dy dt = 1 y t 1 +t 2 y dy = 1 +t 2 dt 1 2 y2 = 1 2 ln(1 +t2 ) +C, y = ln(1 +t 2 ) + 9.
|
|
|
- Marybeth Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 1 of 8 1. (10 points Solve the following initial value problem explicitly. Your answer should be a function in the form y = g(t, where there is no undetermined constant in g. dt = t y +t 2, y(0 = 3. y This equation is separable. After factoring the right hand side of the DE we have it in standard form: dt = 1 y t 1 +t 2 Putting all the y-stuff on the left and all the t-stuff on the right then yields y = t 1 +t 2 dt Both integrals are straightforward: on the left we get 1 2 y2, and on the right (via u-sub if necessary we get 1 2 ln(1 +t2 +C; we may omit absolute value signs, since t is always positive. Hence or, after solving for y, 1 2 y2 = 1 2 ln(1 +t2 +C, y = ± ln(1 +t 2 +C (where we ve absorbed the factor of 2 into the C when multiplying through. Applying the initial condition t = 0, y = 3 give us 3 = ± ln( C = ± C, which means that C = 9 and we must choose the negative square root. Thus the solution to the IVP is y = ln(1 +t
2 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 2 of 8 2. (10 total points Consider the following linear initial value problem: (t 2 4t 5 dt + 2(t + 1y 1 = 0, y(0 = y 0. (a (3 points Using the existence and uniqueness theorem for linear differential equations, state the maximum interval on which a unique solution to the above IVP is guaranteed to exist. First we put the linear equation in standard form by dividing through by (t 2 4t 5: 2(t dt t 2 4t 5 y = 1 t 2 4t 5. Note that (t 2 4t 5 = (t + 1(t 5, so we get cancellation in the term in front of y, so the above equation simplifies to ( 2 dt + 1 y = t 5 (t + 1(t 5. From this we see that f (t = ( 2 t 5 is continuous on the intervals t < 5 and t > 5, while 1 g(t = (t+1(t 5 is continuous on the intervals t < 1, 1 < t < 5 and t > 5. The largest interval surrounding the initial condition time t = 0 on which both f and g are continuous is thus 1 < t < 5. Hence we are guaranteed a unique solution to the IVP for 1 < t < 5.
3 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 3 of 8 (b (7 points Solve the above differential equation for the case y 0 = 1 5. Our integrating factor is µ(t = e f (tdt = e 2 t 5 dt = e 2ln t 5 = (t 5 2. here we may omit the absolute value signs at the end as anything square is always at least zero. The general solution to the DE is then y(t = 1 ( µ(tg(t dt +C µ(t = (t 5 2 ( (t 5 2 (t + 1(t 5 ( (t 5 = (t 5 2 dt +C (t + 1 ( = (t dt +C (t + 1 = (t 5 2 (t 6ln(t + 1 +C = t 6ln(t + 1 +C (t 5 2. dt +C Applying the IC t = 0,y = 1 5 gives us 1 5 so C = 5. The solution to the IVP is therefore = 0 6ln( C (0 5 2 = C 25, y = t 6ln(t (t 5 2. Note that if you plot the above function you ll see that it has vertical asymptotes at t = 1 and t = 5, thereby confirming that the solution is valid on the interval 1 < t < 5.
4 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 4 of 8 3. (10 total points The slope field to the differential equation = f (x,y is plotted below for 0 x 5, 5 y 5: (a (4 points Circle the differential equation that corresponds to the above slope field. = x(y + 1 = x(y + 1 = x(y 1 = x(y 1 We see that has an equilibrium solution at y = 1. This is the case for = x(y 1 and = x(y 1 but not so for the other two equations, ruling them out. Moreover we see from the slope field that is negative for t > 0 and y > 1 and positive for t > 0 and y < 1. This is the case when f (x,y = x(y 1 but not so for f (x,y = x(y 1. We conclude that the slope field is that of the differential equation = x(y 1. (b (6 points Let y = φ(x be the solution to the differential equation you circled above that satisfies the initial condition y(0 = 0. Use Euler s method with a step size of h = 0.5 to estimate the value of the solution at x = 1.5. You may use decimal approximations in your final answer (but keep at least 4 digits precision at all points. Recall that Euler s method for the IVP = f (x,y, y(x 0 = y 0 with step size h is given by the scheme Set x 0 and y 0 to be the given initial conditions for n 0 set x n+1 = x n + h and y n+1 = y 0 + h f (x n,y n. For us we have h = 0.5 and f (x,y = x(y 1, so we have x 0 = 0 and y 0 = 0 x 1 = 2 1 and y 1 = y 0 + h f (x 0,y 0 = [ 0(0 1] = 0 x 2 = 1 and y 2 = y 1 + h f (x 1,y 1 = [ 1 2 (0 1] = 1 4 x 2 = 3 2 and y 3 = y 2 + h f (x 2,y 2 = [ 1( 1 4 1] = 5 8 At this point we stop, as we ve reached x 3 = 1.5. Our estimate for φ(1.5 is thus y 3 = 5 8 =
5 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 5 of 8 4. (10 total points Consider the autonomous differential equation dt = sin2 (y K, where K is a constant such that y = π 3 is an equilibrium solution. (a (5 points Find K, and state whether y = π 3 is a stable, unstable or semistable equilibrium solution. Be sure to justify your answer. Recall that an autonomous equation dt = f (y has an equilibrium solution y = C if f (C = 0. So here we know ( π ( f = sin 2 π K = Hence ( K = sin 2 π ( 2 3 = = Now recall that to ascertain whether y = C is a stable, unstable or semistable equilibrium solution to dt = f (y we can evaluate d f at C; if the derivative is negative we have a stable solution, if the derivative is positve we have an unstable solution, and if the derivative is zero we need to do more work. Here we have d f = 2sin(ycos(y = sin(2y, which evaluated at y = π 3 is 3 2, ie. positive. Thus the equilibrium solution y = π 3 is unstable. Alternately you can draw a picture of f (y versus y, and indicate that f (y < 0 to the immediate left of y = π 3, and positive to the immediate right. (b (5 points Suppose y = φ(t is the unique solution to the differential equation satisfying the initial condition y(0 = 0. Find lim t φ(t. To answer this question one can draw a graph of f (y vs. y. We see that f (y is negative for y = 0, so φ(t is thus decreasing initially. In fact, φ(t will continue decreasing as it approaches the first negative y-value for which f (y = 0. We are guaranteed that the solution φ(t to the DE will never cross this y-value, since that corresponds to a (stable equilibrium solution, and two separate solutions having the same y-value at the same time would violate uniqueness. Our conclusion then is that φ(t asymptotes to the first negative root of f (y = sin 2 (y 3 4. To find this we set sin 2 (y 3 4 = 0 and solve for y. The first negative solution is y = π 3. Hence lim t φ(t = π 3.
