Preface... (vii) Acknowledgement... (ix)
|
|
|
- Sydney Anthony Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preface... (vii) Acknowledgement... (ix) Chapter 1 Measurement Systems An Overview and Basic Concepts Introduction The Process of Measurement Scope of Instrumentation Jargon of Instrumentation Basic Principles of Measurement Direct Comparison Indirect Comparison Complexity of Measurement Methods Primary Measurement Secondary Measurement Tertiary Measurement Applications of Measuring Instruments Instruments for Monitoring Instruments for Controlling Instruments for Experiments and Analysis Generalized Input-Output Model of Measurement System Stages of the Measuring System Types of Inputs Desired Inputs Interfering Inputs Modifying Inputs Classification of Instruments Manual and Automatic Instruments Active (Self-operated) and Passive (Power-operated) Instruments Self-contained and Remote Indicating Instruments The extent or degree of illumination Deflection (luminous and Null intensity) Output is Instruments measured in 22the units Candela Analog and Digital Instruments Detecting, Recording, Monitoring and Controlling Instruments Mechanical, Electrical and Electronic Instruments 24
2 (xii) Contents 1.11 Objectives of Instrumentation 25 Summary 26 Key Concepts 27 Review Questions 29 Multiple Choice Questions 31 Answers 33 Chapter 2 Characteristics of Instruments Introduction Static and Dynamic Quantities Static Characteristics Range Span Accuracy Precision Calibration Drift Sensitivity Threshold Resolution Tolerance Readability and Least Count Backlash Zero Stability Stiction (Static Friction) Dynamic Characteristics Speed of Response and Measuring Lag Fidelity and Dynamic Error Overshoot Dead Time and Dead Zone Frequency of Response Modeling for Dynamic Performance Systems of Various Orders Zero Order System First Order System Second Order System Standard Test Signals Step Signal Ramp Signal Parabolic Signal Simple Harmonic Input (Sinusoidal) Impulse Signal Dynamic Response of First Order System Unit Step Response of First Order System (Step Input) Unit Ramp Response of First Order System (Ramp Input) Harmonic Sinusoidal Response of First Order System 61
3 (xiii) 2.9 Dynamic Response of Second Order System Step Response of Second Order System Harmonic/Sinusoidal Response of Second Order System 64 Summary 67 Key Concepts 67 Review Questions 69 Multiple Choice Questions 71 Answers 73 Chapter 3 Inaccuracies in Instruments Introduction Terminology Terms used to Describe Inaccuracy in the Instrument Error of Measurement and Measurement of Error Error of Measurement Measurement of Errors Error Sources/Causes of Error Classification of Errors Random Errors (or Precision or Accidental Error) Disturbance in the Equipment Fluctuating Experimental or Environmental Conditions Systematic Error (or Bias Error) Calibration Error Gross Errors or Human Errors Operational Errors Observation Errors Equipment Defects and Instrumental Errors Inherent Defects Misusing or Mishandling Errors Loading Errors Illegitimate Errors Blunders and Chaotic Errors Other Errors Backlash Mechanical Friction Hysteresis Drift Reading Error 95 Summary 95 Key Concepts 96 Review Questions 98 Multiple Choice Questions 98 Answers 100
4 (xiv) Contents Chapter 4 Transducers and Measurement of Displacement Introduction Classification of Transucers Mechanical Transducers Electromechanical Transducers Merits Classification of Electromechanical Transducers Resistive Type Transducers Variable Resistance Transducers Sliding Contact Devices The Pots The Resistance Strain Gauges Thermistors Inductive Type Transducers Non-Self-Generating Variable Self Inductance-Single Coil Type Transducer Non-Self-Generating Variable Self Inductance Two Coil (or Single Coil with Center Tap) Type Transducer Non-Self-Generating Variable Mutual Inductance Two Coil Transducer Non-Self-Generating Variable Mutual Inductance Three Coil Transducer Self Generating Type Inductive Transducers Eddy Current Transducers Magnetometer Search Coil Capacitive Transducers Piezoelectric Transducers Photoelectric Effects Photo Emissive Photo Conductive Transducers Photo Voltaic Cells Hall Effect Magnetostrictive Transducer Ionization Transducers Digital Displacement Transducers 133 Summary 135 Key Concepts 136 Review Questions 137 Multiple Choice Questions 138 Answers 140 Chapter 5 Measurement of Temperature Introduction Basic Concepts of Temperature Measurement of Temperature Temperature Measuring Instruments 149
5 (xv) 5.4 Measurement of Temperature by Changes in Physical Dimensions Measurement of Temperature by Expansion of Solids Measurement of Temperature by using Expansion of Liquids Pressure Thermometers Electrical Effects on Temperature Thermo Resistive Elements Fundamentals of Thermo Electricity Laws of Thermo-Electric Power Measurement of Temperature by Electrical Methods Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) or Electrical- Resistance Thermometers Thermistors (Thermal Resistors) Thermocouples Semiconductor Junction Temperature Sensors The Linear Quartz Thermometer Thermometers using Changes in Emitted Thermal Radiation-Pyrometers Types of Pyrometers Total Radiation Pyrometer Optical Pyrometer or Disappearing Filament Pyrometer or Monochromatic Brightness Radiation Thermometer Infrared Pyrometer Temperature Measurement by Changes in Chemical Phase 188 Summary 189 Key Concepts 190 Review Questions 192 Multiple Choice Questions 194 Answers 195 Chapter 6 Measurement of Pressure Introduction Definitions And Terminology Atmospheric Pressure (P A ) Absolute Pressure (P ABS ) Gauge Pressure (P > P A ) Vacuum Pressure (P A > P or P < P A ) Relation between Absolute, Gauge, Atmospheric and Vacuum Pressure Static Pressure Total or Stagnation Pressure Dynamic or Impact or Velocity Pressure Classification of Pressure Measuring Devices Dead Weight Tester 204
