Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 3, Day 1
|
|
|
- Dina Berry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 3, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 3.e students know there are two kinds of volcanoes: one kind with violent eruptions producing steep slopes and the other kind with voluminous lava flows producing gentle slopes. PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Volcanic eruptions are caused by magma (a mixture of liquid rocks, crystals, and dissolved gas) expelled onto Earth s surface. The geothermal gradient is the rate at which temperature increases with depth. As pressure increases in the Earth, the melting temperatures change. Minerals melt at a single given temperature at any given pressure. Since rocks are a mixture of minerals, they melt over a range of temperatures. 2. Vocabulary Word Wall. Introduce 3-5 important words from today s reading magma lava Show, say, explain, expand, explode or buzz about the word briefly Show, say, define the word quickly and add to the word wall. READ 3. Review the vocabulary and concepts previously covered in this chapter. 4. Read directions for investigation/activity. 5. Read text. Ch. 18.1, pp
2 RESPOND 6. Fix the facts. Clarify what s important. Discuss the reading and add 3-5 events/concepts to the billboard Students might mention: Temperature increases with depth below the Earth s surface. Even though temperatures are high enough, most rocks in the Earth s lower crust and upper mantle do not form magma due to the effect of pressure. The presence of water also affects the melting temperature of rocks and minerals. 7. Post information on the billboard. Add new information to ongoing projects on the wall. EXPLORE 8. Explore today s investigation with inquiry activities. 9. Explore today s simulation with inquiry activities. 10. Collect data and post. One possible activity: Where are the Volcanoes? Procedure: Students locate, identify general information about volcanoes Discussion: Discuss what students perceive about volcanoes affect on people Key question: Where do we find volcanoes throughout the world? Source: df EXTEND 11. Prompt every student to write a short product tied to today s reading. 12. Close with a short summary. Extend the reading to the students lives or to the world
3 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 3, Day 2 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 3.e PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. There are three major types of magma. All magmas contain gas dissolved in liquid. As magma rises towards the surface and pressure decreases the gas forms a separate vapor phase, much like a carbonated beverage bottled under pressure releases bubbles when opened. Gas gives magmas their explosive character. 2. Vocabulary Word Wall. Introduce 3-5 important words from today s reading basaltic magma andesitic magma rhyolitic magma Show, say, explain, expand, explode or buzz about the word briefly Show, say, define the word quickly and add to the word wall. READ 3. Review the vocabulary and concepts previously covered in this chapter. 4. Read directions for investigation/activity. 5. Read text. Ch. 18.1, pp
4 RESPOND 6. Fix the facts. Clarify what s important. Discuss the reading and add 3-5 events/concepts to the billboard Students might mention: There are three major types of magma: basaltic, andesitic, and rhyolitic. The volcanoes in Hawaii are made of basalt. 7. Post information on the billboard. Add new information to ongoing projects on the wall. EXPLORE 8. Explore today s investigation with inquiry activities. 9. Explore today s simulation with inquiry activities. 10. Collect data and post. One possible activity: Cake Batter Lava Procedure: Students use cake batter to simulate lava flow Discussion: Discuss the effects of viscosity and friction on flow patterns (water compared to thicker substances) Key question: How did the two experimental flows compare? Source: EXTEND 11. Prompt every student to write a short product tied to today s reading. 12. Close with a short summary. Extend the reading to the students lives or to the world
5 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 3, Day 3 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 3.e PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Viscosity is the resistance to flow, the opposite of fluidity. The viscosity of magma depends on its composition and temperature. Higher silica content magmas have higher viscosity than lower silica content magmas. Lower temperature magmas have higher viscosity than higher temperature magmas. Viscosity is an important property in determining the eruptive behaviors of magmas. 2. Vocabulary Word Wall. Introduce 3-5 important words from today s reading viscosity silica Show, say, explain, expand, explode or buzz about the word briefly Show, say, define the word quickly and add to the word wall. READ 3. Review the vocabulary and concepts previously covered in this chapter. 4. Read directions for investigation/activity. 5. Read text. Ch. 18.1, p. 475
6 RESPOND 6. Fix the facts. Clarify what s important. Discuss the reading and add 3-5 events/concepts to the billboard Students might mention: The temperature and composition of magma determines its viscosity. The amount of silica increases its viscosity. Basaltic magma has the lowest viscosity of the three major types. 7. Post information on the billboard. Add new information to ongoing projects on the wall. EXPLORE 8. Explore today s investigation with inquiry activities. 9. Explore today s simulation with inquiry activities. 10. Collect data and post. One possible activity: Viscosity Procedure: Students explore the viscosity of different solutions Discussion: Discuss the difference between quantitative and qualitative data Key question: Why is the viscosity of magma important? Source: EXTEND 11. Prompt every student to write a short product tied to today s reading. 12. Close with a short summary. Extend the reading to the students lives or to the world
