Solutions to Assignment 2
|
|
|
- Dale Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MTHE 237 Fall 2015 Solutions to Assignment 2 Problem 1 Solve the following differential equations with the given initial conditions: a) b) y y = 2te 2t, y(0) = 1 y +y = e t, y(0) = 2 Hint: Check if the equations are exact. If needed, find appropriate integrating factors. It can be verified that the equation is not exact. Hence, we need to find an integrating factor. We learned in class that, if M y N t N is only a function of t, say is equal to P(t), then (P(t)) µ(t) = e is an integrating factor. a) In this example, we obtain P(t) = 1. Hence µ(t) = e t Hence, the equation with the integrating factor becomes: d (ye t ) = 2te t Using integration by parts for the right hand side of the equation: ye t = (2te t 2e t +C) one obtains If y(0) = 1, it follows that Hence, C = 3, and y = (2te 2t 2e 2t +Ce t ) 1 = 2+C. y(t) = 2te 2t 2e 2t +3e t b) For this example, an integrating factor is µ(t) = e t. Solving the equation leads to with y(0) = 2, it follows that c = 3/2. y(t) = 1 2 et ce t, Problem 2 Solve the following differential equation: ty +(t+1)y = t, y(ln(2)) = 1,t > 0
2 The equation is not exact. Using the same argumentwe used in the previousquestion, we find the integrating factor to be µ(t) = e t Thus, (yte t ) = e t +C and It follows by integration by parts that y(t) = ( e t t+c)e t. y(t) = (t 1+Ce t )/t. Since y(ln(2)) = 1, we find that C = 2. Thus the solution is y(t) = (t 1+2e t )/t. Problem 3 Consider a lake of (water) volume V containing Q(t) amount of pollutant, evenly distributed throughout the lake with a concentration c(t) = Q(t) V. Suppose water from a river containing a concentration k of pollutant enters the lake at a rate r (in units of volume/time) per time, and water to a canal leaves the lake with the same rate (hence, the volume of the lake is a constant). Furthermore, suppose that pollutants are also added directly to the lake by humans at a constant rate P. Express the evolution of the amount of pollutant in the lake as a differential equation. If at time t = 0, the concentration of pollutant at the lake is c 0, find an expression for the concentration c(t) as a function of time. What happens to the concentration as t? The rate of change in the amount of pollutant is = (P +rk) rc, or = (P +rk) rq/v, Hence, we have +(r/v)q = (P +rk), This is in a familiar form and the solution to this is given by: Initial value satisfies: Hence As t becomes larger, the total amount converges to Q(t) = (P +rk)(v/r) +(P +rk +C)e rt/v. c 0 V = (P +rk)(v/r) +(P +rk +C), Q(t) = (P +rk)(v/r)+(c 0 V (P +rk))e rt/v. (P +rk)(v/r),
3 and the concentration converges to k + P r. Problem 4 Obtain the general solution to the differential equation dy dx = y2 +2xy x 2, x > 0,y > 0 This is an equation with homogenous coefficients. Writing y = vx, we obtain the equation: v +x dx = v2 +2v, leading to ( 1 v 1 ) = dx v +1 x. Solving this equation leads to: v ln( x ) = ln( v +1 )+c Since the domain of the integration is the area given by x > 0,y > 0, it follows that x = Ky x+y, is the general implicit solution where K is a constant. Problem 5 Obtain the general solution to the differential equation (3x 2 +y 2 )dx+2xydy = 0. Here we observe that the equation is exact, hence, there is no need for an additional integrating factor. It follows that a function F such that F x = 3x2 +y 2 and F y = 2xy is F(x,y) = x 3 +xy 2. Hence, the general solution is given by: for some constant c. x 3 +xy 2 = c, Problem 6 Show that satisfies F(x,y) = x x 0 M(t, )+ y F(x,y) = M(x,y) x
4 if F(x,y) = N(x,y), y y M(x,y) = x N(x,y), and these are continuous in the domain of the integration. Let us first consider yf(x,y). By the fundamental theorem of calculus: y F(x,y) = ( x M(t, )+ y x 0 = y y = y (G(x,y) G(x,)) ) In the above G(x,y) is the anti-derivative of N(x,y) in the y variable. We now work with y = N(x,y) (1) x F(x,y) = ( x M(t, )+ x x 0 = M(x, )+ x = M(x, )+ y y 0 y y ) y = M(x, )+ s = M(x, )+M(x,y) M(x, ) = M(x,y) (2) x M(x,s)ds (3) In the above, (2) follows from the fact that xn(x,s) is continuous (you are encouraged to show why this holds; you can usetaylor s formula with a remainder term for the term N(x+h,s) for h > 0) and (3) follows from the hypothesis that s M(x,s) = x N(x,s), x,s. (4) Problem 7 Suppose that a rocket is launched from the surface of the earth with an initial velocity v 0 = 2gR, where R is the radius of earth (assuming a spherical earth!) and g is the gravitational acceleration at the surface of the earth and the differential equation characterization the motion is given by where x is the distance from the surface of the earth. = gr2 /(R+x) 2,
5 Find an expression for the velocity v(x) in terms of the distance x from the surface of the earth. First, observe that, by the chain rule: = dx dx = gr2 /(R+x) 2 Thus, Hence, we obtain: dx v = gr2 /(R+x) 2. gr 2 /(R+x) 2 dx = v +C. It follows that gr 2 /(R+x) = v 2 /2+C. For x = 0, the initial condition is given by v(0) = 2gR, as such C = 0. Hence, it follows that v(x) = R 2g (R+x).
