Department of Physics IIT Kanpur, Semester II,
|
|
|
- Franklin Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Physics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 7-8 PHYA: Physics II Solution # 4 Instructors: AKJ & SC Solution 4.: Force with image charges (Griffiths rd ed. Prob.6 As far as force is concerned, this problem is the same if we remove the grounded conducting plate and simply put an image charge +q at z d and an image charge q at z d. Therefore, the force on the charge +q is given by F q 4πɛ (d + q (4d + q ] (6d ẑ q 4πɛ d ] ẑ q 9 6 4πɛ d 7ẑ Solution 4.: Infinite-line image charge (Griffiths rd ed. Prob.9 This problem is an extension of the problem in which a point charge is placed above an infinite grounded conducting plane. So, in order to obtain the correct potential, we need to put an infinite line charge λ running parallel to the x-axis at a distance d from the x y plane. (see Fig.. FIG. : (a Let s first find the potential at a point (y, z on the y z plane. Assume that the distance of the point (y, z from the top infinite line charge is given by the magnitude of the vector ŝ + ; similarly the distance of the point (y, z from the bottom infinite line charge is given by the magnitude of the vector ŝ. Taking the potential V at x y plane to be the reference, the potential due to top infinite line charge can be shown to be V + λ ( s+. Similarly, the potential due to the bottom infinite line charge can be shown to be 4πɛ d V + λ ( s. Therefore the total potential at (y, z is given by 4πɛ d V (y, z λ ( s+ 4πɛ d λ ( s 4πɛ λ 4πɛ λ 4πɛ s + ( s s + + λ ( s 4πɛ d y + (z + d ] y + (z d
2 V (b The induced charge density is given by σ ɛ, where ˆn is the vector in the direction perpendicular to n the surface. In the present problem, ˆn ẑ. Therefore, V σ ɛ n ɛ V z z λ y + (z + d ]] ɛ z 4πɛ y + (z d z ] λ (z + d (z d ɛ 4πɛ y + (z + d y + (z d λ d ɛ 4πɛ y + z + d ] y + d λd π(y + d z Solution 4.: Far-field potential (Griffiths rd ed. Prob.6 In this problem, a point r on the sphere is represented in the (r, θ, φ coordinates. An observation point r is represented in the (r, θ, φ coordinates. The angle between the vectors r and r is represented by α. So, the formula for multipole expansion of potential V can be written as V (r 4πɛ n r n+ r n P n (cos αρ(rdτ Now, since we are interested in observation points along z-axis only, the angle α between the two vectors in essentially the angle θ. Therefore we can write the above expression as V (r 4πɛ n z n+ Let s calculate the above potential term by term in the limit z R. r n P n (cos θρ(rdτ. Monopole term: We have V mono (r ρ(rdτ 4πɛ z k Rr ] 4πɛ z (R r sin θ r sin θdrdθdφ 4πɛ z kr (R r sin θdrdθdφ The r-integral yields R (R rdr (Rr r R R R. Therefore, the monopole potential is zero: V mono (r 4πɛ z kr (R r sin θdrdθdφ
3 . Dipole term: We have V dip (r 4πɛ z rp (cos θρ(rdτ 4πɛ z r cos θρ(rdτ 4πɛ z r cos θ k Rr ] (R r sin θ r sin θdrdθdφ The θ-integral yields π sin θ cos θdθ sin θ π V dip (r 4πɛ z r cos θ (. Therefore, the dipole potential is also zero: k Rr (R r sin θ ] r sin θdrdθdφ. Quadrupole term: We have V quad (r 4πɛ z 4πɛ z 8πɛ z r P (cos θρ(rdτ r ( cos θ /ρ(rdτ r ( cos θ k Rr ] (R r sin θ r sin θdrdθdφ The three integrals can be calculated as follows: r integral : θ integral : φ integral : Therefore, R π π ( r r (R rdr R r4 R ( cos θ sin θdθ dφ π V quad (r π kr 8πɛ z R4 6 sin θdθ π So, the approximate potential is the potential of the quadrupole: ( π ( ( π sin 4 θdθ π 9 π ( ( R4 π (π kπ R πɛ 48z V (r V quad (r kπ R 5 4πɛ 48z Solution 4.4: Potential due to a four-charge system (Griffiths rd ed. Prob.7 The total charge of the system is zero. So, the monopole term in the potential would be zero. Now, let s calculate the dipole term see Fig. ]. We have Therefore, p (qa qaẑ + ( qa q( aŷ qaẑ V V dipole p ˆr 4πɛ r qaẑ ˆr 4πɛ r qa cos θ 4πɛ r
4 x z +q a µ a a -q a -q +q r y FIG. : Solution 4.5: Far-field Potential due to a spherical-charge distribution (Griffiths rd ed. Prob.8 (a From the symmetry in the problem it is clear that the net dipole moment will be in the z direction. Therefore p rρ(rdτ zẑρ(rdτ zρ(rdτẑ zσdaẑ (R cos θ(k cos θr sin θdθdφẑ πr k πr k π 4πR k ẑ cos θ sin θdθẑ π ( cos θ ẑ (b We find that the total charge of the system is zero. So, there will be no monopole contribution to the far-field potential. However since the dipole moment is not zero, the first contribution will be from the dipole term and the far-field potential can be written as V V dipole p ˆr 4πɛ r 4πR k ẑ ˆr 4πɛ r 4πR k cos θ 4πɛ r kr cos θ ɛ r Solution 4.6: Electric field of a pure dipole (Griffiths rd ed. Prob. The electric field of a pure dipole is given by p E dip (r ( cos θˆr + sin θˆθ 4πɛ r (p cos θˆr p cos θˆr + p sin θˆθ 4πɛ r 4πɛ r (p ˆrˆr (p ˆrˆr (p ˆθˆθ] (p ˆrˆr p] 4πɛ r Solution 4.7: Field and potential due to a three-charge system (Griffiths rd ed. Prob. 4
5 The total charge of the three-charge system is q. Therefore the monopole contribution is not zero and is given by V mono 4πɛ q r q 4πɛ r The dipole moment p of the charge system is p qaẑ + qa q( a]ŷ qaẑ. So, the dipole contribution to the potential is V dip p ˆr 4πɛ r qa cos θ 4πɛ r Therefore, the potential up to two terms in the multipole expansion is given by V V mono + V dip q ( qa cos θ + 4πɛ r r The electric field E is given by E V q 4πɛ r ˆr + ar ( ] cos θˆr + sin θˆθ x z +q a a a -q -q r y FIG. : 5
Electromagnetism: Worked Examples. University of Oxford Second Year, Part A2
 Electromagnetism: Worked Examples University of Oxford Second Year, Part A2 Caroline Terquem Department of Physics caroline.terquem@physics.ox.ac.uk Michaelmas Term 2017 2 Contents 1 Potentials 5 1.1 Potential
Electromagnetism: Worked Examples University of Oxford Second Year, Part A2 Caroline Terquem Department of Physics caroline.terquem@physics.ox.ac.uk Michaelmas Term 2017 2 Contents 1 Potentials 5 1.1 Potential
Homework Assignment 4 Solution Set
 Homework Assignment 4 Solution Set PHYCS 442 7 February, 24 Problem (Griffiths 2.37 If the plates are sufficiently large the field near them does not depend on d. The field between the plates is zero (the
Homework Assignment 4 Solution Set PHYCS 442 7 February, 24 Problem (Griffiths 2.37 If the plates are sufficiently large the field near them does not depend on d. The field between the plates is zero (the
