Note on Time Consistency
|
|
|
- Daniel Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Note on Time Consistency Danyang Xie HKUST 2011 dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
2 Time Consistency Kydland and Prescott (JPE 1977) Rules Rather than Discretion: the Inconsistency of Optimal Plans The rst paper to introduce the issue of time inconsistency in a general framework Other important contributions Stanley Fischer (JEDC 1980) on Fiscal Policy Barro and Gordon (JME 1983) on Monetary Policy Lucas and Stokey (JME 1983) on Fiscal and Monetary Policy dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
3 Kydland and Prescott (JPE 1977) Optimal Control Theory (the ones we have been using) Find optimal policy based on current situation Often, such optimal policy will cease to be optimal once a future date arrives. Reason: Bygones are bygones. People are forward looking. They form expectations about what the government will do in the future. Concept of time consistency A Two-Period Example Suppose teh social objective function is given by, S(x 1, x 2, π 1, π 2 ) where x represents actions and π represents policies. dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
4 Government s Problem Government choose π 1 and π 2 : max S(x 1, x 2, π 1, π 2 ) subject to : x 1 = X 1 (π 1, π 2 ) x 2 = X 2 (x 1, π 1, π 2 ) Namely max S(X 1 (π 1, π 2 ), X 2 (X 1 (π 1, π 2 ), π 1, π 2 ), π 1, π 2 ) dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
5 At t = 1, when the government plans for π 1 and π 2 S X 1 + S X2 x 1 π 1 x 2 S x 1 X 1 π 2 + S x 2 X 1 + X 2 x 1 π 1 π 1 X2 X 1 + X 2 x 1 π 2 π 2 + S = 0 π 1 + S = 0 (1) π 2 But when the government arrives at time t = 2, the problem becomes: max π 2 S(x 1, X 2 (x 1, π 1, π 2 ), π 1, π 2 ) and the FOC becomes: S x 2 X 2 π 2 + S π 2 = 0 (2) Note that (1) and (2) are usually di erent, so the optimal policy is usally time inconsistent. dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
6 When will the Policy be Time Consistent? The su cient condition is: S + S X 2 X1 = 0 x 1 x 2 x 1 π 2 In other words, if X 1 π 2 = 0 (Action in Period 1 is independent of π 2 ) or if x S 1 + x S X 2 2 x 1 (direct + indirect e ect = 0) dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
7 Stanley Fischer (JEDC 1980): Benevolent Dissembling Government A Two-Period Model The representative agent has the following preferences: ln c 1 + δ [ln c 2 + α ln(1 n) + β ln g] (3) where 1 n is leisure (chosen by the individual) and g is public goods (chosen by the government). Social Optimum: maximize (3) subject to: c 1 + S e c 2 + g (1 + r)s + wn where e is the endowment, F (S, n) = (1 + r)s + wn is the production function. The rst best allocation is easy to calculate. dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
8 Distortionary Taxes Suppose that lump-sum taxes are not available, and the only possible taxes are τ n and τ k on labor and capital, respectively. The competitive equilibrium can be obtained from maximizing: ln(e S) + δ [ln [(1 + r τ k )S + (1 τ n )wn] + α ln(1 n) + β ln g] FOCs yields: c i = C i (r, w, τ k, τ n, g), i = 1, 2 n = N(r, w, τ k, τ n, g) dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
9 Benevolent Government Assume that the government shares the same objective as the representative agent. The government s problem is then: max ln C 1(r, w, τ k, τ n, g) τ n,τ k,g +δ [ln C 2 (r, w, τ k, τ n, g) + α ln(1 N(r, w, τ k, τ n, g)) + β ln g] subject to: τ k S + τ n wn = g Let the solution be denoted τ n, τ k, and g. dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
10 Time Inconsistency At Period 2, after consumers made their saving decisions, the new problem for the representative agent becomes: max ln [(1 + r τ k )S + (1 τ n )wn] + α ln(1 n) + β ln g now, the only decision variable is n. What will be the government s optimal choices of τ n, τ k and g now? Simple: setting τ n = 0, which completely removes the distortion. Time inconsistency arises even when the private agents and the government share the same objective function. Suppose that the individuals trusted the government in period 1 and then government decides to reform in period 2 by setting τ n = 0, we denote this outcome the cheating outcome. We use τ n = 0 and τ k to denote the cheating policy. dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
11 How to nd a time consistent policy This is also called optimal discretionary policy. And it is derived from backward induction. We know that at period 2, τ n = 0 and τ k, g, satisfying τ k S a = g are the only policies that are credible. And the individual will choose: c 2 = (1 + r τ k )S + w 1 + α 1 n = αc 2 w Back to period 1, the representative agent maximizes: ln(e S) + δ ln (1 + r τ k )S + w 1 + α α (1 + r τ + k )S + w α ln + β ln g w 1 + α which leads to S = S(τ k ). The government then maximizes welfare subject to τ k S(τ k ) = g and obtains the consistent policy ˆτ n = 0 and ˆτ k. dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
12 How to Rank the welfare under di erent policies First Best (FB): U S.O. Rules: U Discretion: Ũ Cheating: Û dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
13 A Numerical Example Parameter values: e = 3, 1 + r = 1.5, w = 1, α = 0.25, β = 0.5, δ = 0.9. In all cases, the public goods will be g = 0.5c 2 and is omitted from the table. U c 1 S c 2 n FB τ k τ e k τ n τ e n ^ ~ dxie (HKUST) Note on Time Consistency / 13
The Time Consistency Problem - Theory and Applications
 The Time Consistency Problem - Theory and Applications Nils Adler and Jan Störger Seminar on Dynamic Fiscal Policy Dr. Alexander Ludwig November 30, 2006 Universität Mannheim Outline 1. Introduction 1.1