6 (xvi) Contents 6.5 Manometers Piezometer U-Tube Manometer Single Column Manometer U-Tube Differential Manometer Inverted U-tube Differential Manometer Mechanical Displacement Type Gauges Ring Balance Manometer Bell Type Pressure Gauges Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge Tip Travel of Bourdon Tube Errors and their Rectification (in Bourdon Tube) Bourdon Tube Shapes and Configurations Elastic Diaphragm Gauges Bellows Gauges Strain Gauge Pressure Cells The McLeod Gauge Formula for Errors Thermal Conductivity Gauges Pirani Gauge Thermocouple Type Conductivity Gauge Ionization Gauge 238 Summary 239 Key Concepts 239 Review Questions 241 Numerical Problems 243 Multiple Choice Questions 244 Answers 246 Chapter 7 Flow Measurement Introduction Nature of Flow Classification of Flow Measurements Primary or Quantity Methods Tilting Trap Meter Positive Displacement Meters Flow (Obstruction) Meters Venturi Meter Orifice Meter or Orifice Plate Flow-Nozzle Meter Variable Area Meter or Rotameter Turbine Meters Magnetic Flow Meters Vortex Shedding Flow Meters 272
7 (xvii) 7.9 Measurement of Fluid Velocities Total - Pressure Probe (Pitot Static Tube) Direction - Sensing Probes or Yaw-Angle Probe Anemometers Hot Wire Anemometers Hot Film Anemometers Measurement by Scattering Laser Doppler Anemometry Ultrasonic Anemometry The Interferometer The Schlieren The Shadow Graph Calibration of Flow Measuring Devices Flow-Visualization Techniques Dye Injection Chemical Precipitates Smoke Trails and Smoke Wire Hydrogen Bubble Visualization Laser Induced Fluorescence 288 Summary 289 Key Concepts 289 Review Questions 291 Multiple Choice Questions 293 Answers 295 Chapter 8 Measurement of Liquid Level Introduction Measurement of Liquid Level Classification of Liquid-Level Measurement Methods Direct Liquid Level Measurement Devices Sight Glass Tube Float Gauges Float-Tape Liquid Level Gauges Float Shaft Liquid Level Gauge Indirect Liquid Level Measurement Devices Hydrostatic Pressure Devices (Bubbler or Purge System) Hydrostatic Pressure Devices for Open Tanks Hydrostatic Pressure Devices for Closed Tanks: Bubbler or Purge System Electric Liquid Level Sensors Rheostat Operated by a Float Capacitive Liquid Level Sensor Gamma Ray Liquid Level Sensor Ultrasonic Liquid Level Gauge 315
8 (xviii) Contents 8.11 Inductive Methods or Magnetic Level Indicator Cryogenic Fuel Level Indicator 317 Summary 319 Key Concepts 319 Review Questions 320 Multiple Choice Questions 321 Answers 323 Chapter 9 Measurement of Speed Introduction Classification of Tachometers Mechanical Tachometers Revolution Counter and Timer Tachoscope Hand Speed Indicator (Modified Tachoscope) Slipping Clutch Tachometer Centrifugal Force Tachometer Vibrating Reed Tachometer Electrical Tachometers Drag Cup Tachometers (Automobile Speedometers) Commutated Capacitor Tachometer Tacho Generators Inductive Pick up Tachometer Capacity Type Pick-up Tachometer Photo Electric Tachometer Stroboscope 343 Summary 346 Key Concepts 346 Review Questions 348 Multiple Choice Questions 349 Answers 352 Chapter 10 Measurement of Vibration and Acceleration Introduction Vibration Measurement Transducers used in Vibration Measurement Fixed Reference Type Transducer Seismic Type Transducer List of Transducers/Instruments used to Measure Vibration/Acceleration Piezo Electric Accelerometer Seismic Displacement Sensing Accelerometer Strain - Gauge Accelerometer Capacitance Vibration Sensor/Accelerometer 364
9 (xix) Variable Induction Type Accelerometer LVDT - Accelerometer Reed Type Vibrometer Vibration Measurement using Stroboscope Factors Affecting the Choice of Transducers Calibration of Vibration Transducers Servo Accelerometer Digital Accelerometer 374 Summary 376 Key Concepts 377 Review Questions 378 Multiple Choice Questions 379 Answers 381 Chapter 11 Measurement of Force, Torque and Power Introduction Methods of Measurement of Force Direct Method Indirect Method Equal Arm Balance Unequal Arm Balance Pendulum Scale (Multi-Lever Type) Elastic Force Meter (Proving Ring) Strain Gauge Load Cell Hydraulic Load Cell Pneumatic Load Cells Measurement of Torque and Power Definitions of Torque and Power Relation between Torque and Power Dynamometers Mechanical/Prony Brake Dynamometer Hydraulic Dynamometer Eddy Current Dynamometer Electrical Generator Type Driving Dynamometer Transmission Dynamometer Torsion Meter Mechanical Torsion Meter Optical Torsion Meter Electrical Torsion Meters (Torque Measurement using Slotted Discs) Strain Gauge Torsion Meter 409 (Strain Gauges on Rotating Shafts) 409
10 (xx) Contents Summary 411 Key Concepts 411 Review Questions 413 Multiple Choice Questions 415 Answers 416 Chapter 12 Strain and Stress Measurement Introduction Fundamentals of Stress and Strain Strain Measurement Positive Strain Negative Strain The Electrical Resistance Strain Gauge The Metallic Resistance Strain Gauge Types of Strain Gauges Unbonded Strain Gauge Bonded Strain Gauges Selection and Preparation of Bonded Strain Gauge Surface - Preparation and Mounting of Strain Gauges Grid Materials Backing, Base or Carrier Material Bonding Materials or Cements (Adhesive) Factors Affecting Selection of Bonded Metallic Strain Gauges Temperature Compensation Temperature Compensation using an Adjacent Arm Compensating Gauge Self Temperature Compensation Gauge Rosettes (Multiple Grids) Wheatstone Bridge Circuit One Active Strain Gauge (Quarter Bridge) or Tension Measurement using Strain Gauge Two Active Strain Gauges (Half Bridge) or Tension and Compression Measuring Strain Gauges Calibration Applications of Strain Gauges 451 Summary 451 Key Concepts 452 Review Questions 454 Multiple Choice Questions 455 Answers 457 Chapter 13 Measurement of Viscosity and Surface Tension Introduction The Jargon of Viscosity 462
