Past Mass Extinctions
|
|
|
- Shauna Miles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Past Mass Extinctions Past Extinction/Causes Effects, future implications Major Events Pleistocene events Ordovician-Silurian extinction,, about 439 million years ago, caused by a drop in sea levels as glaciers formed, then by rising sea levels as glaciers melted. The toll: 25 percent of marine families and 60 percent of marine genera. Late Devonian extinction, about 364 million years ago, cause unknown. It killed 22 percent of marine families and 57 percent of marine genera. Little is known about land organisms at the time. 1
2 Permian-Triassic extinction, about 251 million years ago.. The Permian-Triassic catastrophe was Earths worst mass extinction, killing 95 percent of all species, 53 percent of marine families, 84 percent of marine genera and an estimated 70 percent of land species such as plants, insects and vertebrate animals. Past Mass Extinctions Fig. I. Reconstructions of the ancient seabed in southern China immediately before (a) and after (b) the Permo Triassic mass extinction. Note the richness of reef life and the burrowing infauna before the crisis, and the absence of such species after. A marine fauna of 100 or more species is reduced to four or five. Past Mass Extinctions CAUSES VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS: Fire, smoke, debris into atmosphere Loss of land, lava flow Aerosols in air become acid rain EXAMPLE: End-Permian Extinctions, 250 mya 2
3 End Triassic extinction,, roughly 199 million to 214 million years ago, The death toll: 22 percent of marine families, 52 percent of marine genera. Vertebrate deaths are unclear. Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction,, about 65 million years ago,. The extinction killed 16 percent of marine families, 47 percent of marine genera (the classification above species) and 18 percent of land vertebrate families, including the dinosaurs. Past Mass Extinctions CAUSES ASTEROID HITS EARTH: Impact Theory Creates tsunamis, fires, launches debris & smoke into atmosphere Darkness lasts for years, impact winter EXAMPLE: Cretaceous-Tertiary extinctions (KT Boundary), 65 mya 3
4 Past Mass Extinctions CAUSES SEA LEVEL CHANGE: Interior continental seas drain Drop in primary production, collapse in food chain Change in topography, terrain, affects wind patterns, climate Seasonal climates develop, deserts emerge EXAMPLE: KT Boundary Past Mass Extinctions CAUSES CLIMATE CHANGE: Cooling, oling, from glaciation or darkness Warming, from greenhouse gases EXAMPLE: Pleistocene Megafauna extinctions Past Mass Extinctions CAUSES HUMANS AS HUNTERS Overkill Theory for Pleistocene megafauna extinctions HUMANS AS FARMERS Habitat destruction and fragmentation from human population 4
5 Past Mass Extinctions Effects Evolutionary impacts: : debate about the role of mass extinction events in spurring new evolutionary directions and opportunities. Biodiversity: : While the loss of biodiversity is catastrophic at the time of the event, it has rebounded each time, and perhaps will rebound again despite the current rate of extinctions Quaternary Events/Extinctions of the Past Where have all the Megafauna gone...? I. The Facts: once there were megafauna. now there are none Extinctions occurred Climate Changed Humans came to North America II. The Explanations Climate- Evolution Overkill (P.A. Martin) Other Alternatives (a compromise?) III. Conclusions Extinctions happen everyday Will we ever know..do we care???? Megafaunal Extinction Megafauna: > 44kg (100 lbs) mostly large grazers, browsers and carnivores Pleistocene: 2 MYA- 12KYA 5
6 Mastodon Some examples Mammoth Doedicurus (Glyptodon) Woolly rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis)* Beautiful armadillo (Dasypus bellus) 6
7 Giant Ground Sloth Shasta Ground Sloth American camel Stag Moose Irish Elk Muskoxen 7
8 Dire wolf Short faced bear Smilodons 8
9 Extinctions occurred without replacement!!!!!!!!!!!!! Mammoths (Mammuthus) and American Lions (Felis atrox) in the late Pleistocene of Alaska Explanations: Climate change Pleistocene Overkill Human occupation of N. America directly caused extinction of larger mammals Climatic Change?: Extinctions occurred with an episode of climatic change Magnitude of change are correlated with the magnitude of extinctions Mechanisms identified that link climatic change with extinctions given with type of change, extinctions would be the expected result 9