The Time Consistency Problem - Theory and Applications Nils Adler and Jan Störger Seminar on Dynamic Fiscal Policy Dr. Alexander Ludwig November 30, 2006 Universität Mannheim Outline 1. Introduction 1.1
Handout: Competitive Equilibrium
 1 Competitive equilibrium Handout: Competitive Equilibrium Definition 1. A competitive equilibrium is a set of endogenous variables (Ĉ, N s, N d, T, π, ŵ), such that given the exogenous variables (G, z,
1 Competitive equilibrium Handout: Competitive Equilibrium Definition 1. A competitive equilibrium is a set of endogenous variables (Ĉ, N s, N d, T, π, ŵ), such that given the exogenous variables (G, z,
Macroeconomic Theory and Analysis V Suggested Solutions for the First Midterm. max
 Macroeconomic Theory and Analysis V31.0013 Suggested Solutions for the First Midterm Question 1. Welfare Theorems (a) There are two households that maximize max i,g 1 + g 2 ) {c i,l i} (1) st : c i w(1
Macroeconomic Theory and Analysis V31.0013 Suggested Solutions for the First Midterm Question 1. Welfare Theorems (a) There are two households that maximize max i,g 1 + g 2 ) {c i,l i} (1) st : c i w(1
SGZ Macro Week 3, Lecture 2: Suboptimal Equilibria. SGZ 2008 Macro Week 3, Day 1 Lecture 2
 SGZ Macro Week 3, : Suboptimal Equilibria 1 Basic Points Effects of shocks can be magnified (damped) in suboptimal economies Multiple equilibria (stationary states, dynamic paths) in suboptimal economies
SGZ Macro Week 3, : Suboptimal Equilibria 1 Basic Points Effects of shocks can be magnified (damped) in suboptimal economies Multiple equilibria (stationary states, dynamic paths) in suboptimal economies
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes.
 14.452. Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes. Olivier Blanchard May 12, 2007 Nr. 1 Look at three issues: Time consistency. The inflation bias. The trade-off between inflation and activity. Implementation and
14.452. Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes. Olivier Blanchard May 12, 2007 Nr. 1 Look at three issues: Time consistency. The inflation bias. The trade-off between inflation and activity. Implementation and
Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 8: Optimal Minimum Wage and Introduction to Capital Taxation
 Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 8: Optimal Minimum Wage and Introduction to Capital Taxation Matteo Paradisi November 1, 2016 In this Section we develop a theoretical analysis of optimal minimum
Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 8: Optimal Minimum Wage and Introduction to Capital Taxation Matteo Paradisi November 1, 2016 In this Section we develop a theoretical analysis of optimal minimum
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 2
 Macroeconomic Theory, Fall 03 SEF, HKU Instructor: Dr. Yulei Luo October 03 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set. 0 points] Consider the following Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans model with fiscal policy. First, we
Macroeconomic Theory, Fall 03 SEF, HKU Instructor: Dr. Yulei Luo October 03 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set. 0 points] Consider the following Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans model with fiscal policy. First, we
Macroeconomic Theory and Analysis Suggested Solution for Midterm 1
 Macroeconomic Theory and Analysis Suggested Solution for Midterm February 25, 2007 Problem : Pareto Optimality The planner solves the following problem: u(c ) + u(c 2 ) + v(l ) + v(l 2 ) () {c,c 2,l,l
Macroeconomic Theory and Analysis Suggested Solution for Midterm February 25, 2007 Problem : Pareto Optimality The planner solves the following problem: u(c ) + u(c 2 ) + v(l ) + v(l 2 ) () {c,c 2,l,l
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 9: Macroeconomics policy, credibility, and politics Ben J. Heijdra Department of Economics & Econometrics University of Groningen 1 September
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 9: Macroeconomics policy, credibility, and politics Ben J. Heijdra Department of Economics & Econometrics University of Groningen 1 September
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK AT ALBANY Department of Economics
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK AT ALBANY Department of Economics Ph. D. Comprehensive Examination: Macroeconomics Fall, 202 Answer Key to Section 2 Questions Section. (Suggested Time: 45 Minutes) For 3 of
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK AT ALBANY Department of Economics Ph. D. Comprehensive Examination: Macroeconomics Fall, 202 Answer Key to Section 2 Questions Section. (Suggested Time: 45 Minutes) For 3 of
University of Pittsburgh Department of Economics Econ 1720: Advanced Macroeconomics Handout 3
 University of Pittsburgh Department of Economics Econ 1720: Advanced Macroeconomics Handout 3 This handout presents how we can use all the results obtained in handouts 1 and 2 in order to characterize
University of Pittsburgh Department of Economics Econ 1720: Advanced Macroeconomics Handout 3 This handout presents how we can use all the results obtained in handouts 1 and 2 in order to characterize
Eco504 Spring 2009 C. Sims MID-TERM EXAM
 Eco504 Spring 2009 C. Sims MID-TERM EXAM This is a 90-minute exam. Answer all three questions, each of which is worth 30 points. You can get partial credit for partial answers. Do not spend disproportionate
Eco504 Spring 2009 C. Sims MID-TERM EXAM This is a 90-minute exam. Answer all three questions, each of which is worth 30 points. You can get partial credit for partial answers. Do not spend disproportionate
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
Problem 1 (30 points)
 Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
HOMEWORK #3 This homework assignment is due at NOON on Friday, November 17 in Marnix Amand s mailbox.