7 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 3, Day 4 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 3.b students know the principal structures that form at the three different kinds of plate boundaries. PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Since magma is less dense than the surrounding rocks it eventually comes in contact with the overlying crust. Magma that solidifies deep in the subsurface is called a pluton or an igneous intrusion. Batholiths are huge intrusions covering an area greater that 100 km. Laccoliths are blister-shaped intrusions that form the core of mountains such as the Black Hills of South Dakota, the Henry mountains of Utah, and others. 2. Vocabulary Word Wall. Introduce 3-5 important words from today s reading plutons batholiths laccoliths stocks Show, say, explain, expand, explode or buzz about the word briefly Show, say, define the word quickly and add to the word wall. READ 3. Review the vocabulary and concepts previously covered in this chapter. 4. Read directions for investigation/activity. 5. Read text. Ch. 18.2, pp
8 RESPOND 6. Fix the facts. Clarify what s important. Discuss the reading and add 3-5 events/concepts to the billboard Students might mention: Intruding magma can affect the crust in several ways: it can enter fissures in rocks, blocks of rocks can break off and sink into the magma and eventually melt, and magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. After cooling the magma form minerals that combine to form intrusive igneous rock bodies. These intrusive rock bodies can be exposed at the Earth s surface by uplift and erosion. 7. Post information on the billboard. Add new information to ongoing projects on the wall. EXPLORE 8. Explore today s investigation with inquiry activities. 9. Explore today s simulation with inquiry activities. 10. Collect data and post. One possible activity: Section 2: Intrusive activity Procedure: Students answer questions based on diagram of igneous intrusions Discussion: Review types of intrusions depicted in the text Source: apter18/section... EXTEND 11. Prompt every student to write a short product tied to today s reading. 12. Close with a short summary. Extend the reading to the students lives or to the world
9 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 3, Day 5 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 3.b PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Intrusions are remnants of past igneous activity and are exposed at the surface by erosion of the overlying rocks and sediments. Other types of intrusions form at shallower depths, such as stocks, sills and dikes. 2. Vocabulary Word Wall. Introduce 3-5 important words from today s reading sill dike Show, say, explain, expand, explode or buzz about the word briefly Show, say, define the word quickly and add to the word wall. READ 3. Review the vocabulary and concepts previously covered in this chapter. 4. Read directions for investigation/activity. 5. Read text. Ch. 18.2, pp
10 RESPOND 6. Fix the facts. Clarify what s important. Discuss the reading and add 3-5 events/concepts to the billboard Students might mention: A sill forms parallel to layers of rock. A dike often forms when magma cuts across cracks in the surrounding rock. Plutons represent the majority of igneous activity on Earth. 7. Post information on the billboard. Add new information to ongoing projects on the wall. EXPLORE 8. Explore today s investigation with inquiry activities. 9. Explore today s simulation with inquiry activities. 10. Collect data and post. One possible activity: Gelatin Volcanoes Procedure: Students inject red food coloring and water into gelatin volcanoes Discussion: Discuss types of plutons Key question: How and why does magma move through volcanoes? Source: EXTEND 11. Prompt every student to write a short product tied to today s reading. 12. Close with a short summary. Extend the reading to the students lives or to the world
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 1, Week 8, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 1, Week 8, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today Standard focus: Earth Sciences 3.c Students know how to explain the properties of rocks based on physical and chemical conditions
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 1, Week 8, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today Standard focus: Earth Sciences 3.c Students know how to explain the properties of rocks based on physical and chemical conditions
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Structure of the Earth
 And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 4, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 4, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. In order to make forecasts, meteorologists must gather accurate weather
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 4, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. In order to make forecasts, meteorologists must gather accurate weather
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
The 3 types of rocks:
 Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 CHAPTER 13 SECTION Volcanoes 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What three conditions can cause magma to form? What is volcanism? What are
CHAPTER 13 SECTION Volcanoes 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What three conditions can cause magma to form? What is volcanism? What are
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 6, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 6, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 5.f students know the interaction of wind patterns, ocean currents, and mountain ranges results in
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 6, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 5.f students know the interaction of wind patterns, ocean currents, and mountain ranges results in
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 7, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.e Students know the Sun is typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.e Students know the Sun is typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Compositional (Chemical) Layers
 Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in and : Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in and Core: High in Heat Flow in the Earth Heat sources: heat from
Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in and : Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in and Core: High in Heat Flow in the Earth Heat sources: heat from
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Igneous Rock Notes. Page #:
 Page #: Igneous Rock Notes Magma and lava form very different types of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form from molten rock, but where does molten rock come from? The temperature inside Earth with depth.
