Global Positioning System(GPS) Global Positioning System(GPS) is a new surveying technique applying space technology designed by the United States
|
|
|
- Meryl Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IV/317 Crustal deformations in the Japanese islands observed with the nationwide continuous GPS observation system Takashi TADA (Crustal Dynamics Department, Geographical Survey Institute, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305 Japan) Abstract The Japanese nationwide continuous GPS observation network has been established in October There are 215 permanent GPS station all over Japanese islands. The observation data have processed in two way. One is real time, on-line processing with the broadcast ephemeris and other is off-line processing with the precise ephemeris. Some interesting results have been obtained since the beginning of the observation. GPS network has revealed with astonishing rapidity crustal deformations, such as associated with destructive earthquakes and tectonic plate motion. These results shows the excellent performance of the permanent type GPS network, although only one year observation. Introduction The Japanese islands locate at the plate boundary between the oceanic plate and the continental plate, such as the Pacific plate, the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Therefore, the steady state crustal deformation due to plate motion is large. In addition, destructive earthquakes have occurred frequently and the crustal deformation associated with those earthquakes have observed. Geographical Survey Institute(GSI) has set the nation wide continuous GPS observation stations about 200 since October There were three large magnitude earthquakes in the past one year in and around the Japanese islands. We would like to report the crustal deformations associated with those earthquakes and also steady state crustal deformation obtained by the GPS network. Global Positioning System(GPS) Global Positioning System(GPS) is a new surveying technique applying space technology designed by the United States
2 IV/318 Department of Defense(DoD). GPS is a satellite dependent navigation system. GPS consists of 24 satellites in six orbital planes, each having four satellites. The satellites operate in circular km orbits at an inclination of 55 degrees with 0.5 sidereal day period. The system has been fully operated since July, GPS is higher accuracy than that of EDM. Especially, interferometric GPS can achieve ppm level relative precision. In addition this high accuracy, GPS has the following characters, 1) three dimensional positioning, 2) no requirement of intervisibility between the observation points, 3) all weather condition, 4) 24-hour operation, 5) short observation time, 6) easy data processing, 7) availability of automatic real time, on line observation, and 8) handy instrumentation and high portability. Role of Geographical Survey Institute The Geographical Survey Institute(GSI) is the major governmental organization for surveying and mapping in Japan, and carries out the basic surveying and mapping of Japan and the associated research connected with them. One of the most important task of GSI is establishment and maintenance of the national geodetic control points, such as the triangulation station and the bench mark. GSI initiated a nationwide triangulation survey using theodolites in 1883 and the nationwide triangulation network consisting of 6000 control points was established in Re-surveys of these control points contribute to the monitoring of crustal movements. According to the national program for earthquake prediction, GSI carried out the monitoring the crustal movements by the precise geodetic distance survey with Electromagnetic Distance Meter(EDM) in The first cycle measurement of 3000 primary control points was completed by The second cycle started in 1984 and completed by 1994, and GPS was used from 1990 changing
3 IV/319 to EDM. Nationwide GPS Network in Japan GSI installed four GPS receiver in March This is the first time of the introduction of GPS to Japan. Since then, GSI intensive experimental observations had carried out under the many conditions. In March 1988, a total of several tens of GPS receivers further introduced to universities and governmental institutes related to the earthquake prediction project. Those receivers are used for the monitoring of crustal deformation by campaign type observation. However, the biggest advantage of GPS observation is on-line, real time remote control ability at permanent stations. Compared to repetition of campaign type GPS observation, continuous observation at permanent GPS stations can achieve at the highest accuracy and temporal resolution. In February 1990, the Crustal Dynamics Department(CDD) of GSI established 3 permanent GPS stations in the Izu peninsula, 150 km southwest of Tokyo, in order to monitor crustal deformation associated with volcanic swarm earthquake activity. In March 1991, another permanent GPS network,consisting of 4 receivers, was established around Unzen volcano, Kyusyu, west Japan, which has been erupting since November Moreover, in March 1992, CDD established a permanent GPS network in the Suruga bay region, central