 Econ 50a second half) Yale University Fall 2006 Prof. Tony Smith HOMEWORK #3 This homework assignment is due at NOON on Friday, November 7 in Marnix Amand s mailbox.. This problem introduces wealth inequality
Econ 50a second half) Yale University Fall 2006 Prof. Tony Smith HOMEWORK #3 This homework assignment is due at NOON on Friday, November 7 in Marnix Amand s mailbox.. This problem introduces wealth inequality
Comprehensive Exam. Macro Spring 2014 Retake. August 22, 2014
 Comprehensive Exam Macro Spring 2014 Retake August 22, 2014 You have a total of 180 minutes to complete the exam. If a question seems ambiguous, state why, sharpen it up and answer the sharpened-up question.
Comprehensive Exam Macro Spring 2014 Retake August 22, 2014 You have a total of 180 minutes to complete the exam. If a question seems ambiguous, state why, sharpen it up and answer the sharpened-up question.
Government The government faces an exogenous sequence {g t } t=0
 Part 6 1. Borrowing Constraints II 1.1. Borrowing Constraints and the Ricardian Equivalence Equivalence between current taxes and current deficits? Basic paper on the Ricardian Equivalence: Barro, JPE,
Part 6 1. Borrowing Constraints II 1.1. Borrowing Constraints and the Ricardian Equivalence Equivalence between current taxes and current deficits? Basic paper on the Ricardian Equivalence: Barro, JPE,
Loss Aversion and the Dynamics of Political Commitment
 Prepared with SEVI S LIDES Loss Aversion and the Dynamics of Political Commitment John Hassler (IIES) José V. Rodriguez Mora (University of Edinburgh) June 4, 2010 Summary (1/2) Political commitment Traditional
Prepared with SEVI S LIDES Loss Aversion and the Dynamics of Political Commitment John Hassler (IIES) José V. Rodriguez Mora (University of Edinburgh) June 4, 2010 Summary (1/2) Political commitment Traditional
TOBB-ETU - Econ 532 Practice Problems II (Solutions)
 TOBB-ETU - Econ 532 Practice Problems II (Solutions) Q: Ramsey Model: Exponential Utility Assume that in nite-horizon households maximize a utility function of the exponential form 1R max U = e (n )t (1=)e
TOBB-ETU - Econ 532 Practice Problems II (Solutions) Q: Ramsey Model: Exponential Utility Assume that in nite-horizon households maximize a utility function of the exponential form 1R max U = e (n )t (1=)e
Redistributive Taxation in a Partial-Insurance Economy
 Redistributive Taxation in a Partial-Insurance Economy Jonathan Heathcote Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Kjetil Storesletten Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Gianluca Violante
Redistributive Taxation in a Partial-Insurance Economy Jonathan Heathcote Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Kjetil Storesletten Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Gianluca Violante
EconS Micro Theory I 1 Recitation #10 - Externalities
 EconS 50 - Micro Theory I Recitation #0 - Externalities Exercise [ Pareto irrelevant externalities] If the two consumers in the economy have preferences U = [x x 2] [x 2 x 2 2] and U 2 = [x 2 x 2 2] [x
EconS 50 - Micro Theory I Recitation #0 - Externalities Exercise [ Pareto irrelevant externalities] If the two consumers in the economy have preferences U = [x x 2] [x 2 x 2 2] and U 2 = [x 2 x 2 2] [x
Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules
 Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University September 2007 1 Welfare-Based Policy Evaluation: Related Literature (ex: Rotemberg and Woodford,
Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University September 2007 1 Welfare-Based Policy Evaluation: Related Literature (ex: Rotemberg and Woodford,
APPENDIX Should the Private Sector Provide Public Capital?
 APPENIX Should the Private Sector Provide Public Capital? Santanu Chatterjee epartment of Economics Terry College of Business University of eorgia Appendix A The appendix describes the optimization problem
APPENIX Should the Private Sector Provide Public Capital? Santanu Chatterjee epartment of Economics Terry College of Business University of eorgia Appendix A The appendix describes the optimization problem
A Solution to the Problem of Externalities When Agents Are Well-Informed
 A Solution to the Problem of Externalities When Agents Are Well-Informed Hal R. Varian. The American Economic Review, Vol. 84, No. 5 (Dec., 1994), pp. 1278-1293 Introduction There is a unilateral externality
A Solution to the Problem of Externalities When Agents Are Well-Informed Hal R. Varian. The American Economic Review, Vol. 84, No. 5 (Dec., 1994), pp. 1278-1293 Introduction There is a unilateral externality
Capital Structure and Investment Dynamics with Fire Sales
 Capital Structure and Investment Dynamics with Fire Sales Douglas Gale Piero Gottardi NYU April 23, 2013 Douglas Gale, Piero Gottardi (NYU) Capital Structure April 23, 2013 1 / 55 Introduction Corporate
Capital Structure and Investment Dynamics with Fire Sales Douglas Gale Piero Gottardi NYU April 23, 2013 Douglas Gale, Piero Gottardi (NYU) Capital Structure April 23, 2013 1 / 55 Introduction Corporate
Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy: Equivalence Results
 Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy: Equivalence Results by Isabel Correia, Juan Pablo Nicolini, and Pedro Teles, JPE 2008 presented by Taisuke Nakata March 1st, 2011 () Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy: Equivalence Results by Isabel Correia, Juan Pablo Nicolini, and Pedro Teles, JPE 2008 presented by Taisuke Nakata March 1st, 2011 () Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Homework 3 - Partial Answers