Department of Physics IIT Kanpur, Semester II,
 Department of Phsics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 7-8 PHYA: Phsics II Solutions # Instructors: AKJ & SC Solution.: (a) At the top of the hill, the gradient of the height function should be ero, that is, h(,
Department of Phsics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 7-8 PHYA: Phsics II Solutions # Instructors: AKJ & SC Solution.: (a) At the top of the hill, the gradient of the height function should be ero, that is, h(,
Summary: Applications of Gauss Law
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Errata Instructor s Solutions Manual Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed Author: David Griffiths Date: September 1, 2004
 Errata Instructor s Solutions Manual Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed Author: David Griffiths Date: September, 004 Page 4, Prob..5 (b): last expression should read y +z +3x. Page 4, Prob..6: at
Errata Instructor s Solutions Manual Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed Author: David Griffiths Date: September, 004 Page 4, Prob..5 (b): last expression should read y +z +3x. Page 4, Prob..6: at
Expansion of 1/r potential in Legendre polynomials
 Expansion of 1/r potential in Legendre polynomials In electrostatics and gravitation, we see scalar potentials of the form V = K d Take d = R r = R 2 2Rr cos θ + r 2 = R 1 2 r R cos θ + r R )2 Use h =
Expansion of 1/r potential in Legendre polynomials In electrostatics and gravitation, we see scalar potentials of the form V = K d Take d = R r = R 2 2Rr cos θ + r 2 = R 1 2 r R cos θ + r R )2 Use h =
PHY481 - Outline of solutions to Homework 3
 1 PHY481 - Outline of solutions to Homework 3 Problem 3.8: We consider a charge outside a conducting sphere that is neutral. In order that the sphere be neutral, we have to introduce a new image charge
1 PHY481 - Outline of solutions to Homework 3 Problem 3.8: We consider a charge outside a conducting sphere that is neutral. In order that the sphere be neutral, we have to introduce a new image charge
Electromagnetism Answers to Problem Set 9 Spring 2006
 Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
Indiana University Physics P331: Theory of Electromagnetism Review Problems #3
 Indiana University Physics P331: Theory of Electromagnetism Review Problems #3 Note: The final exam (Friday 1/14 8:00-10:00 AM will be comprehensive, covering lecture and homework material pertaining to
Indiana University Physics P331: Theory of Electromagnetism Review Problems #3 Note: The final exam (Friday 1/14 8:00-10:00 AM will be comprehensive, covering lecture and homework material pertaining to
Problem Set #4: 4.1,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 25th)
 Chapter 4 Multipoles, Dielectrics Problem Set #4: 4.,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 5th 4. Multipole expansion Consider a localized distribution of charges described by ρ(x contained entirely in a sphere of
Chapter 4 Multipoles, Dielectrics Problem Set #4: 4.,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 5th 4. Multipole expansion Consider a localized distribution of charges described by ρ(x contained entirely in a sphere of
Electric fields in matter
 Electric fields in matter November 2, 25 Suppose we apply a constant electric field to a block of material. Then the charges that make up the matter are no longer in equilibrium: the electrons tend to
Electric fields in matter November 2, 25 Suppose we apply a constant electric field to a block of material. Then the charges that make up the matter are no longer in equilibrium: the electrons tend to
Physics 3323, Fall 2016 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 2016
 Physics 3323, Fall 26 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 26. What s my charge? A spherical region of radius R is filled with a charge distribution that gives rise to an electric field inside of the form E E /R 2
Physics 3323, Fall 26 Problem Set 2 due Sep 9, 26. What s my charge? A spherical region of radius R is filled with a charge distribution that gives rise to an electric field inside of the form E E /R 2
Magnetostatics III Magnetic Vector Potential (Griffiths Chapter 5: Section 4)
 Dr. Alain Brizard Electromagnetic Theory I PY ) Magnetostatics III Magnetic Vector Potential Griffiths Chapter 5: Section ) Vector Potential The magnetic field B was written previously as Br) = Ar), 1)
Dr. Alain Brizard Electromagnetic Theory I PY ) Magnetostatics III Magnetic Vector Potential Griffiths Chapter 5: Section ) Vector Potential The magnetic field B was written previously as Br) = Ar), 1)
Topic 7. Electric flux Gauss s Law Divergence of E Application of Gauss Law Curl of E
 Topic 7 Electric flux Gauss s Law Divergence of E Application of Gauss Law Curl of E urface enclosing an electric dipole. urface enclosing charges 2q and q. Electric flux Flux density : The number of field
Topic 7 Electric flux Gauss s Law Divergence of E Application of Gauss Law Curl of E urface enclosing an electric dipole. urface enclosing charges 2q and q. Electric flux Flux density : The number of field
FORMULA SHEET FOR QUIZ 2 Exam Date: November 8, 2017
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II November 5, 207 Prof. Alan Guth FORMULA SHEET FOR QUIZ 2 Exam Date: November 8, 207 A few items below are marked
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II November 5, 207 Prof. Alan Guth FORMULA SHEET FOR QUIZ 2 Exam Date: November 8, 207 A few items below are marked
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 110A. Homework #7. Benjamin Stahl. March 3, 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS A Homework #7 Benjamin Stahl March 3, 5 GRIFFITHS, 5.34 It will be shown that the magnetic field of a dipole can written in the following
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS A Homework #7 Benjamin Stahl March 3, 5 GRIFFITHS, 5.34 It will be shown that the magnetic field of a dipole can written in the following
The dielectrophoretic force on dielectric spherical objects
 10064 - Physics Project The dielectrophoretic force on dielectric spherical objects Andreas Ammitzbøll s042191 Janosch Michael Cristoph Rauba s042606 Marco Haller Schultz s042357 Supervisors: Niels Asger
10064 - Physics Project The dielectrophoretic force on dielectric spherical objects Andreas Ammitzbøll s042191 Janosch Michael Cristoph Rauba s042606 Marco Haller Schultz s042357 Supervisors: Niels Asger
