Spada Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Piazzale Aldo Moro, 5 I-00185, Rome, ITALY 1 Introduction AMS-02 is a space-borne magnetic spectrometer
Antimatter and DM search in space with AMS-02 Francesca R. Spada Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Piazzale Aldo Moro, 5 I-00185, Rome, ITALY 1 Introduction AMS-02 is a space-borne magnetic spectrometer
PAMELA satellite: fragmentation in the instrument
 PAMELA satellite: fragmentation in the instrument Alessandro Bruno INFN, Bari (Italy) for the PAMELA collaboration Nuclear Physics for Galactic CRs in the AMS-02 era 3-4 Dec 2012 LPSC, Grenoble The PAMELA
PAMELA satellite: fragmentation in the instrument Alessandro Bruno INFN, Bari (Italy) for the PAMELA collaboration Nuclear Physics for Galactic CRs in the AMS-02 era 3-4 Dec 2012 LPSC, Grenoble The PAMELA
Gamma ray and antiparticles (e + and p) as tools to study the propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy
 Gamma ray and antiparticles (e + and p) as tools to study the propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy INFN Sez. La Sapienza, Rome, Italy E-mail: paolo.lipari@roma1.infn.it The spectra of cosmic rays observed
Gamma ray and antiparticles (e + and p) as tools to study the propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy INFN Sez. La Sapienza, Rome, Italy E-mail: paolo.lipari@roma1.infn.it The spectra of cosmic rays observed
High-energy Gamma Rays detection with the AMS-02 electromagnetic calorimeter. F. Pilo for the AMS-02 ECAL Group INFN Sezione di Pisa, Italy
 Frascati Physics Series Vol. 58 (2014) Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics May 18-24, 2014 High-energy Gamma Rays detection with the AMS-02 electromagnetic calorimeter F. Pilo for the
Frascati Physics Series Vol. 58 (2014) Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics May 18-24, 2014 High-energy Gamma Rays detection with the AMS-02 electromagnetic calorimeter F. Pilo for the
DARK MATTER SEARCHES WITH AMS-02 EXPERIMENT
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES WITH AMS-02 EXPERIMENT A.Malinin a, For AMS Collaboration IPST, University of Maryland, MD-20742, College Park, USA Abstract. The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), to be installed
DARK MATTER SEARCHES WITH AMS-02 EXPERIMENT A.Malinin a, For AMS Collaboration IPST, University of Maryland, MD-20742, College Park, USA Abstract. The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), to be installed
Introduction History of Cosmic Ray Studies: Origin, Propagation, Spectrum, Composition
 Etat actuel et Perspectives de la Physique d'astro-particule Daniel Haas DPNC Geneva Introduction History of Cosmic Ray Studies: Origin, Propagation, Spectrum, Composition Selected Experiments & Results
Etat actuel et Perspectives de la Physique d'astro-particule Daniel Haas DPNC Geneva Introduction History of Cosmic Ray Studies: Origin, Propagation, Spectrum, Composition Selected Experiments & Results
AMS Results on the Properties of the Fluxes of Elementary Particles and Nuclei in Primary Cosmic Rays
 AMS Results on the Properties of the Fluxes of Elementary Particles and Nuclei in Primary Cosmic Rays Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA E-mail: Andrei.Kounine@cern.ch Precision measurements
AMS Results on the Properties of the Fluxes of Elementary Particles and Nuclei in Primary Cosmic Rays Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA E-mail: Andrei.Kounine@cern.ch Precision measurements
PoS(ICRC2017)1076. Studies of Cosmic-Ray Proton Flux with the DAMPE Experiment
 Studies of Cosmic-Ray Proton Flux with the DAMPE Experiment,, Jing-Jing Zang,Tie-Kuang Dong, Antonio Surdo,, Stefania Vitillo 5, on behalf of the DAMPE collaboration Key Laboratory of Dark Matter and Space
Studies of Cosmic-Ray Proton Flux with the DAMPE Experiment,, Jing-Jing Zang,Tie-Kuang Dong, Antonio Surdo,, Stefania Vitillo 5, on behalf of the DAMPE collaboration Key Laboratory of Dark Matter and Space
Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02
 Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02 Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 96822, HI, US E-mail: bindi@hawaii.edu AMS-02 collaboration The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02 Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 96822, HI, US E-mail: bindi@hawaii.edu AMS-02 collaboration The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
AMS-02 measurement of cosmic ray positrons and electrons
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings 7 75 (16) 466 47 www.elsevier.com/locate/nppp AMS- measurement of cosmic ray positrons and electrons Z.L. Weng a, V. Vagelli
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings 7 75 (16) 466 47 www.elsevier.com/locate/nppp AMS- measurement of cosmic ray positrons and electrons Z.L. Weng a, V. Vagelli
Experimental review of high-energy e e + and p p spectra
 Experimental review of high-energy e e + and p p spectra Luca Baldini INFN Pisa luca.baldini@pi.infn.it TeV Particle Astrophysics, July 15 2009 Outline Measurement of the singly charged component of the
Experimental review of high-energy e e + and p p spectra Luca Baldini INFN Pisa luca.baldini@pi.infn.it TeV Particle Astrophysics, July 15 2009 Outline Measurement of the singly charged component of the
Cosmic Ray Composition
 + = Cosmic Ray Composition Stéphane Coutu The Pennsylvania State University 3 rd rd School on Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics Arequipa,, Peru August 28-29, 29, 2008 1/ 30 Outline Cosmic Rays: Origin and Propagation;
+ = Cosmic Ray Composition Stéphane Coutu The Pennsylvania State University 3 rd rd School on Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics Arequipa,, Peru August 28-29, 29, 2008 1/ 30 Outline Cosmic Rays: Origin and Propagation;
AMS-02 Antiprotons Reloaded
 AMS-02 Antiprotons Reloaded Rolf Kappl Bethe Center for Theoretical Physics & Physikalisches Institut der Universität Bonn based on RK, Annika Reinert, Martin Wolfgang Winkler JCAP 10 (2015) 034, arxiv:1506.04145
AMS-02 Antiprotons Reloaded Rolf Kappl Bethe Center for Theoretical Physics & Physikalisches Institut der Universität Bonn based on RK, Annika Reinert, Martin Wolfgang Winkler JCAP 10 (2015) 034, arxiv:1506.04145
Lomonosov Moscow State University. NUCLEON Chemical Composition and Energy Spectra of Cosmic Rays at TeV
 Lomonosov Moscow State University NUCLEON Chemical Composition and Energy Spectra of Cosmic Rays at 1-1000 TeV D. Podorozhny for Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 11-14, 2018 NUCLEON
Lomonosov Moscow State University NUCLEON Chemical Composition and Energy Spectra of Cosmic Rays at 1-1000 TeV D. Podorozhny for Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 11-14, 2018 NUCLEON
Spectral Intensities of Antiprotons and the Lifetime Of Cosmic Rays
 Spectral Intensities of Antiprotons and the Lifetime Of Cosmic Rays Physics Department and McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences Washington University, St. Louis, MO 63130, USA E-mail: cowsik@wustl.edu
Spectral Intensities of Antiprotons and the Lifetime Of Cosmic Rays Physics Department and McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences Washington University, St. Louis, MO 63130, USA E-mail: cowsik@wustl.edu
Results from the PAMELA Space Experiment
 Results from the PAMELA Space Experiment Emiliano Mocchiutti INFN Trieste, Italy On behalf of the PAMELA collaboration VULCANO Workshop 2014 Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics 18th -
Results from the PAMELA Space Experiment Emiliano Mocchiutti INFN Trieste, Italy On behalf of the PAMELA collaboration VULCANO Workshop 2014 Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics 18th -
Payload for Antimatter Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics. PAMELA MissioN 17 December 2010 Prepared by FatiH KAYA
 Payload for Antimatter Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics PAMELA MissioN 17 December 2010 Prepared by FatiH KAYA Astropartical Physics İssue To inform. What Powered the Big Bang? Inflation
Payload for Antimatter Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics PAMELA MissioN 17 December 2010 Prepared by FatiH KAYA Astropartical Physics İssue To inform. What Powered the Big Bang? Inflation
