Annals of Mathematics
|
|
|
- Rhoda Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of Mathematics Asymptotically Neutral Distributions of Electrons and Polynomial Approximation Author(s): Jacob Korevaar Source: The Annals of Mathematics, Second Series, Vol. 80, No. 3 (Nov., 1964), pp Published by: Annals of Mathematics Stable URL: Accessed: 30/06/ :40 Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use, available at. JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use provides, in part, that unless you have obtained prior permission, you may not download an entire issue of a journal or multiple copies of articles, and you may use content in the JSTOR archive only for your personal, non-commercial use. Please contact the publisher regarding any further use of this work. Publisher contact information may be obtained at. Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission. JSTOR is a not-for-profit service that helps scholars, researchers, and students discover, use, and build upon a wide range of content in a trusted digital archive. We use information technology and tools to increase productivity and facilitate new forms of scholarship. For more information about JSTOR, please contact support@jstor.org. Annals of Mathematics is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to The Annals of Mathematics.
2 Asymptotically Neutral Distributions of Electrons and Polynomial Approximation* By JACOB KOREVAAR 1. Introduction and results Let D be a bounded simply connected region (connected open set) in the complex plane. We wish to approximate holomorphic functions in D by polynomials; the error must become uniformly small on every fixed closed subset of D. By Runge's theorem such approximation is always possible. However, we impose an additional condition: the zeros of the approximating polynomials must belong to a prescribed set P. Polynomials whose zeros lie in P will be referred to as F-polynomials. It will be assumed for simplicity that F and D are disjoint. P will be called a polynomial approximation set relative to D if and only if every zero free holomorphic function in D can be approximated by F-polynomials. It may be observed that, if F is a polynomial approximation set and J is a simple arc in D, then every continuous function on J can be uniformly approximated by F-polynomials. G. R. MacLane [4] has shown that every rectifiable Jordan curve is a polynomial approximation set relative to its interior. Recently M. D. Thompson [5] gave a new proof of this result, extending it to a different special class of Jordan curves. M.D. Thompson [5] and the author [3] have also considered certain unbounded sets F. In the present paper we determine all bounded sets F that can serve as polynomial approximation sets relative to D. The discussion will be based on the notion of "asymptotically neutral families". A family of finite sequences (1.1) Zn1, Zn2,... Zen (with n = no co) of points ("electrons") on F will be called asymptotically neutral relative to D if and only if (1.2) Z. - 0 as n = nj o, ql,kz uniformly on every closed subset of D. It may be noted that the sum in (1.2) represents the (complex conjugate of the) electrostatic field at z due to * Work supported by contract NONR at Stanford University.
3 404 JACOB KOREVAAR electrons at the points (1.1), assuming forces inversely proportional to the distance. MAIN THEOREM. Let D be a bounded simply connected region, F a bounded set disjoint from D. Then each of the following four statements implies the others: ( i ) F is a polynomial approximation set relative to D; (ii) for some point C E F, the function 1/(C - z) can be approximated by F-polynomials in D; (iii) F contains an asymptotically neutral family relative to D; (iv) clos F divides the plane, and D belongs to a bounded component of its complement. COROLLARY. Let D be an arbitrary bounded simply connected region. Then (a) if E is any given closed subset of D, it is possible to place a large number of electrons on the boundary OD in such a way that the resulting electrostatic field is uniformly weak on E; (/l) the boundary OD is a polynomial approximation set relative to D. The main theorem has an extension to the case of unbounded sets F which belong to a half-plane; the corollary remains valid for arbitrary bounded open sets D with connected complement. These extensions will be discussed in a separate paper. It is an interesting physical problem if part (a) of the corollary can be extended to the case of arbitrary, or at least fairly general, three-dimensional bounded regions D with connected complement. Indeed, suppose such a region D is the interior of a negatively charged hollow conductor SD. Experiments indicate that the charges are distributed over SD in such a way that there is no measurable electrostatic field in the interior D. Can this phenomenon be explained by a model where the charges consist entirely of free electrons? The author wishes to thank M. D. Thompson and S. Hellerstein who were in on the early stages of the work, and above all Professor Beurling whose detailed comments on the manuscript led to great simplifications; in particular, the present proof of Theorem 5.1 is due to him. 2. The implications (i) (ii) (iii) - (iv) That (i) implies (ii) is trivial. (ii) (iii). Suppose that for some point C E F the function 1/(C - z) can be approximated by F-polynomials, uniformly on every closed subset of D. Then, by logarithmic differentiation, the function - 1/(C - z) is the limit of finite sums of the form
