Deformation cycles of great subduction earthquakes in a viscoelastic Earth
|
|
|
- Shannon Felicity Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deformation cycles of great subduction earthquakes in a viscoelastic Earth Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada School of Earth and Ocean Science, University of Victoria???? (Drawn by Roy Hyndman)
2 Global Isostatic Adjustment (GIA) (or Post-glacial rebound) Nansen (1928) established Fennoscandian ice sheet history Haskell (1935) determined a mantle viscosity of Pa s Commonly accepted global average today: Pa s Viscosity of honey at room temperature: about 1000 Pa s
3 When plate tectonics just gained recognition: 1-D stress diffusion model of Elssaser (1969), Bott and Dean (1973)
4
5 Based on 1-D stress diffusion model of Elssaser (1969), Bott and Dean (1973) seaward landward opposing motion landward motion seaward motion Saw-tooth solution by Wang (1995)
6 Earth rheology for different timescales Viscous Viscoelastic Elastic Time-independent plasticity (shallow depths) Mantle convection Post-glacial rebound Earthquake cycle Post-seismic deformation Earthquake rupture millions of years millennia centuries decades years seconds
7 Strain ε σ σ Time T M = C η M /µ T K transient = C η K /µ creep µ µ C = M o /M o_ref η M elastic Maxwell viscous body ε σ n (n 1) ηk Kelvin body Bi-viscous Burgers body
8 We ve come a long way in monitoring and modeling earthquake deformation 1973 (Bott and Dean) Today 1984 (Thatcher and Rundle) Wang, Hu, He (Nature, 2012)
9 How do we observe a full earthquake cycle? Subduction earthquake cycles a few hundred years Modern geodesy (GPS) less than two decades
10 Japan: Two years after the M 9 Tohoku earthquake GSI website (February 2013) 11 March August 2013 East component Japan Trench 1 m Vertical component North component
11 Japan and Sumatra: shortly after a great earthquake All sites move seaward GSI website (February 2013) Japan Trench 1 m Grijalva et al (2009)
12 Alaska and Chile: ~ 40 years after a great earthquake: Opposing motion of coastal and inland sites M = M = Freymueller et al. (2009) Wang et al. (2007)
13 Cascadia: ~ 300 years after a M ~ 9 earthquake: All sites move landward Wells and Simpson (2001)
14 Inter-seismic 2 (Cascadia) Inter-seismic 1 (Alaska, Chile) Post-seismic (Japan, Sumatra) Coast line Wholesale landward opposing motion Wholesale seaward Co-seismic Coast line
15 Rupture Afterslip Stress relaxation Stress relaxation Characteristic timescales: Afterslip months to a few years Viscoelastic relaxation (transient) a few years Viscoelastic relaxation (steady-state) a few decades Locking length of the earthquake cycle
16 A couple of years About four decades Three centuries
17 Based on 1-D stress diffusion model of Elssaser (1969), Bott and Dean (1973) seaward landward landward motion seaward motion Saw-tooth solution by Wang (1995)
18 T K = C η K /µ= 4 yr T M = C η M /µ = 80 yr Central part of Sumatra mesh µ η M µ η K
19 Central part of Chile mesh Central part of Cascadia mesh Using exactly the same rheology as for Sumatra
20 Assigning coseismic slip and afterslip distributions Chlieh et al. (2007) Moreno et al. (2009) Priest et al. (2009) Details important Details less important Details unimportant
21 A couple of years About four decades Three centuries Wang, Hu, He (Nature, 2012)
22 Characteristic timescales used in the model: Afterslip 1.25 yrs Viscoelastic relaxation (transient) 4 years Viccoelastic relaxation (steady-state) 80 years Locking length of the earthquake cycle
23 Cascadia since the 1700 earthquake Nootka Sound England and France began to fight in eastern North America (Queen Anne s War). Captain Chirikov (Russia) landed on northwest coast of North America (Prince of Wales Island). Captain Cook sailed along west coast of North America and traded with native people at Nootka Sound. Dr. Wang lectures at ICTP Workshop on Megathrust earthquakes and Tsunamis Model by Hu, 2011, PhD thesis
24 1995 Antofagasta earthquake, N. Chile (M w = 8.0) Displacements (dominated by co-seismic) Velocities (2 years after earthquake) Data from Klotz et al. (1999) and Khazaradze and Klotz (2003)
25 COLI Motion of GPS station COLI following M 8.0 Jalisco, Mexico, earthquake of 1995 (Márquez Azúa et al., 2002)
26 large aftershock 2001 rupture area epicentre AREQ Motion of GPS station AREQ following M 8.4 Peru earthquake of June 2001 Displacement (cm) Perfettini et al., 2005 Courtesy of M. Chlieh North East Up M June 2001
27 Cascadia Chile Alaska Landward motion Sumatra Japan Seaward motion T M = C η M /µ Offshore postseismic New frontier Coastal Inland C = M o /M o_ref Wang, Hu, He (Nature, 2012)
28 Location of seaward-landward motion transition for different earthquake sizes Cascadia Chile Alaska Sumatra Japan T M = C η M /µ C = M o /M o_ref Offshore postseismic New frontier With afterslip No afterslip Wang, Hu, He (Nature, 2012)
29 Wang, Hu, and He (2012, Nature)? Related question: Can viscoelastic relaxation be ignored in short-term postseismic deformation?