From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition
 New Views of the Universe December 8 th 13 th, 2005, Chicago From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition Jörg R. Hörandel University of Karlsruhe www-ik.fzk.de/~joerg New Views of
New Views of the Universe December 8 th 13 th, 2005, Chicago From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition Jörg R. Hörandel University of Karlsruhe www-ik.fzk.de/~joerg New Views of
PoS(ICRC2015)540. Uncertainties on propagation parameters: impact on the interpretation of the positron fraction
 Uncertainties on propagation parameters: impact on the interpretation of the positron fraction Mathieu Boudaud a, Sandy Aupetit a, Sami Caroff b, Antje Putze a, Geneviève Bélanger a, a, Corine Goy b, Vincent
Uncertainties on propagation parameters: impact on the interpretation of the positron fraction Mathieu Boudaud a, Sandy Aupetit a, Sami Caroff b, Antje Putze a, Geneviève Bélanger a, a, Corine Goy b, Vincent
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 18 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 18 Nov 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 18 Nov 2014](/thumbs/94/119022614.jpg) SNSN-XXX-YY November 15,2014 Cosmic Ray Physics arxiv:1411.4642v2 [astro-ph.he] 18 Nov 2014 Domenico D Urso 1 Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), sez. Perugia Via A. Pascoli, I-06123 Perugia,
SNSN-XXX-YY November 15,2014 Cosmic Ray Physics arxiv:1411.4642v2 [astro-ph.he] 18 Nov 2014 Domenico D Urso 1 Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), sez. Perugia Via A. Pascoli, I-06123 Perugia,
W.R. Webber. New Mexico State University, Astronomy Department, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA
 Interstellar Spectra of Primary Cosmic Ray Nuclei from H through Fe Measured at Voyager and a Comparison with Higher Energy Measurements of These Same Nuclei Made Near the Earth An Interpretation of the
Interstellar Spectra of Primary Cosmic Ray Nuclei from H through Fe Measured at Voyager and a Comparison with Higher Energy Measurements of These Same Nuclei Made Near the Earth An Interpretation of the
Performance of the AMS-02 Electromagnetic Calorimeter in Space
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Performance of the AMS-02 Electromagnetic Calorimeter in Space To cite this article: G Gallucci and the AMS-02 ECAL group 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 587
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Performance of the AMS-02 Electromagnetic Calorimeter in Space To cite this article: G Gallucci and the AMS-02 ECAL group 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 587
SIMULATION OF THE GAMMA-RAY GALACTIC DISTRIBUTION AS SEEN BY THE AMS-02
 SIMULATION OF THE GAMMA-RAY GALACTIC DISTRIBUTION AS SEEN BY THE AMS-02 M. Mollá 1, J.Alcaraz 1, J.Berdugo 1, J.Bolmont 2, J.Casaus 1, E.Lanciotti 1, C.Mañá 1, C.Palomares 1, E.Sánchez 1, F.J.Rodríguez
SIMULATION OF THE GAMMA-RAY GALACTIC DISTRIBUTION AS SEEN BY THE AMS-02 M. Mollá 1, J.Alcaraz 1, J.Berdugo 1, J.Bolmont 2, J.Casaus 1, E.Lanciotti 1, C.Mañá 1, C.Palomares 1, E.Sánchez 1, F.J.Rodríguez
Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration
 Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
Relative abundance of elements at Earth
 Relative abundance of elements at Earth cosmic rays - solar system ~ 1 GeV/n Si = 100 JRH, Adv. Space Res. 41 (2008) 442 TRACER Energy Spectra for individual elements D. Müller et al., ICRC 2007 Energy
Relative abundance of elements at Earth cosmic rays - solar system ~ 1 GeV/n Si = 100 JRH, Adv. Space Res. 41 (2008) 442 TRACER Energy Spectra for individual elements D. Müller et al., ICRC 2007 Energy
The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station
 The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station Ignacio Sevilla 1 on behalf of the AMS Collaboration CIEMAT, Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas Medioambientales y Tecnológicas, Av.
The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station Ignacio Sevilla 1 on behalf of the AMS Collaboration CIEMAT, Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas Medioambientales y Tecnológicas, Av.
