b. By Proterozoic, - protected from solar radiation if about 10 M below surface of water - dominated by
|
|
|
- Aleesha Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I. Diversification of Life A. Review 1. Hadean Eon a. b. 2. Archaean Eon a. Earliest fossils of b. Establishment of three major domains B. Proterozoic Eon (2.5 bya mya) 1. Emergence of the a. Rock cycles begin to leave b. Most Archaean Deposits more c. Prolonged period of continental growth 2. Developed assembly of land masses - major continents by late Proterozoic a. - Greenland, N. America, England, Siberia, initially S. America b. - Africa, India, Antarctica, Australia - eventually included 3. Early Biosphere a. Archaean Atmosphere measured to contain primarily b. By Proterozoic, - protected from solar radiation if about 10 M below surface of water - dominated by c. Conversion from primordial heterotrophs to autotrophs was key to atmosphere - trace amounts of O2 released via - microbial autotrophs, cyanobacteria, d. Poisonous Oxygen - Initial insurgence of atmospheric O2 detectable as early as 2.2 bya - Early on Earth dominated by Prokaryotic life - increase in O2 - many early dominant forms i. Retreat to specialized environments 4. Diversification of Form Began with the a. resting stage of b. Earliest fossil record dates to about - acritarch fossils abundant by 800 mya c. Rapid divergence into variety of early Eukaryote lineages
2 5. a. Earliest evidence of b. Found initially in Ediacara Hills in Australia - more than 20 sites with Ediacaran fauna now known c. rocks dated to about 620 mya mya d. Variety of forms found from - soft-bodied - most resemble sponges, jellyfish, sea pens, comb-jellies i. - some may be worms (extremely rare) i. e. Dramatic increase in - occurs as get nearer the - reflects new modes of locomotion - reflect insurgence of f. Gap in the fossil record - sediments during interval appear to be - Predator dominance theory i. Rise of hunters * Ediacaran fauna unable to protect against new mobile predators * II. The Phanerozic Eon A. The Cambrian Explosion 1. Cambrian Period 2. Cambrian deposits suddenly full of diversity a. - Most famous fossil bed - British Columbia - discovered in 1909 by Charles Walcott b., from China - discovered more recently 3. Represents a. known major recognizable body plans found b. most forms - some Poriferan (sponge) and Cnidarian (e.g. sea pens, jellyfish) forms persist c. includes some body plans unknown from previous fossils or from extant taxa - grouped in the
3 d. Marrella - Cambrian shrimp-like crusteacean e. Leanchoilia, arthropod (crusteacean/scorpion/insect-like animal) f. Nectocaris: a probable arrow worm 4. How are fossils reconstructed? a. via comparison of extant species - some are very similar i. e.g. Aysheaia * ii. * - some unlike known taxa but have recognizable components i. e.g. Opabinia - some have proven difficult due to limited remains i. e.g. Anomalocaris - some just plain difficult i. e.g. Wiwaxia * Originally completely confounded * Recent theories suggesting mollusk * More recently assigned to ii. Hallucenagenia
4 5. (1980s & 1990s) a. estimates of the timing of the origin of lineages - estimates for earliest divergence times b. search for earlier fossils c. 6. Conditions causing Cambrian Diversification a. - allowed development of multicellular structures - allowed increase in - allowed increase in b. Increased - allowed - predation created selection gradient for - increase in hard body parts allowed for dramatic increase in 7. a. Major diversification of body plans associated with changes at genetic level - all multicellular organisms have system of organizing cells in space and time during development i.cells differentiate according to ii. Cells differentiate - how control of cell signaling acts as mechanism for evolution is among least well known areas b. What are Homeotic Loci? - genes that carry information for i. Typically refer to Homeotic genes in general as - Found in all animal phyla studied c. Hox loci are organized in gene complexes - occur together in