 Homework 3 - Partial Answers Jonathan Heathcote Due in Class on Tuesday February 28th In class we outlined two versions of the stochastic growth model: a planner s problem, and an Arrow-Debreu competitive
Homework 3 - Partial Answers Jonathan Heathcote Due in Class on Tuesday February 28th In class we outlined two versions of the stochastic growth model: a planner s problem, and an Arrow-Debreu competitive
Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I
 14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
problem. max Both k (0) and h (0) are given at time 0. (a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
Proper Welfare Weights for Social Optimization Problems
 Proper Welfare Weights for Social Optimization Problems Alexis Anagnostopoulos (Stony Brook University) Eva Cárceles-Poveda (Stony Brook University) Yair Tauman (IDC and Stony Brook University) June 24th
Proper Welfare Weights for Social Optimization Problems Alexis Anagnostopoulos (Stony Brook University) Eva Cárceles-Poveda (Stony Brook University) Yair Tauman (IDC and Stony Brook University) June 24th
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Lecture 15. Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model. Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD I Semestre 2017 Last updated: July 3, 2017
 Lecture 15 Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD I Semestre 2017 Last updated: July 3, 2017 Universidad de Costa Rica EC3201 - Teoría Macroeconómica 2 Table of contents
Lecture 15 Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD I Semestre 2017 Last updated: July 3, 2017 Universidad de Costa Rica EC3201 - Teoría Macroeconómica 2 Table of contents
Macro I - Practice Problems - Growth Models
 Macro I - Practice Problems - Growth Models. Consider the infinitely-lived agent version of the growth model with valued leisure. Suppose that the government uses proportional taxes (τ c, τ n, τ k ) on
Macro I - Practice Problems - Growth Models. Consider the infinitely-lived agent version of the growth model with valued leisure. Suppose that the government uses proportional taxes (τ c, τ n, τ k ) on
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model
 A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
u(c t, x t+1 ) = c α t + x α t+1
 Review Questions: Overlapping Generations Econ720. Fall 2017. Prof. Lutz Hendricks 1 A Savings Function Consider the standard two-period household problem. The household receives a wage w t when young
Review Questions: Overlapping Generations Econ720. Fall 2017. Prof. Lutz Hendricks 1 A Savings Function Consider the standard two-period household problem. The household receives a wage w t when young
ECON607 Fall 2010 University of Hawaii Professor Hui He TA: Xiaodong Sun Assignment 2
 ECON607 Fall 200 University of Hawaii Professor Hui He TA: Xiaodong Sun Assignment 2 The due date for this assignment is Tuesday, October 2. ( Total points = 50). (Two-sector growth model) Consider the
ECON607 Fall 200 University of Hawaii Professor Hui He TA: Xiaodong Sun Assignment 2 The due date for this assignment is Tuesday, October 2. ( Total points = 50). (Two-sector growth model) Consider the
Neoclassical Growth Models: II
 Neoclassical Growth Models: II Mark Huggett 2 2 Georgetown November, 2017 Growth Model: Balanced Growth Neoclassical Growth Model is the workhorse model in macroeconomics. Solow (1956) provided a theoretical
Neoclassical Growth Models: II Mark Huggett 2 2 Georgetown November, 2017 Growth Model: Balanced Growth Neoclassical Growth Model is the workhorse model in macroeconomics. Solow (1956) provided a theoretical
Introduction to General Equilibrium: Framework.
 Introduction to General Equilibrium: Framework. Economy: I consumers, i = 1,...I. J firms, j = 1,...J. L goods, l = 1,...L Initial Endowment of good l in the economy: ω l 0, l = 1,...L. Consumer i : preferences
Introduction to General Equilibrium: Framework. Economy: I consumers, i = 1,...I. J firms, j = 1,...J. L goods, l = 1,...L Initial Endowment of good l in the economy: ω l 0, l = 1,...L. Consumer i : preferences
1 Recursive Competitive Equilibrium
 Feb 5th, 2007 Let s write the SPP problem in sequence representation: max {c t,k t+1 } t=0 β t u(f(k t ) k t+1 ) t=0 k 0 given Because of the INADA conditions we know that the solution is interior. So
Feb 5th, 2007 Let s write the SPP problem in sequence representation: max {c t,k t+1 } t=0 β t u(f(k t ) k t+1 ) t=0 k 0 given Because of the INADA conditions we know that the solution is interior. So
Loss Aversion in Politics Supplementary Material Online Appendix
 Loss Aversion in Politics Supplementary Material Online Appendix Alberto Alesina Francesco Passarelli y February 207 Contents. A Parametric Model 2. An example: Fiscal Policy 3. Projection Bias - Subsection
Loss Aversion in Politics Supplementary Material Online Appendix Alberto Alesina Francesco Passarelli y February 207 Contents. A Parametric Model 2. An example: Fiscal Policy 3. Projection Bias - Subsection
Equilibrium Conditions for the Simple New Keynesian Model
 Equilibrium Conditions for the Simple New Keynesian Model Lawrence J. Christiano August 4, 04 Baseline NK model with no capital and with a competitive labor market. private sector equilibrium conditions
Equilibrium Conditions for the Simple New Keynesian Model Lawrence J. Christiano August 4, 04 Baseline NK model with no capital and with a competitive labor market. private sector equilibrium conditions
