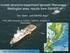
A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred km (63.3 mi) ESE of Suva, Fiji at a depth of km (378 miles).
|
|
|
- Gervais Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred km (63.3 mi) ESE of Suva, Fiji at a depth of km (378 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google
2 The Modified-Mercalli Intensity scale is a twelve-stage scale, from I to XII, that indicates the severity of ground shaking. Due to the depth of km (378 miles), the area nearest the earthquake experienced only light shaking. Modified Mercalli Intensity Perceived Shaking Extreme Violent Severe Very Strong Strong Moderate Light Weak Not Felt Image courtesy of the US Geological Survey USGS Estimated shaking Intensity from M 7.8 Earthquake
3 The USGS PAGER map shows the population exposed to different Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) levels. The USGS estimates that 295,000 people felt light shaking from this earthquake. USGS PAGER Population Exposed to Earthquake Shaking The color coded contour lines outline regions of MMI intensity. The total population exposure to a given MMI value is obtained by summing the population between the contour lines. The estimated population exposure to each MMI Intensity is shown in the table. Image courtesy of the US Geological Survey
4 The blue arrows show the motion of the Pacific Plate with respect to the Australian Plate. The epicenter of the earthquake is shown by the red star while the white square outlines the area of historic seismicity shown on the next slide. Fiji Tonga Trench This earthquake occurred within the Pacific Plate where it subducts beneath the Australian Plate at this ocean ocean convergent plate boundary. The rate of convergence at the location of this earthquake is about 81 mm/yr (8.1 cm/yr). Notice that the rate and direction of motion of the Pacific Plate change with distance north from New Zealand. These changes remind us that lithospheric plate motions are actually relative rotations of spherical shells along Earth s surface rather than linear motions of flat plates. Australia Plate Australian Plate Pacific Plate
5 Regional historical seismicity in the northern Tonga Trench is shown on the map below with earthquakes color coded by depth. Notice that earthquakes are shallow near the Tonga Trench on the east side of the map area. As the Pacific Plate subducts towards the west beneath the Australian Plate, earthquakes within the Pacific Plate increase in depth from east to west. This earthquake occurred within the subducting Pacific Plate and fits this general depth pattern. Earthquake Australian Plate Tonga Trench Pacific Plate Explore this view at See a 3-D view on the next slide. Image from IRIS Earthquake Browser
6 A deep-focus earthquake has a hypocenter depth exceeding 300 km. Deep earthquakes occur exclusively within subducting oceanic lithosphere, especially within old oceanic lithosphere that is subducting rapidly. The physical mechanism of rupture of deep focus earthquakes is different than earthquakes that occur at a shallow depth. This earthquake occurred within the subducting Pacific Plate. Australian Plate Earthquake Pacific Plate USGS Centroid Moment Tensor Solution This modified screen capture from the 3-D feature of IRIS Earthquake Browser shows a cross sectional view from the earthquakes on the previous slide. Image from IRIS Earthquake Browser
7 According to the USGS, the Pacific Plate slab at this location shows evidence of significant distortion at depth, with deep earthquakes associated with this subduction zone spanning several hundreds of kilometers laterally. Some authors have proposed this is evidence for a large slab fragment in this region, with a sub-horizontal geometry lying to the west of the main, steep Wadati-Benioff zone of the currently subducting Pacific slab. In this context, the September 6, 2018 earthquake (and perhaps the August 18, 2018 M 8.2 event before it) lies within the sub-horizontal relic slab. Regional Seismicity Sept 06, 2017 Sept 06, D View Explore this view at
8 To produce earthquakes, rocks must be brittle. Brittle rock accumulates elastic energy as they bend then rapidly releases that energy during earthquake rupture. With the exception of subducting oceanic plates, rock in Earth s mantle below about 100 km depth is viscoelastic and cannot rupture to produce earthquakes. Rocks are brittle at low temperatures but become viscoelastic when they reach temperatures of about 600 C. Rapidly subducting cool oceanic plates, however, can remain brittle up to about 700 km in the hot mantle. The deepest earthquakes are thought to be due to phase changes of minerals in the high pressure and temperature conditions at those depths. Exploring a three-dimensional view from the IRIS Earthquake Browser.