5 d. Correlation between - 3 end genes expresse d in - 5 end genes expresse d in - Deletion experiments demonstrate association of genes with segment specific expression e. All Hox genes contain bp sequence - Homeotic genes act as i.bind DNA of other loci f. Changes in Hox clusters led to major diversification - Hox gene homologs - Hox genes found even in jellyfish and sponges - likely that Hox genes - Can Map Hox gene condition to phylogeny of animals i.allows ii. Other genes likely arose - Can associate shifts in major taxa with i. Specific clusters associate with ii. e.g. addition of Abd-b g. Why don t we get new maj or mutant body plans continuing to show up? - It worked early when environment was wide open - ecological condition favor evolution of larger and more diverse body plans i. Favored use of ii. more efficient and complex * - eventually niche space becomes i. Competition for ii. Mutations seen as deleterious
EVOLUTION OF COMPLEX LIFE FORMS
 0.002 0.6 1.0 1.9 2.8 Ancestral humans Diversification of mammals Invasion of the land Diversification of animals Origin of the major eukaryotic groups Eukaryotic cells abundant Atmospheric oxygen plentiful
0.002 0.6 1.0 1.9 2.8 Ancestral humans Diversification of mammals Invasion of the land Diversification of animals Origin of the major eukaryotic groups Eukaryotic cells abundant Atmospheric oxygen plentiful
Outline 11: Fossil Record of Early Life Life in the Precambrian
 Outline 11: Fossil Record of Early Life Life in the Precambrian Time Line 0.545 BY animals with hard parts, start of the Phanerozoic Eon 0.600 BY first animals, no hard parts 2.0 BY first definite eukaryotes
Outline 11: Fossil Record of Early Life Life in the Precambrian Time Line 0.545 BY animals with hard parts, start of the Phanerozoic Eon 0.600 BY first animals, no hard parts 2.0 BY first definite eukaryotes
Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon
 Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon Proterozoic Eon is ~ 1.95 billion years in duration, from 2.5 Ga to 0.543 Ga 2.5 Ga 1.6 Ga 1.0 Ga 0.54 Ga Paleoproterozoic Era Mesoproterozoic Era Neoproterozoic Era PROTEROZOIC
Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon Proterozoic Eon is ~ 1.95 billion years in duration, from 2.5 Ga to 0.543 Ga 2.5 Ga 1.6 Ga 1.0 Ga 0.54 Ga Paleoproterozoic Era Mesoproterozoic Era Neoproterozoic Era PROTEROZOIC
Radiation and Evolution of Metazoans: The Cambrian Explosion and the Burgess Shale Fossils. Geology 331, Paleontology
 Radiation and Evolution of Metazoans: The Cambrian Explosion and the Burgess Shale Fossils Geology 331, Paleontology Marshall, 2006 Halkierids, which produced some of the small, shelly fossils of the Early
Radiation and Evolution of Metazoans: The Cambrian Explosion and the Burgess Shale Fossils Geology 331, Paleontology Marshall, 2006 Halkierids, which produced some of the small, shelly fossils of the Early
5/4/05 Biol 473 lecture
 5/4/05 Biol 473 lecture animals shown: anomalocaris and hallucigenia 1 The Cambrian Explosion - 550 MYA THE BIG BANG OF ANIMAL EVOLUTION Cambrian explosion was characterized by the sudden and roughly simultaneous
5/4/05 Biol 473 lecture animals shown: anomalocaris and hallucigenia 1 The Cambrian Explosion - 550 MYA THE BIG BANG OF ANIMAL EVOLUTION Cambrian explosion was characterized by the sudden and roughly simultaneous
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Development of Life. Stephen Eikenberry 06 September 2012 AST 2037
 Development of Life Stephen Eikenberry 06 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolution This time with a capital E Reproduction occurs via DNA Any change in the DNA from one generation to the next creates mutation
Development of Life Stephen Eikenberry 06 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolution This time with a capital E Reproduction occurs via DNA Any change in the DNA from one generation to the next creates mutation
Evolution of Life and the Atmosphere
 Evolution of Life and the Atmosphere White board used for Evolution of the Atmosphere and Early Evolution of Life The Pitfalls of Preservation It is obvious that a major change occurred in the Earth s
Evolution of Life and the Atmosphere White board used for Evolution of the Atmosphere and Early Evolution of Life The Pitfalls of Preservation It is obvious that a major change occurred in the Earth s
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
The Geological Time Scale. Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of Canada.
