1D and 2D Inversion of the Magnetotelluric Data for Brine Bearing Structures Investigation
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1D and 2D Inversion of the Magnetotelluric Data for Brine Bearing Structures Investigation Behrooz Oskooi *, Isa Mansoori Kermanshahi * * Institute of Geophysics, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran. boskooi@ut.ac.ir, Isa_Mansoori@yahoo.com Abstract A detailed standard Magnetotelluric (MT) study was conducted to recognize brine bearing layers in depths of less than 1200 m in northeast of Iran close to southeastern shore of Caspian sea. Long and medium period natural-field MT method has proved very useful for subsurface mapping purpose by determining the resistivity of the near surface structure. MT data were analyzed and modeled using a 1D inversion scheme. Then corresponding data on eight profiles were inverted using 2D inversion schemes. To have the best possible interpretation all possible modes (TE-, TM-, TE+TM- and DET-data) were examined. Down to 2 km, the resistivity model obtained from the MT data is consistent with the geological information from a 1200 m borehole in the area. Analysis of the MT data-set suggests signatures of salt water reservoirs in the area which are distinguished potentially positive to contain Iodine. Due to the very conductive nature of the sediments regardless of all difficulties in the interpretation stage because of the lack of a considerable resistivity contrast we could recognize the more conductive zones in the less conductive host as layers of saline water. Key words: conductivity, Iodine, magnetotelluric, 1D and 2D inversion, resistivity. 1. Introduction Conductive structures are ideal targets for Magnetotelluric method when located in a considerably resistive host. They produce strong variations in underground electrical resistivity. In cases where the electrical resistivity of the target is not substantially different from that of it would 291
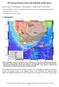
2 be quite difficult to reach a promising result. Despite this limitation, we could get some useful results in our study. Dashli-Boroon area is located in Golestan province in northeastern part of Iran right at the border with Turkmenistan. Geologically it is a part of Kopeh-Dagh sedimentary basin. Kopeh-Dagh has been formed by the last orogeny phase of Alpine and the erosion followed. Topography relief is very smooth and basically it is a flat plain consisting loesses occurring naturally between the Elburz mountain range and the desert of Turkmenistan. Quaternary sediments including clay and evaporates and particularly salt are impenetrable. An MT survey was carried out using GMS05 (Metronix, Germany) and MTU2000 (Uppsala University, Sweden) systems in February MT data were collected at 60 sites in a network of 2 by 2 km meshes along eight EW profiles (Fig. 1). For data processing a code from Smirnov (2003) was used. 1D and 2D inversions are conducted to resolve the conductive structures. 1D inversion of the determinant (DET) data using a code from Pedersen (2004) as well as the 2D inversion of TE-, TM-, TE+TM- and DET-mode data using a code from Siripunvaraporn and Egbert (2000) were performed. A supplementary goal of this work is to evaluate the possibility of using surface MT measurements on the very conductive sediments to monitor the underground salt water bearing layers or bodies. Our concern which is followed in the current paper, only in the frame of one- and two- dimensional (1D and 2D) interpretation, is to emphasis on the characteristics of the extremely conductive structures which are supposed to bear Iodine in economic meanings. Based upon the MT results some sites were proposed for detail exploration by excavating deep exploration boreholes. As results the resistivity sections show a clear picture of the resistivity changes both laterally and with depth. 2. MT data acquisition In February 2007, an MT survey was carried out at 60 sites in Dashli-Boroon area. All MT-sites are marked on the location map of Fig. 1. The magnetic declination in the area is less than 4 o i.e. in the range of error of the array setup so that the geographic north is approximately the same as the magnetic north. The MT sites were projected onto eight EW lines for later 2D modeling. A regular grid mesh of 2 km was organized for the sites due to easy transportation in the plain. The study area has a topographic relief of about maximum ±10 m which can be disregarded when using 2D inversion scheme compared with the 2 km depth of investigation. 292
3 In this study, data within a period range of s were analyzed. MT data were processed using a modern robust technique to obtain complete impedance tensor. The vertical magnetic components from various sites are not available due to an unknown source of noise which contaminated the data, therefore, we missed induction arrows which would be used to confirm the dimensionality analysis of the data. Overnight MT recording for minimum 12 hours per site have been arranged. Long time data collection was necessary to recover the proper signals from noise using statistical approaches. The problem with the unexpected noise could be dealt only by removing the noisy stacks manually since remote reference systems were not used for data acquisition. 3. MT data processing MT data were processed as single sites using a robust routine from Smirnov (2003). The final results of processing for data from most sites were of a reasonable quality. For some sites very bad electric field data were gathered in either x or y direction most probably due to the currents directed from some power-lines in the area. Only one main component of the impedance was used for further analysis for such sites. 4. Dimensionality of the subsurface structures in the region General morphology of the quaternary deposits shows no tendency to judge about the dimensionality. From the data itself Swift's skew (Swift, 1967) were estimated in order to analyze the dimensionality of the data. Swift's skew, defined as the ratio of the on- and off-diagonal impedance elements, approaches zero when the medium is 1D or 2D. In the case of our data, Swift's skews shown in Fig. 2 are generally less than 0.2, which shows a good indicator for almost 1D or 2D structures. The regional strike of the survey area was calculated by applying a routine from Smirnov (2003). Relatively stable regional strike estimates defined a principle direction of about 90 o from magnetic north at most of the sites at period range 10 to 100 s. This would correspond to both NS and EW strike directions. Since we do not have the tipper data due to the noisy vertical component of the magnetic field we cannot approve the either strike direction, therefore we would take the determinant data in the inversion stage. 293
