Igneous Rocks. By: Abboud Suliman Ahmed. With Some Graphics from Press et al., Understanding Earth, 4th Ed.
|
|
|
- Christine Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Igneous Rocks With Some Graphics from Press et al., Understanding Earth, 4th Ed. (Copyright 2004 by W. H. Freeman & Company) By: Abboud Suliman Ahmed
2 Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from molten rock (magma) crystallizing below earth's surface or from volcanic activity. They commonly form at plate boundaries and are commonly exposed in mountainous areas. Igneous rocks form from molten rock (magma) crystallizing below earth's surface or from volcanic activity. They commonly form at plate boundaries and are commonly exposed in mountainous areas. Igneous rocks form from crystallization of magma at depth (within the earth's crust) or at the surface (from volcanic eruptions) There are two (2) basic types or forms of igneous rocks: 1. Plutonic rocks = intrusive igneous rocks = igneous rocks that form from cooling magma at depth 2. Extrusive igneous rocks = igneous rocks that form from volcanic activity (at or near surface)
3
4 Key Terminology Plutonic Intrusive Extrusive Volcanic Texture Phaneritic Aphanitic Porphyritic Glassy Vesicular Pyroclastic Magma Lava Bowen s Reaction Series Assimilation Partial melting Fractional crystallization Discordant Concordant Dike Stock Batholith Sill Laccolith Lopolith
5
6
7 Table. 5.2 Felsic Intermediate Mafic Granite Granodiorite Diorite Gabbro Rhyolite Dacite Andesite Basalt Viscosity Melting Temperature
8 Bowen's Reaction Series- Olivine Plagioclase (Ca-feldspar) Pyroxene Amphibole Biotite Orthoclase (K-feldspar) Muscovite Quartz Plagioclase (Na-feldspar)
9 Common Minerals
10 General characteristics of magma Igneous rocks form as molten rock cools and solidifies General characteristics of magma: Parent material of igneous rocks Forms from partial melting of rocks Magma at surface is called lava
11 General characteristics of magma General characteristic of magma Rocks formed from lava = extrusive, or volcanic rocks Rocks formed from magma at depth = intrusive, or plutonic rocks
12 The Rock Cycle- Minerals form rocks All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are divided into 3 categories Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are heated and squeezed Sedimentary- non-crystalline- smaller pieces or chemicals from other rocks
13 Magma molten rock below Earth's surface. L ava Igneous formed from Magma and Lava magma on the Earth's surface. Pyroclastic material ( pyro = fire, clastic = debris) Airborne lava cools as it falls
14 Igneous Rock Chemistry Major elements: Approximately 99% of Igneous Rocks are comprised of only eight elements. Oxygen Silicon Aluminum Iron Calcium Sodium Potassium Magnesium The amount of silica (SiO 2 ) determines the mineral content and general color of igneous rocks.
15 Rare Elements: Trace elements are those which occur in very low concentrations in common rocks (usually < 0.1 % by weight). Their concentrations are therefore commonly expressed in parts per million (ppm; 1 ppm = 10-4 weight%). Unlike major elements, trace elements tend to concentrate in fewer minerals, and are therefore more useful in formulating models for magmatic differentiation, and in some cases, in predicting the source of a particular magma. Trace elements most commonly used for the interpretation of the petrogenesis of igneous rocks include: Ni, Cr, Sc, V, Rb, Ba, Sr, Zr, Y, Nb and the rare earth elements (La to Lu).
16 عندما تتبلور المعادن االساسية من الصهير تسمح بعض المعادن المكونة للعناصر النادرة بدخول بنيتها البلورية حيث وضع العلم Goldschmidt عام 1937 قاعدة توضح سلوك العناصر النادرة تسمى قاعدة )Goldschmidt( و هى كاالتى: 1 -عناصر مستترة :)Camouflage( ويسمى االحالل بالتخفى - ايون اساسى )A( و ايون نادر )B( A ++ = B ++ A R = B R مثال mg++ : R=0.80 A و co++ R=0.83 A
17 )Capture( : حالتين A R = B R A ++ B ++++ K + Ba ++ R=1.33 A R=1.34 A A R > B R A +++ = B االسر
18 3 -القبول )Admission( : حالتين A R = B R A +++ = B + mg++ Li+ مثال : R=0.68 A R=0.66A A R < B R A +++ = B +++
19 Sources of Heat for Melting Heat from below a. : Heat moves upward (by conduction and convection) from the very hot (>5000 C) core through the mantle and crust. Minerals start to crystallize from a cooling magma between 1200 C C.
