Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 1
|
|
|
- Dana Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page Exercises 2.: Division of Polynomials. Divide, assuming the divisor is not equal to zero. a) x 3 + 2x 2 7x + 4 ) x + ) b) 3x 4 4x 2 2x + 3 ) x 4) 7. *) If fx) = dx)qx) + rx) and degdx)) = 3 and degfx)) = 7, what are the possible degrees of rx)? State examples of the equation for each degree. 8. **) Note that the sum of the powers of 2 is less than the next power of 2. That is c) d) e) x 3 ) x ) x 4 ) x ) x 5 ) x ) + 2 = 3 = = 7 = = 5 = 6 f) x 3 4x 2 2x + ) x 3) 2. For fx) = x 2)x 2 + 3x + 4) + 6 find: Explain why this is true. Hint: Divide x n by x and substitute a special value for x. a) The divisor. b) The quotient. c) The remainder. d) The dividend. 3. In each of the following, obtain a quotient and remainder, leaving your answers in the form fx) = dx)qx) + rx). a) b) c) d) e) f) 5x 3 2x 2 9x + 5 ) x + ) x 4 + 3x 3 2x 2 + 7x + 2 ) 2x 3) 2x 4 + 5x 3 4x 2 3x + 4 ) x 2 + 3x + 5 ) x 3 + kx 2 + x + ) x ) x 5 + 6x 2 x + ) x 2 7x + ) x 3 + x 2 + x + ) x + k) 4. Divide x 3 + a + b)x 2 + ab + c)x + ac by x + a. 5. *) If fx) = dx)qx) + rx), what conditions on fx) isare) required for rx) to vanish? 6. *) If fx) = dx)qx) + rx) and degdx)) = 2, what are the possible degrees of rx)?
2 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 2 Exercises 2.2: The Remainder Theorem. Explain how to find the remainder of x 3 +4x 2 2x+3 divided by x Find the remainder of each of the following divisions. a) x 3 + 4x 2 + 2x 7 ) x + ) b) c) d) x 4 3x 2 3x + 5 ) x 2) x 7 2x 5 + 3x 3 4x + 5 ) x + 5) x 4 + 6x 3 + 9x 2 7x + 3 ) x 9) 7. Let fx) be a polynomial that has remainder 3 when divided by x 2. Find the remainder when each polynomial is divided by x 2. a) fx) + 3 b) 3x + )fx) c) fx) + 5x + 2 d) [fx)] 2 + 2fx) 8. Find the remainder when a polynomial fx) is divided by: e) f) 3x 5 + 2x ) x 5) x 4 2x 3 + 3x 2 x + 5 ) x + ) a) ax + b, a 0 b) x a)x b) g) x 3 + kx 2 x + 4 ) x + ) h) x 3 + ax 2 + bx + c ) x ) 3. Find the value of k in each of the following. 9. Outline an approach for finding the remainder of an n-th degree polynomial fx) divided by x a )x a 2 ) x a k ) where k < n. a) When x 3 + kx 2 3x + is divided by x, the remainder is 2. b) When x 3 kx 2 x + 4 is divided by x 2, the remainder is 9. c) When x 4 + kx 3 + 4x is divided by x + 3, the remainder is When x 3 + ax 2 + bx + 3 is divided by x 5, the remainder is 2 and when it is divided by x + 3, the remainder is 7. What are the values of a and b? 5. When ax 4 + bx 3 + 3x 2 2x + is divided by x +, the remainder is 3 and when it is divided by x 2, the remainder is 5. What are the values of a and b? 6. Find the remainder for each of the following. a) b) c) x 5 + 4x 3 2x 2 + ) x + )x + 2) x 5 2x 4 + 3x 3 2x 2 + x 5 ) x )x 3) x 6 + 2x 2 ) x 2)x + 3)
3 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 3 Exercises 2.3: The Factor Theorem. Given the polynomial fx) = x 3 + 5x 2 + 6x + 8: a) Show that f 4) = 0. b) Using long division, show that x + 4 divides fx). 2. If x 2 is a factor of fx), what is the value of f2)? 3. If f 3) = 0, then what must be a factor of fx)? 4. Which of the following polynomials have x + as a factor? a) x 3 2x b) x 3 x 2 + x + 3 c) x 4 + 6x 3 x 2 5x + d) x 3 + 5x 2 3x 7 e) 4x 3 + 4x 2 2x + 3 f) 2x 5 x 4 x 3 + x 2 + 0x + 5. Given the polynomial fx) = 4x 3 + 7x 2 + 8x + 9: a) Show that f 3) = 0. b) Find a linear factor of fx). b) Use long division to find the remaining factors of fx). 6. Find k so that x + 2 is a factor of x 3 + 2kx + 3x Find k so that x 4 is a factor of 2x 3 kx x Factor completely by finding one factor, then using long division to find the remaining factors. a) x 3 4x 2 + x + 6 e) x 4 x 3 3x 2 + x + 2 f) x 3 + 3x 2 + 6x + 4 g) 2x 3 x 2 7x + 2 h) x 4 5x Using a sum or difference of cubes, factor the following. a) x 3 8 b) x c) 8a 3 64b 3 d) 625z 3 40 e) a + b) 3 b 3 f) a + b + ) 3 a + b ) 3 0. Use the Factor Theorem to show that 2x 3 x 2 + 5x + 8 is not divisible by x 2 + x 6.. Show that x y is a factor of each of the following. For each exercise, find the other factor. a) x 4 y 4 b) x 5 y 5 c) x 6 y 6 d) x n y n 2. *) When is x + y a factor of x n + y n? 3. Completely factor x 5 + y 5. b) x 3 3x 2 4x + 2 c) x 3 x x 25 d) 2x 3 5x 2 4x + 3
4 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 4 Exercises 2.4: Solving Polynomial Equations. Write a polynomial equation with zeros at x =, 0, Write a polynomial equation with zeros at x = 3, 5, Find all polynomial equations with zeros 0,, Find all polynomial equations with zeros, Solve the following equations: a) x + )x 2) = 0 b) x )x 3) = 0 c) 2x + )x 5) = 0 d) x 3) 2 = 0 e) x 2 + 2x + = 0 f) x 2 + 7x + 2 = 0 g) x 2 + 3x 30 = 0 h) 2x 2 5x + 3 = 0 i) 6x 2 + 7x + 2 = 0 j) 0x x + 0 = 0 6. Solve the following equations. a) x 2 + 5x + 2 = 0 b) 2x 2 7x + 2 = 0 c) 3x 2 6x 4 = 0 d) 7x 2 4x 3 = 0 e) 4x 2 8x 3 = 0 f) x 2 25x + 6 = 0 7. Solve the following equations. a) x + 3) 2 = x + ) 2 b) a 2 + a 2 + 3a = 5a 2 c) m 5) 2 = m 2 d) 5y = y 2 + 3y e) z 3 + 3z = 5z 2 + 8z 3 f) p 3 + 4p = p + ) 3 8. Solve the following equations. a) b) c) d) x + + x = 2 2x + 4x 3 = 5 x x x + 2 = 6 2x x 4x 2x + = 3 9. Solve the following equations. State any necessary restrictions. a) x 2 + mx + n = 0 b) ax 2 + bx = 0 c) ax 2 + b = 0 d) kx 2 + k + )x + k + 2 = 0 0. Write and solve an equation that finds three consecutive integers that have a product of 76.. Find the value of k such that x 3 +5x 2 +kx+ gives the same remainder when divided by x and x The tensile strength of a new composite material is modeled by the function S = 8 + 5T T 3, where T is the annealing temperature in 000 K.