9 Regional tectonics of this earthquake (click for animation).
10 The record of the earthquake in Bend, Oregon (BNOR) is illustrated below. Bend is 9213 km (5725 miles, 83 ) from the location of this earthquake. Following the earthquake, it took 11 minutes and 22 seconds for the compressional P waves to travel a curved path through the mantle to Bend, Oregon. PP PP is a compressional wave that bounced off the surface midway between the earthquake and the recording station. P S Surface Waves S waves are shear waves that follow the same path through the mantle as P waves. S waves took 20 minutes and 52 seconds to travel from the earthquake to Bend. Surface waves traveled the 9213 km (5725 miles) along the perimeter of the Earth from the earthquake to the recording station. Because this was a deep earthquake, little seismic energy was partitioned into surface waves.
11 Teachable Moments are a service of The Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology Education & Public Outreach and The University of Portland Please send feedback to tkb@iris.edu To receive automatic notifications of new Teachable Moments subscribe at
Magnitude 8.2 FIJI. A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of km (350 miles).
 A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred 364.8 km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 563.4 km (350 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google The
A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred 364.8 km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 563.4 km (350 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google The
Magnitude 7.5 PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 33 kilometers (20 miles) southwest of Tari, Papua New Guinea, at a depth of 35 km (22 miles). Papua New Guinea is located on the eastern half of the island of New Guinea,
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 33 kilometers (20 miles) southwest of Tari, Papua New Guinea, at a depth of 35 km (22 miles). Papua New Guinea is located on the eastern half of the island of New Guinea,
Magnitude 7.0 NEW CALEDONIA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
7.1 FIJI 1, :57:22 UTC
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 141 km (88 miles) northeast of Ndoi Island, Fiji, and 313 km (194 mi) west-northwest of Nuku alofa, Tonga according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 141 km (88 miles) northeast of Ndoi Island, Fiji, and 313 km (194 mi) west-northwest of Nuku alofa, Tonga according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports
Magnitude 7.1 PERU. There are early reports of homes and roads collapsed leaving one dead and several dozen injured.
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
Magnitude 7.6 HONDURAS
 A magnitude 7.6 earthquake has occurred in the Caribbean between Honduras and the Cayman Islands approximately 125 miles (202 km) north-northeast of Barra Patuca, Honduras, and 188 miles (303 km) southwest
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake has occurred in the Caribbean between Honduras and the Cayman Islands approximately 125 miles (202 km) north-northeast of Barra Patuca, Honduras, and 188 miles (303 km) southwest
Magnitude 7.1 SOUTH SANDWICH ISLANDS
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake occurred at a depth of 164.7 km (102 miles) in the South Sandwich Islands, an uninhabited British territory off the coast of Argentina in the southern Atlantic Ocean. Antarctica
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake occurred at a depth of 164.7 km (102 miles) in the South Sandwich Islands, an uninhabited British territory off the coast of Argentina in the southern Atlantic Ocean. Antarctica
Magnitude 7.2 OAXACA, MEXICO
 A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
Magnitude 7.0 VANUATU
 A major earthquake struck in the southwest Pacific Ocean at a depth of 27 km beneath the island of Melampa in the Vanuatu island chain. There are no reports of damage. The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
A major earthquake struck in the southwest Pacific Ocean at a depth of 27 km beneath the island of Melampa in the Vanuatu island chain. There are no reports of damage. The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
Magnitude 7.5 PALU, INDONESIA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 80.8 km (50.2 mi) north of Palu, Indonesia at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). This earthquake triggered a tsunami with wave heights up to 2 m (6.6 ft) that an official
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 80.8 km (50.2 mi) north of Palu, Indonesia at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). This earthquake triggered a tsunami with wave heights up to 2 m (6.6 ft) that an official
Magnitude 8.3 SEA OF OKHOTSK
 A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
Magnitude 7.0 PERU. This region of the Andes is a sparsely populated area, there were no immediate reports of injuries or damage.
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred in southeastern Peru on Friday about 27 kilometers northeast of the town of Azángaro, Peru, near the border with Bolivia. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 257.4
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred in southeastern Peru on Friday about 27 kilometers northeast of the town of Azángaro, Peru, near the border with Bolivia. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 257.4
Magnitude 7.4 SOUTH GEORGIA ISLAND REGION
 A magnitude 7.4 earthquake occurred in the South Georgia Island Region. South Georgia Island is a British territory in the South Atlantic Ocean that lies about 800 miles east of the Falkland Islands. It
A magnitude 7.4 earthquake occurred in the South Georgia Island Region. South Georgia Island is a British territory in the South Atlantic Ocean that lies about 800 miles east of the Falkland Islands. It
A magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck 255 km (158 miles) southwest of Tonga, according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports of damage.