6 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 6 of 8 5. (10 total points + 3 bonus points Water hyacinth is a particularly aggressive invasive plant species in lakes in the southern US. One of the reasons is that it grows very quickly: under good conditions a population will grow at a rate proportional to its own size, with its biomass increasing by a factor of e = every 14 days. Suppose a water hyacinth population establishes itself in a large lake in Florida where conditions are close to ideal. When ecologists discover the population it has a biomass of 750kg. Removal efforts begin immediately; however, because it takes some time to train local volunteers to remove the weed efficiently, the rate R(t at which water hyacinth can be removed from the lake is given by the function R(t = 600 ( 1 e t, where t is measured in weeks since the beginning of the removal effort, and R(t is in kg/week. (a (7 points Establish an initial value problem and solve it to find an explicit formula for the biomass of water hyacinth in the lake at time t. Let y(t be the biomass in kg of water hyacinth in the lake at a time t, where t is measured in weeks, and t = 0 corresponds to the beginning of removal efforts. In the absence of any removal effort, the above paragraph tells us that y would grow at a rate proportional to y, i.e. dt = ry for some r > 0. Solving this preliminary DE with y(0 = y 0 yields y = y 0 e rt We know if that left unchecked biomass increases by a factor of e every 2 weeks. In mathematics this statement is y(2 y(0 = e But y(2 y(0 = y 0e 2r y 0 e 0 = e2r so e 2r = e. Solving for r by taking logs on both sides yields r = 1 2. Now in reality the rate at which y grows is reduced by the rate of removal R(t. Hence the water hyacinth in the lake obeys the differential equation subject to the initial condition y(0 = 750. [Solution continued on the next page] dt = 1 2 y 600( 1 e t
7 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 7 of 8 To solve this IVP, note that it is linear. In standard form we have dt 1 2 y = 600( 1 e t, i.e. f (t = 1 2 and g(t = 600(1 e t. The integrating factor is thus µ(t = e f (tdt = e 1 2 dt = e 1 2 t, and so the general solution is given by y(t = 1 ( µ(tg(t dt +C µ(t = e 1 2 ( 600 t e 1 2 t (1 e t dt +C = e 1 2 ( 600 t e 1 2 t dt e 3 2 t dt +C ( = e 1 2 t 1200e 1 2 t 400e 2 3t +C = e t +Ce 1 2 t. Applying the initial condition y(0 = 750 yields 750 = e 0 +Ce 0, so C = 50. Hence the biomass in the lake at time t is given by the function y(t = e t 50e 1 2 t. (b (3 points Will efforts to completely remove the water hyacinth from the lake be successful? Justify your answer. We see that the solution y(t = e t 50e 1 2 t has an exponentially growing term with a negative coefficient; this term will eventually dominate the other two terms and so lim t y(t =. Thus there must be some point in the future where y(t = 0, i.e. there is no more water hyacinth in the lake. Thus yes, the removal effort under the assumptions above will ultimately be successful.
8 Math 307A, Winter 2014 Midterm 1 Solutions Page 8 of 8 (c (Bonus: 3 points If the answer to the above question is yes, estimate how many weeks it will take for the water hyacinth to be removed completely from the lake. If the answer to the above question is no, estimate how many weeks it will take for the water hyacinth to reach 10000kg biomass. You may use decimal approximations in your final answer (but keep at least 4 digits precision at all points. We seek the time where there is no more water hyacinth in the lake, i.e. the t for which y(t = 0. Thus we must solve the equation e t 50e 1 2 t = 0. This equation can in fact be solved exactly through logs and cubic equations, but it s ugly; there s no way I m expecting you to do this in an exam. The best simplifying observation we can make is that 50e 1 2 t increases exponentially in size with time, while 400e t decreases exponentially. So if t is more than a few units in size we can expect the 400e t term in the above expression to be negligible in size compared to the 50e 1 2 t term. It thus makes sense to discard the 400e t term and solve instead for t in the equation e 1 2 t = 0. We thus get that e t 2 = 24 so t = 2ln(24 = 4ln(6 = Indeed, if we plug this t-value into y(t = e t 50e t 2 we get e 4ln = = This is only a hair below zero (considering the starting value for y of We therefore expect the t-value for which y(t = to be just slightly less than our estimate (In fact, the true solution to the equation is so our estimate is accurate to 2 decimal places. y = 4ln(6 = y = , In other words, the lake will be cleared of invasive water hyacinth in just under weeks time.
