Quiz Nine (9:30-9:35 AM)
|
|
|
- Jayson Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quiz Nine (9:30-9:35 AM)
2 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALAAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 25: Paleozoic 2: More Laurentia! Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick
3 Last Time The Paleozoic of North America 1) Laurentian passive continental margin sedimentation 2) Central North America 3) The Grand Canyon (geology) (web notes 24)
4 Consider: Equator: 1) passive continental margin 2) shallow marine water (shelf) 3) tropical climate All the way from Labrador to Alabama 1+2+3= Fossil. Limestone, oolite, quartz arenite etc.
5 The Humber zone is a region of undeformed, passive continental margin rocks
6 Classic Paleozoic reef rocks (stromatolites, rugose and tabulate corals), quartz arenite sandstone, shallow marine dolostone, even some evaporites
7 A sudden (localized) deepening occurred (transgression) and above that.
8 Thrust faulting A Thrust Faulting A
9 Cratonic Sequences Ignoring tectonics for a moment and you ll see that sea water covers much of the craton in these 2 paleogeographic images, but not always to the same extent Middle Ordovician Early Devonian
10 Cratonic Sequences When continents flood during transgressions, sediment is deposited. When regressions occur, erosion takes place producing unconformities (disconformities) Thick sedimentary packages between disconformities are called cratonic (depositional) sequences.
11 Cratonic Sequences When continents flood during transgressions, sediment is deposited. When regressions occur, erosion takes place producing unconformities (disconformities) Thick sedimentary packages between disconformities are called cratonic (depositional sequences). asins have thick sequences (shorter disconformities) Arches/domes have thin sequences (longer disconformities)
12 Cratonic Sequences
13 Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 1) ack to Newfoundland 2) Eastern Laurentian Orogenies (Appalachians) 3) Other Laurentian Orogenies (Antler, Ouachita) (web notes 25)
14 The Humber zone is a region of undeformed, passive continental margin rocks
15 Thrust faulting
16 A Even though this coastline of Laurentia was a passive continental margin, a plate tectonic boundary was rapidly approaching A
17 Laurentia A Island arc altica A The resulting Taconic Orogeny first depressed the seafloor (localized transgression) and then pushed previously deposited passive continental margin sediments up into thrust fault mountains. There was only minimal metamorphism and igneous intrusions. Middle Ordovician
18 Laurentia altica Middle Ordovician
19 Laurentia altica Middle Ordovician
20 Laurentia A The next tectonic event (the Acadian Orogeny) was caused by the approach of altica altica A altica altica Late Ordovician
21 A The Acadian Orogeny was more extensive and more intense (metamorphism and lots of igneous intrusions) A Early Devonian
22 The Acadian Orogeny was more extensive and more intense (metamorphism and lots of igneous intrusions) Early Devonian
23 Lastly, along comes Gondwanna and. A well you get the idea. A Mississippian
24 Lastly, along comes Gondwanna and. A well you get the idea. A Pennsylvannian Suture zone
25 Lastly, along comes Gondwanna and. well you get the idea. Pennsylvanian
26 Other Laurentian Orogenies Period Permian Pensylvannian Mississippian Devonian Silurian North America Alleghenian Orogeny* (SE) Ouachita Orogeny (S) Acadian Orogeny* (E) Antler Orogeny (W) Ordovician Cambrian Taconic Orogeny* (NE)
27 Other Laurentian Orogenies Period Permian Pensylvannian Mississippian Devonian Silurian North America Alleghenian Orogeny* (SE) Ouachita Orogeny (S) Acadian Orogeny* (E) Antler Orogeny (W) Ordovician Cambrian Taconic Orogeny* (NE) Antler Orogeny
28 Other Laurentian Orogenies Period Permian Pensylvannian Mississippian Devonian Silurian North America Alleghenian Orogeny* (SE) Ouachita Orogeny (S) Acadian Orogeny* (E) Antler Orogeny (W) Ordovician Cambrian Taconic Orogeny* (NE)
29 Other Laurentian Orogenies Period Permian Pensylvannian Mississippian Devonian Silurian North America Alleghenian Orogeny* (SE) Ouachita Orogeny (S) Acadian Orogeny* (E) Antler Orogeny (W) Ordovician Cambrian Taconic Orogeny* (NE)
30 Other Laurentian Orogenies Period Permian Pensylvannian Mississippian Devonian Silurian North America Alleghenian Orogeny* (SE) Ouachita Orogeny (S) Acadian Orogeny* (E) Antler Orogeny (W) Ordovician Cambrian Taconic Orogeny* (NE) Ouachita Orogeny
31 Today s Homework 1. Catch up on your sleep! Next Time 1. Paleozoic Geology of Alabama
Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1:
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1: Laurentia Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time (before the exam) The Cambrian Explosion A) Why a Cambrian explosion B)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1: Laurentia Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time (before the exam) The Cambrian Explosion A) Why a Cambrian explosion B)
GY 112: Earth History
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 31: Mesozoic Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Overview A) The end of the Paleozoic B) Mesozoic time frame and evolutionary
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 31: Mesozoic Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Overview A) The end of the Paleozoic B) Mesozoic time frame and evolutionary
Chapter 10. Early Paleozoic Events
 Chapter 10 Early Paleozoic Events The Phanerozoic Eon Consists of three eras (from oldest to youngest): Paleozoic = "ancient life" (542-251 m.y. ago) Mesozoic = "middle life" (251-65.5 m.y. ago) Cenozoic
Chapter 10 Early Paleozoic Events The Phanerozoic Eon Consists of three eras (from oldest to youngest): Paleozoic = "ancient life" (542-251 m.y. ago) Mesozoic = "middle life" (251-65.5 m.y. ago) Cenozoic
GY 112 Lecture Notes Laurentia in the Paleozoic (non-tectonics)
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Laurentia in the Paleozoic (non-tectonics) Lecture Goals: A) Eastern Laurentia (pre-orogenic deposition) B) Central North America (Depositional
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Laurentia in the Paleozoic (non-tectonics) Lecture Goals: A) Eastern Laurentia (pre-orogenic deposition) B) Central North America (Depositional
Quiz 12 Bonus 2 (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz 12 Bonus 2 (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 32 and 33: Mesozoic Sedimentation Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Tectonics A) The Triassic
Quiz 12 Bonus 2 (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 32 and 33: Mesozoic Sedimentation Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Tectonics A) The Triassic
GY 111 Lecture Notes Thrust Faults and the Appalachian Mountains
 GY 111 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2007-08) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Thrust Faults B) The Appalachian Mountains GY 111 Lecture Notes Thrust Faults and the Appalachian Mountains Reference: Press et al., 2004,
GY 111 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2007-08) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Thrust Faults B) The Appalachian Mountains GY 111 Lecture Notes Thrust Faults and the Appalachian Mountains Reference: Press et al., 2004,
251 Million years. 299 Million years. 318 Million years. 359 Million years
 The Late Paleozoic 251 Million years 299 Million years 318 Million years 359 Million years Major Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did
The Late Paleozoic 251 Million years 299 Million years 318 Million years 359 Million years Major Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM ONLY WRITE ON THE ANSWER SHEET!
 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM ONLY WRITE ON THE ANSWER SHEET! Multiple Choice Questions (30 points) for each question, please choose the best answer and circle your answer on the answer sheet (do not write
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM ONLY WRITE ON THE ANSWER SHEET! Multiple Choice Questions (30 points) for each question, please choose the best answer and circle your answer on the answer sheet (do not write
3/5/05 Dr. Stewart 1
 I. Physiography of Appalachian Mountains A. Introduction 1. These mountains extend from NE Canada to Georgia 2. They are the remains of a deeply eroded, ancient mountain chain once larger than the Himalayans
I. Physiography of Appalachian Mountains A. Introduction 1. These mountains extend from NE Canada to Georgia 2. They are the remains of a deeply eroded, ancient mountain chain once larger than the Himalayans
Ordovician. System. Cambrian. System
 443 495 543 Late Middle Early Late Middle Early Ordovician System Cambrian System Earth History, Ch. 13 1 Ch. 13 Review: Early Paleozoic life & Burgess Shale fauna Most animal phyla originated in Cambrian;
443 495 543 Late Middle Early Late Middle Early Ordovician System Cambrian System Earth History, Ch. 13 1 Ch. 13 Review: Early Paleozoic life & Burgess Shale fauna Most animal phyla originated in Cambrian;
Why is it called the "Inland Basins" Region?
