IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
|
|
|
- Silvia Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where applicable! Provide concise, but detailed answers to essay and fill-in questions. TURN IN YOUR 882 ES SCANTRON AND ANSWER SHEET ONLY! MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1. Obsidian exhibits this texture. a. Aphanitic b. Glassy c. Porphyritic d. Phaneritic e. Pyroclastic 2. Rocks that contain crystals that are roughly equal in size and can t be identified with the naked eye but require the aid of a microscope, exhibits this texture: a. Aphanitic b. Glassy c. Porphyritic d. Phaneritic e. Pyroclastic 3. The texture of an igneous rock a. Is controlled by the composition of magma. b. Is the shape of the rock body c. Determines the color of the rock d. Is caused by leaching. e. Records the rock's cooling history. 4. Lava is molten rock: a. in the subsurface b. on the surface c. both A & B d. none of these 5. Magma is molten rock: a. in the subsurface b. on the surface c. both A & B d. none of these 6. Consider the Bowen's reaction series. Which mineral(s) would you expect to see as a phenocryst in porphyritic basalt? a. quartz c. sodium-rich plagioclase e. answers d. or f. b. orthoclase (potassium feldspar) d. calcium-rich plagioclase f. olivine 7. Igneous rocks produced in association with subduction zone volcanism most generally are: a. Basaltic in composition. b. Ultramafic in composition. c. Andesitic in composition. d. Both basaltic in composition and ultramafic in composition. 8. Extrusive Igneous rock is formed a. by crystallization of molten rock b. on the surface of the Earth c. below the surface of the Earth d. by changes in mineral composition e. answers a. and b. f. answers a. and c. 9. This igneous texture is characterized by two distinctively different crystal sizes. a. Aphanitic b. Glassy c. Porphyritic d. Phaneritic e. Pyroclastic 10. Rhyolite and Granite a. Have a similar mineral composition b. Have a similar texture c. Answers A. and B. d. Are in no way similar 11. Which of the factors listed below affects the melting point of rock and sediment? a. Composition of the material d. Water content b. The confining pressure e. All of the these c. Only composition of the material and the confining pressure 12. Select the fine grained (aphanitic) rock, which is composed mainly of sodium-rich plagioclase feldspar, amphibole, and biotite mica from the list below: a. Basalt b. Andesite c. Granite d. Diorite e. Gabbro 13. is characterized by extremely coarse mineral grains (larger than 1-inch)? a. Pumice b. Obsidian c. Granite d. Pegmatite 1
2 14. Which of the following minerals crystallize first in Bowen's reaction series? a. quartz b. olivine c. muscovite d. biotite 15. Which of the following minerals crystallizes last in Bowen's reaction series? a. quartz b. olivine c. muscovite d. biotite 16. Select the coarse grained (phaneritic) rock, which is composed mainly of calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar, olivine, and pyroxene from the list below: a. Basalt b. Andesite c. Granite d. Diorite e. Gabbro 17. Xenoliths are associated most closely with which magmatic process? a. intrusion c. columnar jointing b. magmatic differentation; (magma mixing) d. magmatic differentation; (assimilation) 18. Layered plutons with more mafic compositions on the bottom and more felsic toward the top are associated most closely with which magmatic process? a. Magma migration (fractional crystallization) c. crystal settling (fractional crystallization) b. magmatic differentation; (magma mixing) d. magmatic differentation; (assimilation) 19. A mushroom-shaped igneous mass situated in a near-surface environment is a(n) a. Batholith b. Laccolith c. Stock d. Dike e. Sill 20. The very last minerals to crystallize on Bowen's Reaction Series result in igneous rocks with a composition. a. mafic b. ultramafic c. felsic d. intermediate 21. Batholiths are typically a. Intrusive d. Larger than other plutons b. Associated with major mountain belts e. Phaneritic c. All of these 22. Hydrothermal veins are typically: a. Extrusive d. Aphanitic e. irregularly shaped b. Smaller than other types of plutons c. Answers b. and e. 23. A is an open cavity in a volcanic rock that was filled by a gas bubble when the lava was still mainly liquid? a. porphyrocryst b. vesicle c. xenocryst d. phenocryst 24. Which of the following lists magma types in order of decreasing viscosity (i.e., the most viscous listed first)? a. Basaltic, andesitic, granitic