1. (10 points) Find the general solution to the following second-order differential equation:
 Math 307A, Winter 014 Midterm Solutions Page 1 of 8 1. (10 points) Find the general solution to the following second-order differential equation: 4y 1y + 9y = 9t. To find the general solution to this nonhomogeneous
Math 307A, Winter 014 Midterm Solutions Page 1 of 8 1. (10 points) Find the general solution to the following second-order differential equation: 4y 1y + 9y = 9t. To find the general solution to this nonhomogeneous
Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I
 Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I Problem 1: (1) [8 points] Draw a direction field for the given differential equation y 0 = t + y. (2) [8 points] Based on the direction field, determine the behavior
Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I Problem 1: (1) [8 points] Draw a direction field for the given differential equation y 0 = t + y. (2) [8 points] Based on the direction field, determine the behavior
MIDTERM 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 MIDTERM 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Problem 1. Give an example of: (a) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y) such that all solutions with y(0) > 0 satisfy y(t) = +. lim t + (b) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y)
MIDTERM 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Problem 1. Give an example of: (a) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y) such that all solutions with y(0) > 0 satisfy y(t) = +. lim t + (b) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y)
First Order ODEs, Part II
 Craig J. Sutton craig.j.sutton@dartmouth.edu Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Math 23 Differential Equations Winter 2013 Outline Existence & Uniqueness Theorems 1 Existence & Uniqueness Theorems
Craig J. Sutton craig.j.sutton@dartmouth.edu Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Math 23 Differential Equations Winter 2013 Outline Existence & Uniqueness Theorems 1 Existence & Uniqueness Theorems
California State University Northridge MATH 280: Applied Differential Equations Midterm Exam 1
 California State University Northridge MATH 280: Applied Differential Equations Midterm Exam 1 October 9, 2013. Duration: 75 Minutes. Instructor: Jing Li Student Name: Student number: Take your time to
California State University Northridge MATH 280: Applied Differential Equations Midterm Exam 1 October 9, 2013. Duration: 75 Minutes. Instructor: Jing Li Student Name: Student number: Take your time to
Solutions to Math 53 First Exam April 20, 2010
 Solutions to Math 53 First Exam April 0, 00. (5 points) Match the direction fields below with their differential equations. Also indicate which two equations do not have matches. No justification is necessary.
Solutions to Math 53 First Exam April 0, 00. (5 points) Match the direction fields below with their differential equations. Also indicate which two equations do not have matches. No justification is necessary.
Exam Basics. midterm. 1 There will be 9 questions. 2 The first 3 are on pre-midterm material. 3 The next 1 is a mix of old and new material.
 Exam Basics 1 There will be 9 questions. 2 The first 3 are on pre-midterm material. 3 The next 1 is a mix of old and new material. 4 The last 5 questions will be on new material since the midterm. 5 60
Exam Basics 1 There will be 9 questions. 2 The first 3 are on pre-midterm material. 3 The next 1 is a mix of old and new material. 4 The last 5 questions will be on new material since the midterm. 5 60
First Order Differential Equations
 First Order Differential Equations 1 Finding Solutions 1.1 Linear Equations + p(t)y = g(t), y() = y. First Step: Compute the Integrating Factor. We want the integrating factor to satisfy µ (t) = p(t)µ(t).
First Order Differential Equations 1 Finding Solutions 1.1 Linear Equations + p(t)y = g(t), y() = y. First Step: Compute the Integrating Factor. We want the integrating factor to satisfy µ (t) = p(t)µ(t).
Old Math 330 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
µ = e R p(t)dt where C is an arbitrary constant. In the presence of an initial value condition
 MATH 3860 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM The final exam will be comprehensive. It will cover materials from the following sections: 1.1-1.3; 2.1-2.2;2.4-2.6;3.1-3.7; 4.1-4.3;6.1-6.6; 7.1; 7.4-7.6; 7.8. The following
MATH 3860 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM The final exam will be comprehensive. It will cover materials from the following sections: 1.1-1.3; 2.1-2.2;2.4-2.6;3.1-3.7; 4.1-4.3;6.1-6.6; 7.1; 7.4-7.6; 7.8. The following
Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s
 Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth
Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth
First Order ODEs, Part I
 Craig J. Sutton craig.j.sutton@dartmouth.edu Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Math 23 Differential Equations Winter 2013 Outline 1 2 in General 3 The Definition & Technique Example Test for
Craig J. Sutton craig.j.sutton@dartmouth.edu Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Math 23 Differential Equations Winter 2013 Outline 1 2 in General 3 The Definition & Technique Example Test for
20D - Homework Assignment 1
 0D - Homework Assignment Brian Bowers (TA for Hui Sun) MATH 0D Homework Assignment October 7, 0. #,,,4,6 Solve the given differential equation. () y = x /y () y = x /y( + x ) () y + y sin x = 0 (4) y =
0D - Homework Assignment Brian Bowers (TA for Hui Sun) MATH 0D Homework Assignment October 7, 0. #,,,4,6 Solve the given differential equation. () y = x /y () y = x /y( + x ) () y + y sin x = 0 (4) y =
MATH 353 LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 1 FIRST ORDER ODES
 MATH 353 LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 1 FIRST ORDER ODES J. WONG (FALL 2017) What did we cover this week? Basic definitions: DEs, linear operators, homogeneous (linear) ODEs. Solution techniques for some classes
MATH 353 LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 1 FIRST ORDER ODES J. WONG (FALL 2017) What did we cover this week? Basic definitions: DEs, linear operators, homogeneous (linear) ODEs. Solution techniques for some classes
Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17
 Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17 July 8, 2017 Section 2.3 Problem 4. A tank with capacity of 500 gallons originally contains 200 gallons of water with 100 pounds of salt in solution. Water containing
Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17 July 8, 2017 Section 2.3 Problem 4. A tank with capacity of 500 gallons originally contains 200 gallons of water with 100 pounds of salt in solution. Water containing
1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Let us consider a first order differential equation of the form dy
 .. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Let us consider a first order differential equation of the form dy = f(x, y). In this section we aim to understand the solution
.. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Let us consider a first order differential equation of the form dy = f(x, y). In this section we aim to understand the solution
Sect2.1. Any linear equation:
 Sect2.1. Any linear equation: Divide a 0 (t) on both sides a 0 (t) dt +a 1(t)y = g(t) dt + a 1(t) a 0 (t) y = g(t) a 0 (t) Choose p(t) = a 1(t) a 0 (t) Rewrite it in standard form and ḡ(t) = g(t) a 0 (t)
Sect2.1. Any linear equation: Divide a 0 (t) on both sides a 0 (t) dt +a 1(t)y = g(t) dt + a 1(t) a 0 (t) y = g(t) a 0 (t) Choose p(t) = a 1(t) a 0 (t) Rewrite it in standard form and ḡ(t) = g(t) a 0 (t)
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end.