 Learning Series: Rocks of the Southeastern U. S. The BIG Picture Why is it called the "Inland Basins" Region? Inland from the mountains, the Earth s crust was buckled (downwarped) into a series of depressions
Learning Series: Rocks of the Southeastern U. S. The BIG Picture Why is it called the "Inland Basins" Region? Inland from the mountains, the Earth s crust was buckled (downwarped) into a series of depressions
GY 112L Earth History
 GY 112L Earth History Lab 2 Vertical Successions and Sequences of Events GY 112L Instructors: Douglas Haywick, James Connors, Mary Anne Connors Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama
GY 112L Earth History Lab 2 Vertical Successions and Sequences of Events GY 112L Instructors: Douglas Haywick, James Connors, Mary Anne Connors Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama
The Building of a Continent. Delving into Deep Time
 The Building of a Continent Delving into Deep Time Methods for Studying the Past Identifying orogenies Mountain building events Mountains erode Can t study topography Study the evidence they leave behind
The Building of a Continent Delving into Deep Time Methods for Studying the Past Identifying orogenies Mountain building events Mountains erode Can t study topography Study the evidence they leave behind
Earth Science. Name Block. Unit 3 Review Worksheet. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 21: Rock Deformation Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) How long is long? B) Geological time divisions Web notes 20 Geological
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 21: Rock Deformation Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) How long is long? B) Geological time divisions Web notes 20 Geological
Cambrian Sedimentary Deposits - The Sauk Sequence
 Cambrian Sedimentary Deposits - The Sauk Sequence During Cambrian, there were no vascular plants on the land, so the landscape was barren. Erosion was active and severe without plant roots to hold the
Cambrian Sedimentary Deposits - The Sauk Sequence During Cambrian, there were no vascular plants on the land, so the landscape was barren. Erosion was active and severe without plant roots to hold the
Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built?
 Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built? The Grand Tetons, Wyoming First a Brief Review of Sea Floor Spreading Prop: Test 3 Invitations Break-Up of a Continent and Origin of an Ocean
Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built? The Grand Tetons, Wyoming First a Brief Review of Sea Floor Spreading Prop: Test 3 Invitations Break-Up of a Continent and Origin of an Ocean
The Building of the NYC Region
 The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
Geologic History A B1
 Geologic History A B1 1. A whalebone that originally contained 200 grams of radioactive carbon-14 now contains 25 grams of carbon- 14. How many carbon-14 half-lives have passed since this whale was alive?
Geologic History A B1 1. A whalebone that originally contained 200 grams of radioactive carbon-14 now contains 25 grams of carbon- 14. How many carbon-14 half-lives have passed since this whale was alive?
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
GY 112L: Earth History
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Lecture 1: Rock Review Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Introductory Agenda 1. Contact info for D. Haywick 2. GY 112L Course Outline (syllabus)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Lecture 1: Rock Review Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Introductory Agenda 1. Contact info for D. Haywick 2. GY 112L Course Outline (syllabus)
Plate tectonics model for the continental collisions during Late Paleozoic
 Alleghanian orogeny During Late Paleozoic, northwestern Africa collided with southeastern North America, causing the Alleghanian orogeny, and building the Appalachian mountains. The orogeny began during
Alleghanian orogeny During Late Paleozoic, northwestern Africa collided with southeastern North America, causing the Alleghanian orogeny, and building the Appalachian mountains. The orogeny began during
Geoscience 001 Fall Rock Identification and Contextual Interpretation
 Geoscience 00 Fall 2005 Rock Identification and Contextual Interpretation The purpose of this week s lab is to gain some more experience and practice in identifying rocks and then interpreting the geologic
Geoscience 00 Fall 2005 Rock Identification and Contextual Interpretation The purpose of this week s lab is to gain some more experience and practice in identifying rocks and then interpreting the geologic
GY 112 Lecture Notes Significance of Fossils: Paleogeography Interpretations
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Significance of Fossils: Paleogeography Interpretations Lecture Goals: A) What is paleogeography? B) How it works (Late Cambrian fantasy example)
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Significance of Fossils: Paleogeography Interpretations Lecture Goals: A) What is paleogeography? B) How it works (Late Cambrian fantasy example)
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION. 444 million years ago
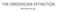 THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
Unit 5: Earth s History Practice Problems
 Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Chapter 15. The Late Paleozoic World
 Chapter 15 The Late Paleozoic World Guiding Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did terrestrial floras change on a global scale in late Paleozoic
Chapter 15 The Late Paleozoic World Guiding Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did terrestrial floras change on a global scale in late Paleozoic
GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 22: Reefs Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Shelves Definition and a bit of history Factors controlling shelf sedimentation
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 22: Reefs Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Shelves Definition and a bit of history Factors controlling shelf sedimentation
Continental drift
 Plate Tectonics Continental drift Continental drift Continental drift Continental drift Continental drift Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Continental Drift and Paleomagnetism Paleomagnetism Renewed interest
Plate Tectonics Continental drift Continental drift Continental drift Continental drift Continental drift Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Continental Drift and Paleomagnetism Paleomagnetism Renewed interest
Quiz Four (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Four (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Fossils Part 1: Telling Time Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) Stable isotopes of use to geology (fractionation)
Quiz Four (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Fossils Part 1: Telling Time Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) Stable isotopes of use to geology (fractionation)
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 3: The Rock Cycle Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. Alfred Wegener and Drifting Continents 2. The Plate Tectonic Revolution 3.