Tutorial 3 - Solutions Electromagnetic Waves
 Tutorial 3 - Solutions Electromagnetic Waves You can find formulas you require for vector calculus at the end of this tutorial. 1. Find the Divergence and Curl of the following functions - (a) k r ˆr f
Tutorial 3 - Solutions Electromagnetic Waves You can find formulas you require for vector calculus at the end of this tutorial. 1. Find the Divergence and Curl of the following functions - (a) k r ˆr f
Scattering. March 20, 2016
 Scattering March 0, 06 The scattering of waves of any kind, by a compact object, has applications on all scales, from the scattering of light from the early universe by intervening galaxies, to the scattering
Scattering March 0, 06 The scattering of waves of any kind, by a compact object, has applications on all scales, from the scattering of light from the early universe by intervening galaxies, to the scattering
Physics 3323, Fall 2016 Problem Set 7 due Oct 14, 2016
 Physics 333, Fll 16 Problem Set 7 due Oct 14, 16 Reding: Griffiths 4.1 through 4.4.1 1. Electric dipole An electric dipole with p = p ẑ is locted t the origin nd is sitting in n otherwise uniform electric
Physics 333, Fll 16 Problem Set 7 due Oct 14, 16 Reding: Griffiths 4.1 through 4.4.1 1. Electric dipole An electric dipole with p = p ẑ is locted t the origin nd is sitting in n otherwise uniform electric
Solution Set Eight. 1 Problem #1: Toroidal Electromagnet with Gap Problem #4: Self-Inductance of a Long Solenoid. 9
 : Solution Set Eight Northwestern University, Electrodynamics I Wednesday, March 9, 6 Contents Problem #: Toroidal Electromagnet with Gap. Problem #: Electromagnetic Momentum. 3 3 Problem #3: Type I Superconductor.
: Solution Set Eight Northwestern University, Electrodynamics I Wednesday, March 9, 6 Contents Problem #: Toroidal Electromagnet with Gap. Problem #: Electromagnetic Momentum. 3 3 Problem #3: Type I Superconductor.
The Helmholtz theorem at last!
 Problem. The Helmholtz theorem at last! Recall in class the Helmholtz theorem that says that if if E =0 then E can be written as E = φ () if B =0 then B can be written as B = A (2) (a) Let n be a unit
Problem. The Helmholtz theorem at last! Recall in class the Helmholtz theorem that says that if if E =0 then E can be written as E = φ () if B =0 then B can be written as B = A (2) (a) Let n be a unit
3. Calculating Electrostatic Potential
 3. Calculating Electrostatic Potential 3. Laplace s Equation 3. The Method of Images 3.3 Separation of Variables 3.4 Multipole Expansion 3.. Introduction The primary task of electrostatics is to study
3. Calculating Electrostatic Potential 3. Laplace s Equation 3. The Method of Images 3.3 Separation of Variables 3.4 Multipole Expansion 3.. Introduction The primary task of electrostatics is to study
week 3 chapter 28 - Gauss s Law
 week 3 chapter 28 - Gauss s Law Here is the central idea: recall field lines... + + q 2q q (a) (b) (c) q + + q q + +q q/2 + q (d) (e) (f) The number of electric field lines emerging from minus the number
week 3 chapter 28 - Gauss s Law Here is the central idea: recall field lines... + + q 2q q (a) (b) (c) q + + q q + +q q/2 + q (d) (e) (f) The number of electric field lines emerging from minus the number
Electromagnetism Answers to Problem Set 8 Spring Jackson Prob. 4.1: Multipole expansion for various charge distributions
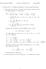 Electromagnetism 76 Answers to Problem Set 8 Spring 6. Jackson Prob. 4.: Multipole expansion for various charge distributions (a) In the first case, we have 4 charges in the xy plane at distance a from
Electromagnetism 76 Answers to Problem Set 8 Spring 6. Jackson Prob. 4.: Multipole expansion for various charge distributions (a) In the first case, we have 4 charges in the xy plane at distance a from
0.4. math. r r = r 2 + r 2 2r r cos(θ ) 0.5. Coordiates.
 .. Electrostatics... Multipole. F = E(r) = E(r) = S n qq i r r i 3 (r r i) i= n i= q i r r i 3 (r r i) d 3 r ρ(r ) 3 (r r ) ds E(r) = 4πQ enclosed E(r) = 4πρ(r ) E(r) = Φ(r) d 3 r ρ(r ) r dl E W = q(φ(r
.. Electrostatics... Multipole. F = E(r) = E(r) = S n qq i r r i 3 (r r i) i= n i= q i r r i 3 (r r i) d 3 r ρ(r ) 3 (r r ) ds E(r) = 4πQ enclosed E(r) = 4πρ(r ) E(r) = Φ(r) d 3 r ρ(r ) r dl E W = q(φ(r
Physics 7B Midterm 2 Solutions - Fall 2017 Professor R. Birgeneau
 Problem 1 Physics 7B Midterm 2 Solutions - Fall 217 Professor R. Birgeneau (a) Since the wire is a conductor, the electric field on the inside is simply zero. To find the electric field in the exterior
Problem 1 Physics 7B Midterm 2 Solutions - Fall 217 Professor R. Birgeneau (a) Since the wire is a conductor, the electric field on the inside is simply zero. To find the electric field in the exterior
Multipole moments. November 9, 2015
 Multipole moments November 9, 5 The far field expansion Suppose we have a localized charge distribution, confined to a region near the origin with r < R. Then for values of r > R, the electric field must
Multipole moments November 9, 5 The far field expansion Suppose we have a localized charge distribution, confined to a region near the origin with r < R. Then for values of r > R, the electric field must
G( x x, t) = 1 (2π) 3. d 3 k e k2 t/µσ e i k ( x x ) A( k, t)e k x d 3 k. A( x, t) = 1
 Physics 505 Fall 2005 Homework Assignment #10 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 6: 6.3, 6.4, 6.14, 6.18 6.3 The homogeneous diffusion equation (5.160) for the vector potential for quasi-static fields in
Physics 505 Fall 2005 Homework Assignment #10 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 6: 6.3, 6.4, 6.14, 6.18 6.3 The homogeneous diffusion equation (5.160) for the vector potential for quasi-static fields in
Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 2005/10/17 Electro Dynamic
 Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 5//7 Name Electro Dynamic. () Write Gauss Law in differential form. E( r) =ρ( r)/ɛ, or D = ρ, E= electricfield,ρ=volume charge density, ɛ =permittivity
Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 5//7 Name Electro Dynamic. () Write Gauss Law in differential form. E( r) =ρ( r)/ɛ, or D = ρ, E= electricfield,ρ=volume charge density, ɛ =permittivity
1. (3) Write Gauss Law in differential form. Explain the physical meaning.
 Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about
Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about
CHAPTER 11 RADIATION 4/13/2017. Outlines. 1. Electric Dipole radiation. 2. Magnetic Dipole Radiation. 3. Point Charge. 4. Synchrotron Radiation
 CHAPTER 11 RADIATION Outlines 1. Electric Dipole radiation 2. Magnetic Dipole Radiation 3. Point Charge Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 4. Synchrotron Radiation
CHAPTER 11 RADIATION Outlines 1. Electric Dipole radiation 2. Magnetic Dipole Radiation 3. Point Charge Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 4. Synchrotron Radiation
Physics 506 Winter 2008 Homework Assignment #4 Solutions. Textbook problems: Ch. 9: 9.6, 9.11, 9.16, 9.17
 Physics 56 Winter 28 Homework Assignment #4 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 9: 9.6, 9., 9.6, 9.7 9.6 a) Starting from the general expression (9.2) for A and the corresponding expression for Φ, expand
Physics 56 Winter 28 Homework Assignment #4 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 9: 9.6, 9., 9.6, 9.7 9.6 a) Starting from the general expression (9.2) for A and the corresponding expression for Φ, expand
Physics 222, Spring 2010 Quiz 3, Form: A
 Physics 222, Spring 2010 Quiz 3, Form: A Name: Date: Instructions You must sketch correct pictures and vectors, you must show all calculations, and you must explain all answers for full credit. Neatness
Physics 222, Spring 2010 Quiz 3, Form: A Name: Date: Instructions You must sketch correct pictures and vectors, you must show all calculations, and you must explain all answers for full credit. Neatness
(b) For the system in question, the electric field E, the displacement D, and the polarization P = D ɛ 0 E are as follows. r2 0 inside the sphere,
 PHY 35 K. Solutions for the second midterm exam. Problem 1: a The boundary conditions at the oil-air interface are air side E oil side = E and D air side oil side = D = E air side oil side = ɛ = 1+χ E.
PHY 35 K. Solutions for the second midterm exam. Problem 1: a The boundary conditions at the oil-air interface are air side E oil side = E and D air side oil side = D = E air side oil side = ɛ = 1+χ E.
Fall Lee - Midterm 2 solutions
 Fall 2009 - Lee - Midterm 2 solutions Problem 1 Solutions Part A Because the middle slab is a conductor, the electric field inside of the slab must be 0. Parts B and C Recall that to find the electric
Fall 2009 - Lee - Midterm 2 solutions Problem 1 Solutions Part A Because the middle slab is a conductor, the electric field inside of the slab must be 0. Parts B and C Recall that to find the electric
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination January 8, 216 (Friday) 9: am - 12: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination January 8, 216 (Friday) 9: am - 12: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct
Magnetostatics and the vector potential
 Magnetostatics and the vector potential December 8, 2015 1 The divergence of the magnetic field Starting with the general form of the Biot-Savart law, B (x 0 ) we take the divergence of both sides with
Magnetostatics and the vector potential December 8, 2015 1 The divergence of the magnetic field Starting with the general form of the Biot-Savart law, B (x 0 ) we take the divergence of both sides with
Physics 6C Review 1. Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz. July 16, Figure 1: Coulombs Law
 Physics 6C Review 1 Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz July 16, 2012 1 Review 1.1 Coulombs Law Figure 1: Coulombs Law The steps for solving any problem of this type
Physics 6C Review 1 Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz July 16, 2012 1 Review 1.1 Coulombs Law Figure 1: Coulombs Law The steps for solving any problem of this type
Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
E&M. 1 Capacitors. January 2009
 E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
Electrodynamics II: Lecture 9
 Electrodynamics II: Lecture 9 Multipole radiation Amol Dighe Sep 14, 2011 Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation Outline 1 Multipole
Electrodynamics II: Lecture 9 Multipole radiation Amol Dighe Sep 14, 2011 Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation Outline 1 Multipole
Chapter 27. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Electric Flux Field lines penetrating an area A perpendicular to the field The product of EA is the flux, Φ In general: Φ E = E A sin θ Electric
Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Electric Flux Field lines penetrating an area A perpendicular to the field The product of EA is the flux, Φ In general: Φ E = E A sin θ Electric
EM radiation - Lecture 14
 EM radiation - Lecture 14 1 Review Begin with a review of the potentials, fields, and Poynting vector for a point charge in accelerated motion. The retarded potential forms are given below. The source
EM radiation - Lecture 14 1 Review Begin with a review of the potentials, fields, and Poynting vector for a point charge in accelerated motion. The retarded potential forms are given below. The source
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics
 Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.4 Magnetic Vector Potential 5.1.1 The Vector Potential In electrostatics, E Scalar potential (V) In magnetostatics, B E B V A Vector potential (A) (Note) The name is potential,
Chapter 5. Magnetostatics 5.4 Magnetic Vector Potential 5.1.1 The Vector Potential In electrostatics, E Scalar potential (V) In magnetostatics, B E B V A Vector potential (A) (Note) The name is potential,
Electrostatics. Chapter Maxwell s Equations
 Chapter 1 Electrostatics 1.1 Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic behavior can be described using a set of four fundamental relations known as Maxwell s Equations. Note that these equations are observed,
Chapter 1 Electrostatics 1.1 Maxwell s Equations Electromagnetic behavior can be described using a set of four fundamental relations known as Maxwell s Equations. Note that these equations are observed,