d. Basaltic, granitic, andesitic b. Granitic, andesitic, basaltic e. Granitic, basaltic, andesitic c. Andesitic, granitic, basaltic 25. Magma tends to rise toward Earth's surface principally because a. Water is an abundant constituent of magma. b. Silica is abundant in magma. c. Magma is a fluid. d. Rocks become less dense when they melt. e. None of these 26. The tabular and concordant igneous intrusive body is called a(n) a. Batholith b. Laccolith c. Stock d. Dike e. Sill 27. Rocks of the Hawaiian Islands would be expected to have: a. A mafic (basaltic) composition. b. Textures such as Phaneritic and Pegmatitic. c. High iron content. d. dark color e. answers a., c., and d. f. answers a., b., c., 28. Rocks of the Sierra Nevada Mountains would be expected to have: a. A felsic (granitic) composition. b. Textures such as Phaneritic and Pegmatitic. c. High iron content. d. dark color e. answers a. and b. f. answers c. and d. 29. The tabular and discordant igneous intrusive body is called a(n) a. Batholith b. Laccolith c. Stock d. Dike e. Sill 2
3 30. Changing the composition of magma by incorporating surrounding host rock is known as. a. assimilation b. partial melting c. magma mixing d. differentiation 31. The Sierra Nevada Mountains of California are composed primarily of this igneous structure. a. Batholith b. Laccolith c. Stock d. Dike e. Sill Igneous Activity: For the following question(s) match the description with the appropriate texture. A. porphyritic B. phaneritic C. aphanitic D. glassy 32. mineral grains are of roughly equal size and coarse enough to be seen without a microscope or magnifying glass 33. magma cools and consolidates without growth of mineral grains 34. a magnifying glass or microscope is needed to see individual mineral grains 35. rock has two or more, distinctly different-sized populations of mineral grains Match the following rocks to their equivalent aphanitic or phaneritic igneous rocks. A. andesite B. rhyolite C. gabbro 36. basalt 37. granite 38. diorite Volcanism: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 39. Most of the active volcanoes on Earth are located in a belt known as the a. Ring of Fire d. Circum-Atlantic belt b. Mid-Pacific ridge e. Gulf Coast zone c. Red Sea rift 40. Which of the following factors help determine whether a volcanic eruption will be violent or relatively quiescent (gentle)? a. Amount of dissolved gas in the magma b. Temperature of the magma c. Composition of the magma d. All of the above e. Only amount of dissolved gas in the magma and temperature of the magma 41. A basaltic lava flow with a rough, jagged surface in which the dissolved gasses have escaped, is known as lava. a. Pillow b. Aa c. Pahoehoe d. Lapilli e. None of these 42. A basaltic lava flow with a smooth, ropy surface in which the dissolved gasses have yet to escape, is known as lava. a. Pillow b. Aa c. Pahoehoe d. Lapilli e. None of these 43. The oceanic ridge system is the major site of: a. Spreading center volcanism. b. Formation of magma by partial melting of mantle rocks. c. Formation of basaltic magma. d. All of these e. Both a. and b. 44. Felsic lavas cool to form: a. basalt b. granite c. rhyolite d. diorite e. andesite 45. Violent volcanic activity is often associated with a. Fissure eruptions c. Shield volcanoes e. answers b. and/or d. b. Resurgent Calderas d. Composite cones f. Cinder cones 46. The most violent volcanic activity is associated with the combined eruption and subsequent collapse of the volcanic structure and is associated with the following type of volcanic structure: a. Fissure eruptions c. Shield volcanoes e. Cinder cones b. Resurgent Calderas d. Composite cones 47. Mount St. Helens is an example of a 48. Mafic magmas cool to form: a. basalt b. granite c. rhyolite d. diorite e. gabbro 3
4 49. The Aleutian Islands in Alaska are associated with a. Intraplate volcanism d. Spreading center volcanism b. Subduction zone volcanism e. Intercrustal volcanism c. Geothermal volcanism 50. The Columbia Plateau in the northwestern United States is an excellent example of a. Silica-rich lava flows d. site of former fissure eruptions b. An eroded shield volcano e. both c. and d. c. Flood Basalts 51. In 1902, the town of St. Pierre was destroyed and its population of 28,000 to 30,000 killed due to: a. A fast-moving aa lava flow that engulfed the town b. A rain of volcanic bombs c. An avalanche of incandescent volcanic ash and dust called a nueé ardenté. d. An earthquake that was generated by the