Introduction to Cosmic Rays Data Analysis Issues. Nicola De Simone INFN and University of Rome Tor Vergata
 Introduction to Cosmic Rays Data Analysis Issues Nicola De Simone INFN and University of Rome Tor Vergata SciNeGHE 2010 - Data Analysis Tutorial Trieste, September 8-9, 2010 The physics of PAMELA PRL 102,
Introduction to Cosmic Rays Data Analysis Issues Nicola De Simone INFN and University of Rome Tor Vergata SciNeGHE 2010 - Data Analysis Tutorial Trieste, September 8-9, 2010 The physics of PAMELA PRL 102,
Measurement of CR anisotropies with the AMS detector on the ISS
 Measurement of CR anisotropies with the AMS detector on the ISS J. Casaus ( CIEMAT Spain ) on behalf of the AMS Collaboration Origin of excess of positrons Positron fraction shows an excess above 10 GeV
Measurement of CR anisotropies with the AMS detector on the ISS J. Casaus ( CIEMAT Spain ) on behalf of the AMS Collaboration Origin of excess of positrons Positron fraction shows an excess above 10 GeV
Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary. Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! Ilias Cholis, 08/09/2017
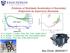 C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays. TeVPA Aug. 7, Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan
 Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays TeVPA Aug. 7, 2017 Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan Elementary Particles in Space There are hundreds of different kinds of charged
Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays TeVPA Aug. 7, 2017 Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan Elementary Particles in Space There are hundreds of different kinds of charged
Antimatter in Space. Mirko Boezio INFN Trieste, Italy. PPC Torino July 14 th 2010
 Antimatter in Space Mirko Boezio INFN Trieste, Italy PPC 2010 - Torino July 14 th 2010 Astrophysics and Cosmology compelling Issues Apparent absence of cosmological Antimatter Nature of the Dark Matter
Antimatter in Space Mirko Boezio INFN Trieste, Italy PPC 2010 - Torino July 14 th 2010 Astrophysics and Cosmology compelling Issues Apparent absence of cosmological Antimatter Nature of the Dark Matter
PAMELA: a Satellite Experiment for Antiparticles Measurement in Cosmic Rays
 PAMELA: a Satellite Experiment for Antiparticles Measurement in Cosmic Rays PAMELA scientific objectives Detector s overview Subsystems description PAMELA status Massimo Bongi Universita degli Studi di
PAMELA: a Satellite Experiment for Antiparticles Measurement in Cosmic Rays PAMELA scientific objectives Detector s overview Subsystems description PAMELA status Massimo Bongi Universita degli Studi di
Precision Cosmic Ray physics with space-born experiment
 Precision Cosmic Ray physics with space-born experiment Marco Incagli a Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), Pisa, Italy Abstract. More than 100 years after their discoveries, cosmic rays have
Precision Cosmic Ray physics with space-born experiment Marco Incagli a Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), Pisa, Italy Abstract. More than 100 years after their discoveries, cosmic rays have
AMS : A Cosmic Ray Observatory
 Nuclear Physics B (Proc. Suppl.) 150 (2006) 24 29 www.elsevierphysics.com AMS : A Cosmic Ray Observatory Jean-Pierre Vialle a for the AMS collaboration a Laboratoire d'annecy-le-vieux de Physique des Particules
Nuclear Physics B (Proc. Suppl.) 150 (2006) 24 29 www.elsevierphysics.com AMS : A Cosmic Ray Observatory Jean-Pierre Vialle a for the AMS collaboration a Laboratoire d'annecy-le-vieux de Physique des Particules
Parameters Sensitive to the Mass Composition of Cosmic Rays and Their Application at the Pierre Auger Observatory
 WDS'12 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 137 141, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7378-226-9 MATFYZPRESS Parameters Sensitive to the Mass Composition of Cosmic Rays and Their Application at the Pierre Auger
WDS'12 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 137 141, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7378-226-9 MATFYZPRESS Parameters Sensitive to the Mass Composition of Cosmic Rays and Their Application at the Pierre Auger
Topics. 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: 2. AMS-02 good candidates for Dark Matter space search
 Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1 The PAMELA apparatus. The PAMELA apparatus is inserted inside a pressurized container (2 mm aluminum window) attached to the Russian Resurs-DK1 satellite. The apparatus, approximately 13 cm tall and
1 The PAMELA apparatus. The PAMELA apparatus is inserted inside a pressurized container (2 mm aluminum window) attached to the Russian Resurs-DK1 satellite. The apparatus, approximately 13 cm tall and
The AMS-02 Anticoincidence Counter
 The AMS-02 Anticoincidence Counter, W. Karpinski, Th. Kirn, K. Lübelsmeyer, St. Schael, M. Wlochal on behalf of the AMS-02 Collaboration philip.doetinchem@rwth-aachen.de I. Phys. Inst. B, RWTH Aachen University
The AMS-02 Anticoincidence Counter, W. Karpinski, Th. Kirn, K. Lübelsmeyer, St. Schael, M. Wlochal on behalf of the AMS-02 Collaboration philip.doetinchem@rwth-aachen.de I. Phys. Inst. B, RWTH Aachen University
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants
 Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Cosmic-Ray Isotopic Identification with the Geomagnetic Field for Space Experiments.