 Math 307, Midterm 2 Winter 2013 Name: Instructions. DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end. There
Math 307, Midterm 2 Winter 2013 Name: Instructions. DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end. There
1. Why don t we have to worry about absolute values in the general form for first order differential equations with constant coefficients?
 1. Why don t we have to worry about absolute values in the general form for first order differential equations with constant coefficients? Let y = ay b with y(0) = y 0 We can solve this as follows y =
1. Why don t we have to worry about absolute values in the general form for first order differential equations with constant coefficients? Let y = ay b with y(0) = y 0 We can solve this as follows y =
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 2930 Worksheet Final Exam Review
 Math 293 Worksheet Final Exam Review Week 14 November 3th, 217 Question 1. (* Solve the initial value problem y y = 2xe x, y( = 1 Question 2. (* Consider the differential equation: y = y y 3. (a Find the
Math 293 Worksheet Final Exam Review Week 14 November 3th, 217 Question 1. (* Solve the initial value problem y y = 2xe x, y( = 1 Question 2. (* Consider the differential equation: y = y y 3. (a Find the
Sample Questions, Exam 1 Math 244 Spring 2007
 Sample Questions, Exam Math 244 Spring 2007 Remember, on the exam you may use a calculator, but NOT one that can perform symbolic manipulation (remembering derivative and integral formulas are a part of
Sample Questions, Exam Math 244 Spring 2007 Remember, on the exam you may use a calculator, but NOT one that can perform symbolic manipulation (remembering derivative and integral formulas are a part of
MATH 307: Problem Set #3 Solutions
 : Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
: Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
Math 116 Second Midterm November 14, 2012
 Math 6 Second Midterm November 4, Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 problems. Note that
Math 6 Second Midterm November 4, Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 problems. Note that
MATH 307 Introduction to Differential Equations Autumn 2017 Midterm Exam Monday November
 MATH 307 Introduction to Differential Equations Autumn 2017 Midterm Exam Monday November 6 2017 Name: Student ID Number: I understand it is against the rules to cheat or engage in other academic misconduct
MATH 307 Introduction to Differential Equations Autumn 2017 Midterm Exam Monday November 6 2017 Name: Student ID Number: I understand it is against the rules to cheat or engage in other academic misconduct
= 2e t e 2t + ( e 2t )e 3t = 2e t e t = e t. Math 20D Final Review
 Math D Final Review. Solve the differential equation in two ways, first using variation of parameters and then using undetermined coefficients: Corresponding homogenous equation: with characteristic equation
Math D Final Review. Solve the differential equation in two ways, first using variation of parameters and then using undetermined coefficients: Corresponding homogenous equation: with characteristic equation
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
APPM 2360: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 2017
 APPM 36: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 17 On the front of your Bluebook write: (1) your name, () your instructor s name, (3) your recitation section number and () a grading table. Text books, class notes,
APPM 36: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 17 On the front of your Bluebook write: (1) your name, () your instructor s name, (3) your recitation section number and () a grading table. Text books, class notes,
Math 310 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations Final Examination August 9, Instructor: John Stockie
 Make sure this exam has 15 pages. Math 310 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations inal Examination August 9, 2006 Instructor: John Stockie Name: (Please Print) Student Number: Special Instructions
Make sure this exam has 15 pages. Math 310 Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations inal Examination August 9, 2006 Instructor: John Stockie Name: (Please Print) Student Number: Special Instructions
Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214. Due 6/29
 Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214 Due 6/29 Section 2.5 1. (Problems 3 and 5 from B&D) The following problems involve differential equations of the form dy = f(y). For each, sketch the graph of f(y) versus y, determine
Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214 Due 6/29 Section 2.5 1. (Problems 3 and 5 from B&D) The following problems involve differential equations of the form dy = f(y). For each, sketch the graph of f(y) versus y, determine
1 y 2 dy = (2 + t)dt 1 y. = 2t + t2 2 + C 1 2t + t 2 /2 + C. 1 t 2 /2 + 2t 1. e y y = 2t 2. e y dy = 2t 2 dt. e y = 2 3 t3 + C. y = ln( 2 3 t3 + C).
