E8 TCP. Politecnico di Milano Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
|
|
|
- Scarlett Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E8 TP Politecnico di Milano Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione
2 Exercises o onsider the connection in the figure A =80 kbit/s τ =0 ms R =? τ =? B o o o Host A wants to know the capacity and propagation delay of link and to this purpose sends to host B two echo messages: M length l=000 [byte], and Mlength l=500 [byte]; for each of them it measures the Round-Trip-Time (RTT) equal to 780 [ms] and 30 [ms] respectively. In the replies, B uses the same message lengths. alculate and τ assuming header legths negligible.
3 Solution R A B =80 kbit/s τ =0 ms =? τ =? = = τ τ τ τ m m RTT m m RTT
4 Solution A =80 Kbit/s τ =0ms R =? τ =? B = = τ = τ + τ = τ
5 Solution A =80 kbit/s τ =0ms R =? τ =? B τ = τ = = = = kbit/s = 30 ms 8000 = ;
6 Exercises o onsider the network in the figure where links are biderectional and with the same rate in both directions A τ R τ 3 o Between A and B a TP connection is active and already with a stable rate. o Assume MSS=50 [byte] and RVWND small than WND and equal to 4 segments R 3 τ 3 B
7 Exercises o alculate the time necessary to transfer a sequence of 04 [kbit] coming form upper layer (from transmission of first segment to reception of the last AK). Assume n Length Header IP: HIP n Length Header TP: HTP n Length Header lower layers: HLL n No error n No interfering traffic n AK length negligible o Which is the value of the window that would allow a continuous transmission on link?
8 Solution o 04 [kbit] are equal to 3000 [byte] and to 5 segments of 50 [byte] (MSS) o Each packet on the link has a total length of n L=MSS+ HIP + HTP + HLL
9 Solution a) RTT = L + L L τ + + τ τ 3 If L 4 RTT L Ttot = (5 / 4) RTT + (4 ) = 3RTT + 3 L
10 Solution a) Otherwise transmission is continuous: 5 5 Ttot = 5 L + RTT
11 Solution 3 b) The minimum value of the window that allows continuous transmission can be calculated forcing RTT to be smaller that the transmission time of the window: RTT w L w L L L L + τ τ τ 3 = 3 5 5
12 Exercises 3 o onsider the connection in the figure between two hosts A and B. A has to transfer a sequence of 00 segments of maximum length using TP. alculate the time necessary assuming: n MSS=000 [bit] n Header lengths at all layers negligible n onnection is open by A and the length of control packets for connection setup is negligible n AK length neglible n SSTHRESH equal to 5 MSS
13 Solution 3 o T=000 [bit] / [Mb/s] = [ms] o RTT = 6. [ms] + T = 7. [ms] o Transmission is discontinuous until WT < RTT, so until W=8 MSS MSS 4 MSS 5 MSS 6 MSS 7 MSS TX continuous T transfer = 6.[ms] + 6 RTT + 75 T + 6. [ms] Set up First 5 MSS Last 75 MSS =30.6 [ms] AK last MSS
14 Exercises 4 o At time 0 a TP connection between host A and l host B is activated. alculate the time when transmission on link becomes continuous assuming n Header lengths negligible n Bidirectional and symmetric links n RWND = 4000 [byte] and SSTHRESH = 400 [byte] n MSS = 00 [byte] n AK size = setup control packet size = 0 [byte] n onnection open by host A o How much time does it takes to transfer a file of [kbyte] (from connection setup to reception of last AK)? (Note that: byte = 8 bit, kbyte= 000 byte = 8000 bit) A =5 Kb/s τ =5ms R =50 Kb/s τ =5ms R 3 =00 Kb/s τ 3 =5ms B
15 Solution 4 o o o o We have: n T =00 x 8 [bit] / 5 [kbit/s] =64 ms, T =½ T =3 ms, T 3 = ½ T = 6 ms n RTT= T + T +T 3 + (τ +τ +τ 3 )+ (Tack + Tack + Tack3) = 3.ms n T setup = (Tack + Tack + Tack3) + (τ +τ +τ 3 ) =.4 ms Link is the bottleneck and transmission is continuous when: n WT > RTT so n W > RTT/ T =3,3 The time transmission becomes continuous is n T c = T setup + 3 RTT =.4 [ms] [ms] = 75 [ms]
16 Solution 4 o File to transfer is [kbyte], equal to 0 MSS. o The time necessary is: n T c = T setup + 4 RTT + 3 T =.5 [s] ongestion avoidance 4 MSS
17 Exercises 5 o o o A TP connection is used to transfer a file of 39.5 [kbyte] using the following parameters: n MSS=500 [byte] n RTT = 500 [ms] n timeout T = *RTT. Assume the initial conditions are: n RWND = [kbyte] n SSTHRESH = 8 [kbyte] n WND = 500 [byte] Assume also that: n There is an error at time 3 [s] (all segments are lost) n At time 4,5 [s] receiver indicates RWND = [kbyte] a) Draw the evolution over time of: n WND n SSTHRESH n RWND b) alculate the time to transfer the file.