20 b. : i. 3 o C /100 m (30 o C/km) ii. iii. Geothermal Gradient At great depth temperature alone would melt rock BUT high pressure may cause it to remain solid. Not the same everywhere (i.e., It s higher in volcanic regions).
21 c) Radioactive Decay Heat byproduct during decay. High concentration may cause temperature to increase with depth at a rate greater than the geothermal gradient.
22 d) Friction Rock grinding past rock Active Mountain building regions. Friction of moving and shifting rock masses in regions of mountain building may combine with heat from other sources to melt rock.
23 Melting due to the Addition of Volatiles
24 Viscosity of Magma/ Lava Viscosity- important for volcanic activity the resistance of a liquid to flow high viscosity = thick and stiff low viscosity = thin and "runny".
25 Convergent Margins- flux melting
26 Divergent Boundary
27 Hot Spots (e.g. Hawaii)
28 Silica Tetrahedron Silicon Oxygen Silicates are classified on the basis of Si-O polymerism
29 The Silicate structures are known from X-rays. The complexity of igneous rocks are attributed to complexity of silicate structures. Decompositions of mineral depends on silicate structures
30 [SiO 4 ] 4- Independent tetrahedra Nesosilicates Si : O 1 : 4 Example: Olivine group (Fe,mg) 2 SiO 4
31 Garnet A 3 B 2 Si 3 O 12 Usually B is Aluminum, A divalent (Mg,Fe,Mn,Ca) 3 (Fe 3+,Cr,Al) 2 Si 3 O 12 characteristic colors: Pyrope Mg 3 Al 2 Si 3 O 12 deep red to black Almandine Fe 3 Al 2 Si 3 O 12 deep brownish red Spessartine Mn 3 Al 2 Si 3 O 12 brownish red to black Grossular Ca 3 Al 2 Si 3 O 12 yellow-green to brown Andradite Ca 3 Fe 2 Si 3 O 12 variable-yellow, green, brown, black Uvarovite Ca 3 Cr 2 Si 3 O 12 emerald green
32 Common Nesosilicates: The Aluminosilicates Kyanite, Sillimanite, Andalusite Al 2 SiO 5 = Al 2 (SiO 4 )O Topaz Al 2 SiO 4 (F,OH) 2,
33 Si 2 O 7 ] 6- Double tetrahedra Sorosilicates Si : O 2 : 7 Double silicon tetrahedra linked by one bridging oxygen Sorosilicates commonly also contain independent silica tetrahedra (SiO 4 ) -4 Typically monoclinic symmetry
34 Epidote Group Zoisite/Clinozoisite CaAl 3 O(SiO 4 )(Si 2 O 7 )(OH) Epidote Ca 2 (Fe,Al)Al 2 O(SiO 4 )(Si 2 O 7 )(OH)
35 Cyclosilicates n[sio 3 ] 2- n = 3, 4, 6 Si : O 1 : 3 N=3, [Si 3 O 9 ] 6- N=4, [Si 4 O 12 ] 8- N=6, [Si 6 O 18 ] 12- Beryl, Be 3 Al 2 (Si 6 O 18 )
36 Inosilicates single chains [SiO 3 ] 2- Si : O 1 : 3 Example: Pyroxine group (Fe,mg) SiO 3 Diopside, camg si 2 o 6 Augite, ca (mg, Fe) si 2 o 6
37 Inosilicates Double- chains [Si 4 O 11 ] 6- Si : O 4 : 11 Example: amphibole minerals Actinolite, ca 2 (mg,fe) 5 Si 8 O 22 (OH) 2
38 Phyllosilicates Sheets of tetrahedra [Si 2 O 5 ] 2- Si : O 2 : 5 Mica group: Muscovite, KAl 2 (AlSi 3 )O 10 (OH) 2
39 Tectosilicates [SiO 2 ] Si : O 1 : 2 3-D frameworks of tetrahedral: fully polymerized quartz and the silica minerals feldspars feldspathoids zeolites Examples: Quartz, SiO 2. Orthoclase, KAlSi 3 O 8. Plagioclase, CaAl 2 Si 2 O 8
40
41 Plate Tectonic - Igneous Genesis 1. Mid-ocean Ridges 2. Intracontinental Rifts 3. Island Arcs 4. Active Continental Margins 5. Back-arc Basins 6. Ocean Island Basalts 7. Miscellaneous Intra- Continental Activity kimberlites, carbonatites, anorthosites...