4 In the following section, results of 1D inversion of the determinant data and 2D inversion of the determinant data, TE-, TM-mode data and joint inversion of TE- and TM-mode data are described. 5. Near-surface distortions in EM induction The static shift of MT apparent resistivity sounding curves is a classic example of the galvanic effect. MT sounding curves are shifted upward when measuring directly over surficial resistive bodies and they are depressed over conductive patches. The physical principles governing electromagnetic (EM) distortions due to near-surface inhomogenities have been understood for several decades and several methods appeared to correct these distortions. Two of these methods are: use of invariant response parameters like the determinant data (Pedersen and Engels, 2005) and curve shifting (Jiracek, 1990). We did try to conduct DC-Electrical sounding in the region with no success due to extremely strong EM coupling which arose because of very highly conductive surface layer. That is why we used only the determinant data to proceed with the inversion. 6. Inversion Depending on the dimensionality of the field structure defined by the geology, tectonics and MT data 1D, 2D and 3D modeling can be applied on the data. Models explain the data if their responses fit the measured data within their errors. Generally, the better the fit between measured and predicted data, the better the model resolution. 1D as well as 2D inversion of the determinant (DET) data were performed using a code from Pedersen (2004) and a code from Siripunvaraporn and Egbert (2000), respectively. The data were calculated as apparent resistivities and phases. To avoid of probable unrealistic small errors on the data for the 2D approximation an error floor of 5% on the apparent resistivity was defined. MT data were collected in the period range which by taking into account that the average resistivity of the area is extremely low we consider a maximum depth penetration of about 2 km for our models One dimensional inversion 294
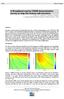
5 1D inversion of the determinant data (DET) was performed. The determinant provides a useful average of the impedance for all current directions. Furthermore it is unique and independent of the strike direction. Regardless of the true dimensionality 1D inversion of MT data and, in particular, inversion of rotationally invariant data like the determinants, provides an overview of the subsurface conductivity in a feasible sense. Based on the results of 1D inversion, a reasonable starting model and strategy can be constructed for higher order inversions of 2D or 3D. An examples of 1D modeling together with the data and calculated model responses is shown in Fig Two dimensional inversion Data along eight profiles were corrected were taken for 2D inversion purpose. Apparent resistivity and phase data exhibit fairly different characteristics in TE- and TM-mode and 2D modeling would therefore be expected to provide a more reasonable approximation of the true subsurface structure. Moreover, the results of the data analysis with respect to the dimensionality and the surface and deep geology of the area indicate that a 2D inversion of the MT data is required. 2D inversions of the determinant data (DET) profiles are performed in using the code of Siripunvaraporn and Egbert (2000). Starting with a half-space or a priori model as the initial model, for all models, convergence to a possible minimum RMS misfit was achieved after limited numbers of iterations. Root mean squared (RMS) of data misfit normalized by data error is used to control the data-fit. The resulting models using the determinant data, data-fit and residuals along profiles E2 and E3 are shown in Figs. 4 and 5. The residuals are simply the arithmetic difference between the observed and calculated data. In some cases there is a large misfit which most probably is due to 3D structures, since outliers in the residuals are seen quite frequently. A shallow conductor is identified as a horizontal layer in all resistivity sections at depth about 300 m. Sites 4 and 6 along the profile E2 and sites 3 and 6 along profile E3 show conductive bodies in larger depths. Data, model responses and residuals are plotted as a function of station in corresponding figures. For an easy comparison resistivity sections along all profiles are shown in Fig
6 7. Conclusions 1D and 2D modelling of the MT data at various sites and along profiles revealed remarkable signatures of the conductivity structures down to the depth of 2 km. Our MT investigation resolved the area very conductive which could be expected considering the common geology of the area. By depth we discovered even higher conductivities which somehow prove the idea of salt water bearing layers possibly containing Iodine minerals. Two very conductive layers are resolved in depth from 300 m to 400 m and from 800 m. The bottom of the second conductor could not be estimated accurately due to the problem of limitation on the penetration depth. 8. Acknowledgement Professor Laust Pedersen from Uppsala University in Sweden is acknowledged for lending us the MTU2000 system which was used for the measurements at some sites. The last version of the processing software from Maxim Smirnov is also gratefully appreciated. The research council of the University of Tehran is acknowledged for financial supports. 9. References Jiracek, G.,1990. Near-surface and topographic distortions in electromagnetic induction. Surveys in Geophysics, 11, Pedersen, L.B., 2004, Determination of the regularization level of truncated singular-value decomposition inversion: The case of 1D inversion of MT data. Geophysical Prospecting 52, Pedersen, L.B., Engels, M., Routine 2D inversion of magnetotelluric data using the determinant of the impedance tensor. Geophysics 70, G33-G41. Siripunvaraporn, W., Egbert, G., An efficient data-subspace inversion method for 2-D magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 65, Smirnov, M. Yu., 2003, Magnetotelluric data processing with a robust statistical procedure having a high breakdown point. Geophys. J. Int. 152, 1-7. Swift, C. M., 1967, A magnetotelluric investigation of electrical conductivity anomaly in the southwestern United States, PhD Thesis Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA. 296
7 Fig. 1. A sketch of the MT-sites in Dashli-Boroon, north of Iran. 297
8 (a) (b) Fig. 2. Swift s skew values for all sites along profiles 3 (a) and 5 (b). 298
9 Rho (ohmm) Fig. 3. Data-fit and the model for 1D inversion of the data from site E12, a) Apparent resistivity, b) Phase, c) Swift s skew, d) 1D model. 299
10 Fig. 4. Data, model responses, residuals and the model of 2D inversion for data along profile E2. Fig. 5. Data, model responses, residuals and the model of 2D inversion for data along profile E3. 300
11 Fig. 6. 2D models along all 8 profiles for an easy comparison. 301
A resolution comparison of horizontal and vertical magnetic transfer functions
 Journal of the Earth and Space Physics, Vol. 40, No. 3, 2014, P. 47-53 A resolution comparison of horizontal and vertical magnetic transfer functions Habibian Dehkordi, B. 1 and Oskooi, B. 2 1 Assitant
Journal of the Earth and Space Physics, Vol. 40, No. 3, 2014, P. 47-53 A resolution comparison of horizontal and vertical magnetic transfer functions Habibian Dehkordi, B. 1 and Oskooi, B. 2 1 Assitant
MT Prospecting. Map Resistivity. Determine Formations. Determine Structure. Targeted Drilling
 MT Prospecting Map Resistivity Determine Formations Determine Structure Targeted Drilling Cross-sectional interpretation before and after an MT survey of a mineral exploration prospect containing volcanic
MT Prospecting Map Resistivity Determine Formations Determine Structure Targeted Drilling Cross-sectional interpretation before and after an MT survey of a mineral exploration prospect containing volcanic
Comparison of 1-D, 2-D and 3-D Inversion Approaches of Interpreting Electromagnetic Data of Silali Geothermal Area
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Comparison of 1-D, 2-D and 3-D Inversion Approaches of Interpreting Electromagnetic Data of Silali Geothermal Area Charles
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Comparison of 1-D, 2-D and 3-D Inversion Approaches of Interpreting Electromagnetic Data of Silali Geothermal Area Charles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary online material for Bai et al., (2). EHS3D MT data collection Broadband magnetotelluric (MT) data were recorded on profiles P, P2 and P4 in the frequency band -.5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary online material for Bai et al., (2). EHS3D MT data collection Broadband magnetotelluric (MT) data were recorded on profiles P, P2 and P4 in the frequency band -.5