 Math 53 First Midterm Page. Solve each of the following initial value problems. (a) y = y + ty, y() = 3. The equation is separable : y = y ( + t). Thus y = y dy = ( + t)dt y = t + t + C t + t / + C. For
Math 53 First Midterm Page. Solve each of the following initial value problems. (a) y = y + ty, y() = 3. The equation is separable : y = y ( + t). Thus y = y dy = ( + t)dt y = t + t + C t + t / + C. For
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Diff. Eq. App.( ) Midterm 1 Solutions
 Diff. Eq. App.(110.302) Midterm 1 Solutions Johns Hopkins University February 28, 2011 Problem 1.[3 15 = 45 points] Solve the following differential equations. (Hint: Identify the types of the equations
Diff. Eq. App.(110.302) Midterm 1 Solutions Johns Hopkins University February 28, 2011 Problem 1.[3 15 = 45 points] Solve the following differential equations. (Hint: Identify the types of the equations
. For each initial condition y(0) = y 0, there exists a. unique solution. In fact, given any point (x, y), there is a unique curve through this point,
 1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Section Objective(s): Constructing Direction Fields. Interpreting Direction Fields. Definition 1.2.1. A first order ODE of the
1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Section Objective(s): Constructing Direction Fields. Interpreting Direction Fields. Definition 1.2.1. A first order ODE of the
MAT 275 Test 1 SOLUTIONS, FORM A
 MAT 75 Test SOLUTIONS, FORM A The differential equation xy e x y + y 3 = x 7 is D neither linear nor homogeneous Solution: Linearity is ruinied by the y 3 term; homogeneity is ruined by the x 7 on the
MAT 75 Test SOLUTIONS, FORM A The differential equation xy e x y + y 3 = x 7 is D neither linear nor homogeneous Solution: Linearity is ruinied by the y 3 term; homogeneity is ruined by the x 7 on the
Agenda Sections 2.4, 2.5
 Agenda Sections 2.4, 2.5 Reminders Read 3.1, 3.2 Do problems for 2.4, 2.5 Homework 1 due Friday Midterm Exam I on 1/23 Lab on Friday (Shapiro 2054) Office hours Tues, Thurs 3-4:30 pm (5852 East Hall) Theorem:
Agenda Sections 2.4, 2.5 Reminders Read 3.1, 3.2 Do problems for 2.4, 2.5 Homework 1 due Friday Midterm Exam I on 1/23 Lab on Friday (Shapiro 2054) Office hours Tues, Thurs 3-4:30 pm (5852 East Hall) Theorem:
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS. MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2 Fall 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2 Fall 208 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up. Version A. A particle
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2 Fall 208 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up. Version A. A particle
Math 307 A - Spring 2015 Final Exam June 10, 2015
 Name: Math 307 A - Spring 2015 Final Exam June 10, 2015 Student ID Number: There are 8 pages of questions. In addition, the last page is the basic Laplace transform table. Make sure your exam contains
Name: Math 307 A - Spring 2015 Final Exam June 10, 2015 Student ID Number: There are 8 pages of questions. In addition, the last page is the basic Laplace transform table. Make sure your exam contains
MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end.
 Math 307A, Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Name: Instructions. DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end. There
Math 307A, Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Name: Instructions. DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end. There
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1
 Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Worksheet 9. Math 1B, GSI: Andrew Hanlon. 1 Ce 3t 1/3 1 = Ce 3t. 4 Ce 3t 1/ =
 Worksheet 9 Math B, GSI: Andrew Hanlon. Show that for each of the following pairs of differential equations and functions that the function is a solution of a differential equation. (a) y 2 y + y 2 ; Ce
Worksheet 9 Math B, GSI: Andrew Hanlon. Show that for each of the following pairs of differential equations and functions that the function is a solution of a differential equation. (a) y 2 y + y 2 ; Ce
Math 216 First Midterm 8 October, 2012
 Math 216 First Midterm 8 October, 2012 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material
Math 216 First Midterm 8 October, 2012 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]
![HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]](/thumbs/73/68538384.jpg) HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
we get y 2 5y = x + e x + C: From the initial condition y(0) = 1, we get 1 5 = 0+1+C; so that C = 5. Completing the square to solve y 2 5y = x + e x 5
 Math 24 Final Exam Solution 17 December 1999 1. Find the general solution to the differential equation ty 0 +2y = sin t. Solution: Rewriting the equation in the form (for t 6= 0),we find that y 0 + 2 t
Math 24 Final Exam Solution 17 December 1999 1. Find the general solution to the differential equation ty 0 +2y = sin t. Solution: Rewriting the equation in the form (for t 6= 0),we find that y 0 + 2 t
Solutions to Math 53 Math 53 Practice Final
 Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014
 Page 1 of 12 Please go to the next page... Sample Midterm 1 ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014 50 points 1. Find the solution of the following initial-value problem 1. Solution (S.O.V) dt = ty2,
Page 1 of 12 Please go to the next page... Sample Midterm 1 ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014 50 points 1. Find the solution of the following initial-value problem 1. Solution (S.O.V) dt = ty2,
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations
 Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 1 August 24, 2017 Question 1. Is the function y = 1 + t a solution to the differential equation How about the function y = 1 + 2t? How about
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 1 August 24, 2017 Question 1. Is the function y = 1 + t a solution to the differential equation How about the function y = 1 + 2t? How about
Math 116 Second Midterm November 17, 2010
 Math 6 Second Midterm November 7, Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are problems. Note that
Math 6 Second Midterm November 7, Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are problems. Note that
Section , #5. Let Q be the amount of salt in oz in the tank. The scenario can be modeled by a differential equation.