5 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 5 a) Graph the function. b) What restricted domain of the function makes physical sense? c) What is the approximate maximum strength of the material? d) What is the minimum strength of the material? 3. **) Show that the product of two consecutive natural numbers can never be a perfect square. Exercises 2.5: Solving Polynomial Equations, Part 2. Solve the following equations: a) x + )x + 2)x + 3)x + 4) = 0 b) x )x 2)x 3)x 4) = 0 c) x + )x )x + 2)x 2) = 0 d) x + )x 2 + 4x + 2) = 0 e) x 3 + 3x 2 x 3 = 0 f) 2x 3 3x 2 2x + 3 = 0 g) 4x 4 2x 3 3x x 24 = 0 h) x 4 + 5x 3 + 5x 2 5x 6 = 0 i) x 4 + 6x 3 + 3x 2 26x 24 = 0 j) 30x 3 53x 2 2x + 6 = 0 2. Solve the following equations: a) x 3 + 9x 2 + 9x + 3 = 0 b) x 3 + 0x 2 50x 24 = 0 c) x 4 3x 3 2x 2 72x 28 = 0 3. Explain why every cubic equation has at least one real root. 4. Find the complete family of polynomials that have zeros and 2. Then find two different cubic functions that pass through the point 3, 5).
6 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 6 Exercises 2.6: Graphs of Rational Functions. Graph the following functions. For each graph, state the domain and range, the y-intercept and any asymptotes. For parts f) amd i), consider the three cases n > 0, n = 0 and n = k < 0. Exercises 2.7: Graphs of Rational Functions, Part 2. Graph the following functions. For each graph, state the domain and range, the y-intercept and any asymptotes. a) y = x a) y = x 2 b) y = x 2 c) y = x 5 d) y = x + 2 e) y = x + 3 f) y = x + n g) h) y = 5 x y = 3 x i) y = n x + n 2. Graph the function y = / x. What are the vertical and horizontal asymptotes, the domain and range of the function? Repeat the exercise if the function undergoes the transformation x x a and y y b. 3. Plot the function y = /x n for n =, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 on the same graph. Find domain, range, vertical and horizontal asymptotes. Summarize your findings and hypothesize for n N. 4. Draw the graph that has horizontal asymptote at y = 5 and vertical asymptote at x = 3, with y- intercept x = 5. If the graph is a translation of the function y = a/x, find the equation of the graph and the x-intercept. b) y = c) y = d) y = e) y = x 2) 2 x 2)x + ) x + 2) 2 5 x 2 3x + 2 f) y = x + 3) 2 g) y = h) y = x 2 + 7x x 2 4x 2 i) y = x n) 2 2. Relate the functions fx) = /x 2 and gx) = x a) 2 + b by a simple transformation. How are the graphs related? 3. Graph the following functions using a table of values. State the domain, range, any intercepts and any asymptotes. a) y = x 2 + x + b) y = x 2 + c) y = x 2 + 2x + 5
7 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 7 4. Describe any qualitative differences between the graphs in Exercises #, #2, and #3. Why do these differences exist? 5. **) The Witch of Agnesi is constructed by considering a circle of radius a and centre 0, a) and drawing a line OA from the origin to the line y = 2a which is point A. The x-coordinate of the Witch is given by the x-coordinate of the point A and the y- coordinate of the intersection of OA with the circle. a) Draw a diagram that represents the description given. b) Show that the coordinates of the Witch are given by x = 2a cot θ and y = a cos 2θ), where θ [0, π]. c) Eliminate θ in the two equations to find the equation of the Witch y = 8a 3 /x 2 + 4a 2 ). d) Draw a graph of the Witch. e) State the domain, range, any intercepts and asymptotes. Exercises 2.8: Graphs of Rational Functions, Part 3. Graph the following functions. For each graph, state the domain and range, any intercepts, holes and any asymptotes. a) y = b) y = c) y = x x + )x ) 3x x + )x 2) 2x + x 3)x ) d) y = x xx + ) e) y = 2x xx + 2) f) y = 3 x + x 2 2. Graph the following functions, simplifying first if necessary. For each graph, state the domain and range, any intercepts, holes and any asymptotes. a) y = b) y = c) y = d) y = e) y = f) y = x + x )x + 3) x + 2 x 2)x + )x + 4) 2x x )2x 3)x 2) x ) 2 xx )x 2) 2 x + ) 3x + x + ) 2 x ) 3 x 2 x ) 3 x + ) 2 x + 2) 2 2x ) 2 x 2) 3
8 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 8 3. Graph the following functions, simplifying first if necessary. For each graph, state the domain and range, any intercepts, holes and any asymptotes. a) y = b) y = c) y = d) y = e) y = f) y = x + x 2 + 3x + 2 x 2 x 3 + 2x 2 5x 6 x 2 2x 3 x 2 8x + 4 x 2 + 6x 3 + 3x x 2 2x 5 x 3 + 7x x 2 + 3x 2 x 4 3x 3 9x 2 40x 84 Exercises 2.9: Graphs of Rational Functions, Part 4. Graph the following functions. For each graph, state the domain and range, any intercepts, holes and any asymptotes. a) y = + x + b) y = 3 + c) y = x + )x 2) x + x + 3)x 2) d) y = + x xx 2) e) y = + 2x x )x + 2) f) y = 4 + x x )x + ) 2. Simplify each function using factoring and/or long division and then graph each function to determine its key features. a) y = x + x + 2 b) y = x x 2 c) y = d) y = e) y = f) y = x + )x 2) x )x + 2) x 2)x 3) x 2)x + ) x + 2)x + ) 2 x )x + )x 2) x )x + )2 xx + )x + 2)
9 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 9 3. Simplify each function using factoring and/or long division and then graph each function to determine its key features. a) y = x2 2x + x 2 + 7x + 2 b) y = x2 + 5x 6 x 2 7x 44 c) y = x2 3x 0 2x 2 + 5x 3 d) y = 2x3 5x 2 x + 6 x 3 3x 2 + 3x e) y = f) y = x 3 x 3 + 4x 2 4x 6 x 2 6x 2 + x 0 Graphs of Rational Func- Exercises 2.0: tions, Part 5. Graph the following functions. For each graph, state the domain and range, any intercepts and any asymptotes. a) y = 2x + + x + b) y = x x 2 c) y = x 4 + d) y = 3x 5 + 3x x )x + 2) x x + )x ) e) y = x 6 x + x + 2) 2 f) y = x 2 x + ) 2 x ) 2 x 2) 2. Simplify each function using factoring and/or long division and then graph each function to determine its key features. a) y = x2 x + b) y = c) y = x + 2)x + ) x 2 x )x + ) x 3 d) y = x2 x ) x + )x ) e) y = x )x + )2 x 2)x ) f) y = x + ) 2 x 2) 3 x 2)x + 3)x + 4) 2
10 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 0 3. Simplify each function using factoring and/or long division and then graph each function to determine its key features. a) y = x2 2x 3 x 2 b) y = x2 5x 24 x c) y = 0x2 7x 20 3x 2 d) y = 2x3 + x 2 25x + 2 x 2 6x + 8 e) y = x 3 2x x 24 f) y = 30x4 + 2x 3 + 4x 2 64x 96 x 3 x 2 4x + 24 Exercises 2.: Review. Divide the following. a) 2x 3 + 4x 2 7x + ) x + 4) b) 6x 4 2x 3 + 4x 2 3x 7 ) x + 7) c) 3x 3 + 4x 2 5 ) x 2) d) 6x 4 + 2x + ) 3x + ) e) 7x 4 + 5x 3 + 3x 2 9x + 4 ) x 2 + 3x 4) 2. Divide the following. a) 6x 3 x 4 + 2x + 3 ) x + ) b) x 3 + x 2 x + 5 ) x + ) 4. *) Graph the function y = x 3 /x ) by a table of values and by using long division. To what function do the asymptotes appear to be converging for large positive and negative values of x? c) d) e) x 4 + 3x 3 7x 2 + 2x + 3 ) x + 5) x 6 + x 4 x ) 2x ) x 6 + 3x 2 x + ) x 2 + 5x 3) 3. Find the remainder of each of the following divisions. a) b) c) d) x 4 6x 3 + x ) x + 4) x 7 + 5x ) x 3) 3x 5 + 2x 2 + 5x + ) x )x + 2) 3x 4 + 2x 3 + 5x 2 + 2x + ) x 2 + 3x + 2) 4. Find the value of k so that when x 3 + 7x 2 kx + 3 is divided by x 4, the remainder is If x + is a factor of fx), then evaluate f ). 6. Show that x + is a factor of x 3 x 2 7x 5.