First-Order ODEs. Chapter Separable Equations. We consider in this chapter differential equations of the form dy (1.1)
 Chapter 1 First-Order ODEs We consider in this chapter differential equations of the form dy (1.1) = F (t, y), where F (t, y) is a known smooth function. We wish to solve for y(t). Equation (1.1) is called
Chapter 1 First-Order ODEs We consider in this chapter differential equations of the form dy (1.1) = F (t, y), where F (t, y) is a known smooth function. We wish to solve for y(t). Equation (1.1) is called
Elementary Differential Equations
 Elementary Differential Equations George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 310 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Differential Equations January 2014 1 /
Elementary Differential Equations George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 310 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Differential Equations January 2014 1 /
MATH 251 Examination I July 1, 2013 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I July 1, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems,
MATH 251 Examination I July 1, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems,
M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 2013
 M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 013 Section.6 3. Consider the equation: (3x xy + )dx + (6y x + 3)dy = 0. Let M(x, y) = 3x xy + and N(x, y) = 6y x + 3. Since: y = x = N We can conclude that this
M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 013 Section.6 3. Consider the equation: (3x xy + )dx + (6y x + 3)dy = 0. Let M(x, y) = 3x xy + and N(x, y) = 6y x + 3. Since: y = x = N We can conclude that this
Homework Solutions: , plus Substitutions
 Homework Solutions: 2.-2.2, plus Substitutions Section 2. I have not included any drawings/direction fields. We can see them using Maple or by hand, so we ll be focusing on getting the analytic solutions
Homework Solutions: 2.-2.2, plus Substitutions Section 2. I have not included any drawings/direction fields. We can see them using Maple or by hand, so we ll be focusing on getting the analytic solutions
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY. MATH 2610 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practice for test 1 solutions
 VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2610 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practice for test 1 solutions The first test will cover all material discussed up to (including) section 4.5. Important: The solutions below
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2610 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Practice for test 1 solutions The first test will cover all material discussed up to (including) section 4.5. Important: The solutions below
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1
 Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 5, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
First Order ODEs, Part I
 Craig J. Sutton craig.j.sutton@dartmouth.edu Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Math 23 Differential Equations Winter 2013 Outline 1 2 in General 3 The Definition & Technique Example Test for
Craig J. Sutton craig.j.sutton@dartmouth.edu Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College Math 23 Differential Equations Winter 2013 Outline 1 2 in General 3 The Definition & Technique Example Test for
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
First Order Differential Equations Lecture 3
 First Order Differential Equations Lecture 3 Dibyajyoti Deb 3.1. Outline of Lecture Differences Between Linear and Nonlinear Equations Exact Equations and Integrating Factors 3.. Differences between Linear
First Order Differential Equations Lecture 3 Dibyajyoti Deb 3.1. Outline of Lecture Differences Between Linear and Nonlinear Equations Exact Equations and Integrating Factors 3.. Differences between Linear
An Introduction to Differential Equations
 An Introduction to Differential Equations Let's start with a definition of a differential equation. A differential equation is an equation that defines a relationship between a function and one or more
An Introduction to Differential Equations Let's start with a definition of a differential equation. A differential equation is an equation that defines a relationship between a function and one or more
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations
 Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 2 February 1st, 2019 Learning Goals Solve linear first order ODEs analytically. Solve separable first order ODEs analytically. Questions
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 2 February 1st, 2019 Learning Goals Solve linear first order ODEs analytically. Solve separable first order ODEs analytically. Questions
= 2e t e 2t + ( e 2t )e 3t = 2e t e t = e t. Math 20D Final Review
 Math D Final Review. Solve the differential equation in two ways, first using variation of parameters and then using undetermined coefficients: Corresponding homogenous equation: with characteristic equation
Math D Final Review. Solve the differential equation in two ways, first using variation of parameters and then using undetermined coefficients: Corresponding homogenous equation: with characteristic equation
Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214. Due 6/29
 Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214 Due 6/29 Section 2.5 1. (Problems 3 and 5 from B&D) The following problems involve differential equations of the form dy = f(y). For each, sketch the graph of f(y) versus y, determine
Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214 Due 6/29 Section 2.5 1. (Problems 3 and 5 from B&D) The following problems involve differential equations of the form dy = f(y). For each, sketch the graph of f(y) versus y, determine
MIDTERM 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 MIDTERM 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Problem 1. Give an example of: (a) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y) such that all solutions with y(0) > 0 satisfy y(t) = +. lim t + (b) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y)
MIDTERM 1 PRACTICE PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Problem 1. Give an example of: (a) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y) such that all solutions with y(0) > 0 satisfy y(t) = +. lim t + (b) an ODE of the form y (t) = f(y)
Math Applied Differential Equations
 Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Existence and Uniqueness The following theorem gives sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of a solution to the IVP for first order nonlinear
Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Existence and Uniqueness The following theorem gives sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of a solution to the IVP for first order nonlinear
Lecture Notes 1. First Order ODE s. 1. First Order Linear equations A first order homogeneous linear ordinary differential equation (ODE) has the form
 Lecture Notes 1 First Order ODE s 1. First Order Linear equations A first order homogeneous linear ordinary differential equation (ODE) has the form This equation we rewrite in the form or From the last
Lecture Notes 1 First Order ODE s 1. First Order Linear equations A first order homogeneous linear ordinary differential equation (ODE) has the form This equation we rewrite in the form or From the last
Lecture 7 - Separable Equations
 Lecture 7 - Separable Equations Separable equations is a very special type of differential equations where you can separate the terms involving only y on one side of the equation and terms involving only
Lecture 7 - Separable Equations Separable equations is a very special type of differential equations where you can separate the terms involving only y on one side of the equation and terms involving only
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]
![HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]](/thumbs/73/68538384.jpg) HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
Find the Fourier series of the odd-periodic extension of the function f (x) = 1 for x ( 1, 0). Solution: The Fourier series is.