eruption of Mt. Pelee e. None of these 52. The most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity is also associated with outgassing by volcanoes, which also produced much of the compounds in our atmosphere and oceans. a. Chlorine b. Carbon dioxide c. Sulfur oxide d. Water vapor e. Nitrogen 53. Which one of the following statements is false regarding the devastating May 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens? a. The mountain was substantially enlarged by the lava flows b. Great quantities of volcanic ash were propelled high into the atmosphere c. Mudflows (lahars) triggered by the volcanic activity caused tremendous damage d. The main impact of the initial blast was directed laterally rather than vertically e. Answers b., c., and d. f. Answers a., b., and c., 54. The more viscous a lava, the more: a. gently it erupts c. violently it erupts e. silica it contains b. iron and magnesium it contains d. answers c. and e. f. answers a. and b. 55. Gabbro is the coarse-grained equivalent of this igneous rock. a. Basalt b. Pumice c. Granite d. Diorite e. Gabbro 56. Mt. Kilauea in Hawaii is an example of a: 57. Spreading center volcanism most generally produces rocks, which are a. Granitic in composition d. Basaltic in composition b. Andesitic in composition e. Ultramafic in composition c. None of these 58. The type of volcano usually created when andesitic lavas are extruded following a pyroclastic eruption is a: 59. A volcano built almost exclusively from fluid, basaltic lava is called a 60. Shiprock, New Mexico, is thought to be such a feature. 61. Cinder cones a. Have very steep slopes. b. Are usually less than 300 meters (~1000 feet) high c. Frequently occur in groups d. Consist largely of pyroclastic material e. All of these 62. Which of the following consists of pyroclastic debris? a. Ash b. Bombs c. Cinders d. all of these 63. Mt. Vesuvius (near Naples, Italy) (also destroyed Pompeii and Herculaneum) is an example of a: 4
5 64. Bulbous masses associated with volcanoes that extrude highly viscous material that tend to plug up the volcanic cone are called: a. Shield volcanoes c. Cinder cones e. Composite cones b. Lava or obsidian domes d. Volcanic necks For the following item(s), choose from one of the following answers. A. composite cone/stratovolcanoes B. shield volcanoes C. cinder cones 65. the big volcanoes of Hawaii 66. massive, gently sloping volcanoes built of successive, basaltic lava flows 67. large, fairly steep-sided cones composed of lavas and pyroclastic layers 68. small cones built during one, short, eruptive episode 69. the volcanoes of the Cascade Mountains True = A, False = B 70. Aphanitic textures contain large mineral grains; that are visible, but less than an inch in size. 71. Partial melting produces a magma having a lower silica content than the original magma. 72. A sill is a tabular and discordant pluton. 73. The process of magmatic differentiation can generate residual, more felsic magmas from mafic magmas such as basalt. 74. A Xenolith is an inclusion of foreign or country rock enclosed within intrusive rock and is an indication that assimilation has occurred. 75. Felsic, Intermediate, and Mafic are all terms to describe the textures of magma. 76. The discontinuous series of Bowen s Reaction Series consists of ferromagnesian minerals. 77. The continuous series of Bowen s Reaction Series consists of ferromagnesian minerals. 78. A laccolith is a mushroom-shaped pluton that forms from the inflation of a sill. 79. Mafic lava is more fluid (or more liquid) than Andesitic (intermediate) lava. 80. The larger the percentage of silica in magma, the more viscous it is. 81. Assimilation occurs when magma partially melts and incorporates the surrounding country rock. 82. Bowen's reaction series predicts the texture of igneous rocks 83. Plagioclase feldspar is an important mineral in granite and other felsic rocks. 84. Glassy igneous rocks form when magma cools too quickly for mineral grains to grow. 85. The smaller the percentage of silica in magma, the less viscous it is. 86. Pegmatitic textures contain very large mineral grains, over an inch in size. 87. All present-day active volcanoes are associated with activity at plate boundaries. 88. The largest volcanoes found on Earth are of the composite cone variety. 89. Strato-volcanoes are also known as cinder cone volcanoes. 90. Andesitic magma is more likely to form pyroclastic debris than Mafic magma. 91. A vesicle forms due to the preservation of the shape of gas bubbles that are escaping from a cooling magma. 