42 Binary phase diagram for a solid solution of Olivine Fayallite (Fa) % Fo (Mg 2 SiO 4 ) Forsterite (Fo)
43 quartz hornblende feldspar
44 Olivine (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Pyroxene (Mg,Fe)SiO 3 Amphibole Ca 2 (Mg,Fe) 5 Si (OH) 2 Biotite Mica K(Mg,Fe) 3 AlSi 3 O 10 (OH) 2 Single tetrahedra No cleavage Single chains Double chains 2 cleavages (90 o ) 2 cleavages (60 o and 120 o ) Sheets 1 cleavage
45 Olivine Found in mafic and ultramafic igneous rocks, can be found as beach sand from volcanic islands, used in manufacturing of basic refractories, or as magnesium ore, gem quality peridot Micas - Found in igneous (pegmatities and granites) and metamorphic rocks (schists and amphibolites), used for elect and heat insulation, paper products, fireproof paint and dry lubricants Hematite Found in extrusive igneous rocks and secondary mineral of sed deposits (oxidizing environment), most important iron ore, red ochre pigments and polishing powders
46
47 Hornblende a member of the amphibole group
48 Potassium feldspar
49 Plagioclase feldspar
50
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS
 PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
10/20/2015. How is magma different from lava? Magma is molten rock below the Earth s surface. Lava is magma that flows out onto Earth s surface.
 Chapter 5 What are igneous rocks? How do they form? Igneous rocks are rocks that form when molten material cools and crystallizes. Molten material can be either magma or lava. How is magma different from
Chapter 5 What are igneous rocks? How do they form? Igneous rocks are rocks that form when molten material cools and crystallizes. Molten material can be either magma or lava. How is magma different from
9/4/2015. Feldspars White, pink, variable Clays White perfect Quartz Colourless, white, red, None
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Block: Igneous Rocks. From this list, select the terms which answer the following questions.
 Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
REMINDER. MOVIE: Rocks that Originate Underground 5:41 to 12:40
 REMINDER 2 chapters covered next week Sedimentary Rocks Soils and Weathering (first half) Learn vocabulary for both! Turn to Neighbor: Without using your book or notes, try to remember which te mineral
REMINDER 2 chapters covered next week Sedimentary Rocks Soils and Weathering (first half) Learn vocabulary for both! Turn to Neighbor: Without using your book or notes, try to remember which te mineral
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
IGNEOUS ROCKS. SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks?
 Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Silicates. The most common group of minerals forming the silicate Earth
 Silicates The most common group of minerals forming the silicate Earth 25% of all minerals (~1000) 40% of rock forming minerals 90% of earth s crust i.e those minerals you are likely to find ~100 of earth
Silicates The most common group of minerals forming the silicate Earth 25% of all minerals (~1000) 40% of rock forming minerals 90% of earth s crust i.e those minerals you are likely to find ~100 of earth
Student Name: College: Grade:
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
The 3 types of rocks:
 Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures
 Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures Pauling s Rules A coordination polyhedron of anions forms around a cation Ionic distance determined by radii Coordination number determined by radius ratio. May
Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures Pauling s Rules A coordination polyhedron of anions forms around a cation Ionic distance determined by radii Coordination number determined by radius ratio. May
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity
 Summary IGNEOUS ROCKS AND METAMORPHIC ROCKS DERIVED FROM IGNEOUS parents make up about 95 percent of Earth s crust. Furthermore, the mantle, which accounts for more than 82 percent of Earth s volume, is
Summary IGNEOUS ROCKS AND METAMORPHIC ROCKS DERIVED FROM IGNEOUS parents make up about 95 percent of Earth s crust. Furthermore, the mantle, which accounts for more than 82 percent of Earth s volume, is
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle
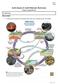 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite B) fluorite C) galena D) talc
 1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite B) fluorite C) galena D) talc 2. Which material is made mostly of the mineral quartz? A) sulfuric acid B) pencil lead C) plaster of paris D)
1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite B) fluorite C) galena D) talc 2. Which material is made mostly of the mineral quartz? A) sulfuric acid B) pencil lead C) plaster of paris D)
Silicate Structures. Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and. Elemental Abundance in Crust. Elemental Abundance in Crust: Pauling s s Rules
 Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and Silicate Structures February 6, 2007 Elemental Abundance in Crust Fe Ion O 2- Si 4+ Al 3+, 3+ Ca Na + K + Mg mol % 2.6 1.4 mol% x charge 4.8 3.8 2.6 1.4 3.8 Sum
Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and Silicate Structures February 6, 2007 Elemental Abundance in Crust Fe Ion O 2- Si 4+ Al 3+, 3+ Ca Na + K + Mg mol % 2.6 1.4 mol% x charge 4.8 3.8 2.6 1.4 3.8 Sum
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks - 1. Environment of Formation - Magma - Plutonic - rock that formed within the Earth. Intrusive - Earth s crust.