 Review for Final Exam. Monday /09, :45-:45pm in CC-403. Exam is cumulative, -4 problems. 5 grading attempts per problem. Problems similar to homeworks. Integration and LT tables provided. No notes, no
Review for Final Exam. Monday /09, :45-:45pm in CC-403. Exam is cumulative, -4 problems. 5 grading attempts per problem. Problems similar to homeworks. Integration and LT tables provided. No notes, no
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B Calculus Section 3A: - First order ODEs.
 MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2010. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures. Calculus Section 3A: - First order ODEs. Created and compiled by Chris Tisdell S1: What is an ODE? S2: Motivation S3: Types and orders
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2010. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures. Calculus Section 3A: - First order ODEs. Created and compiled by Chris Tisdell S1: What is an ODE? S2: Motivation S3: Types and orders
Chain Rule. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
Lectures on Differential Equations
 Lectures on Differential Equations Philip Korman Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Cincinnati Cincinnati Ohio 4522-0025 Copyright @ 2008, by Philip L. Korman Contents First Order Equations
Lectures on Differential Equations Philip Korman Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Cincinnati Cincinnati Ohio 4522-0025 Copyright @ 2008, by Philip L. Korman Contents First Order Equations
y0 = F (t0)+c implies C = y0 F (t0) Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where I.e., f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) wheref is any antiderivative 2.
 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous
Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative
![The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative](/thumbs/96/128959530.jpg) 1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
First order differential equations
 First order differential equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T. First
First order differential equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T. First
More Techniques. for Solving First Order ODE'S. and. a Classification Scheme for Techniques
 A SERIES OF CLASS NOTES FOR 2005-2006 TO INTRODUCE LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, AND APPLIED MATHEMATICIANS DE CLASS NOTES 1 A COLLECTION OF HANDOUTS ON FIRST ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL
A SERIES OF CLASS NOTES FOR 2005-2006 TO INTRODUCE LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, AND APPLIED MATHEMATICIANS DE CLASS NOTES 1 A COLLECTION OF HANDOUTS ON FIRST ORDER ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL
MATH 251 MATH 251: Multivariate Calculus MATH 251 FALL 2005 FINAL EXAM FALL 2005 FINAL EXAM EXAMINATION COVER PAGE Professor Moseley
 MATH 5 MATH 5: Multivariate Calculus MATH 5 FALL 5 FINAL EXAM FALL 5 FINAL EXAM EXAMINATION COVER PAGE Professor Moseley PRINT NAME ( ) Last Name, First Name MI (What you wish to be called) ID # EXAM DATE
MATH 5 MATH 5: Multivariate Calculus MATH 5 FALL 5 FINAL EXAM FALL 5 FINAL EXAM EXAMINATION COVER PAGE Professor Moseley PRINT NAME ( ) Last Name, First Name MI (What you wish to be called) ID # EXAM DATE
Lesson 10 MA Nick Egbert
 Overview There is no new material for this lesson, we just apply our knowledge from the previous lesson to some (admittedly complicated) word problems. Recall that given a first-order linear differential
Overview There is no new material for this lesson, we just apply our knowledge from the previous lesson to some (admittedly complicated) word problems. Recall that given a first-order linear differential
2.2 Separable Equations
 2.2 Separable Equations Definition A first-order differential equation that can be written in the form Is said to be separable. Note: the variables of a separable equation can be written as Examples Solve
2.2 Separable Equations Definition A first-order differential equation that can be written in the form Is said to be separable. Note: the variables of a separable equation can be written as Examples Solve
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Tutorial-1, MA 108 (Linear Algebra)
 Tutorial-1, MA 108 (Linear Algebra) 1. Verify that the function is a solution of the differential equation on some interval, for any choice of the arbitrary constants appearing in the function. (a) y =
Tutorial-1, MA 108 (Linear Algebra) 1. Verify that the function is a solution of the differential equation on some interval, for any choice of the arbitrary constants appearing in the function. (a) y =
Section 2.2 Homogeneous DEs (related to separable DEs) Key Terms: Homogeneous Functions. Degree of a term. First Order DEs of Homogeneous type
 Section. Homogeneous DEs (related to separable DEs) Key Terms: Homogeneous Functions Degree of a term First Order DEs of Homogeneous type From experiences in your study of mathematics you have encountered
Section. Homogeneous DEs (related to separable DEs) Key Terms: Homogeneous Functions Degree of a term First Order DEs of Homogeneous type From experiences in your study of mathematics you have encountered
Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations In the sciences and engineering, mathematical models are developed to aid in the understanding of physical phenomena. These models often yield an equation that
Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations In the sciences and engineering, mathematical models are developed to aid in the understanding of physical phenomena. These models often yield an equation that
Math Applied Differential Equations
 Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Basic Definitions and Concepts A differential equation is an equation that involves one or more of the derivatives (first derivative, second derivative,
Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Basic Definitions and Concepts A differential equation is an equation that involves one or more of the derivatives (first derivative, second derivative,
HOMEWORK # 3 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK # 3 SOLUTIONS TJ HITCHMAN. Exercises from the text.. Chapter 2.4. Problem 32 We are to use variation of parameters to find the general solution to y + 2 x y = 8x. The associated homogeneous equation
HOMEWORK # 3 SOLUTIONS TJ HITCHMAN. Exercises from the text.. Chapter 2.4. Problem 32 We are to use variation of parameters to find the general solution to y + 2 x y = 8x. The associated homogeneous equation
MATH 1207 R02 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SOLUTION
 MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
Lectures on Differential Equations
 Lectures on Differential Equations Philip Korman Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Cincinnati Cincinnati Ohio 4522-0025 Copyright @ 2008, by Philip L. Korman Chapter First Order Equations.
Lectures on Differential Equations Philip Korman Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Cincinnati Cincinnati Ohio 4522-0025 Copyright @ 2008, by Philip L. Korman Chapter First Order Equations.
MATH 353 LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 1 FIRST ORDER ODES
 MATH 353 LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 1 FIRST ORDER ODES J. WONG (FALL 2017) What did we cover this week? Basic definitions: DEs, linear operators, homogeneous (linear) ODEs. Solution techniques for some classes
MATH 353 LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 1 FIRST ORDER ODES J. WONG (FALL 2017) What did we cover this week? Basic definitions: DEs, linear operators, homogeneous (linear) ODEs. Solution techniques for some classes
7.1. Calculus of inverse functions. Text Section 7.1 Exercise:
 Contents 7. Inverse functions 1 7.1. Calculus of inverse functions 2 7.2. Derivatives of exponential function 4 7.3. Logarithmic function 6 7.4. Derivatives of logarithmic functions 7 7.5. Exponential
Contents 7. Inverse functions 1 7.1. Calculus of inverse functions 2 7.2. Derivatives of exponential function 4 7.3. Logarithmic function 6 7.4. Derivatives of logarithmic functions 7 7.5. Exponential
Review For the Final: Problem 1 Find the general solutions of the following DEs. a) x 2 y xy y 2 = 0 solution: = 0 : homogeneous equation.
 Review For the Final: Problem 1 Find the general solutions of the following DEs. a) x 2 y xy y 2 = 0 solution: y y x y2 = 0 : homogeneous equation. x2 v = y dy, y = vx, and x v + x dv dx = v + v2. dx =
Review For the Final: Problem 1 Find the general solutions of the following DEs. a) x 2 y xy y 2 = 0 solution: y y x y2 = 0 : homogeneous equation. x2 v = y dy, y = vx, and x v + x dv dx = v + v2. dx =
MATH1013 Calculus I. Derivatives II (Chap. 3) 1
 MATH1013 Calculus I Derivatives II (Chap. 3) 1 Edmund Y. M. Chiang Department of Mathematics Hong Kong University of Science & Technology October 16, 2013 2013 1 Based on Briggs, Cochran and Gillett: Calculus
MATH1013 Calculus I Derivatives II (Chap. 3) 1 Edmund Y. M. Chiang Department of Mathematics Hong Kong University of Science & Technology October 16, 2013 2013 1 Based on Briggs, Cochran and Gillett: Calculus
MATH 307: Problem Set #3 Solutions
 : Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
: Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I
 Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I Problem 1: (1) [8 points] Draw a direction field for the given differential equation y 0 = t + y. (2) [8 points] Based on the direction field, determine the behavior
Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I Problem 1: (1) [8 points] Draw a direction field for the given differential equation y 0 = t + y. (2) [8 points] Based on the direction field, determine the behavior
Lecture 6, September 1, 2017
 Engineering Mathematics Fall 07 Lecture 6, September, 07 Escape Velocity Suppose we have a planet (or any large near to spherical heavenly body) of radius R and acceleration of gravity at the surface of
Engineering Mathematics Fall 07 Lecture 6, September, 07 Escape Velocity Suppose we have a planet (or any large near to spherical heavenly body) of radius R and acceleration of gravity at the surface of
ODE Homework Solutions of Linear Homogeneous Equations; the Wronskian
 ODE Homework 3 3.. Solutions of Linear Homogeneous Equations; the Wronskian 1. Verify that the functions y 1 (t = e t and y (t = te t are solutions of the differential equation y y + y = 0 Do they constitute
ODE Homework 3 3.. Solutions of Linear Homogeneous Equations; the Wronskian 1. Verify that the functions y 1 (t = e t and y (t = te t are solutions of the differential equation y y + y = 0 Do they constitute
dt 2 roots r = 1 and r =,1, thus the solution is a linear combination of e t and e,t. conditions. We havey(0) = c 1 + c 2 =5=4 and dy (0) = c 1 + c
 MAE 305 Assignment #3 Solutions Problem 9, Page 8 The characteristic equation for d y,y =0isr, = 0. This has two distinct roots r = and r =,, thus the solution is a linear combination of e t and e,t. That
MAE 305 Assignment #3 Solutions Problem 9, Page 8 The characteristic equation for d y,y =0isr, = 0. This has two distinct roots r = and r =,, thus the solution is a linear combination of e t and e,t. That
Lecture 10 - Second order linear differential equations