11 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 7. Factor the following. a) x 3 + 6x 2 + x + 6 b) x 3 + 4x 2 + x 6 c) x 4 + 3x 3 + x 2 3x 2 d) 2x 4 x 3 7x x Factor 27x 3 8y 6 using difference of cubes. 9. Solve the following equations. a) x 3 3x 2 = 0 b) x 3 2x 2 x + 2 = 0 c) x 3 5x 2 8x + 2 = 0 d) 6x 3 + 5x 2 7x 6 = 0 e) x 3 + 3x 2 40x = 0 f) x 3 28x = 0 g) h) x x + + 2x + x + 2 = 5 x x + = 4 x Graph the following. For each function, state the domain, range, any intercepts, holes and asymptotes. a) y = x b) y = x c) y = 3 x + 2 d) y = 5 x + 3 e) y = f) y = 4 x + )x 5) 3x + 2 2x )x + 3) g) y = 6x2 7x 3 x )x 2) 2 h) y = x n x ) 2n, n Z. Graph the following. For each function, state the domain, range, any intercepts, holes and asymptotes. a) y = 2x x + 4 b) y = x 8 x 2 c) y = d) y = e) y = x + x x + 5) 2 x + 2)x + 5) x 2 x 2 + 7x 8 f) y = 2 x g) y = 2x x 2 + h) y = x3 + 2x + 6 x + )x 2) i) y = x n x ) n, n Z 2. Draw the graph similar to y = a/x b) that has horizontal asymptote y = 2, vertical asymptote x = and passes through the point 4, 7).
12 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 2 Exercises 2.: Solutions Division of Polynomials. Division. a) x + )x 2 + x 8) + 2 b) x 4)3x 2 2x 0) 37 c) x )x 2 + x + ) d) x )x 3 + x 2 + x + ) e) x )X 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x + ) f) x 3)x 2 x 5) 4 2. Classifying division. a) x 2 b) x 2 + 3x + 4 c) 6 d) x 3 + x 2 2x 2 3. Division. a) x + )5x 2 7x 2) + 7 b) 2x 3) 2 x x x + 3 ) c) x 2 + 3x + 5)2x 2 x ) + 35x + 59 d) x ) x 2 + k + )x + k + 2) ) + k + 3 e) x 2 7x+)x 3 +7x 2 +48x+335)+2298x 334 f) x + k) x 2 + k)x + k 2 k + ) + k + k 2 k 3 4. x + a)x 2 + bx + c). 5. For rx) to vanish, dx) must be a factor of fx). 6. The possible degrees of rx) are zero and one. 7. The possible degrees of rx) are zero, one and two. 8. Notice that x n )/x ) = x n + x n x 2 + x +. When x = 2, this means that 2 n = 2 n + 2 n Therefore, we see that when n =, the left side is 2, and the right side is. When n = 2, the left side is 4 = 3, and the right side is 3 = 2 +. And so on. Exercises 2.2: Solutions The Remainder Theorem. r = f4) = Finding remainders. a) 6 b) 3 c) d) 604 e) 9322 f) 2 g) 4 k h) + a + b + c 3. Finding k. a) k = 3 b) k = 4 c) k = a = , b = a = 7 6, b = 6 6. Finding remainders. a) rx) = 65x + 59 b) rx) = 55x 59 c) rx) = 35x Finding remainders. a) 6 b) 2 c) 20 d) 5 8. Finding remainders. a) r = f a ) b b) rx) = fa) fb) a b x afb)+bfa) a b
13 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 3 Solutions The Factor Theo- Exercises 2.3: rem 0. x 2 + x 6 = x + 3)x 2); f 3) 0 and f2) 0 therefore not divisible.. f 4) = 4) ) ) + 8 = 0 2. f2) = 0 3. x + 3 is a factor of fx) 4. Factors. a) Factor. b) Factor. c) Factor. d) Factor. e) Not factor. f) Not factor.. Other factors. a) x 3 + yx 2 + y 2 x + y 3 b) x 4 + yx 3 + y 2 x 2 + y 3 x + y 4 c) x 5 + x 4 y + x 3 y 2 + x 2 y 3 + xy 4 + y 5 d) x n + x n 2 y + x n 3 y xy n 2 + y n 2. When n is an odd positive integer. 3. x 5 + y 5 = x + y)x 4 x 3 y + x 2 y 2 xy 3 + y 4 ) 5. fx) = x + 3)4x 2 + 5x + 3), quadratic factor has complex roots. 6. k = k = Factoring. a) fx) = x + )x 2)x 3) b) fx) = x + 2)x 2)x 3) c) fx) = x )x 5) 2 d) fx) = x + )2x )x 3) e) fx) = x )x + ) 2 x 2) f) fx) = x + )x 2 + 2x + 4) g) fx) = x 2) 2x ) 2x ) h) fx) = x + 2)x 2)x + )x ) 9. Factoring a sum or difference of cubes. a) x 2)x 2 + 2x + 4) b) x + 7)x 2 7x + 49) c) 8 a 4 /3 b ) a /3 b + 4 2/3 b 2) d) 55z 2)25z 2 0z + 4) e) aa 2 + 3ab + 3b 2 ) f) 23a 2 + 3b 2 + 2ab + )
14 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 4 Exercises 2.4: Solving Polynomial Equations. x )x)x + ) = 0 2. y = x 3)x 5)x + 2) = 0 3. kx a x ) b x 2) c = 0 4. kx ) a x 2) 2 = 0 5. Solving equations. a) x =, x = 2 b) x =, x = 3 c) x = 2, x = 5 d) x = 3 e) x = f) x = 3, x = 4 g) x = 5, x = 2 h) x = 3 2, x = 2 i) x = 2 3, 2 j) x = 2 5, Solving equations. a) x = ) 2 5 ± 2 b) x = ) 4 7 ± 33 c) x = ) 3 8 ± 76 d) x = ) 7 7 ± 70 e) x = ) 28 8 ± 6279 f) x = 2, x = 3 7. Solving equations. b) x = ) 20 3 ± 9 c) No solution. d) x = ) 4 3 ± 7 9. Solving equations. a) x = 2 m ± ) m 2 4n, m 2 4n b) x = 0, x = b a, a 0 c) x = ±, ab < 0, a 0 d) x = 2k b a k ± 3k 2 6k + 3k 2 6k + 0 ), k 0, 0. Solutions of x 3 + 3x 2 + 2x 76 = 0 are x =, x = 2 and x = 3.. k = T 2.803, the maximum strength is S and the minimum is S = Let n, n + be two consecutive natural numbers. Suppose that nn+) = k 2, where k Z. Then n 2 + n k 2 = 0. The discriminant is D = + 4k 2. Since D can t be an integer, then n can t be an integer, which means that there can be no two consecutive natural numbers that are perfect squares. a) x = 2 b) No solution. c) m = ) 2 ± 3 d) y = 0, y = 2 e) z = 0, z = ) 4 5 ± 09 f) p = 0, p = 3 8. Solving equations. a) x = ) 2 ± 5