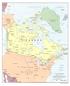 Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
8/23/2014. Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom
 The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom continue to be researched and debated, as new fossil
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom continue to be researched and debated, as new fossil
GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Eukaryote Life forms (Acritarchs) B) Metazoans (Ediacaran Fauna) GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms Textbook reference: Levin 7 th edition
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Eukaryote Life forms (Acritarchs) B) Metazoans (Ediacaran Fauna) GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms Textbook reference: Levin 7 th edition
Animal Diversity. Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 9/20/2017
 Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Which of these organisms are animals? Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Animals share the same: Nutritional
Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Which of these organisms are animals? Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Animals share the same: Nutritional
Proterozoic Life and Environments
 Proterozoic Life and Environments (or: 3 billion years in 70 minutes) Cambrian Explosion Origin of Life Great Oxygenation Event Origin of Life Early Life Localities >2.5 Ga Named localities: >3.2 Ga Isua
Proterozoic Life and Environments (or: 3 billion years in 70 minutes) Cambrian Explosion Origin of Life Great Oxygenation Event Origin of Life Early Life Localities >2.5 Ga Named localities: >3.2 Ga Isua
First, an supershort History of the Earth by Eon
 HISTORY OF LIFE WRITTEN IN THE ROCKS (geological record): notice how at first no life, very simple if for billions of years, complex life only recently 600 mya In these chapters, two primary themes: History
HISTORY OF LIFE WRITTEN IN THE ROCKS (geological record): notice how at first no life, very simple if for billions of years, complex life only recently 600 mya In these chapters, two primary themes: History
Tracing Evolutionary History (Outline)
 Tracing Evolutionary History (Outline) Four stages leading to emergence of living cells Geophysical conditions impact on biodiversity: - continental drift and volcanism, earthquakes and meteorites Living
Tracing Evolutionary History (Outline) Four stages leading to emergence of living cells Geophysical conditions impact on biodiversity: - continental drift and volcanism, earthquakes and meteorites Living
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma)
 The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
Aim: Who were the first animals to evolve? Date: October 24, 2013 Catalyst: Throwback Thursday
 Aim: Who were the first animals to evolve? Date: October 24, 2013 Catalyst: Throwback Thursday! 1. What is the difference between vascular and non-vascular plants? 2. What are three major adaptations of
Aim: Who were the first animals to evolve? Date: October 24, 2013 Catalyst: Throwback Thursday! 1. What is the difference between vascular and non-vascular plants? 2. What are three major adaptations of
3. Evolutionary change is random because gene mutations are random. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 9, 2015, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D. Survival
Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 9, 2015, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D. Survival
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology
 Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Calculating extra credit from clicker points. Total points through last week: Participation: 6 x 2 = 12 Performance: = 26
 Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 10, 2016, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D.
Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 10, 2016, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D.
HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH
 HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH EARTH S HISTORY Earth s age: - about 4.6 billion years old (big bang) First life forms appeared ~3.5 billion years ago How did life arise? 1. Small organic molecules were synthesized
HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH EARTH S HISTORY Earth s age: - about 4.6 billion years old (big bang) First life forms appeared ~3.5 billion years ago How did life arise? 1. Small organic molecules were synthesized
Energy Requirement Energy existed in several forms satisfied condition 2 (much more UV than present no ozone layer!)
 Biology 10 Chapter 19-3 p 553-558 Earth s Early History Objectives Describe the hypotheses scientists have about early Earth, and the origin of life. Describe the theory of how eukaryotic cells formed.
Biology 10 Chapter 19-3 p 553-558 Earth s Early History Objectives Describe the hypotheses scientists have about early Earth, and the origin of life. Describe the theory of how eukaryotic cells formed.
