Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
|
|
|
- Trevor Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Given ff(zz) = gg(zz) + h(zz), where ff, gg, h are complex valued functions of a complex variable zz. Which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) If ff(zz) is differentiable at zz 0, then gg(zz) and h(zz) are also differentiable at zz 0. (B) If gg(zz) and h(zz) are differentiable at zz 0, then ff(zz) is also differentiable at zz 0. (C) If ff(zz) is continuous at zz 0, then it is differentiable at zz 0. (D) If ff(zz) is differentiable at zz 0, then so are its real and imaginary parts. Q.2 We have a set of 3 linear equations in 3 unknowns. XX YY means XX and YY are equivalent statements and XX YY means XX and YY are not equivalent statements. P: There is a unique solution. Q: The equations are linearly independent. : All eigenvalues of the coefficient matrix are nonzero. S: The determinant of the coefficient matrix is nonzero. Which one of the following is TUE? (A) PP QQ SS (C) PP QQ SS (B) PP QQ SS (D) PP QQ SS Q.3 Match the following. P. Stokes s Theorem 1. DD. dddd = QQ Q. Gauss s Theorem 2. ff(zz)dddd = 0. Divergence Theorem 3. (. AA)dddd = AA. dddd S. Cauchy s Integral Theorem 4. ( AA). dddd = AA. dddd (A) P-2 Q-1-4 S-3 (B) P-4 Q-1-3 S-2 (C) P-4 Q-3-1 S-2 (D) P-3 Q-4-2 S-1 Q.4 The Laplace transform of ff(tt) = 2 tt ππ is ss 3 2. The Laplace transform of gg(tt) = 1 ππππ is (A) 3ss (B) ss 1 2 (C) ss 1 2 (D) ss 3 2 Q.5 Match the following. Instrument Type Used for P. Permanent magnet moving coil 1. DC Only Q. Moving iron connected through current transformer 2. AC Only. ectifier 3. AC and DC S. Electrodynamometer (A) P-1 Q-2-1 S-3 (B) P-1 Q-3-1 S-2 (C) P-1 Q-2-3 S-3 (D) P-3 Q-1-2 S-1 EE 1/15
2 Q.6 A 3-phase balanced load which has a power factor of is connected to a balanced supply. The power consumed by the load is 5 kw. The power is measured by the two-wattmeter method. The readings of the two wattmeters are (A) 3.94 kw and 1.06 kw (C) 5.00 kw and 0.00 kw (B) 2.50 kw and 2.50 kw (D) 2.96 kw and 2.04 kw Q.7 A capacitive voltage divider is used to measure the bus voltage VV bbbbbb in a high-voltage 50 Hz AC system as shown in the figure. The measurement capacitors CC 1 and CC 2 have tolerances of ±10% on their nominal capacitance values. If the bus voltage VV bbbbbb is 100 kv rms, the maximum rms output voltage VV oooooo (in kv), considering the capacitor tolerances, is. C 1 1µF ± 10% v bus C 2 9µF ± 10% v out Q.8 In the following circuit, the input voltage V in is 100 sin(100ππtt). For 100ππππππ = 50, the average voltage across (in Volts) under steady-state is nearest to V in C C (A) 100 (B) 31.8 (C) 200 (D) 63.6 Q.9 Two semi-infinite dielectric regions are separated by a plane boundary at yy = 0. The dielectric constants of region 1 (yy < 0) and region 2 (yy > 0) are 2 and 5, respectively. egion 1 has uniform electric field EE = 3aa xx + 4aa yy + 2aa zz, where aa xx, aa yy, and aa zz are unit vectors along the xx, yy and zz axes, respectively. The electric field in region 2 is (A) 3aa xx + 1.6aa yy + 2aa zz (C) 1.2aa xx + 4aa yy + 0.8aa zz (B) 1.2aa xx + 4aa yy + 2aa zz (D) 3aa xx + 10aa yy + 0.8aa zz EE 2/15
3 Q.10 A circular turn of radius 1 m revolves at 60 rpm about its diameter aligned with the x-axis as shown in the figure. The value of µ 0 is 4ππ 10 7 in SI unit. If a uniform magnetic field intensity HH = 10 7 zz A/m is applied, then the peak value of the induced voltage, V turn ( in Volts), is. Z H V turn X Q.11 The operational amplifier shown in the figure is ideal. The input voltage (in Volt) is VV ii = 2 sin(2π 2000t). The amplitude of the output voltage VV oo (in Volt) is. 0.1 µ F 1 k Ω 1 k Ω V i - + V o Q.12 In the following circuit, the transistor is in active mode and VV CC = 2 V. To get VV CC = 4 V, we replace CC with CC. Then the ratio CC / CC is. +10 V C B V C Q.13 Consider the following Sum of Products expression, F. FF = AAAAAA + AA BB CC + AABB CC + AA BBBB + AA BB CC The equivalent Product of Sums expression is (A) FF = (AA + BB + CC)(AA + BB + CC) (AA + BB + CC) (B) FF = (AA + BB + CC )(AA + BB + CC)(AA + BB + CC ) (C) FF = (AA + BB + CC )(AA + BB + CC ) (AA + BB + CC) (D) FF = (AA + BB + CC)(AA + BB + CC ) (AA + BB + CC) EE 3/15