15 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 5 Exercises 2.5: Solving Polynomial Equations, Part 2. Solving equations. a) x =, x = 2, x = 3, x = 4 b) x =, x = 2, x = 3, x = 4 c) x = ±, x = ±2 d) x =, x = 2 ± 2 e) x = 3, x =, x = f) x =, x =, x = 3 2 g) x = 2, x = 3, x = 4, x = 4 h) x = 3, x = 2, x = 2, x = i) x = 4, x = 3, x =, x = 2 j) x = 2, x = 2 3, x = Solving equations. a) x = 3, x = 3 ± 8 b) x = 4, 7 ± 43 c) No solution. 3. If the polynomial has real coefficients and the roots are complex, the roots must be in conjugate pairs. Since a cubic has three roots, the third root must be 4. y = kx ) a x 2) 3 a, where a {, 2}. y = 5 2 x )x 2)2, y = 5 4 x )2 x 2). Exercises 2.: Solutions Review. Division. a) x + 4) x 2 4x + 9 ) 35 b) x + 7) 6x 3 44x x 287 ) c) x 2) 3x 2 2x 4 ) 3 d) 3x + ) 2x x x + 6 ) e) 2. Division. x 2 + 3x 4 ) 7x 2 6x + 79 ) 294x a) x + ) x 3 + 7x 2 7x + 9 ) 6 b) x + ) x 2 ) + 6 c) x + 5) x 3 2x 2 + 3x 3 ) + 68 d) 2x ) 2 x5 + 4 x4 3 8 x x x + ) e) x 2 + 5x 3 ) x 4 5x x 2 55x + 862) x Remainders. a) 49 b) 2235 c) 36x 25 d) 46x + 45
16 Unit 2 Rational Functionals Exercises MHF 4UI Page 6 4. k = f ) = Evaluate f ) = Factoring. a) x + )x + 2)x + 3) b) x )x + 2)x + 3) c) x )x + ) 2 x + 2) d) x + 2)2x + 3)x 4)x 5) 8. 3x 2y 2 )9x 2 + 6xy 2 + 4y 4 ) 9. Solving. a) x = 4 x = x = 3 b) x = x = x = 2 c) x = x = 2 x = 6 d) x = 2 x = 3 x = 3 2 e) x = 0 x = 5 x = 8 f) x = 0 x = ±8 2 g) x = 5 ± 73 4 h) x = 23 ± 89 0
Chapter 2 Formulas and Definitions:
 Chapter 2 Formulas and Definitions: (from 2.1) Definition of Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n,a n 1,...,a 2,a 1,a 0 be real numbers with a n 0. The function given by f (x)
Chapter 2 Formulas and Definitions: (from 2.1) Definition of Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n,a n 1,...,a 2,a 1,a 0 be real numbers with a n 0. The function given by f (x)
Power and Polynomial Functions. College Algebra
 Power and Polynomial Functions College Algebra Power Function A power function is a function that can be represented in the form f x = kx % where k and p are real numbers, and k is known as the coefficient.
Power and Polynomial Functions College Algebra Power Function A power function is a function that can be represented in the form f x = kx % where k and p are real numbers, and k is known as the coefficient.
, a 1. , a 2. ,..., a n
 CHAPTER Points to Remember :. Let x be a variable, n be a positive integer and a 0, a, a,..., a n be constants. Then n f ( x) a x a x... a x a, is called a polynomial in variable x. n n n 0 POLNOMIALS.
CHAPTER Points to Remember :. Let x be a variable, n be a positive integer and a 0, a, a,..., a n be constants. Then n f ( x) a x a x... a x a, is called a polynomial in variable x. n n n 0 POLNOMIALS.
Chapter 2 notes from powerpoints
 Chapter 2 notes from powerpoints Synthetic division and basic definitions Sections 1 and 2 Definition of a Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n-1,, a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Chapter 2 notes from powerpoints Synthetic division and basic definitions Sections 1 and 2 Definition of a Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n-1,, a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form P (x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers
Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form P (x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers
A Partial List of Topics: Math Spring 2009
 A Partial List of Topics: Math 112 - Spring 2009 This is a partial compilation of a majority of the topics covered this semester and may not include everything which might appear on the exam. The purpose
A Partial List of Topics: Math 112 - Spring 2009 This is a partial compilation of a majority of the topics covered this semester and may not include everything which might appear on the exam. The purpose
Section Properties of Rational Expressions
 88 Section. - Properties of Rational Expressions Recall that a rational number is any number that can be written as the ratio of two integers where the integer in the denominator cannot be. Rational Numbers:
88 Section. - Properties of Rational Expressions Recall that a rational number is any number that can be written as the ratio of two integers where the integer in the denominator cannot be. Rational Numbers:
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Quadratic Functions Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Quadratic Functions Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions
Question 1: The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some Polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case.