 ICRC 11 - Beijing 11-18 August 11 Cosmic-Ray Isotopic Identification with the Geomagnetic Field for Space Experiments. W. GILLARD, F. BARAO, L. DEROME L The cosmic-ray diffusion: A two zone diffusion model
ICRC 11 - Beijing 11-18 August 11 Cosmic-Ray Isotopic Identification with the Geomagnetic Field for Space Experiments. W. GILLARD, F. BARAO, L. DEROME L The cosmic-ray diffusion: A two zone diffusion model
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114, A02103, doi: /2008ja013689, 2009
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013689, 2009 Galactic propagation of cosmic ray nuclei in a model with an increasing diffusion coefficient at low
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013689, 2009 Galactic propagation of cosmic ray nuclei in a model with an increasing diffusion coefficient at low
The NUCLEON Space Experiment Preliminary Results. Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, Moscow, , Russia
 The NUCLEON Space Experiment Preliminary Results A. Turundaevskiy a1, E.Atkin a, V.Bulatov c, V.Dorokhov c, N.Gorbunov d, S.Filippov c, V.Grebenyuk d, D.Karmanov a, I.Kovalev a, I.Kudryashov a, M.Merkin
The NUCLEON Space Experiment Preliminary Results A. Turundaevskiy a1, E.Atkin a, V.Bulatov c, V.Dorokhov c, N.Gorbunov d, S.Filippov c, V.Grebenyuk d, D.Karmanov a, I.Kovalev a, I.Kudryashov a, M.Merkin
Study of muon bundles from extensive air showers with the ALICE detector at CERN LHC
 doi:.88/174-6596/718/5/0509 Study of muon bundles from extensive air showers with the ALICE detector at CERN LHC K Shtejer 1, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica dell'università and Sezione INFN, Turin, Italy Centro
doi:.88/174-6596/718/5/0509 Study of muon bundles from extensive air showers with the ALICE detector at CERN LHC K Shtejer 1, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica dell'università and Sezione INFN, Turin, Italy Centro
The Ring Imaging Cherenkov detector of the AMS experiment: test beam results with a prototype
 The Ring Imaging Cherenkov detector of the AMS experiment: test beam results with a prototype Luísa Arruda LIP - Lisbon 1 AMS-02 on the International Space Station The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer is a
The Ring Imaging Cherenkov detector of the AMS experiment: test beam results with a prototype Luísa Arruda LIP - Lisbon 1 AMS-02 on the International Space Station The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer is a
Momentum spectra of atmospheric pions, muons, electrons and positrons at balloon altitudes
 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 23 (1997) 1751 1763. Printed in the UK PII: S0954-3899(97)82178-0 Momentum spectra of atmospheric pions, muons, electrons and positrons at balloon altitudes A Codino, M T
J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 23 (1997) 1751 1763. Printed in the UK PII: S0954-3899(97)82178-0 Momentum spectra of atmospheric pions, muons, electrons and positrons at balloon altitudes A Codino, M T
Rare Components in Cosmic Rays with AMS-02
 Rare Components in Cosmic Rays with AMS-02 TAUP Sendai Sep.07 IEKP - Andreas Sabellek Universität (TH) for the AMS Collaboration The AMS Project: History and Future 1998 2008 again ready for launch AMS-01
Rare Components in Cosmic Rays with AMS-02 TAUP Sendai Sep.07 IEKP - Andreas Sabellek Universität (TH) for the AMS Collaboration The AMS Project: History and Future 1998 2008 again ready for launch AMS-01
P A M E L A Payload for Antimatter / Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics
 P A M E L A Payload for Antimatter / Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics Mark Pearce KTH, Department of Physics, Stockholm, Sweden SLAC Summer Institute / 2007-08-07 Overview Indirect searches
P A M E L A Payload for Antimatter / Matter Exploration and Light-nuclei Astrophysics Mark Pearce KTH, Department of Physics, Stockholm, Sweden SLAC Summer Institute / 2007-08-07 Overview Indirect searches
Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa 2.0
 Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa. G Rastegarzade B Parvizi,, Physics Department, Semnan University, Semnan, P.O. Box 596-599, Iran Email: G_ rastegar@alum.sharif.edu Abstract
Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa. G Rastegarzade B Parvizi,, Physics Department, Semnan University, Semnan, P.O. Box 596-599, Iran Email: G_ rastegar@alum.sharif.edu Abstract
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park
 99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN. = GeV at RHIC
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Questions 1pc = 3 ly = km
 Cosmic Rays Historical hints Primary Cosmic Rays: - Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum - Composition - Origin and Propagation - The knee region and the ankle Secondary CRs: -shower development - interactions Detection:
Cosmic Rays Historical hints Primary Cosmic Rays: - Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum - Composition - Origin and Propagation - The knee region and the ankle Secondary CRs: -shower development - interactions Detection:
Galactic Cosmic Ray Propagation in the AMS 02 Era
 Galactic Cosmic Ray Propagation in the AMS 02 Era I Science case 1. Galactic Cosmic Rays 2. AMS 02 II Collaboration LAPP/LAPTh/LPSC 1. Teams and context 2. Support asked for the project III Conclusions
Galactic Cosmic Ray Propagation in the AMS 02 Era I Science case 1. Galactic Cosmic Rays 2. AMS 02 II Collaboration LAPP/LAPTh/LPSC 1. Teams and context 2. Support asked for the project III Conclusions
The space mission PAMELA
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 518 (2004) 153 157 The space mission PAMELA Marco Circella Departimento di Fiscia, Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, University di Bari, INFN
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 518 (2004) 153 157 The space mission PAMELA Marco Circella Departimento di Fiscia, Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, University di Bari, INFN
THE ELECTROMAGNETIC CALORIMETER OF THE AMS-02 EXPERIMENT
 SF2A 2012 S. Boissier, P. de Laverny, N. Nardetto, R. Samadi, D. Valls-Gabaud and H. Wozniak (eds) THE ELECTROMAGNETIC CALORIMETER OF THE AMS-02 EXPERIMENT M. Vecchi 1, L. Basara 2, G. Bigongiari 3, F.