30 Coast line Inter-seismic 2 (Cascadia) Inter-seismic 1 (Alaska, Chile) Post-seismic (Japan, Sumatra) opposing motion? Wholesale landward opposing motion Wholesale seaward Co-seismic Seafloor geodesy Coast line
31 Fujimoto, 2014
32 Too fast for locking Wrong direction for afterslip Rupture model: Iinuma et al. (2012) Land GPS: Ozawa et al. (2011) Seafloor GPS: Sato et al.; Kido et al. (2011) Land GPS: Ozawa et al. (2012) Seafloor GPS: Watanabe et al. (submitted) and this work
33 Upper plate Rupture area Incoming plate Asymmetric rupture
34 Upper plate Rupture area Incoming plate Model by T. Sun Eastward displacement normalized by maximum fault slip Upper plate Rupture area Incoming plate Time since earthquake (years)
35 Mantle wedge viscosity: ηm = 1.9 x 1018 Pa s ηk = 2.5 x 1017 Pa s
36
37 Sun et al., 2014 Nature
38 Sun et al., 2014 Nature
39 Contours lines: afterslip
40 Ozawa et al. (2012): Afterslip in elastic Earth fully explains 8-month postseismic motion of land GPS sites
41 Summary Interseismic deformation is not a mirror image of coseismic deformation Elastic model only provides an equivalent kinematic description (all elastic models of interseismic locking need revision) (Steady-state) mantle wedge viscosity ~ Pa s (very low!) Timescale of postseismic reversal of motion direction depends on earthquake size (longer for larger earthquakes) Transient rheology and afterslip are both responsible for short-term post-seismic deformation Rupture asymmetry leads to immediate motion reversal in the rupture area (important for constraining afterslip) All elastic models over-estimate afterslip downdip of rupture zone and under-estimate shallow afterslip Seafloor geodesy will soon bring more breakthrough discoveries
What scientists know and do not know about the big one at Cascadia
 What scientists know and do not know about the big one at Cascadia Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada The Cascadia Subduction Zone M 7.3, 1946 Rupture
What scientists know and do not know about the big one at Cascadia Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada The Cascadia Subduction Zone M 7.3, 1946 Rupture
Three-dimensional viscoelastic finite element model for postseismic deformation of the great 1960 Chile earthquake
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003163, 2004 Three-dimensional viscoelastic finite element model for postseismic deformation of the great 1960 Chile earthquake Y. Hu, 1 K.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003163, 2004 Three-dimensional viscoelastic finite element model for postseismic deformation of the great 1960 Chile earthquake Y. Hu, 1 K.