Dynamic Optimization: An Introduction
 Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Time Consistency of Optimal Monetary and Fiscal Policy in a Small Open Economy
 Time Consistency of Optimal Monetary and Fiscal Policy in a Small Open Economy Xuan Liu 1 Department of Economics East Carolina University Brewster A-432 Greenville, NC 27858, USA 252-328-1470 O E-mail:
Time Consistency of Optimal Monetary and Fiscal Policy in a Small Open Economy Xuan Liu 1 Department of Economics East Carolina University Brewster A-432 Greenville, NC 27858, USA 252-328-1470 O E-mail:
Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy
 Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Economics 522 Esteban Rossi-Hansberg Princeton University Spring 2014 ERH (Princeton University ) Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Spring 2014 1 / 34 Restuccia and Rogerson
Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Economics 522 Esteban Rossi-Hansberg Princeton University Spring 2014 ERH (Princeton University ) Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Spring 2014 1 / 34 Restuccia and Rogerson
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC)
 Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Optimal Monetary Policy with Informational Frictions
 Optimal Monetary Policy with Informational Frictions George-Marios Angeletos Jennifer La O July 2017 How should fiscal and monetary policy respond to business cycles when firms have imperfect information
Optimal Monetary Policy with Informational Frictions George-Marios Angeletos Jennifer La O July 2017 How should fiscal and monetary policy respond to business cycles when firms have imperfect information
In the Ramsey model we maximized the utility U = u[c(t)]e nt e t dt. Now
![In the Ramsey model we maximized the utility U = u[c(t)]e nt e t dt. Now In the Ramsey model we maximized the utility U = u[c(t)]e nt e t dt. Now](/thumbs/89/100962140.jpg) PERMANENT INCOME AND OPTIMAL CONSUMPTION On the previous notes we saw how permanent income hypothesis can solve the Consumption Puzzle. Now we use this hypothesis, together with assumption of rational
PERMANENT INCOME AND OPTIMAL CONSUMPTION On the previous notes we saw how permanent income hypothesis can solve the Consumption Puzzle. Now we use this hypothesis, together with assumption of rational
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Interest Rate Liberalization and Capital Misallocation 1
 Interest Rate Liberalization and Capital Misallocation 1 Zheng Liu 1 Pengfei Wang 2 Zhiwei Xu 3 1 Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco 2 Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 3 Shanghai Jiao
Interest Rate Liberalization and Capital Misallocation 1 Zheng Liu 1 Pengfei Wang 2 Zhiwei Xu 3 1 Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco 2 Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 3 Shanghai Jiao
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 5: The government budget deficit Ben J. Heijdra Department of Economics & Econometrics University of Groningen 1 September 2009 Foundations of
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 5: The government budget deficit Ben J. Heijdra Department of Economics & Econometrics University of Groningen 1 September 2009 Foundations of
Macroeconomics I. University of Tokyo. Lecture 12. The Neo-Classical Growth Model: Prelude to LS Chapter 11.
 Macroeconomics I University of Tokyo Lecture 12 The Neo-Classical Growth Model: Prelude to LS Chapter 11. Julen Esteban-Pretel National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies The Cass-Koopmans Model: Environment
Macroeconomics I University of Tokyo Lecture 12 The Neo-Classical Growth Model: Prelude to LS Chapter 11. Julen Esteban-Pretel National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies The Cass-Koopmans Model: Environment
Recursive Methods Recursive Methods Nr. 1
 Nr. 1 Outline Today s Lecture Dynamic Programming under Uncertainty notation of sequence problem leave study of dynamics for next week Dynamic Recursive Games: Abreu-Pearce-Stachetti Application: today
Nr. 1 Outline Today s Lecture Dynamic Programming under Uncertainty notation of sequence problem leave study of dynamics for next week Dynamic Recursive Games: Abreu-Pearce-Stachetti Application: today
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 47 Introduction Authors:
Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 47 Introduction Authors:
Neoclassical Growth Model / Cake Eating Problem
 Dynamic Optimization Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna, Austria by Gabriel S. Lee February 1-4, 2008 An Overview and Introduction to Dynamic Programming using the Neoclassical Growth Model and Cake
Dynamic Optimization Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna, Austria by Gabriel S. Lee February 1-4, 2008 An Overview and Introduction to Dynamic Programming using the Neoclassical Growth Model and Cake
Optimal Income Taxation: Mirrlees Meets Ramsey
 Optimal Income Taxation: Mirrlees Meets Ramsey Jonathan Heathcote Minneapolis Fed Hitoshi Tsujiyama University of Minnesota and Minneapolis Fed ASSA Meetings, January 2012 The views expressed herein are
Optimal Income Taxation: Mirrlees Meets Ramsey Jonathan Heathcote Minneapolis Fed Hitoshi Tsujiyama University of Minnesota and Minneapolis Fed ASSA Meetings, January 2012 The views expressed herein are
Equilibrium Conditions and Algorithm for Numerical Solution of Kaplan, Moll and Violante (2017) HANK Model.