10 Many combined reasons for extinction based on climate changes Increased Seasonality Decrease plant diversity Increased anti herbivory mechanisms Restricted resources Gestation/Breeding and Birth (Kiltie) Increased Seasonality Axelrod (1967) argues early interglacials were more equitable than the early Holocene. It is this loss of equitability that caused extinction Decrease plant diversity Plaid vs. Stripes Gunthrie argues changing seasonal regimes at the end of the Pleistocene led to an increasingly homogeneous plant community with decreased quality and quantity of plant resources available Plaids: mongastrics: mammoths, horses, camels vs. Stripes: : ruminants: antelopes, sheep, bison 10
11 Anti-herbivory mechanisms Plants may have evolved with increase anti-herbivory mechanisms Restricted resources led to decreased faunal diversity, body size and led to extinction Gestation/Breeding and Birth (Kiltie) Shifting birthing and breeding to accommodate drastic climatic changes isn't feasible for megafauna in short time spans. Having offspring during a cold season or delaying mating may comprise a population s viability Social Organs Giant Irish Elk 11
12 Extinctions have occurred before Or was it people?? Paul Martin: 1973 The Discovery of America Pleistocene Overkill Human occupation of N. America directly caused extinction of larger mammals. Pleistocene Overkill Gradual destruction of fauna over thousands of years Suddenly in as little as 100 years 12
13 Nature of human impact classified as 3 types: BLITZKRIEG Effect INNOVATION Effect ATTRITION Effect: Blitzkrieg: rapid deployment of human populations w/ big game hunting= rapid demise of big game Innovation: long established human populations adopt new hunting technologies and erase fauna stressed by climate. Advanced technology- Clovis point 13
14 ATTRITION: extinction takes place relatively slowly after a long history of human activity b/c loss of habitat and competition for resources in Conclusion... It seems to me that it is a combination of factors. Populations could have been stressed to the breaking point due to climatic changes and the consequent changes in plant life, gestation and fertility. Then humans came along and were the final straw. It seems implausible to rule out one over the other, when we have evidence of the two occurring simultaneously. Historic examples Moa New Zealand Elephant Bird -- Madagascar 14
15 More recent extinctions Colonization Hunting Habitat Loss Invasions Mass Extinctions-- --Today On average, one extinction happens somewhere on earth every 20 minutes. (Levin, p6) Ecologists estimate that half of all living bird and mammal species will be gone within 200 or 300 years. (Levin, p6) Mass Extinctions: FUTURE IMPLICATIONS Do today s s extinction rates compare? Will human disturbance lead to ecosystem decay and mass extinction? Or will it lead to fragmented islands that lead to more speciation and evolution? 15
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
Causes of Extinction
 Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
The Phanerozoic Eon. 542 mya Present. Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras
 542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
The History of Life on Earth
 8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
Please take out your fill-in notes again, and we will continue learning about extinct creatures.
 Today s Topic Evolution: Extinction Learning Goal: SWBAT explain why creatures go extinct from Earth, and why some recently-extinct creatures have gone extinct. Please take out your fill-in notes again,
Today s Topic Evolution: Extinction Learning Goal: SWBAT explain why creatures go extinct from Earth, and why some recently-extinct creatures have gone extinct. Please take out your fill-in notes again,
The Great Ice Ages. Copyright abcteach.com 2001 Graphics from Art Today
 The Great Ice Ages The Great Ice Ages occurred during the Pleistocene epoch. The word epoch means time period. This period began about 2.5 million years ago and ended roughly 10,000 years ago. During the
The Great Ice Ages The Great Ice Ages occurred during the Pleistocene epoch. The word epoch means time period. This period began about 2.5 million years ago and ended roughly 10,000 years ago. During the
What is the Earth s time scale?
 Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Final Exam Comprehensive Question:
 Notes 2/24 Exams to be returned at End of Class See last slide of the day Essay Outline (50 pts) Due March 8 (2 weeks from today) ExCredit #1 due Tues 3/1 Book O Day: Allan Eckert s The Silent Sky Final
Notes 2/24 Exams to be returned at End of Class See last slide of the day Essay Outline (50 pts) Due March 8 (2 weeks from today) ExCredit #1 due Tues 3/1 Book O Day: Allan Eckert s The Silent Sky Final
The History of Life, the Universe and Everything or What do you get when you multiply six by nine. Chapters 17 (skim) and 18
 The History of Life, the Universe and Everything or What do you get when you multiply six by nine Chapters 17 (skim) and 18 The Origin of Life The problem: Life begets life. There must be a beginning,
The History of Life, the Universe and Everything or What do you get when you multiply six by nine Chapters 17 (skim) and 18 The Origin of Life The problem: Life begets life. There must be a beginning,
Unit 2: Geology of Tsikw aye (Mesa Prieta)
 Unit 2 page 9 Name: Date: GEOLOGIC HISTORY OF MESA PRIETA: Student Information Sheet: Activity 2 Looking at Mesa Prieta today, with its tumbled black basalt boulders, prickly pear cacti and an occasional
Unit 2 page 9 Name: Date: GEOLOGIC HISTORY OF MESA PRIETA: Student Information Sheet: Activity 2 Looking at Mesa Prieta today, with its tumbled black basalt boulders, prickly pear cacti and an occasional
LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts...
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts... Date: 19 April 2018 I. Time & Life on Earth geologic time scale o divided into named
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts... Date: 19 April 2018 I. Time & Life on Earth geologic time scale o divided into named
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION. 444 million years ago
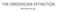 THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
Module 9: Earth's History Topic 3 Content: A Tour of Geologic Time Notes
 The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
What Happened to the Dinosaurs?
 A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
ESA's Rosetta spacecraft What are habitable exoplanets? Is there an Earth 2.0?
 ESA's Rosetta spacecraft - 2009 What are habitable exoplanets? Is there an Earth 2.0? Christina Hedges (Institute of Astronomy) For the past 20 years, since the discovery of planets outside our solar system,
ESA's Rosetta spacecraft - 2009 What are habitable exoplanets? Is there an Earth 2.0? Christina Hedges (Institute of Astronomy) For the past 20 years, since the discovery of planets outside our solar system,
Ecology. Part 4. Populations Part 5. Communities Part 6. Biodiversity and Conservation
 Ecology Part 4. Populations Part 5. Communities Part 6. Biodiversity and Conservation Population Ecology: Population Growth Models Population Limiting Factors Population growth models Logistic
Ecology Part 4. Populations Part 5. Communities Part 6. Biodiversity and Conservation Population Ecology: Population Growth Models Population Limiting Factors Population growth models Logistic
Page 143: Geologic Time
 Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
EVOLUTION. Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations.
 EVOLUTION Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations. Sources of genetic variation: genetic recombination by sexual reproduction (produces new combinations of genes) mutation
EVOLUTION Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations. Sources of genetic variation: genetic recombination by sexual reproduction (produces new combinations of genes) mutation
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life
 Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries
 ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries Introduction to Natural Hazards Natural Hazards: Geological and climatic events that pose a threat to human populations, property and activities. Typically uncontrollable
ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries Introduction to Natural Hazards Natural Hazards: Geological and climatic events that pose a threat to human populations, property and activities. Typically uncontrollable
Causes of Extinctions?
 Causes of Extinctions? Around 12,800 years ago, tens of millions of large animals abruptly became extinct, including mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed tigers, giant armadillos, giant beavers, American
Causes of Extinctions? Around 12,800 years ago, tens of millions of large animals abruptly became extinct, including mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed tigers, giant armadillos, giant beavers, American
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families end Ord.
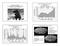 Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Microevolution and macroevolution Microevolution: evolution occurring within populations p Adaptive and neutral changes in allele frequencies Macroevolution: evolution
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Microevolution and macroevolution Microevolution: evolution occurring within populations p Adaptive and neutral changes in allele frequencies Macroevolution: evolution
Chapter 3: Changing Climates
 Chapter 3: Changing Climates Practice, page 369 1. It was these collisions that caused the final upthrusts of the rock formations that would become the Rocky Mountains and their foothills. As this rock
Chapter 3: Changing Climates Practice, page 369 1. It was these collisions that caused the final upthrusts of the rock formations that would become the Rocky Mountains and their foothills. As this rock
(continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037
 Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
Why has climate changed in the past? There are 3 main theories: 1) The eruption theory 2) The sunspot theory 3) The orbital theory
 Climate and Change Why has climate changed in the past? There are 3 main theories: 1) The eruption theory 2) The sunspot theory 3) The orbital theory The eruption theory: When a volcano erupts it throws
Climate and Change Why has climate changed in the past? There are 3 main theories: 1) The eruption theory 2) The sunspot theory 3) The orbital theory The eruption theory: When a volcano erupts it throws
STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Social Studies - Read the article "The Earliest Americans" and complete the Build Your Map Skills page and Extinct Animals of North America page.