Page #: Igneous Rock Notes Magma and lava form very different types of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form from molten rock, but where does molten rock come from? The temperature inside Earth with depth.
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!!
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways.
 A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
When magma is ejected by a volcano or other vent, the material is called lava. Magma that has cooled into a solid is called igneous rock.
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Let s Rock! What is rock? Rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals that may also include organic matter. Most rock is made of minerals, but some rock is made of nonmineral material
Let s Rock! What is rock? Rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals that may also include organic matter. Most rock is made of minerals, but some rock is made of nonmineral material
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 5, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 5, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.d students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than are the stars
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 5, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.d students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than are the stars
Week: Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: Period: 7 Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 No School 14 O *Greenhand Conference *Vocabulary *Volcano Movie 15 E *Volcano
clementaged.weebly.com Name: Period: 7 Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 No School 14 O *Greenhand Conference *Vocabulary *Volcano Movie 15 E *Volcano
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
Earth s Changing Surface
 Earth s Changing Surface Earthquakes and Volcanoes Key Concepts What causes earthquakes? What causes volcanoes to form? How do earthquakes and volcanoes change Earth s surface? What do you think? Read
Earth s Changing Surface Earthquakes and Volcanoes Key Concepts What causes earthquakes? What causes volcanoes to form? How do earthquakes and volcanoes change Earth s surface? What do you think? Read
Volcano Vocabulary ROCK CYCLE. Igneous REMELTED REMELTED BURIED BURIED HEAT ERODED DEPOSITED. Metamorphic Sedimentary ERODED, TRANSPORTED DEPOSITED
 Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Block: Igneous Rocks. From this list, select the terms which answer the following questions.
 Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 9, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 9, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 2.a Students know that the solar system is located on the outer edge of the disk-shaped Milky Way galaxy,
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 9, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 2.a Students know that the solar system is located on the outer edge of the disk-shaped Milky Way galaxy,
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
What Do You See? Learning Outcomes Goals Learning Outcomes Think About It Identify classify In what kinds of environments do igneous rocks form?
 Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Grade 7 Science Revision Sheet for third term final exam
 Grade 7 Science Revision Sheet for third term final exam Material for the final exam : 1- Chapter 4 sections 1+2+3+4 [rock cycle + igneous rocks + sedimentary rocks + metamorphic rocks ] pages from the
Grade 7 Science Revision Sheet for third term final exam Material for the final exam : 1- Chapter 4 sections 1+2+3+4 [rock cycle + igneous rocks + sedimentary rocks + metamorphic rocks ] pages from the
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
10/20/2015. How is magma different from lava? Magma is molten rock below the Earth s surface. Lava is magma that flows out onto Earth s surface.
 Chapter 5 What are igneous rocks? How do they form? Igneous rocks are rocks that form when molten material cools and crystallizes. Molten material can be either magma or lava. How is magma different from
Chapter 5 What are igneous rocks? How do they form? Igneous rocks are rocks that form when molten material cools and crystallizes. Molten material can be either magma or lava. How is magma different from
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle What are minerals? A mineral is a naturally occurring, usually inorganic solid that has a defininite crystalline structure and chemical composition. Naturally occuring =
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle What are minerals? A mineral is a naturally occurring, usually inorganic solid that has a defininite crystalline structure and chemical composition. Naturally occuring =
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Before the term black hole was coined in 1967, these
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Before the term black hole was coined in 1967, these
Week: Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 19 E 20 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Volcano Notes *Bill Nye Notes 21 E 22
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 19 E 20 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Volcano Notes *Bill Nye Notes 21 E 22
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
Magma Why don t all volcanoes look and act the same?
 Lesson Plan 7 Discuss What shapes can volcanoes be? (revisit photos if necessary) --Cone shaped -Ruapehu, Taranaki, Rangitoto, White Island, Ngauruhoe --Crater (caldera) shaped-taupo & Rotorua --Fissures-
Lesson Plan 7 Discuss What shapes can volcanoes be? (revisit photos if necessary) --Cone shaped -Ruapehu, Taranaki, Rangitoto, White Island, Ngauruhoe --Crater (caldera) shaped-taupo & Rotorua --Fissures-
Volcano Unit Pre Assessment. Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two.