11 (xxi) 13.3 Classification of Viscometers Capillary Tube Viscometer Efflux Viscometers Redwood Viscometer Saybolt Viscometer Engler Viscometer Falling Sphere Viscometer Rotating Cylinder Viscometers Rotating Cylinder Viscometer (Concentric Cylinders Type) Rotating Cylinder Electrical Viscometer Surface Tension Measurement of Surface Tension Effects of Surface Tension Methods of Measuring Surface Tension Instruments used to Measure Surface Tension Du Noüy Ring Tensiometer Du Noüy-Padday Tensiometer Wilhelmy Plate Tensiometer Bubble Pressure Tensiometer Goniometer/ Tensiometer Some More Methods Spinning Drop Method Drop Volume Method Capillary Rise Method Stalagmometric Method Sessile Drop Method Vibrational Frequency of Levitated Drops Method Resonant Oscillations of Spherical/ Hemispherical Liquid Drop Method 480 Summary 481 Key Concepts 482 Review Questions 484 Multiple Choice Questions 484 Answers 486 Chapter 14 Measurement of Humidity/ Dampness and Density/Specific Gravity Introduction Terminology List of Instruments used to Measure Humidity Psychrometers (Wet and Dry Bulb Thermometers) Sling Psychrometer 493
12 (xxii) Contents 14.6 Absorption Hygrometers Mechanical Humidity Sensing Absorption Hygrometer Electrical Humidity Sensing Absorption Hygrometer Dew Point Meter Fundamentals of Density and Specific Gravity Instruments to Measure Specific Gravity and Density Pycnometer Hydrometers Simple Hydrometer Photo-Electric Hydrometer Differential Type Bubbler Systems Differential Type Bubbler System with Two Vessels Attached by a Manometer and Reference Column Method Differential Type Bubbler System with Single Vessel Attached and Pressure Gauge Special Applications of Hydrometers 508 Summary 509 Key Concepts 509 Review Questions 511 Multiple Choice Questions 512 Answers 514 Chapter 15 Elements of Control Systems Introduction Basic Components of a Control System Control Systems Terminology Types of Control Systems Open Loop Control Systems (Non- Feedback Systems) Closed Loop or Feedback Control Systems Advantages of Feedback Control Systems Positive and Negative Feedback Differences between Open Loop and Closed Loop Systems Servo Mechanism Requirements of a Control System Stability Accuracy Speed of Response Control Systems Case Studies Speed Control System in Automobiles Speed Control System in IC Engines Temperature Control System of the Passenger Compartment of a Car Automatic Tank-Level Control System 540
13 (xxiii) Appendix 549 Index Liquid Level Control System (Automatic and Manual) Feedback System in Nature Biological System Position Control System Missile Launching and Guidance System 542 Summary 543 Key Concepts 544 Review Questions 545 Multiple Choice Questions 547 Answers 548
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS Code : A70343 Class : IV B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS Code : A70343 Class : IV B. Tech
III B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SYSTEMS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75
 R10 Set No: 1 1. (a) Distinguish between accuracy and Precision. Which of these is more desirable during the act of measurement and why? (b) Discuss the necessity and importance of dynamic performance
R10 Set No: 1 1. (a) Distinguish between accuracy and Precision. Which of these is more desirable during the act of measurement and why? (b) Discuss the necessity and importance of dynamic performance
 Set No. 1 1. (a) Differentiate among Desired, Modifying and Interfering inputs. (b) How do you eliminate the effects of interfering and modifying inputs? Explain 2. (a) Define the term Transducer and explain
Set No. 1 1. (a) Differentiate among Desired, Modifying and Interfering inputs. (b) How do you eliminate the effects of interfering and modifying inputs? Explain 2. (a) Define the term Transducer and explain
2. (a) Differentiate between rare metal thermocouples and base metal thermocouples.
 Code No: R05410304 Set No. 1 1. (a) Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurement with suitable examples. (b) What are desired, modifying and interfering inputs for an instrumentation
Code No: R05410304 Set No. 1 1. (a) Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurement with suitable examples. (b) What are desired, modifying and interfering inputs for an instrumentation
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
Siddharth Institute of Engineering & Technology
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
 Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control. The General Control System
 WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/ INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II
 Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/2011-12 2011 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full
Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (EIE)/SEM-5/EI-501/2011-12 2011 INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION II Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full
Control Engineering BDA30703
 Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Transducers. EEE355 Industrial Electronics
 Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
: INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Measuring Instruments
COURSE TITLE : INSTRUMENTATION AND PROCESS CONTROL COURSE CODE : 6071 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Measuring Instruments
Experimentation. Third Edition. Wheeler. Ahmad R. Ganji. School of Engineering. With Third Edition contributions by. V. V. Krishnan. Brian S.