LETTER. Prevalence of viscoelastic relaxation after the 2011 Tohoku-oki earthquake
 doi:10.1038/nature13778 Prevalence of viscoelastic relaxation after the 2011 Tohoku-oki earthquake Tianhaozhe Sun 1, Kelin Wang 1,2, Takeshi Iinuma 3, Ryota Hino 3, Jiangheng He 2, Hiromi Fujimoto 3, Motoyuki
doi:10.1038/nature13778 Prevalence of viscoelastic relaxation after the 2011 Tohoku-oki earthquake Tianhaozhe Sun 1, Kelin Wang 1,2, Takeshi Iinuma 3, Ryota Hino 3, Jiangheng He 2, Hiromi Fujimoto 3, Motoyuki
Elizabeth H. Hearn modified from W. Behr
 Reconciling postseismic and interseismic surface deformation around strike-slip faults: Earthquake-cycle models with finite ruptures and viscous shear zones Elizabeth H. Hearn hearn.liz@gmail.com modified
Reconciling postseismic and interseismic surface deformation around strike-slip faults: Earthquake-cycle models with finite ruptures and viscous shear zones Elizabeth H. Hearn hearn.liz@gmail.com modified
High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation
 High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation L.L.A. Vermeersen (1), H. Schotman (1), M.-W. Jansen (1), R. Riva (1) and R. Sabadini (2) (1) DEOS,
High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation L.L.A. Vermeersen (1), H. Schotman (1), M.-W. Jansen (1), R. Riva (1) and R. Sabadini (2) (1) DEOS,
What is the LAB Dynamically: Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Rheology from Post-loading Deformation
 What is the LAB Dynamically: Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Rheology from Post-loading Deformation Roland Bürgmann, UC Berkeley With contributions by Pascal Audet, Daula Chandrasekhar, Georg Dresen, Andy
What is the LAB Dynamically: Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Rheology from Post-loading Deformation Roland Bürgmann, UC Berkeley With contributions by Pascal Audet, Daula Chandrasekhar, Georg Dresen, Andy
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2016) 205, 1455 1472 Advance Access publication 2016 March 7 GJI Geodynamics and tectonics doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw086 Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2016) 205, 1455 1472 Advance Access publication 2016 March 7 GJI Geodynamics and tectonics doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw086 Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation
} based on composition
 Learning goals: Predict types of earthquakes that will happen at different plate boundaries based on relative plate motion vector vs. strike (vector subtraction) Understand interseismic and coseismic deformation,
Learning goals: Predict types of earthquakes that will happen at different plate boundaries based on relative plate motion vector vs. strike (vector subtraction) Understand interseismic and coseismic deformation,
Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes
 1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller
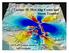 Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Interseismic locking of the plate interface in the northern Cascadia subduction zone, inferred from inversion of GPS data
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 231 (5) 239 247 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Interseismic locking of the plate interface in the northern Cascadia subduction zone, inferred from inversion of GPS data
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 231 (5) 239 247 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Interseismic locking of the plate interface in the northern Cascadia subduction zone, inferred from inversion of GPS data
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a
 The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
Earthquakes and Tsunamis
 Earthquakes and Tsunamis Kenji Satake Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo 1 Part I 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami 2 Fukushima Dai ichi NPP accident Earthquake ground motion Reactors automatically
Earthquakes and Tsunamis Kenji Satake Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo 1 Part I 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami 2 Fukushima Dai ichi NPP accident Earthquake ground motion Reactors automatically
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE
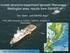 crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes
 Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Megathrust Earthquakes
 Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Tianhaozhe Sun B.Sc., Tongji University, A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of
 Crustal Deformation Associated with Great Subduction Earthquakes by Tianhaozhe Sun B.Sc., Tongji University, 2011 A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR
Crustal Deformation Associated with Great Subduction Earthquakes by Tianhaozhe Sun B.Sc., Tongji University, 2011 A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR
Rheology of the Mantle and Plates (part 1): Deformation mechanisms and flow rules of mantle minerals
 (part 1): Deformation mechanisms and flow rules of mantle minerals What is rheology? Rheology is the physical property that characterizes deformation behavior of a material (solid, fluid, etc) solid mechanics
(part 1): Deformation mechanisms and flow rules of mantle minerals What is rheology? Rheology is the physical property that characterizes deformation behavior of a material (solid, fluid, etc) solid mechanics
Differentiating earthquake tsunamis from other sources; how do we tell the difference?