SF2A 2012 S. Boissier, P. de Laverny, N. Nardetto, R. Samadi, D. Valls-Gabaud and H. Wozniak (eds) THE ELECTROMAGNETIC CALORIMETER OF THE AMS-02 EXPERIMENT M. Vecchi 1, L. Basara 2, G. Bigongiari 3, F.
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.:
 PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis
 Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis Donghwa Kang for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration Karlsruhe Institute of Technology 20 th ISVHECRI 21 25 May 2018, Nagoya, Japan Status & Prospect KASCADE
Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis Donghwa Kang for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration Karlsruhe Institute of Technology 20 th ISVHECRI 21 25 May 2018, Nagoya, Japan Status & Prospect KASCADE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Selecting electrons in ATIC ATIC is a calorimetric instrument and, as such, relies upon the difference in the development of the cascades (showers) initiated by protons and electrons. Moreover, the
1. Selecting electrons in ATIC ATIC is a calorimetric instrument and, as such, relies upon the difference in the development of the cascades (showers) initiated by protons and electrons. Moreover, the
The KASCADE-Grande Experiment
 The KASCADE-Grande Experiment O. Sima 1 for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration 2 1 University of Bucharest, Romania 2 https://web.ikp.kit.edu/kascade/ CSSP14 Sinaia 2014 Overview 1. KASCADE-Grande experimental
The KASCADE-Grande Experiment O. Sima 1 for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration 2 1 University of Bucharest, Romania 2 https://web.ikp.kit.edu/kascade/ CSSP14 Sinaia 2014 Overview 1. KASCADE-Grande experimental
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments
 Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
Low-Energy Cosmic Rays
 Low-Energy Cosmic Rays Cosmic rays, broadly defined, are charged particles from outside the solar system. These can be electrons, protons, or ions; the latter two dominate the number observed. They are
Low-Energy Cosmic Rays Cosmic rays, broadly defined, are charged particles from outside the solar system. These can be electrons, protons, or ions; the latter two dominate the number observed. They are
The USINE propagation code and recent results from an MCMC analysis
 The USINE propagation code and recent results from an MCMC analysis Antje Putze B. Coste (LPSC), L. Derome (LPSC), F. Donato (INFN Torino), & D. Maurin (LPSC) The Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics
The USINE propagation code and recent results from an MCMC analysis Antje Putze B. Coste (LPSC), L. Derome (LPSC), F. Donato (INFN Torino), & D. Maurin (LPSC) The Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics
1. New Mexico State University, Department of Astronomy, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA
 A Comparison of the Galactic Cosmic Ray H, He and C/O Nuclei Spectra Measured Between ~5 and 500 MeV/nuc Beyond 122 AU at Voyager 1 with the Predictions of a Diffusion Model for Propagation in the Galaxy
A Comparison of the Galactic Cosmic Ray H, He and C/O Nuclei Spectra Measured Between ~5 and 500 MeV/nuc Beyond 122 AU at Voyager 1 with the Predictions of a Diffusion Model for Propagation in the Galaxy
Eun-Suk Seo Inst. for Phys. Sci. & Tech. and Department of Physics University of Maryland. Cosmic Rays Eun-Suk Seo
 Eun-Suk Seo Inst. for Phys. Sci. & Tech. and Department of Physics University of Maryland Cosmic Rays Eun-Suk Seo 1 Cosmic Rays Eun-Suk Seo 2 How do cosmic accelerators work? BESS ATIC CREAM, TRACER Elemental
Eun-Suk Seo Inst. for Phys. Sci. & Tech. and Department of Physics University of Maryland Cosmic Rays Eun-Suk Seo 1 Cosmic Rays Eun-Suk Seo 2 How do cosmic accelerators work? BESS ATIC CREAM, TRACER Elemental
N U C L E O N. Satellite Mission. Present status.