PHYS 281: Midterm Exam
 PHYS 28: Midterm Exam October 28, 200, 8:00-9:20 Last name (print): Initials: No calculator or other aids allowed PHYS 28: Midterm Exam Instructor: B. R. Sutherland Date: October 28, 200 Time: 8:00-9:20am
PHYS 28: Midterm Exam October 28, 200, 8:00-9:20 Last name (print): Initials: No calculator or other aids allowed PHYS 28: Midterm Exam Instructor: B. R. Sutherland Date: October 28, 200 Time: 8:00-9:20am
Phys. 506 Electricity and Magnetism Winter 2004 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 5 Total 40 Points. 1. Problem Points
 Phys. 56 Electricity and Magnetism Winter 4 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 5 Total 4 Points. Problem. Points The partial-wave analysis presented in Chapter.4 applied to the case of a perfectly conducting
Phys. 56 Electricity and Magnetism Winter 4 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 5 Total 4 Points. Problem. Points The partial-wave analysis presented in Chapter.4 applied to the case of a perfectly conducting
Dielectrics - III. Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 Dielectrics - III Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We continue with our discussion of dielectric medium. Example : Dielectric Sphere in a uniform
Dielectrics - III Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We continue with our discussion of dielectric medium. Example : Dielectric Sphere in a uniform
Examples of Dielectric Problems and the Electric Susceptability. 2 A Dielectric Sphere in a Uniform Electric Field
 Examples of Dielectric Problems and the Electric Susceptability Lecture 10 1 A Dielectric Filled Parallel Plate Capacitor Suppose an infinite, parallel plate capacitor filled with a dielectric of dielectric
Examples of Dielectric Problems and the Electric Susceptability Lecture 10 1 A Dielectric Filled Parallel Plate Capacitor Suppose an infinite, parallel plate capacitor filled with a dielectric of dielectric
Vector Potential for the Magnetic Field
 Vector Potential for the Magnetic Field Let me start with two two theorems of Vector Calculus: Theorem 1: If a vector field has zero curl everywhere in space, then that field is a gradient of some scalar
Vector Potential for the Magnetic Field Let me start with two two theorems of Vector Calculus: Theorem 1: If a vector field has zero curl everywhere in space, then that field is a gradient of some scalar
Phys 0175 Midterm Exam II Solutions Feb 25, m e te rs
 Phys 075 Midterm Eam II Solutions Feb 25, 2009. (6 pts) Locations F and G are just outside two uniformly charged large metal plates, which are 3 cm apart. Measured along the path indicated by the dotted
Phys 075 Midterm Eam II Solutions Feb 25, 2009. (6 pts) Locations F and G are just outside two uniformly charged large metal plates, which are 3 cm apart. Measured along the path indicated by the dotted
Phys. 505 Electricity and Magnetism Fall 2003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 1
 Phys. 505 Electricity and Magnetism Fall 2003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set Problem.3 a): By symmetry, the solution must be of the form ρ(x) = ρ(r) = Qδ(r R)f, with a constant f to be specified by the condition
Phys. 505 Electricity and Magnetism Fall 2003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set Problem.3 a): By symmetry, the solution must be of the form ρ(x) = ρ(r) = Qδ(r R)f, with a constant f to be specified by the condition
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 2912 PHYSICS 2B (ADVANCED) ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN
 CC0936 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 91 PHYSICS B (ADVANCED) SEMESTER, 014 TIME ALLOWED: 3 HOURS ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN INSTRUCTIONS: This paper consists
CC0936 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 91 PHYSICS B (ADVANCED) SEMESTER, 014 TIME ALLOWED: 3 HOURS ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN INSTRUCTIONS: This paper consists
AP Physics C. Eddy Currents.
 AP Physics C. Eddy Currents. A very strong magnet e.g., a neodymium-iron-boron alloy dropped down a vertical copper pipe does not fall with constant acceleration, but instead glides down at a constant
AP Physics C. Eddy Currents. A very strong magnet e.g., a neodymium-iron-boron alloy dropped down a vertical copper pipe does not fall with constant acceleration, but instead glides down at a constant
Electrodynamics Exam Solutions
 Electrodynamics Exam Solutions Name: FS 215 Prof. C. Anastasiou Student number: Exercise 1 2 3 4 Total Max. points 15 15 15 15 6 Points Visum 1 Visum 2 The exam lasts 18 minutes. Start every new exercise
Electrodynamics Exam Solutions Name: FS 215 Prof. C. Anastasiou Student number: Exercise 1 2 3 4 Total Max. points 15 15 15 15 6 Points Visum 1 Visum 2 The exam lasts 18 minutes. Start every new exercise
xy 2 e 2z dx dy dz = 8 3 (1 e 4 ) = 2.62 mc. 12 x2 y 3 e 2z 2 m 2 m 2 m Figure P4.1: Cube of Problem 4.1.
 Problem 4.1 A cube m on a side is located in the first octant in a Cartesian coordinate system, with one of its corners at the origin. Find the total charge contained in the cube if the charge density
Problem 4.1 A cube m on a side is located in the first octant in a Cartesian coordinate system, with one of its corners at the origin. Find the total charge contained in the cube if the charge density
Council of Student Organizations De La Salle University Manila
 Council of Student Organizations De La Salle University Manila PHYENG2 Quiz 1 Problem Solving: 1. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the force of +Q on q o at (i) P 1 and (ii) P 2 in Fig 1a below.
Council of Student Organizations De La Salle University Manila PHYENG2 Quiz 1 Problem Solving: 1. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the force of +Q on q o at (i) P 1 and (ii) P 2 in Fig 1a below.