 Differentiating earthquake tsunamis from other sources; how do we tell the difference? David Tappin (1), Stephan Grilli (2), Jeffrey Harris (2), Timothy Masterlark (3), James Kirby (4), Fengyan Shi Shi
Differentiating earthquake tsunamis from other sources; how do we tell the difference? David Tappin (1), Stephan Grilli (2), Jeffrey Harris (2), Timothy Masterlark (3), James Kirby (4), Fengyan Shi Shi
Tsunami potential and modeling
 Tsunami potential and modeling GEORGE PRIEST OREGON DEPT. OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES NEWPORT COASTAL FIELD OFFICE April 7, 2012 GeoPRISMS Cascadia Workshop, Portland, Oregon What creates most uncertainty
Tsunami potential and modeling GEORGE PRIEST OREGON DEPT. OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL INDUSTRIES NEWPORT COASTAL FIELD OFFICE April 7, 2012 GeoPRISMS Cascadia Workshop, Portland, Oregon What creates most uncertainty
Supplementary Figure 1 Published rupture models of the Tohoku-oki earthquake that included tsunami data as constraints. Each curve is labeled with
 Supplementary Figure 1 Published rupture models of the Tohoku-oki earthquake that included tsunami data as constraints. Each curve is labeled with its model number as in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2. This
Supplementary Figure 1 Published rupture models of the Tohoku-oki earthquake that included tsunami data as constraints. Each curve is labeled with its model number as in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2. This
Regional Geodesy. Shimon Wdowinski. MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region. University of Miami
 MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
Title. Author(s)Heki, Kosuke. CitationScience, 332(6036): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information. A Tale of Two Earthquakes
 Title A Tale of Two Earthquakes Author(s)Heki, Kosuke CitationScience, 332(6036): 1390-1391 Issue Date 2011-06-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/48524 Type article (author version) File Information
Title A Tale of Two Earthquakes Author(s)Heki, Kosuke CitationScience, 332(6036): 1390-1391 Issue Date 2011-06-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/48524 Type article (author version) File Information
Pure and Applied Geophysics. AKEMI NODA, 1,4 TSUTOMU TAKAHAMA, 1 TAKESHI KAWASATO, 2 and MITSUHIRO MATSU URA Introduction
 Pure Appl. Geophys. 175 (2018), 559 572 Ó 2017 The Author(s) This article is an open access publication https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1682-z Pure and Applied Geophysics Interpretation of Offshore
Pure Appl. Geophys. 175 (2018), 559 572 Ó 2017 The Author(s) This article is an open access publication https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1682-z Pure and Applied Geophysics Interpretation of Offshore
Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements
 Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise
 GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
Depth (Km) + u ( ξ,t) u = v pl. η= Pa s. Distance from Nankai Trough (Km) u(ξ,τ) dξdτ. w(x,t) = G L (x,t τ;ξ,0) t + u(ξ,t) u(ξ,t) = v pl
 Slip history during one earthquake cycle at the Nankai subduction zone, inferred from the inversion analysis of levelling data with a viscoelastic slip response function Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura, Akira Nishitani
Slip history during one earthquake cycle at the Nankai subduction zone, inferred from the inversion analysis of levelling data with a viscoelastic slip response function Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura, Akira Nishitani
Magnitude 7.7 QUEEN CHARLOTTE ISLANDS REGION
 A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
Great earthquakes and new insights into subduction seismogenesis
 Great earthquakes and new insights into subduction seismogenesis Heather R. DeShon Southern Methodist University GeoPRISMS DLP Georgia Southwestern State University Feb. 27th, 2013 The earth, the very
Great earthquakes and new insights into subduction seismogenesis Heather R. DeShon Southern Methodist University GeoPRISMS DLP Georgia Southwestern State University Feb. 27th, 2013 The earth, the very
Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake
 Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake 51 Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake Tetsuro IMAKIIRE, Shinzaburo OZAWA, Hiroshi YARAI, Takuya NISHIMURA
Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake 51 Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake Tetsuro IMAKIIRE, Shinzaburo OZAWA, Hiroshi YARAI, Takuya NISHIMURA
Contributions of poroelastic rebound and a weak volcanic arc to the postseismic deformation of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake
 Hu et al. Earth, Planets and Space 2014, 66:106 FULL PAPER Open Access Contributions of poroelastic rebound and a weak volcanic arc to the postseismic deformation of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake Yan Hu 1*,
Hu et al. Earth, Planets and Space 2014, 66:106 FULL PAPER Open Access Contributions of poroelastic rebound and a weak volcanic arc to the postseismic deformation of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake Yan Hu 1*,
Three-dimensional viscoelastic interseismic deformation model for the Cascadia subduction zone
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 295 306, 2001 Three-dimensional viscoelastic interseismic deformation model for the Cascadia subduction zone Kelin Wang, Jiangheng He, Herb Dragert, and Thomas S. James Pacific
Earth Planets Space, 53, 295 306, 2001 Three-dimensional viscoelastic interseismic deformation model for the Cascadia subduction zone Kelin Wang, Jiangheng He, Herb Dragert, and Thomas S. James Pacific
Supplementary Material
 1 Supplementary Material 2 3 4 Interseismic, megathrust earthquakes and seismic swarms along the Chilean subduction zone (38-18 S) 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 1 GPS data set We combined in a single data set
1 Supplementary Material 2 3 4 Interseismic, megathrust earthquakes and seismic swarms along the Chilean subduction zone (38-18 S) 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 1 GPS data set We combined in a single data set
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake
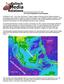 News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
Seismic Activity and Crustal Deformation after the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake
 J-RAPID Symposium March 6-7, 2013 Seismic Activity and Crustal Deformation after the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Y. Honkura Tokyo Institute of Technology Japan Science and Technology
J-RAPID Symposium March 6-7, 2013 Seismic Activity and Crustal Deformation after the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Y. Honkura Tokyo Institute of Technology Japan Science and Technology
Magnitude 7.0 N of ANCHORAGE, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies?
 Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies? F. Riguzzi 1, R. Devoti 1, G. Pietrantonio 1, M. Crespi 2, C. Doglioni 2, A.R. Pisani 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia 2 Università
Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies? F. Riguzzi 1, R. Devoti 1, G. Pietrantonio 1, M. Crespi 2, C. Doglioni 2, A.R. Pisani 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia 2 Università
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation following the 1999 M 7.4 İzmit earthquake from GPS measurements
 Geophys. J. Int. (2009) doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04228.x Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation following the 1999 M 7.4 İzmit earthquake from GPS measurements L. Wang, 1,2 R. Wang, 1 F. Roth, 1 B.
Geophys. J. Int. (2009) doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04228.x Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation following the 1999 M 7.4 İzmit earthquake from GPS measurements L. Wang, 1,2 R. Wang, 1 F. Roth, 1 B.
Magnitude 7.9 SE of KODIAK, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
A viscoelastic model of interseismic strain concentration in Niigata-Kobe Tectonic Zone of central Japan
 Earth Planets Space, 55, 667 675, 2003 A viscoelastic model of interseismic strain concentration in Niigata-Kobe Tectonic Zone of central Japan Mamoru Hyodo 1 and Kazuro Hirahara 2 1 Graduate School of
Earth Planets Space, 55, 667 675, 2003 A viscoelastic model of interseismic strain concentration in Niigata-Kobe Tectonic Zone of central Japan Mamoru Hyodo 1 and Kazuro Hirahara 2 1 Graduate School of
Additional earthquakes parameters are put in the order of a clock-wise sense geographically, except Sumatra and Java, where they are from west to
 1380 986 950 Additional earthquakes parameters are put in the order of a clock-wise sense geographically, except Sumatra and Java, where they are from west to east. s, g, and t in Data type denotes seismic,
1380 986 950 Additional earthquakes parameters are put in the order of a clock-wise sense geographically, except Sumatra and Java, where they are from west to east. s, g, and t in Data type denotes seismic,
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March
 Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Seismic and flexure constraints on lithospheric rheology and their dynamic implications
 Seismic and flexure constraints on lithospheric rheology and their dynamic implications Shijie Zhong Dept. of Physics, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, USA Acknowledgement: A. B. Watts Dept. of
Seismic and flexure constraints on lithospheric rheology and their dynamic implications Shijie Zhong Dept. of Physics, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, USA Acknowledgement: A. B. Watts Dept. of
Internal Layers of the Earth
 Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry. Planetary Surfaces
 Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Magnitude 8.3 SEA OF OKHOTSK
 A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
Long-term Crustal Deformation in and around Japan, Simulated by a 3-D Plate Subduction Model
 Long-term Crustal Deformation in and around Japan, Simulated by a 3-D Plate Subduction Model Chihiro Hashimoto (1) and Mitsuhiro Matsu ura (2) (1) Institute of Frontier Research for Earth Evolution, Japan
Long-term Crustal Deformation in and around Japan, Simulated by a 3-D Plate Subduction Model Chihiro Hashimoto (1) and Mitsuhiro Matsu ura (2) (1) Institute of Frontier Research for Earth Evolution, Japan
Why short-term crustal shortening leads to mountain building in the Andes, but not in Cascadia?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L08301, doi:10.1029/2009gl037347, 2009 Why short-term crustal shortening leads to mountain building in the Andes, but not in Cascadia?
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L08301, doi:10.1029/2009gl037347, 2009 Why short-term crustal shortening leads to mountain building in the Andes, but not in Cascadia?
Tsunami and earthquake in Chile Part 2
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE GENERAL JRC JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen Global Security and Crisis Management Unit CriTech Sunday, 28 February 2010 Executive
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE GENERAL JRC JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen Global Security and Crisis Management Unit CriTech Sunday, 28 February 2010 Executive
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling
 The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
Far-reaching transient motions after Mojave earthquakes require broad mantle flow beneath a strong crust
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L19302, doi:10.1029/2007gl030959, 2007 Far-reaching transient motions after Mojave earthquakes require broad mantle flow beneath a strong
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L19302, doi:10.1029/2007gl030959, 2007 Far-reaching transient motions after Mojave earthquakes require broad mantle flow beneath a strong
7.1 FIJI 1, :57:22 UTC
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 141 km (88 miles) northeast of Ndoi Island, Fiji, and 313 km (194 mi) west-northwest of Nuku alofa, Tonga according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 141 km (88 miles) northeast of Ndoi Island, Fiji, and 313 km (194 mi) west-northwest of Nuku alofa, Tonga according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports
Magnitude 7.1 PERU. There are early reports of homes and roads collapsed leaving one dead and several dozen injured.