 Introduction to Engineering Experimentation Third Edition Anthony J. Ahmad R. Wheeler Ganji School of Engineering San Francisco State University With Third Edition contributions by V. V. Krishnan San Francisco
Introduction to Engineering Experimentation Third Edition Anthony J. Ahmad R. Wheeler Ganji School of Engineering San Francisco State University With Third Edition contributions by V. V. Krishnan San Francisco
12. A signal established as a standard of comparison for a feed back control system by virtue of its
 INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS 2 MID ONLINE BITS www.uandistar.org 1. "A function of the controlled output, which is compared with the reference input to obtain the actuating signal" is called as
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS 2 MID ONLINE BITS www.uandistar.org 1. "A function of the controlled output, which is compared with the reference input to obtain the actuating signal" is called as
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
 Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester. Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE
 INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
Overview. Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples
 Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
COURSE OF Prepared By: MUHAMMAD MOEEN SULTAN Department of Mechanical Engineering UET Lahore, KSK Campus
 COURSE OF Active and passive instruments Null-type and deflection-type instruments Analogue and digital instruments In active instruments, the external power source is usually required to produce an output
COURSE OF Active and passive instruments Null-type and deflection-type instruments Analogue and digital instruments In active instruments, the external power source is usually required to produce an output
Unit 57: Mechatronic System
 Unit 57: Mechatronic System Unit code: F/60/46 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 - SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES 2 Understand electro-mechanical models and components in mechatronic systems and products
Unit 57: Mechatronic System Unit code: F/60/46 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME 2 TUTORIAL 2 - SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES 2 Understand electro-mechanical models and components in mechatronic systems and products
COURSE TEMPLATE. The Course content covers the following broad topics: 1. Experimental Analysis:
 COURSE TEMPLATE 1. Department centre Proposing the course Applied Mechanics. Course Title Experimental Methods 3. L-T-P Structure 3-0- 4. Credits 4 5. Course Number AML 130 6. Status ( Category for Program)
COURSE TEMPLATE 1. Department centre Proposing the course Applied Mechanics. Course Title Experimental Methods 3. L-T-P Structure 3-0- 4. Credits 4 5. Course Number AML 130 6. Status ( Category for Program)
Sensors and transducers
 Sensors and transducers Measurement is an important subsystem of a mechatronics system. Its main function is to collect the information on system status and to feed it to the micro-processor(s) for controlling
Sensors and transducers Measurement is an important subsystem of a mechatronics system. Its main function is to collect the information on system status and to feed it to the micro-processor(s) for controlling
UNIT 2 STRAIN MEASURMENTS, FORCE MEASUREMENTS. Therefore, resistance strain gauges are also known as piezo-resistive gauges.
 UNIT 2 STRAIN MEASURMENTS, FORCE MEASUREMENTS STRAIN MEASURMENTS Introduction: When a metal conductor is stretched or compressed, its resistance changes an account of the fact that both length and diameter
UNIT 2 STRAIN MEASURMENTS, FORCE MEASUREMENTS STRAIN MEASURMENTS Introduction: When a metal conductor is stretched or compressed, its resistance changes an account of the fact that both length and diameter
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Subject Code : Page No: 1/
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17434 Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17434 Page No: 1/ Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY, Kazhipattur, Chennai DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING
 ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY, Kazhipattur, Chennai-603 103 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING 2 Marks and 16 Marks QUESTION BANK Course code / Course Name: EI2251 / INDUSTRIAL
ANAND INSTITUTE OF HIGHER TECHNOLOGY, Kazhipattur, Chennai-603 103 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING 2 Marks and 16 Marks QUESTION BANK Course code / Course Name: EI2251 / INDUSTRIAL
= A x (t) + B utt), by d{ _-=-=-
 M.Tech. [ 24 103 ] Degree Examination ndustrial Process nstrumentation First Semester COMPUTER CONTROL OF PROCESSES (Effective from the Admitted Batch of2003-2004) Time: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 100 Answer
M.Tech. [ 24 103 ] Degree Examination ndustrial Process nstrumentation First Semester COMPUTER CONTROL OF PROCESSES (Effective from the Admitted Batch of2003-2004) Time: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 100 Answer
1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16]
![1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16]](/thumbs/96/127822274.jpg) Code No: RR320204 Set No. 1 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 2. Distinguish between deterministic signals and
Code No: RR320204 Set No. 1 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 2. Distinguish between deterministic signals and
Earlier Lecture. In the earlier lecture, we have seen non metallic sensors like Silicon diode, Cernox and Ruthenium Oxide.
 41 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen non metallic sensors like Silicon diode, Cernox and Ruthenium Oxide. Silicon diodes have negligible i 2 R losses. Cernox RTDs offer high response
41 1 Earlier Lecture In the earlier lecture, we have seen non metallic sensors like Silicon diode, Cernox and Ruthenium Oxide. Silicon diodes have negligible i 2 R losses. Cernox RTDs offer high response
Overview. Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples
 Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Instrumentation, Measurements, and Experiments in Fluids
 E. Rathakrishnan Instrumentation, Measurements, and Experiments in Fluids (^)CRC \V* CRC Press J Taylor &F rancis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group,
E. Rathakrishnan Instrumentation, Measurements, and Experiments in Fluids (^)CRC \V* CRC Press J Taylor &F rancis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group,
LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F)
 LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F) LIST OF THE EXPERIMENT S. NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT PAGE NO FROM TO 1. To measure stress and strain using strain gauge mounted on a cantilever
LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F) LIST OF THE EXPERIMENT S. NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT PAGE NO FROM TO 1. To measure stress and strain using strain gauge mounted on a cantilever
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
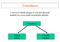 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Unit 3 Transducers. Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers
 Unit 3 Transducers Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers Introduction to transducers A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to other form. It converts the measurand to a usable electrical
Unit 3 Transducers Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers Introduction to transducers A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to other form. It converts the measurand to a usable electrical
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Code : A50422 Class : III -
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Code : A50422 Class : III -
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK. : G.Lakshminarayana, Asst.
 ` INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK Name Code Class Branch P a g e : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation : A504 : III - B. Tech
` INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK Name Code Class Branch P a g e : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation : A504 : III - B. Tech
Measurement and Industrial Instrumentation
 Measurement and Industrial Instrumentation ME 3225 Credit: 3.00 Measurement of Linear & Angular Velocity Presented By Md. Shariful Islam Lecturer Department of Mechanical Engineering Khulna University
Measurement and Industrial Instrumentation ME 3225 Credit: 3.00 Measurement of Linear & Angular Velocity Presented By Md. Shariful Islam Lecturer Department of Mechanical Engineering Khulna University
1 Attempt any FIVE of the following: 20. a) What is measurement? Explain its significance. 4M. ANS: (Definition 01 M and significance 03M)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Slide 1. Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic Fields Strain Pressure Displacement and Rotation Acceleration Electronic Sensors
 Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design
 Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design S.T. Smith University of North Carolina at Charlotte, USA and D.G. Chetwynd University of Warwick, UK GORDON AND BREACH SCIENCE PUBLISHERS Switzerland Australia
Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design S.T. Smith University of North Carolina at Charlotte, USA and D.G. Chetwynd University of Warwick, UK GORDON AND BREACH SCIENCE PUBLISHERS Switzerland Australia
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Series tore word. Acknowledgements
 Series tore word p. xi Preface p. xiii Acknowledgements p. xv Disclaimer p. xvii Introduction p. 1 The instrumental age p. 2 Measurements and the climate record p. 2 Clouds and rainfall p. 3 Standardisation
Series tore word p. xi Preface p. xiii Acknowledgements p. xv Disclaimer p. xvii Introduction p. 1 The instrumental age p. 2 Measurements and the climate record p. 2 Clouds and rainfall p. 3 Standardisation
Part 2. Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour)
 Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3
 Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3 Prerequisites: Sl. No. Subject Description Level of Study 01 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering 02 Electrical & Electronics Measurement
Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3 Prerequisites: Sl. No. Subject Description Level of Study 01 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering 02 Electrical & Electronics Measurement
radiation, 150 Bomb calorimeter, 375 Bourdon gauge, 253 bridge full, 259, 264, 435 half, 259, 260 quarter, 259 burst signal, 308
 R 2,55 R 2 Adj,55 β, diameter ratio, 319 γ,ratio of specific heats, 326 acceleration, 436 accelerometer, 441 Fiber Optic, 448 Piezoelectric, 445 accuracy, 6, 44 acousto-optic cell, 413 aliases, 80 Alphatron
R 2,55 R 2 Adj,55 β, diameter ratio, 319 γ,ratio of specific heats, 326 acceleration, 436 accelerometer, 441 Fiber Optic, 448 Piezoelectric, 445 accuracy, 6, 44 acousto-optic cell, 413 aliases, 80 Alphatron
APPLICATIONS OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS
 APPLICATIONS OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS 1) Measurements on Structures or Machinery Casings: Accelerometers and Velocity Sensors Used in gas turbines, axial compressors, small and mid-size pumps. These sensors
APPLICATIONS OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS 1) Measurements on Structures or Machinery Casings: Accelerometers and Velocity Sensors Used in gas turbines, axial compressors, small and mid-size pumps. These sensors
Scheme & Solutions of 14EI 505 (OCT-2018)
 Scheme & Solutions of 14EI 505 (OCT-2018) Prepared By: P. Vinodh Babu Associate Professor Department of EIE Bapatla Engineering College Bapatla-522102 Phone numbers: 9490126829, 7386014802 Hall Ticket
Scheme & Solutions of 14EI 505 (OCT-2018) Prepared By: P. Vinodh Babu Associate Professor Department of EIE Bapatla Engineering College Bapatla-522102 Phone numbers: 9490126829, 7386014802 Hall Ticket
BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) Course Title
 Part Ins. hrs / Week Dur.Hr CIA Marks Total Marks Credit Page 1 of 6 BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE-641 046 B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) REVISED SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS (CBCS PATTERN) (For
Part Ins. hrs / Week Dur.Hr CIA Marks Total Marks Credit Page 1 of 6 BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE-641 046 B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) REVISED SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS (CBCS PATTERN) (For
Instrumentation & Measurement AAiT. Chapter 3. Transducers and Their Response
 3.1 Transducer Chapter 3 Transducers and Their Response Instrument Society of America defines a sensor or transducer as a device which provides a usable output in response to a specified measured. Here
3.1 Transducer Chapter 3 Transducers and Their Response Instrument Society of America defines a sensor or transducer as a device which provides a usable output in response to a specified measured. Here
Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015
 Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015 I. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2) A. What is Fluid Mechanics? 1. What is a fluid? 2. What is mechanics? B. Classification of Fluid Flows 1. Viscous
Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015 I. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2) A. What is Fluid Mechanics? 1. What is a fluid? 2. What is mechanics? B. Classification of Fluid Flows 1. Viscous
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Course Code : A50422
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Course Code : A50422
The secondary winding have equal no. of turns. The secondary windings are placed identically on either side of the primary winding.