 Class X - NCERT Maths EXERCISE NO:.1 Question 1: The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some Polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
Class X - NCERT Maths EXERCISE NO:.1 Question 1: The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some Polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
Polynomial Functions and Models
 1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 4: Polynomial Functions and Rational Functions Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models
1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 4: Polynomial Functions and Rational Functions Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models
Downloaded from
 Question 1: Exercise 2.1 The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case. (i) (ii) (iii) Page 1 of 24 (iv) (v) (v) Page
Question 1: Exercise 2.1 The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x), in each case. (i) (ii) (iii) Page 1 of 24 (iv) (v) (v) Page
Functions and Equations
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Euclid eworkshop # Functions and Equations c 006 CANADIAN
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Euclid eworkshop # Functions and Equations c 006 CANADIAN
( 3) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
 81 Instruction: Determining the Possible Rational Roots using the Rational Root Theorem Consider the theorem stated below. Rational Root Theorem: If the rational number b / c, in lowest terms, is a root
81 Instruction: Determining the Possible Rational Roots using the Rational Root Theorem Consider the theorem stated below. Rational Root Theorem: If the rational number b / c, in lowest terms, is a root
 Student: Date: Instructor: kumnit nong Course: MATH 105 by Nong https://xlitemprodpearsoncmgcom/api/v1/print/math Assignment: CH test review 1 Find the transformation form of the quadratic function graphed
Student: Date: Instructor: kumnit nong Course: MATH 105 by Nong https://xlitemprodpearsoncmgcom/api/v1/print/math Assignment: CH test review 1 Find the transformation form of the quadratic function graphed
10/22/16. 1 Math HL - Santowski SKILLS REVIEW. Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions. Lesson Objectives. (A) Rational Functions
 Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Reading Mathematical Expressions & Arithmetic Operations Expression Reads Note
 Math 001 - Term 171 Reading Mathematical Expressions & Arithmetic Operations Expression Reads Note x A x belongs to A,x is in A Between an element and a set. A B A is a subset of B Between two sets. φ
Math 001 - Term 171 Reading Mathematical Expressions & Arithmetic Operations Expression Reads Note x A x belongs to A,x is in A Between an element and a set. A B A is a subset of B Between two sets. φ
AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES
 AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES 1 SURDS A root such as 3 that cannot be written exactly as a fraction is IRRATIONAL An expression that involves irrational roots is in SURD FORM e.g. 2 3 3 + 2 and 3-2 are
AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES 1 SURDS A root such as 3 that cannot be written exactly as a fraction is IRRATIONAL An expression that involves irrational roots is in SURD FORM e.g. 2 3 3 + 2 and 3-2 are
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Chapter 3
 Polynomial and Rational Functions Chapter 3 Quadratic Functions and Models Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions Quadratic function: Function of the form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c (a, b and c real numbers, a 0) -30
Polynomial and Rational Functions Chapter 3 Quadratic Functions and Models Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions Quadratic function: Function of the form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c (a, b and c real numbers, a 0) -30
Ch 7 Summary - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 Ch 7 Summary - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 1. An open-top box is to be made by cutting congruent squares of side length x from the corners of a 8.5- by 11-inch sheet of cardboard and bending up the sides. a)
Ch 7 Summary - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 1. An open-top box is to be made by cutting congruent squares of side length x from the corners of a 8.5- by 11-inch sheet of cardboard and bending up the sides. a)
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Prep-Year Math Program Math Term 161 Recitation (R1, R2)
 Math 001 - Term 161 Recitation (R1, R) Question 1: How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 1 (b) Finite (c) 0 (d) Infinite (e) Question : A will contain how many elements
Math 001 - Term 161 Recitation (R1, R) Question 1: How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 1 (b) Finite (c) 0 (d) Infinite (e) Question : A will contain how many elements
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences
 Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identify the degree of each polynomial. a. 3x 4 2x 3 3x 2 x 7 b. x 1 c. 0.2x 1.x 2 3.2x 3 d. 20 16x 2 20x e. x x 2 x 3 x 4 x f. x 2 6x 2x 6 3x 4 8
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identify the degree of each polynomial. a. 3x 4 2x 3 3x 2 x 7 b. x 1 c. 0.2x 1.x 2 3.2x 3 d. 20 16x 2 20x e. x x 2 x 3 x 4 x f. x 2 6x 2x 6 3x 4 8
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
Algebra II Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 Algebra II Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Algebra II Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Polynomial Functions
 Polynomial Functions Polynomials A Polynomial in one variable, x, is an expression of the form a n x 0 a 1 x n 1... a n 2 x 2 a n 1 x a n The coefficients represent complex numbers (real or imaginary),
Polynomial Functions Polynomials A Polynomial in one variable, x, is an expression of the form a n x 0 a 1 x n 1... a n 2 x 2 a n 1 x a n The coefficients represent complex numbers (real or imaginary),
6x 3 12x 2 7x 2 +16x 7x 2 +14x 2x 4
 2.3 Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions Name: Pre-calculus. Date: Block: 1. Long Division of Polynomials. We have factored polynomials of degree 2 and some specific types of polynomials of degree 3 using
2.3 Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions Name: Pre-calculus. Date: Block: 1. Long Division of Polynomials. We have factored polynomials of degree 2 and some specific types of polynomials of degree 3 using
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
CHAPTER 2 POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
Pre-Calculus: Functions and Their Properties (Solving equations algebraically and graphically, matching graphs, tables, and equations, and
 Pre-Calculus: 1.1 1.2 Functions and Their Properties (Solving equations algebraically and graphically, matching graphs, tables, and equations, and finding the domain, range, VA, HA, etc.). Name: Date:
Pre-Calculus: 1.1 1.2 Functions and Their Properties (Solving equations algebraically and graphically, matching graphs, tables, and equations, and finding the domain, range, VA, HA, etc.). Name: Date:
Lesson 2.1: Quadratic Functions
 Quadratic Functions: Lesson 2.1: Quadratic Functions Standard form (vertex form) of a quadratic function: Vertex: (h, k) Algebraically: *Use completing the square to convert a quadratic equation into standard
Quadratic Functions: Lesson 2.1: Quadratic Functions Standard form (vertex form) of a quadratic function: Vertex: (h, k) Algebraically: *Use completing the square to convert a quadratic equation into standard
Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions. Factoring Review. We will talk about 3 Types: ALWAYS FACTOR OUT FIRST! Ex 2: Factor x x + 64
 Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions Factoring Review We will talk about 3 Types: 1. 2. 3. ALWAYS FACTOR OUT FIRST! Ex 1: Factor x 2 + 5x + 6 Ex 2: Factor x 2 + 16x + 64 Ex 3: Factor 4x 2 + 6x 18 Ex 4: Factor
Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions Factoring Review We will talk about 3 Types: 1. 2. 3. ALWAYS FACTOR OUT FIRST! Ex 1: Factor x 2 + 5x + 6 Ex 2: Factor x 2 + 16x + 64 Ex 3: Factor 4x 2 + 6x 18 Ex 4: Factor
6.1 Polynomial Functions
 6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
A101 ASSESSMENT Quadratics, Discriminant, Inequalities 1
 Do the questions as a test circle questions you cannot answer Red (1) Solve a) 7x = x 2-30 b) 4x 2-29x + 7 = 0 (2) Solve the equation x 2 6x 2 = 0, giving your answers in simplified surd form [3] (3) a)
Do the questions as a test circle questions you cannot answer Red (1) Solve a) 7x = x 2-30 b) 4x 2-29x + 7 = 0 (2) Solve the equation x 2 6x 2 = 0, giving your answers in simplified surd form [3] (3) a)
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
Chapter 8. Exploring Polynomial Functions. Jennifer Huss
 Chapter 8 Exploring Polynomial Functions Jennifer Huss 8-1 Polynomial Functions The degree of a polynomial is determined by the greatest exponent when there is only one variable (x) in the polynomial Polynomial
Chapter 8 Exploring Polynomial Functions Jennifer Huss 8-1 Polynomial Functions The degree of a polynomial is determined by the greatest exponent when there is only one variable (x) in the polynomial Polynomial
Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials
 Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials Higher 5. Quadratics and Polynomials Section A - Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic R1 I have
Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials Higher 5. Quadratics and Polynomials Section A - Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic R1 I have
Assessment Exemplars: Polynomials, Radical and Rational Functions & Equations
 Class: Date: Assessment Exemplars: Polynomials, Radical and Rational Functions & Equations 1 Express the following polynomial function in factored form: P( x) = 10x 3 + x 2 52x + 20 2 SE: Express the following
Class: Date: Assessment Exemplars: Polynomials, Radical and Rational Functions & Equations 1 Express the following polynomial function in factored form: P( x) = 10x 3 + x 2 52x + 20 2 SE: Express the following
Chapter 4E - Combinations of Functions
 Fry Texas A&M University!! Math 150!! Chapter 4E!! Fall 2015! 121 Chapter 4E - Combinations of Functions 1. Let f (x) = 3 x and g(x) = 3+ x a) What is the domain of f (x)? b) What is the domain of g(x)?
Fry Texas A&M University!! Math 150!! Chapter 4E!! Fall 2015! 121 Chapter 4E - Combinations of Functions 1. Let f (x) = 3 x and g(x) = 3+ x a) What is the domain of f (x)? b) What is the domain of g(x)?