 Day 2 Social Studies - Read the article "" and complete the Build Your Map Skills page and Extinct Animals of North America page. Language Arts - Draw a self-portrait of yourself in the center of a piece
Day 2 Social Studies - Read the article "" and complete the Build Your Map Skills page and Extinct Animals of North America page. Language Arts - Draw a self-portrait of yourself in the center of a piece
Opinion: People are causing a mass extinction on Earth; some try to stop it
 Opinion: People are causing a mass extinction on Earth; some try to stop it By Scientific American, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.21.14 Word Count 784 A giant tortoise named "Lonesome George" is seen in
Opinion: People are causing a mass extinction on Earth; some try to stop it By Scientific American, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.21.14 Word Count 784 A giant tortoise named "Lonesome George" is seen in
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Mesozoic Era 251 m.y.a 65.5 m.y.a
 Mesozoic Cenozoic notes.notebook Mesozoic & Cenozoic 251 m.y.a Present at the end of the Permian, 90% of marine organisms and more than 70% of land organisms died. because resources and space were readily
Mesozoic Cenozoic notes.notebook Mesozoic & Cenozoic 251 m.y.a Present at the end of the Permian, 90% of marine organisms and more than 70% of land organisms died. because resources and space were readily
Patterns of Evolution: A. Mass Extinctions. B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution. E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium
 : A. Mass Extinctions B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium 1 A. Mass Extinctions: Over the past 540 million years, life on Earth has passed
: A. Mass Extinctions B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium 1 A. Mass Extinctions: Over the past 540 million years, life on Earth has passed
Geologic Time. Mr. Skirbst
 Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
Origin of Species Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 1 Origin of Species Lecture 5 Winter 2014 The beauty and genius of a work of art may be reconceived, though its first material expression be destroyed; a vanished harmony may yet again inspire the composer;
1 Origin of Species Lecture 5 Winter 2014 The beauty and genius of a work of art may be reconceived, though its first material expression be destroyed; a vanished harmony may yet again inspire the composer;
Origin of Species Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Origin of Species Lecture 5 Winter 2014 The beauty and genius of a work of art may be reconceived, though its first material expression be destroyed; a vanished harmony may yet again inspire the composer;
Origin of Species Lecture 5 Winter 2014 The beauty and genius of a work of art may be reconceived, though its first material expression be destroyed; a vanished harmony may yet again inspire the composer;
Biogeography. An ecological and evolutionary approach SEVENTH EDITION. C. Barry Cox MA, PhD, DSc and Peter D. Moore PhD
 Biogeography An ecological and evolutionary approach C. Barry Cox MA, PhD, DSc and Peter D. Moore PhD Division of Life Sciences, King's College London, Fmnklin-Wilkins Building, Stamford Street, London
Biogeography An ecological and evolutionary approach C. Barry Cox MA, PhD, DSc and Peter D. Moore PhD Division of Life Sciences, King's College London, Fmnklin-Wilkins Building, Stamford Street, London
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION. α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate
 EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate 1 SPECIES AND GENERA EXTINCTION CURVES INDICATE THAT MOST SPECIES ONLY PERSIST FOR A FEW MILLION YEARS.
EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate 1 SPECIES AND GENERA EXTINCTION CURVES INDICATE THAT MOST SPECIES ONLY PERSIST FOR A FEW MILLION YEARS.
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
3ALB 4 HUMAN EVOLUTION, OUR GLOBAL DIASPORA AND THE RISE OF CIVILIZATION.