Exploration of Geothermal High Enthalpy Resources using Magnetotellurics an Example from Chile
 Exploration of Geothermal High Enthalpy Resources using Magnetotellurics an Example from Chile Ulrich Kalberkamp, Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR), Stilleweg 2, 30655 Hannover,
Exploration of Geothermal High Enthalpy Resources using Magnetotellurics an Example from Chile Ulrich Kalberkamp, Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR), Stilleweg 2, 30655 Hannover,
Data Repository Comeau et al., (2015)
 Data Repository 2015087 Comeau et al., (2015) 1. Magnetotelluric data Owing to the remote location, and large distance from sources of electromagnetic noise, most stations were characterized by high quality
Data Repository 2015087 Comeau et al., (2015) 1. Magnetotelluric data Owing to the remote location, and large distance from sources of electromagnetic noise, most stations were characterized by high quality
Invariants of rotation of axes and indicators of
 Invariants of rotation of axes and indicators of dimensionality in magnetotellurics F.E.M. Lilley 1 and J.T. Weaver 2 1 Research School of Earth Sciences, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT
Invariants of rotation of axes and indicators of dimensionality in magnetotellurics F.E.M. Lilley 1 and J.T. Weaver 2 1 Research School of Earth Sciences, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT
Magnetotelluric Array and Magnetic Magnetotelluric Surveys
 Magnetotelluric Array and Magnetic Magnetotelluric Surveys Dr. Wen J Whan JTech Co., Ltd.; wwj@jtech.com.tw Abstract. Surveys using synchronous MT array could further reduce the local noise. Multi variance
Magnetotelluric Array and Magnetic Magnetotelluric Surveys Dr. Wen J Whan JTech Co., Ltd.; wwj@jtech.com.tw Abstract. Surveys using synchronous MT array could further reduce the local noise. Multi variance
APPENDIX A: Magnetotelluric Data in Relation to San Pedro Mesa Structural. The San Pedro Mesa structural high (discussed in main text of paper) was
 Page of DR for GSA Special Paper 9, Chapter, Geophysical constraints APPENDIX A: Magnetotelluric Data in Relation to San Pedro Mesa Structural High The San Pedro Mesa structural high (discussed in main
Page of DR for GSA Special Paper 9, Chapter, Geophysical constraints APPENDIX A: Magnetotelluric Data in Relation to San Pedro Mesa Structural High The San Pedro Mesa structural high (discussed in main
3D MAGNETOTELLURIC SURVEY AT THE YANAIZU-NISHIYAMA GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NORTHERN JAPAN
 3D MAGNETOTELLURIC SURVEY AT THE YANAIZU-NISHIYAMA GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NORTHERN JAPAN Toshihiro Uchida 1, Shinichi Takakura 1, Takumi Ueda 1, Masaho Adachi 2, Hitoshi Ozeki 2, Kunikazu Kamada 3, Tatsuya
3D MAGNETOTELLURIC SURVEY AT THE YANAIZU-NISHIYAMA GEOTHERMAL FIELD, NORTHERN JAPAN Toshihiro Uchida 1, Shinichi Takakura 1, Takumi Ueda 1, Masaho Adachi 2, Hitoshi Ozeki 2, Kunikazu Kamada 3, Tatsuya
B033 Improving Subsalt Imaging by Incorporating MT Data in a 3D Earth Model Building Workflow - A Case Study in Gulf of Mexico
 B033 Improving Subsalt Imaging by Incorporating MT Data in a 3D Earth Model Building Workflow - A Case Study in Gulf of Mexico E. Medina* (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Golfré Andreasi (WesternGeco),
B033 Improving Subsalt Imaging by Incorporating MT Data in a 3D Earth Model Building Workflow - A Case Study in Gulf of Mexico E. Medina* (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Golfré Andreasi (WesternGeco),
Three Dimensional Inversions of MT Resistivity Data to Image Geothermal Systems: Case Study, Korosi Geothermal Prospect
 PROCEEDINGS, 42nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 13-15, 2017 SGP-TR-212 Three Dimensional Inversions of MT Resistivity Data to Image Geothermal
PROCEEDINGS, 42nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 13-15, 2017 SGP-TR-212 Three Dimensional Inversions of MT Resistivity Data to Image Geothermal
Resistivity structure of Sumikawa geothermal field, northeastern Japan, obtained from magnetotelluric data. Toshihiro Uchida
 Resistivity structure of Sumikawa geothermal field, northeastern Japan, obtained from magnetotelluric data Toshihiro Geological Survey of Japan 1-1-3 Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 35, Japan ABSTRACT: Resistivity
Resistivity structure of Sumikawa geothermal field, northeastern Japan, obtained from magnetotelluric data Toshihiro Geological Survey of Japan 1-1-3 Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 35, Japan ABSTRACT: Resistivity
THREE DIMENSIONAL INVERSIONS OF MT RESISTIVITY DATA TO IMAGE GEOTHERMAL SYSTEMS: CASE STUDY, KOROSI GEOTHERMAL PROSPECT.
 Proceedings, 6 th African Rift Geothermal Conference Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2 nd 4 th November 2016 THREE DIMENSIONAL INVERSIONS OF MT RESISTIVITY DATA TO IMAGE GEOTHERMAL SYSTEMS: CASE STUDY, KOROSI GEOTHERMAL
Proceedings, 6 th African Rift Geothermal Conference Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2 nd 4 th November 2016 THREE DIMENSIONAL INVERSIONS OF MT RESISTIVITY DATA TO IMAGE GEOTHERMAL SYSTEMS: CASE STUDY, KOROSI GEOTHERMAL
Integrated Geophysical Model for Suswa Geothermal Prospect using Resistivity, Seismics and Gravity Survey Data in Kenya
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Integrated Geophysical Model for Suswa Geothermal Prospect using Resistivity, Seismics and Gravity Survey Data in Kenya
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Integrated Geophysical Model for Suswa Geothermal Prospect using Resistivity, Seismics and Gravity Survey Data in Kenya
The relative influence of different types of magnetotelluric data on joint inversions
 Earth Planets Space, 55, 243 248, 23 The relative influence of different types of magnetotelluric data on joint inversions Anna Gabàs and Alex Marcuello GRC Geodinàmica i Anàlisi de Conques, Departament
Earth Planets Space, 55, 243 248, 23 The relative influence of different types of magnetotelluric data on joint inversions Anna Gabàs and Alex Marcuello GRC Geodinàmica i Anàlisi de Conques, Departament
Hamed Aber 1 : Islamic Azad University, Science and Research branch, Tehran, Iran. Mir Sattar Meshin chi asl 2 :
 Present a Proper Pattern for Choose Best Electrode Array Based on Geological Structure Investigating in Geoelectrical Tomography, in order to Get the Highest Resolution Image of the Subsurface Hamed Aber
Present a Proper Pattern for Choose Best Electrode Array Based on Geological Structure Investigating in Geoelectrical Tomography, in order to Get the Highest Resolution Image of the Subsurface Hamed Aber
A Brief Introduction to Magnetotellurics and Controlled Source Electromagnetic Methods
 A Brief Introduction to Magnetotellurics and Controlled Source Electromagnetic Methods Frank Morrison U.C. Berkeley With the help of: David Alumbaugh Erika Gasperikova Mike Hoversten Andrea Zirilli A few
A Brief Introduction to Magnetotellurics and Controlled Source Electromagnetic Methods Frank Morrison U.C. Berkeley With the help of: David Alumbaugh Erika Gasperikova Mike Hoversten Andrea Zirilli A few
An Experimental Magnetotelluric Short Sounding During High Sun Spot Activity Cycle in 2013
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 An Experimental Magnetotelluric Short Sounding During High Sun Spot Activity Cycle in 2013 Lendriadi AGUNG and Imam B.
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 An Experimental Magnetotelluric Short Sounding During High Sun Spot Activity Cycle in 2013 Lendriadi AGUNG and Imam B.