4 DISTRIBUTIONS OF ELECTRONS AND POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 405 (2.1) 1_, with XjkE. The number vj of terms in the sum (2.1) must tend to infinity, for, otherwise, a suitable subsequence of the sums (2.1) would tend to a finite sum 1l/(zk - z) with Zk C cios F. It follows that the sequences C9 Cjl9...s 9 civi j = 1, form an asymptotically neutral family relative to D. (iii) (iv). Suppose that F contains an asymptotically neutral family (1.1) relative to D, and let U denote the union of the points occurring in the sequences (1.1). LEMMA 2.1. Clos U divides the plane, and D belongs to a bounded component of its complement. PROOF. Let D' be the component of the complement of clos U which contains D, and suppose that D' is unbounded. Define 1 1 (2.2) f.(z) - E z n = n- )co. n klznk -Z The fn(z) are holomorphic in D', uniformly bounded on any given compact subset, and tend to zero in D. Hence by Vitali's theorem, fn(z) 0 every- - where in D', contradicting the fact that at any finite point z0 far from the bounded set U, the fn(z) are bounded away from zero. Thus D' must be bounded. 3. Asymptotically neutral families If clos F contains an asymptotically neutral family, so does P. Hence in discussing the implication (iv) y (iii) it may be assumed that F is closed. Suppose now that F divides the plane, and that the component D+ of complement F which contains D is bounded. It will be shown that F has a fairly well-behaved subset which carries an asymptotically neutral family. Let Do be the unbounded component of complement clos D+. Then Do is a simply connected region which contains the point at infinity. The boundary F- = OD- is part of OD+, hence part of F. It may be observed that if F is a Jordan curve, then D+ = interior F, Do = exterior F, and F- F. THEOREM 3.1. F- contains an asymptotically neutral family relative to D. The points of any such family are dense on F-. For every point C E c-9 the function 1/(C - z) can be approximated by F--polynomials in D. The nth roots of unity, n = 1, 2,..., form an asymptotically neutral family on the unit circumference. Indeed, in this case the sum in (1.2) is
5 406 JACOB KOREVAAR equal to the negative of the logarithmic derivative of I - 1, and it is easy to see that this quantity tends to 0 uniformly on any disc z p < 1. In the general case we introduce the one-to-one conformal mapping z = D(W) of the exterior I w > 1 of the unit circle in the extended w-plane onto the region Do in the extended z-plane, normalized by the conditions b(oo) = co, V(co) > 0. We extend the mapping to the boundary by setting 4)(ei0) - limr 1, J(rei0) wherever the limit exists; for the exceptional points e"9 (which form a set of vanishing outer logarithmic capacity [1]), we take.i(ei0) equal to one of the radial limit values. Then all points z = b(ei0) belong to F-; it will be shown that there exist asymptotically neutral families on F- consisting of images of suitably shifted roots of unity. Images of roots of unity have been used before, notably as interpolation points by Fejer [2]. That they should play a role in the present problem is entirely natural. Indeed, writing (b(ei0) = (0) one has.b(rei0) p(0) as r I 1 for almost all 0, and boundedly on (0, 2wc); it follows that 27r 1 do= 1 dw2 1 =0 0 P (0) - z lwl=r>l (w)- Z iw (o) - z for all z E D. Thus if 9(0) is sufficiently well-behaved, the special Riemann sums (3.1 27r An (3.1) n, P~'9(27rk/n) - z will be good approximations, for large n, to the value 0 of the integral. For the special case where F = F- is a rectifiable Jordan curve, M. D. Thompson [5] has shown that the sums (3.1) are so small in the interior of F that the points 9(27ck/n), k 1, *--, n, n 1, 2, *--, form an asymptotically neutral family. 4. Proof of Theorem 3.1 (the implication (iv) -- (iii)) We first prove a simple lemma on infinite series. LEMMA 4.1. Let a(n) > 0, E'na(n) I < co. Then (4.1) lim infn NO n2 Ea1a(in) = -. PROOF. Suppose that (4.1) is false. Then there are numbers r > 0 and A such that for every prime p? A,
6 DISTRIBUTIONS OF ELECTRONS AND POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 407 p,= la(vp)? rjp. Summing over p one obtains (4.2) L p(n)a(n) > 2 A'/P =a where p(n) is the sum of the different prime factors? A of n. Now p(n) <n, hence (4.2) contradicts the convergence of 10na(n). This contradiction establishes (4.1). We are now ready for the principal lemma. LEMMA 4.2. Let Do and 9(0) be as in? 3, let D* = complement clos Do, and define (4.3) An(0 Z) 1 zed*. k~=1 (0( + 2Wrk/n) - z Then there is a sequence of integers nj co such that for almost all 0, *40(s Z) ) 0as j co, uniformly on every closed subset of D*. PROOF. Let d)(w) be the function which maps I w > 1 onto D- defined in? 3. For z E D*, the equation t 1 b(u) ) z,1,zw defines a one-to-one conformal mapping of I w 1 > 1 onto a bounded region R(z) in the t-plane; the point w co corresponds to t = 0. The image R(z) will be contained in the disc I t < 1/a(z), where J(z) denotes the distance between z and Do. Thus by the area formula Setting Jq7n I c (z) I2 < 1/J2(z) - (4.4) D* 1 cn(z) 122(z)da(z) = a(- ) it follows that the series 'iina(n) converges. We now observe that 1-1 I ch(z)e (( - z hence by Parseval's formula + (0, z) - n{jc(z)e-in0 + C2,(z)e 2inO +... } 2 r (4.5) do I *.(0, z) 12J2(z)da(z) =2n2 27 a(vn). h By Lemma 4.1, the right-hand side of (4.5) tends to zero for a sequence
7 408 JACOB KOREVAAR of integers n tending to infinity. Thus for a suitable subsequence {nj}, I * +(A z) 2J2(z)da(z) -, 0 as j -> co for almost all 0. It follows that, for any one of these 0, and for z belonging to the closed subset of D* where J(z)? 2s > 0, uniformly as j >co. 0(0, Z) = I 2 72 I <-Z I <e 2 (? A, n )da(c) 0 PROOF OF THEOREM 3.1. Lemma 4.2 proves the existence of asymptotically neutral families on F- relative to D c D*. We next show that the union U of the points occurring in any asymptotically neutral family (1.1) on F- is dense on W-. Consider a small disc A with center C F-. Such a disc contains points of D+ as well as points of Do. Now by Lemma 2.1, it is impossible to go from D to infinity without crossing clos U. Thus A must contain infinitely many points of U, and hence C eclos U. We can then write C = lim Zflh, where h = h(n) and n o co through a suitable sequence. Thus, using the same n, - z irni ~kh (n) ZEnk - Z uniformly on every closed subset of D. Integrating and exponentiating, we obtain the final statement of the theorem. 5. The implication (iv) (i) If clos F is a polynomial approximation set, then so is F; hence, we may again assume that F is closed. Suppose now that F divides the plane, and that D belongs to a bounded component of its complement. Let F- be the subset of F defined in? 3. We will use Theorem 3.1 to prove that every zero free holomorphic function f(z) in D can be approximated by F--polynomials. By the Borel-Caratheodory inequality, it is sufficiento show that every harmonic function log I f (z) I can be approximated by sums of the form (5.1) X + n>1log IZk - z with X real, ZkGP-. The maximum principle, finally, shows that it is sufficiento consider approximation on rectifiable Jordan curves in D. Thus the desired result will follow from THEOREM 5.1. For any rectifiable Jordan curve y in D, let C(z) denote the Banach space of all real-valued continuous functions on -y under the maximum norm, and let A(z) be the subset of all uniform limits on -i of