 Equilibrium Conditions and Algorithm for Numerical Solution of Kaplan, Moll and Violante (2017) HANK Model. January 8, 2018 1 Introduction This document describes the equilibrium conditions of Kaplan,
Equilibrium Conditions and Algorithm for Numerical Solution of Kaplan, Moll and Violante (2017) HANK Model. January 8, 2018 1 Introduction This document describes the equilibrium conditions of Kaplan,
Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion
 14.05 Lecture Notes Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion A large number of private agents play against a government. Government objective. The government objective is given by the following loss function:
14.05 Lecture Notes Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion A large number of private agents play against a government. Government objective. The government objective is given by the following loss function:
Intro Prefs & Voting Electoral comp. Voter Turnout Agency GIP SIP Rent seeking Partisans. 7. Special-interest politics
 7. Special-interest politics Motivation Why do some groups in society receive more generous support than other (e.g. farmers)? Homogeneity in interests which allows more efficient organization of lobby
7. Special-interest politics Motivation Why do some groups in society receive more generous support than other (e.g. farmers)? Homogeneity in interests which allows more efficient organization of lobby
The New Keynesian Model
 The New Keynesian Model Basic Issues Roberto Chang Rutgers January 2013 R. Chang (Rutgers) New Keynesian Model January 2013 1 / 22 Basic Ingredients of the New Keynesian Paradigm Representative agent paradigm
The New Keynesian Model Basic Issues Roberto Chang Rutgers January 2013 R. Chang (Rutgers) New Keynesian Model January 2013 1 / 22 Basic Ingredients of the New Keynesian Paradigm Representative agent paradigm
Department of Economics Working Paper Series
 Department of Economics Working Paper Series On the Existence and Characterization of Markovian Equilibrium in Models with Simple Non-Paternalistic Altruism Olivier F. Morand University of Connecticut
Department of Economics Working Paper Series On the Existence and Characterization of Markovian Equilibrium in Models with Simple Non-Paternalistic Altruism Olivier F. Morand University of Connecticut
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 6: The Government Budget Deficit
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 6 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 6: The Government Budget Deficit Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 6 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 6: The Government Budget Deficit Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter
1 The social planner problem
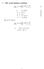 The social planner problem max C t;k t+ U t = E t X t C t () that can be written as: s.t.: Y t = A t K t (2) Y t = C t + I t (3) I t = K t+ (4) A t = A A t (5) et t i:i:d: 0; 2 max C t;k t+ U t = E t "
The social planner problem max C t;k t+ U t = E t X t C t () that can be written as: s.t.: Y t = A t K t (2) Y t = C t + I t (3) I t = K t+ (4) A t = A A t (5) et t i:i:d: 0; 2 max C t;k t+ U t = E t "
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I. Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form:
 Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Organizational Equilibrium with Capital
 Organizational Equilibrium with Capital Marco Bassetto, Zhen Huo, and José-Víctor Ríos-Rull FRB of Chicago, New York University, University of Pennsylvania, UCL, CAERP HKUST Summer Workshop in Macroeconomics
Organizational Equilibrium with Capital Marco Bassetto, Zhen Huo, and José-Víctor Ríos-Rull FRB of Chicago, New York University, University of Pennsylvania, UCL, CAERP HKUST Summer Workshop in Macroeconomics
Chapter 3 Task 1-4. Growth and Innovation Fridtjof Zimmermann
 Chapter 3 Task 1-4 Growth and Innovation Fridtjof Zimmermann Recept on how to derive the Euler-Equation (Keynes-Ramsey-Rule) 1. Construct the Hamiltonian Equation (Lagrange) H c, k, t, μ = U + μ(side Condition)
Chapter 3 Task 1-4 Growth and Innovation Fridtjof Zimmermann Recept on how to derive the Euler-Equation (Keynes-Ramsey-Rule) 1. Construct the Hamiltonian Equation (Lagrange) H c, k, t, μ = U + μ(side Condition)
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Department of Economics Economics 754 Topics in Political Economy Fall 2005 Allan Drazen. Exercise Set I
 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Department of Economics Economics 754 Topics in Political Economy Fall 005 Allan Drazen Exercise Set I The first four exercises are review of what we did in class on 8/31. The next
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Department of Economics Economics 754 Topics in Political Economy Fall 005 Allan Drazen Exercise Set I The first four exercises are review of what we did in class on 8/31. The next
U b (x b ) = xb 1x b 2 x a 1. means the consumption of good i by an h-type person.
 Chapter 9 Welfare Exercise 9. In a two-commodity exchange economy there are two large equalsized groups of traders. Each trader in group a has an endowment of 300 units of commodity ; each person in group
Chapter 9 Welfare Exercise 9. In a two-commodity exchange economy there are two large equalsized groups of traders. Each trader in group a has an endowment of 300 units of commodity ; each person in group
Business Cycles: The Classical Approach
 San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
Time-Consistent Public Expenditures
 Time-Consistent Public Expenditures Paul Klein, a Per Krusell, b José-Víctor Ríos-Rull c, a University of Western Ontario b University of Rochester, Institute for International Economic Studies, and CEPR
Time-Consistent Public Expenditures Paul Klein, a Per Krusell, b José-Víctor Ríos-Rull c, a University of Western Ontario b University of Rochester, Institute for International Economic Studies, and CEPR
1 Jan 28: Overview and Review of Equilibrium
 1 Jan 28: Overview and Review of Equilibrium 1.1 Introduction What is an equilibrium (EQM)? Loosely speaking, an equilibrium is a mapping from environments (preference, technology, information, market