 Section.3.5.3, #5. Let Q be the amount of salt in oz in the tank. The scenario can be modeled by a differential equation dq = 1 4 (1 + sin(t) ) + Q, Q(0) = 50. (1) 100 (a) The differential equation given
Section.3.5.3, #5. Let Q be the amount of salt in oz in the tank. The scenario can be modeled by a differential equation dq = 1 4 (1 + sin(t) ) + Q, Q(0) = 50. (1) 100 (a) The differential equation given
Section 2.1 (First Order) Linear DEs; Method of Integrating Factors. General first order linear DEs Standard Form; y'(t) + p(t) y = g(t)
 Section 2.1 (First Order) Linear DEs; Method of Integrating Factors Key Terms/Ideas: General first order linear DEs Standard Form; y'(t) + p(t) y = g(t) Integrating factor; a function μ(t) that transforms
Section 2.1 (First Order) Linear DEs; Method of Integrating Factors Key Terms/Ideas: General first order linear DEs Standard Form; y'(t) + p(t) y = g(t) Integrating factor; a function μ(t) that transforms
MATH 251 Examination I July 1, 2013 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I July 1, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems,
MATH 251 Examination I July 1, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems,
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems) y + 2y + y cos(x 2 y) = 0, y(0) = 2, y (0) = 4.
 Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Math 266 Midterm Exam 2
 Math 266 Midterm Exam 2 March 2st 26 Name: Ground Rules. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use one 4-by-6
Math 266 Midterm Exam 2 March 2st 26 Name: Ground Rules. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use one 4-by-6
AMATH 351 Mar 15, 2013 FINAL REVIEW. Instructor: Jiri Najemnik
 AMATH 351 Mar 15, 013 FINAL REVIEW Instructor: Jiri Najemni ABOUT GRADES Scores I have so far will be posted on the website today sorted by the student number HW4 & Exam will be added early next wee Let
AMATH 351 Mar 15, 013 FINAL REVIEW Instructor: Jiri Najemni ABOUT GRADES Scores I have so far will be posted on the website today sorted by the student number HW4 & Exam will be added early next wee Let
Math 122 Fall Handout 11: Summary of Euler s Method, Slope Fields and Symbolic Solutions of Differential Equations
 1 Math 122 Fall 2008 Handout 11: Summary of Euler s Method, Slope Fields and Symbolic Solutions of Differential Equations The purpose of this handout is to review the techniques that you will learn for
1 Math 122 Fall 2008 Handout 11: Summary of Euler s Method, Slope Fields and Symbolic Solutions of Differential Equations The purpose of this handout is to review the techniques that you will learn for
Math 106 Answers to Exam 3a Fall 2015
 Math 6 Answers to Exam 3a Fall 5.. Consider the curve given parametrically by x(t) = cos(t), y(t) = (t 3 ) 3, for t from π to π. (a) (6 points) Find all the points (x, y) where the graph has either a vertical
Math 6 Answers to Exam 3a Fall 5.. Consider the curve given parametrically by x(t) = cos(t), y(t) = (t 3 ) 3, for t from π to π. (a) (6 points) Find all the points (x, y) where the graph has either a vertical
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative
![The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative](/thumbs/96/128959530.jpg) 1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 12 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP
 MATH 12 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. Vector-valued functions 1 2. Differentiating and integrating vector-valued functions 3 3. Velocity and Acceleration 4 Over the past two weeks we have developed
MATH 12 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. Vector-valued functions 1 2. Differentiating and integrating vector-valued functions 3 3. Velocity and Acceleration 4 Over the past two weeks we have developed
MATH 251 Examination I February 23, 2017 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I February 23, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I February 23, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Chapter 4: Higher Order Linear Equations
 Chapter 4: Higher Order Linear Equations MATH 351 California State University, Northridge April 7, 2014 MATH 351 (Differential Equations) Ch 4 April 7, 2014 1 / 11 Sec. 4.1: General Theory of nth Order
Chapter 4: Higher Order Linear Equations MATH 351 California State University, Northridge April 7, 2014 MATH 351 (Differential Equations) Ch 4 April 7, 2014 1 / 11 Sec. 4.1: General Theory of nth Order
M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 2013
 M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 013 Section.6 3. Consider the equation: (3x xy + )dx + (6y x + 3)dy = 0. Let M(x, y) = 3x xy + and N(x, y) = 6y x + 3. Since: y = x = N We can conclude that this
M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 013 Section.6 3. Consider the equation: (3x xy + )dx + (6y x + 3)dy = 0. Let M(x, y) = 3x xy + and N(x, y) = 6y x + 3. Since: y = x = N We can conclude that this
Exam 4 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 4 Spring Section and/or TA:
 Exam 4 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may
Exam 4 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or notes may
MATH 251 Examination I October 9, 2014 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 9, 2014 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 9, 2014 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Math 23: Differential Equations (Winter 2017) Midterm Exam Solutions
 Math 3: Differential Equations (Winter 017) Midterm Exam Solutions 1. [0 points] or FALSE? You do not need to justify your answer. (a) [3 points] Critical points or equilibrium points for a first order
Math 3: Differential Equations (Winter 017) Midterm Exam Solutions 1. [0 points] or FALSE? You do not need to justify your answer. (a) [3 points] Critical points or equilibrium points for a first order
Math 1310 Final Exam
 Math 1310 Final Exam December 11, 2014 NAME: INSTRUCTOR: Write neatly and show all your work in the space provided below each question. You may use the back of the exam pages if you need additional space