18 Solution 5 We have: o # segments = 39,5 [Kbyte] / 500 [byte] = 79 MSS o RWND = [Kbyte] / 500 [byte] = 4 MSS o SSTHRESH = 8 [Kbyte] / 500 [byte] = 6 MSS o Time Out = s
19 Solution RWND TimeOut 0 SSTHRESH MSS WND Secondi o Transfer time T=8.5s
20 Exercises 6 o onsider the following connection A τ R τ B o A has to transfer an application message of M bytes to B using UDP a) Assuming the maximum length of UDP segments is m bytes (data only), and denoting with HLL, HIP, HUDP header length of lower layers, IP and UDP respectively, calculate the time necessary to transfer the message
21 Exercises 6 A τ R τ B b) As in a) but assuming on link is active a layer protocol with ARQ mechanism of stop-and-wait type (AK length negligible)
22 Solution 6 A τ R τ B o # of maximum length segments: M n = m o Length of last segment: l = M M m m
23 Solution 6 A τ R τ B a) Transfer time: if l + h m + h n m + h + l + h l + h + τ + +τ
24 Solution 6 A τ R τ B a) Transfer time: if l + h m + h n m + h m + h l + h + τ + + +τ
25 Solution 6 A τ R τ B b) Transfer time: m + h if m + h τ + m + h m + h + τ τ + l h + + n + + τ
26 Solution 6 A τ R τ B b) Transfer time: n if m + h m + h l + h + τ + m + h l + h + τ + +τ
27 Notations and Measure units o [byte] = 8 [bit] o [kbyte] = 000 [byte] = 8000 [bit] o [Mbyte] = 8 [Mbit] o [ms] = 0-3 [s] o [µs] = 0-6 [s] o [ns] = 0-9 [s]
CSE 123: Computer Networks
 CSE 123: Computer Networks Total points: 40 Homework 1 - Solutions Out: 10/4, Due: 10/11 Solutions 1. Two-dimensional parity Given below is a series of 7 7-bit items of data, with an additional bit each
CSE 123: Computer Networks Total points: 40 Homework 1 - Solutions Out: 10/4, Due: 10/11 Solutions 1. Two-dimensional parity Given below is a series of 7 7-bit items of data, with an additional bit each
Wireless Internet Exercises
 Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
cs/ee/ids 143 Communication Networks
 cs/ee/ids 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Transport Text: Walrand & Parakh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, Caltech Agenda Internetworking n Routing across LANs, layer2-layer3 n DHCP n NAT Transport layer
cs/ee/ids 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Transport Text: Walrand & Parakh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, Caltech Agenda Internetworking n Routing across LANs, layer2-layer3 n DHCP n NAT Transport layer
Computer Networks ( Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions)
 Computer Networks ( Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions). Concept Of Layering 0. Ans: (b) Sol: Data Link Layer is responsible for decoding bit stream into frames. 0. Ans: (c) Sol: Network Layer has the
Computer Networks ( Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions). Concept Of Layering 0. Ans: (b) Sol: Data Link Layer is responsible for decoding bit stream into frames. 0. Ans: (c) Sol: Network Layer has the
PIQI-RCP: Design and Analysis of Rate-Based Explicit Congestion Control
 PIQI-RCP: Design and Analysis of Rate-Based Explicit Congestion Control Saurabh Jain Joint work with Dr. Dmitri Loguinov June 21, 2007 1 Agenda Introduction Analysis of RCP QI-RCP PIQI-RCP Comparison Wrap
PIQI-RCP: Design and Analysis of Rate-Based Explicit Congestion Control Saurabh Jain Joint work with Dr. Dmitri Loguinov June 21, 2007 1 Agenda Introduction Analysis of RCP QI-RCP PIQI-RCP Comparison Wrap
Leopold Franzens University Innsbruck. Responding to Spurious Loss Events in TCP/IP. Master Thesis. Institute of Computer Science
 Leopold Franzens University Innsbruck Institute of Computer Science Distributed and Parallel Systems Group Responding to Spurious Loss Events in TCP/IP Master Thesis Supervisor: Dr. Michael Welzl Author:
Leopold Franzens University Innsbruck Institute of Computer Science Distributed and Parallel Systems Group Responding to Spurious Loss Events in TCP/IP Master Thesis Supervisor: Dr. Michael Welzl Author:
Reliable Data Transport: Sliding Windows
 Reliable Data Transport: Sliding Windows 6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture 23 Exclusive! A Brief History of the Internet guest lecture by Prof. Hari Balakrishnan Wenesday December 4, 2013, usual 6.02 lecture time
Reliable Data Transport: Sliding Windows 6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture 23 Exclusive! A Brief History of the Internet guest lecture by Prof. Hari Balakrishnan Wenesday December 4, 2013, usual 6.02 lecture time
Min Congestion Control for High- Speed Heterogeneous Networks. JetMax: Scalable Max-Min
 JetMax: Scalable Max-Min Min Congestion Control for High- Speed Heterogeneous Networks Yueping Zhang Joint work with Derek Leonard and Dmitri Loguinov Internet Research Lab Department of Computer Science
JetMax: Scalable Max-Min Min Congestion Control for High- Speed Heterogeneous Networks Yueping Zhang Joint work with Derek Leonard and Dmitri Loguinov Internet Research Lab Department of Computer Science
A Mathematical Model of the Skype VoIP Congestion Control Algorithm
 A Mathematical Model of the Skype VoIP Congestion Control Algorithm Luca De Cicco, S. Mascolo, V. Palmisano Dipartimento di Elettrotecnica ed Elettronica, Politecnico di Bari 47th IEEE Conference on Decision
A Mathematical Model of the Skype VoIP Congestion Control Algorithm Luca De Cicco, S. Mascolo, V. Palmisano Dipartimento di Elettrotecnica ed Elettronica, Politecnico di Bari 47th IEEE Conference on Decision
Concise Paper: Deconstructing MPTCP Performance
 04 IEEE nd International Conference on Network Protocols Concise Paper: Deconstructing MPTCP Performance Behnaz Arzani, Alexander Gurney, Sitian Cheng, Roch Guerin and Boon Thau Loo University Of Pennsylvania
04 IEEE nd International Conference on Network Protocols Concise Paper: Deconstructing MPTCP Performance Behnaz Arzani, Alexander Gurney, Sitian Cheng, Roch Guerin and Boon Thau Loo University Of Pennsylvania
Modelling Packet Delay in Ethernet and IP Networks
 Modelling Packet Delay in Ethernet and IP Networks Dominik Schneuwly Dr. André Vallat Slide 1.1 Introduction Is it possible to transfer time and frequency over packet switched networks with accuracies
Modelling Packet Delay in Ethernet and IP Networks Dominik Schneuwly Dr. André Vallat Slide 1.1 Introduction Is it possible to transfer time and frequency over packet switched networks with accuracies
Modeling and Simulation NETW 707
 Modeling and Simulation NETW 707 Lecture 6 ARQ Modeling: Modeling Error/Flow Control Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides
Modeling and Simulation NETW 707 Lecture 6 ARQ Modeling: Modeling Error/Flow Control Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides
TCP over Cognitive Radio Channels