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 3: The Rock Cycle Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. Alfred Wegener and Drifting Continents 2. The Plate Tectonic Revolution 3.
Quiz Three (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Three (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 7 & 8: Dating Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. William Smith and Water 2. Stratigraphic Principles 3.
Quiz Three (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 7 & 8: Dating Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. William Smith and Water 2. Stratigraphic Principles 3.
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life
 Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 9: Walther s Law Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda 1. Walther s Law 2. Sequence stratigraphy 3. Markov Chain Analysis Named
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 9: Walther s Law Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda 1. Walther s Law 2. Sequence stratigraphy 3. Markov Chain Analysis Named
Name: Date: Period: Page 1
 Name: Date: Period: Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the three bedrock outcrops below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, are located within 15 kilometers
Name: Date: Period: Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the three bedrock outcrops below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, are located within 15 kilometers
Geology of the Batemans Bay region. Geological evolution. The Lachlan Orogen
 Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 1 The word orogen is derived from the ancient Greek language word for mountain building. The Lachlan Orogen The rocks exposed in the Batemans Bay are part of the geological
Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 1 The word orogen is derived from the ancient Greek language word for mountain building. The Lachlan Orogen The rocks exposed in the Batemans Bay are part of the geological
There are numerous seams on the surface of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift There are numerous seams on the surface of the Earth Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift There are numerous seams on the surface of the Earth Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP
 L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
GY 112L: Earth History Lab
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 11 Paleozoic Part 2 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 (Lab 8 exercises) 1) Sponges & Stromatoporoids 2)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 11 Paleozoic Part 2 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 (Lab 8 exercises) 1) Sponges & Stromatoporoids 2)
Mesozoic Earth History
 Mesozoic Earth History The Mesozoic Era 251-66 MYA Breakup of Pangea Changes in air and oceanic currents Evolution of new terrestrial and marine life Opening of the Atlantic Ocean Basin Rocky Mountains
Mesozoic Earth History The Mesozoic Era 251-66 MYA Breakup of Pangea Changes in air and oceanic currents Evolution of new terrestrial and marine life Opening of the Atlantic Ocean Basin Rocky Mountains
GY 112: Earth History
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 4: Clever Thinking: Geological Principles Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. Formation of the solar system 2. Formation and differentiation
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 4: Clever Thinking: Geological Principles Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. Formation of the solar system 2. Formation and differentiation
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS. LANDFORMS of NYS. Landforms. Creation of NYS Landforms 9/22/2011
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS LANDFORMS of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2011 Landforms The basis of present-day landforms (surface features) is the bedrock geology that has been worked on by the forces
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS LANDFORMS of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2011 Landforms The basis of present-day landforms (surface features) is the bedrock geology that has been worked on by the forces
TIME. Does not give the. Places events in sequencee 1 st, 2 nd, 3 rd. Gives a. exact date of an event. event. Radioactive Dating.
 Geologic History TIME Places events in sequencee 1 st, 2 nd, 3 rd Does not give the exact date of an event Gives a date or time of an event Uses the Law of Superposition Radioactive Dating Youngest Law
Geologic History TIME Places events in sequencee 1 st, 2 nd, 3 rd Does not give the exact date of an event Gives a date or time of an event Uses the Law of Superposition Radioactive Dating Youngest Law
GY 112 Lecture Notes Rock Review
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Rock Review Lecture Goals: A) Recap of rock types B) Recap of the rock cycle C) Sedimentary rocks: their role in earth history Textbook reference:
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Rock Review Lecture Goals: A) Recap of rock types B) Recap of the rock cycle C) Sedimentary rocks: their role in earth history Textbook reference:
Unconformities are depositional contacts that overlie rocks distinctly older than they are. They are often called gaps in the sedimentary record.