 Lecture 10 - Second order linear differential equations In the first part of the course, we studied differential equations of the general form: = f(t, y) In other words, is equal to some expression involving
Lecture 10 - Second order linear differential equations In the first part of the course, we studied differential equations of the general form: = f(t, y) In other words, is equal to some expression involving
Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s
 Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth
Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth
Math 23: Differential Equations (Winter 2017) Midterm Exam Solutions
 Math 3: Differential Equations (Winter 017) Midterm Exam Solutions 1. [0 points] or FALSE? You do not need to justify your answer. (a) [3 points] Critical points or equilibrium points for a first order
Math 3: Differential Equations (Winter 017) Midterm Exam Solutions 1. [0 points] or FALSE? You do not need to justify your answer. (a) [3 points] Critical points or equilibrium points for a first order
Differential Equations Class Notes
 Differential Equations Class Notes Dan Wysocki Spring 213 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Classification of Differential Equations 6 2.1 Linear vs. Non-Linear.................................. 7 2.2 Seperable
Differential Equations Class Notes Dan Wysocki Spring 213 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Classification of Differential Equations 6 2.1 Linear vs. Non-Linear.................................. 7 2.2 Seperable
Solutions to Math 53 Math 53 Practice Final
 Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
Math 2a Prac Lectures on Differential Equations
 Math 2a Prac Lectures on Differential Equations Prof. Dinakar Ramakrishnan 272 Sloan, 253-37 Caltech Office Hours: Fridays 4 5 PM Based on notes taken in class by Stephanie Laga, with a few added comments
Math 2a Prac Lectures on Differential Equations Prof. Dinakar Ramakrishnan 272 Sloan, 253-37 Caltech Office Hours: Fridays 4 5 PM Based on notes taken in class by Stephanie Laga, with a few added comments
CALCULUS MATH*2080 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM
 CALCULUS MATH*28 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Sample Final Exam Page of 2 Prof. R.Gentry Print Your Name Student No. SIGNATURE Mark This exam is worth 45% of your final grade. In Part I In Part II In part III In
CALCULUS MATH*28 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Sample Final Exam Page of 2 Prof. R.Gentry Print Your Name Student No. SIGNATURE Mark This exam is worth 45% of your final grade. In Part I In Part II In part III In
for any C, including C = 0, because y = 0 is also a solution: dy
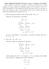 Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
1 In-class part. 1.1 Problems. Practice Final, Math 3350
 Practice Final, Math 3350 1 In-class part The in-class part of the final is 2 1 hours, and will be roughly the size of this practice test. At least 2 one problem from this practice in-class test will appear
Practice Final, Math 3350 1 In-class part The in-class part of the final is 2 1 hours, and will be roughly the size of this practice test. At least 2 one problem from this practice in-class test will appear
2tdt 1 y = t2 + C y = which implies C = 1 and the solution is y = 1
 Lectures - Week 11 General First Order ODEs & Numerical Methods for IVPs In general, nonlinear problems are much more difficult to solve than linear ones. Unfortunately many phenomena exhibit nonlinear
Lectures - Week 11 General First Order ODEs & Numerical Methods for IVPs In general, nonlinear problems are much more difficult to solve than linear ones. Unfortunately many phenomena exhibit nonlinear
Solutions Definition 2: a solution
 Solutions As was stated before, one of the goals in this course is to solve, or find solutions of differential equations. In the next definition we consider the concept of a solution of an ordinary differential
Solutions As was stated before, one of the goals in this course is to solve, or find solutions of differential equations. In the next definition we consider the concept of a solution of an ordinary differential
Math 240 Calculus III
 DE Higher Order Calculus III Summer 2015, Session II Tuesday, July 28, 2015 Agenda DE 1. of order n An example 2. constant-coefficient linear Introduction DE We now turn our attention to solving linear
DE Higher Order Calculus III Summer 2015, Session II Tuesday, July 28, 2015 Agenda DE 1. of order n An example 2. constant-coefficient linear Introduction DE We now turn our attention to solving linear
Introduction to Differential Equations
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Differential Equations 1.1 Basic Terminology Most of the phenomena studied in the sciences and engineering involve processes that change with time. For example, it is well known
Chapter 1 Introduction to Differential Equations 1.1 Basic Terminology Most of the phenomena studied in the sciences and engineering involve processes that change with time. For example, it is well known
Math 31S. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Exam 1
 Math 31S. Rumbos Fall 2011 1 Solutions to Exam 1 1. When people smoke, carbon monoxide is released into the air. Suppose that in a room of volume 60 m 3, air containing 5% carbon monoxide is introduced
Math 31S. Rumbos Fall 2011 1 Solutions to Exam 1 1. When people smoke, carbon monoxide is released into the air. Suppose that in a room of volume 60 m 3, air containing 5% carbon monoxide is introduced
EXAM 3 MAT 167 Calculus I Spring is a composite function of two functions y = e u and u = 4 x + x 2. By the. dy dx = dy du = e u x + 2x.