 1/43 TCP over Cognitive Radio Channels Sudheer Poojary Department of ECE, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore IEEE-IISc I-YES seminar 19 May 2016 2/43 Acknowledgments The work presented here was done
1/43 TCP over Cognitive Radio Channels Sudheer Poojary Department of ECE, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore IEEE-IISc I-YES seminar 19 May 2016 2/43 Acknowledgments The work presented here was done
IEEE abc-01/22r1
 Project IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group Title An ARQ proposal for consideration by TG3/4 MAC group Date Submitted 2001-08 -31 Source(s) Yigal Leiba Itzik Kitroser
Project IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group Title An ARQ proposal for consideration by TG3/4 MAC group Date Submitted 2001-08 -31 Source(s) Yigal Leiba Itzik Kitroser
Impact of Cross Traffic Burstiness on the Packet-scale Paradigm An Extended Analysis
 Impact of ross Traffic Burstiness on the Packet-scale Paradigm An Extended Analysis Rebecca Lovewell and Jasleen Kaur Technical Report # TR11-007 Department of omputer Science University of North arolina
Impact of ross Traffic Burstiness on the Packet-scale Paradigm An Extended Analysis Rebecca Lovewell and Jasleen Kaur Technical Report # TR11-007 Department of omputer Science University of North arolina
A Stochastic Model for TCP with Stationary Random Losses
 A Stochastic Model for TCP with Stationary Random Losses Eitan Altman, Kostya Avrachenkov Chadi Barakat INRIA Sophia Antipolis - France ACM SIGCOMM August 31, 2000 Stockholm, Sweden Introduction Outline
A Stochastic Model for TCP with Stationary Random Losses Eitan Altman, Kostya Avrachenkov Chadi Barakat INRIA Sophia Antipolis - France ACM SIGCOMM August 31, 2000 Stockholm, Sweden Introduction Outline
Advanced Topicson Network Socket Programming
 Advanced Topics on Network Socket Programming Computer Science Department, University of Crete Manolis Surligas surligas@csduocgr October 18, 2017 Manolis Surligas (CSD, UoC) Advanced Topicson Network
Advanced Topics on Network Socket Programming Computer Science Department, University of Crete Manolis Surligas surligas@csduocgr October 18, 2017 Manolis Surligas (CSD, UoC) Advanced Topicson Network
Socket Programming. Daniel Zappala. CS 360 Internet Programming Brigham Young University
 Socket Programming Daniel Zappala CS 360 Internet Programming Brigham Young University Sockets, Addresses, Ports Clients and Servers 3/33 clients request a service from a server using a protocol need an
Socket Programming Daniel Zappala CS 360 Internet Programming Brigham Young University Sockets, Addresses, Ports Clients and Servers 3/33 clients request a service from a server using a protocol need an
Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales. Rolf Riedi
 Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales Rolf Riedi Dept of Statistics Stochastic Systems and Modelling in Networking and Finance Part II Dependable Adaptive Systems and Mathematical Modeling Kaiserslautern,
Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales Rolf Riedi Dept of Statistics Stochastic Systems and Modelling in Networking and Finance Part II Dependable Adaptive Systems and Mathematical Modeling Kaiserslautern,
A Quantitative View: Delay, Throughput, Loss
 A Quantitative View: Delay, Throughput, Loss Antonio Carzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano September 27, 2017 Outline Quantitative analysis of data transfer concepts for network applications
A Quantitative View: Delay, Throughput, Loss Antonio Carzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano September 27, 2017 Outline Quantitative analysis of data transfer concepts for network applications
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Processor Sharing Flows in the Internet
 STANFORD HPNG TECHNICAL REPORT TR4-HPNG4 Processor Sharing Flows in the Internet Nandita Dukkipati, Nick McKeown Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 9434-93, USA nanditad, nickm
STANFORD HPNG TECHNICAL REPORT TR4-HPNG4 Processor Sharing Flows in the Internet Nandita Dukkipati, Nick McKeown Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 9434-93, USA nanditad, nickm
Lan Performance LAB Ethernet : CSMA/CD TOKEN RING: TOKEN
 Lan Performance LAB Ethernet : CSMA/CD TOKEN RING: TOKEN Ethernet Frame Format 7 b y te s 1 b y te 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 b y te s 4-1 5 0 0 b y te s 4 b y te s P r e a m b le S ta r t F r
Lan Performance LAB Ethernet : CSMA/CD TOKEN RING: TOKEN Ethernet Frame Format 7 b y te s 1 b y te 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 b y te s 4-1 5 0 0 b y te s 4 b y te s P r e a m b le S ta r t F r
Rate adaptation, Congestion Control and Fairness: A Tutorial. JEAN-YVES LE BOUDEC Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)
 Rate adaptation, Congestion Control and Fairness: A Tutorial JEAN-YVES LE BOUDEC Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) December 2000 2 Contents 31 Congestion Control for Best Effort: Theory 1
Rate adaptation, Congestion Control and Fairness: A Tutorial JEAN-YVES LE BOUDEC Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) December 2000 2 Contents 31 Congestion Control for Best Effort: Theory 1
A Globally Stable Adaptive Congestion Control Scheme for Internet-Style Networks with Delay 1
 A Globally Stable Adaptive ongestion ontrol Scheme for Internet-Style Networks with Delay Tansu Alpcan 2 and Tamer Başar 2 (alpcan, tbasar)@control.csl.uiuc.edu Abstract In this paper, we develop, analyze
A Globally Stable Adaptive ongestion ontrol Scheme for Internet-Style Networks with Delay Tansu Alpcan 2 and Tamer Başar 2 (alpcan, tbasar)@control.csl.uiuc.edu Abstract In this paper, we develop, analyze
Stability Analysis of TCP/RED Communication Algorithms
 Stability Analysis of TCP/RED Communication Algorithms Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada ljilja@cs.sfu.ca http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/~ljilja Collaborators Mingjian Liu and Hui Zhang
Stability Analysis of TCP/RED Communication Algorithms Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada ljilja@cs.sfu.ca http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/~ljilja Collaborators Mingjian Liu and Hui Zhang
Stability Analysis of TCP/RED Communication Algorithms
 Stability Analysis of TCP/RED Communication Algorithms Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada ljilja@cs.sfu.ca http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/~ljilja Collaborators Mingjian Liu and Hui Zhang
Stability Analysis of TCP/RED Communication Algorithms Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada ljilja@cs.sfu.ca http://www.ensc.sfu.ca/~ljilja Collaborators Mingjian Liu and Hui Zhang
Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers
 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 8, Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers Ashvin Lakshmikantha Coordinated Science Lab
Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 8, Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers Ashvin Lakshmikantha Coordinated Science Lab
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
WiFi MAC Models David Malone
 WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
Analysis of random-access MAC schemes
 Analysis of random-access MA schemes M. Veeraraghavan and Tao i ast updated: Sept. 203. Slotted Aloha [4] First-order analysis: if we assume there are infinite number of nodes, the number of new arrivals
Analysis of random-access MA schemes M. Veeraraghavan and Tao i ast updated: Sept. 203. Slotted Aloha [4] First-order analysis: if we assume there are infinite number of nodes, the number of new arrivals
A New TCP/AQM System Analysis
 A ew TCP/AQM System Analysis Qin Xu, Fan Li, Jinsheng Sun, and Moshe Zukerman, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:37.24v [cs.i] 4 Jul 23 Abstract The fluid model has been used extensively to guide designs of AQM schemes
A ew TCP/AQM System Analysis Qin Xu, Fan Li, Jinsheng Sun, and Moshe Zukerman, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:37.24v [cs.i] 4 Jul 23 Abstract The fluid model has been used extensively to guide designs of AQM schemes
Analysis of TCP Westwood+ in high speed networks
 Analysis of TCP Westwood+ in high speed networks 1 E. Altman, C. Barakat, S. Mascolo, N. Möller and J. Sun Abstract TCP Westwood+ is modelled and analyzed using stochastic recursive equations. It is shown
Analysis of TCP Westwood+ in high speed networks 1 E. Altman, C. Barakat, S. Mascolo, N. Möller and J. Sun Abstract TCP Westwood+ is modelled and analyzed using stochastic recursive equations. It is shown
CS276 Homework 1: ns-2
 CS276 Homework 1: ns-2 Erik Peterson October 28, 2006 1 Part 1 - Fairness between TCP variants 1.1 Method After learning ns-2, I wrote a script (Listing 3) that runs a simulation of one or two tcp flows
CS276 Homework 1: ns-2 Erik Peterson October 28, 2006 1 Part 1 - Fairness between TCP variants 1.1 Method After learning ns-2, I wrote a script (Listing 3) that runs a simulation of one or two tcp flows
Chapter 5. Elementary Performance Analysis
 Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
Networked Control Systems
 Networked Control Systems Simulation & Analysis J.J.C. van Schendel DCT 2008.119 Traineeship report March till June 2008 Coaches: Supervisor TU/e: Prof. Dr. D. Nesic, University of Melbourne Dr. M. Tabbara,
Networked Control Systems Simulation & Analysis J.J.C. van Schendel DCT 2008.119 Traineeship report March till June 2008 Coaches: Supervisor TU/e: Prof. Dr. D. Nesic, University of Melbourne Dr. M. Tabbara,
Modeling Impact of Delay Spikes on TCP Performance on a Low Bandwidth Link
 Modeling Impact of Delay Spikes on TCP Performance on a Low Bandwidth Link Pasi Lassila and Pirkko Kuusela Networking Laboratory Helsinki University of Technology (HUT) Espoo, Finland Email: {Pasi.Lassila,Pirkko.Kuusela
Modeling Impact of Delay Spikes on TCP Performance on a Low Bandwidth Link Pasi Lassila and Pirkko Kuusela Networking Laboratory Helsinki University of Technology (HUT) Espoo, Finland Email: {Pasi.Lassila,Pirkko.Kuusela
Tuning the TCP Timeout Mechanism in Wireless Networks to Maximize Throughput via Stochastic Stopping Time Methods
 Tuning the TCP Timeout Mechanism in Wireless Networks to Maximize Throughput via Stochastic Stopping Time Methods George Papageorgiou and John S. Baras Abstract We present an optimization problem that
Tuning the TCP Timeout Mechanism in Wireless Networks to Maximize Throughput via Stochastic Stopping Time Methods George Papageorgiou and John S. Baras Abstract We present an optimization problem that
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 1: Theory. JY Le Boudec 2018
 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 1: Theory JY Le Boudec 2018 1 Contents 1. What is the problem; congestion collapse 2. Efficiency versus Fairness 3. Definitions of fairness 4. Additive Increase
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 1: Theory JY Le Boudec 2018 1 Contents 1. What is the problem; congestion collapse 2. Efficiency versus Fairness 3. Definitions of fairness 4. Additive Increase
Modelling an Isolated Compound TCP Connection
 Modelling an Isolated Compound TCP Connection Alberto Blanc and Denis Collange Orange Labs 905 rue Albert Einstein Sophia Antipolis, France {Email: alberto.blanc,denis.collange}@orange-ftgroup.com Konstantin
Modelling an Isolated Compound TCP Connection Alberto Blanc and Denis Collange Orange Labs 905 rue Albert Einstein Sophia Antipolis, France {Email: alberto.blanc,denis.collange}@orange-ftgroup.com Konstantin
Window Size. Window Size. Window Size. Time. Time. Time
 A Spectrum of TCP-friendly Window-based Congestion Control Algorithms Λ Shudong Jin Liang Guo Ibrahim Matta Azer Bestavros Computer Science Department Boston University Boston, MA 5 fjins, guol, matta,
A Spectrum of TCP-friendly Window-based Congestion Control Algorithms Λ Shudong Jin Liang Guo Ibrahim Matta Azer Bestavros Computer Science Department Boston University Boston, MA 5 fjins, guol, matta,
These are special traffic patterns that create more stress on a switch
 Myths about Microbursts What are Microbursts? Microbursts are traffic patterns where traffic arrives in small bursts. While almost all network traffic is bursty to some extent, storage traffic usually
Myths about Microbursts What are Microbursts? Microbursts are traffic patterns where traffic arrives in small bursts. While almost all network traffic is bursty to some extent, storage traffic usually
FLAME Flexible Lightweight Active Measurement Environment
 FLAME Flexible Lightweight Active Measurement Environment Marcos L. Kirszenblatt Thiago B. Cardozo Artur Ziviani Antônio Tadeu A. Gomes National Laboratory for Scientific Computing (LNCC) {marcoslk,thiagoc,ziviani,atagomes}@lncc.br
FLAME Flexible Lightweight Active Measurement Environment Marcos L. Kirszenblatt Thiago B. Cardozo Artur Ziviani Antônio Tadeu A. Gomes National Laboratory for Scientific Computing (LNCC) {marcoslk,thiagoc,ziviani,atagomes}@lncc.br
Time. Lakshmi Ganesh. (slides borrowed from Maya Haridasan, Michael George)
 Time Lakshmi Ganesh (slides borrowed from Maya Haridasan, Michael George) The Problem Given a collection of processes that can... only communicate with significant latency only measure time intervals approximately
Time Lakshmi Ganesh (slides borrowed from Maya Haridasan, Michael George) The Problem Given a collection of processes that can... only communicate with significant latency only measure time intervals approximately