 UNCONFORMITIES Unconformities are depositional contacts that overlie rocks distinctly older than they are. They are often called gaps in the sedimentary record. The contact represents time when no sediment
UNCONFORMITIES Unconformities are depositional contacts that overlie rocks distinctly older than they are. They are often called gaps in the sedimentary record. The contact represents time when no sediment
The Paleozoic Era. Otter Creek Wilderness, Monongahela National Forest, WV
 23 What You ll Learn How the Appalachian and Ouachita Mountains formed. When and on what scale three mass extinctions occurred. Why coal is common in Pennsylvanian-aged rocks. How the development of seeds
23 What You ll Learn How the Appalachian and Ouachita Mountains formed. When and on what scale three mass extinctions occurred. Why coal is common in Pennsylvanian-aged rocks. How the development of seeds
GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced 451/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit P.M. THURSDAY, 10 January 2008 (1 hour) Examiner Question
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced 451/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit P.M. THURSDAY, 10 January 2008 (1 hour) Examiner Question
C) Trenton limestone
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the core section below, and your knowledge of Earth Science. The core section shows the subsurface bedrock geology for
1. Base your answer to the following question on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the core section below, and your knowledge of Earth Science. The core section shows the subsurface bedrock geology for
A TRIP THROUGH VIRGINIA GEOLOGY FROM AN ENGINEER S PERSPECTIVE
 A TRIP THROUGH VIRGINIA GEOLOGY FROM AN ENGINEER S PERSPECTIVE Bob Moss, PE Principal Engineer ECS Mid Atlantic, LLC The Engineer Parent WHY IS AN UNDERSTANDING OF LOCAL GEOLOGY IMPORTANT? It provides
A TRIP THROUGH VIRGINIA GEOLOGY FROM AN ENGINEER S PERSPECTIVE Bob Moss, PE Principal Engineer ECS Mid Atlantic, LLC The Engineer Parent WHY IS AN UNDERSTANDING OF LOCAL GEOLOGY IMPORTANT? It provides
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
LANDFORMS of NYS. Landforms. Exercise 4 9/13/2012. TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS. Physiographic map of NYS and vicinity showing Surface Features
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS LANDFORMS of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Landforms REMINDER: The basis of present-day landforms (surface features) is the bedrock geology that has been worked on by
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS LANDFORMS of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Landforms REMINDER: The basis of present-day landforms (surface features) is the bedrock geology that has been worked on by
PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS. Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES. Faulting. Folding 9/6/2012. TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS GRADATIONAL TECTONIC
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
Shield was above sea-level during the Cambrian and provided the sediment for the basins.
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
Earth History Exam. The remains of an early dinosaur could be found at reference point A. A B. B C. C D. D. page 1
 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables and your knowledge of Earth science. The accompanying cross section shows undisturbed sedimentary bedrock.
Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables and your knowledge of Earth science. The accompanying cross section shows undisturbed sedimentary bedrock.