8 DISTRIBUTIONS OF ELECTRONS AND POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 409 sums (5.1). Then A(z) = C-(). PROOF. It is not clear a priori that A(z) is a vector space. In order to apply the usual method of testing by continuous linear functionals, we therefore begin by looking for a large subset of A(z) which is a subspace of CQz). By Theorem 3.1, -log I z I c A(-Y) for every C e r-. It follows that for every integer v and every pair of points 4', 4" E (5.2) >(log I C"-z I-log IC'-z l) E A(i). At each point C of the connected set F-, there is at least one "tangential" direction s with the following property: there are sequences {JC},{"} of points on F- such that C X -",, and the direct-ion of the vector from ' to C" converges to s. For such sequences, log - z - log I - z - log I C - z I uniformly for z C a. Thus by (5.2), alog I - z e A('y) as for every tangential direction s at C c F- and every real number X. We let A0(,Y) c A(') be the closed subspace of C(z) generated by the functions (a/as) log I - z I and the constant 1, and will prove that A,(y) = C(7). Suppose on the contrary that A,(-) # C(z). Then there exists a real measure dpa # 0 on y such that log -zi df(z) -0 = d(z) = 0 for all C e F- and corresponding tangential directions s. Now consider the logarithmic potential u(g) = 5 log - z I dp(z) The function u(c) is harmonic outside y and vanishes at infinity. At each point C e F-, we have Ou/Os = 0 for every tangential direction s. We will show that u(c) = constant on F-. Since d~i? 0, the function u(c) cannot be constant everywhere outside y (or it would vanish and then di = 0). Thus the holomorphic function Ou/8t - itu/&r2 can have only a finite number of zeros C, on F-. Let C be a point of F- different from the X. Since grad u(c) / 0, the set F- has a unique tangential direction s at C (we, of course, identify opposite directions). This tangential direction, furthermore, must
9 410 JACOB KOREVAAR depend continuously on C. Thus for the part of F- in a small disc about C, all small chords have approximately the same direction. It follows that F- coincides locally with a smooth Jordan arc, and that u() = constant locally on F-. Since F- is connected and u(c) is continuous on F-, u(c) = constant on F-. We conclude that u(c) = constant outside a; hence, u(c) = 0, dse- 0, and Ao(7) = A(Y) =-C7) UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN REFERENCES 1. A. BEURLING, Ensembles exceptionnels, Acta Math., 72 (1939), L. FEJPR, Interpolation und konforme Abbildung, Gdttinger Nachrichten, 1918, J. KOREVAAR, Approximation by polynomials whose zeros lie in a given set (Survey). Tagung uber Approximationstheorie, Oberwolfach, 1963, to appear. 4. G. R. MACLANE, Polynomials with zeros on a rectifiable Jordan curve, Duke Math. J., 16 (1949), M. D. THOMPSON, Approximation by polynomials whose zeros lie on a curve, Ph. D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin, To appear in Duke Math. J (Received November 19, 1963) (Revised January 3, 1964)
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 On Runs of Residues Author(s): D. H. Lehmer and Emma Lehmer Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 13, No. 1 (Feb., 1962), pp. 102-106 Published by: American Mathematical Society
On Runs of Residues Author(s): D. H. Lehmer and Emma Lehmer Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 13, No. 1 (Feb., 1962), pp. 102-106 Published by: American Mathematical Society
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 On the Bound for a Pair of Consecutive Quartic Residues of a Prime Author(s): R. G. Bierstedt and W. H. Mills Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 14, No. 4 (Aug., 1963), pp.
On the Bound for a Pair of Consecutive Quartic Residues of a Prime Author(s): R. G. Bierstedt and W. H. Mills Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 14, No. 4 (Aug., 1963), pp.
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 !"#$%%&"%&"'()"*+,&%$-,./',%+"0()%$)-"&%$"!$1,'$/$2"#3/+)"4%-/,+5!6'(%$7589":6;/3"
!"#$%%&"%&"'()"*+,&%$-,./',%+"0()%$)-"&%$"!$1,'$/$2"#3/+)"4%-/,+5!6'(%$7589":6;/3"
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 The Indices of Torsion-Free Subgroups of Fuchsian Groups Author(s): R. G. Burns and Donald Solitar Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 89, No. 3 (Nov., 1983), pp. 414-418 Published
The Indices of Torsion-Free Subgroups of Fuchsian Groups Author(s): R. G. Burns and Donald Solitar Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 89, No. 3 (Nov., 1983), pp. 414-418 Published
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Uncountably Many Inequivalent Analytic Actions of a Compact Group on Rn Author(s): R. S. Palais and R. W. Richardson, Jr. Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 14, No. 3 (Jun.,
Uncountably Many Inequivalent Analytic Actions of a Compact Group on Rn Author(s): R. S. Palais and R. W. Richardson, Jr. Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 14, No. 3 (Jun.,
Biometrika Trust. Biometrika Trust is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Biometrika.
 Biometrika Trust A Stagewise Rejective Multiple Test Procedure Based on a Modified Bonferroni Test Author(s): G. Hommel Source: Biometrika, Vol. 75, No. 2 (Jun., 1988), pp. 383-386 Published by: Biometrika
Biometrika Trust A Stagewise Rejective Multiple Test Procedure Based on a Modified Bonferroni Test Author(s): G. Hommel Source: Biometrika, Vol. 75, No. 2 (Jun., 1988), pp. 383-386 Published by: Biometrika
Definition We say that a topological manifold X is C p if there is an atlas such that the transition functions are C p.