Japan, where is considered to be the seismic source region of the coming Tokai Earthquake. And CDD began a continuous GPS observation at the Iriomote island, located western margin of the Ryukyu arc, in December We could achieved a high precision, sub-cm precision for about 10 km baseline, and obtained some significant results concerning to the crustal deformation associated with earthquake and volcanic activities through these small GPS network experiences. On the basis of success in monitoring of crustal deformation by the permanent type observation of GPS, a new project of establishing a wide and dense GPS network in the Kanto-Tokai region was proposed by CDD in April Kanto and Tokai region, central Japan, are designated as Areas for intensified observation for earthquake prediction by the
4 IV/320 Coordinating Committee for Earthquake Prediction(CCEP). This project intends to establish a GPS monitoring network in order to observe precursory crustal deformation preceding earthquake generation and volcano eruption. CDD named this new network COSMOS-G2(COntinuous Strain MOnitoring System with GPS by GSI). The COSMOS-G2 network consists of 110 permanent type GPS stations. Fig.1 shows the COSMOS-G2 network. We designed the COSMOS-G2 network as densely as possible. Average spacing between GPS stations is km. Actually, the number and the density of stations of the COSMOS-G2 network is the first of its kind in the world. The COSMOS-G2 project was adopted in the supplementary budget of Japanese government in FY The COSMOS-G2 network came into operation in March On the other hand, Geodetic Department(GD) of GSI proposed a permanent type GPS network covered all over Japan, behind CDD one year. The aims of this project are, to establish a new 3- dimensional geodetic network instead of the conventional one, and to monitor tectonic movement in the Japanese Islands. This new network was named GRAPES(GPS Regional Array for Precise Surveying and Physical Earth Science). Fortunately, GRAPES was adopted in the second supplementary budget of Japanese government in FY 1993 and established in October Fig.2 shows the GRAPES network. GRAPES has 104 GPS stations in all over Japan and its average spacing is l km. Thus, we have two GPS sub-networks in Japan. Both subnetwork have a similar system. A GPS antenna is equipped on the top of a 5 m stainless pillar with a 2 m firm ground base(phot.1). The antenna is covered with a radome. A receiver, a modem, and a battery are kept inside of the pillar. A brass maker is attached to each station for site preservation. The data collected at each station are transferred to data centers at GSI by a high speed modem through a public telephone line. Currently, the data from each sub-network are processed independently with its own strategy. Since the COSMOS-G2 requires a quick turnaround of the results for the real time monitoring, a broadcast ephemeris is used with Bernese Processing
5 IV/321 Engine and the observation window is set to be 12 hours. On the hands, GRAPES requires the highest precision to detect tectonic movements in an over 100 km scale. Thus, 24 hour data are off-line processed with a precise ephemeris from the International GPS Service for Geodynamics(IGS) using the GAMIT software. In response to the recent sequence of destructive earthquakes, GSI plans to expand the number of stations up to 640 in March 1996 as shown in Fig.3 and the current two sub-networks will be integrated into one new system, a nationwide GPS network. Furthermore, the total number of GPS stations will be expand up to about 1000 in the end of With these expansion, the Japanese islands will be covered by a dense GPS network with the average spacing of about 20 km. The Japanese nationwide GPS network is the largest and most dense permanent GPS network in the world. Kurile Islands Earthquake(M=8.1) The nationwide GPS network became operational from September 27,1994. On October 4, 1994, i.e., 1 week after the operation, a large earthquake, which earthquake magnitude M=8.1, hit the northern part of Hokkaido, and the southwestern part of the Kurile islands. It is well known as the 1994 Kurile islands earthquake. The epicenter was about 200 km east off the Nemuro peninsula in Hokkaido, but the eastern part of Hokkaido strongly shook with JIVIA seismic intensity 5. It was afraid that the station pillars of GPS tilted by the strong shaking. The stability of the pillar at Nemuro on site was checked and it was concluded that there were no problems in the pillar. Thus, all GPS stations survived the shaking and provided us continuous observation data of the quake. A preliminary result on the coseismic crustal deformation was reported to the public on October 6, 1994, proving the quickness of continuous GPS network in monitoring crustal deformation. It needs 2-3 years to obtain the same result by the conventional method. Because all stations in Hokkaido could be displaced from the earthquake, it was assumed that the Usuda station, Honshu, Japan was the fixed point in the analysis. Usuda is located about 1100 km southwest of the epicenter, so it is considered that the coseismic