 UNIT 4 DISPLACEMENT MEASURMENT Electrical comparator Working principle of Electrical comparators: These instruments are based on the theory of Wheatstone A.C. Bridge. When the bridge is electrically balanced,
UNIT 4 DISPLACEMENT MEASURMENT Electrical comparator Working principle of Electrical comparators: These instruments are based on the theory of Wheatstone A.C. Bridge. When the bridge is electrically balanced,
5) Define Instrumental error These are the errors inherent in measuring instrument because of their mechanical structure.
 EI1252- TRANSDUCER ENGINEERING TWO MARKS Q & A UNIT 1 1) What is instrument? It is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity or variable. 2) Add 826 ± 5 to 628 ± 3. N1 = 826 ± 5 ( =
EI1252- TRANSDUCER ENGINEERING TWO MARKS Q & A UNIT 1 1) What is instrument? It is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity or variable. 2) Add 826 ± 5 to 628 ± 3. N1 = 826 ± 5 ( =
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
CHAPTER (13) FLOW MEASUREMENTS
 CHAPTER (13) FLOW MEASUREMENTS 09/12/2010 Dr. Munzer Ebaid 1 Instruments for the Measurements of Flow Rate 1. Direct Methods: Volume or weight measurements. 2. Indirect Methods: Venturi meters, Orifices
CHAPTER (13) FLOW MEASUREMENTS 09/12/2010 Dr. Munzer Ebaid 1 Instruments for the Measurements of Flow Rate 1. Direct Methods: Volume or weight measurements. 2. Indirect Methods: Venturi meters, Orifices
14CH406. Chemical Engineering Scheme of Valuation Process Instrumentation Maximum : 60 Marks (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 April, 2018 Fourth Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. II/IV B.Tech. (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION 14CH406 Chemical Engineering Scheme of Valuation Process Instrumentation
April, 2018 Fourth Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. II/IV B.Tech. (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION 14CH406 Chemical Engineering Scheme of Valuation Process Instrumentation
ME 515 Mechatronics. Overview of Computer based Control System
 ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
Cryogenic Instrumentation I Thermometry OUTLINE Thermometry Pt (pure metal) Temperature Ranges of Thermometer Application Typical Resistive Thermal
 Cryogenic Instrumentation I 1. Thermometry 2. anges of Application 3. Constant Volume 4. Thermocouples 5. Time esponse Data 6. 4 Terminal esistance Measurement OUTLINE 8. Pt (pure metal) 9. Typical esistive
Cryogenic Instrumentation I 1. Thermometry 2. anges of Application 3. Constant Volume 4. Thermocouples 5. Time esponse Data 6. 4 Terminal esistance Measurement OUTLINE 8. Pt (pure metal) 9. Typical esistive
1. Mark the correct statement(s)
 1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
e453.eps 1 Change (or the absolute value) in the measured physical variable 2 Change in the sensor property is translated into low-power-level
 3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION
 MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION 17434 Subject Title: Industrial Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION 17434 Subject Title: Industrial Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
vii Preface ix Acknowledgements
 Series Preface vii Preface ix Acknowledgements xi Chapter 1: Introduction 1 1.1 Brief History of Underwater Sound Transducers..... 2 1.2 Underwater Transducer Applications... 9 1.3 General Description
Series Preface vii Preface ix Acknowledgements xi Chapter 1: Introduction 1 1.1 Brief History of Underwater Sound Transducers..... 2 1.2 Underwater Transducer Applications... 9 1.3 General Description
Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems. Prof. Ramat, Stefano
 Preparatory Course (task NA 3.6) Basics of experimental testing and theoretical background Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems Prof. Ramat, Stefano Transducers A
Preparatory Course (task NA 3.6) Basics of experimental testing and theoretical background Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems Prof. Ramat, Stefano Transducers A
HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES, EQUIPMENT AND WATER DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEMS Vol. II Flow Measuring Techniques - Andreas Müller
 FLOW MEASURING TECHNIQUES Andreas Müller Swiss Institute for Hydromechanics and Water Resources Management, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, Switzerland Keywords: Indirect Methods, Measuring
FLOW MEASURING TECHNIQUES Andreas Müller Swiss Institute for Hydromechanics and Water Resources Management, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, Switzerland Keywords: Indirect Methods, Measuring
Viscometry for Liquids
 S. V. Gupta Viscometry for Liquids Calibration of Viscometers ^ Springer 1 Flow Through Capillary 1 1.1 Types of Flow 1 1.1.1 Turbulent Flow 1 1.1.2 Laminar Flow 2 1.2 Motion in Laminar Flow 2 1.3 Unit
S. V. Gupta Viscometry for Liquids Calibration of Viscometers ^ Springer 1 Flow Through Capillary 1 1.1 Types of Flow 1 1.1.1 Turbulent Flow 1 1.1.2 Laminar Flow 2 1.2 Motion in Laminar Flow 2 1.3 Unit
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC G COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION PHYSICS (NOTES omitted) INSTRUMENTS G01 MEASURING (counting G06M); TESTING (NOTES omitted) G01P MEASURING LINEAR OR ANGULAR SPEED, ACCELERATION, DECELERATION, OR
CPC G COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION PHYSICS (NOTES omitted) INSTRUMENTS G01 MEASURING (counting G06M); TESTING (NOTES omitted) G01P MEASURING LINEAR OR ANGULAR SPEED, ACCELERATION, DECELERATION, OR
US06CPHY06 Instrumentation and Sensors UNIT 2 Part 2 Pressure Measurements
 US06CPHY06 Instrumentation and Sensors UNIT 2 Part 2 Pressure Measurements Pressure Measurements What is Pressure? Pressure: Force exerted by a fluid on unit surface area of a container i.e. P = F/A. Units
US06CPHY06 Instrumentation and Sensors UNIT 2 Part 2 Pressure Measurements Pressure Measurements What is Pressure? Pressure: Force exerted by a fluid on unit surface area of a container i.e. P = F/A. Units
4/3/2019. Advanced Measurement Systems and Sensors. Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi. Chapter one. Introduction to Measurement Systems
 Advanced Measurement Systems and Sensors Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter one Introduction to Measurement Systems 1 Outlines Control and measurement systems Transducer/sensor definition and classifications