Alg Review/Eq & Ineq (50 topics, due on 01/19/2016)
 Course Name: MAC 1140 Spring 16 Course Code: XQWHD-P4TU6 ALEKS Course: PreCalculus Instructor: Van De Car Course Dates: Begin: 01/11/2016 End: 05/01/2016 Course Content: 307 topics Textbook: Coburn: Precalculus,
Course Name: MAC 1140 Spring 16 Course Code: XQWHD-P4TU6 ALEKS Course: PreCalculus Instructor: Van De Car Course Dates: Begin: 01/11/2016 End: 05/01/2016 Course Content: 307 topics Textbook: Coburn: Precalculus,
More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4
 MATH 11009: More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4 Dividend: The number or expression you are dividing into. Divisor: The number or expression you are dividing by. Synthetic division: Synthetic division
MATH 11009: More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4 Dividend: The number or expression you are dividing into. Divisor: The number or expression you are dividing by. Synthetic division: Synthetic division
Review all the activities leading to Midterm 3. Review all the problems in the previous online homework sets (8+9+10).
 MA109, Activity 34: Review (Sections 3.6+3.7+4.1+4.2+4.3) Date: Objective: Additional Assignments: To prepare for Midterm 3, make sure that you can solve the types of problems listed in Activities 33 and
MA109, Activity 34: Review (Sections 3.6+3.7+4.1+4.2+4.3) Date: Objective: Additional Assignments: To prepare for Midterm 3, make sure that you can solve the types of problems listed in Activities 33 and
College Algebra Notes
 Metropolitan Community College Contents Introduction 2 Unit 1 3 Rational Expressions........................................... 3 Quadratic Equations........................................... 9 Polynomial,
Metropolitan Community College Contents Introduction 2 Unit 1 3 Rational Expressions........................................... 3 Quadratic Equations........................................... 9 Polynomial,
Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models
 Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models Learning Objectives: 1. Identify Polynomial Functions and Their Degree 2. Graph Polynomial Functions Using Transformations 3. Identify the Real Zeros of a Polynomial
Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models Learning Objectives: 1. Identify Polynomial Functions and Their Degree 2. Graph Polynomial Functions Using Transformations 3. Identify the Real Zeros of a Polynomial
UMUC MATH-107 Final Exam Information
 UMUC MATH-07 Final Exam Information What should you know for the final exam? Here are some highlights of textbook material you should study in preparation for the final exam. Review this material from
UMUC MATH-07 Final Exam Information What should you know for the final exam? Here are some highlights of textbook material you should study in preparation for the final exam. Review this material from
Chapter Five Notes N P U2C5
 Chapter Five Notes N P UC5 Name Period Section 5.: Linear and Quadratic Functions with Modeling In every math class you have had since algebra you have worked with equations. Most of those equations have
Chapter Five Notes N P UC5 Name Period Section 5.: Linear and Quadratic Functions with Modeling In every math class you have had since algebra you have worked with equations. Most of those equations have
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
f(x) = 2x + 5 3x 1. f 1 (x) = x + 5 3x 2. f(x) = 102x x
 1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
2 the maximum/minimum value is ( ).
 Math 60 Ch3 practice Test The graph of f(x) = 3(x 5) + 3 is with its vertex at ( maximum/minimum value is ( ). ) and the The graph of a quadratic function f(x) = x + x 1 is with its vertex at ( the maximum/minimum
Math 60 Ch3 practice Test The graph of f(x) = 3(x 5) + 3 is with its vertex at ( maximum/minimum value is ( ). ) and the The graph of a quadratic function f(x) = x + x 1 is with its vertex at ( the maximum/minimum
Polynomial Functions. Linear Graphs and Linear Functions 1.3
 Polynomial Functions Linear Graphs and Linear Functions 1.3 Forms for equations of lines (linear functions) Ax + By = C Standard Form y = mx +b Slope-Intercept (y y 1 ) = m(x x 1 ) Point-Slope x = a Vertical
Polynomial Functions Linear Graphs and Linear Functions 1.3 Forms for equations of lines (linear functions) Ax + By = C Standard Form y = mx +b Slope-Intercept (y y 1 ) = m(x x 1 ) Point-Slope x = a Vertical
POLYNOMIALS. x + 1 x x 4 + x 3. x x 3 x 2. x x 2 + x. x + 1 x 1
 POLYNOMIALS A polynomial in x is an expression of the form p(x) = a 0 + a 1 x + a x +. + a n x n Where a 0, a 1, a. a n are real numbers and n is a non-negative integer and a n 0. A polynomial having only
POLYNOMIALS A polynomial in x is an expression of the form p(x) = a 0 + a 1 x + a x +. + a n x n Where a 0, a 1, a. a n are real numbers and n is a non-negative integer and a n 0. A polynomial having only
Algebra III Chapter 2 Note Packet. Section 2.1: Polynomial Functions
 Algebra III Chapter 2 Note Packet Name Essential Question: Section 2.1: Polynomial Functions Polynomials -Have nonnegative exponents -Variables ONLY in -General Form n ax + a x +... + ax + ax+ a n n 1
Algebra III Chapter 2 Note Packet Name Essential Question: Section 2.1: Polynomial Functions Polynomials -Have nonnegative exponents -Variables ONLY in -General Form n ax + a x +... + ax + ax+ a n n 1
n The coefficients a i are real numbers, n is a whole number. The domain of any polynomial is R.
 Section 4.1: Quadratic Functions Definition: A polynomial function has the form P ( x ) = a x n+ a x n 1+... + a x 2+ a x + a (page 326) n n 1 2 1 0 The coefficients a i are real numbers, n is a whole
Section 4.1: Quadratic Functions Definition: A polynomial function has the form P ( x ) = a x n+ a x n 1+... + a x 2+ a x + a (page 326) n n 1 2 1 0 The coefficients a i are real numbers, n is a whole
b n x n + b n 1 x n b 1 x + b 0
 Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Class IX Chapter 2 Polynomials Maths
 NCRTSOLUTIONS.BLOGSPOT.COM Class IX Chapter 2 Polynomials Maths Exercise 2.1 Question 1: Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are No. It can be observed that the
NCRTSOLUTIONS.BLOGSPOT.COM Class IX Chapter 2 Polynomials Maths Exercise 2.1 Question 1: Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are No. It can be observed that the
4 Unit Math Homework for Year 12
 Yimin Math Centre 4 Unit Math Homework for Year 12 Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Topic 3 Polynomials Part 2 1 3.2 Factorisation of polynomials and fundamental theorem of algebra...........
Yimin Math Centre 4 Unit Math Homework for Year 12 Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Topic 3 Polynomials Part 2 1 3.2 Factorisation of polynomials and fundamental theorem of algebra...........