 Volcano Unit Pre Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select
Volcano Unit Pre Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features
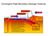 Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
NAME IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY INTRUSION OF MAGMA
 NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY INTRUSION OF MAGMA 1. The summit of Mauna Loa is 8192 m above the floor of the Pacific Ocean, but only 4169 m of this is above sea level. About 150 m of ocean-floor
NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY INTRUSION OF MAGMA 1. The summit of Mauna Loa is 8192 m above the floor of the Pacific Ocean, but only 4169 m of this is above sea level. About 150 m of ocean-floor
A R O U N D W E G O COLOR CODE THE PATHWAY TO IGNEOUS ROCKS!
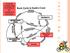 COLOR CODE THE PATHWAY TO IGNEOUS ROCKS! A R O U N D W E G O VOCABULARY FOR IGNEOUS ROCKS IGNEOUS ORIGINS volcanoes active volcano dormant volcano magma plutonic rocks intrusives lava volcanic rocks extrusives
COLOR CODE THE PATHWAY TO IGNEOUS ROCKS! A R O U N D W E G O VOCABULARY FOR IGNEOUS ROCKS IGNEOUS ORIGINS volcanoes active volcano dormant volcano magma plutonic rocks intrusives lava volcanic rocks extrusives
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
NOTE OUTLINE : Chap 5 & 6: Rocks
 Name Period NOTE OUTLINE : Chap 5 & 6: Rocks Objectives 1. Identify and explain characteristics of igneous rocks. This means that if I am given an igneous rock I: a. Can use grain size to identify a rock
Name Period NOTE OUTLINE : Chap 5 & 6: Rocks Objectives 1. Identify and explain characteristics of igneous rocks. This means that if I am given an igneous rock I: a. Can use grain size to identify a rock
Primary Structures in Igneous Rocks. Engr. Sultan Ahmed Khoso
 Primary Structures in Igneous Rocks Engr. Sultan Ahmed Khoso Primary Structures in Igneous Rocks Primary Structures developed in the igneous rock during the time of cooling, crystallization and solidification
Primary Structures in Igneous Rocks Engr. Sultan Ahmed Khoso Primary Structures in Igneous Rocks Primary Structures developed in the igneous rock during the time of cooling, crystallization and solidification
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community
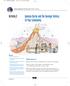 Ch 1 Bedrock Geology 9/17/04 12:48 PM Page 14 Activity 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community Goals In this activity you will: Identify several igneous rocks using a rock chart. Describe
Ch 1 Bedrock Geology 9/17/04 12:48 PM Page 14 Activity 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community Goals In this activity you will: Identify several igneous rocks using a rock chart. Describe
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Chapter 11 Section 2 VOLCANOES TB 337
 Chapter 11 Section 2 VOLCANOES TB 337 http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/volcanoes/ I. How do volcanoes form? Rising Magma leads to eruptions. Magma (solids and gases) are spewed out to form cone-shape
Chapter 11 Section 2 VOLCANOES TB 337 http://www.brainpop.com/science/earthsystem/volcanoes/ I. How do volcanoes form? Rising Magma leads to eruptions. Magma (solids and gases) are spewed out to form cone-shape
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 3 Content: Volcanoes - The Basics Notes. Volcanoes The Basics
 Volcanoes The Basics 1 Hello, my name is Dr. Simpson, and I am a volcanologist. I am here to explain some basic information about volcanoes to you. 3 I think we should get started by taking a look at the
Volcanoes The Basics 1 Hello, my name is Dr. Simpson, and I am a volcanologist. I am here to explain some basic information about volcanoes to you. 3 I think we should get started by taking a look at the
Study Guide: Unit 3. Density and Pressure: You should be able to answer the types of questions given in the end of module questions.
 IDS 102 Study Guide: Unit 3 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the third exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. In the Focus On section you will find
IDS 102 Study Guide: Unit 3 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the third exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. In the Focus On section you will find
Section 5. Rock Units and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 5 Rock Units and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Recognize that rocks are arranged in Earth s crust as well-defined
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 5 Rock Units and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Recognize that rocks are arranged in Earth s crust as well-defined
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Hafeet mountain. Rocks
 Hafeet mountain Rocks There are several steps that lead to form the rocks Weathering Erosion Deposition Heat and pressure Weathering Ice (expand inside the rock fractures) Plants (grows through fractures
Hafeet mountain Rocks There are several steps that lead to form the rocks Weathering Erosion Deposition Heat and pressure Weathering Ice (expand inside the rock fractures) Plants (grows through fractures