(a) Consider a sphere of charge with radius a and charge density ρ(r) that varies with radius as. ρ(r) = Ar n for r a
 Physics 7B Midterm 2 - Fall 207 Professor R. Birgeneau Total Points: 00 ( Problems) This exam is out of 00 points. Show all your work and take particular care to explain your steps. Partial credit will
Physics 7B Midterm 2 - Fall 207 Professor R. Birgeneau Total Points: 00 ( Problems) This exam is out of 00 points. Show all your work and take particular care to explain your steps. Partial credit will
Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
 8.07 Lecture 37: December 12, 2012 (THE LAST!) RADIATION Radiation: infinity. Electromagnetic fields that carry energy off to At large distances, E ~ and B ~ fall off only as 1=r, so the Poynting vector
8.07 Lecture 37: December 12, 2012 (THE LAST!) RADIATION Radiation: infinity. Electromagnetic fields that carry energy off to At large distances, E ~ and B ~ fall off only as 1=r, so the Poynting vector
PHY 2049 FALL 2000 EXAM 1
 PHY 09 FALL 000 EXAM 1 1. Figure below shows three arrangements of electric field lines. A proton is released from point X. It is accelerated by the electric field toward point Y. Points X and Y have eual
PHY 09 FALL 000 EXAM 1 1. Figure below shows three arrangements of electric field lines. A proton is released from point X. It is accelerated by the electric field toward point Y. Points X and Y have eual
Steady and unsteady diffusion
 Chapter 5 Steady and unsteady diffusion In this chapter, we solve the diffusion and forced convection equations, in which it is necessary to evaluate the temperature or concentration fields when the velocity
Chapter 5 Steady and unsteady diffusion In this chapter, we solve the diffusion and forced convection equations, in which it is necessary to evaluate the temperature or concentration fields when the velocity
MP204 Electricity and Magnetism
 MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS SEMESTER 2 2016 2017 MP204 Electricity and Magnetism Prof. S. J. Hands, Dr. M. Haque and Dr. J.-I. Skullerud Time allowed: 1 1 2 hours Answer ALL questions MP204, 2016 2017, May Exam
MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS SEMESTER 2 2016 2017 MP204 Electricity and Magnetism Prof. S. J. Hands, Dr. M. Haque and Dr. J.-I. Skullerud Time allowed: 1 1 2 hours Answer ALL questions MP204, 2016 2017, May Exam
Solution Set of Homework # 2. Friday, September 09, 2017
 Temple University Department of Physics Quantum Mechanics II Physics 57 Fall Semester 17 Z. Meziani Quantum Mechanics Textboo Volume II Solution Set of Homewor # Friday, September 9, 17 Problem # 1 In
Temple University Department of Physics Quantum Mechanics II Physics 57 Fall Semester 17 Z. Meziani Quantum Mechanics Textboo Volume II Solution Set of Homewor # Friday, September 9, 17 Problem # 1 In
Solutions to PS 2 Physics 201
 Solutions to PS Physics 1 1. ke dq E = i (1) r = i = i k eλ = i k eλ = i k eλ k e λ xdx () (x x) (x x )dx (x x ) + x dx () (x x ) x ln + x x + x x (4) x + x ln + x (5) x + x To find the field for x, we
Solutions to PS Physics 1 1. ke dq E = i (1) r = i = i k eλ = i k eλ = i k eλ k e λ xdx () (x x) (x x )dx (x x ) + x dx () (x x ) x ln + x x + x x (4) x + x ln + x (5) x + x To find the field for x, we
Dielectrics. Lecture 20: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 What are dielectrics? Dielectrics Lecture 20: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay So far we have been discussing electrostatics in either vacuum or in a conductor.
What are dielectrics? Dielectrics Lecture 20: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay So far we have been discussing electrostatics in either vacuum or in a conductor.
Physics 7B, Speliotopoulos Final Exam, Fall 2014 Berkeley, CA
 Physics 7B, Speliotopoulos Final Exam, Fall 4 Berkeley, CA Rules: This final exam is closed book and closed notes. In particular, calculators are not allowed during this exam. Cell phones must be turned
Physics 7B, Speliotopoulos Final Exam, Fall 4 Berkeley, CA Rules: This final exam is closed book and closed notes. In particular, calculators are not allowed during this exam. Cell phones must be turned
NYU Physics Preliminary Examination in Electricity & Magnetism Fall 2011
 This is a closed-book exam. No reference materials of any sort are permitted. Full credit will be given for complete solutions to the following five questions. 1. An impenetrable sphere of radius a carries
This is a closed-book exam. No reference materials of any sort are permitted. Full credit will be given for complete solutions to the following five questions. 1. An impenetrable sphere of radius a carries
Lecture notes for ELECTRODYNAMICS.
 Lecture notes for 640-343 ELECTRODYNAMICS. 1 Summary of Electrostatics 1.1 Coulomb s Law Force between two point charges F 12 = 1 4πɛ 0 Q 1 Q 2ˆr 12 r 1 r 2 2 (1.1.1) 1.2 Electric Field For a charge distribution:
Lecture notes for 640-343 ELECTRODYNAMICS. 1 Summary of Electrostatics 1.1 Coulomb s Law Force between two point charges F 12 = 1 4πɛ 0 Q 1 Q 2ˆr 12 r 1 r 2 2 (1.1.1) 1.2 Electric Field For a charge distribution:
MP204 Electricity and Magnetism
 MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS SEMESTER 2, REPEAT 2016 2017 MP204 Electricity and Magnetism Prof. S. J. Hands, Dr. M. Haque and Dr. J.-I. Skullerud Time allowed: 1 1 2 hours Answer ALL questions MP204, 2016 2017,
MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS SEMESTER 2, REPEAT 2016 2017 MP204 Electricity and Magnetism Prof. S. J. Hands, Dr. M. Haque and Dr. J.-I. Skullerud Time allowed: 1 1 2 hours Answer ALL questions MP204, 2016 2017,
Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 2, 3, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap. 2. 2π nx i a. ( ) = G n.
 Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Chapter 21 Electric Charge and the Electric Field
 Chapter 21 Electric Charge and the Electric Field 1 Electric Charge Electrostatics is the study of charges when they are stationery. Figure 1: This is Fig. 21.1 and it shows how negatively charged objects
Chapter 21 Electric Charge and the Electric Field 1 Electric Charge Electrostatics is the study of charges when they are stationery. Figure 1: This is Fig. 21.1 and it shows how negatively charged objects
Jackson 6.4 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Jackson 6.4 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell PROBLEM: A uniformly magnetized and conducting sphere of radius R and total magnetic moment m = 4πMR 3
Jackson 6.4 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell PROBLEM: A uniformly magnetized and conducting sphere of radius R and total magnetic moment m = 4πMR 3
The Electric Field of a Dipole
 The Electric Field of a Dipole We have already seen an induced electric dipole. Natural dipoles also exist. What kind of electric field do they produce? Overall the dipole is neutral. But, the test charge
The Electric Field of a Dipole We have already seen an induced electric dipole. Natural dipoles also exist. What kind of electric field do they produce? Overall the dipole is neutral. But, the test charge
A Catalog of Hidden Momenta
 A Catalog of Hidden Momenta David J. Griffiths Department of Physics, Reed College Portland, Oregon 9722 May 12, 218 Abstract Electromagnetic fields carry momentum: P em = ɛ (E B dτ. But if the center-of-energy
A Catalog of Hidden Momenta David J. Griffiths Department of Physics, Reed College Portland, Oregon 9722 May 12, 218 Abstract Electromagnetic fields carry momentum: P em = ɛ (E B dτ. But if the center-of-energy
Spherical volume averages of static electric and magnetic fields using Coulomb and Biot-Savart laws. Abstract
 Spherical volume averages of static electric and magnetic fields using Coulomb and Biot-Savart laws Ben Yu-Kuang Hu Department of Physics, University of Akron, Akron, OH 44325-4001 arxiv:0902.0037v1 [physics.class-ph]
Spherical volume averages of static electric and magnetic fields using Coulomb and Biot-Savart laws Ben Yu-Kuang Hu Department of Physics, University of Akron, Akron, OH 44325-4001 arxiv:0902.0037v1 [physics.class-ph]
Module I: Electromagnetic waves
 Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lectures 10-11: Multipole radiation Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation
Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lectures 10-11: Multipole radiation Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation
Quiz 4 (Discussion Session) Phys 1302W.400 Spring 2018
 Quiz 4 (Discussion ession) Phys 1302W.400 pring 2018 This group quiz consists of one problem that, together with the individual problems on Friday, will determine your grade for quiz 4. For the group problem,
Quiz 4 (Discussion ession) Phys 1302W.400 pring 2018 This group quiz consists of one problem that, together with the individual problems on Friday, will determine your grade for quiz 4. For the group problem,
Questions Chapter 22 Electric Fields
 Questions Chapter 22 Electric Fields 22-1 What is Physics? 22-2 The Electric Field 22-3 Electric Field Lines 22-4 Electric Field due to a Point Charge 22-5 Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole 22-6
Questions Chapter 22 Electric Fields 22-1 What is Physics? 22-2 The Electric Field 22-3 Electric Field Lines 22-4 Electric Field due to a Point Charge 22-5 Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole 22-6
(a) Show that electric field and magnetic field have units (force)/area or energy/volume.
 Problem. Units (a) how that electric field and magnetic field have units (force)/area or energy/volume. (b) A rule of thumb that you may need in the lab is that coaxial cable has a capcitance of 2 pf/foot.
Problem. Units (a) how that electric field and magnetic field have units (force)/area or energy/volume. (b) A rule of thumb that you may need in the lab is that coaxial cable has a capcitance of 2 pf/foot.
Problem Set #3: 2.11, 2.15, 2.21, 2.26, 2.40, 2.42, 2.43, 2.46 (Due Thursday Feb. 27th)
 Chapter Electrostatics Problem Set #3:.,.5,.,.6,.40,.4,.43,.46 (Due Thursday Feb. 7th). Coulomb s Law Coulomb showed experimentally that for two point charges the force is - proportional to each of the
Chapter Electrostatics Problem Set #3:.,.5,.,.6,.40,.4,.43,.46 (Due Thursday Feb. 7th). Coulomb s Law Coulomb showed experimentally that for two point charges the force is - proportional to each of the
Electromagnetism - Lecture 10. Magnetic Materials
 Electromagnetism - Lecture 10 Magnetic Materials Magnetization Vector M Magnetic Field Vectors B and H Magnetic Susceptibility & Relative Permeability Diamagnetism Paramagnetism Effects of Magnetic Materials
Electromagnetism - Lecture 10 Magnetic Materials Magnetization Vector M Magnetic Field Vectors B and H Magnetic Susceptibility & Relative Permeability Diamagnetism Paramagnetism Effects of Magnetic Materials
Physics 7B Final Exam: Monday December 14th, 2015 Instructors: Prof. R.J. Birgeneau/Dr. A. Frano
 Physics 7B Final Exam: Monday December 14th, 15 Instructors: Prof. R.J. Birgeneau/Dr. A. Frano Total points: 1 (7 problems) Show all your work and take particular care to explain what you are doing. Partial
Physics 7B Final Exam: Monday December 14th, 15 Instructors: Prof. R.J. Birgeneau/Dr. A. Frano Total points: 1 (7 problems) Show all your work and take particular care to explain what you are doing. Partial
Physics 505 Fall 2005 Homework Assignment #7 Solutions
 Physics 505 Fall 005 Homework Assignment #7 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 4: 4.10 Ch. 5: 5.3, 5.6, 5.7 4.10 Two concentric conducting spheres of inner and outer radii a and b, respectively, carry charges
Physics 505 Fall 005 Homework Assignment #7 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 4: 4.10 Ch. 5: 5.3, 5.6, 5.7 4.10 Two concentric conducting spheres of inner and outer radii a and b, respectively, carry charges
S12.1 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS 12 (ODD NUMBERS)
 OLUTION TO PROBLEM 2 (ODD NUMBER) 2. The electric field is E = φ = 2xi + 2y j and at (2, ) E = 4i + 2j. Thus E = 2 5 and its direction is 2i + j. At ( 3, 2), φ = 6i + 4 j. Thus the direction of most rapid
OLUTION TO PROBLEM 2 (ODD NUMBER) 2. The electric field is E = φ = 2xi + 2y j and at (2, ) E = 4i + 2j. Thus E = 2 5 and its direction is 2i + j. At ( 3, 2), φ = 6i + 4 j. Thus the direction of most rapid
Phys102 General Physics II. Chapter 24: Gauss s Law
 Phys102 General Physics II Gauss Law Chapter 24: Gauss s Law Flux Electric Flux Gauss Law Coulombs Law from Gauss Law Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor Application of Gauss Law Charged
Phys102 General Physics II Gauss Law Chapter 24: Gauss s Law Flux Electric Flux Gauss Law Coulombs Law from Gauss Law Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor Application of Gauss Law Charged
Queen s University at Kingston. Faculty of Arts and Science. Department of Physics PHYSICS 106. Final Examination.