 13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Large Deviations, Linear Statistics, and Scaling Limits for Mahler Ensemble of Complex Random Polynomials
 Large Deviations, Linear Statistics, and Scaling Limits for Mahler Ensemble of Complex Random Polynomials Maxim L. Yattselev joint work with Christopher D. Sinclair International Conference on Approximation
Large Deviations, Linear Statistics, and Scaling Limits for Mahler Ensemble of Complex Random Polynomials Maxim L. Yattselev joint work with Christopher D. Sinclair International Conference on Approximation
The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 100, No. 8. (Oct., 1993), pp
 A Visual Explanation of Jensen's Inequality Tristan Needham The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 100, No. 8. (Oct., 1993), pp. 768-771. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9890%28199310%29100%3a8%3c768%3aaveoji%3e2.0.co%3b2-8
A Visual Explanation of Jensen's Inequality Tristan Needham The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 100, No. 8. (Oct., 1993), pp. 768-771. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9890%28199310%29100%3a8%3c768%3aaveoji%3e2.0.co%3b2-8
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 The Relationship Between the Zeros of Best Approximations and Differentiability Author(s): Peter B. Borwein Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 92, No. 4, (Dec., 1984), pp. 528-532
The Relationship Between the Zeros of Best Approximations and Differentiability Author(s): Peter B. Borwein Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 92, No. 4, (Dec., 1984), pp. 528-532
The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 104, No. 8. (Oct., 1997), pp
 Newman's Short Proof of the Prime Number Theorem D. Zagier The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 14, No. 8. (Oct., 1997), pp. 75-78. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=2-989%2819971%2914%3a8%3c75%3anspotp%3e2..co%3b2-c
Newman's Short Proof of the Prime Number Theorem D. Zagier The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 14, No. 8. (Oct., 1997), pp. 75-78. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=2-989%2819971%2914%3a8%3c75%3anspotp%3e2..co%3b2-c
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 On the Probability of Covering the Circle by Rom Arcs Author(s): F. W. Huffer L. A. Shepp Source: Journal of Applied Probability, Vol. 24, No. 2 (Jun., 1987), pp. 422-429 Published by: Applied Probability
On the Probability of Covering the Circle by Rom Arcs Author(s): F. W. Huffer L. A. Shepp Source: Journal of Applied Probability, Vol. 24, No. 2 (Jun., 1987), pp. 422-429 Published by: Applied Probability
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Modalities in Ackermann's "Rigorous Implication" Author(s): Alan Ross Anderson and Nuel D. Belnap, Jr. Source: The Journal of Symbolic Logic, Vol. 24, No. 2 (Jun., 1959), pp. 107-111 Published by: Association
Modalities in Ackermann's "Rigorous Implication" Author(s): Alan Ross Anderson and Nuel D. Belnap, Jr. Source: The Journal of Symbolic Logic, Vol. 24, No. 2 (Jun., 1959), pp. 107-111 Published by: Association
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 A Generic Property of the Bounded Syzygy Solutions Author(s): Florin N. Diacu Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 116, No. 3 (Nov., 1992), pp. 809-812 Published by: American
A Generic Property of the Bounded Syzygy Solutions Author(s): Florin N. Diacu Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 116, No. 3 (Nov., 1992), pp. 809-812 Published by: American
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
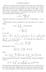 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Merging of Opinions with Increasing Information Author(s): David Blackwell and Lester Dubins Source: The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, Vol. 33, No. 3 (Sep., 1962), pp. 882-886 Published by: Institute
Merging of Opinions with Increasing Information Author(s): David Blackwell and Lester Dubins Source: The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, Vol. 33, No. 3 (Sep., 1962), pp. 882-886 Published by: Institute
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Biometrika Trust. Biometrika Trust is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Biometrika.
 Biometrika Trust An Improved Bonferroni Procedure for Multiple Tests of Significance Author(s): R. J. Simes Source: Biometrika, Vol. 73, No. 3 (Dec., 1986), pp. 751-754 Published by: Biometrika Trust Stable
Biometrika Trust An Improved Bonferroni Procedure for Multiple Tests of Significance Author(s): R. J. Simes Source: Biometrika, Vol. 73, No. 3 (Dec., 1986), pp. 751-754 Published by: Biometrika Trust Stable
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 6625 Author(s): Nicholas Strauss, Jeffrey Shallit, Don Zagier Source: The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 99, No. 1 (Jan., 1992), pp. 66-69 Published by: Mathematical Association of America Stable
6625 Author(s): Nicholas Strauss, Jeffrey Shallit, Don Zagier Source: The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 99, No. 1 (Jan., 1992), pp. 66-69 Published by: Mathematical Association of America Stable
11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C. 1.1 Holomorphic Functions
 11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C 1.1 Holomorphic Functions A domain Ω in the complex plane C is a connected, open subset of C. Let z o Ω and f a map f : Ω C. We say that f is real differentiable at z o if there
11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C 1.1 Holomorphic Functions A domain Ω in the complex plane C is a connected, open subset of C. Let z o Ω and f a map f : Ω C. We say that f is real differentiable at z o if there
E. DROR, W. G. DWYER AND D. M. KAN
 Self Homotopy Equivalences of Postnikov Conjugates Author(s): E. Dror, W. G. Dwyer, D. M. Kan Reviewed work(s): Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 74, No. 1 (Apr., 1979), pp.
Self Homotopy Equivalences of Postnikov Conjugates Author(s): E. Dror, W. G. Dwyer, D. M. Kan Reviewed work(s): Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 74, No. 1 (Apr., 1979), pp.
Hyperbolic Component Boundaries
 Hyperbolic Component Boundaries John Milnor Stony Brook University Gyeongju, August 23, 2014 Revised version. The conjectures on page 16 were problematic, and have been corrected. The Problem Hyperbolic