Peter R. Milligan. Stephan Thiel. Geoscience Australia. The University of Adelaide. MT acquisition & processing
 Magnetotelluric acquisition & processing, with examples from the Gawler Craton, Curnamona Province and Curnamona- Gawler Link transects in South Australia Peter R. Milligan Geoscience Australia Stephan
Magnetotelluric acquisition & processing, with examples from the Gawler Craton, Curnamona Province and Curnamona- Gawler Link transects in South Australia Peter R. Milligan Geoscience Australia Stephan
Special Section Marine Control-Source Electromagnetic Methods
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 7, NO. MARCH-APRIL 7 ; P. WA63 WA7, FIGS. 9/43647 Special Section Marine Control-Source Electromagnetic Methods D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling: Part The effect of
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 7, NO. MARCH-APRIL 7 ; P. WA63 WA7, FIGS. 9/43647 Special Section Marine Control-Source Electromagnetic Methods D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling: Part The effect of
IRETHERM: Multidimensional Geophysical Modelling of the Southern Margin of the Dublin Basin
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 IRETHERM: Multidimensional Geophysical Modelling of the Southern Margin of the Dublin Basin Jan Vozar 1, Alan G. Jones
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 IRETHERM: Multidimensional Geophysical Modelling of the Southern Margin of the Dublin Basin Jan Vozar 1, Alan G. Jones
Three-dimensional geophysical modelling of the Alalobeda geothermal field
 Three-dimensional geophysical modelling of the Alalobeda geothermal field Daniele Rizzello 1, Egidio Armadillo 2, Claudio Pasqua 2,3, Massimo Verdoya 2, Solomon Kebede 4, Andarge Mengiste 4, Getenesh H/Giorgis
Three-dimensional geophysical modelling of the Alalobeda geothermal field Daniele Rizzello 1, Egidio Armadillo 2, Claudio Pasqua 2,3, Massimo Verdoya 2, Solomon Kebede 4, Andarge Mengiste 4, Getenesh H/Giorgis
Magnetotelluric Survey in an Extremely Noisy Environment at the Pohang Low-Enthalpy Geothermal Area, Korea
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005 Antalya, Turkey, 24-29 April 2005 Magnetotelluric Survey in an Extremely Noisy Environment at the Pohang Low-Enthalpy Geothermal Area, Korea Toshihiro Uchida
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005 Antalya, Turkey, 24-29 April 2005 Magnetotelluric Survey in an Extremely Noisy Environment at the Pohang Low-Enthalpy Geothermal Area, Korea Toshihiro Uchida
Tu Olym 01 Quantitative Depth to Bedrock Extraction from AEM Data
 Tu Olym 01 Quantitative Depth to Bedrock Extraction from AEM Data H. Anschütz (NGI), C. Christensen (Queen's University) & A.A. Pfaffhuber* (NGI) SUMMARY A new road segment is being planned northeast of
Tu Olym 01 Quantitative Depth to Bedrock Extraction from AEM Data H. Anschütz (NGI), C. Christensen (Queen's University) & A.A. Pfaffhuber* (NGI) SUMMARY A new road segment is being planned northeast of
Subsurface Conductivity Obtained from DC Railway Signal Propagation with a Dipole Model
 Subsurface Conductivity Obtained from DC Railway Signal Propagation with a Dipole Model Anne Neska Institute of Geophysics PAS, Ul. Ks. Janusza 64, 01-452 Warszawa, Poland, email: anne@igf.edu.pl Abstract
Subsurface Conductivity Obtained from DC Railway Signal Propagation with a Dipole Model Anne Neska Institute of Geophysics PAS, Ul. Ks. Janusza 64, 01-452 Warszawa, Poland, email: anne@igf.edu.pl Abstract
Gravity-Magnetic & Magneto-Telluric surveys in Purnea Onland Basin, India - A case history.
 P-281 Gravity-Magnetic & Magneto-Telluric surveys in Purnea Onland Basin, India - A case history. Summary A.K. Roy, D.P. Paine*, S. Sett, and H.N. Bhattacharya, ONGC This paper describes a case history
P-281 Gravity-Magnetic & Magneto-Telluric surveys in Purnea Onland Basin, India - A case history. Summary A.K. Roy, D.P. Paine*, S. Sett, and H.N. Bhattacharya, ONGC This paper describes a case history
AND HORSEFLY PROSPECTS, N.W. BRITISH COLUMBIA NTS, 103H/ll, 14 FOR ATNA RESOURCES LTD DELTA GEOSCIENCE LTD
 AND HORSEFLY PROSPECTS, N.W. BRITISH COLUMBIA NTS, 103H/ll, 14 FOR ATNA RESOURCES LTD BY DELTA GEOSCIENCE LTD FE T A. HENDRICKSON, P.GEO. 1 . TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction............. Page 1. Personnel..........
AND HORSEFLY PROSPECTS, N.W. BRITISH COLUMBIA NTS, 103H/ll, 14 FOR ATNA RESOURCES LTD BY DELTA GEOSCIENCE LTD FE T A. HENDRICKSON, P.GEO. 1 . TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction............. Page 1. Personnel..........
The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration
 The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration Adele Manzella CNR - Via Moruzzi 1 56124 PISA, Italy manzella@igg.cnr.it Foreword MT is one of the most used geophysical methods for geothermal exploration.
The Role of Magnetotellurics in Geothermal Exploration Adele Manzella CNR - Via Moruzzi 1 56124 PISA, Italy manzella@igg.cnr.it Foreword MT is one of the most used geophysical methods for geothermal exploration.
RESISTIVITY SURVEYING AND ELECTROMAGNETIC METHODS
 Presented at Short Course VII on Surface Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP and LaGeo, in Santa Tecla and Ahuachapán, El Salvador, March 14-22, 2015. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
Presented at Short Course VII on Surface Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP and LaGeo, in Santa Tecla and Ahuachapán, El Salvador, March 14-22, 2015. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
CHARACTERIZATION OF SOIL PROFILE OF DHAKA CITY USING ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY TOMOGRAPHY (ERT)
 CHARACTERIZATION OF SOIL PROFILE OF DHAKA CITY USING ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY TOMOGRAPHY (ERT) Mehedi Ahmed ANSARY 1, B.S. Pushpendue BISWAS 2 and Abul KHAIR 3 1 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering
CHARACTERIZATION OF SOIL PROFILE OF DHAKA CITY USING ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY TOMOGRAPHY (ERT) Mehedi Ahmed ANSARY 1, B.S. Pushpendue BISWAS 2 and Abul KHAIR 3 1 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering
Tu 23P1 06 Mapping Possible Flowpaths of Contaminants through Surface and Cross-borehole Spectral Timedomain Induced Polarization
 Tu 23P1 06 Mapping Possible Flowpaths of Contaminants through Surface and Cross-borehole Spectral Timedomain Induced Polarization T. Bording* (Aarhus University), G. Fiandaca (Aarhus University), P.K.
Tu 23P1 06 Mapping Possible Flowpaths of Contaminants through Surface and Cross-borehole Spectral Timedomain Induced Polarization T. Bording* (Aarhus University), G. Fiandaca (Aarhus University), P.K.
Geological Mapping using Geophysics
 Geological Mapping using Geophysics Pugin, A.J.M. and T.H. Larson Illinois State Geological Survey, 615 E Peabody Dr., Champaign, IL 61820; E-mail: A.J.M. Pugin at pugin@isgs.uiuc.edu Mapping Techniques.
Geological Mapping using Geophysics Pugin, A.J.M. and T.H. Larson Illinois State Geological Survey, 615 E Peabody Dr., Champaign, IL 61820; E-mail: A.J.M. Pugin at pugin@isgs.uiuc.edu Mapping Techniques.