 A magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck 255 km (158 miles) southwest of Tonga, according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports of damage. The earthquake hit at 5:19 am local time and was centered
A magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck 255 km (158 miles) southwest of Tonga, according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports of damage. The earthquake hit at 5:19 am local time and was centered
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.6 PERU
 Two deep 7.6 magnitude earthquakes have shaken a sparsely populated jungle region near the Peru-Brazil border in southeast Peru. There were no immediate reports of injuries or damage. The second M 7.6
Two deep 7.6 magnitude earthquakes have shaken a sparsely populated jungle region near the Peru-Brazil border in southeast Peru. There were no immediate reports of injuries or damage. The second M 7.6
Magnitude 7.0 N of ANCHORAGE, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
Magnitude 7.9 SE of KODIAK, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
Magnitude 7.3 IRAQ. Early reports indicate that 140 have been killed with over 800 injuries reported. Sunday, November 12, 2017 at 18:18:17 UTC
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred in the northern border region of Iran and Iraq centered about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Baghdad at a depth of 33.9 km (21 miles). The earthquake was felt
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred in the northern border region of Iran and Iraq centered about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Baghdad at a depth of 33.9 km (21 miles). The earthquake was felt
Magnitude 7.5 NEW BRITAIN REGION, PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Sunday, approximately 54 km (33 miles) southeast of Kokopo. Residents reported strong ground shaking for about five minutes.
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Sunday, approximately 54 km (33 miles) southeast of Kokopo. Residents reported strong ground shaking for about five minutes.
Magnitude 7.5 NEW BRITAIN REGION, PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Tuesday, approximately 130 km (81 mi) southsouthwest of Kokopo at a depth of 42 km (26.1 mi). There are reports of some structural
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Tuesday, approximately 130 km (81 mi) southsouthwest of Kokopo at a depth of 42 km (26.1 mi). There are reports of some structural
Magnitude 7.1 PHILIPPINES
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
Magnitude 7.0 PAPUA, INDONESIA
 A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.4 SOLOMON ISLANDS
 A magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck near the Solomon Islands on Sunday morning local time; there were no immediate reports of damage. The earthquake was centered 100 km (60 miles) south of Kira Kira, a town
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck near the Solomon Islands on Sunday morning local time; there were no immediate reports of damage. The earthquake was centered 100 km (60 miles) south of Kira Kira, a town
Magnitude 7.3 OFFSHORE EL SALVADOR
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck off the Pacific coast of Central America late Monday night, early reports indicate one death. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 40 km (24.9 miles). Its epicenter was
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck off the Pacific coast of Central America late Monday night, early reports indicate one death. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 40 km (24.9 miles). Its epicenter was
Magnitude 7.8 SCOTIA SEA
 A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred in the South Orkney Island region in the Scotia Sea. According to the USGS, this earthquake is the latest in a series of moderate-tolarge earthquakes to strike this
A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred in the South Orkney Island region in the Scotia Sea. According to the USGS, this earthquake is the latest in a series of moderate-tolarge earthquakes to strike this
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Magnitude 8.2 NORTHWEST OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
Magnitude 7.6 SOUTH OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 A powerful aftershock struck off northern Chile prompting an evacuation of the coastal area and raising fears of a tsunami. This magnitude 7.6 earthquake is the largest of a series of aftershocks following
A powerful aftershock struck off northern Chile prompting an evacuation of the coastal area and raising fears of a tsunami. This magnitude 7.6 earthquake is the largest of a series of aftershocks following
Magnitude 7.7 QUEEN CHARLOTTE ISLANDS REGION
 A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
Magnitude 7.3 NEPAL. Tuesday, May 12, 2015 at 07:05:19 UTC
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred near Mount Everest. Early reports suggest 32 people have been killed and at least 1,000 were injured in the earthquake. The region is still in recovery from a 7.8
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred near Mount Everest. Early reports suggest 32 people have been killed and at least 1,000 were injured in the earthquake. The region is still in recovery from a 7.8
Magnitude 6.9 GULF OF CALIFORNIA
 A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
Tsunami waves swept away houses and cars in northern Japan and pushed ships aground.
 Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Magnitude 6.3 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
Magnitude 5.8 VIRGINIA
 An earthquake in central Virginia was felt across much of the East Coast on Tuesday, causing light damage and forcing hundreds of thousands of people to evacuate buildings in New York, Washington and other
An earthquake in central Virginia was felt across much of the East Coast on Tuesday, causing light damage and forcing hundreds of thousands of people to evacuate buildings in New York, Washington and other
Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
What is an Earthquake?
 Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? Earthquake - sometimes violent shaking of ground caused by movement of Earth s tectonic plates; creates seismic waves Often followed by smaller earthquakes (aftershocks);
Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? Earthquake - sometimes violent shaking of ground caused by movement of Earth s tectonic plates; creates seismic waves Often followed by smaller earthquakes (aftershocks);
Internal Layers of the Earth
 Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES
 UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
Magnitude 7.0 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A powerful 7.0-magnitude earthquake shook much of New Zealand's South Island early Saturday morning local time. USGS A damaged building near Manchester St. New Zealand Herald Photo / Colin Cross A car
A powerful 7.0-magnitude earthquake shook much of New Zealand's South Island early Saturday morning local time. USGS A damaged building near Manchester St. New Zealand Herald Photo / Colin Cross A car
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
Lecture 4: Earthquakes and Seismic Waves
 Lecture 4: Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Key Questions 1. What are the sources for EQs in the PNW? 2. What is a seismograph and seismogram? 3. What is the difference between Richter magnitudes and Mercalli
Lecture 4: Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Key Questions 1. What are the sources for EQs in the PNW? 2. What is a seismograph and seismogram? 3. What is the difference between Richter magnitudes and Mercalli
Magnitude 6.5 OFFSHORE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
Multi-station Seismograph Network
 Multi-station Seismograph Network Background page to accompany the animations on the website: IRIS Animations Introduction One seismic station can give information about how far away the earthquake occurred,
Multi-station Seismograph Network Background page to accompany the animations on the website: IRIS Animations Introduction One seismic station can give information about how far away the earthquake occurred,
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches in the Sumatra Subduction Zone
 IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March
 Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Chapter 15. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection? At the boundaries friction causes plates to stick together.
 Chapter 15 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? As with volcanoes, earthquakes are not randomly distributed over the globe At the boundaries friction causes plates to stick together.
Chapter 15 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? As with volcanoes, earthquakes are not randomly distributed over the globe At the boundaries friction causes plates to stick together.
CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY. Earth Formation Plate Tectonics Sources of Earthquakes...
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY Earth Formation... 1-2 Plate Tectonics... 1-2 Sources of Earthquakes... 1-3 Earth Faults... 1-4 Fault Creep... 1-5 California Faults... 1-6 Earthquake
CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY Earth Formation... 1-2 Plate Tectonics... 1-2 Sources of Earthquakes... 1-3 Earth Faults... 1-4 Fault Creep... 1-5 California Faults... 1-6 Earthquake
Preliminary report on the Canterbury Earthquake South Island of New Zealand , M 6.3
 Preliminary report on the Canterbury Earthquake South Island of New Zealand 21.02.2011, M 6.3 Kyriazis Pitilakis and the group of - Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece. General 2 General 147 people
Preliminary report on the Canterbury Earthquake South Island of New Zealand 21.02.2011, M 6.3 Kyriazis Pitilakis and the group of - Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece. General 2 General 147 people
Objectives. Vocabulary
 Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
How do we explain Wegener s observations? With the Theory of Seafloor Spreading. So, in which way was Wegener correct?
 So, in which way was Wegener correct? A. His hypothesis of Continental Drift was correct: continents move through the ocean basins. B. He was correct that continents move. C. He was correct that the continents
So, in which way was Wegener correct? A. His hypothesis of Continental Drift was correct: continents move through the ocean basins. B. He was correct that continents move. C. He was correct that the continents
Earthquakes. Forces Within Eartth. Faults form when the forces acting on rock exceed the rock s strength.
 Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy.
 Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
20.1 Earthquakes. Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES. Earthquakes and plate boundaries 500 UNIT 6 EARTH S STRUCTURE
 Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 1: Earthquakes Section 2: Volcanoes Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics 1 Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Elastic Rebound
Table of Contents Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 1: Earthquakes Section 2: Volcanoes Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics 1 Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Elastic Rebound
The Theory of Seafloor Spreading: How do we explain Wegener s observations? With the Theory of Seafloor Spreading
 So, in which way was Wegener correct? A. His hypothesis of Continental Drift was correct: continents move through the ocean basins. B. He was correct that continents move. C. He was correct that the continents
So, in which way was Wegener correct? A. His hypothesis of Continental Drift was correct: continents move through the ocean basins. B. He was correct that continents move. C. He was correct that the continents
Dynamic Earth A B1. Which type of plate boundary is located at the Jordan Fault? (1) divergent (3) convergent (2) subduction (4) transform
 Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education
 Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education www.earthobservatory.sg Preparation: Before doing this investigation, complete two introductory investigations using GPS data from UNAVCO
Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education www.earthobservatory.sg Preparation: Before doing this investigation, complete two introductory investigations using GPS data from UNAVCO
C) 10:20:40 A) the difference between the arrival times of the P -wave and the S -wave
 1. The arrival time of the first earthquake P-wave at a seismograph station was 10:11:20 (hours:minutes:seconds). If the epicenter of the earthquake is 8000 km away, what was the approximate arrival time
1. The arrival time of the first earthquake P-wave at a seismograph station was 10:11:20 (hours:minutes:seconds). If the epicenter of the earthquake is 8000 km away, what was the approximate arrival time
I. INTRODUCTION II. EARTHQUAKES
 2018 IJSRST Volume 4 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Iraq Earthquake Contour Maps Bashair A.R. Mohammed *1, Israa H. Mohammed 2, Tariq N. Ataiwe
2018 IJSRST Volume 4 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Iraq Earthquake Contour Maps Bashair A.R. Mohammed *1, Israa H. Mohammed 2, Tariq N. Ataiwe
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
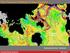 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
Dynamic Crust Regents Review
 Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 - What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
- What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
Moho (Mohorovicic discontinuity) - boundary between crust and mantle
 Earth Layers Dynamic Crust Unit Notes Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust Continental Crust Thicker Less Dense Made of Granite Oceanic Crust Thinner More Dense Made of Basalt Moho (Mohorovicic
Earth Layers Dynamic Crust Unit Notes Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust Continental Crust Thicker Less Dense Made of Granite Oceanic Crust Thinner More Dense Made of Basalt Moho (Mohorovicic
What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics?
 What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics? The tectonic plates are moving, but with varying rates and directions. What hypotheses have been proposed to explain the plate motion? Convection Cells in the Mantle
What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics? The tectonic plates are moving, but with varying rates and directions. What hypotheses have been proposed to explain the plate motion? Convection Cells in the Mantle
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior The crust of the Earth is made up of floating tectonic plates- huge continent-sized chunks of solid rock floating on molten rock. Rock masses along the boundaries
Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior The crust of the Earth is made up of floating tectonic plates- huge continent-sized chunks of solid rock floating on molten rock. Rock masses along the boundaries
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2
 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE
 crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
Physical Geography. Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Volcanism. Chapter 12 GEOGRAPHY Earthquakes and Volcanoes. What are Earthquakes?
 Physical Geography GEOGRAPHY 1710 DAVID R. SALLEE Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Chapter 12 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes? The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated
Physical Geography GEOGRAPHY 1710 DAVID R. SALLEE Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Chapter 12 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes? The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES
 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a
 The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide
 How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide Standard Addressed: Grades 6-8: Scientific Inquiry 1 B/1, 2 Mathematical Inquiry 2 C/2 Technology and Science 3 A/2 Processes that shape the
How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide Standard Addressed: Grades 6-8: Scientific Inquiry 1 B/1, 2 Mathematical Inquiry 2 C/2 Technology and Science 3 A/2 Processes that shape the
THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR
 JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast
 Earthquakes Ch. 12 Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? It s the shaking and trembling of the Earth s crust due to plate movement. The plates move, rocks along
Earthquakes Ch. 12 Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? It s the shaking and trembling of the Earth s crust due to plate movement. The plates move, rocks along
5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate the approximate radius of the earth, inner core, and outer core.
 Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do over 90% of earthquakes occur? 3. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? 4. What are the formulae for P and S velocity 5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate
Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do over 90% of earthquakes occur? 3. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? 4. What are the formulae for P and S velocity 5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate
A. rift valley B. deep trench C. volcanic cone D. uplifted mountain. A. a volcanic island arc B. a large watershed area
 DC Practice Test Dynamic Crust PRCTICE TEST Zimm's Earth Science 2013 1. Which feature would most likely be forming at converging continental tectonic plate boundaries?. rift valley. deep trench C.