Advanced Measurement Systems and Sensors Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter one Introduction to Measurement Systems 1 Outlines Control and measurement systems Transducer/sensor definition and classifications
Measurements in Mechatronic design. Transducers
 Measurements in Mechatronic design Transducers Quantities Current Voltage Torque Force Magnetic flux Distance Temperature Measurement system Physical quanties Transducer Signal conditioning Measurement
Measurements in Mechatronic design Transducers Quantities Current Voltage Torque Force Magnetic flux Distance Temperature Measurement system Physical quanties Transducer Signal conditioning Measurement
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN SEMESTER) Branch: EEE QUESTION BANK
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN SEMESTER) Branch: EEE QUESTION BANK
Transducers. ME 3251 Thermal Fluid Systems
 Transducers ME 3251 Thermal Fluid Systems 1 Transducers Transform values of physical variables into equivalent electrical signals Converts a signal from one form to another form 2 Types of Transducers
Transducers ME 3251 Thermal Fluid Systems 1 Transducers Transform values of physical variables into equivalent electrical signals Converts a signal from one form to another form 2 Types of Transducers
Lecture 20. Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature MECH 373. Instrumentation and Measurements
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE
ELECTRONIC SENSORS PREAMBLE. This note gives a brief introduction to sensors. The focus is. on sensor mechanisms. It describes in general terms how
 ELECTRONIC SENSORS PREAMBLE This note gives a brief introduction to sensors. The focus is on sensor mechanisms. It describes in general terms how sensors work. It covers strain gage sensors in detail.
ELECTRONIC SENSORS PREAMBLE This note gives a brief introduction to sensors. The focus is on sensor mechanisms. It describes in general terms how sensors work. It covers strain gage sensors in detail.
Index. Index. More information. in this web service Cambridge University Press
 A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
Mechanical Sensors 1.
 DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN Mechanical Sensors 1. Sources and additional materials (recommended) Lambert Miklós: Szenzorok elmélet (ISBN 978-963-874001-1-3) Bp. 2009 Jacob Fraden: Handbook of Modern Sensors (ISBN
DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN Mechanical Sensors 1. Sources and additional materials (recommended) Lambert Miklós: Szenzorok elmélet (ISBN 978-963-874001-1-3) Bp. 2009 Jacob Fraden: Handbook of Modern Sensors (ISBN
15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have
 105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
1 THE CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE
 1 THE CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE 1 1.1 Historical Perspective, 2 1.2 Early Definitions of Temperature, 9 1.3 A Simple Qualitative Definition of Temperature, 10 1.4 Units of Temperature for Various Temperature
1 THE CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE 1 1.1 Historical Perspective, 2 1.2 Early Definitions of Temperature, 9 1.3 A Simple Qualitative Definition of Temperature, 10 1.4 Units of Temperature for Various Temperature
Measurement Techniques for Engineers. Motion and Vibration Measurement
 Measurement Techniques for Engineers Motion and Vibration Measurement Introduction Quantities that may need to be measured are velocity, acceleration and vibration amplitude Quantities useful in predicting
Measurement Techniques for Engineers Motion and Vibration Measurement Introduction Quantities that may need to be measured are velocity, acceleration and vibration amplitude Quantities useful in predicting
Lecture 19. Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
INTRODUCTION TO SCA\ \I\G TUNNELING MICROSCOPY
 INTRODUCTION TO SCA\ \I\G TUNNELING MICROSCOPY SECOND EDITION C. JULIAN CHEN Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia University, New York OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface
INTRODUCTION TO SCA\ \I\G TUNNELING MICROSCOPY SECOND EDITION C. JULIAN CHEN Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics, Columbia University, New York OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION, 2005.
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION, 2005 0031 PHYSICS Time: 2 Hours 1. This paper consists of sections A, B and C. 2.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND VOCATIONAL TRAINING FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION, 2005 0031 PHYSICS Time: 2 Hours 1. This paper consists of sections A, B and C. 2.
Gaseous CEMS technology
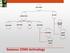 GAS CEMS EXTRACTIVE IN-SITU COLD DRY HOT WET DRY DILUTION PROBE/ POINT IN-STACK CROSS STACK OUT OF STACK Gaseous CEMS technology Probe (at stack) Heated filter Heated sample line Condenser Pump Analyzers
GAS CEMS EXTRACTIVE IN-SITU COLD DRY HOT WET DRY DILUTION PROBE/ POINT IN-STACK CROSS STACK OUT OF STACK Gaseous CEMS technology Probe (at stack) Heated filter Heated sample line Condenser Pump Analyzers
TRANSDUCERS transducer Measurand
 TRANSDUCERS Transduction: transformation of one form of energy into another form. Sensing with specificity the input energy from the measurand by means of a "sensing element" and then transforming it into
TRANSDUCERS Transduction: transformation of one form of energy into another form. Sensing with specificity the input energy from the measurand by means of a "sensing element" and then transforming it into
FLOW MEASUREMENT. INC 102 Fundamental of Instrumentation and Process Control 2/2560
 FLOW MEASUREMENT INC 102 Fundamental of Instrumentation and Process Control 2/2560 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. INTRODUCTION B. LOCAL FLOW MEASUREMENT B.1 Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) B.2 Laser doppler anemometry
FLOW MEASUREMENT INC 102 Fundamental of Instrumentation and Process Control 2/2560 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. INTRODUCTION B. LOCAL FLOW MEASUREMENT B.1 Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) B.2 Laser doppler anemometry
Temperature Scales. Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties. Temperature. Temperature Scale
 Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Angular Correlation Experiments
 Angular Correlation Experiments John M. LoSecco April 2, 2007 Angular Correlation Experiments J. LoSecco Notre Dame du Lac Nuclear Spin In atoms one can use the Zeeman Effect to determine the spin state.