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements
 Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
September 16, 2010 Magnetic surveying
 September 16, 2010 Magnetic surveying After today, you will be able to Sketch anomalies over objects at any location, and explain how you derived the pattern. Explain the relation between dipoles and real
September 16, 2010 Magnetic surveying After today, you will be able to Sketch anomalies over objects at any location, and explain how you derived the pattern. Explain the relation between dipoles and real
Electrical Resistivity Survey for Delineating Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer
 Electrical Resistivity Survey for Delineating Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer Sung-Ho Song*, Gyu-Sang Lee*, Jin-Sung Kim*, Baekuk Seong*, Young-gyu Kim*, Myung-Ha Woo* and Namsik Park** Abstract
Electrical Resistivity Survey for Delineating Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer Sung-Ho Song*, Gyu-Sang Lee*, Jin-Sung Kim*, Baekuk Seong*, Young-gyu Kim*, Myung-Ha Woo* and Namsik Park** Abstract
Estimating vertical and horizontal resistivity of the overburden and the reservoir for the Alvheim Boa field. Folke Engelmark* and Johan Mattsson, PGS
 Estimating vertical and horizontal resistivity of the overburden and the reservoir for the Alvheim Boa field. Folke Engelmark* and Johan Mattsson, PGS Summary Towed streamer EM data was acquired in October
Estimating vertical and horizontal resistivity of the overburden and the reservoir for the Alvheim Boa field. Folke Engelmark* and Johan Mattsson, PGS Summary Towed streamer EM data was acquired in October
SEAM2: 3D NON-SEISMIC MODELING OF A COMPLEX MIDDLE EAST O&G PROSPECT
 6th International Symposium on Three-Dimensional Electromagnetics Berkeley, California, USA, March 28-3, 217 SEAM2: 3D NON-SEISMIC MODELING OF A COMPLEX MIDDLE EAST O&G PROSPECT M. D. Watts 1, R. L. Mackie
6th International Symposium on Three-Dimensional Electromagnetics Berkeley, California, USA, March 28-3, 217 SEAM2: 3D NON-SEISMIC MODELING OF A COMPLEX MIDDLE EAST O&G PROSPECT M. D. Watts 1, R. L. Mackie
1. Resistivity of rocks
 RESISTIVITY 1) Resistivity of rocks 2) General principles of resistivity surveying 3) Field procedures, interpretation and examples 4) Summary and conclusions INDUCED POLARIZATION 1) General principles
RESISTIVITY 1) Resistivity of rocks 2) General principles of resistivity surveying 3) Field procedures, interpretation and examples 4) Summary and conclusions INDUCED POLARIZATION 1) General principles
Mapping Silicification in Gold Exploration
 Mapping Silicification in Gold Exploration with Inductive Source Resistivity James Macnae and Patrick McGowan, Lamontagne Geophysics Ltd. Lamontagne Geophysics Ltd. 115 Grant Timmins Drive Kingston, Ontario
Mapping Silicification in Gold Exploration with Inductive Source Resistivity James Macnae and Patrick McGowan, Lamontagne Geophysics Ltd. Lamontagne Geophysics Ltd. 115 Grant Timmins Drive Kingston, Ontario
Magnetotelluric and Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Study of Aquistore CO 2 Sequestration Site, near Estevan, Saskatchewan
 Magnetotelluric and Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Study of Aquistore CO 2 Sequestration Site, near Estevan, Saskatchewan Joe, B, McLeod 1, Ian, J, Ferguson 1, Jim Craven 2, Brian Roberts 2, Eric Roots
Magnetotelluric and Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Study of Aquistore CO 2 Sequestration Site, near Estevan, Saskatchewan Joe, B, McLeod 1, Ian, J, Ferguson 1, Jim Craven 2, Brian Roberts 2, Eric Roots
Geophysics Course Introduction to DC Resistivity
 NORAD supported project in MRRD covering Capacity Building and Institutional Cooperation in the field of Hydrogeology for Faryab Province Afghanistan Geophysics Course Introduction to DC Resistivity By
NORAD supported project in MRRD covering Capacity Building and Institutional Cooperation in the field of Hydrogeology for Faryab Province Afghanistan Geophysics Course Introduction to DC Resistivity By
MT as a tool for geothermal exploration: a case study from Southern Tuscany
 European Geothermal Congress 2013 Pisa, Italy, 3 7 June 2013 MT as a tool for geothermal exploration: a case study from Southern Tuscany Giorgio Buonasorte 1, Ricardo Caranova 2, Adolfo Fiordelisi 1, Carlo
European Geothermal Congress 2013 Pisa, Italy, 3 7 June 2013 MT as a tool for geothermal exploration: a case study from Southern Tuscany Giorgio Buonasorte 1, Ricardo Caranova 2, Adolfo Fiordelisi 1, Carlo
Two-dimensional Inversion of Resistivity and IP Data with Topography
 Two-dimensional Inversion of Resistivity and IP Data with Topography a) Smooth-Model Resistivity (ohm-m) Elevation (m) b) Calculated Apparent Resistivity (ohm-m) 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
Two-dimensional Inversion of Resistivity and IP Data with Topography a) Smooth-Model Resistivity (ohm-m) Elevation (m) b) Calculated Apparent Resistivity (ohm-m) 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
IN RECONNAISSANCE geophysical exploration for oil
 1228 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 14, NO. 8, AUGUST 2017 Joint Inversion of Gravity and Magnetotelluric Data for the Depth-to-Basement Estimation Abstract It is well known that both
1228 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 14, NO. 8, AUGUST 2017 Joint Inversion of Gravity and Magnetotelluric Data for the Depth-to-Basement Estimation Abstract It is well known that both
. Slide 1. Geological Survey of Ethiopia, P.O.Box 2302, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
 The electrical resistivity structure of the Southern Main Ethiopian Rift (around the Lake Abaya geothermal prospect) revealed by magneto-telluric telluric imaging Mohammednur Desissa and Yohanes Lema Geological
The electrical resistivity structure of the Southern Main Ethiopian Rift (around the Lake Abaya geothermal prospect) revealed by magneto-telluric telluric imaging Mohammednur Desissa and Yohanes Lema Geological
Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions
 Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions Folke Engelmark* PGS Multi-Transient EM, Asia-Pacific, Singapore folke.engelmark@pgs.com Summary Successful as
Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions Folke Engelmark* PGS Multi-Transient EM, Asia-Pacific, Singapore folke.engelmark@pgs.com Summary Successful as
POTASH DRAGON CHILE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY TRANSIENT ELECTROMAGNETIC (TEM) METHOD. LLAMARA and SOLIDA PROJECTS SALAR DE LLAMARA, IQUIQUE, REGION I, CHILE
 POTASH DRAGON CHILE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY TRANSIENT ELECTROMAGNETIC (TEM) METHOD LLAMARA and SOLIDA PROJECTS SALAR DE LLAMARA, IQUIQUE, REGION I, CHILE OCTOBER 2012 CONTENT Page I INTRODUCTION 1 II FIELD
POTASH DRAGON CHILE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY TRANSIENT ELECTROMAGNETIC (TEM) METHOD LLAMARA and SOLIDA PROJECTS SALAR DE LLAMARA, IQUIQUE, REGION I, CHILE OCTOBER 2012 CONTENT Page I INTRODUCTION 1 II FIELD
Using Curvature to Map Faults, Fractures
 Using Curvature to Map Faults, Fractures by SATINDER CHOPRA and KURT J. MARFURT Editor s note: Chopra is with Arcis Corp., Calgary, Canada; Marfurt is with the University of Oklahoma. Both are AAPG members.
Using Curvature to Map Faults, Fractures by SATINDER CHOPRA and KURT J. MARFURT Editor s note: Chopra is with Arcis Corp., Calgary, Canada; Marfurt is with the University of Oklahoma. Both are AAPG members.
Geophysics for Environmental and Geotechnical Applications
 Geophysics for Environmental and Geotechnical Applications Dr. Katherine Grote University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Why Use Geophysics? Improve the quality of site characterization (higher resolution and
Geophysics for Environmental and Geotechnical Applications Dr. Katherine Grote University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Why Use Geophysics? Improve the quality of site characterization (higher resolution and
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
We N Geophysical Near-surface Characterization for Static Corrections: Multi-physics Survey in Reggane Field, Algeria
 We N114 01 Geophysical Near-surface Characterization for Static Corrections: Multi-physics Survey in Reggane Field, Algeria A. Pineda* (Repsol), S. Gallo (CGG) & H. Harkas (GRN Sonatrach) SUMMARY We are
We N114 01 Geophysical Near-surface Characterization for Static Corrections: Multi-physics Survey in Reggane Field, Algeria A. Pineda* (Repsol), S. Gallo (CGG) & H. Harkas (GRN Sonatrach) SUMMARY We are
Exploring for geothermal reservoirs using broadband 2-D MT and gravity in Hungary
 KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. An EMGS/RXT company Exploring for geothermal reservoirs using broadband 2-D MT and gravity in Hungary Tulinius, H., Adám, L., Halldórsdóttir, H.,Yu, G., Strack, K.
KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. An EMGS/RXT company Exploring for geothermal reservoirs using broadband 2-D MT and gravity in Hungary Tulinius, H., Adám, L., Halldórsdóttir, H.,Yu, G., Strack, K.
Electrical Surveying (part A)
 Electrical Surveying (part A) Dr. Laurent Marescot Course given at the University of Fribourg (2009) Contact: laurent@tomoquest.com www.tomoquest.com 1 Introduction Electrical surveying Resistivity method
Electrical Surveying (part A) Dr. Laurent Marescot Course given at the University of Fribourg (2009) Contact: laurent@tomoquest.com www.tomoquest.com 1 Introduction Electrical surveying Resistivity method
Investigation of the electrical resistivity and geological structures on the hot springs in Markazi province of Iran using magnetotelluric method
 Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata Vol. 54, n. 3, pp. 245-256; September 2013 DOI 10.4430/bgta0102 Investigation of the electrical resistivity and geological structures on the hot springs in
Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata Vol. 54, n. 3, pp. 245-256; September 2013 DOI 10.4430/bgta0102 Investigation of the electrical resistivity and geological structures on the hot springs in
A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure
 A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure M. Vöge ( 1 ), A. A. Pfaffhuber ( 1 ), K. Hokstad ( 2 ), B. Fotland( 2 ) ( 1 ) Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure M. Vöge ( 1 ), A. A. Pfaffhuber ( 1 ), K. Hokstad ( 2 ), B. Fotland( 2 ) ( 1 ) Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
RESISTIVITY IMAGING IN EASTERN NEVADA USING THE AUDIOMAGNETOTELLURIC METHOD FOR HYDROGEOLOGIC FRAMEWORK STUDIES. Abstract.
 RESISTIVITY IMAGING IN EASTERN NEVADA USING THE AUDIOMAGNETOTELLURIC METHOD FOR HYDROGEOLOGIC FRAMEWORK STUDIES Darcy K. McPhee, U.S. Geological Survey, Menlo Park, CA Louise Pellerin, Green Engineering,
RESISTIVITY IMAGING IN EASTERN NEVADA USING THE AUDIOMAGNETOTELLURIC METHOD FOR HYDROGEOLOGIC FRAMEWORK STUDIES Darcy K. McPhee, U.S. Geological Survey, Menlo Park, CA Louise Pellerin, Green Engineering,
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting SUMMARY
 Simultaneous joint inversion of MT and CSEM data using a multiplicative cost function Aria Abubakar, Maokun Li, Jianguo Liu and Tarek M. Habashy, Schlumberger-Doll Research, Cambridge, MA, USA SUMMARY
Simultaneous joint inversion of MT and CSEM data using a multiplicative cost function Aria Abubakar, Maokun Li, Jianguo Liu and Tarek M. Habashy, Schlumberger-Doll Research, Cambridge, MA, USA SUMMARY
Downloaded 08/29/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 New approach to 3D inversion of MCSEM and MMT data using multinary model transform Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging SUMMARY Marine controlled-source electromagnetic
New approach to 3D inversion of MCSEM and MMT data using multinary model transform Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging SUMMARY Marine controlled-source electromagnetic
Early Analogue Modeling Experiments and Related Studies to Today s Problems of Geo-electromagnetic Exploration
 Journal of Earth Science, Vol. 20, No. 3, p. 618 625, June 2009 ISSN 1674-487X Printed in China DOI: 10.1007/s12583-009-0051-y Early Analogue Modeling Experiments and Related Studies to Today s Problems
Journal of Earth Science, Vol. 20, No. 3, p. 618 625, June 2009 ISSN 1674-487X Printed in China DOI: 10.1007/s12583-009-0051-y Early Analogue Modeling Experiments and Related Studies to Today s Problems
The advantages of complementing MT profiles in 3- D environments with. geomagnetic transfer function and inter- station horizontal magnetic transfer
 Page of The advantages of complementing MT profiles in - D environments with geomagnetic transfer function and inter- station horizontal magnetic transfer function data: Results from a synthetic case study
Page of The advantages of complementing MT profiles in - D environments with geomagnetic transfer function and inter- station horizontal magnetic transfer function data: Results from a synthetic case study
Joint Interpretation of Magnetotelluric and Seismic Models for Exploration of the Gross Schoenebeck Geothermal Site
 Joint Interpretation of Magnetotelluric and Seismic Models for Exploration of the Gross Schoenebeck Geothermal Site G. Muñoz, K. Bauer, I. Moeck, O. Ritter GFZ Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum Introduction
Joint Interpretation of Magnetotelluric and Seismic Models for Exploration of the Gross Schoenebeck Geothermal Site G. Muñoz, K. Bauer, I. Moeck, O. Ritter GFZ Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum Introduction
3D MAGNETOTELLURIC CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COSO GEOTHERMAL FIELD
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 2005 SGP-TR-176 3D MAGNETOTELLURIC CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COSO GEOTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 31-February 2, 2005 SGP-TR-176 3D MAGNETOTELLURIC CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COSO GEOTHERMAL
Magneto-Telluric (MT) Survey in Tendaho Geothermal Prospect, Northeast Ethiopia.
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Magneto-Telluric (MT) Survey in Tendaho Geothermal Prospect, Northeast Ethiopia. Yiheyis Workalemahu Geothermal Resource
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 Magneto-Telluric (MT) Survey in Tendaho Geothermal Prospect, Northeast Ethiopia. Yiheyis Workalemahu Geothermal Resource
Sub-basalt exploration in the Kutch-Saurashtra basin using EM
 Sub-basalt exploration in the Kutch-Saurashtra basin using EM Paper ID: 2003081 Deepankar Borgohain 1, Krishna Kumar 2, U G Marathe 3, Pradipta Mishra 3, Deepak Kumar 1 1.EMGS Asia Pacific Sdn Bhd, 1009
Sub-basalt exploration in the Kutch-Saurashtra basin using EM Paper ID: 2003081 Deepankar Borgohain 1, Krishna Kumar 2, U G Marathe 3, Pradipta Mishra 3, Deepak Kumar 1 1.EMGS Asia Pacific Sdn Bhd, 1009
Western EARS Geothermal Geophysics Context Mar-2016 William Cumming
 Western EARS Geothermal Geophysics Context Mar-2016 William Cumming Cumming Geoscience, Santa Rosa CA wcumming@wcumming.com Office: +1-707-546-1245 Mobile: +1-707-483-7959 Skype: wcumming.com Kibiro Geophysics
Western EARS Geothermal Geophysics Context Mar-2016 William Cumming Cumming Geoscience, Santa Rosa CA wcumming@wcumming.com Office: +1-707-546-1245 Mobile: +1-707-483-7959 Skype: wcumming.com Kibiro Geophysics
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site
 Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
APPLICATION OF ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY TOMOGRAPHY FOR SAND UNDERWATER EXTRACTION
 International Scientific Conference GEOBALCANICA 2018 APPLICATION OF ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY TOMOGRAPHY FOR SAND UNDERWATER EXTRACTION Maya Grigorova Ivaylo Koprev University of Mining and Geology St. Ivan
International Scientific Conference GEOBALCANICA 2018 APPLICATION OF ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY TOMOGRAPHY FOR SAND UNDERWATER EXTRACTION Maya Grigorova Ivaylo Koprev University of Mining and Geology St. Ivan
Geoelectricity. ieso 2010
 Geoelectricity ieso 2010 1 RESISTIVITY SURVEY AT VENETO VILLA GRITTI AT THE TOWN OF TREVISO (VENETO REGION) The survey was carried out to verify the underground presence of the fondations of a rustic building.