6 IV/322 displacement at the Usuda station is negligible small. Twenty-four-hour data from GPS stations in Hokkaido and Usuda with a one-minute interval are processed for two-week period from September 27 to October 12, one week before and one week after the earthquake. For the base line processing, it was used the GAMIT software with National Geodetic Survey(NGS) precise ephemerides and earth rotation parameters from International Earth Rotation Service(IERS) Bulletin. Tropospheric delays are estimated at each station in every 3-hour period. Fig.4 shows a graphic representation of the horizontal crustal displacement vectors associated with the 1994 Kurile islands earthquake in Hokkaido. The nearest station to the epicenter, Nemuro, 170 km west of the epicenter, moved 44 cm to east and 10 cm to down. Since the fixed station is so far from the epicenter, the displacement can be regarded as absolute value. Two possible fault models have been proposed based on this crustal deformation. Because of poor resolution of determination of aftershock hypocenters and lack of information of crustal deformation in the near field, it is impossible to distinguish which model is better. Fig.5 shows the time series of the coordinates at Nemuro before and after the earthquake. Error bar shows twice of the standard deviation. Offset after the main shock in October, 4(day of year 277) are evident in the time series. It is obvious that there are no significant changes in site coordinates for a week before and after the earthquake Off Sanriku Earthquake(M=7.5) On December 29, 1994, a large earthquake with magnitude of 7.5 occurred at far off Sanriku, northeastern Honshu, Japan. Strong shaking of the JMA seismic intensity 6 was recorded at Hachinohe city. There are no damage at the GPS stations and the crustal deformation associated with the earthquake was successfully detected. Fig.6 shows the horizontal crustal displacements at each GPS station analyzed by above mentioned data processing. The Kuji station, northern part of Tohoku, about 200 km far from the epicenter, moved up to 8 cm toward to the epicenter and subsided up
7 IV/323 to 2 cm. The crustal deformations associated with the quake was not so large but a large after effect crustal deformation was observed. Fig.7 shows a time series of dally change in Kuji-Rifu baseline components for about 8 month. A exponential function type post seismic relaxation was recorded at the Kuji station where was nearest station to the epicenter. The relaxation time constant is estimated to be about 60 days. It is considered that this phenomenon is either due to the creep motion of the fault plane or due to the visco-elastic character in the upper mantle. Fig.6 gives a strong impression of superiority of the continuous GPS observation. The off Sanriku earthquake is understood to be a thrust type faulting occurred at the plate boundary between the Pacific and the Okhotsk plates event in the Izu peninsula Since 1978, earthquake swarm and anomalous crustal deformation have frequently occurred in the northeastern Izu peninsula. It is considered that these anomalous crustal activity is caused by magma intrusion into the uppermost crust. In fact,, a submarine volcanic eruption occurred at east off of Ito city in CDD has carried out the continuous GPS monitoring in the eastern Izu peninsula since February In September 11, 1995, An earthquake swarm began to activate at near Ito city. At the same time, a crustal extension was observed with COSMOS-G2. Fig.8 shows an example of the daily distance change between HTS and KMR across the swarm region. A crustal extension correlate to seismic activity has been detected successfully. The monitoring of crustal deformation with COSMOS-G2 has played important role to judge the change in seismic activity, especially the time of ceaseactivity. Steady state crustal deformation So the Japanese islands situate at an active plate boundary, that the crustal strain rate is high as much as ppm/year. But the precision of EDM is low as 1 ppm, then it needs years to observe an effective crustal deformation. Indeed, we needed 15 years to obtain the result which is shown in Fig.9. GPS, on the contrary, is
8 IV/324 high precision, so we can make the period short. It took 2-3 years to obtain a effective result by the campaign type GPS observation, but it took only half year to obtain a similar result to Fig.9 with the continuous GPS observation. Fig.10 shows a horizontal displacement vectors in the western Japan which was obtained with the observation of GRAPES during 6 months. Conclusive remarks The nationwide continuous GPS network is better than conventional geodetic techniques in many ways. The maturity of GPS technology, represented by the state-of-the-art hard&softwares and precise ephemerides, allows few-mm horizontal precision. These factors make the nationwide GPS network into an ideal tool for understanding of dynamics in the earth's interior.
9 IV/325 Phot.1 Station pillar and electronic device of COSMOS-G2 and GRAPES. The antenna is equipped on the top of a 5 m stainless steel pillar with a firm ground base. A receiver, modem and a battery are kept inside of the pillar. A commercial electronic power line and public telephone line are used for the driving power and the data transmission.