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update
 The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
Rheology III. Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep
 Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Tsunami waves swept away houses and cars in northern Japan and pushed ships aground.
 Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen?
 San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
RR#8 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and the map below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map indicates the epicenter (*) of a major earthquake that occurred at 38 N 142 E.
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and the map below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map indicates the epicenter (*) of a major earthquake that occurred at 38 N 142 E.
Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology
 Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology World seismicity (data source: USGS) and velocities relative to ITRF1997 (Sella et
Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology World seismicity (data source: USGS) and velocities relative to ITRF1997 (Sella et
Magnitude 7.0 NEW CALEDONIA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Rosenau, M., Lohrmann, J., Oncken, O. (2009): Shocks in a box: An analog model of subduction earthquake cycles with application to seismotectonic forearc evolution. - Journal of
Originally published as: Rosenau, M., Lohrmann, J., Oncken, O. (2009): Shocks in a box: An analog model of subduction earthquake cycles with application to seismotectonic forearc evolution. - Journal of
A GLOBAL SURGE OF GREAT EARTHQUAKES FROM AND IMPLICATIONS FOR CASCADIA. Thorne Lay, University of California Santa Cruz
 A GLOBAL SURGE OF GREAT EARTHQUAKES FROM 2004-2014 AND IMPLICATIONS FOR CASCADIA Thorne Lay, University of California Santa Cruz Last 10 yrs - 18 great earthquakes: rate 1.8/yr; rate over preceding century
A GLOBAL SURGE OF GREAT EARTHQUAKES FROM 2004-2014 AND IMPLICATIONS FOR CASCADIA Thorne Lay, University of California Santa Cruz Last 10 yrs - 18 great earthquakes: rate 1.8/yr; rate over preceding century
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System
 SRL complex earthquakes 5/22/09 1 Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System Niels Bohr once observed How wonderful that we have met with a paradox. Now we have some hope of making progress. This situation
SRL complex earthquakes 5/22/09 1 Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System Niels Bohr once observed How wonderful that we have met with a paradox. Now we have some hope of making progress. This situation
Magnitude 7.2 OAXACA, MEXICO
 A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
Host researcher:bunichiro Shibazaki (International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, Building Research Institute)
 Invited personnel: Sylvain Barbot (Earth Observatory of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University) James D P Moore (Earth Observatory of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University) Host researcher:bunichiro
Invited personnel: Sylvain Barbot (Earth Observatory of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University) James D P Moore (Earth Observatory of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University) Host researcher:bunichiro
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures
 Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
Constraints on lithosphere and mantle rheology from in-situ observations
 Constraints on lithosphere and mantle rheology from in-situ observations Shijie Zhong Department of Physics University of Colorado at Boulder Collaborators: Archie Paulson and John Wahr on post-glacial
Constraints on lithosphere and mantle rheology from in-situ observations Shijie Zhong Department of Physics University of Colorado at Boulder Collaborators: Archie Paulson and John Wahr on post-glacial
Upper mantle rheology from GRACE and GPS postseismic deformation after the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake
 Upper mantle rheology from GRACE and GPS postseismic deformation after the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake I Panet, F Pollitz, V Mikhailov, M Diament, P Banerjee, K Grijalva To cite this version: I Panet,
Upper mantle rheology from GRACE and GPS postseismic deformation after the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake I Panet, F Pollitz, V Mikhailov, M Diament, P Banerjee, K Grijalva To cite this version: I Panet,
Magnitude 8.2 FIJI. A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of km (350 miles).