Origins of Life. Fundamental Properties of Life. The Tree of Life. Chapter 26
 Origins of Life The Tree of Life Cell is the basic unit of life Today all cells come from pre-existing cells Earth formed ~4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Chapter 26 As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were
Origins of Life The Tree of Life Cell is the basic unit of life Today all cells come from pre-existing cells Earth formed ~4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Chapter 26 As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were
History of Life on Earth
 History of Life on Earth Deep Time 4550 mya to present era eon era era Precambrian Eon Hadean Era Geology Birth of solar system - 4.55 bya Escaping gasses create early atmosphere Earth s core forms - 4.4
History of Life on Earth Deep Time 4550 mya to present era eon era era Precambrian Eon Hadean Era Geology Birth of solar system - 4.55 bya Escaping gasses create early atmosphere Earth s core forms - 4.4
Chapter 19. History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Chapter 12. Life of the Paleozoic
 Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapters 25 and 26. Searching for Homology. Phylogeny
 Chapters 25 and 26 The Origin of Life as we know it. Phylogeny traces evolutionary history of taxa Systematics- analyzes relationships (modern and past) of organisms Figure 25.1 A gallery of fossils The
Chapters 25 and 26 The Origin of Life as we know it. Phylogeny traces evolutionary history of taxa Systematics- analyzes relationships (modern and past) of organisms Figure 25.1 A gallery of fossils The
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion
 Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. Origin
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. Origin
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion
 Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. 1 Origin
Origins of Life & the Cambrian Explosion Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal vents may have served as zones of refuge. 1 Origin
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale
 History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
Summary The Fossil Record Earth s Early History. Name Class Date
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 Summary The History of Life 17 1 The Fossil Record Fossils are preserved traces and remains of ancient life. Scientists who study fossils are called paleontologists. They use
Name Class Date Chapter 17 Summary The History of Life 17 1 The Fossil Record Fossils are preserved traces and remains of ancient life. Scientists who study fossils are called paleontologists. They use
X The evolution of life on Earth.
 X The evolution of life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 10.0 Introduction A combination of the fossil record, biology and genetics allows us to examine the evolution of life on Earth.
X The evolution of life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 10.0 Introduction A combination of the fossil record, biology and genetics allows us to examine the evolution of life on Earth.
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Evolution and diversity of organisms
 Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
Laboratory 7 Geologic Time
 (Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
(Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin of Life. What is Life? The evolutionary tree of life can be documented with evidence. The Origin of Life on Earth is another
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
History of Life on Earth
 Macroevolution Broad pattern of evolution at and above the species level (in contrast to microevolution) History of Life on Earth Chapter 25 Early earth Miller and Urey Experiments ~4.5 billion years old
Macroevolution Broad pattern of evolution at and above the species level (in contrast to microevolution) History of Life on Earth Chapter 25 Early earth Miller and Urey Experiments ~4.5 billion years old
Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014 Evolution of Animals 1 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Nucleoid region Simple No membrane bound organelles Smaller (1-5 nm) Evolutionarily
Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014 Evolution of Animals 1 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Nucleoid region Simple No membrane bound organelles Smaller (1-5 nm) Evolutionarily
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION. Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology
 SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
Geologic Time. Early Earth History
 chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
IX Life on Earth.
 IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
Evolution & Biodiversity: Origins, Niches, & Adaptation
 Evolution & Biodiversity: Origins, Niches, & Adaptation tutorial by Paul Rich Outline 1. Life on Earth prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes; six kingdoms 2. Origins of Life chemical evolution, early life, fossils
Evolution & Biodiversity: Origins, Niches, & Adaptation tutorial by Paul Rich Outline 1. Life on Earth prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes; six kingdoms 2. Origins of Life chemical evolution, early life, fossils
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20)
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
Objectives. Evolution. Darwin 5/30/2012. Pre-Darwin. Genetic change in a population over time.
 Objectives Evolution What is evolution? What lead Darwin to his thoughts 4 Premises of Evolution by Natural Selection Evidence supporting Evolution Genetic change in a population over time. Unifying concept
Objectives Evolution What is evolution? What lead Darwin to his thoughts 4 Premises of Evolution by Natural Selection Evidence supporting Evolution Genetic change in a population over time. Unifying concept
13.1 Biological Classification - Kingdoms and Domains Modern species are divided into three large groups, or domains. Bacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Chapter 13 Prospecting for Biological Gold Biodiversity and Classification 13.1 Biological Classification- How Many Species Exist? Biodiversity is the variety within and among living species Number of
Chapter 13 Prospecting for Biological Gold Biodiversity and Classification 13.1 Biological Classification- How Many Species Exist? Biodiversity is the variety within and among living species Number of
PART 3: FORMATION OF EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE
 PART 3: FORMATION OF EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE 1. Origin of the Universe: there are many theories on the origin of the universe. Paradigm: a widely accepted idea in science. A paradigm shift is a sudden change
PART 3: FORMATION OF EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE 1. Origin of the Universe: there are many theories on the origin of the universe. Paradigm: a widely accepted idea in science. A paradigm shift is a sudden change
Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. The Ever-Changing Earth. Early Life. Evolution and the Fossil Record. Life in the Phanerozoic Eon
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic Eon. 542 mya Present. Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras
 542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
1. Evolution and Classification
 1. Evolution and Classification 1.1 Origin of Life and Plants 1.2 Animal Evolution 1.3 Human Evolution 1.4 Mechanisms of Evolution 1.5 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 1.6 Mechanisms of Speciation 1.7 Classification
1. Evolution and Classification 1.1 Origin of Life and Plants 1.2 Animal Evolution 1.3 Human Evolution 1.4 Mechanisms of Evolution 1.5 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium 1.6 Mechanisms of Speciation 1.7 Classification
UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity
 UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity CHAPTER 14: The History of Life PAST NOW FUTURE? What is this? Earth s Early history Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was formed when many pieces of
UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity CHAPTER 14: The History of Life PAST NOW FUTURE? What is this? Earth s Early history Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was formed when many pieces of
Lecture V Eukaryotes and the Cambrian Explosion.