 3ALB 4 HUMAN EVOLUTION, OUR GLOBAL DIASPORA AND THE RISE OF CIVILIZATION. The record of biodiversity through the last 600 million years indicates a logarithmic increase in species through time. However,
3ALB 4 HUMAN EVOLUTION, OUR GLOBAL DIASPORA AND THE RISE OF CIVILIZATION. The record of biodiversity through the last 600 million years indicates a logarithmic increase in species through time. However,
Science Data Representation Questions: Strategies and Sample Questions
 Science Data Representation Questions: Strategies and Sample Questions Focus on understanding what information is given. Review any additional information given (descriptive paragraphs, headings, scale
Science Data Representation Questions: Strategies and Sample Questions Focus on understanding what information is given. Review any additional information given (descriptive paragraphs, headings, scale
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
11/10/13. How do populations and communities interact and change? Populations. What do you think? Do you agree or disagree? Do you agree or disagree?
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Populations Lesson 2 Changing Populations Lesson 3 Communities Chapter Wrap-Up How do populations and communities interact and change? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Populations Lesson 2 Changing Populations Lesson 3 Communities Chapter Wrap-Up How do populations and communities interact and change? What do you think? Before you begin,
Natural Climate Variability: Longer Term
 Natural Climate Variability: Longer Term Natural Climate Change Today: Natural Climate Change-2: Ice Ages, and Deep Time Geologic Time Scale background: Need a system for talking about unimaginable lengths
Natural Climate Variability: Longer Term Natural Climate Change Today: Natural Climate Change-2: Ice Ages, and Deep Time Geologic Time Scale background: Need a system for talking about unimaginable lengths
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE
 Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
The Evolution of an Ecosystem: Pleistocene Extinctions
 The Evolution of an Ecosystem: Pleistocene Extinctions Elin Whitney-Smith, Ph.D. Geobiology, George Washington University elin@quaternary.net Abstract It is generally assumed that evolution is an issue
The Evolution of an Ecosystem: Pleistocene Extinctions Elin Whitney-Smith, Ph.D. Geobiology, George Washington University elin@quaternary.net Abstract It is generally assumed that evolution is an issue
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils
 Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity. Sunday, October 1, 17
 Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity CHAPTER INTRO: The Dung of the Devil Read and Answer Questions Provided Module 14 The Biodiversity of Earth After reading this module you should be able to understand
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity CHAPTER INTRO: The Dung of the Devil Read and Answer Questions Provided Module 14 The Biodiversity of Earth After reading this module you should be able to understand
EARTH S HISTORY. What is Geology? logy: science. Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its:
 EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
7A Evidence of Evolution
 7A Evidence of Evolution Fossil Evidence & Biogeography 7A analyze and evaluate how evidence of common ancestry among groups is provided by the fossil record, biogeography, and homologies, including anatomical,
7A Evidence of Evolution Fossil Evidence & Biogeography 7A analyze and evaluate how evidence of common ancestry among groups is provided by the fossil record, biogeography, and homologies, including anatomical,
CHAPTER 5. Interactions in the Ecosystem
 CHAPTER 5 Interactions in the Ecosystem 1 SECTION 3.3 - THE ECOSYSTEM 2 SECTION 3.3 - THE ECOSYSTEM Levels of Organization Individual one organism from a species. Species a group of organisms so similar
CHAPTER 5 Interactions in the Ecosystem 1 SECTION 3.3 - THE ECOSYSTEM 2 SECTION 3.3 - THE ECOSYSTEM Levels of Organization Individual one organism from a species. Species a group of organisms so similar
Where did all the dinosaurs go?
 Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
The light at the end of the tunnel is the oncoming 6 th Mass Extinction YOURS! And mankind is the primary cause
 The light at the end of the tunnel is the oncoming 6 th Mass Extinction YOURS! And mankind is the primary cause Preparing to live with climate change We all know what happened to the Dinosaurs 65 million
The light at the end of the tunnel is the oncoming 6 th Mass Extinction YOURS! And mankind is the primary cause Preparing to live with climate change We all know what happened to the Dinosaurs 65 million
Levels of Ecological Organization. Biotic and Abiotic Factors. Studying Ecology. Chapter 4 Population Ecology
 Chapter 4 Population Ecology Lesson 4.1 Studying Ecology Levels of Ecological Organization Biotic and Abiotic Factors The study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environments Scientists
Chapter 4 Population Ecology Lesson 4.1 Studying Ecology Levels of Ecological Organization Biotic and Abiotic Factors The study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environments Scientists
Chapter 4 Population Ecology
 Chapter 4 Population Ecology Lesson 4.1 Studying Ecology Levels of Ecological Organization The study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environments Scientists study ecology at various
Chapter 4 Population Ecology Lesson 4.1 Studying Ecology Levels of Ecological Organization The study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environments Scientists study ecology at various
4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change. Extinctions
 4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change Extinctions General Observations About Extinctions In a system, you cannot change one thing without causing something else to change, Sometimes with unintended
4.0 Billion Years of Earth Environmental Change Extinctions General Observations About Extinctions In a system, you cannot change one thing without causing something else to change, Sometimes with unintended
Cenozoic Era. The Cenozoic Era: Age of Mammals. The Rise of The Mammals. Periods: 1. Neogene 2. Quaternary 3. Paleogene 4.
 Periods: 1. Neogene 2. Quaternary 3. Paleogene 4. Tertiary Cenozoic Era The Cenozoic Era: Age of Mammals The Cenozoic Era is the last and most recent of the geologic eras. Its name means new life coming
Periods: 1. Neogene 2. Quaternary 3. Paleogene 4. Tertiary Cenozoic Era The Cenozoic Era: Age of Mammals The Cenozoic Era is the last and most recent of the geologic eras. Its name means new life coming
The History of Life. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
The Human Animal. Molecular Evidence. Early Homo Evolution
 The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
Western Science Center Questionairre
 Please write the famous quote below next to its author. Spyridon Marinatos: Ralph Waldo Emerson: Henry David Thoreau: Sir William Bragg: Where Are The Dinosaurs? So, where are they anyway? Mineral Composition
Please write the famous quote below next to its author. Spyridon Marinatos: Ralph Waldo Emerson: Henry David Thoreau: Sir William Bragg: Where Are The Dinosaurs? So, where are they anyway? Mineral Composition
Food Web and Ecological Relationships Quiz
 Biology II Ms. Chen Name: Food Web and Ecological Relationships Quiz Date: Multiple Choice (2 pts each) Directions: Circle the best answer. 1. The loss of the producers in an ecosystem would most likely
Biology II Ms. Chen Name: Food Web and Ecological Relationships Quiz Date: Multiple Choice (2 pts each) Directions: Circle the best answer. 1. The loss of the producers in an ecosystem would most likely
UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME
 Name: Date: Period: UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME The earth is 4.6 billion years old. That s a long time! The scale of geologic time is so different from what human beings experience that it s often quite
Name: Date: Period: UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME The earth is 4.6 billion years old. That s a long time! The scale of geologic time is so different from what human beings experience that it s often quite
The Human Animal. Molecular Evidence. H. Habilis Tools. Early Homo Evolution. Relationship with Large Cats. Homo ergaster and Homo erectus
 The Human Animal Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos Human
The Human Animal Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos Human
Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative. Science Standard 7.4.g. Extinction: Past and Present
 7 Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative Science Standard 7.4.g. Extinction: Past and Present California Education and the Environment Initiative Approved by the California
7 Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative Science Standard 7.4.g. Extinction: Past and Present California Education and the Environment Initiative Approved by the California
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Extinctions & Climate Change Student Activity. Diagram interpretation and using research data
 Diagram interpretation and using research data Biodiversity relates to the variety of life found in an area. The number and variety of species is a simple measure of its health i.e. its ability to respond
Diagram interpretation and using research data Biodiversity relates to the variety of life found in an area. The number and variety of species is a simple measure of its health i.e. its ability to respond
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32. Paleoclimate
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life
 Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Risk of extinction and bottleneck effect in Penna model
 Risk of extinction and bottleneck effect in Penna model K. Malarz Faculty of Physics & Applied Computer Science AGH University of Science & Technology Kraków, Poland ZIS, 2007/06/18 1 Introduction A species
Risk of extinction and bottleneck effect in Penna model K. Malarz Faculty of Physics & Applied Computer Science AGH University of Science & Technology Kraków, Poland ZIS, 2007/06/18 1 Introduction A species
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18)
 Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
The big 5 mass extinctions. The asteroid impact hypothesis - Luiz & Walter Alvarez, UC Berkeley (see Science, 5th March, p1214)
 Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
The Human Animal. BIO 1300: The Human Animal
 The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life
 Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
D. Adaptive Radiation
 D. Adaptive Radiation One species new species: A new species: B new species: C new species: D Typically occurs when populations of a single species... invade a variety of new habitats, evolve under different
D. Adaptive Radiation One species new species: A new species: B new species: C new species: D Typically occurs when populations of a single species... invade a variety of new habitats, evolve under different
HOW OLD IS THE EARTH ANYWAYS?