1 Jan 28: Overview and Review of Equilibrium 1.1 Introduction What is an equilibrium (EQM)? Loosely speaking, an equilibrium is a mapping from environments (preference, technology, information, market
The representative agent model
 Chapter 3 The representative agent model 3.1 Optimal growth In this course we re looking at three types of model: 1. Descriptive growth model (Solow model): mechanical, shows the implications of a given
Chapter 3 The representative agent model 3.1 Optimal growth In this course we re looking at three types of model: 1. Descriptive growth model (Solow model): mechanical, shows the implications of a given
On the International Dimension of Fiscal Policy
 On the International Dimension of Fiscal Policy Gianluca Benigno London School of Economics, CEP and CEPR Bianca De Paoli y Bank of England and London School of Economics December 008 Abstract This paper
On the International Dimension of Fiscal Policy Gianluca Benigno London School of Economics, CEP and CEPR Bianca De Paoli y Bank of England and London School of Economics December 008 Abstract This paper
+ τ t R t 1B t 1 + M t 1. = R t 1B t 1 + M t 1. = λ t (1 + γ f t + γ f t v t )
 Eco504, Part II Spring 2006 C. Sims FTPL WITH MONEY 1. FTPL WITH MONEY This model is that of Sims (1994). Agent: [ ] max E β t log C t {C t,m t,b t } t=0 s.t. C t (1 + γ f (v t )) + M t + B t + τ t R t
Eco504, Part II Spring 2006 C. Sims FTPL WITH MONEY 1. FTPL WITH MONEY This model is that of Sims (1994). Agent: [ ] max E β t log C t {C t,m t,b t } t=0 s.t. C t (1 + γ f (v t )) + M t + B t + τ t R t
Eco Spring 2002 Chris Sims OLG EXERCISES
 Eco 504.2 Spring 2002 Chris Sims OLG EXERCISES (1) Suppose in our overlapping generations model the utility function is U ( C 1 (t), ) = log ( C 1 (t) ). Suppose also that instead of being endowed with
Eco 504.2 Spring 2002 Chris Sims OLG EXERCISES (1) Suppose in our overlapping generations model the utility function is U ( C 1 (t), ) = log ( C 1 (t) ). Suppose also that instead of being endowed with
Suggested Solutions to Homework #3 Econ 511b (Part I), Spring 2004
 Suggested Solutions to Homework #3 Econ 5b (Part I), Spring 2004. Consider an exchange economy with two (types of) consumers. Type-A consumers comprise fraction λ of the economy s population and type-b
Suggested Solutions to Homework #3 Econ 5b (Part I), Spring 2004. Consider an exchange economy with two (types of) consumers. Type-A consumers comprise fraction λ of the economy s population and type-b
Competitive Equilibrium and the Welfare Theorems
 Competitive Equilibrium and the Welfare Theorems Craig Burnside Duke University September 2010 Craig Burnside (Duke University) Competitive Equilibrium September 2010 1 / 32 Competitive Equilibrium and
Competitive Equilibrium and the Welfare Theorems Craig Burnside Duke University September 2010 Craig Burnside (Duke University) Competitive Equilibrium September 2010 1 / 32 Competitive Equilibrium and
Monetary Economics Notes
 Monetary Economics Notes Nicola Viegi 2 University of Pretoria - School of Economics Contents New Keynesian Models. Readings...............................2 Basic New Keynesian Model...................
Monetary Economics Notes Nicola Viegi 2 University of Pretoria - School of Economics Contents New Keynesian Models. Readings...............................2 Basic New Keynesian Model...................
Layo Costs and E ciency with Asymmetric Information
 Layo Costs and E ciency with Asymmetric Information Alain Delacroix (UQAM) and Etienne Wasmer (Sciences-Po) September 4, 2009 Abstract Wage determination under asymmetric information generates ine ciencies
Layo Costs and E ciency with Asymmetric Information Alain Delacroix (UQAM) and Etienne Wasmer (Sciences-Po) September 4, 2009 Abstract Wage determination under asymmetric information generates ine ciencies
TheTimeConsistencyof Monetary and Fiscal Policies
 Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department TheTimeConsistencyof Monetary and Fiscal Policies Fernando Alvarez, Patrick J. Kehoe, and Pablo Neumeyer Working Paper 616 April 2002 ABSTRACT Are
Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department TheTimeConsistencyof Monetary and Fiscal Policies Fernando Alvarez, Patrick J. Kehoe, and Pablo Neumeyer Working Paper 616 April 2002 ABSTRACT Are
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
A Concrete Example of the Transfer Problem with Multiple Equilibria. Minwook KANG. 19 August 2015 EGC Report No: 2015/04
 Division of Economics, EGC School of Humanities and Social Sciences Nanyang Technological University 14 Nanyang Drive Singapore 637332 A Concrete Example of the Transfer Problem with Multiple Equilibria
Division of Economics, EGC School of Humanities and Social Sciences Nanyang Technological University 14 Nanyang Drive Singapore 637332 A Concrete Example of the Transfer Problem with Multiple Equilibria
Macroeconomics II Money in the Utility function
 McCless]Prof. McCless UCEMA Prof. McCless UCEMA Macroeconomics II Money in the Utility function [ October, 00 Money in the Utility function Money in the Utility function Alternative way to add money to
McCless]Prof. McCless UCEMA Prof. McCless UCEMA Macroeconomics II Money in the Utility function [ October, 00 Money in the Utility function Money in the Utility function Alternative way to add money to
Taxing capital along the transition - Not a bad idea after all?
 Taxing capital along the transition - Not a bad idea after all? Online appendix Hans Fehr University of Würzburg CESifo and Netspar Fabian Kindermann University of Bonn and Netspar September 2014 In Appendix
Taxing capital along the transition - Not a bad idea after all? Online appendix Hans Fehr University of Würzburg CESifo and Netspar Fabian Kindermann University of Bonn and Netspar September 2014 In Appendix
Extensive Form Games with Perfect Information
 Extensive Form Games with Perfect Information Pei-yu Lo 1 Introduction Recap: BoS. Look for all Nash equilibria. show how to nd pure strategy Nash equilibria. Show how to nd mixed strategy Nash equilibria.
Extensive Form Games with Perfect Information Pei-yu Lo 1 Introduction Recap: BoS. Look for all Nash equilibria. show how to nd pure strategy Nash equilibria. Show how to nd mixed strategy Nash equilibria.