 Lecture V Eukaryotes and the Cambrian Explosion. I. Early Metabolisms. 1. Heterotrophs: Anaerobic; aerobic; 2. Autotrophs: Anoxic; oxygenic. Some Metabolic Pathways Heterotrophy Pathway Energy Source Initial
Lecture V Eukaryotes and the Cambrian Explosion. I. Early Metabolisms. 1. Heterotrophs: Anaerobic; aerobic; 2. Autotrophs: Anoxic; oxygenic. Some Metabolic Pathways Heterotrophy Pathway Energy Source Initial
Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago
 Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago Formed from interstellar gas & dust into molten planet Earth s early atmosphere was hostile, made of carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, nitrogen, sulfur,
Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago Formed from interstellar gas & dust into molten planet Earth s early atmosphere was hostile, made of carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, nitrogen, sulfur,
Biol/Env St 204 Quiz 2 Spring 2008
 Biol/Env St 204 Quiz 2 Spring 2008 Name: 40 points Short-Answer Section (20 points total) 1. In the reading Interview with a Fungus, why did Mr. Pilobolus conclude that fungi characterize mankind as expendable?
Biol/Env St 204 Quiz 2 Spring 2008 Name: 40 points Short-Answer Section (20 points total) 1. In the reading Interview with a Fungus, why did Mr. Pilobolus conclude that fungi characterize mankind as expendable?
Phylogeny & Systematics
 Phylogeny & Systematics Phylogeny & Systematics An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics has revealed that despite
Phylogeny & Systematics Phylogeny & Systematics An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics has revealed that despite
Rare Earth? See Rare Earth, by Ward and Brownlee
 Rare Earth? See Rare Earth, by Ward and Brownlee N to date N = N * f s f p n H f l f i f c L/T N * = 4 x 10 11 f s = 0.2 f p = 1.0 n H = 2 f l = 1.0 N = 1.6 x 10 11 The Goldilocks Effect Earth is Just
Rare Earth? See Rare Earth, by Ward and Brownlee N to date N = N * f s f p n H f l f i f c L/T N * = 4 x 10 11 f s = 0.2 f p = 1.0 n H = 2 f l = 1.0 N = 1.6 x 10 11 The Goldilocks Effect Earth is Just
Bio 100 Study Guide 14.
 Bio 100 Study Guide 14 http://www.swarthmore.edu/natsci/cpurrin1/evolk12/slm/origindayimages/06soup.jpg The Origin of Life - Issues i. Conditions on early earth ii. iii. iv. Abiogenic synthesis organic
Bio 100 Study Guide 14 http://www.swarthmore.edu/natsci/cpurrin1/evolk12/slm/origindayimages/06soup.jpg The Origin of Life - Issues i. Conditions on early earth ii. iii. iv. Abiogenic synthesis organic
Class Webpage. Forms of Diversity. biol170/biol170syl.htm
 Class Webpage http://userwww.sfsu.edu/~efc/classes/ biol170/biol170syl.htm What is an animal? While there are exceptions, five criteria distinguish animals from other life forms. (1)Animals are multicellular,
Class Webpage http://userwww.sfsu.edu/~efc/classes/ biol170/biol170syl.htm What is an animal? While there are exceptions, five criteria distinguish animals from other life forms. (1)Animals are multicellular,
There are 3 parts to this exam. Take your time and be sure to put your name on the top of each page.
 EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY BIOS 30305 EXAM #2 FALL 2011 There are 3 parts to this exam. Take your time and be sure to put your name on the top of each page. Part I. True (T) or False (F) (2 points each). 1)
EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY BIOS 30305 EXAM #2 FALL 2011 There are 3 parts to this exam. Take your time and be sure to put your name on the top of each page. Part I. True (T) or False (F) (2 points each). 1)
Animal Diversity. Features shared by all animals. Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers
 Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1)
 Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1) A) They are multicellular eukaryotes. B) They are heterotrophs. C) Their cells are supported
Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1) A) They are multicellular eukaryotes. B) They are heterotrophs. C) Their cells are supported
Preview. 1.Historical Extinctions 2.Current Extinctions 3.Extinction Factors
 Extinction Preview 1.Historical Extinctions 2.Current Extinctions 3.Extinction Factors 1. Historical Extinctions Most abundant organisms to ever inhabit Earth are prokaryotes 1. Humans Colonization of
Extinction Preview 1.Historical Extinctions 2.Current Extinctions 3.Extinction Factors 1. Historical Extinctions Most abundant organisms to ever inhabit Earth are prokaryotes 1. Humans Colonization of
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Microbes and Origins of Life. Evolution has occurred almost elusively in a microbial world!!!
 Microbes and Origins of Life Evolution has occurred almost elusively in a microbial world!!! Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal
Microbes and Origins of Life Evolution has occurred almost elusively in a microbial world!!! Impact Frustration period forces origins of life into a narrow time period to have gotten started! Hydrothermal
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE. Dr. Bertolotti
 CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
Name. Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 1 18 February 2014
 Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 1 18 February 2014 2 READ THE EXAM OVER CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU BEGIN. IT CONSISTS OF A TOTAL OF 15 QUESTIONS; YOU MUST ANSWER ALL PARTS OF EACH QUESTION.
Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 1 18 February 2014 2 READ THE EXAM OVER CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU BEGIN. IT CONSISTS OF A TOTAL OF 15 QUESTIONS; YOU MUST ANSWER ALL PARTS OF EACH QUESTION.
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
Earth Science. Name Block. Unit 3 Review Worksheet. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Biological Evolution. Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection
 Biological Evolution Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection 1. Linnaean Classification Major Concepts 2. Fossils 3. Radioactive Dating 4. Fossil Record and Genetic Analysis 5. Theory of Evolution Random,
Biological Evolution Darwinian Evolution and Natural Selection 1. Linnaean Classification Major Concepts 2. Fossils 3. Radioactive Dating 4. Fossil Record and Genetic Analysis 5. Theory of Evolution Random,
BIOLOGY 432 Midterm I - 30 April PART I. Multiple choice questions (3 points each, 42 points total). Single best answer.
 BIOLOGY 432 Midterm I - 30 April 2012 Name PART I. Multiple choice questions (3 points each, 42 points total). Single best answer. 1. Over time even the most highly conserved gene sequence will fix mutations.
BIOLOGY 432 Midterm I - 30 April 2012 Name PART I. Multiple choice questions (3 points each, 42 points total). Single best answer. 1. Over time even the most highly conserved gene sequence will fix mutations.
Life on Earth, Lessons Learned
 Life on Earth, Lessons Learned 11-30-2005 Opening Discussion Have you seen anything interesting in the news? How much does the carbon cycle matter to the global warming debate? The key is the timescale.
Life on Earth, Lessons Learned 11-30-2005 Opening Discussion Have you seen anything interesting in the news? How much does the carbon cycle matter to the global warming debate? The key is the timescale.
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 2
 SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 2 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 2 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time.
 Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
Name. Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008
 Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008 1. Use the following list of fossil taxa to answer parts a through g below. (2 pts each) 2 Aegyptopithecus Australopithecus africanus Diacronis
Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008 1. Use the following list of fossil taxa to answer parts a through g below. (2 pts each) 2 Aegyptopithecus Australopithecus africanus Diacronis
Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C.
 Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C. Broad Patterns of Evolution (Ch23) D. Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles (Ch 10)
Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C. Broad Patterns of Evolution (Ch23) D. Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles (Ch 10)
Origins of Life. Fundamental Properties of Life. Conditions on Early Earth. Evolution of Cells. The Tree of Life
 The Tree of Life Chapter 26 Origins of Life The Earth formed as a hot mass of molten rock about 4.5 billion years ago (BYA) -As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were formed from water condensation Life
The Tree of Life Chapter 26 Origins of Life The Earth formed as a hot mass of molten rock about 4.5 billion years ago (BYA) -As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were formed from water condensation Life
EVOLUTION change in populations over time
 EVOLUTION change in populations over time HISTORY ideas that shaped the current theory James Hutton (1785) proposes that Earth is shaped by geological forces that took place over extremely long periods
EVOLUTION change in populations over time HISTORY ideas that shaped the current theory James Hutton (1785) proposes that Earth is shaped by geological forces that took place over extremely long periods
Evolution FROM DARWIN TO THE PRESENT. Part IV: A short history of life on earth
 Evolution FROM DARWIN TO THE PRESENT Part IV: A short history of life on earth Ages of the Earth: a geological time scale Who are the players? Currently we recognize six distinct kingdoms in two main divisions:
Evolution FROM DARWIN TO THE PRESENT Part IV: A short history of life on earth Ages of the Earth: a geological time scale Who are the players? Currently we recognize six distinct kingdoms in two main divisions:
What Are the Protists?
 Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth
 Chapter 4 Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth 4.1 The origin and development of life William Smith was a canal engineer who supervised the excavation
Chapter 4 Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth 4.1 The origin and development of life William Smith was a canal engineer who supervised the excavation
Bio 100 Study Guide 14.
 Bio 100 Study Guide 14 http://www.swarthmore.edu/natsci/cpurrin1/evolk12/slm/origindayimages/06soup.jpg The Origin of Life 1. Conditions on early earth 2. Abiogenic synthesis organic molecules 3. Hot rocks
Bio 100 Study Guide 14 http://www.swarthmore.edu/natsci/cpurrin1/evolk12/slm/origindayimages/06soup.jpg The Origin of Life 1. Conditions on early earth 2. Abiogenic synthesis organic molecules 3. Hot rocks
False. SF Evolution Lecture 5. It s all about SCALE. Fossils and the Origins of Diversity 10/12/11. On the timescale of evolution, we are negligible
 SF Evolution Lecture 5 It s all about SCALE Fossils and the Origins of Diversity We can tip the world into meltdown leaving it lifeless and barren if we are not careful. True or False? False Man is puny
SF Evolution Lecture 5 It s all about SCALE Fossils and the Origins of Diversity We can tip the world into meltdown leaving it lifeless and barren if we are not careful. True or False? False Man is puny
The Supercontinent, Rodinia
 The Supercontinent, Rodinia The supercontinent, Rodinia, as it appeared about 1.1 b.y. ago. The reddish band down the center of the globe is the location of continental collisions and orogeny, including
The Supercontinent, Rodinia The supercontinent, Rodinia, as it appeared about 1.1 b.y. ago. The reddish band down the center of the globe is the location of continental collisions and orogeny, including
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
Chapter Introduction. Chapter Wrap-Up. Explosion
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Chapter Wrap-Up Geologic Time Ancient Earth The Cambrian Explosion How have natural events changed Earth over time? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Chapter Wrap-Up Geologic Time Ancient Earth The Cambrian Explosion How have natural events changed Earth over time? What do you think? Before you begin,
Origin and Evolution of Life
 Origin and Evolution of Life OCN 201 Science of the Sea Biology Lecture 2 The Handfish -BBC Blue Planet!1!1 Evolution Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution I am a creationist
Origin and Evolution of Life OCN 201 Science of the Sea Biology Lecture 2 The Handfish -BBC Blue Planet!1!1 Evolution Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution I am a creationist
Geological Time Line Time hierarchy. Geological Time Line 1/27/2019
 Chapter 3 What the rocks say: how geology and paleontology reveal the history of life Geological Time Line Time hierarchy Eons Eras Periods Epochs Stages The Geologic Time Line - see handouts Geological
Chapter 3 What the rocks say: how geology and paleontology reveal the history of life Geological Time Line Time hierarchy Eons Eras Periods Epochs Stages The Geologic Time Line - see handouts Geological
Lab tomorrow.
 Lab tomorrow https://pages.stolaf.edu/angell/readings/ Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C. Broad Patterns of Evolution
Lab tomorrow https://pages.stolaf.edu/angell/readings/ Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C. Broad Patterns of Evolution