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically
 Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
GY 112: Earth History. Fossils Part:
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Fossils Part: Telling Time Predicting Paleoenvironments Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. Chronostratigraphy versus biostratigraphy 2. Paleontological
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Fossils Part: Telling Time Predicting Paleoenvironments Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1. Chronostratigraphy versus biostratigraphy 2. Paleontological
Quiz Two (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Two (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 5: Clever Thinking 2: Plate Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last time... 1. The first geologists and their
Quiz Two (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 5: Clever Thinking 2: Plate Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last time... 1. The first geologists and their
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 1
 SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 1 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 1 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Matching. Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. 1. hydrothermal vents A. convergent
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Matching. Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. 1. hydrothermal vents A. convergent
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma)
 The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
Mesozoic Earth History Million years ago Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous
 Mesozoic Earth History 245-65 Million years ago Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous Geologic Time Scale www.geo.ucalgary.ca/~macrae/timescale/time_scale.gif Main Happenings in Mesozoic Breakup of Pangaea Lots
Mesozoic Earth History 245-65 Million years ago Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous Geologic Time Scale www.geo.ucalgary.ca/~macrae/timescale/time_scale.gif Main Happenings in Mesozoic Breakup of Pangaea Lots
The Proterozoic Part 1
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History The Proterozoic Part 1 Lectures 18/19: Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The Early Atmosphere 2) The Oceans and Hydrosphere 3)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History The Proterozoic Part 1 Lectures 18/19: Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The Early Atmosphere 2) The Oceans and Hydrosphere 3)
Plio-Pleistocene Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Plio-Pleistocene Geology Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) Cenozoic Tectonics Western North American tectonic provinces Plateaus and canyons
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Plio-Pleistocene Geology Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) Cenozoic Tectonics Western North American tectonic provinces Plateaus and canyons
Fossils: evidence of past life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Today we will discuss places mobility Natural disasters lead to California s beauty Aesthenosphere
 Agenda 2. Geologic History Today we will discuss What Physical Geography is Brief geologic history of California Geography 106 California Geography M. Pesses Antelope Valley College Physical Geographers
Agenda 2. Geologic History Today we will discuss What Physical Geography is Brief geologic history of California Geography 106 California Geography M. Pesses Antelope Valley College Physical Geographers
GY 112 Lecture Notes Mesozoic Sedimentation (North America and Alabama)
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Mesozoic Sedimentation (North America and Alabama) Note: Depending upon the semester (and how verbose Doug gets), these notes may comprise
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Mesozoic Sedimentation (North America and Alabama) Note: Depending upon the semester (and how verbose Doug gets), these notes may comprise
GEL 113 Historical Geology
 GEL 113 Historical Geology COURSE DESCRIPTION: Prerequisites: GEL 111 Corequisites: None This course covers the geological history of the earth and its life forms. Emphasis is placed on the study of rock
GEL 113 Historical Geology COURSE DESCRIPTION: Prerequisites: GEL 111 Corequisites: None This course covers the geological history of the earth and its life forms. Emphasis is placed on the study of rock
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
Name Geo 4 Practice Match the principle on the left (column A) with the definition (or part of the definition) on the right (column B).
 Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B.
 Name Roy G Biv 1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B. Which numbered position best represents the time when humans first appeared in the
Name Roy G Biv 1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B. Which numbered position best represents the time when humans first appeared in the
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Non-ideal Subduction
 Subduction zone cross sections Earthquake locations : black = teleseismic est. gray = local-array est. red line = top of slab seismicity blue line = center of slab seismicity Non-ideal Subduction Oblique
Subduction zone cross sections Earthquake locations : black = teleseismic est. gray = local-array est. red line = top of slab seismicity blue line = center of slab seismicity Non-ideal Subduction Oblique
Review participation point: The evidence for a fluid outer core is:
 DDA1 Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics PS 100 Chapter 28 Review participation point: The evidence for a fluid outer core is: A. Average density of the earth is greater than the density of the crust.
DDA1 Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics PS 100 Chapter 28 Review participation point: The evidence for a fluid outer core is: A. Average density of the earth is greater than the density of the crust.