 HOW OLD IS THE EARTH ANYWAYS? EXAMINING THE CONCEPT OF GEOLOGIC TIME Did you ever wonder about all of the things that have ever happened on Earth and how old it really is? As it turns out, Mother Earth
HOW OLD IS THE EARTH ANYWAYS? EXAMINING THE CONCEPT OF GEOLOGIC TIME Did you ever wonder about all of the things that have ever happened on Earth and how old it really is? As it turns out, Mother Earth
Preview. 1.Historical Extinctions 2.Current Extinctions 3.Extinction Factors
 Extinction Preview 1.Historical Extinctions 2.Current Extinctions 3.Extinction Factors 1. Historical Extinctions Most abundant organisms to ever inhabit Earth are prokaryotes 1. Humans Colonization of
Extinction Preview 1.Historical Extinctions 2.Current Extinctions 3.Extinction Factors 1. Historical Extinctions Most abundant organisms to ever inhabit Earth are prokaryotes 1. Humans Colonization of
By Karen Phillips. 12/06
 By Karen Phillips. 12/06 Questions The First Americans: Who, What, When, Where, How, Why? Who were the first Americans? When did the first Americans start arriving? Where did they come from? Where did
By Karen Phillips. 12/06 Questions The First Americans: Who, What, When, Where, How, Why? Who were the first Americans? When did the first Americans start arriving? Where did they come from? Where did
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Topic outline: Review: evolution and natural selection. Evolution 1. Geologic processes 2. Climate change 3. Catastrophes. Niche.
 Topic outline: Review: evolution and natural selection Evolution 1. Geologic processes 2. Climate change 3. Catastrophes Niche Speciation Extinction Biodiversity Genetic engineering http://www.cengage.com/cgi-wadsworth/course_products_wp.pl?fid=m20b&product_isbn_issn=9780495015987&discipline_number=22
Topic outline: Review: evolution and natural selection Evolution 1. Geologic processes 2. Climate change 3. Catastrophes Niche Speciation Extinction Biodiversity Genetic engineering http://www.cengage.com/cgi-wadsworth/course_products_wp.pl?fid=m20b&product_isbn_issn=9780495015987&discipline_number=22
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Credit: Adapted from NASA/JPL Caltech
 Credit: Adapted from NASA/JPL Caltech Three Puzzling Ice Age Mysteries 1. Sudden return of Ice Age temperatures 12,800 years ago After about 1400 years of warming, temperatures plunged 10 C (50 F) That
Credit: Adapted from NASA/JPL Caltech Three Puzzling Ice Age Mysteries 1. Sudden return of Ice Age temperatures 12,800 years ago After about 1400 years of warming, temperatures plunged 10 C (50 F) That
Earth s Evolution Through Time
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth s Evolution Through Time Earth 9 th edition Chapter 22 Earth s evolution: summary in haiku form Super-continents have come and gone many times: giant bumper cars.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth s Evolution Through Time Earth 9 th edition Chapter 22 Earth s evolution: summary in haiku form Super-continents have come and gone many times: giant bumper cars.
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions
 Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple
Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT
 ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 22 (Chp 15, Chp 14 Pages 288-290) Objectives of Today s Class Chp 15 Global Warming, Part 1: Recent and Future Climate: Recent climate: The Holocene Climate
ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 22 (Chp 15, Chp 14 Pages 288-290) Objectives of Today s Class Chp 15 Global Warming, Part 1: Recent and Future Climate: Recent climate: The Holocene Climate
A brief history of the Earth!
 A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