Math 1310 Final Exam December 11, 2014 NAME: INSTRUCTOR: Write neatly and show all your work in the space provided below each question. You may use the back of the exam pages if you need additional space
Math 116 Final Exam December 17, 2010
 Math 116 Final Exam December 17, 2010 Name: Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 11 pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note that the
Math 116 Final Exam December 17, 2010 Name: Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 11 pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note that the
2tdt 1 y = t2 + C y = which implies C = 1 and the solution is y = 1
 Lectures - Week 11 General First Order ODEs & Numerical Methods for IVPs In general, nonlinear problems are much more difficult to solve than linear ones. Unfortunately many phenomena exhibit nonlinear
Lectures - Week 11 General First Order ODEs & Numerical Methods for IVPs In general, nonlinear problems are much more difficult to solve than linear ones. Unfortunately many phenomena exhibit nonlinear
Euler-Cauchy Using Undetermined Coefficients
 Euler-Cauchy Using Undetermined Coefficients Department of Mathematics California State University, Fresno doreendl@csufresno.edu Joint Mathematics Meetings January 14, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 Second Order
Euler-Cauchy Using Undetermined Coefficients Department of Mathematics California State University, Fresno doreendl@csufresno.edu Joint Mathematics Meetings January 14, 2010 Outline 1 2 3 Second Order
Math 215/255 Final Exam (Dec 2005)
 Exam (Dec 2005) Last Student #: First name: Signature: Circle your section #: Burggraf=0, Peterson=02, Khadra=03, Burghelea=04, Li=05 I have read and understood the instructions below: Please sign: Instructions:.
Exam (Dec 2005) Last Student #: First name: Signature: Circle your section #: Burggraf=0, Peterson=02, Khadra=03, Burghelea=04, Li=05 I have read and understood the instructions below: Please sign: Instructions:.
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Suppose that f is an odd differentiable function. Then (A) f(1); (B) f (1) (C) f(1) f( 1) (D) 0 (E). 1 1 xf (x) =. The
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Suppose that f is an odd differentiable function. Then (A) f(1); (B) f (1) (C) f(1) f( 1) (D) 0 (E). 1 1 xf (x) =. The
Math 307 E - Summer 2011 Pactice Mid-Term Exam June 18, Total 60
 Math 307 E - Summer 011 Pactice Mid-Term Exam June 18, 011 Name: Student number: 1 10 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 Total 60 Complete all questions. You may use a scientific calculator during this examination.
Math 307 E - Summer 011 Pactice Mid-Term Exam June 18, 011 Name: Student number: 1 10 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 Total 60 Complete all questions. You may use a scientific calculator during this examination.
Final exam practice 4 (solutions) UCLA: Math 3B, Winter 2019
 Final exam practice 4 (solutions) Instructor: Noah White Date: UCLA: Math 3B, Winter 2019 This exam has 7 questions, for a total of 80 points. Please print your working and answers neatly. Write your solutions
Final exam practice 4 (solutions) Instructor: Noah White Date: UCLA: Math 3B, Winter 2019 This exam has 7 questions, for a total of 80 points. Please print your working and answers neatly. Write your solutions
LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Homework 5 Solutions
 MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2011 Homework 5 Solutions Note: In what follows, numbers in parentheses indicate the problem numbers for users of the sixth edition. A * indicates that this
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2011 Homework 5 Solutions Note: In what follows, numbers in parentheses indicate the problem numbers for users of the sixth edition. A * indicates that this
Slope Fields: Graphing Solutions Without the Solutions
 8 Slope Fields: Graphing Solutions Without the Solutions Up to now, our efforts have been directed mainly towards finding formulas or equations describing solutions to given differential equations. Then,
8 Slope Fields: Graphing Solutions Without the Solutions Up to now, our efforts have been directed mainly towards finding formulas or equations describing solutions to given differential equations. Then,
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
for any C, including C = 0, because y = 0 is also a solution: dy
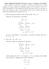 Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I
 SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I First Order differential equations Lecturer: Dr. Philip Ngare (Contacts: pngare@uonbi.ac.ke, Tue 12-2 PM) School of Mathematics, University of Nairobi Feb 26,
SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I First Order differential equations Lecturer: Dr. Philip Ngare (Contacts: pngare@uonbi.ac.ke, Tue 12-2 PM) School of Mathematics, University of Nairobi Feb 26,
8. Qualitative analysis of autonomous equations on the line/population dynamics models, phase line, and stability of equilibrium points (corresponds
 c Dr Igor Zelenko, Spring 2017 1 8. Qualitative analysis of autonomous equations on the line/population dynamics models, phase line, and stability of equilibrium points (corresponds to section 2.5) 1.
c Dr Igor Zelenko, Spring 2017 1 8. Qualitative analysis of autonomous equations on the line/population dynamics models, phase line, and stability of equilibrium points (corresponds to section 2.5) 1.
MATH 124. Midterm 2 Topics
 MATH 124 Midterm 2 Topics Anything you ve learned in class (from lecture and homework) so far is fair game, but here s a list of some main topics since the first midterm that you should be familiar with:
MATH 124 Midterm 2 Topics Anything you ve learned in class (from lecture and homework) so far is fair game, but here s a list of some main topics since the first midterm that you should be familiar with:
Math 217 Practice Exam 1. Page Which of the following differential equations is exact?