Geoelectricity ieso 2010 1 RESISTIVITY SURVEY AT VENETO VILLA GRITTI AT THE TOWN OF TREVISO (VENETO REGION) The survey was carried out to verify the underground presence of the fondations of a rustic building.
Magnetotelluric tensor decomposition: Part II, Examples of a basic procedure
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 63, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1998); P. 1898 1907, 5 FIGS. Magnetotelluric tensor decomposition: Part II, Examples of a basic procedure F. E. M. (Ted) Lilley ABSTRACT The decomposition
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 63, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1998); P. 1898 1907, 5 FIGS. Magnetotelluric tensor decomposition: Part II, Examples of a basic procedure F. E. M. (Ted) Lilley ABSTRACT The decomposition
The Effect of 2-D Resistivity on Magnetic Field
 The Effect of 2-D Resistivity on Magnetic Field M.M. Nordiana 1, Umi Maslinda 2, Hazrul Hisham 2, M.K.A. Nuramalina 2 1 Geophysics Lecturer, Geophysics Section, School of Physics, 11800 Universiti Sains
The Effect of 2-D Resistivity on Magnetic Field M.M. Nordiana 1, Umi Maslinda 2, Hazrul Hisham 2, M.K.A. Nuramalina 2 1 Geophysics Lecturer, Geophysics Section, School of Physics, 11800 Universiti Sains
Geophysics Course Interpreting DC Resistivity Data
 NORAD supported project in MRRD covering Capacity Building and Institutional Cooperation in the field of Hydrogeology for Faryab Province Afghanistan Geophysics Course Interpreting DC Resistivity Data
NORAD supported project in MRRD covering Capacity Building and Institutional Cooperation in the field of Hydrogeology for Faryab Province Afghanistan Geophysics Course Interpreting DC Resistivity Data
Numerical modeling of Z-TEM (airborne AFMAG) responses to guide exploration strategies Bob Lo*, Geotech Ltd., Michael Zang, Exploration Syndicate Inc.
 Bob Lo*, Geotech Ltd., Michael Zang, Exploration Syndicate Inc. Summary Mineral exploration using the Z-TEM or Z-Axis Tipper Electromagnetics, an airborne AFMAG system, has been guided by numerical modeling
Bob Lo*, Geotech Ltd., Michael Zang, Exploration Syndicate Inc. Summary Mineral exploration using the Z-TEM or Z-Axis Tipper Electromagnetics, an airborne AFMAG system, has been guided by numerical modeling
I. Rhineland Brown Coal and Near-surface Electromagnetics
 Vertical Electrical Resistivity Structure of the Garzweiler and Frimmersdorf Coal Seams Inferred from Transient Electromagnetic Data Karam S. I. Farag* and Bülent Tezkan* E-mail: farag@geo.uni-koeln.de
Vertical Electrical Resistivity Structure of the Garzweiler and Frimmersdorf Coal Seams Inferred from Transient Electromagnetic Data Karam S. I. Farag* and Bülent Tezkan* E-mail: farag@geo.uni-koeln.de
ACCURATE SUBSURFACE CHARACTERIZATION FOR HIGHWAY APPLICATIONS USING RESISTIVITY INVERSION METHODS
 ACCURATE SUBSURFACE CHARACTERIZATION FOR HIGHWAY APPLICATIONS USING RESISTIVITY INVERSION METHODS Ioannis F. Louis 1, Filippos I. Louis 2 and Melanie Bastou 3 1 Geophysics & Geothermic Division, Geology
ACCURATE SUBSURFACE CHARACTERIZATION FOR HIGHWAY APPLICATIONS USING RESISTIVITY INVERSION METHODS Ioannis F. Louis 1, Filippos I. Louis 2 and Melanie Bastou 3 1 Geophysics & Geothermic Division, Geology
MT measurements in the Cape Fold Belt, South Africa
 MT measurements in the Cape Fold Belt, South Africa Kristina Tietze 1,2, Ute Weckmann 1,2, Jana Beerbaum 1,2, Juliane Hübert 1,3, Oliver Ritter 1 1 GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, 14473 Potsdam,
MT measurements in the Cape Fold Belt, South Africa Kristina Tietze 1,2, Ute Weckmann 1,2, Jana Beerbaum 1,2, Juliane Hübert 1,3, Oliver Ritter 1 1 GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, 14473 Potsdam,
Integrated interpretation of multimodal geophysical data for exploration of geothermal resources Case study: Yamagawa geothermal field in Japan
 Integrated interpretation of multimodal geophysical data for exploration of geothermal resources Case study: Yamagawa geothermal field in Japan Masashi Endo*(TechnoImaging), Alex Gribenko (TechnoImaging
Integrated interpretation of multimodal geophysical data for exploration of geothermal resources Case study: Yamagawa geothermal field in Japan Masashi Endo*(TechnoImaging), Alex Gribenko (TechnoImaging
Modeling of 3D MCSEM and Sensitivity Analysis
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 5, 2007 641 Modeling of 3D MCSEM and Sensitivity Analysis Zhanxiang He 1, 2, Zhigang Wang 2, Gang Yu 3, Kurt Strack 3, and Haiying Liu 2 1 Department of Geosciences, University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 5, 2007 641 Modeling of 3D MCSEM and Sensitivity Analysis Zhanxiang He 1, 2, Zhigang Wang 2, Gang Yu 3, Kurt Strack 3, and Haiying Liu 2 1 Department of Geosciences, University
Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation
 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation Naser Ebadati
2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation Naser Ebadati
Magnetotelluric (MT) Method
 Magnetotelluric (MT) Method Dr. Hendra Grandis Graduate Program in Applied Geophysics Faculty of Mining and Petroleum Engineering ITB Geophysical Methods Techniques applying physical laws (or theory) to
Magnetotelluric (MT) Method Dr. Hendra Grandis Graduate Program in Applied Geophysics Faculty of Mining and Petroleum Engineering ITB Geophysical Methods Techniques applying physical laws (or theory) to
Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway
 Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway Anwar Bhuiyan*, Eivind Vesterås and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The measured Towed Streamer EM data from a survey in the Barents Sea, undertaken in the Norwegian
Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway Anwar Bhuiyan*, Eivind Vesterås and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The measured Towed Streamer EM data from a survey in the Barents Sea, undertaken in the Norwegian
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Seismic tomography with co-located soft data
 Seismic tomography with co-located soft data Mohammad Maysami and Robert G. Clapp ABSTRACT There is a wide range of uncertainties present in seismic data. Limited subsurface illumination is also common,
Seismic tomography with co-located soft data Mohammad Maysami and Robert G. Clapp ABSTRACT There is a wide range of uncertainties present in seismic data. Limited subsurface illumination is also common,
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2012) 188, 945 958 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05312.x A simple 2-D explanation for negative phases in TE magnetotelluric data K. Selway, 1 S. Thiel
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2012) 188, 945 958 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05312.x A simple 2-D explanation for negative phases in TE magnetotelluric data K. Selway, 1 S. Thiel
INTEGRATION OF BOREHOLE INFORMATION AND RESISTIVITY DATA FOR AQUIFER VULNERABILITY
 INTEGRATION OF BOREHOLE INFORMATION AND RESISTIVITY DATA FOR AQUIFER VULNERABILITY ANDERS V. CHRISTIANSEN 1, ESBEN AUKEN 1 AND KURT SØRENSEN 1 1 HydroGeophysics Group, Aarhus University, Finlandsgade 8,
INTEGRATION OF BOREHOLE INFORMATION AND RESISTIVITY DATA FOR AQUIFER VULNERABILITY ANDERS V. CHRISTIANSEN 1, ESBEN AUKEN 1 AND KURT SØRENSEN 1 1 HydroGeophysics Group, Aarhus University, Finlandsgade 8,
Case Study: University of Connecticut (UConn) Landfill
 Case Study: University of Connecticut (UConn) Landfill Problem Statement:» Locate disposal trenches» Identify geologic features and distinguish them from leachate and locate preferential pathways in fractured
Case Study: University of Connecticut (UConn) Landfill Problem Statement:» Locate disposal trenches» Identify geologic features and distinguish them from leachate and locate preferential pathways in fractured
Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea
 Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea Zhijun Du*, PGS Summary The integrated analysis of controlled
Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea Zhijun Du*, PGS Summary The integrated analysis of controlled
Carpentaria Electrical Conductivity Anomaly, Queensland, as a major structure in the Australian Plate
 Geol. Soc. Australia Spec. Publ. 22, and Geol. Soc. America Spec. Pap. 372 (2003), 141 156 Carpentaria Electrical Conductivity Anomaly, Queensland, as a major structure in the Australian Plate F. E. M.