 EXAM MAT 67 Calculus I Spring 20 Name: Section: I Each answer must include either supporting work or an explanation of your reasoning. These elements are considered to be the main part of each answer and
EXAM MAT 67 Calculus I Spring 20 Name: Section: I Each answer must include either supporting work or an explanation of your reasoning. These elements are considered to be the main part of each answer and
An Overview of Mathematics for Thermodynamics
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Revision 1.1 An Overview of Mathematics for Thermodynamics It is assumed you come to this Physical Chemistry I course with a solid background in Calculus. However, that background
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Revision 1.1 An Overview of Mathematics for Thermodynamics It is assumed you come to this Physical Chemistry I course with a solid background in Calculus. However, that background
Laplace Transform Problems
 AP Calculus BC Name: Laplace Transformation Day 3 2 January 206 Laplace Transform Problems Example problems using the Laplace Transform.. Solve the differential equation y! y = e t, with the initial value
AP Calculus BC Name: Laplace Transformation Day 3 2 January 206 Laplace Transform Problems Example problems using the Laplace Transform.. Solve the differential equation y! y = e t, with the initial value
Applications of First Order Differential Equation
 Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 39 Orthogonal Trajectories How to Find Orthogonal Trajectories Growth and Decay
Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 39 Orthogonal Trajectories How to Find Orthogonal Trajectories Growth and Decay
Math Final Solutions - Spring Jaimos F Skriletz 1
 Math 160 - Final Solutions - Spring 2011 - Jaimos F Skriletz 1 Answer each of the following questions to the best of your ability. To receive full credit, answers must be supported by a sufficient amount
Math 160 - Final Solutions - Spring 2011 - Jaimos F Skriletz 1 Answer each of the following questions to the best of your ability. To receive full credit, answers must be supported by a sufficient amount
MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I February 25, 2016 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
1. Compute the derivatives of the following functions, by any means necessary. f (x) = (1 x3 )(1/2)(x 2 1) 1/2 (2x) x 2 1( 3x 2 ) (1 x 3 ) 2
 Math 51 Exam Nov. 4, 009 SOLUTIONS Directions 1. SHOW YOUR WORK and be thorough in your solutions. Partial credit will only be given for work shown.. Any numerical answers should be left in exact form,
Math 51 Exam Nov. 4, 009 SOLUTIONS Directions 1. SHOW YOUR WORK and be thorough in your solutions. Partial credit will only be given for work shown.. Any numerical answers should be left in exact form,
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Math 201 Solutions to Assignment 1. 2ydy = x 2 dx. y = C 1 3 x3
 Math 201 Solutions to Assignment 1 1. Solve the initial value problem: x 2 dx + 2y = 0, y(0) = 2. x 2 dx + 2y = 0, y(0) = 2 2y = x 2 dx y 2 = 1 3 x3 + C y = C 1 3 x3 Notice that y is not defined for some
Math 201 Solutions to Assignment 1 1. Solve the initial value problem: x 2 dx + 2y = 0, y(0) = 2. x 2 dx + 2y = 0, y(0) = 2 2y = x 2 dx y 2 = 1 3 x3 + C y = C 1 3 x3 Notice that y is not defined for some
MATH 320, WEEK 4: Exact Differential Equations, Applications
 MATH 320, WEEK 4: Exact Differential Equations, Applications 1 Exact Differential Equations We saw that the trick for first-order differential equations was to recognize the general property that the product
MATH 320, WEEK 4: Exact Differential Equations, Applications 1 Exact Differential Equations We saw that the trick for first-order differential equations was to recognize the general property that the product
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Prelim 1 Solutions V2 Math 1120
 Feb., Prelim Solutions V Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Problem ) ( Points) Calculate the following: x a)
Feb., Prelim Solutions V Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Problem ) ( Points) Calculate the following: x a)
Lecture two. January 17, 2019
 Lecture two January 17, 2019 We will learn how to solve rst-order linear equations in this lecture. Example 1. 1) Find all solutions satisfy the equation u x (x, y) = 0. 2) Find the solution if we know
Lecture two January 17, 2019 We will learn how to solve rst-order linear equations in this lecture. Example 1. 1) Find all solutions satisfy the equation u x (x, y) = 0. 2) Find the solution if we know
6.5 Separable Differential Equations and Exponential Growth
 6.5 2 6.5 Separable Differential Equations and Exponential Growth The Law of Exponential Change It is well known that when modeling certain quantities, the quantity increases or decreases at a rate proportional
6.5 2 6.5 Separable Differential Equations and Exponential Growth The Law of Exponential Change It is well known that when modeling certain quantities, the quantity increases or decreases at a rate proportional
The Basics of Physics with Calculus Part II. AP Physics C
 The Basics of Physics with Calculus Part II AP Physics C The AREA We have learned that the rate of change of displacement is defined as the VELOCITY of an object. Consider the graph below v v t lim 0 dx