92. A Nuée ardente is a phenomenon associated with pyroclastic flows. 93. Volcanic vents that emit only gases are called fumaroles. 94. The volcanoes of the Cascade Range are primarily shield volcanoes. 95. Columnar jointing is due to tension cracks that develop in the cooling magma typically found in a volcanic neck as they propagate downwards to form the columns. 96. The volcanic eruptions at Mount St. Helens may be described as extremely quiet or gentle compared to eruptions such as those that occur on the island of Hawaii. 97. Powerful, explosive, pyroclastic eruptions can result in climatic cooling as ash and other particulate matter gets into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and reducing surface temperatures. 5
6 98. Powerful eruptions can result in climatic warming as gaseous matter gets into the atmosphere, which act as greenhouse gasses and increase surface temperatures. 99. Fissure eruptions usually produce intrusive features. Place your answers to the following questions on the answer sheet provided by your instructor. Use the appropriate word, phrase, or short essay to answer the following questions. ESSAY / FILL-IN: 100. Layering of minerals in a magma chamber from more mafic on the bottom to more felsic on the top occurs due to, a specific type of Magmatic differentiation A large, mushroom-shaped pluton commonly formed by the inflation of a sill is a is the name given to molten rock below the Earth's surface Igneous rocks are classified on the basis of mineral composition and? 104. Ca-rich Plagioclase feldspar and Na-rich Plagioclase feldspar are all minerals found on the Branch of Bowen Reaction Series Olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite are all minerals found on the branch of Bowen s reaction series What type of magma composition is commonly erupted on the continents along a subduction zone? 107. A texture refers to rocks composed mainly of visible crystals greater than 1-inch A texture refers to rocks composed mainly of uniform crystals that can only be seen with the aid of a microscope What term(s) denotes the smaller mineral grains in a porphyritic igneous rock? 110. Which tabular, discordant igneous rock body intrudes across bedding planes? 111. Which tabular, concordant igneous rock body intrudes between bedding planes? 112. This type of feature occurs when lava is extruded underwater Which of the three types of volcanoes consists almost entirely of pyroclastic flows? 114. A relatively small, summit depression on a volcano, marking a former eruptive vent, is a Large, volcanic depressions formed by subsidence and collapse are known as What kind of volcanoes are Mt. St. Helens and the other volcanoes of the Cascade range? 117. The most abundant gaseous component of magma that is typically vented via outgassing by a volcano, is What term describes fragmental volcanic material associated with explosive eruptions? 119. is a dangerous, fast moving, hot, turbulent cloud of volcanic gases and fine-sized, pyroclastic particles and most likely buried Pompeii when Mt. Vesuvius (near Naples, Italy) erupted and more recently caused the destruction of St. Pierre on Martinique The Hawaiian Islands are composed almost entirely of the rock What term describes a liquid's flow characteristics? 122. Powerful, explosive, pyroclastic eruptions can result in climatic cooling as ash and other particulate matter gets into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and reducing surface temperatures lava denotes a basaltic lava flow covered with jagged, angular, congealed lava rubble Which basaltic lava flow has a relatively smooth, ropy surface? 125. A fissure eruption produces basalts, which flood an area, and occur along linear features 126. What specific type or subcategory of volcano is associated with the most violent and dangerous eruptions that includes the collapse of the volcano? 127. Composite cone volcanoes are also known as The largest volcanoes on Earth are of the type known as: 129. Another term for a volcanic mudflow is a. 6