Markovian Model of Internetworking Flow Control
 Информационные процессы, Том 2, 2, 2002, стр. 149 154. c 2002 Bogoiavlenskaia. KALASHNIKOV MEMORIAL SEMINAR Markovian Model of Internetworking Flow Control O. Bogoiavlenskaia Petrozavodsk State University
Информационные процессы, Том 2, 2, 2002, стр. 149 154. c 2002 Bogoiavlenskaia. KALASHNIKOV MEMORIAL SEMINAR Markovian Model of Internetworking Flow Control O. Bogoiavlenskaia Petrozavodsk State University
Modelling TCP with a Discrete Time Markov Chain
 Modelling TCP with a Discrete Time Markov Chain José L Gil Motorola josegil@motorola.com ABSTRACT TCP is the most widely used transport protocol in the Internet. The end-to-end performance of most Internet
Modelling TCP with a Discrete Time Markov Chain José L Gil Motorola josegil@motorola.com ABSTRACT TCP is the most widely used transport protocol in the Internet. The end-to-end performance of most Internet
Appendix A Prototypes Models
 Appendix A Prototypes Models This appendix describes the model of the prototypes used in Chap. 3. These mathematical models can also be found in the Student Handout by Quanser. A.1 The QUANSER SRV-02 Setup
Appendix A Prototypes Models This appendix describes the model of the prototypes used in Chap. 3. These mathematical models can also be found in the Student Handout by Quanser. A.1 The QUANSER SRV-02 Setup
Analysis on Packet Resequencing for Reliable Network Protocols
 1 Analysis on Packet Resequencing for Reliable Network Protocols Ye Xia David Tse Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California, Berkeley Abstract Protocols such as
1 Analysis on Packet Resequencing for Reliable Network Protocols Ye Xia David Tse Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California, Berkeley Abstract Protocols such as
Internet Measurement and Data Analysis (7)
 Internet Measurement and Data Analysis (7) Kenjiro Cho 2012-11-14 review of previous class Class 6 Correlation (11/7) Online recommendation systems Distance Correlation coefficient exercise: correlation
Internet Measurement and Data Analysis (7) Kenjiro Cho 2012-11-14 review of previous class Class 6 Correlation (11/7) Online recommendation systems Distance Correlation coefficient exercise: correlation
Unreliable Failure Detectors for Reliable Distributed Systems
 Unreliable Failure Detectors for Reliable Distributed Systems A different approach Augment the asynchronous model with an unreliable failure detector for crash failures Define failure detectors in terms
Unreliable Failure Detectors for Reliable Distributed Systems A different approach Augment the asynchronous model with an unreliable failure detector for crash failures Define failure detectors in terms
Application of Link Layer FEC to DVB-S2 for Railway Scenarios
 Application of Link Layer FEC to DVB-S2 for Railway Scenarios Jiang Lei, M.Angeles. Vázquez Castro, Fausto Vieira Dpt. Telecom. and Systems Engineering Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona Barcelona, Spain
Application of Link Layer FEC to DVB-S2 for Railway Scenarios Jiang Lei, M.Angeles. Vázquez Castro, Fausto Vieira Dpt. Telecom. and Systems Engineering Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona Barcelona, Spain
Analysis of Scalable TCP in the presence of Markovian Losses
 Analysis of Scalable TCP in the presence of Markovian Losses E Altman K E Avrachenkov A A Kherani BJ Prabhu INRIA Sophia Antipolis 06902 Sophia Antipolis, France Email:altman,kavratchenkov,alam,bprabhu}@sophiainriafr
Analysis of Scalable TCP in the presence of Markovian Losses E Altman K E Avrachenkov A A Kherani BJ Prabhu INRIA Sophia Antipolis 06902 Sophia Antipolis, France Email:altman,kavratchenkov,alam,bprabhu}@sophiainriafr
IN THIS PAPER, we describe a design oriented modelling
 616 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL 14, NO 3, JUNE 2006 A Positive Systems Model of TCP-Like Congestion Control: Asymptotic Results Robert Shorten, Fabian Wirth, and Douglas Leith Abstract We
616 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL 14, NO 3, JUNE 2006 A Positive Systems Model of TCP-Like Congestion Control: Asymptotic Results Robert Shorten, Fabian Wirth, and Douglas Leith Abstract We
A Stochastic Model of TCP/IP with Stationary Random Losses
 1 A Stochastic Model of TCP/IP with Stationary Random Losses Eitan Altman, Konstantin Avrachenkov, Chadi Barakat INRIA, 24 route des Lucioles, 692 Sophia Antipolis, France Email:{altman,kavratch,cbarakat}@sophiainriafr
1 A Stochastic Model of TCP/IP with Stationary Random Losses Eitan Altman, Konstantin Avrachenkov, Chadi Barakat INRIA, 24 route des Lucioles, 692 Sophia Antipolis, France Email:{altman,kavratch,cbarakat}@sophiainriafr
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
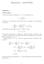 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Communications and Signal Processing Spring 2017 MSE Exam
 Communications and Signal Processing Spring 2017 MSE Exam Please obtain your Test ID from the following table. You must write your Test ID and name on each of the pages of this exam. A page with missing
Communications and Signal Processing Spring 2017 MSE Exam Please obtain your Test ID from the following table. You must write your Test ID and name on each of the pages of this exam. A page with missing
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
Congestion Control. Topics
 Congestion Control Topics Congestion control what & why? Current congestion control algorithms TCP and UDP Ideal congestion control Resource allocation Distributed algorithms Relation current algorithms
Congestion Control Topics Congestion control what & why? Current congestion control algorithms TCP and UDP Ideal congestion control Resource allocation Distributed algorithms Relation current algorithms
Performance analysis of IEEE WLANs with saturated and unsaturated sources
 Performance analysis of IEEE 82.11 WLANs with saturated and unsaturated sources Suong H. Nguyen, Hai L. Vu, Lachlan L. H. Andrew Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures, Technical Report 11811A Swinburne
Performance analysis of IEEE 82.11 WLANs with saturated and unsaturated sources Suong H. Nguyen, Hai L. Vu, Lachlan L. H. Andrew Centre for Advanced Internet Architectures, Technical Report 11811A Swinburne
A model-based approach to control over packet-switching networks, with application to Industrial Ethernet
 A model-based approach to control over packet-switching networks, with application to Industrial Ethernet Universitá di Pisa Centro di Ricerca Interdipartimentale E. Piaggio Laurea specialistica in Ingegneria