4 Q.14 The filters F1 and F2 having characteristics as shown in Figures (a) and (b) are connected as shown in Figure (c). vo/vi vi vo vi vo F1 vo/vi F2 f1 f f2 f (a) /2 (b) +Vsat vi F1 F2 (c) - + -Vsat vo The cut-off frequencies of F1 and F2 are f 1 and f 2 respectively. If f 1 < f 2, the resultant circuit exhibits the characteristic of a (A) Band-pass filter (C) All pass filter (B) Band-stop filter (D) High-Q filter Q.15 When a bipolar junction transistor is operating in the saturation mode, which one of the following statements is TUE about the state of its collector-base (CB) and the base-emitter (BE) junctions? (A) The CB junction is forward biased and the BE junction is reverse biased. (B) The CB junction is reverse biased and the BE junction is forward biased. (C) Both the CB and BE junctions are forward biased. (D) Both the CB and BE junctions are reverse biased. EE 4/15
5 Q.16 The synchronous generator shown in the figure is supplying active power to an infinite bus via two short, lossless transmission lines, and is initially in steady state. The mechanical power input to the generator and the voltage magnitude E are constant. If one line is tripped at time tt 1 by opening the circuit breakers at the two ends (although there is no fault), then it is seen that the generator undergoes a stable transient. Which one of the following waveforms of the rotor angle δδ shows the transient correctly? Synchronous generator Ε δ Xs Line 1 Line 2 Infinite Bus 1 0 (A) δ (B) δ δ = 0 t1 time δ = 0 t1 time (C) δ (D) δ δ = 0 t1 time δ = 0 t1 time EE 5/15
6 Q.17 A 3-bus power system network consists of 3 transmission lines. The bus admittance matrix of the uncompensated system is jj6 jj3 jj4 jj3 jj7 jj5 pu. jj4 jj5 jj8 If the shunt capacitance of all transmission lines is 50% compensated, the imaginary part of the 3 rd row 3 rd column element (in pu) of the bus admittance matrix after compensation is (A) jj7.0 (B) jj8.5 (C) jj7.5 (D) jj9.0 Q.18 A series L circuit is excited at t = 0 by closing a switch as shown in the figure. Assuming zero initial conditions, the value of dd 2 ii at t = ddtt 2 0+ is V L (A) VV LL (B) VV (C) 0 (D) LL 2 Q.19 The current i (in Ampere) in the 2 Ω resistor of the given network is. 1 Ω i 5 V 1 Ω 1 Ω 2 Ω 1 Ω Q.20 Find the transformer ratios aa and bb such that the impedance (ZZ iiii ) is resistive and equals 2.5 Ω when the network is excited with a sine wave voltage of angular frequency of 5000 rad/s. C=10 uf L=1 mh Z in =2.5Ω 1:b 1:a (A) aa = 0.5, bb = 2.0 (B) aa = 2.0, bb = 0.5 (C) aa = 1.0, bb = 1.0 (D) aa = 4.0, bb = 0.5 Q.21 A shunt-connected DC motor operates at its rated terminal voltage. Its no-load speed is 200 radian/second. At its rated torque of 500 Nm, its speed is 180 radian/second. The motor is used to directly drive a load whose load torque T L depends on its rotational speed ωω rr (in radian/second), such that TT LL = 2.78 ωω rr. Neglecting rotational losses, the steady-state speed (in radian/second) of the motor, when it drives this load, is. EE 6/15
7 Q.22 The figure shows the per-phase equivalent circuit of a two-pole three-phase induction motor operating at 50 Hz. The air-gap voltage, VV gg across the magnetizing inductance, is 210 V rms, and the slip, s, is The torque (in Nm) produced by the motor is Ω j0.22 Ω j0.22 Ω V s j6.28 Ω V g 0.05 s Ω Q.23 A 4-pole, separately excited, wave wound DC machine with negligible armature resistance is rated for 230 V and 5 kw at a speed of 1200 rpm. If the same armature coils are reconnected to form a lap winding, what is the rated voltage (in volts) and power (in kw) respectively at 1200 rpm of the reconnected machine if the field circuit is left unchanged? (A) 230 and 5 (B) 115 and 5 (C) 115 and 2.5 (D) 230 and 2.5 Q.24 An open loop control system results in a response of ee 2tt (sin 5tt + cos 5tt) for a unit impulse input. The DC gain of the control system is. Q.25 Nyquist plots of two functions G 1 (s) and G 2 (s) are shown in figure. Im ω= G 2 (s) Im ω ω= 0 G 1 (s) ω 0 Nyquist plot of the product of G 1 (s) and G 2 (s) is (A) Im e (B) e Im ω= 0 ω e 1 e (C) Im (D) Im ω e ω 0 e EE 7/15