7 130. How would you tell the difference between granite and rhyolite? Describe the differences you would observe between the two and their method of formation What kinds of warning signs enable geologists to FORECAST volcanic eruptions? List at least 3 signs that can occur prior to an eruption that may warn of the impending eruption Thoroughly describe a type of magmatic differentiation, use examples if necessary Complete the following figure of a basic rock cycle using the appropriate terminology. A H B G C D F E GEOLOGY 305: IGNEOUS ACTIVITY-CLUES ACROSS 2. This term describes rocks that are high in silica. 7. This term describes rocks that are rich in ferromagnesian minerals, with some Ca-rich Plagioclase feldspar. 9. Another term for a composite cone volcano. 12. These igneous rocks are produced through volcanic activity as opposed to plutonic activity. 13. This concordant rock forms between rock layers due to injection of magma. 14. This rock type describes extrusive rocks produced during a volcanic explosion. 16. This type of volcano has a large, broad volcanic cone with very gentle slopes built up by fluid basaltic lava. 19. This term describes the composition of an igneous rock that contains approximately 50% ferromagnesian and 50% non-ferromagnesian minerals. 23. This rock is a mafic igneous extrusive rock and is aphanitic. 24. This rock is felsic, extrusive and is aphanitic. 25. A general term to describe solidified intrusive bodies. 26. This discordant rock crosscuts pre-existing rock. 27. This type of rock contains large crystals "floating" within a fine-grained matrix. 28. This rock is the volcanic equivalent of diorite. 7
8 DOWN 1. A pyroclastic rock in which most of the fragments are angular and more than 2 mm in diameter. 3. This igneous formation forms at depth in the crust and range in size from a km3 to 100's of km3. 4. This rock is intrusive, phaneritic and mafic. 5. These plutons are smaller than batholiths and have a distinctive mushroom shape. 6. A cone volcano has a volcanic cone consisting of BOTH lava and pyroclastic rocks. 8. s reaction series describes the sequence of crystallization of minerals from magma. 10. This extrusive rock has a glassy texture. 11. A heated cloud of gas and pyroclastic debris ejected almost horizontally from a vent and engulfs all in its path. 15. A deposit of fine-grained pyroclastic material. 17. A volcano is a steep, conical hill built up about a volcanic vent and composed of coarse pyroclastic rock fragments. 18. This extrusive, glassy rock contains numerous vesicles due to trapped gases during cooling of the rock. 20. A term to describe plutonic environments. 21. The Hawaiian Islands represent a or the surface expression of a mantle plume. 22. This rock is phaneritic and contains 70% silica and has abundant quartz and potassium feldspar. 29. This rock is similar to granite but it has less quartz. ANDESITE ASH BASALT BATHOLITH BOWEN BRECCIA CINDER CONE COMPOSITE DIKE DIORITE GEOLOGY 305: IGNEOUS ACTIVITY -WORD LIST EXTRUSIVE OBSIDIAN FELSIC PLUTON GABBRO PORPHYRITIC GRANITE PUMICE HOT SPOT PYROCLASTIC INTERMEDIATE RHYOLITE INTRUSIVE SHIELD LACCOLITH SILL MAFIC STRATOVOLCANO NUÉE ARDENTÉ 8
IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY
 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 300 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 300 Name: Section: IGNEOUS ROCKS AND IGNEOUS ACTIVITY Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary where
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Chapter 5 9/10/2011. Introduction. Volcanoes and Volcanism. Volcanism. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
Block: Igneous Rocks. From this list, select the terms which answer the following questions.
 Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
The 3 types of rocks:
 Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted.
 What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity
 Summary IGNEOUS ROCKS AND METAMORPHIC ROCKS DERIVED FROM IGNEOUS parents make up about 95 percent of Earth s crust. Furthermore, the mantle, which accounts for more than 82 percent of Earth s volume, is
Summary IGNEOUS ROCKS AND METAMORPHIC ROCKS DERIVED FROM IGNEOUS parents make up about 95 percent of Earth s crust. Furthermore, the mantle, which accounts for more than 82 percent of Earth s volume, is
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks. 1) igneous = fiery 2) sedimentary = settled 3) metamorphic = changed form
 Rocks Identified on the basis of composition and texture (arrangement of features). Classification depends on description and interpretation of these features. Three major categories: 1) igneous = fiery
Rocks Identified on the basis of composition and texture (arrangement of features). Classification depends on description and interpretation of these features. Three major categories: 1) igneous = fiery
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways.