 N U C L E O N Satellite Mission. Present status. a) Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University b) DB ARSENAL, Sankt-Peterburg, Russia c) Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna,
N U C L E O N Satellite Mission. Present status. a) Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University b) DB ARSENAL, Sankt-Peterburg, Russia c) Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna,
Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
Dark Matter Particle Explorer: The First Chinese Cosmic Ray and Hard γ-ray Detector in Space
 SPACE SCIENCE ACTIVITIES IN CHINA Dark Matter Particle Explorer: The First Chinese Cosmic Ray and Hard γ-ray Detector in Space AUTHORS CHANG Jin Key Laboratory of Dark Matter and Space Astronomy, Purple
SPACE SCIENCE ACTIVITIES IN CHINA Dark Matter Particle Explorer: The First Chinese Cosmic Ray and Hard γ-ray Detector in Space AUTHORS CHANG Jin Key Laboratory of Dark Matter and Space Astronomy, Purple
PoS(ICRC2015)424. YAC sensitivity for measuring the light-component spectrum of primary cosmic rays at the knee energies
 YAC sensitivity for measuring the light-component spectrum of primary cosmic rays at the knee energies L. M. Zhai a,b, J. Huang a, D. Chen b, M. Shibata c, Y. Katayose c, Ying Zhang a, Xu Chen a, X. B.
YAC sensitivity for measuring the light-component spectrum of primary cosmic rays at the knee energies L. M. Zhai a,b, J. Huang a, D. Chen b, M. Shibata c, Y. Katayose c, Ying Zhang a, Xu Chen a, X. B.
Preliminary results from gamma-ray observations with the CALorimeteric Electron Telescope (CALET)
 Preliminary results from gamma-ray observations with the CALorimeteric Electron Telescope (CALET) Y.Asaoka for the CALET Collaboration RISE, Waseda University 2016/12/15 CTA-Japan Workshop The extreme
Preliminary results from gamma-ray observations with the CALorimeteric Electron Telescope (CALET) Y.Asaoka for the CALET Collaboration RISE, Waseda University 2016/12/15 CTA-Japan Workshop The extreme
New Calculation of Cosmic-Ray Antiproton and Positron Flux
 New Calculation of Cosmic-Ray Antiproton and Positron Flux By Tadao Mitsui Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Tokyo 1996 iii Abstract Cosmic-ray antiproton ( p) and positron (e +
New Calculation of Cosmic-Ray Antiproton and Positron Flux By Tadao Mitsui Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Tokyo 1996 iii Abstract Cosmic-ray antiproton ( p) and positron (e +
Silicon Detectors for the Search of Cosmic Antimatter and Dark Matter
 Silicon Detectors for the Search of Cosmic Antimatter and Dark Matter Piergiorgio Picozza INFN and University of Rome Tor Vergata From e + /e - Colliders to High Energy Astrophysics Trieste, September
Silicon Detectors for the Search of Cosmic Antimatter and Dark Matter Piergiorgio Picozza INFN and University of Rome Tor Vergata From e + /e - Colliders to High Energy Astrophysics Trieste, September
DIETRICH MÜLLER University of Chicago SLAC SUMMER INSTITUTE 2011
 SEARCHES FOR ANTIMATTER DIETRICH MÜLLER University of Chicago SLAC SUMMER INSTITUTE 2011 OUTLINE Early History Baryon Asymmetry of the Universe? Current Limits on Antimatter Nuclei from Distant Galaxies
SEARCHES FOR ANTIMATTER DIETRICH MÜLLER University of Chicago SLAC SUMMER INSTITUTE 2011 OUTLINE Early History Baryon Asymmetry of the Universe? Current Limits on Antimatter Nuclei from Distant Galaxies
Correction for PMT temperature dependence of the LHCf calorimeters
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Correction for PMT temperature dependence of the LHCf calorimeters To cite this article: Eri Matsubayashi and the LHCf collaboration 2015 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Correction for PMT temperature dependence of the LHCf calorimeters To cite this article: Eri Matsubayashi and the LHCf collaboration 2015 J. Phys.: Conf.