 Page 1 of 5 Queen s University at Kingston Faculty of Arts and Science Department of Physics PHYSICS 106 Final Examination April 16th, 2009 Professor: A. B. McLean Time allowed: 3 HOURS Instructions This
Page 1 of 5 Queen s University at Kingston Faculty of Arts and Science Department of Physics PHYSICS 106 Final Examination April 16th, 2009 Professor: A. B. McLean Time allowed: 3 HOURS Instructions This
(b) Show that the charged induced on the hemisphere is: Q = E o a 2 3π (1)
 Problem. Defects This problem will study defects in parallel plate capacitors. A parallel plate capacitor has area, A, and separation, D, and is maintained at the potential difference, V = E o D. There
Problem. Defects This problem will study defects in parallel plate capacitors. A parallel plate capacitor has area, A, and separation, D, and is maintained at the potential difference, V = E o D. There
Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces
 Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces 21.1 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation According to Newton s Law of Universal Graviation, the force on a particle i of mass m i exerted by a particle j of
Lecture 21 Gravitational and Central Forces 21.1 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation According to Newton s Law of Universal Graviation, the force on a particle i of mass m i exerted by a particle j of
Solutions: Homework 2
 Solutions: Homework 2 Ex 2.1: Particle moving in Magnetic Field (a) If the initial velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field B, the magnitude of the Lorentz Force (Eq 1.52) is F = 1 c q qu B ub (1)
Solutions: Homework 2 Ex 2.1: Particle moving in Magnetic Field (a) If the initial velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field B, the magnitude of the Lorentz Force (Eq 1.52) is F = 1 c q qu B ub (1)
CHAPTER 3 POTENTIALS 10/13/2016. Outlines. 1. Laplace s equation. 2. The Method of Images. 3. Separation of Variables. 4. Multipole Expansion
 CHAPTER 3 POTENTIALS Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 Outlines 1. Laplace s equation 2. The Method of Images 3. Separation of Variables 4. Multipole Expansion
CHAPTER 3 POTENTIALS Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 Outlines 1. Laplace s equation 2. The Method of Images 3. Separation of Variables 4. Multipole Expansion
PHYS 110B - HW #4 Spring 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS 11B - HW #4 Spring 4, Solutions by David Pace Any referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased [1.] Problem 8. from Griffiths Reference problem 7.31 figure 7.43. a Let
PHYS 11B - HW #4 Spring 4, Solutions by David Pace Any referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased [1.] Problem 8. from Griffiths Reference problem 7.31 figure 7.43. a Let
Electric Flux. To investigate this, we have to understand electric flux.
 Problem 21.72 A charge q 1 = +5. nc is placed at the origin of an xy-coordinate system, and a charge q 2 = -2. nc is placed on the positive x-axis at x = 4. cm. (a) If a third charge q 3 = +6. nc is now
Problem 21.72 A charge q 1 = +5. nc is placed at the origin of an xy-coordinate system, and a charge q 2 = -2. nc is placed on the positive x-axis at x = 4. cm. (a) If a third charge q 3 = +6. nc is now
Coordinates 2D and 3D Gauss & Stokes Theorems
 Coordinates 2 and 3 Gauss & Stokes Theorems Yi-Zen Chu 1 2 imensions In 2 dimensions, we may use Cartesian coordinates r = (x, y) and the associated infinitesimal area We may also employ polar coordinates
Coordinates 2 and 3 Gauss & Stokes Theorems Yi-Zen Chu 1 2 imensions In 2 dimensions, we may use Cartesian coordinates r = (x, y) and the associated infinitesimal area We may also employ polar coordinates
where the last equality follows from the divergence theorem. Now since we did this for an arbitrary volume τ, it must hold locally:
 8 Electrodynamics Read: Boas Ch. 6, particularly sec. 10 and 11. 8.1 Maxwell equations Some of you may have seen Maxwell s equations on t-shirts or encountered them briefly in electromagnetism courses.
8 Electrodynamics Read: Boas Ch. 6, particularly sec. 10 and 11. 8.1 Maxwell equations Some of you may have seen Maxwell s equations on t-shirts or encountered them briefly in electromagnetism courses.
Homework 7-8 Solutions. Problems
 Homework 7-8 Solutions Problems 26 A rhombus is a parallelogram with opposite sides of equal length Let us form a rhombus using vectors v 1 and v 2 as two adjacent sides, with v 1 = v 2 The diagonals of
Homework 7-8 Solutions Problems 26 A rhombus is a parallelogram with opposite sides of equal length Let us form a rhombus using vectors v 1 and v 2 as two adjacent sides, with v 1 = v 2 The diagonals of
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
PHYS 3327 PRELIM 1. Prof. Itai Cohen, Fall 2010 Friday, 10/15/10. Name: Read all of the following information before starting the exam:
 PHYS 3327 PRELIM 1 Prof. Itai Cohen, Fall 2010 Friday, 10/15/10 Name: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Put your name on the exam now. Show all work, clearly and in order,
PHYS 3327 PRELIM 1 Prof. Itai Cohen, Fall 2010 Friday, 10/15/10 Name: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Put your name on the exam now. Show all work, clearly and in order,
Physics II Fiz Summer 2017
 Physics II Fiz138-22 Summer 2017 Instructor: Dr. Mehmet Burak Kaynar Office: H.U. Physics Eng Dept. SNTG Lab. E-mail: bkaynar@hacettepe.edu.tr Office hours: Wednesday 10:00 11:00 Evaluation Attendance:
Physics II Fiz138-22 Summer 2017 Instructor: Dr. Mehmet Burak Kaynar Office: H.U. Physics Eng Dept. SNTG Lab. E-mail: bkaynar@hacettepe.edu.tr Office hours: Wednesday 10:00 11:00 Evaluation Attendance:
Currents (1) Line charge λ (C/m) with velocity v : in time t, This constitutes a current I = λv (vector). Magnetic force on a segment of length dl is
 Magnetostatics 1. Currents 2. Relativistic origin of magnetic field 3. Biot-Savart law 4. Magnetic force between currents 5. Applications of Biot-Savart law 6. Ampere s law in differential form 7. Magnetic
Magnetostatics 1. Currents 2. Relativistic origin of magnetic field 3. Biot-Savart law 4. Magnetic force between currents 5. Applications of Biot-Savart law 6. Ampere s law in differential form 7. Magnetic