Geol. Soc. Australia Spec. Publ. 22, and Geol. Soc. America Spec. Pap. 372 (2003), 141 156 Carpentaria Electrical Conductivity Anomaly, Queensland, as a major structure in the Australian Plate F. E. M.
DECOMPOSITION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL MAGNETOTELLURIC DATA
 Chapter 13 DECOMPOSITION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL MAGNETOTELLURIC DATA Xavier Garcia and Alan G. Jones Geological Survey of Canada. 615 Booth Street. Ottawa, ON, KIA OE9, Canada Abstract: Decomposition of
Chapter 13 DECOMPOSITION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL MAGNETOTELLURIC DATA Xavier Garcia and Alan G. Jones Geological Survey of Canada. 615 Booth Street. Ottawa, ON, KIA OE9, Canada Abstract: Decomposition of
Monitoring hydraulic stimulation using telluric sounding
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-017-0767-3 FULL PAPER Monitoring hydraulic stimulation using telluric sounding Nigel Rees 1*, Graham Heinson 2 and Dennis Conway 2 Open Access Abstract The telluric sounding
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-017-0767-3 FULL PAPER Monitoring hydraulic stimulation using telluric sounding Nigel Rees 1*, Graham Heinson 2 and Dennis Conway 2 Open Access Abstract The telluric sounding
Distortion Effects on Magnetotelluric Sounding Data Investigated by 3D Modeling of High-Resolution Topography
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Distortion Effects on Magnetotelluric Sounding Data Investigated by 3D Modeling of High-Resolution Topography Mitchel A. Stark 1, Wolfgang Soyer 2, Stephen Hallinan 2, and
GRC Transactions, Vol. 37, 2013 Distortion Effects on Magnetotelluric Sounding Data Investigated by 3D Modeling of High-Resolution Topography Mitchel A. Stark 1, Wolfgang Soyer 2, Stephen Hallinan 2, and
National Geophysical Survey Science Opportunities
 National Geophysical Survey Science Opportunities Anton Ziolkowski Professor of Petroleum Geoscience University of Edinburgh BGS Keyworth 4 April 2016 Outline Brief biography Science opportunities High
National Geophysical Survey Science Opportunities Anton Ziolkowski Professor of Petroleum Geoscience University of Edinburgh BGS Keyworth 4 April 2016 Outline Brief biography Science opportunities High
GPR AS A COST EFFECTIVE BEDROCK MAPPING TOOL FOR LARGE AREAS. Abstract
 GPR AS A COST EFFECTIVE BEDROCK MAPPING TOOL FOR LARGE AREAS Dr. Jutta L. Hager, Hager GeoScience, Inc., Waltham, MA Mario Carnevale, Hager GeoScience, Inc., Waltham, MA Abstract Hager GeoScience, Inc.
GPR AS A COST EFFECTIVE BEDROCK MAPPING TOOL FOR LARGE AREAS Dr. Jutta L. Hager, Hager GeoScience, Inc., Waltham, MA Mario Carnevale, Hager GeoScience, Inc., Waltham, MA Abstract Hager GeoScience, Inc.
Walkaway Seismic Experiments: Stewart Gulch, Boise, Idaho
 Walkaway Seismic Experiments: Stewart Gulch, Boise, Idaho Lee M. Liberty Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface Boise State University Boise, Idaho 1. Summary CGISS conducted walkaway
Walkaway Seismic Experiments: Stewart Gulch, Boise, Idaho Lee M. Liberty Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface Boise State University Boise, Idaho 1. Summary CGISS conducted walkaway
Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, MS 74R316C, One Cyclotron Road, Berkeley CA 94720, USA.
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 The Importance of Full Impedance Tensor Analysis for 3D Magnetotelluric Imaging the Roots of High Temperature Geothermal
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 The Importance of Full Impedance Tensor Analysis for 3D Magnetotelluric Imaging the Roots of High Temperature Geothermal
Application of Ground Penetrating Radar for hydro-geological study
 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 65, February 2006, pp. 160-164 Application of Ground Penetrating Radar for hydro-geological study K K K Singh* Central Mining Research Institute, Dhanbad
Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 65, February 2006, pp. 160-164 Application of Ground Penetrating Radar for hydro-geological study K K K Singh* Central Mining Research Institute, Dhanbad
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
Summary. Introduction
 Noel Black*, Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging, Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, TechnoImaging and The University of Utah Summary Recent studies have inferred the feasibility of time-lapse controlled-source
Noel Black*, Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging, Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, TechnoImaging and The University of Utah Summary Recent studies have inferred the feasibility of time-lapse controlled-source
C031 Quantifying Structural Uncertainty in Anisotropic Depth Imaging - Gulf of Mexico Case Study
 C031 Quantifying Structural Uncertainty in Anisotropic Depth Imaging - Gulf of Mexico Case Study K. Osypov* (WesternGeco), D. Nichols (WesternGeco), Y. Yang (WesternGeco), F. Qiao (WesternGeco), M. O'Briain
C031 Quantifying Structural Uncertainty in Anisotropic Depth Imaging - Gulf of Mexico Case Study K. Osypov* (WesternGeco), D. Nichols (WesternGeco), Y. Yang (WesternGeco), F. Qiao (WesternGeco), M. O'Briain
P Forsmark site investigation. Electric soundings supporting inversion of helicopterborne EM-data. Hans Thunehed, Timo Pitkänen GeoVista AB
 P-03-44 Forsmark site investigation Electric soundings supporting inversion of helicopterborne EM-data Hans Thunehed, Timo Pitkänen GeoVista AB January 2003 Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB Swedish Nuclear
P-03-44 Forsmark site investigation Electric soundings supporting inversion of helicopterborne EM-data Hans Thunehed, Timo Pitkänen GeoVista AB January 2003 Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB Swedish Nuclear