 Name: Date: Period: Minerals and Rocks The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES - Methods to classify igneous rocks: 1. Environment of Formation - Magma - Plutonic - rock that formed within the
Name: Date: Period: Minerals and Rocks The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES - Methods to classify igneous rocks: 1. Environment of Formation - Magma - Plutonic - rock that formed within the
Evolution of the Earth
 Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Topics that will be discussed
 Topics that will be discussed The Rock Cycle Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle -Rocks The parent material for all rocks is MAGMA. What is MAGMA? -Rock forming Minerals Are:
Topics that will be discussed The Rock Cycle Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle -Rocks The parent material for all rocks is MAGMA. What is MAGMA? -Rock forming Minerals Are:
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES
 muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES SHEET SILICATES = PHYLLOSILICATES Phyllon = leaf Large group of mineral including many common minerals: muscovite, biotite, serpentine, chlorite, talc, clay minerals Structure:
muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES SHEET SILICATES = PHYLLOSILICATES Phyllon = leaf Large group of mineral including many common minerals: muscovite, biotite, serpentine, chlorite, talc, clay minerals Structure:
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
About Earth Materials
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way.
 Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Earth Science 11: Minerals
 lname: Date: Earth Science 11: Minerals Purpose: Text Pages: I can identify and classify minerals using their physical and chemical properties 90-111 *This is recommended reading! Matter and Atoms (5.1)
lname: Date: Earth Science 11: Minerals Purpose: Text Pages: I can identify and classify minerals using their physical and chemical properties 90-111 *This is recommended reading! Matter and Atoms (5.1)
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Unit 2: Minerals and Rocks Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5, and splits with cubic cleavage? 6. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the photograph of a sample of gneiss below.
Name: Date: 1. Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5, and splits with cubic cleavage? 6. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the photograph of a sample of gneiss below.
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways.
 A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
Igneous Rocks. Sedimentary Rocks. Metamorphic Rocks
 Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Structure of the Earth
 And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
Shortcuts to mineral formulae
 Silicates JD Price Silicate Structure Silicate Structure (SiO2) Shortcuts to mineral formulae W cations with 8- (Ca 2+, Fe 2+, Mn 2+, Na + ) to 12-fold coordination (K +, Ba 2+ ) X divalent cations in
Silicates JD Price Silicate Structure Silicate Structure (SiO2) Shortcuts to mineral formulae W cations with 8- (Ca 2+, Fe 2+, Mn 2+, Na + ) to 12-fold coordination (K +, Ba 2+ ) X divalent cations in
Thursday, October 4 th
 Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
What is going on here?
 Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
RR#7 - Multiple Choice
 1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? 1) hematite 2) fluorite 3) galena 4) talc 2. Which rock is composed of the mineral halite that formed when seawater evaporated? 1) limestone 2) dolostone
1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? 1) hematite 2) fluorite 3) galena 4) talc 2. Which rock is composed of the mineral halite that formed when seawater evaporated? 1) limestone 2) dolostone
PHY120AExam questions 0.5 points each; 19 True/False, 31 Multiple Choice
 1 PHY120AExam 1 2018 50 questions 0.5 points each; 19 True/False, 31 Multiple Choice True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. F 1. The distribution of volcanoes is random.. F 2. The
1 PHY120AExam 1 2018 50 questions 0.5 points each; 19 True/False, 31 Multiple Choice True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. F 1. The distribution of volcanoes is random.. F 2. The
INTRODUCTION ROCK COLOR
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
Name. GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks
 Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Unit 2 Exam: Rocks & Minerals
 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the 2001 edition of the Earth Science Reference Tables, the map and cross section below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The shaded
Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the 2001 edition of the Earth Science Reference Tables, the map and cross section below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The shaded
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE GEOLOGY Rocks Processes and Products F792 * OCE / 1 3804* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required:
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE GEOLOGY Rocks Processes and Products F792 * OCE / 1 3804* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required:
Metamorphism (means changed form
 Metamorphism (means changed form) is recrystallization without melting of a previously existing rock at depth in response to a change in the environment of temperature, pressure, and fluids. Common minerals
Metamorphism (means changed form) is recrystallization without melting of a previously existing rock at depth in response to a change in the environment of temperature, pressure, and fluids. Common minerals
Rocks. 1) igneous = fiery 2) sedimentary = settled 3) metamorphic = changed form
 Rocks Identified on the basis of composition and texture (arrangement of features). Classification depends on description and interpretation of these features. Three major categories: 1) igneous = fiery
Rocks Identified on the basis of composition and texture (arrangement of features). Classification depends on description and interpretation of these features. Three major categories: 1) igneous = fiery
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification. Thomas Doe
 CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
Classification of Igneous Rocks
 Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures: Glassy- no crystals formed Aphanitic- crystals too small to see by eye Phaneritic- can see the constituent minerals Fine grained- < 1 mm diameter Medium grained-
Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures: Glassy- no crystals formed Aphanitic- crystals too small to see by eye Phaneritic- can see the constituent minerals Fine grained- < 1 mm diameter Medium grained-
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES
 amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
7.1 Magma and Magma Formation
 Physical Geology, 2nd Adapted Edition by Karla Panchuk is used under a CC-BY-ND 4.0 International license. Chapter 7. Igneous Rocks Introduction Learning Objectives After carefully reading this chapter,
Physical Geology, 2nd Adapted Edition by Karla Panchuk is used under a CC-BY-ND 4.0 International license. Chapter 7. Igneous Rocks Introduction Learning Objectives After carefully reading this chapter,
6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
Lab 2: The rock cycle, minerals and igneous rocks. Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin:
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 2: The rock cycle, minerals and igneous rocks Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin: Igneous rocks (from the Latin word, ignis = fire) are
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 2: The rock cycle, minerals and igneous rocks Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin: Igneous rocks (from the Latin word, ignis = fire) are
Florida Atlantic University PETROLOGY -- MIDTERM ONE KEY
 GLY4310 Name 60 points February 7, 2011 14 took exam - Numbers to the left of the question number in red are the number of incorrect responses. Instructor comments are in blue. Florida Atlantic University
GLY4310 Name 60 points February 7, 2011 14 took exam - Numbers to the left of the question number in red are the number of incorrect responses. Instructor comments are in blue. Florida Atlantic University
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
Igneous Processes I: Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures
 Igneous Processes I: Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures Crustal Abundances of Rock Types Igneous Rocks Form by the cooling and hardening (crystallization/glassification) of magma. There
Igneous Processes I: Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures Crustal Abundances of Rock Types Igneous Rocks Form by the cooling and hardening (crystallization/glassification) of magma. There
LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS
 GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 2: Minerals in Gabbroic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common silicate minerals in gabbroic
GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 2: Minerals in Gabbroic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common silicate minerals in gabbroic
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT
 EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT Sources: University of Washington, Texas A&M University, University of Southern Alabama What is an igneous rock (a
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT Sources: University of Washington, Texas A&M University, University of Southern Alabama What is an igneous rock (a
LAB 5: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS
 EESC 2100: Mineralogy LAB 5: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 1: Minerals in Granitic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common minerals in granitoids Students will
EESC 2100: Mineralogy LAB 5: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 1: Minerals in Granitic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common minerals in granitoids Students will
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann
 Earth Materials Systematic subdivision of magmatic rocks Subdivision of magmatic rocks according to their mineral components: Content of quartz SiO 2 ( free quartz presence) Quartz with conchoidal breakage
Earth Materials Systematic subdivision of magmatic rocks Subdivision of magmatic rocks according to their mineral components: Content of quartz SiO 2 ( free quartz presence) Quartz with conchoidal breakage
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
Directed Reading. Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle. made of a. inorganic matter. b. solid organic matter. c. liquid organic matter. d. chemicals.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Rock Cart for High School Students
 Rock Cart for High School Students Goals and Objectives for high school students (9 th 12 th grade): 1) Define igneous rocks 2) Discuss chemical composition of rocks 3) Understand the plate tectonics and
Rock Cart for High School Students Goals and Objectives for high school students (9 th 12 th grade): 1) Define igneous rocks 2) Discuss chemical composition of rocks 3) Understand the plate tectonics and
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Lab 3: Minerals, the rock cycle and igneous rocks. Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin:
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 3: Minerals, the rock cycle and igneous rocks Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin: Igneous rocks (from the Latin word, ignis = fire) are
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 3: Minerals, the rock cycle and igneous rocks Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin: Igneous rocks (from the Latin word, ignis = fire) are
Happy Tuesday. Pull out a ½ sheet of paper
 Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Engineering Geology. Igneous rocks. Hussien Al - deeky
 Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers
 1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
Quiz 1. 3) Which of the following planetary bodies has the least number of impact craters on its surface? A) Mercury B) Mars C) the Moon D) Earth
 Quiz 1 1) Earth's atmosphere is unique among the moons and planets in that A) it has a nitrogen (N2) rich atmosphere. B) it is rich in oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2). C) it is rich in carbon dioxide because
Quiz 1 1) Earth's atmosphere is unique among the moons and planets in that A) it has a nitrogen (N2) rich atmosphere. B) it is rich in oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2). C) it is rich in carbon dioxide because