DC Practice Test Dynamic Crust PRCTICE TEST Zimm's Earth Science 2013 1. Which feature would most likely be forming at converging continental tectonic plate boundaries?. rift valley. deep trench C.
Use complete and thorough answers through this assignment use a different color font. Feel free to use images to help explain!
 Activity 1: Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Webquest: Name Use complete and thorough answers through this assignment use a different color font. Feel free to use images to help explain! Structure
Activity 1: Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Webquest: Name Use complete and thorough answers through this assignment use a different color font. Feel free to use images to help explain! Structure
Name Date Class. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question Florida Progress Monitoring and Benchmark Assessments
 b e n c h m a r k t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e Multiple Choice 1. Geologists obtain indirect evidence about Earth s interior by A measuring pressure differences at Earth s surface.
b e n c h m a r k t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e Multiple Choice 1. Geologists obtain indirect evidence about Earth s interior by A measuring pressure differences at Earth s surface.
Earthquakes. Building Earth s Surface, Part 2. Science 330 Summer What is an earthquake?
 Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
ES Ch 19 Earthquakes 1
 Chapter 19 - Earthquakes Objectives 1. Define stress vs. strain as they apply to rocks. 2. Define faults. 3. Contrast types of seismic waves-3 types according to their type of movement, speed, location
Chapter 19 - Earthquakes Objectives 1. Define stress vs. strain as they apply to rocks. 2. Define faults. 3. Contrast types of seismic waves-3 types according to their type of movement, speed, location
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p ) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by:
 Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Our Dynamic Earth Unit Unit 5
 EARTH SCIENCE REGENTS - SOTO Our Dynamic Earth Unit Unit 5 Mr. Soto - Key 1/1/2013 Our Dynamic Earth Vocabulary List 1 Directions: Define each vocabulary word provided below. You may have to use your Earth
EARTH SCIENCE REGENTS - SOTO Our Dynamic Earth Unit Unit 5 Mr. Soto - Key 1/1/2013 Our Dynamic Earth Vocabulary List 1 Directions: Define each vocabulary word provided below. You may have to use your Earth
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes. Lecture #2
 A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
21. Earthquakes I (p ; 306)
 21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
LECTURE #5: Plate Tectonics: Boundaries & Earthquake Science
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #5: Plate Tectonics: Boundaries & Earthquake Science Date: 23 January 2018 I. Reminder: Exam #1 is scheduled for Feb 1st one week from Thursday o
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #5: Plate Tectonics: Boundaries & Earthquake Science Date: 23 January 2018 I. Reminder: Exam #1 is scheduled for Feb 1st one week from Thursday o
1. What is Wegener s theory of continental drift? 2. What were the 4 evidences supporting his theory? 3. Why wasn t Wegener s theory excepted?
 Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Date: / Page # Version A Page 1
 Name: Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which best describes a major characteristic of both volcanoes and earthquakes? (1) They are centered at the poles. (2) They are located in the same geographic areas. (3) They
Name: Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which best describes a major characteristic of both volcanoes and earthquakes? (1) They are centered at the poles. (2) They are located in the same geographic areas. (3) They
2) In which diagram do the arrows best represent the motions of Earth's crust at the Peru-Chile Trench?
 1966-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) A huge undersea earthquake off the Alaskan coastline could produce a thunderstorm cyclone hurricane tsunami Questions 2 through 4 refer to the following: The map below shows the
1966-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) A huge undersea earthquake off the Alaskan coastline could produce a thunderstorm cyclone hurricane tsunami Questions 2 through 4 refer to the following: The map below shows the
22.5 Earthquakes. The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia.
 The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia. An earthquake is a movement of Earth s lithosphere that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere
The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia. An earthquake is a movement of Earth s lithosphere that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere
SEISMOLOGY. - The study of earthquakes waves and how they move through the body and around the surface of the earth.
 EARTHQUAKES SEISMOLOGY - The study of earthquakes waves and how they move through the body and around the surface of the earth. Seismic Waves - vibrations generated in the earths interior that carry energy
EARTHQUAKES SEISMOLOGY - The study of earthquakes waves and how they move through the body and around the surface of the earth. Seismic Waves - vibrations generated in the earths interior that carry energy