Objective Mathematics
 Multiple choice questions with ONE correct answer : ( Questions No. 1-5 ) 1. If the equation x n = (x + ) is having exactly three distinct real solutions, then exhaustive set of values of 'n' is given
Multiple choice questions with ONE correct answer : ( Questions No. 1-5 ) 1. If the equation x n = (x + ) is having exactly three distinct real solutions, then exhaustive set of values of 'n' is given
2.6. Graphs of Rational Functions. Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc.
 2.6 Graphs of Rational Functions Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. Rational Functions What you ll learn about Transformations of the Reciprocal Function Limits and Asymptotes Analyzing Graphs of Rational Functions
2.6 Graphs of Rational Functions Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. Rational Functions What you ll learn about Transformations of the Reciprocal Function Limits and Asymptotes Analyzing Graphs of Rational Functions
Maths Higher Prelim Content
 Maths Higher Prelim Content Straight Line Gradient of a line A(x 1, y 1 ), B(x 2, y 2 ), Gradient of AB m AB = y 2 y1 x 2 x 1 m = tanθ where θ is the angle the line makes with the positive direction of
Maths Higher Prelim Content Straight Line Gradient of a line A(x 1, y 1 ), B(x 2, y 2 ), Gradient of AB m AB = y 2 y1 x 2 x 1 m = tanθ where θ is the angle the line makes with the positive direction of
Polynomials. Henry Liu, 25 November 2004
 Introduction Polynomials Henry Liu, 25 November 2004 henryliu@memphis.edu This brief set of notes contains some basic ideas and the most well-known theorems about polynomials. I have not gone into deep
Introduction Polynomials Henry Liu, 25 November 2004 henryliu@memphis.edu This brief set of notes contains some basic ideas and the most well-known theorems about polynomials. I have not gone into deep
Course Name: MAT 135 Spring 2017 Master Course Code: N/A. ALEKS Course: Intermediate Algebra Instructor: Master Templates
 Course Name: MAT 135 Spring 2017 Master Course Code: N/A ALEKS Course: Intermediate Algebra Instructor: Master Templates Course Dates: Begin: 01/15/2017 End: 05/31/2017 Course Content: 279 Topics (207
Course Name: MAT 135 Spring 2017 Master Course Code: N/A ALEKS Course: Intermediate Algebra Instructor: Master Templates Course Dates: Begin: 01/15/2017 End: 05/31/2017 Course Content: 279 Topics (207
Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 2.1 Quadratic Functions Date: Example 1: Sketching the Graph of a Quadratic Function a) Graph f(x) = 3 1 x 2 and g(x) = x 2 on the same coordinate plane.
Chapter 2: Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 2.1 Quadratic Functions Date: Example 1: Sketching the Graph of a Quadratic Function a) Graph f(x) = 3 1 x 2 and g(x) = x 2 on the same coordinate plane.
Review for Cumulative Test 2
 Review for Cumulative Test We will have our second course-wide cumulative test on Tuesday February 9 th or Wednesday February 10 th, covering from the beginning of the course up to section 4.3 in our textbook.
Review for Cumulative Test We will have our second course-wide cumulative test on Tuesday February 9 th or Wednesday February 10 th, covering from the beginning of the course up to section 4.3 in our textbook.
PreCalculus: Semester 1 Final Exam Review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A PreCalculus: Semester 1 Final Exam Review Short Answer 1. Determine whether the relation represents a function. If it is a function, state the domain and range. 9. Find the domain
Name: Class: Date: ID: A PreCalculus: Semester 1 Final Exam Review Short Answer 1. Determine whether the relation represents a function. If it is a function, state the domain and range. 9. Find the domain
SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS 1-30
 . Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
. Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
Rational Functions 4.5
 Math 4 Pre-Calculus Name Date Rational Function Rational Functions 4.5 g ( ) A function is a rational function if f ( ), where g ( ) and ( ) h ( ) h are polynomials. Vertical asymptotes occur at -values
Math 4 Pre-Calculus Name Date Rational Function Rational Functions 4.5 g ( ) A function is a rational function if f ( ), where g ( ) and ( ) h ( ) h are polynomials. Vertical asymptotes occur at -values
Using Properties of Exponents
 6.1 Using Properties of Exponents Goals p Use properties of exponents to evaluate and simplify expressions involving powers. p Use exponents and scientific notation to solve real-life problems. VOCABULARY
6.1 Using Properties of Exponents Goals p Use properties of exponents to evaluate and simplify expressions involving powers. p Use exponents and scientific notation to solve real-life problems. VOCABULARY
Algebra 2 Segment 1 Lesson Summary Notes
 Algebra 2 Segment 1 Lesson Summary Notes For each lesson: Read through the LESSON SUMMARY which is located. Read and work through every page in the LESSON. Try each PRACTICE problem and write down the
Algebra 2 Segment 1 Lesson Summary Notes For each lesson: Read through the LESSON SUMMARY which is located. Read and work through every page in the LESSON. Try each PRACTICE problem and write down the
3 What is the degree of the polynomial function that generates the data shown below?
 hapter 04 Test Name: ate: 1 For the polynomial function, describe the end behavior of its graph. The leading term is down. The leading term is and down.. Since n is 1 and a is positive, the end behavior
hapter 04 Test Name: ate: 1 For the polynomial function, describe the end behavior of its graph. The leading term is down. The leading term is and down.. Since n is 1 and a is positive, the end behavior
2. Approximate the real zero of f(x) = x3 + x + 1 to the nearest tenth. Answer: Substitute all the values into f(x) and find which is closest to zero
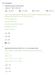 Unit 2 Examples(K) 1. Find all the real zeros of the function. Answer: Simply substitute the values given in all the functions and see which option when substituted, all the values go to zero. That is
Unit 2 Examples(K) 1. Find all the real zeros of the function. Answer: Simply substitute the values given in all the functions and see which option when substituted, all the values go to zero. That is
Factoring Review WS 3.0. Factoring Polynomials Factor and Remainder Theorems. Factoring a Sum or Difference of Cubes Pg. 182 # 1-5
 UNIT POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework Sept. 0.0.0 Factoring Review WS.0 Sept. 1.1.5 Dividing Polnomials Pg. 168 #,, 4, (5 10)doso, 11, 1 Sept...6 Factoring Polnomials Factor and Remainder
UNIT POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework Sept. 0.0.0 Factoring Review WS.0 Sept. 1.1.5 Dividing Polnomials Pg. 168 #,, 4, (5 10)doso, 11, 1 Sept...6 Factoring Polnomials Factor and Remainder
Study Guide for Math 095
 Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
1) The line has a slope of ) The line passes through (2, 11) and. 6) r(x) = x + 4. From memory match each equation with its graph.
 Review Test 2 Math 1314 Name Write an equation of the line satisfying the given conditions. Write the answer in standard form. 1) The line has a slope of - 2 7 and contains the point (3, 1). Use the point-slope
Review Test 2 Math 1314 Name Write an equation of the line satisfying the given conditions. Write the answer in standard form. 1) The line has a slope of - 2 7 and contains the point (3, 1). Use the point-slope
y2 + 4y - 5 c a + b 27 i C) ) (16, ) B) (16 3 3, )
 MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
Solutions 2017 AB Exam
 1. Solve for x : x 2 = 4 x. Solutions 2017 AB Exam Texas A&M High School Math Contest October 21, 2017 ANSWER: x = 3 Solution: x 2 = 4 x x 2 = 16 8x + x 2 x 2 9x + 18 = 0 (x 6)(x 3) = 0 x = 6, 3 but x
1. Solve for x : x 2 = 4 x. Solutions 2017 AB Exam Texas A&M High School Math Contest October 21, 2017 ANSWER: x = 3 Solution: x 2 = 4 x x 2 = 16 8x + x 2 x 2 9x + 18 = 0 (x 6)(x 3) = 0 x = 6, 3 but x
Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet. Types of Functions
 MATH 1142 NAME Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet Types of Functions Now that we have discussed what functions are and some of their characteristics, we will explore different types of functions. Section 0.2
MATH 1142 NAME Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet Types of Functions Now that we have discussed what functions are and some of their characteristics, we will explore different types of functions. Section 0.2
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
6A The language of polynomials. A Polynomial function follows the rule. Degree of a polynomial is the highest power of x with a non-zero coefficient.