A model-based approach to control over packet-switching networks, with application to Industrial Ethernet Universitá di Pisa Centro di Ricerca Interdipartimentale E. Piaggio Laurea specialistica in Ingegneria
Service differentiation without prioritization in IEEE WLANs
 Service differentiation without prioritization in IEEE 8. WLANs Suong H. Nguyen, Student Member, IEEE, Hai L. Vu, Senior Member, IEEE, and Lachlan L. H. Andrew, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Wireless LANs
Service differentiation without prioritization in IEEE 8. WLANs Suong H. Nguyen, Student Member, IEEE, Hai L. Vu, Senior Member, IEEE, and Lachlan L. H. Andrew, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Wireless LANs
Implementation of the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol for Clock Synchronization in the Radio Detection of Ultra-High Energy Neutrinos
 i Implementation of the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol for Clock Synchronization in the Radio Detection of Ultra-High Energy Neutrinos Undergraduate Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment
i Implementation of the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol for Clock Synchronization in the Radio Detection of Ultra-High Energy Neutrinos Undergraduate Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment
Modélisation d une connexion Compound TCP isolée
 INSTITUT NATIONAL DE RECHERCHE EN INFORMATIQUE ET EN AUTOMATIQUE Modélisation d une connexion Compound TCP isolée Alberto Blanc Denis Collange Konstantin Avrachenkov N 6778 Decembre 2008 Thème COM apport
INSTITUT NATIONAL DE RECHERCHE EN INFORMATIQUE ET EN AUTOMATIQUE Modélisation d une connexion Compound TCP isolée Alberto Blanc Denis Collange Konstantin Avrachenkov N 6778 Decembre 2008 Thème COM apport
DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF TCP-LIKE WINDOW CONTROL AND THROUGHPUT PERFORMANCE
 Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan Vol. 41, No. 4, December 1998 1998 The Operations Research Society of Japan DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF TCP-LIKE WINDOW CONTROL AND THROUGHPUT PERFORMANCE Fumio
Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan Vol. 41, No. 4, December 1998 1998 The Operations Research Society of Japan DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR OF TCP-LIKE WINDOW CONTROL AND THROUGHPUT PERFORMANCE Fumio
Electrical Engineering Written PhD Qualifier Exam Spring 2014
 Electrical Engineering Written PhD Qualifier Exam Spring 2014 Friday, February 7 th 2014 Please do not write your name on this page or any other page you submit with your work. Instead use the student
Electrical Engineering Written PhD Qualifier Exam Spring 2014 Friday, February 7 th 2014 Please do not write your name on this page or any other page you submit with your work. Instead use the student
Stochastic Hybrid Systems: Applications to Communication Networks
 research supported by NSF Stochastic Hybrid Systems: Applications to Communication Networks João P. Hespanha Center for Control Engineering and Computation University of California at Santa Barbara Talk
research supported by NSF Stochastic Hybrid Systems: Applications to Communication Networks João P. Hespanha Center for Control Engineering and Computation University of California at Santa Barbara Talk
Compound TCP with Random Losses
 Compound TCP with Random Losses Alberto Blanc 1, Konstantin Avrachenkov 2, Denis Collange 1, and Giovanni Neglia 2 1 Orange Labs, 905 rue Albert Einstein, 06921 Sophia Antipolis, France {alberto.blanc,denis.collange}@orange-ftgroup.com
Compound TCP with Random Losses Alberto Blanc 1, Konstantin Avrachenkov 2, Denis Collange 1, and Giovanni Neglia 2 1 Orange Labs, 905 rue Albert Einstein, 06921 Sophia Antipolis, France {alberto.blanc,denis.collange}@orange-ftgroup.com
Outline. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 18 Error Coding. In the real world. Our beautiful digital world.
 Outline EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 18 Error Coding Errors and error models Parity and Hamming Codes (SECE) Errors in Communications LFSRs Cyclic Redundancy Check
Outline EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 18 Error Coding Errors and error models Parity and Hamming Codes (SECE) Errors in Communications LFSRs Cyclic Redundancy Check
A Utility-Based Congestion Control Scheme for Internet-Style Networks with Delay
 A Utility-Based ongestion ontrol Scheme for Internet-Style Networks with Delay Tansu Alpcan and Tamer Başar (alpcan, tbasar)@control.csl.uiuc.edu Abstract In this paper, we develop, analyze and implement
A Utility-Based ongestion ontrol Scheme for Internet-Style Networks with Delay Tansu Alpcan and Tamer Başar (alpcan, tbasar)@control.csl.uiuc.edu Abstract In this paper, we develop, analyze and implement
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 26 CRCs, LFSRs (and a little power)
 EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 26 CRCs, LFSRs (and a little power) avid Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler
EECS 150 - Components and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 26 CRCs, LFSRs (and a little power) avid Culler Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler
Performance Analysis of the IEEE e Block ACK Scheme in a Noisy Channel
 Performance Analysis of the IEEE 802.11e Block ACK Scheme in a Noisy Channel Tianji Li, Qiang Ni, Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland. Thierry Turletti, Planete Group, INRIA, France. Yang Xiao, University
Performance Analysis of the IEEE 802.11e Block ACK Scheme in a Noisy Channel Tianji Li, Qiang Ni, Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland. Thierry Turletti, Planete Group, INRIA, France. Yang Xiao, University
MPTCP is not Pareto-Optimal: Performance Issues and a Possible Solution
 MPTCP is not Pareto-Optimal: Performance Issues and a Possible Solution Ramin Khalili, Nicolas Gast, Miroslav Popovic, Jean-Yves Le Boudec To cite this version: Ramin Khalili, Nicolas Gast, Miroslav Popovic,
MPTCP is not Pareto-Optimal: Performance Issues and a Possible Solution Ramin Khalili, Nicolas Gast, Miroslav Popovic, Jean-Yves Le Boudec To cite this version: Ramin Khalili, Nicolas Gast, Miroslav Popovic,
Giuseppe Bianchi, Ilenia Tinnirello
 Capacity of WLAN Networs Summary Per-node throughput in case of: Full connected networs each node sees all the others Generic networ topology not all nodes are visible Performance Analysis of single-hop
Capacity of WLAN Networs Summary Per-node throughput in case of: Full connected networs each node sees all the others Generic networ topology not all nodes are visible Performance Analysis of single-hop
Understanding TCP Vegas: A Duality Model