 A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
Igneous Rocks Chapter 3. Igneous rocks form as molten rock cools and crystallizes (solidifies) from either a magma or a lava
 Igneous Rocks Chapter 3 Igneous rocks form as molten rock cools and crystallizes (solidifies) from either a magma or a lava Formation of Igneous Rocks Magma: forms from partially melted rocks INSIDE the
Igneous Rocks Chapter 3 Igneous rocks form as molten rock cools and crystallizes (solidifies) from either a magma or a lava Formation of Igneous Rocks Magma: forms from partially melted rocks INSIDE the
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2
 FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Study guide chapter 9
 Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
 Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Focus Question 7.1 How were the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and Hawaii s Kilauea volcano different? Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980)
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Focus Question 7.1 How were the eruptions of Mount St. Helens and Hawaii s Kilauea volcano different? Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980)
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
 Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980) Largest historic eruption in North America Lowered peak by more than 400 m Destroyed all trees in
Chapter 7 Lecture Outline Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Mount St. Helens eruption (May 18,1980) Largest historic eruption in North America Lowered peak by more than 400 m Destroyed all trees in
Student Name: College: Grade:
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Volcano Vocabulary ROCK CYCLE. Igneous REMELTED REMELTED BURIED BURIED HEAT ERODED DEPOSITED. Metamorphic Sedimentary ERODED, TRANSPORTED DEPOSITED
 Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
What Do You See? Learning Outcomes Goals Learning Outcomes Think About It Identify classify In what kinds of environments do igneous rocks form?
 Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
Critical Thinking 1. Contrast How could you tell the difference between a mafic rock and a felsic rock by looking at them?
 CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
Thursday, October 4 th
 Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
3/24/2016. Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016
 Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
A. What is a volcano?
 VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Some notes on igneous rock by Vince Cronin
 Some notes on igneous rock by Vince Cronin Principle of uniformitarianism: The physical and chemical laws that govern the physical/chemical world are the same now as in the past. (That is, during virtually
Some notes on igneous rock by Vince Cronin Principle of uniformitarianism: The physical and chemical laws that govern the physical/chemical world are the same now as in the past. (That is, during virtually
IGNEOUS ROCKS. SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks?
 Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks and Plutons
 Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks and Plutons Chapter Outline 4.1 Introduction 4.2 The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava 4.3 How Does Magma Originate and Change? 4.4 Igneous Rocks Their Characteristics
Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks and Plutons Chapter Outline 4.1 Introduction 4.2 The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava 4.3 How Does Magma Originate and Change? 4.4 Igneous Rocks Their Characteristics
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Chapter 3: Igneous Rocks 3.2 IGNEOUS ROCK ORIGIN
 Chapter 3: Igneous Rocks Adapted by Lyndsay R. Hauber & Michael B. Cuggy (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
Chapter 3: Igneous Rocks Adapted by Lyndsay R. Hauber & Michael B. Cuggy (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Chapter 5 Volcanoes The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Chapter 5 Volcanoes All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some crystals and varying amounts of dissolved gases Lava is erupted magma The behavior
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Chapter 5 Volcanoes All eruptions involve magma Magma is molten rock that usually contains some crystals and varying amounts of dissolved gases Lava is erupted magma The behavior
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES.
 Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
9/4/2015. Feldspars White, pink, variable Clays White perfect Quartz Colourless, white, red, None
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
INTRODUCTION ROCK COLOR
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
Igneous Processes I: Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures
 Igneous Processes I: Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures Crustal Abundances of Rock Types Igneous Rocks Form by the cooling and hardening (crystallization/glassification) of magma. There
Igneous Processes I: Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures Crustal Abundances of Rock Types Igneous Rocks Form by the cooling and hardening (crystallization/glassification) of magma. There
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community
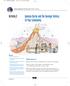 Ch 1 Bedrock Geology 9/17/04 12:48 PM Page 14 Activity 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community Goals In this activity you will: Identify several igneous rocks using a rock chart. Describe
Ch 1 Bedrock Geology 9/17/04 12:48 PM Page 14 Activity 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community Goals In this activity you will: Identify several igneous rocks using a rock chart. Describe