Angular Correlation Experiments John M. LoSecco April 2, 2007 Angular Correlation Experiments J. LoSecco Notre Dame du Lac Nuclear Spin In atoms one can use the Zeeman Effect to determine the spin state.
Units (Different systems of units, SI units, fundamental and derived units)
 Physics: Units & Measurement: Units (Different systems of units, SI units, fundamental and derived units) Dimensional Analysis Precision and significant figures Fundamental measurements in Physics (Vernier
Physics: Units & Measurement: Units (Different systems of units, SI units, fundamental and derived units) Dimensional Analysis Precision and significant figures Fundamental measurements in Physics (Vernier
Solution for Mechanical Measurement & Control
 Solution for Mechanical Measurement & Control December-2015 Index Q.1) a). 2-3 b).3-4 c). 5 d). 6 Q.2) a). 7 b). 7 to 9 c). 10-11 Q.3) a). 11-12 b). 12-13 c). 13 Q.4) a). 14-15 b). 15 (N.A.) Q.5) a). 15
Solution for Mechanical Measurement & Control December-2015 Index Q.1) a). 2-3 b).3-4 c). 5 d). 6 Q.2) a). 7 b). 7 to 9 c). 10-11 Q.3) a). 11-12 b). 12-13 c). 13 Q.4) a). 14-15 b). 15 (N.A.) Q.5) a). 15
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8.
 Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Force and Displacement Measurement
 Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
Lesson 10. Thermomechanical Measurements for Energy Systems (MENR) Measurements for Mechanical Systems and Production (MMER)
 Lesson 10 Thermomechanical Measurements for Energy Systems (MENR) Measurements for Mechanical Systems and Production (MMER) A.Y. 015-16 Zaccaria (Rino ) Del Prete Some VELOCITY measurement techniques linear
Lesson 10 Thermomechanical Measurements for Energy Systems (MENR) Measurements for Mechanical Systems and Production (MMER) A.Y. 015-16 Zaccaria (Rino ) Del Prete Some VELOCITY measurement techniques linear
Sensors for mobile robots
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 2 Sensors for mobile robots Sensors are used to perceive, analyze and understand the environment
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 2 Sensors for mobile robots Sensors are used to perceive, analyze and understand the environment
SUBJECT & PEDAGOGICAL CONTENT STANDARDS FOR PHYSICS TEACHERS (GRADES 9-10)
 SUBJECT & PEDAGOGICAL CONTENT STANDARDS FOR PHYSICS TEACHERS (GRADES 9-10) JULY 2014 2 P a g e 1) Standard 1: Content Knowledge for Grade 9-10 Physics Teacher Understands Models and Scales G9-10PS1.E1.1)
SUBJECT & PEDAGOGICAL CONTENT STANDARDS FOR PHYSICS TEACHERS (GRADES 9-10) JULY 2014 2 P a g e 1) Standard 1: Content Knowledge for Grade 9-10 Physics Teacher Understands Models and Scales G9-10PS1.E1.1)
UNIVERSITY POLYTECHNIC B.I.T., MESRA, RANCHI
 COURSE STRUCTURE Diploma in Technology (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) SEMESTER IV (Total Unit 7.5) Mechanical Course Theory Unit Course Sessional Unit Code Code DAE 4001 Thermal Engineering 1.0 DAE 4002
COURSE STRUCTURE Diploma in Technology (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) SEMESTER IV (Total Unit 7.5) Mechanical Course Theory Unit Course Sessional Unit Code Code DAE 4001 Thermal Engineering 1.0 DAE 4002
INC 331 Industrial Process Measurement. Instrument Characteristics
 INC 331 Industrial Process Measurement Instrument Characteristics Introduction Measurement is the experimental process of acquiring any quantitative information. When doing a measurement, we compare the
INC 331 Industrial Process Measurement Instrument Characteristics Introduction Measurement is the experimental process of acquiring any quantitative information. When doing a measurement, we compare the
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 0031 PHYSICS Time: 2:30 Hours Friday, 28 th November 2014 a.m. Instructions 1. This paper consists
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL FORM TWO SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 0031 PHYSICS Time: 2:30 Hours Friday, 28 th November 2014 a.m. Instructions 1. This paper consists
Velocity Measurement in Free Surface Flows
 Velocity Measurement in Free Surface Flows Generally, the flow is assumed as one dimensional and standard. Pitot tube is used for measurement of velocity using either an inclined manometer or other type
Velocity Measurement in Free Surface Flows Generally, the flow is assumed as one dimensional and standard. Pitot tube is used for measurement of velocity using either an inclined manometer or other type
High School. Prentice Hall. Conceptual Physics South Carolina Science Academic Standards - Physics High School
 Prentice Hall Conceptual Physics 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O High School Scientific Inquiry Standard P-1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of how scientific inquiry and technological
Prentice Hall Conceptual Physics 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O High School Scientific Inquiry Standard P-1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of how scientific inquiry and technological