GY 112 Lab Assignment 2 Vertical Succession and Sequence of Events Cartoons
 Name: Grade /100+5 bonus GY 112 Lab Assignment 2 Vertical Succession and Sequence of Events Cartoons Note: In many of the sequence of events exercises you will be asked to determine the exact order in
Name: Grade /100+5 bonus GY 112 Lab Assignment 2 Vertical Succession and Sequence of Events Cartoons Note: In many of the sequence of events exercises you will be asked to determine the exact order in
Remains or traces of prehistoric life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
43 Misconceptions About Spiders: Teaching a Difficult Concept to Preschool and Elementary Children
 1 Michigan s Ride on the North 5 38 American Plate 19 25 32 Quantitative and Qualitative Differences in Science Writing With a Writing Template Intervention The New Reality of Higher Education: Technology
1 Michigan s Ride on the North 5 38 American Plate 19 25 32 Quantitative and Qualitative Differences in Science Writing With a Writing Template Intervention The New Reality of Higher Education: Technology
Lab 4: Structures and Geologic Maps
 Key Questions: GEOL 1311 Earth Science Lab 4 Structures and Geologic Maps What shapes do rock bodies take in the Earth? How do two-dimensional visualizations of the Earth, such as maps and cross-sections
Key Questions: GEOL 1311 Earth Science Lab 4 Structures and Geologic Maps What shapes do rock bodies take in the Earth? How do two-dimensional visualizations of the Earth, such as maps and cross-sections
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 14: Sedimentary Rocks Part 2: Alluvial Fans and Rivers Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Types of Sediment 2) Sedimentary Rock
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 14: Sedimentary Rocks Part 2: Alluvial Fans and Rivers Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Types of Sediment 2) Sedimentary Rock
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
The Mesozoic. Wednesday, November 30, 11
 The Mesozoic Periods of the Mesozoic Triassic- First period of the Mesozoic era Jurassic Cretaceous- Last period of the Mesozoic era Breakup of Pangaea Stage one (Triassic) Rifting and volcanism, normal
The Mesozoic Periods of the Mesozoic Triassic- First period of the Mesozoic era Jurassic Cretaceous- Last period of the Mesozoic era Breakup of Pangaea Stage one (Triassic) Rifting and volcanism, normal
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE PRECAMBRIAN SHIELD AND THE PHANEROZOIC SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Lab Report (Lab #2) Submitted to: Professor Simone Dumas
 THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE PRECAMBRIAN SHIELD AND THE PHANEROZOIC SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Lab Report (Lab #2) Submitted to: Professor Simone Dumas For the course Introduction to Earth Materials (GE01115) By: Gabriella
THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE PRECAMBRIAN SHIELD AND THE PHANEROZOIC SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Lab Report (Lab #2) Submitted to: Professor Simone Dumas For the course Introduction to Earth Materials (GE01115) By: Gabriella
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Rockall Plateau. OCN 201: Shelf Sediments
 Rockall Plateau OCN 201: Shelf Sediments Classification by Size Classification by Mode of Formation Detrital sediments Transported and deposited as particles Derived from weathering of pre-existing rocks
Rockall Plateau OCN 201: Shelf Sediments Classification by Size Classification by Mode of Formation Detrital sediments Transported and deposited as particles Derived from weathering of pre-existing rocks
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Iowa s Precambrian and Cambrian. University of Northern Iowa Dr. Chad Heinzel
 Iowa s Precambrian and Cambrian University of Northern Iowa Dr. Chad Heinzel Concept of Geologic Formations A body/layer of rock that consists dominantly of a certain lithologic rock type Maybe combined
Iowa s Precambrian and Cambrian University of Northern Iowa Dr. Chad Heinzel Concept of Geologic Formations A body/layer of rock that consists dominantly of a certain lithologic rock type Maybe combined
Geology. Core Ideas/Crosscutting Concepts: The Beginning Earths place in the universe. History Ptolemy Copernicus Brahe Keplers Laws
 Geology The Beginning Earths place in the universe History Ptolemy Copernicus Brahe Keplers Laws Origin of the Solar System Protosun Protoplanets Main Sequence Sun Earth and Moon Planetary differentiation
Geology The Beginning Earths place in the universe History Ptolemy Copernicus Brahe Keplers Laws Origin of the Solar System Protosun Protoplanets Main Sequence Sun Earth and Moon Planetary differentiation
Lithospheric plates. Geology of the Batemans Bay region. Tectonic processes
 1 Lithospheric plates Enormous heat sources in the Earth s deep interior, acquired during the very early history of the planet billions of years ago continue to drive present-day geological at the surface.
1 Lithospheric plates Enormous heat sources in the Earth s deep interior, acquired during the very early history of the planet billions of years ago continue to drive present-day geological at the surface.
Deep Time: How Old Is Old?
 Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Geologic Time. Geologic Events
 Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA. GY 112: Earth History. Lecture 36: Plio-Pleistocene Geology. Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 36: Plio-Pleistocene Geology Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) Cenozoic Overview and Tectonics Western North American tectonic provinces
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 36: Plio-Pleistocene Geology Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time A) Cenozoic Overview and Tectonics Western North American tectonic provinces
3. Bedrock from which entire geologic time period is missing between rock units 5 and 6? The fault most likely occurred after
 Homework # 4 Relative Dating Name: Section: Date: 1. The cross section below represents a portion of Earth s crust. Letters through D are locations within the rock units. 5. The sequence of rock types
Homework # 4 Relative Dating Name: Section: Date: 1. The cross section below represents a portion of Earth s crust. Letters through D are locations within the rock units. 5. The sequence of rock types