The Basics of Physics with Calculus Part II AP Physics C The AREA We have learned that the rate of change of displacement is defined as the VELOCITY of an object. Consider the graph below v v t lim 0 dx
Midterm 1 Solutions Thursday, February 26
 Math 59 Dr. DeTurck Midterm 1 Solutions Thursday, February 26 1. First note that since f() = f( + ) = f()f(), we have either f() = (in which case f(x) = f(x + ) = f(x)f() = for all x, so c = ) or else
Math 59 Dr. DeTurck Midterm 1 Solutions Thursday, February 26 1. First note that since f() = f( + ) = f()f(), we have either f() = (in which case f(x) = f(x + ) = f(x)f() = for all x, so c = ) or else
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 6
 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 6 Today: 3.2 Differentiation Rules; 3.3 Derivatives of higher order. 3.4 Related rates 3.5 Chain Rule 3.6 Derivative of Trig. Functions Next: 3.7 Implicit Differentiation 4.10
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 6 Today: 3.2 Differentiation Rules; 3.3 Derivatives of higher order. 3.4 Related rates 3.5 Chain Rule 3.6 Derivative of Trig. Functions Next: 3.7 Implicit Differentiation 4.10
Study guide - Math 220
 Study guide - Math 220 November 28, 2012 1 Exam I 1.1 Linear Equations An equation is linear, if in the form y + p(t)y = q(t). Introducing the integrating factor µ(t) = e p(t)dt the solutions is then in
Study guide - Math 220 November 28, 2012 1 Exam I 1.1 Linear Equations An equation is linear, if in the form y + p(t)y = q(t). Introducing the integrating factor µ(t) = e p(t)dt the solutions is then in
Math 392 Exam 1 Solutions Fall (10 pts) Find the general solution to the differential equation dy dt = 1
 Math 392 Exam 1 Solutions Fall 20104 1. (10 pts) Find the general solution to the differential equation = 1 y 2 t + 4ty = 1 t(y 2 + 4y). Hence (y 2 + 4y) = t y3 3 + 2y2 = ln t + c. 2. (8 pts) Perform Euler
Math 392 Exam 1 Solutions Fall 20104 1. (10 pts) Find the general solution to the differential equation = 1 y 2 t + 4ty = 1 t(y 2 + 4y). Hence (y 2 + 4y) = t y3 3 + 2y2 = ln t + c. 2. (8 pts) Perform Euler
Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals
 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to use the definition
Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to use the definition
Fundamental Solutions and Green s functions. Simulation Methods in Acoustics
 Fundamental Solutions and Green s functions Simulation Methods in Acoustics Definitions Fundamental solution The solution F (x, x 0 ) of the linear PDE L {F (x, x 0 )} = δ(x x 0 ) x R d Is called the fundamental
Fundamental Solutions and Green s functions Simulation Methods in Acoustics Definitions Fundamental solution The solution F (x, x 0 ) of the linear PDE L {F (x, x 0 )} = δ(x x 0 ) x R d Is called the fundamental
Math 212-Lecture 8. The chain rule with one independent variable
 Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
Math 212-Lecture 8 137: The multivariable chain rule The chain rule with one independent variable w = f(x, y) If the particle is moving along a curve x = x(t), y = y(t), then the values that the particle
sections June 11, 2009
 sections 3.2-3.5 June 11, 2009 Population growth/decay When we model population growth, the simplest model is the exponential (or Malthusian) model. Basic ideas: P = P(t) = population size as a function
sections 3.2-3.5 June 11, 2009 Population growth/decay When we model population growth, the simplest model is the exponential (or Malthusian) model. Basic ideas: P = P(t) = population size as a function
Chapter 6: Functions with severable variables and Partial Derivatives:
 Chapter 6: Functions with severable variables and Partial Derivatives: Functions o several variables: A unction involving more than one variable is called unction with severable variables. Eamples: y (,
Chapter 6: Functions with severable variables and Partial Derivatives: Functions o several variables: A unction involving more than one variable is called unction with severable variables. Eamples: y (,
MAP 2302 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 1
 MAP 2302 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 1 The exam will cover sections 1.2, 1.3, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, and 2.6. All topics from this review sheet or from the suggested exercises are fair game. 1 Give explicit solutions
MAP 2302 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 1 The exam will cover sections 1.2, 1.3, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, and 2.6. All topics from this review sheet or from the suggested exercises are fair game. 1 Give explicit solutions
Chapter 2: First Order ODE 2.4 Examples of such ODE Mo
 Chapter 2: First Order ODE 2.4 Examples of such ODE Models 28 January 2018 First Order ODE Read Only Section! We recall the general form of the First Order DEs (FODE): dy = f (t, y) (1) dt where f (t,
Chapter 2: First Order ODE 2.4 Examples of such ODE Models 28 January 2018 First Order ODE Read Only Section! We recall the general form of the First Order DEs (FODE): dy = f (t, y) (1) dt where f (t,
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems) y + 2y + y cos(x 2 y) = 0, y(0) = 2, y (0) = 4.
 Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
Entrance Exam, Differential Equations April, 7 (Solve exactly 6 out of the 8 problems). Consider the following initial value problem: { y + y + y cos(x y) =, y() = y. Find all the values y such that the
MATH 312 Section 2.4: Exact Differential Equations
 MATH 312 Section 2.4: Exact Differential Equations Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Spring Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Exact Differential Equations 2 Solving an Exact DE 3 Making a DE Exact 4 Conclusion
MATH 312 Section 2.4: Exact Differential Equations Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Spring Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Exact Differential Equations 2 Solving an Exact DE 3 Making a DE Exact 4 Conclusion
Calculus IV - HW 3. Due 7/ Give the general solution to the following differential equations: y = c 1 e 5t + c 2 e 5t. y = c 1 e 2t + c 2 e 4t.
 Calculus IV - HW 3 Due 7/13 Section 3.1 1. Give the general solution to the following differential equations: a y 25y = 0 Solution: The characteristic equation is r 2 25 = r 5r + 5. It follows that the
Calculus IV - HW 3 Due 7/13 Section 3.1 1. Give the general solution to the following differential equations: a y 25y = 0 Solution: The characteristic equation is r 2 25 = r 5r + 5. It follows that the
At time t 0, the velocity of a body moving along the horizontal s-axis is v = t 2 4t + 3.
 Section 3.4 The Derivative as a Rate of Change: Derivative measures the rate of change of a dependent variable to independent variable. If s=f(t) is the function of an object showing the position of the
Section 3.4 The Derivative as a Rate of Change: Derivative measures the rate of change of a dependent variable to independent variable. If s=f(t) is the function of an object showing the position of the
3. Solutions of first order linear ODEs
 10 3. Solutions of first order linear ODEs 3.1. The homogeneous equation and its solutions. A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: (1) ẋ + p(t)x = 0. Homogeneous linear
10 3. Solutions of first order linear ODEs 3.1. The homogeneous equation and its solutions. A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: (1) ẋ + p(t)x = 0. Homogeneous linear
SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I
 SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I First Order differential equations Lecturer: Dr. Philip Ngare (Contacts: pngare@uonbi.ac.ke, Tue 12-2 PM) School of Mathematics, University of Nairobi Feb 26,
SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I First Order differential equations Lecturer: Dr. Philip Ngare (Contacts: pngare@uonbi.ac.ke, Tue 12-2 PM) School of Mathematics, University of Nairobi Feb 26,
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY. MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions
 VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions Directions. This practice test should be used as a study guide, illustrating the concepts that will be emphasized in the
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 2300 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Practice Test 1 Solutions Directions. This practice test should be used as a study guide, illustrating the concepts that will be emphasized in the
Section 9.8 Higher Order Linear Equations
 Section 9.8 Higher Order Linear Equations Key Terms: Higher order linear equations Equivalent linear systems for higher order equations Companion matrix Characteristic polynomial and equation A linear
Section 9.8 Higher Order Linear Equations Key Terms: Higher order linear equations Equivalent linear systems for higher order equations Companion matrix Characteristic polynomial and equation A linear
Basic Theory of Differential Equations
 page 104 104 CHAPTER 1 First-Order Differential Equations 16. The following initial-value problem arises in the analysis of a cable suspended between two fixed points y = 1 a 1 + (y ) 2, y(0) = a, y (0)
page 104 104 CHAPTER 1 First-Order Differential Equations 16. The following initial-value problem arises in the analysis of a cable suspended between two fixed points y = 1 a 1 + (y ) 2, y(0) = a, y (0)
21-256: Partial differentiation
 21-256: Partial differentiation Clive Newstead, Thursday 5th June 2014 This is a summary of the important results about partial derivatives and the chain rule that you should know. Partial derivatives
21-256: Partial differentiation Clive Newstead, Thursday 5th June 2014 This is a summary of the important results about partial derivatives and the chain rule that you should know. Partial derivatives