 Understanding TCP Vegas: A Duality Model Steven Low Departments of CS and EE, Caltech, USA slow@caltech.edu Larry Peterson Limin Wang Department of CS, Princeton University, USA {llp,lmwang}@cs.princeton.edu
Understanding TCP Vegas: A Duality Model Steven Low Departments of CS and EE, Caltech, USA slow@caltech.edu Larry Peterson Limin Wang Department of CS, Princeton University, USA {llp,lmwang}@cs.princeton.edu
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
RESEARCH ON THE DISTRIBUTED PARALLEL SPATIAL INDEXING SCHEMA BASED ON R-TREE
 RESEARCH ON THE DISTRIBUTED PARALLEL SPATIAL INDEXING SCHEMA BASED ON R-TREE Yuan-chun Zhao a, b, Cheng-ming Li b a. Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266510 b. Chinese Academy of
RESEARCH ON THE DISTRIBUTED PARALLEL SPATIAL INDEXING SCHEMA BASED ON R-TREE Yuan-chun Zhao a, b, Cheng-ming Li b a. Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266510 b. Chinese Academy of
Design and Analysis of a Propagation Delay Tolerant ALOHA Protocol for Underwater Networks
 Design and Analysis of a Propagation Delay Tolerant ALOHA Protocol for Underwater Networks Joon Ahn a, Affan Syed b, Bhaskar Krishnamachari a, John Heidemann b a Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering,
Design and Analysis of a Propagation Delay Tolerant ALOHA Protocol for Underwater Networks Joon Ahn a, Affan Syed b, Bhaskar Krishnamachari a, John Heidemann b a Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering,
VISY-Quick Communication Protocol
 VISY-Quick Communication Protocol Rev. Protocol Version Modification VI Version Date Name 0 1.00 First release 2.0.1 2000-03-29 Willmer 1 1.10 New commands date and time (3.2... 3.5) 2.0.2 2000-07-07 Willmer
VISY-Quick Communication Protocol Rev. Protocol Version Modification VI Version Date Name 0 1.00 First release 2.0.1 2000-03-29 Willmer 1 1.10 New commands date and time (3.2... 3.5) 2.0.2 2000-07-07 Willmer
Cross-layer Theoretical Analysis of NC-aided. Cooperative ARQ Protocols in Correlated Shadowed Environments (Extended Version)
 Cross-layer Theoretical Analysis of NC-aided Cooperative ARQ Protocols in Correlated Shadowed Environments (Extended Version) Angelos Antonopoulos, Member, IEEE, Aris S. Lalos, Member, IEEE, arxiv:408.609v
Cross-layer Theoretical Analysis of NC-aided Cooperative ARQ Protocols in Correlated Shadowed Environments (Extended Version) Angelos Antonopoulos, Member, IEEE, Aris S. Lalos, Member, IEEE, arxiv:408.609v
Emulating Low-priority Transport at the Application Layer: A Background Transfer Service
 Emulating Low-priority Transport at the Application Layer: A Background Transfer Service Peter Key Microsoft Research Roger Needham Building 7 J J Thomson Avenure Cambridge, CB3 FB, UK peterkey@microsoftcom
Emulating Low-priority Transport at the Application Layer: A Background Transfer Service Peter Key Microsoft Research Roger Needham Building 7 J J Thomson Avenure Cambridge, CB3 FB, UK peterkey@microsoftcom
M C. Analytical Methods for Network Congestion Control. Steven H. Low Engineering & Applied Science, Caltech
 Analytical Methods for Network Congestion Control Steven H. Low Engineering & Applied Science, Caltech SYNTHESIS LECTURES ON COMMUNICATION NETWORKS & M C Morgan & claypool publishers ABSTRACT The congestion
Analytical Methods for Network Congestion Control Steven H. Low Engineering & Applied Science, Caltech SYNTHESIS LECTURES ON COMMUNICATION NETWORKS & M C Morgan & claypool publishers ABSTRACT The congestion
Nonlinear Instabilities in TCP-RED
 Nonlinear Instabilities in TCP-RED Priya Ranjan, Eyad H. Abed and Richard J. La Abstract This work develops a discrete time feedback system model for a simplified TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) network
Nonlinear Instabilities in TCP-RED Priya Ranjan, Eyad H. Abed and Richard J. La Abstract This work develops a discrete time feedback system model for a simplified TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) network
Resource Allocation and Pricing. R. Srikant University of Illinois
 Resource Allocation and Pricing R. Srikant University of Illinois References The Mathematics of Internet Congestion Control, Birkhauser, 2004. Pricing: Kelly Distributed Resource Allocation: Kelly, Mauloo
Resource Allocation and Pricing R. Srikant University of Illinois References The Mathematics of Internet Congestion Control, Birkhauser, 2004. Pricing: Kelly Distributed Resource Allocation: Kelly, Mauloo
DIMENSIONING BANDWIDTH FOR ELASTIC TRAFFIC IN HIGH-SPEED DATA NETWORKS
 Submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on etworking DIMESIOIG BADWIDTH FOR ELASTIC TRAFFIC I HIGH-SPEED DATA ETWORKS Arthur W. Berger * and Yaakov Kogan Abstract Simple and robust engineering rules for dimensioning
Submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on etworking DIMESIOIG BADWIDTH FOR ELASTIC TRAFFIC I HIGH-SPEED DATA ETWORKS Arthur W. Berger * and Yaakov Kogan Abstract Simple and robust engineering rules for dimensioning
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading
 EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
384Y Project June 5, Stability of Congestion Control Algorithms Using Control Theory with an application to XCP
 384Y Project June 5, 00 Stability of Congestion Control Algorithms Using Control Theory with an application to XCP . Introduction During recent years, a lot of work has been done towards the theoretical
384Y Project June 5, 00 Stability of Congestion Control Algorithms Using Control Theory with an application to XCP . Introduction During recent years, a lot of work has been done towards the theoretical
ATM VP-Based Ring Network Exclusive Video or Data Traffics
 ATM VP-Based Ring Network Exclusive Video or Data Traffics In this chapter, the performance characteristic of the proposed ATM VP-Based Ring Network exclusive video or data traffic is studied. The maximum
ATM VP-Based Ring Network Exclusive Video or Data Traffics In this chapter, the performance characteristic of the proposed ATM VP-Based Ring Network exclusive video or data traffic is studied. The maximum
Internet Congestion Control: Equilibrium and Dynamics
 Internet Congestion Control: Equilibrium and Dynamics A. Kevin Tang Cornell University ISS Seminar, Princeton University, February 21, 2008 Networks and Corresponding Theories Power networks (Maxwell Theory)
Internet Congestion Control: Equilibrium and Dynamics A. Kevin Tang Cornell University ISS Seminar, Princeton University, February 21, 2008 Networks and Corresponding Theories Power networks (Maxwell Theory)
The Analysis of Microburst (Burstiness) on Virtual Switch
 The Analysis of Microburst (Burstiness) on Virtual Switch Chunghan Lee Fujitsu Laboratories 09.19.2016 Copyright 2016 FUJITSU LABORATORIES LIMITED Background What is Network Function Virtualization (NFV)?