8 Q. 26 Q. 55 carry two mark each. Q.26 The volume enclosed by the surface ff(xx, yy) = ee xx over the triangle bounded by the lines xx = yy; xx = 0; yy = 1 in the xxxx plane is. Q.27 Two coins and S are tossed. The 4 joint events HH HH SS, TT TT SS, HH TT SS, TT HH SS have probabilities 0.28, 0.18, 0.30, 0.24, respectively, where HH represents head and TT represents tail. Which one of the following is TUE? (A) The coin tosses are independent. (B) is fair, S is not. (C) S is fair, is not. (D) The coin tosses are dependent. Q.28 A differential equation dddd 0.2ii = 0 is applicable over 10 < tt < 10. If ii(4) = 10, then ii( 5) is dddd. Q.29 Consider a signal defined by Its Fourier Transform is xx(tt) = eejj10tt for t 1 0 for t > 1 (A) (C) 2 sin (ωω 10) ωω 10 2 sin ωω ωω 10 jj10 sin (ωω 10) (B) 2 ee ωω 10 jj10ωω 2 sin ωω (D) ee ωω Q.30 The coils of a wattmeter have resistances 0.01 Ω and 1000 Ω; their inductances may be neglected. The wattmeter is connected as shown in the figure, to measure the power consumed by a load, which draws 25 A at power factor 0.8. The voltage across the load terminals is 30 V. The percentage error on the wattmeter reading is. Load EE 8/15
9 Q.31 A buck converter feeding a variable resistive load is shown in the figure. The switching frequency of the switch S is 100 khz and the duty ratio is 0.6. The output voltage VV OO is 36 V. Assume that all the components are ideal, and that the output voltage is ripple-free. The value of (in Ohm) that will make the inductor current (i L ) just continuous is. S il 5 mh 60 V V Vo Q.32 For the switching converter shown in the following figure, assume steady-state operation. Also assume that the components are ideal, the inductor current is always positive and continuous and switching period is T s. If the voltage V L is as shown, the duty cycle of the switch S is. V in V L L S C V o V L 15 V T s -45 V t Q.33 In the given rectifier, the delay angle of the thyristor T 1 measured from the positive going zero crossing of V s is 30 o. If the input voltage V s is 100 sin(100ππtt) V, the average voltage across (in Volt) under steady-state is. T 1 D 3 D 4 + V s V o D 2 Q.34 For linear time invariant systems, that are Bounded Input Bounded Output stable, which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) The impulse response will be integrable, but may not be absolutely integrable. (B) The unit impulse response will have finite support. (C) The unit step response will be absolutely integrable. (D) The unit step response will be bounded. Q.35 The zz-transform of a sequence xx[nn] is given as XX(zz) = 2zz + 4 4/zz + 3/zz 2. If yy[nn] is the first difference of xx[nn], then YY(zz) is given by (A) 2zz + 2 8/zz + 7/zz 2 3/zz 3 (B) 2zz + 2 6/zz + 1/zz 2 3/zz 3 (C) 2zz 2 + 8/zz 7/zz 2 + 3/zz 3 (D) 4zz 2 8/zz 1/zz 2 + 3/zz 3 EE 9/15
10 Q.36 Two semi-infinite conducting sheets are placed at right angles to each other as shown in the figure. A point charge of +QQ is placed at a distance of dd from both sheets. The net force on the charge is QQ 2 4ππεε 0 KK dd 2, where KK is given by y d +Q d x (A) 0 (B) 1 4 ii 1 4 jj (C) 1 8 ii 1 8 jj (D) ii jj 8 2 Q.37 In the following sequential circuit, the initial state (before the first clock pulse) of the circuit is QQ 1 QQ oo = 00. The state (QQ 1 QQ oo ), immediately after the 333 rd clock pulse is Q 0 Q 1 J 0 Q 0 J 1 Q 1 K 0 Q 0 K 1 Q 1 CLK (A) 00 (B) 01 (C) 10 (D) 11 Q.38 A Boolean function ff(aa, BB, CC, DD) = (1,5,12,15) is to be implemented using an 8 1 multiplexer (A is MSB). The inputs ABC are connected to the select inputs S 2 S 1 S 0 of the multiplexer respectively. Which one of the following options gives the correct inputs to pins 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 in order? (A) DD, 0, DD, 0, 0, 0, DD, DD (B) DD, 1, DD, 1, 1, 1, DD, DD (C) DD, 1, DD, 1, 1, 1, DD, DD (D) DD, 0, DD, 0, 0, 0, DD, DD EE 10/15
11 Q.39 The saturation voltage of the ideal op-amp shown below is ±10 V. The output voltage vv 0 of the following circuit in the steady-state is 1 kω 0.25 µf + 10 V V 2 kω v 0 2 kω (A) square wave of period 0.55 ms. (C) square wave of period 0.25 ms. (B) triangular wave of period 0.55 ms. (D) triangular wave of period 0.25 ms. Q.40 The incremental costs (in upees/mwh) of operating two generating units are functions of their respective powers PP 1 and PP 2 in MW, and are given by where ddcc 1 ddpp 1 = 0.2PP ddcc 2 ddpp 2 = 0.24PP MW PP MW 20 MW PP MW. For a certain load demand, PP 1 and PP 2 have been chosen such that ddcc 1 ddpp 1 = 76 s/mwh and ddcc 2 ddpp 2 = 68.8 s/mwh. If the generations are rescheduled to minimize the total cost, then PP 2 is. Q.41 A composite conductor consists of three conductors of radius each. The conductors are arranged as shown below. The geometric mean radius (GM) (in cm) of the composite conductor is kkkk. The value of kk is EE 11/15