Towards Direction Dependent Fluxes With AMS-02
 Towards Direction Dependent Fluxes With AMS-02 Stefan Zeissler, Karen Andeen, Wim de Boer, Iris Gebauer, Carmen Merx, Nikolay Nikonov, Valerio Vagelli DPG Conference 2015, Wuppertal Institut für Experimentelle
Towards Direction Dependent Fluxes With AMS-02 Stefan Zeissler, Karen Andeen, Wim de Boer, Iris Gebauer, Carmen Merx, Nikolay Nikonov, Valerio Vagelli DPG Conference 2015, Wuppertal Institut für Experimentelle
Cosmic rays and the diffuse gamma-ray emission
 Cosmic rays and the diffuse gamma-ray emission Dipartimento di Fisica, Torino University and INFN Sezione di Torino via P. Giuria 1, 10125 Torino, Italy E-mail: donato@to.infn.it The diffuse γ-ray emission
Cosmic rays and the diffuse gamma-ray emission Dipartimento di Fisica, Torino University and INFN Sezione di Torino via P. Giuria 1, 10125 Torino, Italy E-mail: donato@to.infn.it The diffuse γ-ray emission
Monthly Proton Flux. Solar modulation with AMS. Veronica Bindi, AMS Collaboration
 Solar modulation with AMS Monthly Proton Flux Veronica Bindi, AMS Collaboration Physics and Astronomy Department University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, Hawaii, US 1 AMS on the ISS May 19, 2011 and for
Solar modulation with AMS Monthly Proton Flux Veronica Bindi, AMS Collaboration Physics and Astronomy Department University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, Hawaii, US 1 AMS on the ISS May 19, 2011 and for
Cosmic-ray energy spectrum around the knee
 Cosmic-ray energy spectrum around the knee M. SHIBATA Department of Physics, Yokohama National University, Yokohama, 240-8501, Japan Interesting global and fine structures of cosmic-ray energy spectrum
Cosmic-ray energy spectrum around the knee M. SHIBATA Department of Physics, Yokohama National University, Yokohama, 240-8501, Japan Interesting global and fine structures of cosmic-ray energy spectrum
Limits on Antiprotons in Space from the Shadowing of Cosmic Rays by the Moon
 Limits on Antiprotons in Space from the Shadowing of Cosmic Rays by the Moon Presented by: Yupeng Xu ( ETH Zürich / L3+C collaboration) PhD Students Seminar, PSI, October 1-2, 2003 The L3+C Experiment
Limits on Antiprotons in Space from the Shadowing of Cosmic Rays by the Moon Presented by: Yupeng Xu ( ETH Zürich / L3+C collaboration) PhD Students Seminar, PSI, October 1-2, 2003 The L3+C Experiment
Overview of recent HERMES results
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Cosmic Antimatter. Stéphane. Coutu The Pennsylvania State University. 3 rd. Astrophysics Arequipa,, Peru August 28-29, 29, 2008
 Cosmic Antimatter Stéphane Coutu The Pennsylvania State University 3 rd rd School on Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics Arequipa,, Peru August 28-29, 29, 2008 Outline Cosmic Rays Antimatter: Positrons, Antiprotons
Cosmic Antimatter Stéphane Coutu The Pennsylvania State University 3 rd rd School on Cosmic Rays and Astrophysics Arequipa,, Peru August 28-29, 29, 2008 Outline Cosmic Rays Antimatter: Positrons, Antiprotons
Galactic cosmic rays propagation
 Galactic cosmic rays propagation Side view of the Galaxy The Solar system is 8.5 kpc away from the galactic center. One pc is 3.10 18 cm, so we are at a distance of 2.55 10 17 km and the light from it
Galactic cosmic rays propagation Side view of the Galaxy The Solar system is 8.5 kpc away from the galactic center. One pc is 3.10 18 cm, so we are at a distance of 2.55 10 17 km and the light from it
Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays. Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016
 Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016 CR astrophуsics main problems Sources? - Accelerators? The basic paradigm of CR acceleration
Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016 CR astrophуsics main problems Sources? - Accelerators? The basic paradigm of CR acceleration
Neutral particles energy spectra for 900 GeV and 7 TeV p-p collisions, measured by the LHCf experiment
 Neutral particles energy spectra for 900 GeV and 7 TeV p-p collisions, measured by the LHCf experiment Raffaello D Alessandro 1 Department of Physics Università di Firenze and INFN-Firenze I-50019 Sesto
Neutral particles energy spectra for 900 GeV and 7 TeV p-p collisions, measured by the LHCf experiment Raffaello D Alessandro 1 Department of Physics Università di Firenze and INFN-Firenze I-50019 Sesto
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV
 Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV Andreas Haungs haungs@ik.fzk.de James L. Pinfold August 2006 TeV workshop Madison, US Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph
Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV Andreas Haungs haungs@ik.fzk.de James L. Pinfold August 2006 TeV workshop Madison, US Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph
