REGIONAL GROUND MOTION PREDICTION AND DATABASE
|
|
|
- Jade Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REGIONAL GROUND MOTION PREDICTION AND DATABASE 1.1 Identification of Primary input parameters a. Magnitudes and intensities of historical Earthquake In this recent century, Indonesia has been impacted by a lot of Earthquakes every year. Most of big islands and cities in Indonesia have earth quake occurrences which cause small and big damage. There are many historical earth quake including magnitudes and intensities which were recorded by geologists. Classification Source Area Maximum Magnitude Subduction Zones Sumatra 9.0 Java 8.2 Banda 8.5 Seram 8.4 North Irian Jaya 8.4 Halmahera 8.5 Sangihe Talaud 8.5 North Sulawesi 8.0 Molluca Passage 8.5 Transform Zones Sumatra Fault 7.6 Sukabumi 7.6 Baribis 6.0 Lasem 6.0 Majene-Bulukamba 6.5 Palu-Koro 7.6 Matano 7.6 Sorong 7.6 Ransiki-Lengguru 6.5 Yapen-Mamberano 7.6 Tarera-Aiduna 6.5 Diffuse Seismicity Flores Back-arc 7.0 East Kalimantan 6.0 South Arm Sulawesi 6.0 East Arm Sulawesi 6.0 Southeast Arm Sulawesi 6.0 Central Sulawesi 6.5 South Halmahera 7.0 Central Banda 8.0 Aru 6.0 Salawati-Bintuni Basin 6.0 Central Irian Jaya 8.5 NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 1
2 Seismic Monitoring NO. OCCURANCE May June June April June June March August March April January November June December 2004 LOCATION Padang Prapat Bengkulu Lampung Bengkulu Bengkulu Aceh Tapanuli Padang Lampung Tapanuli Padang Tes Bengkulu Aceh Pasaman Kepahiang Bengkulu Tapanuli Aceh Tarutung Liwa Lampung Bengkulu Bengkulu NAD & Sumatra Utara b. Recent fault lines MAGNITUDE / INTENSITY MMI VII VIII MMI VI, 6.5 MS 7.7 MS MMI VIII 7.1 MS MMI I XI MMI VIII IX, 6.75 MS MMI VIII IX, 7.5 MS MMI VIII 7.6 MS 6.3 MS 6.7 mb 6.1 MW 6.5 MW MMI VIII 7.1 MS 6.0 MS 6.9 MW, 6.1 mb 6.4 MS, 6.6 MW 7.3 SR, 7.9 MW 9.0 SR Indonesia Region is located in a tectonically very complex and very active area. This region consists of four large tectonic plates (Indo Australia plate, Pacific Plate, Eurasian Plate, Philipine Plate) and nine small tectonic plates. The plate with different types of movement that has created subduction zones and fault zones which is continuously active. In addition, there is Back arc zone at some parts, for instance, in the Flores see. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 2
3 c. Source mechanisms There are 3 kinds of mechanisms which cause the earth quake. That are, subduction, Back Arc, and Transform. According to the tectonic line picture above, most of the tectonic line in Sumatera Island are subduction and transform. Generally, this moving is really slow and cannot be sensed by people even it is moving 0 15 cm each year. Sometimes, this moving is locked; hence the energy is collecting in particular part and then the tectonic plate is not able to hold this energy and finally it will be a explosion where it is famous recognized as Earth Quake. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 3
4 Subduction mechanism Back Arc mechanism Transform (fault) mechanism The Australia plate is subducted beneath the Eurasia plate along the Java trench. The direction of convergence is normal to the trench south of Java, but oblique to the trench southwest of Sumatra. It is widely accepted that the oblique subduction of Sumatra is partitioned into normal subduction along the trench and strike slip along the trench parallel Sumatran Fault. d. Source depth 5 years ago, at 26 December 2004, there was a huge earth quake occurred in Sumatera, it also caused a Tsunami which killed people and destroy all buildings where it were close to the coast. Another big earth quake in Sumatra was in Padang which was occurred at last year (30 September 2009). More than a thousand people were killed by 7.5 Magnitude of earth quake. These are databases of each earth quake in Sumatra, especially it were taken near to Aceh province and Padang province. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 4
5 Seism mic Monitoring 1.2 Id dentification n of Primaryy Input Param meters (Seissmic Action Class) a. Seeismic Mode el Th hese picturess below are deescribing the distribution o of earth quakkes in Indonesia. It can be cllearly seen th hat Indonesia s earthquakee source is divvided into 6 zones. It depeends on the frrequency of e earth quake, intensity and magnitude. NHMSE W WS 09/10 (firrdaus.firdaus@uni weim mar.de; ) P Page 5
6 b. Decision upon the type of spectrum Each zone below has different PGA (Peak Ground Acceleration) due to distance of tectonic plate, earth quake source and also geotechnical behavior. These graphs below explain the response spectra of each zone. Every zone is divided into 3 soil properties, which are soft soil, clay soil and stiff soil. The response spectra of stiff soil are the lowest among the others. The clay soil has response spectra in the middle of graphs and the response spectra of soft soil are the highest. C. Comparable to Eurocode 8: M 5.5: Type I; M < 5.5: Type II The tables and graphs below are illustrating the response spectra from EURO code 8 for each type of soils. It can be clearly seen that the response spectra of earth quake with M 5.5 (Type I) is larger than the response spectra of earth quake with M < 5.5 (type II). NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 6
7 After combining the equation of the response spectra from Euro Code and sub soil condition in Indonesia, we could find the new graph as following below: According to these graphs above, we could conclude the result is that the combined response spectra graphs are small then the response spectra of Indonesia. NHMSE WS 09/10 weimar.de; 91128) Page 7
8 d. Location of major cities (Selection of Reference) Indonesia is recognized as archipelago s country which has more than ten thousand islands. 60% of population is concentrating in the Java Island and the rest are distributed in Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi and Irian Island. Most of big cities in Indonesia have big potential to have earth quake due to the location is near to the tectonic plate and active mountain. In this report, I m investigating 2 provinces, that are, Aceh Province (NAD) and Padang Province (Sumatera Barat). e. Decision upon typical and relevant magnitude distance categories There are 2 graphs which are describing a relationship between distance of earth quake source and magnitude in each province. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 8
9 Earth Quake in Aceh No Date Time (UTC) Location Depth (d) Magnitude Hipocentrum (h) Epicentrum (d^2+h^2)^0.5 Latitude (N 0 ) Longitude(E 0 ) [km] [M] [km] [km] 1 26-Dec-04 00:58: '42.00"N 95 58'55.20"E Dec-04 04:21: '36.00"N 92 57'28.80"E Dec-04 09:39: '52.80"N 94 39'0.00"E Dec-04 01:25: '56.40"N 94 12'46.80"E Dec-04 15:06: '3.60"N 94 5'9.60"E Dec-04 19:19: '38.40"N 94 9'43.20"E Dec-04 02:00: '52.80"N 94 40'1.20"E Dec-04 01:21: '24.00"N 93 21'39.60"E Dec-04 12:04: '14.40"N 92 54'46.80"E Dec-04 1:22: '15.60"N 93 59'6.00"E Dec-04 2:24:01 7 7'12.00"N 92 31'58.80"E Dec-04 3:22: '8.40"N 95 5'31.20"E Dec-04 13:46:03 5 6'46.80"N 96 9'43.20"E Dec-04 3:26: '32.40"N 96 24'18.00"E Dec-04 21:06: '15.60"N 96 20'31.20"E Dec-04 3:42: '4.80"N 94 24'10.80"E Jun-06 19:59: '27.60"N 94 10'8.40"E Jan-05 8:27: '31.20"N 95 27'43.20"E Mar-05 17:29: '51.60"N 95 25'22.80"E No Date Time (UTC) Location Earth Quake in Padang Depth (d) Magnitude Hipocentrum (h) Epicentrum (d^2+h^2)^0.5 Latitude (N 0 ) Longitude(E 0 ) [km] [M] [km] [km] 1 30-Sep-09 22:16: Dec-09 1:11: Aug-09 7:38: Sep-09 10:38: Aug-09 20:23: Sep-09 23:47: Aug-09 2:55: Aug-09 11:35: Aug-09 13:55: Aug-09 12:49: Aug-09 9:28: Aug-09 18:50: Aug-09 18:42: Aug-09 10:45: Sep-07 14:13:44 2 8'6.00"S 99 56'6.00"E Sep-07 16:59: '2.40"S 99 56'49.20"E May-07 19:29: '40.80"S 99 52'22.80"E f. Definition of seismic action classes (SAC) Seismic action classes (SAC) is a classification of earth quake s intensity in a country or region where it is dependent on the magnitude, distance, soil condition and source mechanism. The map below is illustrating the SAC in Indonesia. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 9
10 g. Conversion between Intensity, Magnitude and Distance Indonesia s geologists are using an equation from Gutenberg Richter to measure the intensity of earth quake in a particular area. Gutenberg Richter : Io = 1,5 ( M 0,5) I = Io exp. ( 0,0021 X), Where : Io = Intensity at Hypocenter X = Distance between Io and I 1.3 Identification of Primary input parameters (3): subsoil conditions a. Geological and topographical maps The maps below are drawing the geological and topographical condition in Indonesia. It is consisted of several of soil types for instance, metamorphic rock, Mesozoic formation and volcanic formation. It is caused by many active volcano and many tectonic plate in Indonesia. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 10
11 b. Code Spectra These are soil condition properties in Indonesia. Indonesia s geologists divided it into 3 soil type. Those are hard rock, stiff soil and soft soil. Each type has particular period and it is allocated in the specific zone in Indonesia. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 11
12 c. Comparable to Eurocode 8: Table of ground classes These are the ground classes which are classified by Euro code 8 2. Ground Motion Prediction Models (GMPM) There are many attenuation equations which have been determined by scientist and geologist, it is very useful to predict and analysis the earth quake in the future. Each attenuation should be implemented in particular area in order to protect the building or infrastructure toward earth quake. These are several attenuation equation which are determined by earth quake s scientist and geologist. a. Attenuation by Dr. Schwarz (2007) Regression coefficients for Regression type I log (y ) = C 1 + C 2 M + C 3 log (r) + σ P M the magnitude (M w ) (r = (d 2 + h 2 0 ) d is the distance (either epicentral r e or fault distance r JB ) h 0 a coefficient to be determined by iteration P the uncertainty in the prediction For example (5 EQ in Aceh on 24 Dec 2004) EQ1 EQ2 EQ3 EQ4 EQ5 d (km) M NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 12
13 ROCK T [sec] C 1 C 2 C 3 h 0 σ STIFF SOIL T [sec] C 1 C 2 C 3 h 0 σ Regression coefficients for Regression type II log (y ) = C 1 + C 2 M + C 3 log (r) + C 4 S stiff + C 5 S soft + σ P M the magnitude (M w ) (r = (d 2 + h 2 0 ) d is the distance (either epicentral r e or fault distance r JB ) h 0 a coefficient to be determined by iteration P the uncertainty in the prediction For example (5 EQ in Aceh on 24 Dec 2004) EQ1 EQ2 EQ3 EQ4 EQ5 d (km) M T [sec] σ C 1 C 2 h 0 C 3 C 4 C S NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 13
14 b. Formula Murphy O Brein : PGA=10 (0,14 I + 0,24 M) 0,68(log d + 0,7 ) Where: PGA = Peak Ground Acceleration I = Intensity (MMI) M = Magnitude d = distance between EQ source and location c. Boore, Joyner dan Fumal (1997) ln (PGA) = b 1 + b 2 (M W 6.0) + b 3 (M W 6.0) 2 + b 5 ln r + b V ln (V S /V A ) Where: r = (r 2 jb + h 2 ) r jb = distance (km) V S = average velocity of shear wave (m/sec) = 1070 cm/sec b 1 b 1SS = EQ s mechanism strike slip b 1RS = EQ s mechanism reverse slip b 1ALL = unpredicted EQ s mechanism d. Attenuation at Subduction Zone by Young et.al (1997) For rock: ln (PGA) = M W ln[r rup e 0.554Mw ] H Z t For soil: ln (PGA) = M W ln[r e 0.617Mw ] H Z t Where: PGA = peak ground acceleration (g), r rup = shortest distance to rupture (km) H = depth of EQ s source (km) Z t = type of EQ s source (0 for interface and 1 for intraslab) NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 14
15 These are a relationship between PGA value which is calculated by attenuation equation and Intensity level. This table and maps below are determined by the magnitude, distance, soil condition and source mechanism. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 15
16 3. Ground Motion Data and Records (1): Collection and check of availability a. Elaboration of a representative database Indonesia has 64 seismic stations for 33 provinces. Aceh and Padang provinces have 1 seismic station in each province. The detail of each station could be seen in the map and table below In this report, I measuring the earth quake source to the nearest local station. For example, I m collecting data of earth quake in Aceh province where the local station of earth quake was installed in Banda Aceh (capital city of Aceh province) as the center. I decided to make boundary of distance is 450 km because it was one of the big earth quake in Aceh province which had large intensity in Banda Aceh. This method is also used to Padang Province, but the maximum distance is 400 km. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 16
17 b. Decision of an Appropriate Ground Motion Prediction Equations (GMPE) Most of Indonesia s geologists have been using attenuation equation from Boore, Joyner and Fumal. But, in this this report, i m trying to use the attenuation equation from Dr. Schwarz to create the response spectra in Aceh and Padang province because i do not have the soil coefficient from Boore, Joyner dan Fumal equation. c. Search for National or International Data Centers I ve been searching all possibilities to get earth quake digital data. It is necessary to create Time history graph and reliable response spectra. These are several websites that I have searched the earth quake data NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 17
18 d. Search for Database and National Weak and Strong Motion Networks I ve found the important data from website about one of big earth quake in Padang. This website has enclosed the location and time history which was measured at local earth quake station in Padang. I believe, this is much reliable because the distance between earth quake source and station is not so far. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 18
19 3.2 Ground Motion Data and Records a. Time Histories and Response spectra These are the time histories at 12 September The magnitude were 8.5, 7.9 and 7 consecutively, and then the maximum intensity in Padang was VIII. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 19
20 This is the response spectra from time histories above. This is calculated by Matlab and normalized to PGA = Application of ground motions models and tools to the study area Statistical Procedures following EC 8 approach (cf. Schott and Schwarz, 2004) a. Statistical Elaboration of database These are the relationship between Magnitude and distance of earth quake source in each province. There is a rectangular in each graph below. It is determined by making limitation of strong motion where the minimum magnitude is 5,5 and low motion is less than 5,5. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 20
21 No Date Time (UTC) Earth Quake in Aceh Location Latitude (N 0 ) Longitude(E 0 ) Depth ( d) Magnitude Hi pocentrum (h) Epicentrum (d^2+ +h^2)^0.5 [km] [M] [km] [km] 1 26-Dec-04 00:58: '42.00"N 95 58'55.20"E Dec-04 04:21: '36.00"N 92 57'28.80"E Dec-04 09:39: '52.80"N 94 39'0.00"E Dec-04 01:25: '56.40"N 94 12'46.80"E Dec-04 15:06: '3.60"N 94 5'9.60"E Dec-04 19:19: '38.40"N 94 9'43.20"E Dec-04 02:00: '52.80"N 94 40'1.20"E Dec-04 01:21: '24.00"N 93 21'39.60"E Dec-04 12:04: '14.40"N 92 54'46.80"E Dec Dec Dec Dec-04 1:22:26 2:24:01 3:22:57 13:46: '15.60"N 7 7'12.00"N 5 49'8.40"N 5 6'46.80"N 93 59'6.00"E 92 31'58.80"E 95 5'31.20"E 96 9'43.20"E Dec Dec-04 3:26:46 21:06: '32.40"N 96 24'18.00"E 4 28'15.60"N 96 20'31.20"E Dec-04 3:42: '4.80"N 94 24'10.80"E Jun-06 19:59: '27.60"N 94 10'8.40"E Jan-05 8:27: '31.20"N 95 27'43.20"E Mar-05 17:29: '51.60"N 95 25'22.80"E NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 21
22 No Date Time (UTC) Location Earth Quake in Padang b. Prediction of site specific spectra using different GMPE These are the result of site specific spectra by using Dr. Schwarz s attenuation equation. Type I Depth (d) Magnitude Hipocentrum (h) Epicentrum (d^2+h^2)^0.5 Latitude (N 0 ) Longitude(E 0 ) [km] [M] [km] [km] 1 30-Sep-09 22:16: Dec-09 1:11: Aug-09 7:38: Sep-09 10:38: Aug-09 20:23: Sep-09 23:47: Aug-09 2:55: Aug-09 11:35: Aug-09 13:55: Aug-09 12:49: Aug-09 9:28: Aug-09 18:50: Aug-09 18:42: Aug-09 10:45: Sep-07 14:13:44 2 8'6.00"S 99 56'6.00"E Sep-07 16:59: '2.40"S 99 56'49.20"E May-07 19:29: '40.80"S 99 52'22.80"E Type II According to the graphs above, it can be clearly seen that the spectral acceleration for type I is higher than type II for each earth quake. NHMSE WS 09/10 (firdaus.firdaus@uni weimar.de; 91128) Page 22
THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR
 JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
Earth Issue: November 2017
 Earth Issue: November 2017 Earthquake Risk In Indonesia Damage in Banda Aceh During 2004 tsunami Source: US Military The Indonesian archipelago is located at the boundary of three major tectonic plates,
Earth Issue: November 2017 Earthquake Risk In Indonesia Damage in Banda Aceh During 2004 tsunami Source: US Military The Indonesian archipelago is located at the boundary of three major tectonic plates,
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update
 The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
Hazard and Vulnerability of Moderate Seismicity Regions
 Hazard and Vulnerability of Moderate Seismicity Regions presented by Professor Tso-Chien PAN Dean, College of Engineering Director, 25 October 2010 DRM GDLN Session on Earthquake Vulnerability Reduction
Hazard and Vulnerability of Moderate Seismicity Regions presented by Professor Tso-Chien PAN Dean, College of Engineering Director, 25 October 2010 DRM GDLN Session on Earthquake Vulnerability Reduction
TSUNAMI AND EARTHQUAKE ACTIVITY IN INDONESIA *
 LOCAL TSUNAMI WARNING AND MITIGATION TSUNAMI AND EARTHQUAKE ACTIVITY IN INDONESIA * Nanang T. Puspito Department of Geophysics and Meteorology, Institute of Technology Bandung (ITB) Address: Jalan Ganeca
LOCAL TSUNAMI WARNING AND MITIGATION TSUNAMI AND EARTHQUAKE ACTIVITY IN INDONESIA * Nanang T. Puspito Department of Geophysics and Meteorology, Institute of Technology Bandung (ITB) Address: Jalan Ganeca
Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake Risk in Indonesia
 過去の火災事例 MM I TTSS UU I SSUU MMI I TTOO MMOO I NN SSUURR AA NN CC EE GG RR OOUUPP INTTEERRI I ISSK AASSI IAA PPTTEE LLTTD... Earthquake Risk in Indonesia October 2009 In Indonesia, the Sumatra Earthquake
過去の火災事例 MM I TTSS UU I SSUU MMI I TTOO MMOO I NN SSUURR AA NN CC EE GG RR OOUUPP INTTEERRI I ISSK AASSI IAA PPTTEE LLTTD... Earthquake Risk in Indonesia October 2009 In Indonesia, the Sumatra Earthquake
5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate the approximate radius of the earth, inner core, and outer core.
 Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do over 90% of earthquakes occur? 3. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? 4. What are the formulae for P and S velocity 5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate
Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do over 90% of earthquakes occur? 3. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? 4. What are the formulae for P and S velocity 5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate
GEOLOGICAL HAZARD MITIGATION STRATEGY IN INDONESIA
 GEOLOGICAL HAZARD MITIGATION STRATEGY IN INDONESIA Surono Head of Geological Agency presented in: The 2nd Global Summit of Research Institutes for Disaster Risk Reduction Kihada Hall, Uji Campus, Kyoto
GEOLOGICAL HAZARD MITIGATION STRATEGY IN INDONESIA Surono Head of Geological Agency presented in: The 2nd Global Summit of Research Institutes for Disaster Risk Reduction Kihada Hall, Uji Campus, Kyoto
RR#8 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and the map below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map indicates the epicenter (*) of a major earthquake that occurred at 38 N 142 E.
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and the map below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map indicates the epicenter (*) of a major earthquake that occurred at 38 N 142 E.
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Determination of the seismicity and peak ground acceleration for Lombok Island: An evaluation on tectonic setting
 4 TH ICRMCE, SOLO, 11-12 JULY 2018 Determination of the seismicity and peak ground acceleration for Lombok Island: An evaluation on tectonic setting Didi S. Agustawijaya, Heri Sulistiyono, Ikhwan Elhuda
4 TH ICRMCE, SOLO, 11-12 JULY 2018 Determination of the seismicity and peak ground acceleration for Lombok Island: An evaluation on tectonic setting Didi S. Agustawijaya, Heri Sulistiyono, Ikhwan Elhuda
DATA BASE DEVELOPMENT OF ETA (ESTIMATED TIME OF ARRIVAL) FOR TSUNAMI DISASTER MITIGATION AT SOUTHWESTERN CITIES OF ACEH, INDONESIA
 6 th South China Sea Tsunami Workshop Nanyang Technology University, Singapore, 6-8 November 2013 DATA BASE DEVELOPMENT OF ETA (ESTIMATED TIME OF ARRIVAL) FOR TSUNAMI DISASTER MITIGATION AT SOUTHWESTERN
6 th South China Sea Tsunami Workshop Nanyang Technology University, Singapore, 6-8 November 2013 DATA BASE DEVELOPMENT OF ETA (ESTIMATED TIME OF ARRIVAL) FOR TSUNAMI DISASTER MITIGATION AT SOUTHWESTERN
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA
 FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
Magnitude 7.0 PAPUA, INDONESIA
 A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
Chapter 3. Geology & Tectonics
 Chapter 3 Geology & Tectonics 3.1 Geology The general geological features of Indonesia are shown in Figure 3.1. The basement formation is metamorphic and it is intruded with plutonic formations. They are
Chapter 3 Geology & Tectonics 3.1 Geology The general geological features of Indonesia are shown in Figure 3.1. The basement formation is metamorphic and it is intruded with plutonic formations. They are
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake
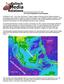 News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Magnitude 7.5 PALU, INDONESIA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 80.8 km (50.2 mi) north of Palu, Indonesia at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). This earthquake triggered a tsunami with wave heights up to 2 m (6.6 ft) that an official
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 80.8 km (50.2 mi) north of Palu, Indonesia at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). This earthquake triggered a tsunami with wave heights up to 2 m (6.6 ft) that an official
Lessons from the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the Asian tsunami
 Lessons from the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the Asian tsunami Kenji Satake National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Outline 1. The largest earthquake in the last 40 years 2. Tsunami
Lessons from the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the Asian tsunami Kenji Satake National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Outline 1. The largest earthquake in the last 40 years 2. Tsunami
Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy.
 Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
The Challenge of Earthquake Disaster in Indonesia. Hery Harjono Indonesian Institute of Sciences
 The Challenge of Earthquake Disaster in Indonesia Hery Harjono Indonesian Institute of Sciences * Presented at the J-Rapid Symposium, Sendai, Japan, March 6-7, 2013 INTRODUCTION The 2004 Giant Sumatran-Andaman
The Challenge of Earthquake Disaster in Indonesia Hery Harjono Indonesian Institute of Sciences * Presented at the J-Rapid Symposium, Sendai, Japan, March 6-7, 2013 INTRODUCTION The 2004 Giant Sumatran-Andaman
Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education
 Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education www.earthobservatory.sg Preparation: Before doing this investigation, complete two introductory investigations using GPS data from UNAVCO
Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education www.earthobservatory.sg Preparation: Before doing this investigation, complete two introductory investigations using GPS data from UNAVCO
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND SEISMIC INPUT TO TSUNAMI MODELING FOR MICROZONATION OF MEURAXA DISTRICT CITY OF BANDA ACEH
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND SEISMIC INPUT TO TSUNAMI MODELING FOR MICROZONATION OF MEURAXA DISTRICT CITY OF BANDA ACEH I W. Sengara 1, Hendarto 1, P. Sumiartha 1, H. Latief 1, S.B. Kusuma 1 and Munirwansjah
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND SEISMIC INPUT TO TSUNAMI MODELING FOR MICROZONATION OF MEURAXA DISTRICT CITY OF BANDA ACEH I W. Sengara 1, Hendarto 1, P. Sumiartha 1, H. Latief 1, S.B. Kusuma 1 and Munirwansjah
Seismic Hazard & Risk Assessment
 Seismic Hazard & Risk Assessment HAZARD ASSESSMENT INVENTORY OF ELEMENTS AT RISK VULNERABILITIES RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY AND SOFTWARE LOSS RESULTS Event Local Site Effects: Attenuation of Seismic Energy
Seismic Hazard & Risk Assessment HAZARD ASSESSMENT INVENTORY OF ELEMENTS AT RISK VULNERABILITIES RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY AND SOFTWARE LOSS RESULTS Event Local Site Effects: Attenuation of Seismic Energy
Dynamic Crust Regents Review
 Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes
 Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
Earthquake Occurrences in the Northern Part of Indonesia
 JULY 2009, NO. 11 Contents: Earthquake Occurrences in the Northern Part of Indonesia 2008-2009 Published by PT. Asuransi MAIPARK Indonesia Board of Advisors Frans Y. Sahusilawane Bisma Subrata Board of
JULY 2009, NO. 11 Contents: Earthquake Occurrences in the Northern Part of Indonesia 2008-2009 Published by PT. Asuransi MAIPARK Indonesia Board of Advisors Frans Y. Sahusilawane Bisma Subrata Board of
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
log 4 0.7m log m Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module 1 Seismology Exercise Problems :
 Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates.
 Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
ESTIMATION OF SEDIMENT THICKNESS BY USING MICROTREMOR OBSERVATIONS AT PALU CITY, INDONESIA. Pyi Soe Thein. 11 November 2013
 ESTIMATION OF SEDIMENT THICKNESS BY USING MICROTREMOR OBSERVATIONS AT PALU CITY, INDONESIA By Pyi Soe Thein 11 November 2013 Outlines Introduction Research objectives Research analyses Microtremor Single
ESTIMATION OF SEDIMENT THICKNESS BY USING MICROTREMOR OBSERVATIONS AT PALU CITY, INDONESIA By Pyi Soe Thein 11 November 2013 Outlines Introduction Research objectives Research analyses Microtremor Single
7 Ground Motion Models
 7 Ground Motion Models 7.1 Introduction Ground motion equations are often called attenution relations but they describe much more than just the attenutation of the ground motion; they describe the probability
7 Ground Motion Models 7.1 Introduction Ground motion equations are often called attenution relations but they describe much more than just the attenutation of the ground motion; they describe the probability
2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes
 2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes Lecture 10: Characterisation of seismic motion Aurel Stratan, Politehnica University of Timisoara 07/04/2017 European Erasmus Mundus Master Course Sustainable
2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes Lecture 10: Characterisation of seismic motion Aurel Stratan, Politehnica University of Timisoara 07/04/2017 European Erasmus Mundus Master Course Sustainable
Dynamic Earth A B1. Which type of plate boundary is located at the Jordan Fault? (1) divergent (3) convergent (2) subduction (4) transform
 Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Ground Motion Prediction Equations: Past, Present, and Future
 Ground Motion Prediction Equations: Past, Present, and Future The 2014 William B. Joyner Lecture David M. Boore As presented at the SMIP15 meeting, Davis, California, 22 October 2015 The William B. Joyner
Ground Motion Prediction Equations: Past, Present, and Future The 2014 William B. Joyner Lecture David M. Boore As presented at the SMIP15 meeting, Davis, California, 22 October 2015 The William B. Joyner
STRONG GROUND MOTION ATTENUATION IN THE SEA OF JAPAN (OKHOTSK-AMUR PLATES BOUNDARY) REGION
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 197 STRONG GROUND MOTION ATTENUATION IN THE SEA OF JAPAN (OKHOTSK-AMUR PLATES BOUNDARY) REGION Laxman
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 197 STRONG GROUND MOTION ATTENUATION IN THE SEA OF JAPAN (OKHOTSK-AMUR PLATES BOUNDARY) REGION Laxman
SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR JAPAN AFTER THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI MEGA-THRUST EARTHQUAKE (Mw9.0)
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR JAPAN AFTER THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT FOR JAPAN AFTER THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI
COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES
 COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES Madlazim Physics Department, Faculty Mathematics and Sciences of Surabaya State University (UNESA) Jl. Ketintang, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia. e-mail:
COULOMB STRESS CHANGES DUE TO RECENT ACEH EARTHQUAKES Madlazim Physics Department, Faculty Mathematics and Sciences of Surabaya State University (UNESA) Jl. Ketintang, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia. e-mail:
What is a Tsunami? Tsu = harbor Nami = wave (Japanese terms)
 Tsunami Hazard What is a Tsunami? Tsu = harbor Nami = wave (Japanese terms) A tsunami is a series of travelling waves most commonly generated by vertical displacements of the sea floor associated with
Tsunami Hazard What is a Tsunami? Tsu = harbor Nami = wave (Japanese terms) A tsunami is a series of travelling waves most commonly generated by vertical displacements of the sea floor associated with
PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007
 PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007 EARTHQUAKE DETAILS The U. S. Geological Survey (USGS) informed a strong earthquake struck west Sumatra on Tuesday March 6, 2007 at 10:49 with a magnitude
PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007 EARTHQUAKE DETAILS The U. S. Geological Survey (USGS) informed a strong earthquake struck west Sumatra on Tuesday March 6, 2007 at 10:49 with a magnitude
LESSON LEARNED FROM THE EFFECT OF RECENT FAR FIELD SUMATRA EARTHQUAKES TO PENINSULAR MALAYSIA
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 416 LESSON LEARNED FROM THE EFFECT OF RECENT FAR FIELD SUMATRA EARTHQUAKES TO PENINSULAR MALAYSIA Azlan
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 416 LESSON LEARNED FROM THE EFFECT OF RECENT FAR FIELD SUMATRA EARTHQUAKES TO PENINSULAR MALAYSIA Azlan
ATTENUATION FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP OF SUBDUCTION MECHANISM AND FAR FIELD EARTHQUAKE
 ATTENUATION FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP OF SUBDUCTION MECHANISM AND FAR FIELD EARTHQUAKE Rozaimi Mohd Noor 1, Saffuan Wan Ahmad 2, Azlan Adnan 1 and Ramli Nazir 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
ATTENUATION FUNCTION RELATIONSHIP OF SUBDUCTION MECHANISM AND FAR FIELD EARTHQUAKE Rozaimi Mohd Noor 1, Saffuan Wan Ahmad 2, Azlan Adnan 1 and Ramli Nazir 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi
Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
We have previously looked at artificial seismograms such as this one here.
 We have previously looked at artificial seismograms such as this one here. S P A realistic Seismic Record Each vertical line = 1 minute Each horizontal line = 15 minutes Seismic station PMM is in Parkfield,
We have previously looked at artificial seismograms such as this one here. S P A realistic Seismic Record Each vertical line = 1 minute Each horizontal line = 15 minutes Seismic station PMM is in Parkfield,
Earthquakes Physical Geology 2017 Part 1: Exploring Earthquake distributions. Home butto California Earthquakes: 1) 2) 3) above
 Earthquakes Physical Geology 2017 Adapted from a lab by Jennifer Wenner This lab is designed to give you experience exploring seismicity associated with different plate boundaries. You will examine seismograms
Earthquakes Physical Geology 2017 Adapted from a lab by Jennifer Wenner This lab is designed to give you experience exploring seismicity associated with different plate boundaries. You will examine seismograms
Earthquakes in Canada
 Earthquakes in Canada Maurice Lamontagne, Ph.D., ing. Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada 1 What is an Earthquake? P S P S P PS 2 2 Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger
Earthquakes in Canada Maurice Lamontagne, Ph.D., ing. Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada 1 What is an Earthquake? P S P S P PS 2 2 Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger
Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches in the Sumatra Subduction Zone
 IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
IJMS 2017 vol. 4 (2): 49-54 International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies (IJMS) Volume 4, Issue 2, 2017 DOI: http://doi.org/10.4038/ijms.v4i2.22 Seismic Activity near the Sunda and Andaman Trenches
EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE FOR SITE- SPECIFIC AMPLIFICATION FACTORS USED IN US BUILDING CODES
 EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE FOR SITE- SPECIFIC AMPLIFICATION FACTORS USED IN US BUILDING CODES Roger D BORCHERDT And Thomas E FUMAL SUMMARY Site-specific amplification factors, F
EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE FOR SITE- SPECIFIC AMPLIFICATION FACTORS USED IN US BUILDING CODES Roger D BORCHERDT And Thomas E FUMAL SUMMARY Site-specific amplification factors, F
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS. Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
The Subsurface Soil Effects Study Using the Short and Long Predominant Periods From H/V Spectrum In Yogyakarta City
 Paper ID 90 The Subsurface Soil Effects Study Using the Short and Long Predominant Periods From H/V Spectrum In Yogyakarta City Z.L. Kyaw 1,2*, S. Pramumijoyo 2, S. Husein 2, T.F. Fathani 3, J. Kiyono
Paper ID 90 The Subsurface Soil Effects Study Using the Short and Long Predominant Periods From H/V Spectrum In Yogyakarta City Z.L. Kyaw 1,2*, S. Pramumijoyo 2, S. Husein 2, T.F. Fathani 3, J. Kiyono
28 th March 2005 magnitude 8.7 earthquake Northern Sumatra, Indonesia
 29 th March 2005 GAPResponse 28 th March 2005 magnitude 8.7 earthquake Northern Sumatra, Indonesia Russell Blong T: +61 2 8209 4288 F: +61 2 9241 2441 E: russell.blong@benfieldgroup.com Ben Miliauskas
29 th March 2005 GAPResponse 28 th March 2005 magnitude 8.7 earthquake Northern Sumatra, Indonesia Russell Blong T: +61 2 8209 4288 F: +61 2 9241 2441 E: russell.blong@benfieldgroup.com Ben Miliauskas
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2
 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic.
 Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic. IANAS GENERAL ASSEMBLY Punta Cana, 16-20 July, 2013 TECTONIC PLATES AND EARTHQUAKES Pacific
Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic. IANAS GENERAL ASSEMBLY Punta Cana, 16-20 July, 2013 TECTONIC PLATES AND EARTHQUAKES Pacific
Chapter 15. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection? At the boundaries friction causes plates to stick together.
 Chapter 15 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? As with volcanoes, earthquakes are not randomly distributed over the globe At the boundaries friction causes plates to stick together.
Chapter 15 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? As with volcanoes, earthquakes are not randomly distributed over the globe At the boundaries friction causes plates to stick together.
Name: Date: Bell: The Sumatra Earthquake and Tsunami December 26, 2004
 Name: Date: Bell: The Sumatra Earthquake and Tsunami December 26, 2004 Introduction: The incredible damage and tragic loss of life resulting from the 9.0 magnitude earthquake and ensuing tsunami was shocking
Name: Date: Bell: The Sumatra Earthquake and Tsunami December 26, 2004 Introduction: The incredible damage and tragic loss of life resulting from the 9.0 magnitude earthquake and ensuing tsunami was shocking
A. rift valley B. deep trench C. volcanic cone D. uplifted mountain. A. a volcanic island arc B. a large watershed area
 DC Practice Test Dynamic Crust PRCTICE TEST Zimm's Earth Science 2013 1. Which feature would most likely be forming at converging continental tectonic plate boundaries?. rift valley. deep trench C.
DC Practice Test Dynamic Crust PRCTICE TEST Zimm's Earth Science 2013 1. Which feature would most likely be forming at converging continental tectonic plate boundaries?. rift valley. deep trench C.