12 Q.42 A 3-phase transformer rated for 33 kv/11 kv is connected in delta/star as shown in figure. The current transformers (CTs) on low and high voltage sides have a ratio of 500/5. Find the currents ii 1 and ii 2, if the fault current is 300 A as shown in figure. a b c i 1 i A (A) ii 1 = 1/ 3 AA, ii 2 = 0 AA (C) ii 1 = 0 AA, ii 2 = 1/ 3 AA (B) ii 1 = 0 AA, ii 2 = 0 AA (D) ii 1 = 1/ 3 AA, ii 2 = 1/ 3 AA Q.43 A balanced (positive sequence) three-phase AC voltage source is connected to a balanced, star connected load through a star-delta transformer as shown in the figure. The line-to-line voltage rating is 230 V on the star side, and 115 V on the delta side. If the magnetizing current is neglected and II ss = A, then what is the value of II pp in Ampere? Ip a A Is B b c C (A) (B) (C) (D) Q.44 In the given network VV 1 = V, VV 2 = V, VV 3 = V. The phasor current ii (in Ampere) is -j1 V 1 V 2 j1 V 3 i (A) (B) (C) (D) EE 12/15
13 Q.45 A symmetrical square wave of 50% duty cycle has amplitude of ±15 V and time period of 0.4ππ ms. This square wave is applied across a series LC circuit with = 5 Ω, LL = 10 mh, and CC = 4 µf. The amplitude of the 5000 rad/s component of the capacitor voltage (in Volt) is. L C Q.46 Two identical coils each having inductance L are placed together on the same core. If an overall inductance of αααα is obtained by interconnecting these two coils, the minimum value of αα is. Q.47 A three-winding transformer is connected to an AC voltage source as shown in the figure. The number of turns are as follows: NN 1 = 100, NN 2 = 50, NN 3 = 50. If the magnetizing current is neglected, and the currents in two windings are II 2 = 2 30 A and II 3 = A, then what is the value of the current II 1 in Ampere? I 1 N2 I2 I 3 N 1 N3 (A) 1 90 (B) (C) 4 90 (D) Q.48 With an armature voltage of 100 V and rated field winding voltage, the speed of a separately excited DC motor driving a fan is 1000 rpm, and its armature current is 10 A. The armature resistance is 1 Ω. The load torque of the fan load is proportional to the square of the rotor speed. Neglecting rotational losses, the value of the armature voltage (in Volt) which will reduce the rotor speed to 500 rpm is. Q.49 A three-phase, 11 kv, 50 Hz, 2 pole, star connected, cylindrical rotor synchronous motor is connected to an 11 kv, 50 Hz source. Its synchronous reactance is 50 Ω per phase, and its stator resistance is negligible. The motor has a constant field excitation. At a particular load torque, its stator current is 100 A at unity power factor. If the load torque is increased so that the stator current is 120 A, then the load angle (in degrees) at this load is. Q.50 A 220 V, 3-phase, 4-pole, 50 Hz inductor motor of wound rotor type is supplied at rated voltage and frequency. The stator resistance, magnetizing reactance, and core loss are negligible. The maximum torque produced by the rotor is 225 % of full load torque and it occurs at 15% slip. The actual rotor resistance is 0.03 Ω/phase. The value of external resistance (in Ohm) which must be inserted in a rotor phase if the maximum torque is to occur at start is. EE 13/15
14 Q.51 Two three-phase transformers are realized using single-phase transformers as shown in the figure. A2 A1 a1 a2 B2 B1 b1 b2 V1 C2 C1 c1 c2 A2 A1 a1 a2 B2 B1 b1 b2 V2 C2 C1 c1 c2 The phase difference (in degree) between voltages V 1 and V 2 is. Q.52 The following discrete-time equations result from the numerical integration of the differential equations of an un-damped simple harmonic oscillator with state variables xx and yy. The integration time step is h. xx kk+1 xx kk h yy kk+1 yy kk h = yy kk = xx kk For this discrete-time system, which one of the following statements is TUE? (A) The system is not stable for h > 0 (B) The system is stable for h > 1 ππ (C) The system is stable for 0 < h < 1 2ππ (D) The system is stable for 1 2ππ < h < 1 ππ EE 14/15
15 Q.53 The unit step response of a system with the transfer function GG(ss) = 1 2ss the following waveforms? (A) (B) y 1 1+ss y 2 is given by which one of 0 5 t t (C) y (D) y t 0 5 t Q.54 An open loop transfer function G(s) of a system is KK GG(ss) = ss(ss + 1)(ss + 2) For a unity feedback system, the breakaway point of the root loci on the real axis occurs at, (A) 0.42 (B) 1.58 (C) 0.42 and 1.58 (D) none of the above Q.55 For the system governed by the set of equations: ddxx 1 / dt = 2 xx 1 + xx 2 + u ddxx 2 / dt = 2 xx 1 + u y = 3 xx 1 the transfer function Y(s)/U(s) is given by (A) 3(s+1)/(ss 2 2s + 2) (B) 3(2s+1)/(ss 2 2s + 1) (C) (s+1)/(ss 2 2s + 1) (D) 3(2s+1)/(ss 2 2s + 2) END OF THE QUESTION PAPE EE 15/15