 A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred 364.8 km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 563.4 km (350 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google The
A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred 364.8 km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 563.4 km (350 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google The
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
overlie the seismogenic zone offshore Costa Rica, making the margin particularly well suited for combined land and ocean geophysical studies (Figure
 Chapter 1 Introduction Historically, highly destructive large magnitude (M w >7.0) underthrusting earthquakes nucleate along the shallow segment of subduction zone megathrust fault, and this region of
Chapter 1 Introduction Historically, highly destructive large magnitude (M w >7.0) underthrusting earthquakes nucleate along the shallow segment of subduction zone megathrust fault, and this region of
Surface changes caused by erosion and sedimentation were treated by solving: (2)
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA
 Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Course Business. Today: isostasy and Earth rheology, paper discussion
 Course Business Today: isostasy and Earth rheology, paper discussion Next week: sea level and glacial isostatic adjustment Email did you get my email today? Class notes, website Your presentations: November
Course Business Today: isostasy and Earth rheology, paper discussion Next week: sea level and glacial isostatic adjustment Email did you get my email today? Class notes, website Your presentations: November
Using deformation rates in Northern Cascadia to constrain time-dependent stress- and slip-rate on the megathrust
 Using deformation rates in Northern Cascadia to constrain time-dependent stress- and slip-rate on the megathrust Lucile Bruhat Paul Segall Stanford University 1 50 Interseismic period for the Cascadia
Using deformation rates in Northern Cascadia to constrain time-dependent stress- and slip-rate on the megathrust Lucile Bruhat Paul Segall Stanford University 1 50 Interseismic period for the Cascadia
Interplate coupling and transient slip along the subduction interface beneath Oaxaca, Mexico
 Geophys. J. Int. (2008) 175, 269 290 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03910.x Interplate coupling and transient slip along the subduction interface beneath Oaxaca, Mexico F. Correa-Mora, 1 C. DeMets, 1 E.
Geophys. J. Int. (2008) 175, 269 290 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03910.x Interplate coupling and transient slip along the subduction interface beneath Oaxaca, Mexico F. Correa-Mora, 1 C. DeMets, 1 E.
Crustal deformation and fault slip during the seismic cycle in the North Chile subduction zone, from GPS and InSAR observations
 Geophys J Int (24) 158, 695 711 doi: 11111/j1365-246X242326x Crustal deformation and fault slip during the seismic cycle in the North Chile subduction zone, from GPS and InSAR observations M Chlieh, 1,
Geophys J Int (24) 158, 695 711 doi: 11111/j1365-246X242326x Crustal deformation and fault slip during the seismic cycle in the North Chile subduction zone, from GPS and InSAR observations M Chlieh, 1,
Azimuth with RH rule. Quadrant. S 180 Quadrant Azimuth. Azimuth with RH rule N 45 W. Quadrant Azimuth
 30 45 30 45 Strike and dip notation (a) N30 E, 45 SE ("Quadrant"): the bearing of the strike direction is 30 degrees east of north and the dip is 45 degrees in a southeast (SE) direction. For a given strike,
30 45 30 45 Strike and dip notation (a) N30 E, 45 SE ("Quadrant"): the bearing of the strike direction is 30 degrees east of north and the dip is 45 degrees in a southeast (SE) direction. For a given strike,
Two Decades of Spatiotemporal Variations in Subduction Zone Coupling Offshore Japan
 Smith ScholarWorks Geosciences: Faculty Publications Geosciences 2-1-16 Two Decades of Spatiotemporal Variations in Subduction Zone Coupling Offshore Japan John P. Loveless Smith College, jloveles@smith.edu
Smith ScholarWorks Geosciences: Faculty Publications Geosciences 2-1-16 Two Decades of Spatiotemporal Variations in Subduction Zone Coupling Offshore Japan John P. Loveless Smith College, jloveles@smith.edu
RECENT COMPREHENSIVE TSUNAMI MODELING FOR COASTAL OREGON
 RECENT COMPREHENSIVE TSUNAMI MODELING FOR COASTAL OREGON Speaker: George R. Priest, Oregon Dept. of Geology and Mineral Industries Pardee Keynote Symposium Great Earthquakes, the Cascadia Subduction Zone,
RECENT COMPREHENSIVE TSUNAMI MODELING FOR COASTAL OREGON Speaker: George R. Priest, Oregon Dept. of Geology and Mineral Industries Pardee Keynote Symposium Great Earthquakes, the Cascadia Subduction Zone,
AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE GEODESY : Another Effort for Earthquake Hazard Monitoring
 AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE GEODESY : Another Effort for Earthquake Hazard Monitoring Andreas H., Irwan M., H.Z.Abidin, D. Darmawan, D.A. Sarsito, M. Gamal Geodesy Research Group Department of Geodetic
AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE GEODESY : Another Effort for Earthquake Hazard Monitoring Andreas H., Irwan M., H.Z.Abidin, D. Darmawan, D.A. Sarsito, M. Gamal Geodesy Research Group Department of Geodetic
Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One
 Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One Introduction If you marked all the earthquakes from the past century on a world map, you'd notice that most tend to occur along certain lines around
Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One Introduction If you marked all the earthquakes from the past century on a world map, you'd notice that most tend to occur along certain lines around
Syllabus and Course Description Geophysical Geodesy Fall 2013 GPH 411/611
 Syllabus and Course Description Geophysical Geodesy Fall 2013 GPH 411/611 Course Location: LME 422 Course Time: Tuesday & Thursday 12:00-1:15 Units: 3 Instructor Name: Bill Hammond Office Location: SEM
Syllabus and Course Description Geophysical Geodesy Fall 2013 GPH 411/611 Course Location: LME 422 Course Time: Tuesday & Thursday 12:00-1:15 Units: 3 Instructor Name: Bill Hammond Office Location: SEM
Regional deformation and kinematics from GPS data
 Regional deformation and kinematics from GPS data Jessica Murray, Jerry Svarc, Elizabeth Hearn, and Wayne Thatcher U. S. Geological Survey Acknowledgements: Rob McCaffrey, Portland State University UCERF3
Regional deformation and kinematics from GPS data Jessica Murray, Jerry Svarc, Elizabeth Hearn, and Wayne Thatcher U. S. Geological Survey Acknowledgements: Rob McCaffrey, Portland State University UCERF3
Forearc deformation across time scales - a tale of fluids, locking and transients
 Forearc deformation across time scales - a tale of fluids, locking and transients Modified from Scholz, 1998; Bilek & Lay, 2002; and Schwartz & Rokosky, 2007 Onno Oncken, GFZ Potsdam with M. Moreno, P.