 Page 1 1. Which of the following differential equations is exact? (a) (3x x 3 )dx + (3x 3x 2 ) d = 0 (b) sin(x) dx + cos(x) d = 0 (c) x 2 x 2 = 0 (d) (1 + e x ) + (2 + xe x ) d = 0 CORRECT dx (e) e x dx
Page 1 1. Which of the following differential equations is exact? (a) (3x x 3 )dx + (3x 3x 2 ) d = 0 (b) sin(x) dx + cos(x) d = 0 (c) x 2 x 2 = 0 (d) (1 + e x ) + (2 + xe x ) d = 0 CORRECT dx (e) e x dx
Solving Differential Equations: First Steps
 30 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 3 Solving Differential Equations Solving Differential Equations: First Steps Now we start answering the question which is the theme of this book given a differential
30 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 3 Solving Differential Equations Solving Differential Equations: First Steps Now we start answering the question which is the theme of this book given a differential
1. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal
 . Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
Lectures in Differential Equations
 Lectures in Differential Equations David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University last revised December 2016 1 Contents Contents 2 1 First-order linear equations 4 1.1 What is a differential
Lectures in Differential Equations David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University last revised December 2016 1 Contents Contents 2 1 First-order linear equations 4 1.1 What is a differential
Math 266: Autonomous equation and population dynamics
 Math 266: Autonomous equation and population namics Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Autonomous equation An autonomous equation is a differential equation which only involves the unknown function y and its
Math 266: Autonomous equation and population namics Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Autonomous equation An autonomous equation is a differential equation which only involves the unknown function y and its
Your exam contains 5 problems. The entire exam is worth 70 points. Your exam should contain 6 pages; please make sure you have a complete exam.
 MATH 124 (PEZZOLI) WINTER 2017 MIDTERM #2 NAME TA:. Section: Instructions: Your exam contains 5 problems. The entire exam is worth 70 points. Your exam should contain 6 pages; please make sure you have
MATH 124 (PEZZOLI) WINTER 2017 MIDTERM #2 NAME TA:. Section: Instructions: Your exam contains 5 problems. The entire exam is worth 70 points. Your exam should contain 6 pages; please make sure you have
Honors Calculus Quiz 9 Solutions 12/2/5
 Honors Calculus Quiz Solutions //5 Question Find the centroid of the region R bounded by the curves 0y y + x and y 0y + 50 x Also determine the volumes of revolution of the region R about the coordinate
Honors Calculus Quiz Solutions //5 Question Find the centroid of the region R bounded by the curves 0y y + x and y 0y + 50 x Also determine the volumes of revolution of the region R about the coordinate
Math 116 Second Midterm November 12, 2014
 Math 6 Second Midterm November 2, 204 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this eam until you are told to do so. 2. This eam has 3 pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note
Math 6 Second Midterm November 2, 204 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this eam until you are told to do so. 2. This eam has 3 pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note
Modeling with differential equations
 Mathematical Modeling Lia Vas Modeling with differential equations When trying to predict the future value, one follows the following basic idea. Future value = present value + change. From this idea,
Mathematical Modeling Lia Vas Modeling with differential equations When trying to predict the future value, one follows the following basic idea. Future value = present value + change. From this idea,
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM II MATH 2373, FALL 2016 ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM II MATH 7, FALL 6 ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutely complete review. For completeness you must also make sure that you know how to do all
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR MIDTERM II MATH 7, FALL 6 ANSWER KEY This list of problems is not guaranteed to be an absolutely complete review. For completeness you must also make sure that you know how to do all
Autonomous Equations and Stability Sections
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Autonomous Equations and Stability Sections 2.4-2.5 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Fall 2012 Autonomous Differential
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Autonomous Equations and Stability Sections 2.4-2.5 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Fall 2012 Autonomous Differential
Module 2: Reflecting on One s Problems
 MATH55 Module : Reflecting on One s Problems Main Math concepts: Translations, Reflections, Graphs of Equations, Symmetry Auxiliary ideas: Working with quadratics, Mobius maps, Calculus, Inverses I. Transformations
MATH55 Module : Reflecting on One s Problems Main Math concepts: Translations, Reflections, Graphs of Equations, Symmetry Auxiliary ideas: Working with quadratics, Mobius maps, Calculus, Inverses I. Transformations
Math 116 Practice for Exam 2
 Math 116 Practice for Exam 2 Generated November 11, 2016 Name: SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section Number: 1. This exam has 9 questions. Note that the problems are not of equal difficulty, so you may want to
Math 116 Practice for Exam 2 Generated November 11, 2016 Name: SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section Number: 1. This exam has 9 questions. Note that the problems are not of equal difficulty, so you may want to
MAT292 - Fall Term Test 1 - October 23, DO NOT WRITE ON THE QR CODE AT THE TOP OF THE PAGES.
 MAT292 - Fall 2017 Term Test 1 - October 23, 2017 Time allotted: 100 minutes Total marks: 60 Aids permitted: None Full Name: Last First Student Number: Email: @mail.utoronto.ca Instructions DO NOT WRITE
MAT292 - Fall 2017 Term Test 1 - October 23, 2017 Time allotted: 100 minutes Total marks: 60 Aids permitted: None Full Name: Last First Student Number: Email: @mail.utoronto.ca Instructions DO NOT WRITE
Math53: Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 2004
 Math53: Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 2004 Unit 2 Summary Second- and Higher-Order Ordinary Differential Equations Extremely Important: Euler s formula Very Important: finding solutions to linear
Math53: Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 2004 Unit 2 Summary Second- and Higher-Order Ordinary Differential Equations Extremely Important: Euler s formula Very Important: finding solutions to linear