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
EE-GATE-2015 PAPER-02 General Aptitude. Q. No. 1 5 Carry One Mark Each
 EE-GATE-5 PAPER- www.gateforum.com General Aptitude Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. A generic term that includes various items of clothing such as a skirt, a pair of trousers and a shirt as fabric textile
EE-GATE-5 PAPER- www.gateforum.com General Aptitude Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. A generic term that includes various items of clothing such as a skirt, a pair of trousers and a shirt as fabric textile
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
+ ( )= with initial condition
 Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Department of Electrical Engineering PhD. Admission Test Full Marks: 90 Time 90 minutes Date: 02.2.204 NAME: Appl. No: Write your answer on the question paper ONLY. All questions carry equal marks. PART
Electrical Machines and Energy Systems: Operating Principles (Part 1) SYED A Rizvi
 Electrical Machines and Energy Systems: Operating Principles (Part 1) SYED A Rizvi AC Machines Operating Principles: Rotating Magnetic Field The key to the functioning of AC machines is the rotating magnetic
Electrical Machines and Energy Systems: Operating Principles (Part 1) SYED A Rizvi AC Machines Operating Principles: Rotating Magnetic Field The key to the functioning of AC machines is the rotating magnetic
ELEC273 Lecture Notes Set 11 AC Circuit Theorems
 ELEC273 Lecture Notes Set C Circuit Theorems The course web site is: http://users.encs.concordia.ca/~trueman/web_page_273.htm Final Exam (confirmed): Friday December 5, 207 from 9:00 to 2:00 (confirmed)
ELEC273 Lecture Notes Set C Circuit Theorems The course web site is: http://users.encs.concordia.ca/~trueman/web_page_273.htm Final Exam (confirmed): Friday December 5, 207 from 9:00 to 2:00 (confirmed)
SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS. ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems
 SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Power System Faults 3 Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow
SECTION 7: FAULT ANALYSIS ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Power System Faults 3 Faults in three-phase power systems are short circuits Line-to-ground Line-to-line Result in the flow
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
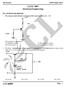 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Electrical Machines and Energy Systems: Operating Principles (Part 2) SYED A Rizvi
 Electrical Machines and Energy Systems: Operating Principles (Part 2) SYED A Rizvi AC Machines Operating Principles: Synchronous Motor In synchronous motors, the stator of the motor has a rotating magnetic
Electrical Machines and Energy Systems: Operating Principles (Part 2) SYED A Rizvi AC Machines Operating Principles: Synchronous Motor In synchronous motors, the stator of the motor has a rotating magnetic
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
Electronic Circuits. Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang Integrated Systems Laboratory
 Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang 6. Transimpedance Amplifiers, Voltage Regulators, Logarithmic Amplifiers, Anti-Logarithmic Amplifiers Transimpedance Amplifiers Sensing an input current ii in
Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang 6. Transimpedance Amplifiers, Voltage Regulators, Logarithmic Amplifiers, Anti-Logarithmic Amplifiers Transimpedance Amplifiers Sensing an input current ii in
(C) 4 5 (A) 2 3 (B) 3 4 (D) 1. Sol. Given : The impulse response g(t) of system G. The overall impulse response of two cascaded blocks. i.e.
 One Mark Questions ( 5) Q. The impulse response g(t) of a system G, is as shown in figure (a). What is the maximum value attained by the impulse response of two cascaded blocks of G as shown in figure
One Mark Questions ( 5) Q. The impulse response g(t) of a system G, is as shown in figure (a). What is the maximum value attained by the impulse response of two cascaded blocks of G as shown in figure
SECTION - A. A current impulse, 5δ(t), is forced through a capacitor C. The voltage, Vc(t), across the capacitor is given by. 5 t C.
 SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
SETION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..5) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 12
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 12 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 12 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL
 Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
Chapter 3 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROL . INTRODUCTION TO EXCITATION SYSTEM The basic function of an excitation system is to provide direct current to the field winding of the synchronous generator. The excitation
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Electric Machines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
GATEFORUM- India s No.1 institute for GATE training 1
 EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
EE-GATE-03 PAPER Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each. Given a vector field F = y xax yzay = x a z, the line integral F.dl evaluated along a segment on the x-axis from x= to x= is -.33 (B) 0.33 (D) 7 : (B) x 0.
LO 1: Three Phase Circuits
 Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
Course: EEL 2043 Principles of Electric Machines Class Instructor: Dr. Haris M. Khalid Email: hkhalid@hct.ac.ae Webpage: www.harismkhalid.com LO 1: Three Phase Circuits Three Phase AC System Three phase
GATE-2015 ELECTRICAL ENGG 7th February 2015 Forenoon Session
 Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
Page Section - I (General Aptitude) Q. Which one of the following combinations is incorrect? Acquiescence - Submission Wheedle - Roundabout Flippancy - Lightness Profligate - Extravagant Q. Didn t you
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electric Power Engineering Department
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electric Power Engineering Department EE471: Electrical Machines-II Tutorial # 2: 3-ph Induction Motor/Generator Question #1 A 100 hp, 60-Hz, three-phase
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Electric Power Engineering Department EE471: Electrical Machines-II Tutorial # 2: 3-ph Induction Motor/Generator Question #1 A 100 hp, 60-Hz, three-phase
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
ECE 585 Power System Stability
 Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Homework 1, Due on January 29 ECE 585 Power System Stability Consider the power system below. The network frequency is 60 Hz. At the pre-fault steady state (a) the power generated by the machine is 400
Analog Circuits Part 1 Circuit Theory
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 1 Circuit Theory, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Circuit Theory
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 1 Circuit Theory, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Circuit Theory
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines. Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015
 ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
ECE 325 Electric Energy System Components 7- Synchronous Machines Instructor: Kai Sun Fall 2015 1 Content (Materials are from Chapters 16-17) Synchronous Generators Synchronous Motors 2 Synchronous Generators
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
POWER SEMICONDUCTOR BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES
 POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
POWER SEMICONDUCT BASED ELECTRIC DRIVES [Time: 3 Hrs] [Max. Marks: 80] Instructions: Solve any six questions from Q.No (1 or 2), Q.No (3 or 4), Q.No (5 or 6), Q.No (7 or 8), Q.No (9 or 10), Q.No (11 or
 TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
TELANGANA/ANDHRA PRADESH TRANSCO/GENCO/DISCUM Assistant Engineer Examination ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Previous Paper 7) AP TRANSCO - AP GENCO-AE QUESTION PAPER 1. In two wattmeter method of 3-phase power
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University College of Engineering. Electrical Engineering Department EE 3360 Electrical Machines (II)
 Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Phy207 Final Exam (Form1) Professor Zuo Fall Signature: Name:
 #1-25 #26 Phy207 Final Exam (Form1) Professor Zuo Fall 2018 On my honor, I have neither received nor given aid on this examination #27 Total Signature: Name: ID number: Enter your name and Form 1 (FM1)
#1-25 #26 Phy207 Final Exam (Form1) Professor Zuo Fall 2018 On my honor, I have neither received nor given aid on this examination #27 Total Signature: Name: ID number: Enter your name and Form 1 (FM1)
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
SECTION 5: POWER FLOW. ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems
 SECTION 5: POWER FLOW ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Nodal Analysis 3 Consider the following circuit Three voltage sources VV sss, VV sss, VV sss Generic branch impedances Could be
SECTION 5: POWER FLOW ESE 470 Energy Distribution Systems 2 Introduction Nodal Analysis 3 Consider the following circuit Three voltage sources VV sss, VV sss, VV sss Generic branch impedances Could be
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION
 EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
EE 6501 POWER SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What is single line diagram? A Single line diagram is diagrammatic representation of power system in which the components are represented by
PART I (STATISTICS / MATHEMATICS STREAM) ATTENTION : ANSWER A TOTAL OF SIX QUESTIONS TAKING AT LEAST TWO FROM EACH GROUP - S1 AND S2.
 PART I (STATISTICS / MATHEMATICS STREAM) ATTENTION : ANSWER A TOTAL OF SIX QUESTIONS TAKING AT LEAST TWO FROM EACH GROUP - S1 AND S2. GROUP S1: Statistics 1. (a) Let XX 1,, XX nn be a random sample from
PART I (STATISTICS / MATHEMATICS STREAM) ATTENTION : ANSWER A TOTAL OF SIX QUESTIONS TAKING AT LEAST TWO FROM EACH GROUP - S1 AND S2. GROUP S1: Statistics 1. (a) Let XX 1,, XX nn be a random sample from
Dynamics of the synchronous machine
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamics of the synchronous machine Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 38 Time constants and
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamics of the synchronous machine Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 38 Time constants and
 Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each GATE question papers: Electrical Engineering 00 (EE) Published by:. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe x dx, is equal to o 0 e /e. Divergence of the threedimensional
Q. No. 5 Carry One Mark Each GATE question papers: Electrical Engineering 00 (EE) Published by:. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe x dx, is equal to o 0 e /e. Divergence of the threedimensional
Introduction to Synchronous. Machines. Kevin Gaughan
 Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system.
 1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits
 Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
Sinusoidal Response of RLC Circuits Series RL circuit Series RC circuit Series RLC circuit Parallel RL circuit Parallel RC circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit R-L Series Circuit Instantaneous
ENGG4420 LECTURE 7. CHAPTER 1 BY RADU MURESAN Page 1. September :29 PM
 CHAPTER 1 BY RADU MURESAN Page 1 ENGG4420 LECTURE 7 September 21 10 2:29 PM MODELS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Electric circuits contain sources of electric voltage and current and other electronic elements such
CHAPTER 1 BY RADU MURESAN Page 1 ENGG4420 LECTURE 7 September 21 10 2:29 PM MODELS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Electric circuits contain sources of electric voltage and current and other electronic elements such
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B
 GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. 1. For the circuit shown in the figure, the voltage and current expressions are v(t) = and. The average power measured by the Wattmeter
GATE 2012 Electrical Engineering Set - B Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. 1. For the circuit shown in the figure, the voltage and current expressions are v(t) = and. The average power measured by the Wattmeter
EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4
 EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4 Chapter 4. Direct Current Electric Machines and Motion Devices Permanent Magnet DC Electric Machines Radial Topology Simulation and Experimental Studies
EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4 Chapter 4. Direct Current Electric Machines and Motion Devices Permanent Magnet DC Electric Machines Radial Topology Simulation and Experimental Studies
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
GATE 2011 Electrical Engineering Set C
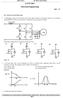 Electrical Engineering Set C Q. - Q.25 Carry One Mark each.. A three-phase current source inverter used for the speed control of an induction motor is to be realized using MOSFET switches as shown below.
Electrical Engineering Set C Q. - Q.25 Carry One Mark each.. A three-phase current source inverter used for the speed control of an induction motor is to be realized using MOSFET switches as shown below.
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power Factor Improvement
 Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Salman bin AbdulazizUniversity College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 2050Electrical Circuit Laboratory Power Factor Improvement Experiment # 4 Objectives: 1. To introduce the concept
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 08 General Aptitude (GA) Set6 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Since you have gone off the, the sand is likely to damage the car. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) course,
GATE 08 General Aptitude (GA) Set6 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Since you have gone off the, the sand is likely to damage the car. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) course,
Chapter 31 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively
 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively In the LC circuit the charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally (with period T and angular
Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively In the LC circuit the charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally (with period T and angular
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State. Y. Baghzouz
 EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
Exam 2 Fall 2015
 1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2015 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2015 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
Generators. What its all about
 Generators What its all about How do we make a generator? Synchronous Operation Rotor Magnetic Field Stator Magnetic Field Forces and Magnetic Fields Force Between Fields Motoring Generators & motors are
Generators What its all about How do we make a generator? Synchronous Operation Rotor Magnetic Field Stator Magnetic Field Forces and Magnetic Fields Force Between Fields Motoring Generators & motors are
Behaviour of synchronous machine during a short-circuit (a simple example of electromagnetic transients)
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability (a simple example of electromagnetic transients) Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 25 Objectives
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability (a simple example of electromagnetic transients) Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 25 Objectives
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
PHYS 241 EXAM #2 November 9, 2006
 1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT I: INTRODUCTION PART: A 1. Define per unit value of an electrical quantity. Write equation for base impedance with respect to 3-phase system. 2. What is bus admittance
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03
![Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03](/thumbs/94/118747664.jpg) EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
EE 4 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 03 II/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 016 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS NETWORK ANALYSIS Time: Three Hours Answer Question
VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON:
 VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON: 10EE35 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION BY DR. M.S. RAVIPRAKASHA PROFESSOR & HEAD DEPT. OF E&E ENGG. MALNAD COLLEGE OF ENGG. HASSAN 573 201. SUBJECT CODE
VTU E-LEARNING NOTES ON: 10EE35 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION BY DR. M.S. RAVIPRAKASHA PROFESSOR & HEAD DEPT. OF E&E ENGG. MALNAD COLLEGE OF ENGG. HASSAN 573 201. SUBJECT CODE
Modeling of Symmetrical Squirrel Cage Induction Machine with MatLab Simulink
 Modeling of Symmetrical Squirrel Cage Induction Machine with MatLab Simulink Marcus Svoboda *, Lucian Tutelea *, Gheorghe Madescu **, Marius Biriescu *, Martian Mot ** * University POLITEHNICA Timisoara/Electrical
Modeling of Symmetrical Squirrel Cage Induction Machine with MatLab Simulink Marcus Svoboda *, Lucian Tutelea *, Gheorghe Madescu **, Marius Biriescu *, Martian Mot ** * University POLITEHNICA Timisoara/Electrical
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
79 CHAPTER 6 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 6.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase and three-phase self-excited induction generators has been presented
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 24 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 24 Electrical
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam 613 303 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A (TWO MARK
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 26 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Recently increase in energy demand and limited energy sources in the world caused the researchers
26 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF THREE PHASE AND SINGLE PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 3.1. INTRODUCTION Recently increase in energy demand and limited energy sources in the world caused the researchers
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 9 Transmission Line Steady State Operation Welcome to lesson 9, in Power
The synchronous machine (detailed model)
 ELEC0029 - Electric Power System Analysis The synchronous machine (detailed model) Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct February 2018 1 / 6 Objectives The synchronous
ELEC0029 - Electric Power System Analysis The synchronous machine (detailed model) Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct February 2018 1 / 6 Objectives The synchronous
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2013 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2013 Caribbean Examinations Council
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2013 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY Copyright 2013 Caribbean Examinations Council
Circuit Analysis-II. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 5 Monday 23 rd April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
SSC-JE EE POWER SYSTEMS: GENERATION, TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems: Generation, Transmission and Distribution Power Systems:
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
6 CHAPTER 5 STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 5.. INTRODUCTION The steady-state analysis of six-phase SEIG has been discussed in the previous chapters. In this chapter,
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
PS12038 Intellimod Module Application Specific IPM 25 Amperes/1200 Volts
 D M SQ PINS G L A F H K E J D VV QQ PP C 24 2 9 6 3 9 7 8 7 4 2 8 RR (4 PLACES) B N P Q R S Y EE XX V T LL DD GG TT SS X 2 3 4 GG T C FF LABEL T C 6 DD GG GG U P 2 N 3 NC 4 U V 6 W TERMINAL CODE 9 GND
D M SQ PINS G L A F H K E J D VV QQ PP C 24 2 9 6 3 9 7 8 7 4 2 8 RR (4 PLACES) B N P Q R S Y EE XX V T LL DD GG TT SS X 2 3 4 GG T C FF LABEL T C 6 DD GG GG U P 2 N 3 NC 4 U V 6 W TERMINAL CODE 9 GND
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering. EE 1352 Power System Analysis
 B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, April / May 2010 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 1352 Power System Analysis (Regulation 2008) Time: Three hours Answer all questions Part A (10
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines
 Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A
 EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A 1. What are the advantages of an inter connected system? The advantages of an inter-connected system are
EE2351 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT I THE POWER SYSTEM AN OVERVIEW AND MODELLING PART A 1. What are the advantages of an inter connected system? The advantages of an inter-connected system are
SECTION 5: CAPACITANCE & INDUCTANCE. ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I
 SECTION 5: CAPACITANCE & INDUCTANCE ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I 2 Fluid Capacitor Fluid Capacitor 3 Consider the following device: Two rigid hemispherical shells Separated by an impermeable elastic
SECTION 5: CAPACITANCE & INDUCTANCE ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I 2 Fluid Capacitor Fluid Capacitor 3 Consider the following device: Two rigid hemispherical shells Separated by an impermeable elastic
Introduction. Energy is needed in different forms: Light bulbs and heaters need electrical energy Fans and rolling miles need mechanical energy
 Introduction Energy is needed in different forms: Light bulbs and heaters need electrical energy Fans and rolling miles need mechanical energy What does AC and DC stand for? Electrical machines Motors
Introduction Energy is needed in different forms: Light bulbs and heaters need electrical energy Fans and rolling miles need mechanical energy What does AC and DC stand for? Electrical machines Motors
Angular Momentum, Electromagnetic Waves
 Angular Momentum, Electromagnetic Waves Lecture33: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay As before, we keep in view the four Maxwell s equations for all our discussions.
Angular Momentum, Electromagnetic Waves Lecture33: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay As before, we keep in view the four Maxwell s equations for all our discussions.
Revision : Thermodynamics
 Revision : Thermodynamics Formula sheet Formula sheet Formula sheet Thermodynamics key facts (1/9) Heat is an energy [measured in JJ] which flows from high to low temperature When two bodies are in thermal
Revision : Thermodynamics Formula sheet Formula sheet Formula sheet Thermodynamics key facts (1/9) Heat is an energy [measured in JJ] which flows from high to low temperature When two bodies are in thermal
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA
 EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
EXPERIMENT 07 TO STUDY DC RC CIRCUIT AND TRANSIENT PHENOMENA DISCUSSION The capacitor is a element which stores electric energy by charging the charge on it. Bear in mind that the charge on a capacitor