Hyperbolic Component Boundaries John Milnor Stony Brook University Gyeongju, August 23, 2014 Revised version. The conjectures on page 16 were problematic, and have been corrected. The Problem Hyperbolic
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Fermat's Little Theorem: Proofs That Fermat Might Have Used Author(s): Bob Burn Source: The Mathematical Gazette, Vol. 86, No. 507 (Nov., 2002), pp. 415-422 Published by: The Mathematical Association Stable
Fermat's Little Theorem: Proofs That Fermat Might Have Used Author(s): Bob Burn Source: The Mathematical Gazette, Vol. 86, No. 507 (Nov., 2002), pp. 415-422 Published by: The Mathematical Association Stable
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD
 MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 16 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 16 Nov 2017 arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 16 Nov 2017](/thumbs/89/97833093.jpg) Julia Sets of Orthogonal Polynomials arxiv:603.04937v3 [math.cv] 6 Nov 207 Jacob Stordal Christiansen, Christian Henriksen, Henrik Laurberg Pedersen and Carsten Lunde Petersen September 24, 208 Abstract
Julia Sets of Orthogonal Polynomials arxiv:603.04937v3 [math.cv] 6 Nov 207 Jacob Stordal Christiansen, Christian Henriksen, Henrik Laurberg Pedersen and Carsten Lunde Petersen September 24, 208 Abstract
Part V. 17 Introduction: What are measures and why measurable sets. Lebesgue Integration Theory
 Part V 7 Introduction: What are measures and why measurable sets Lebesgue Integration Theory Definition 7. (Preliminary). A measure on a set is a function :2 [ ] such that. () = 2. If { } = is a finite
Part V 7 Introduction: What are measures and why measurable sets Lebesgue Integration Theory Definition 7. (Preliminary). A measure on a set is a function :2 [ ] such that. () = 2. If { } = is a finite
The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 16, No. 2. (Mar., 1985), pp
 On Rearrangements of the Alternating Harmonic Series Fon Brown; L. O. Cannon; Joe Elich; David G. Wright The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 16, No. 2. (Mar., 1985), pp. 135-138. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0746-8342%28198503%2916%3a2%3c135%3aorotah%3e2.0.co%3b2-q
On Rearrangements of the Alternating Harmonic Series Fon Brown; L. O. Cannon; Joe Elich; David G. Wright The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 16, No. 2. (Mar., 1985), pp. 135-138. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0746-8342%28198503%2916%3a2%3c135%3aorotah%3e2.0.co%3b2-q
A UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR MONOGENIC FUNCTIONS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Series A. I. Mathematica Volumen 8, 993, 05 6 A UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR MONOGENIC FUNCTIONS Jörg Winkler Technische Universität Berlin, Fachbereich 3, Mathematik Straße
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Series A. I. Mathematica Volumen 8, 993, 05 6 A UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR MONOGENIC FUNCTIONS Jörg Winkler Technische Universität Berlin, Fachbereich 3, Mathematik Straße
Invariant subspaces for operators whose spectra are Carathéodory regions
 Invariant subspaces for operators whose spectra are Carathéodory regions Jaewoong Kim and Woo Young Lee Abstract. In this paper it is shown that if an operator T satisfies p(t ) p σ(t ) for every polynomial
Invariant subspaces for operators whose spectra are Carathéodory regions Jaewoong Kim and Woo Young Lee Abstract. In this paper it is shown that if an operator T satisfies p(t ) p σ(t ) for every polynomial
LECTURE-15 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS
 LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
Journal of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 2, No. 2. (Apr., 1989), pp
 An Estimate for Character Sums Nicholas M. Katz Journal of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 2, No. 2. (Apr., 1989), pp. 197-200. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0894-0347%28198904%292%3a2%3c197%3aaefcs%3e2.0.co%3b2-l
An Estimate for Character Sums Nicholas M. Katz Journal of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 2, No. 2. (Apr., 1989), pp. 197-200. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0894-0347%28198904%292%3a2%3c197%3aaefcs%3e2.0.co%3b2-l
CARATHEODORY'S THEOREM ON BOUNDARY ELEMENTS OF AN ARBITRARY PLANE REGION
 KODAI MATH. SEM. REP 21 (1969), 413 417 CARATHEODORY'S THEOREM ON BOUNDARY ELEMENTS OF AN ARBITRARY PLANE REGION BY NOBUYUKI SUITA 1. Introduction. Let Δ be a simply connected hyperbolic region. By denning
KODAI MATH. SEM. REP 21 (1969), 413 417 CARATHEODORY'S THEOREM ON BOUNDARY ELEMENTS OF AN ARBITRARY PLANE REGION BY NOBUYUKI SUITA 1. Introduction. Let Δ be a simply connected hyperbolic region. By denning
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION
 POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 The Variance of the Product of Random Variables Author(s): Leo A. Goodman Source: Journal of the American Statistical Association, Vol. 57, No. 297 (Mar., 1962), pp. 54-60 Published by: American Statistical
The Variance of the Product of Random Variables Author(s): Leo A. Goodman Source: Journal of the American Statistical Association, Vol. 57, No. 297 (Mar., 1962), pp. 54-60 Published by: American Statistical
(x 1, y 1 ) = (x 2, y 2 ) if and only if x 1 = x 2 and y 1 = y 2.
 1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 1 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 1 Jul 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 1 Jul 2013](/thumbs/73/68493566.jpg) Carleson measures on planar sets Zhijian Qiu Department of mathematics, Southwestern University of Finance and Economics arxiv:1307.0424v1 [math.ca] 1 Jul 2013 Abstract In this paper, we investigate what
Carleson measures on planar sets Zhijian Qiu Department of mathematics, Southwestern University of Finance and Economics arxiv:1307.0424v1 [math.ca] 1 Jul 2013 Abstract In this paper, we investigate what
Fundamental Properties of Holomorphic Functions
 Complex Analysis Contents Chapter 1. Fundamental Properties of Holomorphic Functions 5 1. Basic definitions 5 2. Integration and Integral formulas 6 3. Some consequences of the integral formulas 8 Chapter
Complex Analysis Contents Chapter 1. Fundamental Properties of Holomorphic Functions 5 1. Basic definitions 5 2. Integration and Integral formulas 6 3. Some consequences of the integral formulas 8 Chapter
Problem set 1, Real Analysis I, Spring, 2015.