The Analysis of Microburst (Burstiness) on Virtual Switch Chunghan Lee Fujitsu Laboratories 09.19.2016 Copyright 2016 FUJITSU LABORATORIES LIMITED Background What is Network Function Virtualization (NFV)?
Giuseppe Bianchi, Ilenia Tinnirello
 Capacity of WLAN Networs Summary Ł Ł Ł Ł Arbitrary networ capacity [Gupta & Kumar The Capacity of Wireless Networs ] Ł! Ł "! Receiver Model Ł Ł # Ł $%&% Ł $% '( * &%* r (1+ r Ł + 1 / n 1 / n log n Area
Capacity of WLAN Networs Summary Ł Ł Ł Ł Arbitrary networ capacity [Gupta & Kumar The Capacity of Wireless Networs ] Ł! Ł "! Receiver Model Ł Ł # Ł $%&% Ł $% '( * &%* r (1+ r Ł + 1 / n 1 / n log n Area
Performance Effects of Two-way FAST TCP
 Performance Effects of Two-way FAST TCP Fei Ge a, Sammy Chan b, Lachlan L. H. Andrew c, Fan Li b, Liansheng Tan a, Moshe Zukerman b a Dept. of Computer Science, Huazhong Normal University, Wuhan, P.R.China
Performance Effects of Two-way FAST TCP Fei Ge a, Sammy Chan b, Lachlan L. H. Andrew c, Fan Li b, Liansheng Tan a, Moshe Zukerman b a Dept. of Computer Science, Huazhong Normal University, Wuhan, P.R.China
Multiaccess Problem. How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users?
 Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Modeling and Stability of PERT
 Modeling Stability of PET Yueping Zhang yueping@cs.tamu.edu I. SYSTEM MODEL Our modeling of PET is composed of three parts: window adjustment ED emulation queuing behavior. We start with the window dynamics.
Modeling Stability of PET Yueping Zhang yueping@cs.tamu.edu I. SYSTEM MODEL Our modeling of PET is composed of three parts: window adjustment ED emulation queuing behavior. We start with the window dynamics.
Data byte 0 Data byte 1 Data byte 2 Data byte 3 Data byte 4. 0xA Register Address MSB data byte Data byte Data byte LSB data byte
 SFP200 CAN 2.0B Protocol Implementation Communications Features CAN 2.0b extended frame format 500 kbit/s Polling mechanism allows host to determine the rate of incoming data Registers The SFP200 provides
SFP200 CAN 2.0B Protocol Implementation Communications Features CAN 2.0b extended frame format 500 kbit/s Polling mechanism allows host to determine the rate of incoming data Registers The SFP200 provides
Elliptic Curves. Giulia Mauri. Politecnico di Milano website:
 Elliptic Curves Giulia Mauri Politecnico di Milano email: giulia.mauri@polimi.it website: http://home.deib.polimi.it/gmauri May 13, 2015 Giulia Mauri (DEIB) Exercises May 13, 2015 1 / 34 Overview 1 Elliptic
Elliptic Curves Giulia Mauri Politecnico di Milano email: giulia.mauri@polimi.it website: http://home.deib.polimi.it/gmauri May 13, 2015 Giulia Mauri (DEIB) Exercises May 13, 2015 1 / 34 Overview 1 Elliptic
STABLE AND SCALABLE CONGESTION CONTROL FOR HIGH-SPEED HETEROGENEOUS NETWORKS
 STABLE AND SCALABLE CONGESTION CONTROL FOR HIGH-SPEED HETEROGENEOUS NETWORKS A Dissertation by YUEPING ZHANG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
STABLE AND SCALABLE CONGESTION CONTROL FOR HIGH-SPEED HETEROGENEOUS NETWORKS A Dissertation by YUEPING ZHANG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
On the Resource Utilization and Traffic Distribution of Multipath. Transmission Control
 On the Resource Utilization and Traffic Distribution of Multipath Transmission Control UMass Computer Science Technical Report UM-CS-2011-005 Bo Jiang 1, Yan Cai 2, Don Towsley 1 1 {bjiang, towsley}@cs.umass.edu
On the Resource Utilization and Traffic Distribution of Multipath Transmission Control UMass Computer Science Technical Report UM-CS-2011-005 Bo Jiang 1, Yan Cai 2, Don Towsley 1 1 {bjiang, towsley}@cs.umass.edu
Approximate Fairness with Quantized Congestion Notification for Multi-tenanted Data Centers
 Approximate Fairness with Quantized Congestion Notification for Multi-tenanted Data Centers Abdul Kabbani Stanford University Joint work with: Mohammad Alizadeh, Masato Yasuda, Rong Pan, and Balaji Prabhakar
Approximate Fairness with Quantized Congestion Notification for Multi-tenanted Data Centers Abdul Kabbani Stanford University Joint work with: Mohammad Alizadeh, Masato Yasuda, Rong Pan, and Balaji Prabhakar
A Simple Throughput Model for TCP Veno
 A Simle Throughut Model for TCP Veno Bin Zhou, Cheng Peng Fu, Dah-Ming Chiu, Chiew Tong Lau, and Lek Heng Ngoh School of Comuter Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singaore 639798 Email: {zhou00,
A Simle Throughut Model for TCP Veno Bin Zhou, Cheng Peng Fu, Dah-Ming Chiu, Chiew Tong Lau, and Lek Heng Ngoh School of Comuter Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singaore 639798 Email: {zhou00,
On Buffer Limited Congestion Window Dynamics and Packet Loss
 On Buffer Limited Congestion Windo Dynamics and Packet Loss A. Fekete, G. Vattay Communication Netorks Laboratory, Eötvös University Pázmány P. sétány /A, Budapest, Hungary 7 Abstract The central result
On Buffer Limited Congestion Windo Dynamics and Packet Loss A. Fekete, G. Vattay Communication Netorks Laboratory, Eötvös University Pázmány P. sétány /A, Budapest, Hungary 7 Abstract The central result