Forearc deformation across time scales - a tale of fluids, locking and transients Modified from Scholz, 1998; Bilek & Lay, 2002; and Schwartz & Rokosky, 2007 Onno Oncken, GFZ Potsdam with M. Moreno, P.
The importance of the South-American plate motion and the Nazca Ridge subduction on flat subduction below South Peru
 Chapter 7 The importance of the South-American plate motion and the Nazca Ridge subduction on flat subduction below South Peru Abstract Flat subduction near Peru occurs only where the thickened crust of
Chapter 7 The importance of the South-American plate motion and the Nazca Ridge subduction on flat subduction below South Peru Abstract Flat subduction near Peru occurs only where the thickened crust of
Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 243 248, 2001 Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough Phil R. Cummins, Takane Hori, and Yoshiyuki Kaneda Frontier Research Program for Subduction Dynamics,
Earth Planets Space, 53, 243 248, 2001 Splay fault and megathrust earthquake slip in the Nankai Trough Phil R. Cummins, Takane Hori, and Yoshiyuki Kaneda Frontier Research Program for Subduction Dynamics,
LAB: PLATE TECTONICS GOAL: Calculate rates of plate movement
 Name LAB: PLATE TECTONICS GOAL: Calculate rates of plate movement Rates of plate movement are calculated by measuring the distance rocks have moved since they formed. Rates are expressed in cm per year
Name LAB: PLATE TECTONICS GOAL: Calculate rates of plate movement Rates of plate movement are calculated by measuring the distance rocks have moved since they formed. Rates are expressed in cm per year
Seismic and aseismic fault slip before and during the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 637 642, 2011 Seismic and aseismic fault slip before and during the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake Shin ichi Miyazaki 1, Jeffery J. McGuire 2, and Paul
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 637 642, 2011 Seismic and aseismic fault slip before and during the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake Shin ichi Miyazaki 1, Jeffery J. McGuire 2, and Paul
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
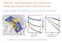 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Title. Author(s)Fujii, Yoshiaki; Kodama, Jun-ichi; Fukuda, Daisuke. CitationProceedings ISRM Congress 2015, 2015: 513. Issue Date
 Title Giant Earthquakes are Occurring at Lunar Phases Spec Author(s)Fujii, Yoshiaki; Kodama, Jun-ichi; Fukuda, Daisuke CitationProceedings ISRM Congress 2015, 2015: 513 Issue Date 2015-05- Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5113
Title Giant Earthquakes are Occurring at Lunar Phases Spec Author(s)Fujii, Yoshiaki; Kodama, Jun-ichi; Fukuda, Daisuke CitationProceedings ISRM Congress 2015, 2015: 513 Issue Date 2015-05- Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5113
Magnitude 8.2 NORTHWEST OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Plate Tectonics 2. Ocean crust forms at mid-ocean ridges (with magnetic stripes )
 Plate Tectonics 2 Ocean crust forms at mid-ocean ridges (with magnetic stripes )! some more evidence for plate tectonics: (1)! magnetic stripes (conclusion) and (2) seeing it live with high-precision GPS!
Plate Tectonics 2 Ocean crust forms at mid-ocean ridges (with magnetic stripes )! some more evidence for plate tectonics: (1)! magnetic stripes (conclusion) and (2) seeing it live with high-precision GPS!