 Problem set 1, Real Analysis I, Spring, 015. (1) Let f n : D R be a sequence of functions with domain D R n. Recall that f n f uniformly if and only if for all ɛ > 0, there is an N = N(ɛ) so that if n
Problem set 1, Real Analysis I, Spring, 015. (1) Let f n : D R be a sequence of functions with domain D R n. Recall that f n f uniformly if and only if for all ɛ > 0, there is an N = N(ɛ) so that if n
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL
 PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences
 Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences Monday, October 28, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 3 due November 15, 2013 at 5 PM. Last time we derived Cauchy's Integral Formula, which we will present in somewhat generalized
Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences Monday, October 28, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 3 due November 15, 2013 at 5 PM. Last time we derived Cauchy's Integral Formula, which we will present in somewhat generalized
Complex Analysis Homework 9: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Riemann sphere and rational maps
 Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 17, No. 5. (Oct., 1966), pp
 On the Existence and Uniqueness of the Real Logarithm of a Matrix Walter J. Culver Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 17, No. 5. (Oct., 1966), pp. 1146-1151. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9939%28196610%2917%3a5%3c1146%3aoteauo%3e2.0.co%3b2-b
On the Existence and Uniqueness of the Real Logarithm of a Matrix Walter J. Culver Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 17, No. 5. (Oct., 1966), pp. 1146-1151. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9939%28196610%2917%3a5%3c1146%3aoteauo%3e2.0.co%3b2-b
The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 21, No. 4. (Sep., 1990), pp
 Tabular Integration by Parts David Horowitz The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 21, No. 4. (Sep., 1990), pp. 307-311. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0746-8342%28199009%2921%3a4%3c307%3atibp%3e2.0.co%3b2-o
Tabular Integration by Parts David Horowitz The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 21, No. 4. (Sep., 1990), pp. 307-311. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0746-8342%28199009%2921%3a4%3c307%3atibp%3e2.0.co%3b2-o
The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 24, No. 4. (Sep., 1993), pp
 Taylor Polynomial Approximations in Polar Coordinates Sheldon P. Gordon The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 24, No. 4. (Sep., 1993), pp. 325-330. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0746-8342%28199309%2924%3a4%3c325%3atpaipc%3e2.0.co%3b2-m
Taylor Polynomial Approximations in Polar Coordinates Sheldon P. Gordon The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 24, No. 4. (Sep., 1993), pp. 325-330. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0746-8342%28199309%2924%3a4%3c325%3atpaipc%3e2.0.co%3b2-m
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM. 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces
 8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 515
 THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 515 Proposition 1 (=comment on page 17). If A is an algebra, then any finite union or finite intersection of sets in A is also in A. Proposition 2 (=Proposition 1.1). For every
THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 515 Proposition 1 (=comment on page 17). If A is an algebra, then any finite union or finite intersection of sets in A is also in A. Proposition 2 (=Proposition 1.1). For every
PROBLEMS. (b) (Polarization Identity) Show that in any inner product space
 1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
Examples of Dual Spaces from Measure Theory
 Chapter 9 Examples of Dual Spaces from Measure Theory We have seen that L (, A, µ) is a Banach space for any measure space (, A, µ). We will extend that concept in the following section to identify an
Chapter 9 Examples of Dual Spaces from Measure Theory We have seen that L (, A, µ) is a Banach space for any measure space (, A, µ). We will extend that concept in the following section to identify an
Part IB Complex Analysis
 Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
MORE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOREM
 MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
Annals of Mathematics
 Annals of Mathematics The Clifford-Klein Space Forms of Indefinite Metric Author(s): Joseph A. Wolf Reviewed work(s): Source: The Annals of Mathematics, Second Series, Vol. 75, No. 1 (Jan., 1962), pp.
Annals of Mathematics The Clifford-Klein Space Forms of Indefinite Metric Author(s): Joseph A. Wolf Reviewed work(s): Source: The Annals of Mathematics, Second Series, Vol. 75, No. 1 (Jan., 1962), pp.
Mathematical Association of America
 Mathematical Association of America http://www.jstor.org/stable/2975232. Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions of Use, available at. http://www.jstor.org/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp
Mathematical Association of America http://www.jstor.org/stable/2975232. Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions of Use, available at. http://www.jstor.org/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp
arxiv: v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 2013 arxiv: v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 2013](/thumbs/86/93829905.jpg) SHAPES OF POLYNOMIAL JULIA SETS KATHRYN A. LINDSEY arxiv:209.043v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 203 Abstract. Any Jordan curve in the complex plane can be approximated arbitrarily well in the Hausdorff topology by
SHAPES OF POLYNOMIAL JULIA SETS KATHRYN A. LINDSEY arxiv:209.043v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 203 Abstract. Any Jordan curve in the complex plane can be approximated arbitrarily well in the Hausdorff topology by
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Plurisubharmonic Functions and Pseudoconvex Domains
 Plurisubharmonic Functions and Pseudoconvex Domains Thomas Jackson June 8, 218 1 Introduction The purpose of this project is to give a brief background of basic complex analysis in several complex variables
Plurisubharmonic Functions and Pseudoconvex Domains Thomas Jackson June 8, 218 1 Introduction The purpose of this project is to give a brief background of basic complex analysis in several complex variables
A NOTE ON THE DEGREE OF POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION*
 1936.] DEGREE OF POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 873 am = #121 = #212= 1 The trilinear form associated with this matrix is x 1 yiz2+xiy2zi+x2yizi, which is equivalent to L under the transformations Xi = xi, X2
1936.] DEGREE OF POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 873 am = #121 = #212= 1 The trilinear form associated with this matrix is x 1 yiz2+xiy2zi+x2yizi, which is equivalent to L under the transformations Xi = xi, X2
Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r
![Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r](/thumbs/77/75527144.jpg) 2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 204 Cauchy and Runge Under the Same Roof. These notes can be used as an alternative to Section 5.5 of Chapter 2 in the textbook. They assume the theorem on winding numbers of the
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 204 Cauchy and Runge Under the Same Roof. These notes can be used as an alternative to Section 5.5 of Chapter 2 in the textbook. They assume the theorem on winding numbers of the
Stanford Mathematics Department Math 205A Lecture Supplement #4 Borel Regular & Radon Measures
 2 1 Borel Regular Measures We now state and prove an important regularity property of Borel regular outer measures: Stanford Mathematics Department Math 205A Lecture Supplement #4 Borel Regular & Radon