Solutions to Macro Final 2006
 Solutions to Macro Final 6 th December 6 1 Problem 1 1.1 Part A Rewrite the utility function as U = ln(n) + ln (c) γ ln ( c) Notice that since the agent taes c as a constant, it will not factor into the
Solutions to Macro Final 6 th December 6 1 Problem 1 1.1 Part A Rewrite the utility function as U = ln(n) + ln (c) γ ln ( c) Notice that since the agent taes c as a constant, it will not factor into the
Delegation, Time Inconsistency and Sustainable Equilibrium
 Working Paper 2008:15 Department of Economics Delegation, Time Inconsistency and Sustainable Equilibrium Henrique S. Basso Department of Economics Working paper 2008:15 Uppsala University October 2008
Working Paper 2008:15 Department of Economics Delegation, Time Inconsistency and Sustainable Equilibrium Henrique S. Basso Department of Economics Working paper 2008:15 Uppsala University October 2008
Externalities and PG. MWG- Chapter 11
 Externalities and PG MWG- Chapter 11 Simple Bilateral Externality When external e ects are present, CE are not PO. Assume: 1 Two consumers i = 1, 2 2 The actions of these consumers do not a ect prices
Externalities and PG MWG- Chapter 11 Simple Bilateral Externality When external e ects are present, CE are not PO. Assume: 1 Two consumers i = 1, 2 2 The actions of these consumers do not a ect prices
5. Externalities and Public Goods. Externalities. Public Goods types. Public Goods
 5. Externalities and Public Goods 5. Externalities and Public Goods Externalities Welfare properties of Walrasian Equilibria rely on the hidden assumption of private goods: the consumption of the good
5. Externalities and Public Goods 5. Externalities and Public Goods Externalities Welfare properties of Walrasian Equilibria rely on the hidden assumption of private goods: the consumption of the good
ECON2285: Mathematical Economics
 ECON2285: Mathematical Economics Yulei Luo Economics, HKU September 17, 2018 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ME September 17, 2018 1 / 46 Static Optimization and Extreme Values In this topic, we will study goal
ECON2285: Mathematical Economics Yulei Luo Economics, HKU September 17, 2018 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ME September 17, 2018 1 / 46 Static Optimization and Extreme Values In this topic, we will study goal
Optimal taxation with monopolistic competition
 Optimal taxation with monopolistic competition Leslie J. Reinhorn Economics Department University of Durham 23-26 Old Elvet Durham DH1 3HY United Kingdom phone +44 191 334 6365 fax +44 191 334 6341 reinhorn@hotmail.com
Optimal taxation with monopolistic competition Leslie J. Reinhorn Economics Department University of Durham 23-26 Old Elvet Durham DH1 3HY United Kingdom phone +44 191 334 6365 fax +44 191 334 6341 reinhorn@hotmail.com
Education Policies and Taxation without Commitment
 Education Policies and Taxation without Commitment Sebastian Findeisen University of Mannheim, CEPR Dominik Sachs European University Institute, CEPR This version: August 27, 2016 Abstract We study the
Education Policies and Taxation without Commitment Sebastian Findeisen University of Mannheim, CEPR Dominik Sachs European University Institute, CEPR This version: August 27, 2016 Abstract We study the
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Novasbe February 2016 Francesco Franco (Novasbe) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 8 The Social Planner Solution Notice no intertemporal issues (Y t =
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Novasbe February 2016 Francesco Franco (Novasbe) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 8 The Social Planner Solution Notice no intertemporal issues (Y t =
AAEC 6524: Environmental Theory and Policy Analysis. Outline. Theory of Externalities and Public Goods. Klaus Moeltner Spring 2019.
 AAEC 6524: Theory and Policy Analysis Theory of Externalities and Public Goods Klaus Moeltner Spring 2019 January 21, 2019 Outline Overarching and Related Fields and Microeconomics (consumer, firm, s)
AAEC 6524: Theory and Policy Analysis Theory of Externalities and Public Goods Klaus Moeltner Spring 2019 January 21, 2019 Outline Overarching and Related Fields and Microeconomics (consumer, firm, s)
CER-ETH - Center of Economic Research at ETH Zurich
 CER-ETH - Center of Economic Research at ETH Zurich Economics Working Paper Series Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich Intergenerational Transfers,
CER-ETH - Center of Economic Research at ETH Zurich Economics Working Paper Series Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich Intergenerational Transfers,
The Basic New Keynesian Model, the Labor Market and Sticky Wages
 The Basic New Keynesian Model, the Labor Market and Sticky Wages Lawrence J. Christiano August 25, 203 Baseline NK model with no capital and with a competitive labor market. private sector equilibrium
The Basic New Keynesian Model, the Labor Market and Sticky Wages Lawrence J. Christiano August 25, 203 Baseline NK model with no capital and with a competitive labor market. private sector equilibrium
Production subsidies and redistribution
 Journal of Economic Theory 142 (2008) 73 99 www.elsevier.com/locate/jet Production subsidies and redistribution Marina Azzimonti a,, Eva de Francisco b, Per Krusell c a Department of Economics, University
Journal of Economic Theory 142 (2008) 73 99 www.elsevier.com/locate/jet Production subsidies and redistribution Marina Azzimonti a,, Eva de Francisco b, Per Krusell c a Department of Economics, University
Optimal Mirrleesian Income Taxation with Tax Avoidance
 Optimal Mirrleesian Income Taxation with Tax Avoidance Daniel Moncayo January 30, 2014 Introduction People have more than one way to respond to taxation. The labor supply elasticity alone can t explain
Optimal Mirrleesian Income Taxation with Tax Avoidance Daniel Moncayo January 30, 2014 Introduction People have more than one way to respond to taxation. The labor supply elasticity alone can t explain
5. Externalities and Public Goods
 5. Externalities and Public Goods Welfare properties of Walrasian Equilibria rely on the hidden assumption of private goods: the consumption of the good by one person has no effect on other people s utility,
5. Externalities and Public Goods Welfare properties of Walrasian Equilibria rely on the hidden assumption of private goods: the consumption of the good by one person has no effect on other people s utility,
Production subsidies and redistribution
 Production subsidies and redistribution Marina Azzimonti, Eva de Francisco, and Per Krusell December, 2006 Abstract Who gains from stimulating output? We explore a dynamic model with production subsidies
Production subsidies and redistribution Marina Azzimonti, Eva de Francisco, and Per Krusell December, 2006 Abstract Who gains from stimulating output? We explore a dynamic model with production subsidies