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project
 TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project Introduction The EarthScope Project is an undertaking funded by the National Science Foundation in partnership with the United States Geological Survey and
TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project Introduction The EarthScope Project is an undertaking funded by the National Science Foundation in partnership with the United States Geological Survey and
Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One
 Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One Introduction If you marked all the earthquakes from the past century on a world map, you'd notice that most tend to occur along certain lines around
Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One Introduction If you marked all the earthquakes from the past century on a world map, you'd notice that most tend to occur along certain lines around
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments
 Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Modelling Subduction Zone Seismogenic Hazards in Southeast Asia for Seismic Hazard Assessments Vicki-Ann Dimas 1,2 and Gary Gibson 3 1. Corresponding Author. Seismic Hazard Analyst, Seismology Research
Hideaki Kawasaki 1), Yoshikazu Yamaguchi 2), Takashi Sasaki 3) and Kenji Inagaki 4)
 Characteristics of Seismic Vibrations on Rock Foundation of Dam Sites and Attenuation Relationships of Acceleration Response Spectra at Dam Foundations in Japan by Hideaki Kawasaki 1), Yoshikazu Yamaguchi
Characteristics of Seismic Vibrations on Rock Foundation of Dam Sites and Attenuation Relationships of Acceleration Response Spectra at Dam Foundations in Japan by Hideaki Kawasaki 1), Yoshikazu Yamaguchi
Quake in Indonesia. A series of earthquakes strike the island nation.
 Quake in Indonesia A series of earthquakes strike the island nation. A series of earthquakes rocked the Indonesian island of Sumatra in Southeast Asia. On March 6, 2007, a 6.3-magnitude 1 quake destroyed
Quake in Indonesia A series of earthquakes strike the island nation. A series of earthquakes rocked the Indonesian island of Sumatra in Southeast Asia. On March 6, 2007, a 6.3-magnitude 1 quake destroyed
Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 2016, electronic supplementary material
 1 Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 016, electronic supplementary material Submarine landslides offshore Vancouver Island along the northern Cascadia margin, British Columbia: why preconditioning is likely
1 Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 016, electronic supplementary material Submarine landslides offshore Vancouver Island along the northern Cascadia margin, British Columbia: why preconditioning is likely
Using ArcGIS to Analyze Earthquake Patterns in Java Island, Indonesia
 Using ArcGIS to Analyze Earthquake Patterns in Java Island, Indonesia Presented By: Abdul Latif Ashadi For GIS Course (CRP 514) section 01 Instructor: Dr. Baqer M. Al-Ramadan INTRODUCTION Indonesia Region,
Using ArcGIS to Analyze Earthquake Patterns in Java Island, Indonesia Presented By: Abdul Latif Ashadi For GIS Course (CRP 514) section 01 Instructor: Dr. Baqer M. Al-Ramadan INTRODUCTION Indonesia Region,
Tsunami and earthquake in Chile Part 2
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE GENERAL JRC JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen Global Security and Crisis Management Unit CriTech Sunday, 28 February 2010 Executive
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE GENERAL JRC JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen Global Security and Crisis Management Unit CriTech Sunday, 28 February 2010 Executive
Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
(First Edition: prepared on 29/12/2003)
 (First Edition: prepared on 29/12/2003) Dr Sassan Eshghi 1 and Dr Mehdi Zaré 2 International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Tehran, P.O.Box: 19395/3913, IRAN e-mails: 1)s.eshghi@iiees.ac.ir,
(First Edition: prepared on 29/12/2003) Dr Sassan Eshghi 1 and Dr Mehdi Zaré 2 International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Tehran, P.O.Box: 19395/3913, IRAN e-mails: 1)s.eshghi@iiees.ac.ir,
Investigation of Sumatran Fault Aceh Segment derived from Magnetotelluric Data
 Investigation of Sumatran Fault Aceh Segment derived from Magnetotelluric Data Nurhasan 1, D. Sutarno 1, Y Ogawa 2, F. Kimata 3, D Sugiyanto 4 1 Physics Department, Bandung Institute of Technology, Bandung,
Investigation of Sumatran Fault Aceh Segment derived from Magnetotelluric Data Nurhasan 1, D. Sutarno 1, Y Ogawa 2, F. Kimata 3, D Sugiyanto 4 1 Physics Department, Bandung Institute of Technology, Bandung,
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard. Earthquake Environment
 Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Earthquakes!! Be sure to fill in your notes sheet as you go through the power point!
 Earthquakes!! Be sure to fill in your notes sheet as you go through the power point! Plate Boundary Review Click on the link below to try some plate boundary movement simulations. The link will take you
Earthquakes!! Be sure to fill in your notes sheet as you go through the power point! Plate Boundary Review Click on the link below to try some plate boundary movement simulations. The link will take you
Lab 13: Patterns of Crustal Activity
 Name: Earth Science Lab 13: Patterns of Crustal Activity Date: Class: Introduction: Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain ranges do not occur randomly. There are special zones in which they occur. Scientists
Name: Earth Science Lab 13: Patterns of Crustal Activity Date: Class: Introduction: Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain ranges do not occur randomly. There are special zones in which they occur. Scientists
Earthquakes. Photo credit: USGS
 Earthquakes Earthquakes Photo credit: USGS Pancaked Building - 1985 Mexico City Earthquakes don t kill people - buildings do! An earthquake is the motion or trembling of the ground produced by sudden displacement
Earthquakes Earthquakes Photo credit: USGS Pancaked Building - 1985 Mexico City Earthquakes don t kill people - buildings do! An earthquake is the motion or trembling of the ground produced by sudden displacement
Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 - What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
- What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire
 Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
DIRECT HAZARD ANALYSIS OF INELASTIC RESPONSE SPECTRA
 DIRECT HAZARD ANALYSIS OF INELASTIC RESPONSE SPECTRA ABSTRACT Y. Bozorgnia, M. Hachem, and K.W. Campbell Associate Director, PEER, University of California, Berkeley, California, USA Senior Associate,
DIRECT HAZARD ANALYSIS OF INELASTIC RESPONSE SPECTRA ABSTRACT Y. Bozorgnia, M. Hachem, and K.W. Campbell Associate Director, PEER, University of California, Berkeley, California, USA Senior Associate,
Magnitude 7.1 PHILIPPINES
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
Usability of the Next Generation Attenuation Equations for Seismic Hazard Assessment in Malaysia
 Azlan Adnan, Patrick Liq Yee Tiong, Yue Eng Chow/ International Journal of Engineering Vol. 2 Issue 1, Jan-Feb 212, pp.639-644 Usability of the Next Generation Attenuation Equations for Seismic Hazard
Azlan Adnan, Patrick Liq Yee Tiong, Yue Eng Chow/ International Journal of Engineering Vol. 2 Issue 1, Jan-Feb 212, pp.639-644 Usability of the Next Generation Attenuation Equations for Seismic Hazard
Ground-Motion Attenuation Relationships for Subduction- Zone Earthquakes in Northern Taiwan
 Ground-Motion Attenuation Relationships for Subduction- Zone Earthquakes in Northern Taiwan Lin, P.S., Lee, C.T. Bulletin of the Seismology Society of America (2008) Presenter: Yang Pei-Xin Adviser: Lee
Ground-Motion Attenuation Relationships for Subduction- Zone Earthquakes in Northern Taiwan Lin, P.S., Lee, C.T. Bulletin of the Seismology Society of America (2008) Presenter: Yang Pei-Xin Adviser: Lee
PRELIMINARY STUDY OF THE 2011 JAPAN EARTHQUAKE (M 9.0) GROUND MOTION RECORDS V1.01
 Cite as: F. De Luca, E. Chioccarelli, I. Iervolino (), Preliminary study of the Japan earthquake ground motion record V., available at http://www.reluis.it. PRELIMINARY STUDY OF THE JAPAN EARTHQUAKE (M
Cite as: F. De Luca, E. Chioccarelli, I. Iervolino (), Preliminary study of the Japan earthquake ground motion record V., available at http://www.reluis.it. PRELIMINARY STUDY OF THE JAPAN EARTHQUAKE (M
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code
 Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard.
 Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
SHAKE, RATTLE, AND ROLL INVESTIGATING EARTHQUAKES
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) SHAKE, RATTLE, AND ROLL INVESTIGATING EARTHQUAKES The city of San Francisco was destroyed by a 7.8 magnitude earthquake that ruptured gas lines and set the city ablaze. March 28, 1964
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) SHAKE, RATTLE, AND ROLL INVESTIGATING EARTHQUAKES The city of San Francisco was destroyed by a 7.8 magnitude earthquake that ruptured gas lines and set the city ablaze. March 28, 1964
A note on ground motion recorded during Mw 6.1 Mae Lao (Northern Thailand) earthquake on 5 May 2014
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia A note on ground motion recorded during Mw 6.1 Mae Lao
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 2015, Sydney, Australia A note on ground motion recorded during Mw 6.1 Mae Lao
Liquefaction Potential Post-Earthquake in Yogyakarta
 The 17 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical Conference Taipei, Taiwan, May 10~13, 2010 Liquefaction Potential Post-Earthquake in Yogyakarta AGUS SETYO MUNTOHAR 1 and S.P.R. WARDANI 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
The 17 th Southeast Asian Geotechnical Conference Taipei, Taiwan, May 10~13, 2010 Liquefaction Potential Post-Earthquake in Yogyakarta AGUS SETYO MUNTOHAR 1 and S.P.R. WARDANI 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
Year 8 Level: 5-8 GEOGRAPHY Time: 1:30min
 Year 8 Level: 5-8 GEOGRAPHY Time: 1:30min Name: Class: Answer all questions in the space provided. 1. Label the diagram below using the following words; (4) mantle, crust, outer core, inner core 2. Write
Year 8 Level: 5-8 GEOGRAPHY Time: 1:30min Name: Class: Answer all questions in the space provided. 1. Label the diagram below using the following words; (4) mantle, crust, outer core, inner core 2. Write
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan
 Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
The Indian Ocean. Copyright 2010 LessonSnips
 The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
FORCES ON EARTH. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
"The Natural Disasters, like The Sumatra Tsunami had taught us before -BUT" U Than Myint President Myanmar Engineering Society
 "The Natural Disasters, like The Sumatra Tsunami had taught us before -BUT" U Than Myint President Myanmar Engineering Society Present Day Regional Tectonic Setting of South East Asia Tsunami-generated
"The Natural Disasters, like The Sumatra Tsunami had taught us before -BUT" U Than Myint President Myanmar Engineering Society Present Day Regional Tectonic Setting of South East Asia Tsunami-generated
Magnitude 7.3 NEPAL. Tuesday, May 12, 2015 at 07:05:19 UTC
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred near Mount Everest. Early reports suggest 32 people have been killed and at least 1,000 were injured in the earthquake. The region is still in recovery from a 7.8
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred near Mount Everest. Early reports suggest 32 people have been killed and at least 1,000 were injured in the earthquake. The region is still in recovery from a 7.8
Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L
 6.10: Tectonic Plates Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L 1 On March 11, 2011, an earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale rocked the sea floor. It made a giant wave, which grew as tall as 30 feet (9.14 meters)
6.10: Tectonic Plates Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L 1 On March 11, 2011, an earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale rocked the sea floor. It made a giant wave, which grew as tall as 30 feet (9.14 meters)
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes and seismic hazard in Sweden
 Earthquakes and seismic hazard in Sweden Björn Lund, Roland Roberts & Reynir Bödvarsson Uppsala University Outline Nordic and Swedish seismicity Comparison to plate boundary seismicity in Japan. Extrapolation
Earthquakes and seismic hazard in Sweden Björn Lund, Roland Roberts & Reynir Bödvarsson Uppsala University Outline Nordic and Swedish seismicity Comparison to plate boundary seismicity in Japan. Extrapolation
What causes an earthquake? Giant snakes, turtles, catfish, and spiders?
 What causes an earthquake? Giant snakes, turtles, catfish, and spiders? What causes an earthquake? The movement of Earth s plates creates enormous forces that squeeze or pull the rock in the crust as if
What causes an earthquake? Giant snakes, turtles, catfish, and spiders? What causes an earthquake? The movement of Earth s plates creates enormous forces that squeeze or pull the rock in the crust as if
Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan
 Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan T. Annaka* and H. Yashiro* * Tokyo Electric Power Services Co., Ltd., Japan ** The Tokio Marine and Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.,
Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan T. Annaka* and H. Yashiro* * Tokyo Electric Power Services Co., Ltd., Japan ** The Tokio Marine and Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.,
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