2 1 Borel Regular Measures We now state and prove an important regularity property of Borel regular outer measures: Stanford Mathematics Department Math 205A Lecture Supplement #4 Borel Regular & Radon
Lebesgue Measure on R n
 CHAPTER 2 Lebesgue Measure on R n Our goal is to construct a notion of the volume, or Lebesgue measure, of rather general subsets of R n that reduces to the usual volume of elementary geometrical sets
CHAPTER 2 Lebesgue Measure on R n Our goal is to construct a notion of the volume, or Lebesgue measure, of rather general subsets of R n that reduces to the usual volume of elementary geometrical sets
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Conformal Mappings. Chapter Schwarz Lemma
 Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Closed sets of approximation on non-compact Riemann surfaces
 Closed sets of approximation on non-compact Riemann surfaces Nadya Askaripour and André Boivin Blacksburg March 2013 Complex Approximation Closed sets of Approximation Extension Theorem Example Complex
Closed sets of approximation on non-compact Riemann surfaces Nadya Askaripour and André Boivin Blacksburg March 2013 Complex Approximation Closed sets of Approximation Extension Theorem Example Complex
Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall F(x) = 1 x. f(t)dt. t 1 2. tf 2 (t)dt. and g(t, x) = 2 t. 2 t
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall 2. Let f L 2 (, ) be given. (a) Prove that ( x 2 f(t) dt) 2 x x t f(t) 2 dt. (b) Given part (a), prove that F L 2 (, ) 2 f L 2 (, ), where F(x) = x (a) Using
Analysis Comprehensive Exam Questions Fall 2. Let f L 2 (, ) be given. (a) Prove that ( x 2 f(t) dt) 2 x x t f(t) 2 dt. (b) Given part (a), prove that F L 2 (, ) 2 f L 2 (, ), where F(x) = x (a) Using
American Journal of Mathematics, Vol. 109, No. 1. (Feb., 1987), pp
 A Simple Algorithm for Cyclic Vectors Nicholas M. Katz American Journal of Mathematics, Vol. 109, No. 1. (Feb., 1987), pp. 65-70. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9327%28198702%29109%3a1%3c65%3aasafcv%3e2.0.co%3b2-a
A Simple Algorithm for Cyclic Vectors Nicholas M. Katz American Journal of Mathematics, Vol. 109, No. 1. (Feb., 1987), pp. 65-70. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9327%28198702%29109%3a1%3c65%3aasafcv%3e2.0.co%3b2-a
Simply Connected Domains
 Simply onnected Domains Generaliing the losed urve Theorem We have shown that if f() is analytic inside and on a closed curve, then f()d = 0. We have also seen examples where f() is analytic on the curve,
Simply onnected Domains Generaliing the losed urve Theorem We have shown that if f() is analytic inside and on a closed curve, then f()d = 0. We have also seen examples where f() is analytic on the curve,
Part II. Riemann Surfaces. Year
 Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 57, No. 2. (Jun., 1976), pp
 Elliptic Curves and Dedekind Domains Michael Rosen Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 57, No. 2. (Jun., 1976), pp. 197-201. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9939%28197606%2957%3a2%3c197%3aecadd%3e2.0.co%3b2-7
Elliptic Curves and Dedekind Domains Michael Rosen Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 57, No. 2. (Jun., 1976), pp. 197-201. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9939%28197606%2957%3a2%3c197%3aecadd%3e2.0.co%3b2-7
INDEX. Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem, for sequences, boundary points, bounded functions, 142 bounded sets, 42 43
 INDEX Abel s identity, 131 Abel s test, 131 132 Abel s theorem, 463 464 absolute convergence, 113 114 implication of conditional convergence, 114 absolute value, 7 reverse triangle inequality, 9 triangle
INDEX Abel s identity, 131 Abel s test, 131 132 Abel s theorem, 463 464 absolute convergence, 113 114 implication of conditional convergence, 114 absolute value, 7 reverse triangle inequality, 9 triangle
5.3 The Upper Half Plane
 Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Mind Association. Oxford University Press and Mind Association are collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Mind.
 Mind Association Response to Colyvan Author(s): Joseph Melia Source: Mind, New Series, Vol. 111, No. 441 (Jan., 2002), pp. 75-79 Published by: Oxford University Press on behalf of the Mind Association
Mind Association Response to Colyvan Author(s): Joseph Melia Source: Mind, New Series, Vol. 111, No. 441 (Jan., 2002), pp. 75-79 Published by: Oxford University Press on behalf of the Mind Association
UNIFORM DENSITIES OF REGULAR SEQUENCES IN THE UNIT DISK. Peter L. Duren, Alexander P. Schuster and Kristian Seip
 UNIFORM DENSITIES OF REGULAR SEQUENCES IN THE UNIT DISK Peter L. Duren, Alexander P. Schuster and Kristian Seip Abstract. The upper and lower uniform densities of some regular sequences are computed. These
UNIFORM DENSITIES OF REGULAR SEQUENCES IN THE UNIT DISK Peter L. Duren, Alexander P. Schuster and Kristian Seip Abstract. The upper and lower uniform densities of some regular sequences are computed. These
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
On the Length of Lemniscates
 On the Length of Lemniscates Alexandre Eremenko & Walter Hayman For a monic polynomial p of degree d, we write E(p) := {z : p(z) =1}. A conjecture of Erdős, Herzog and Piranian [4], repeated by Erdős in
On the Length of Lemniscates Alexandre Eremenko & Walter Hayman For a monic polynomial p of degree d, we write E(p) := {z : p(z) =1}. A conjecture of Erdős, Herzog and Piranian [4], repeated by Erdős in
Part II. Geometry and Groups. Year
 Part II Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2014 Paper 4, Section I 3F 49 Define the limit set Λ(G) of a Kleinian group G. Assuming that G has no finite orbit in H 3 S 2, and that Λ(G),
Part II Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2014 Paper 4, Section I 3F 49 Define the limit set Λ(G) of a Kleinian group G. Assuming that G has no finite orbit in H 3 S 2, and that Λ(G),
On Bank-Laine functions
 Computational Methods and Function Theory Volume 00 0000), No. 0, 000 000 XXYYYZZ On Bank-Laine functions Alastair Fletcher Keywords. Bank-Laine functions, zeros. 2000 MSC. 30D35, 34M05. Abstract. In this
Computational Methods and Function Theory Volume 00 0000), No. 0, 000 000 XXYYYZZ On Bank-Laine functions Alastair Fletcher Keywords. Bank-Laine functions, zeros. 2000 MSC. 30D35, 34M05. Abstract. In this
Pervasive Function Spaces
 Anthony G. O Farrell http://www.maths.may.ie/staff/aof/ Bȩndlewo, 23-7-2009 Anthony G. O Farrell http://www.maths.may.ie/staff/aof/ Bȩndlewo, 23-7-2009 Joint with I. Netuka (Prague) and M.A. Sanabria (La
Anthony G. O Farrell http://www.maths.may.ie/staff/aof/ Bȩndlewo, 23-7-2009 Anthony G. O Farrell http://www.maths.may.ie/staff/aof/ Bȩndlewo, 23-7-2009 Joint with I. Netuka (Prague) and M.A. Sanabria (La
Journal of Applied Probability, Vol. 13, No. 3. (Sep., 1976), pp
 Buffon's Problem with a Long Needle Persi Diaconis Journal of Applied Probability, Vol. 13, No. 3. (Sep., 1976), pp. 614-618. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0021-9002%28197609%2913%3a3%3c614%3abpwaln%3e2.0.co%3b2-p
Buffon's Problem with a Long Needle Persi Diaconis Journal of Applied Probability, Vol. 13, No. 3. (Sep., 1976), pp. 614-618. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0021-9002%28197609%2913%3a3%3c614%3abpwaln%3e2.0.co%3b2-p
l(y j ) = 0 for all y j (1)
 Problem 1. The closed linear span of a subset {y j } of a normed vector space is defined as the intersection of all closed subspaces containing all y j and thus the smallest such subspace. 1 Show that
Problem 1. The closed linear span of a subset {y j } of a normed vector space is defined as the intersection of all closed subspaces containing all y j and thus the smallest such subspace. 1 Show that
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Convex Real Projective Structures on Closed Surfaces are Closed Author(s): Suhyoung Choi and William M. Goldman Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 118, No. 2 (Jun., 1993), pp.