 Unit Mathematical Methods Chapter 6: Polynomials Objectives To add, subtract and multiply polynomials. To divide polynomials. To use the remainder theorem, factor theorem and rational-root theorem to identify
Unit Mathematical Methods Chapter 6: Polynomials Objectives To add, subtract and multiply polynomials. To divide polynomials. To use the remainder theorem, factor theorem and rational-root theorem to identify
Math 120, Sample Final Fall 2015
 Math 10, Sample Final Fall 015 Disclaimer: This sample final is intended to help students prepare for the final exam The final exam will be similar in structure and type of problems, however the actual
Math 10, Sample Final Fall 015 Disclaimer: This sample final is intended to help students prepare for the final exam The final exam will be similar in structure and type of problems, however the actual
MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions
 MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions Name: Student Number: Answer all questions. Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown. Remarks by me in italics and would not be required in a test - J.P. Question
MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions Name: Student Number: Answer all questions. Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown. Remarks by me in italics and would not be required in a test - J.P. Question
ACT MATH MUST-KNOWS Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions
 Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
UNC Charlotte 2004 Algebra with solutions
 with solutions March 8, 2004 1. Let z denote the real number solution to of the digits of z? (A) 13 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 (E) 17 3 + x 1 = 5. What is the sum Solution: E. Square both sides twice to get
with solutions March 8, 2004 1. Let z denote the real number solution to of the digits of z? (A) 13 (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 (E) 17 3 + x 1 = 5. What is the sum Solution: E. Square both sides twice to get
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review
 Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Polynomial Functions
 Polynomial Functions Equations and Graphs Characteristics The Factor Theorem The Remainder Theorem http://www.purplemath.com/modules/polyends5.htm 1 A cross-section of a honeycomb has a pattern with one
Polynomial Functions Equations and Graphs Characteristics The Factor Theorem The Remainder Theorem http://www.purplemath.com/modules/polyends5.htm 1 A cross-section of a honeycomb has a pattern with one
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Order of Operations Expression Variable Coefficient
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Order of Operations Expression Variable Coefficient
MATHEMATICAL METHODS UNIT 1 CHAPTER 4 CUBIC POLYNOMIALS
 E da = q ε ( B da = 0 E ds = dφ. B ds = μ ( i + μ ( ε ( dφ 3 MATHEMATICAL METHODS UNIT 1 CHAPTER 4 CUBIC POLYNOMIALS dt dt Key knowledge The key features and properties of cubic polynomials functions and
E da = q ε ( B da = 0 E ds = dφ. B ds = μ ( i + μ ( ε ( dφ 3 MATHEMATICAL METHODS UNIT 1 CHAPTER 4 CUBIC POLYNOMIALS dt dt Key knowledge The key features and properties of cubic polynomials functions and
Algebra II Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra II Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Complex Numbers Complex Number (examples)
Algebra II Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Complex Numbers Complex Number (examples)
3. Use absolute value notation to write an inequality that represents the statement: x is within 3 units of 2 on the real line.
 PreCalculus Review Review Questions 1 The following transformations are applied in the given order) to the graph of y = x I Vertical Stretch by a factor of II Horizontal shift to the right by units III
PreCalculus Review Review Questions 1 The following transformations are applied in the given order) to the graph of y = x I Vertical Stretch by a factor of II Horizontal shift to the right by units III
Polynomial Review Problems
 Polynomial Review Problems 1. Find polynomial function formulas that could fit each of these graphs. Remember that you will need to determine the value of the leading coefficient. The point (0,-3) is on
Polynomial Review Problems 1. Find polynomial function formulas that could fit each of these graphs. Remember that you will need to determine the value of the leading coefficient. The point (0,-3) is on
The Graph of a Quadratic Function. Quadratic Functions & Models. The Graph of a Quadratic Function. The Graph of a Quadratic Function
 8/1/015 The Graph of a Quadratic Function Quadratic Functions & Models Precalculus.1 The Graph of a Quadratic Function The Graph of a Quadratic Function All parabolas are symmetric with respect to a line
8/1/015 The Graph of a Quadratic Function Quadratic Functions & Models Precalculus.1 The Graph of a Quadratic Function The Graph of a Quadratic Function All parabolas are symmetric with respect to a line
5.4 - Quadratic Functions
 Fry TAMU Spring 2017 Math 150 Notes Section 5.4 Page! 92 5.4 - Quadratic Functions Definition: A function is one that can be written in the form f (x) = where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. (What
Fry TAMU Spring 2017 Math 150 Notes Section 5.4 Page! 92 5.4 - Quadratic Functions Definition: A function is one that can be written in the form f (x) = where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. (What
Pre-Algebra 2. Unit 9. Polynomials Name Period
 Pre-Algebra Unit 9 Polynomials Name Period 9.1A Add, Subtract, and Multiplying Polynomials (non-complex) Explain Add the following polynomials: 1) ( ) ( ) ) ( ) ( ) Subtract the following polynomials:
Pre-Algebra Unit 9 Polynomials Name Period 9.1A Add, Subtract, and Multiplying Polynomials (non-complex) Explain Add the following polynomials: 1) ( ) ( ) ) ( ) ( ) Subtract the following polynomials:
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers
 Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions
 Chapter 3 Lecture Notes Page 1 of 72 Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions Objectives: Compare two different forms of writing a quadratic function Find the equation of a quadratic function (given points) Application
Chapter 3 Lecture Notes Page 1 of 72 Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions Objectives: Compare two different forms of writing a quadratic function Find the equation of a quadratic function (given points) Application
MAT116 Final Review Session Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 MAT116 Final Review Session Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Quadratic Function A quadratic function is defined by a quadratic or second-degree polynomial. Standard Form f x = ax 2 + bx + c,
MAT116 Final Review Session Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Quadratic Function A quadratic function is defined by a quadratic or second-degree polynomial. Standard Form f x = ax 2 + bx + c,
Calculus First Semester Review Name: Section: Evaluate the function: (g o f )( 2) f (x + h) f (x) h. m(x + h) m(x)
 Evaluate the function: c. (g o f )(x + 2) d. ( f ( f (x)) 1. f x = 4x! 2 a. f( 2) b. f(x 1) c. f (x + h) f (x) h 4. g x = 3x! + 1 Find g!! (x) 5. p x = 4x! + 2 Find p!! (x) 2. m x = 3x! + 2x 1 m(x + h)
Evaluate the function: c. (g o f )(x + 2) d. ( f ( f (x)) 1. f x = 4x! 2 a. f( 2) b. f(x 1) c. f (x + h) f (x) h 4. g x = 3x! + 1 Find g!! (x) 5. p x = 4x! + 2 Find p!! (x) 2. m x = 3x! + 2x 1 m(x + h)
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Higher Order Polynomials and Factoring Roots of Polynomial Equations Problem Set Solve each polynomial equation using factoring. Then check your solution(s).
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Higher Order Polynomials and Factoring Roots of Polynomial Equations Problem Set Solve each polynomial equation using factoring. Then check your solution(s).
A Library of Functions
 LibraryofFunctions.nb 1 A Library of Functions Any study of calculus must start with the study of functions. Functions are fundamental to mathematics. In its everyday use the word function conveys to us
LibraryofFunctions.nb 1 A Library of Functions Any study of calculus must start with the study of functions. Functions are fundamental to mathematics. In its everyday use the word function conveys to us
Midterm Review. Name: Class: Date: ID: A. Short Answer. 1. For each graph, write the equation of a radical function of the form y = a b(x h) + k.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Midterm Review Short Answer 1. For each graph, write the equation of a radical function of the form y = a b(x h) + k. a) b) c) 2. Determine the domain and range of each function.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Midterm Review Short Answer 1. For each graph, write the equation of a radical function of the form y = a b(x h) + k. a) b) c) 2. Determine the domain and range of each function.
Warm-Up. Use long division to divide 5 into
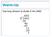 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