Convex Real Projective Structures on Closed Surfaces are Closed Author(s): Suhyoung Choi and William M. Goldman Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 118, No. 2 (Jun., 1993), pp.
The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 81, No. 4. (Apr., 1974), pp
 Everywhere Differentiable, Nowhere Monotone, Functions Y. Katznelson; Karl Stromberg The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 81, No. 4. (Apr., 1974), pp. 349-354. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9890%28197404%2981%3a4%3c349%3aednmf%3e2.0.co%3b2-j
Everywhere Differentiable, Nowhere Monotone, Functions Y. Katznelson; Karl Stromberg The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 81, No. 4. (Apr., 1974), pp. 349-354. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0002-9890%28197404%2981%3a4%3c349%3aednmf%3e2.0.co%3b2-j
COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS
 Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
Theorems. Theorem 1.11: Greatest-Lower-Bound Property. Theorem 1.20: The Archimedean property of. Theorem 1.21: -th Root of Real Numbers
 Page 1 Theorems Wednesday, May 9, 2018 12:53 AM Theorem 1.11: Greatest-Lower-Bound Property Suppose is an ordered set with the least-upper-bound property Suppose, and is bounded below be the set of lower
Page 1 Theorems Wednesday, May 9, 2018 12:53 AM Theorem 1.11: Greatest-Lower-Bound Property Suppose is an ordered set with the least-upper-bound property Suppose, and is bounded below be the set of lower
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 On the Hahn-Banach Extension Property Author(s): Jonathan M. Borwein Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 86, No. 1, (Sep., 1982), pp. 42-46 Published by: American Mathematical
On the Hahn-Banach Extension Property Author(s): Jonathan M. Borwein Source: Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 86, No. 1, (Sep., 1982), pp. 42-46 Published by: American Mathematical
Chapter 6: The metric space M(G) and normal families
 Chapter 6: The metric space MG) and normal families Course 414, 003 04 March 9, 004 Remark 6.1 For G C open, we recall the notation MG) for the set algebra) of all meromorphic functions on G. We now consider
Chapter 6: The metric space MG) and normal families Course 414, 003 04 March 9, 004 Remark 6.1 For G C open, we recall the notation MG) for the set algebra) of all meromorphic functions on G. We now consider
LECTURE-13 : GENERALIZED CAUCHY S THEOREM
 LECTURE-3 : GENERALIZED CAUCHY S THEOREM VED V. DATAR The aim of this lecture to prove a general form of Cauchy s theorem applicable to multiply connected domains. We end with computations of some real
LECTURE-3 : GENERALIZED CAUCHY S THEOREM VED V. DATAR The aim of this lecture to prove a general form of Cauchy s theorem applicable to multiply connected domains. We end with computations of some real
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
The Periodogram and its Optical Analogy.
 The Periodogram and Its Optical Analogy Author(s): Arthur Schuster Reviewed work(s): Source: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character,
The Periodogram and Its Optical Analogy Author(s): Arthur Schuster Reviewed work(s): Source: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character,
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
b 0 + b 1 z b d z d
 I. Introduction Definition 1. For z C, a rational function of degree d is any with a d, b d not both equal to 0. R(z) = P (z) Q(z) = a 0 + a 1 z +... + a d z d b 0 + b 1 z +... + b d z d It is exactly
I. Introduction Definition 1. For z C, a rational function of degree d is any with a d, b d not both equal to 0. R(z) = P (z) Q(z) = a 0 + a 1 z +... + a d z d b 0 + b 1 z +... + b d z d It is exactly
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Bounded Infinite Sequences/Functions : Orders of Infinity
 Bounded Infinite Sequences/Functions : Orders of Infinity by Garimella Ramamurthy Report No: IIIT/TR/2009/247 Centre for Security, Theory and Algorithms International Institute of Information Technology
Bounded Infinite Sequences/Functions : Orders of Infinity by Garimella Ramamurthy Report No: IIIT/TR/2009/247 Centre for Security, Theory and Algorithms International Institute of Information Technology
Indeed, if we want m to be compatible with taking limits, it should be countably additive, meaning that ( )
 Lebesgue Measure The idea of the Lebesgue integral is to first define a measure on subsets of R. That is, we wish to assign a number m(s to each subset S of R, representing the total length that S takes
Lebesgue Measure The idea of the Lebesgue integral is to first define a measure on subsets of R. That is, we wish to assign a number m(s to each subset S of R, representing the total length that S takes
Finite-dimensional spaces. C n is the space of n-tuples x = (x 1,..., x n ) of complex numbers. It is a Hilbert space with the inner product
 Chapter 4 Hilbert Spaces 4.1 Inner Product Spaces Inner Product Space. A complex vector space E is called an inner product space (or a pre-hilbert space, or a unitary space) if there is a mapping (, )
Chapter 4 Hilbert Spaces 4.1 Inner Product Spaces Inner Product Space. A complex vector space E is called an inner product space (or a pre-hilbert space, or a unitary space) if there is a mapping (, )
Chapter 3: Baire category and open mapping theorems
 MA3421 2016 17 Chapter 3: Baire category and open mapping theorems A number of the major results rely on completeness via the Baire category theorem. 3.1 The Baire category theorem 3.1.1 Definition. A
MA3421 2016 17 Chapter 3: Baire category and open mapping theorems A number of the major results rely on completeness via the Baire category theorem. 3.1 The Baire category theorem 3.1.1 Definition. A
Analysis-3 lecture schemes
 Analysis-3 lecture schemes (with Homeworks) 1 Csörgő István November, 2015 1 A jegyzet az ELTE Informatikai Kar 2015. évi Jegyzetpályázatának támogatásával készült Contents 1. Lesson 1 4 1.1. The Space
Analysis-3 lecture schemes (with Homeworks) 1 Csörgő István November, 2015 1 A jegyzet az ELTE Informatikai Kar 2015. évi Jegyzetpályázatának támogatásával készült Contents 1. Lesson 1 4 1.1. The Space