10 IV/326
11 IV/327
12 IV/328 The Grapes GPS Regional Array for PrEcise Surveying (and Physical Earth Science) will appear in April 1996 with 620 stations. covers whole Japan with 25 km interval. Fig.3 Feature GRAPES network (March 1996).
13
14 IV/330
15 IV/331 Fig.6 Horizontal crustal displacement vectors associated with the Off Sanriku earthquake.
16 IV/332
17 IV/333
18 IV/334
19 IV/335
Case study of Japan: Reference Frames in Practice
 Case study of Japan: Reference Frames in Practice Basara Miyahara and Koji Matsuo Sponsors: 1 Outline Introduction - Geodetic reference frame of Japan - GEONET : continuous GNSS observation system Geometric
Case study of Japan: Reference Frames in Practice Basara Miyahara and Koji Matsuo Sponsors: 1 Outline Introduction - Geodetic reference frame of Japan - GEONET : continuous GNSS observation system Geometric
Case Study of Japan: Crustal deformation monitoring with GNSS and InSAR
 Technical Seminar Reference Frame in Practice, Case Study of Japan: Crustal deformation monitoring with GNSS and InSAR Basara Miyahara miyahara-b96ip@milt.go.jp Geospatial Information Authority of Japan
Technical Seminar Reference Frame in Practice, Case Study of Japan: Crustal deformation monitoring with GNSS and InSAR Basara Miyahara miyahara-b96ip@milt.go.jp Geospatial Information Authority of Japan
How GNSS CORS in Japan works for geodetic control and disaster mitigations
 ICG Working Group D Reference Frames, Timing and Applications How GNSS CORS in Japan works for geodetic control and disaster mitigations ICG11, Nov. 7-11, 2016, Sochi, Russia Hiromichi TSUJI Geodetic Observation
ICG Working Group D Reference Frames, Timing and Applications How GNSS CORS in Japan works for geodetic control and disaster mitigations ICG11, Nov. 7-11, 2016, Sochi, Russia Hiromichi TSUJI Geodetic Observation
Aseismic slip and low-frequency earthquakes in the Bungo channel, southwestern Japan
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L769, doi:1.19/3gl19381, Aseismic slip and low-frequency earthquakes in the Bungo channel, southwestern Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, 1 Yuki Hatanaka, 1 Masaru Kaidzu,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L769, doi:1.19/3gl19381, Aseismic slip and low-frequency earthquakes in the Bungo channel, southwestern Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, 1 Yuki Hatanaka, 1 Masaru Kaidzu,
Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake
 Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake 51 Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake Tetsuro IMAKIIRE, Shinzaburo OZAWA, Hiroshi YARAI, Takuya NISHIMURA
Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake 51 Crustal deformation by the Southeast-off Kii Peninsula Earthquake Tetsuro IMAKIIRE, Shinzaburo OZAWA, Hiroshi YARAI, Takuya NISHIMURA
The impact of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on Tsukuba 32-m station
 7th IVS General Meeting Madrid, Spain March 4-9 2012 The impact of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on Tsukuba 32-m station SHINOBU KURIHARA K. Kokado, J. Kuroda, M. Ishihara and R.
7th IVS General Meeting Madrid, Spain March 4-9 2012 The impact of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on Tsukuba 32-m station SHINOBU KURIHARA K. Kokado, J. Kuroda, M. Ishihara and R.
ESTIMATES OF HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE 1999 TAIWAN EARTHQUAKE
 ESTIMATES OF HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE 1999 TAIWAN EARTHQUAKE C. C. Chang Department of Surveying and Mapping Engineering Chung Cheng Institute of Technology, Taiwan, ROC ABSTRACT A
ESTIMATES OF HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE 1999 TAIWAN EARTHQUAKE C. C. Chang Department of Surveying and Mapping Engineering Chung Cheng Institute of Technology, Taiwan, ROC ABSTRACT A
Earthquake. What is it? Can we predict it?
 Earthquake What is it? Can we predict it? What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate
Earthquake What is it? Can we predict it? What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate
68. Izu-Torishima. Summary. Latitude: 30 29'02" N, Longitude: '11" E, Elevation: 394 m (Ioyama) (Elevation Point) (68.
 68. Izu-Torishima Latitude: 30 29'02" N, Longitude: 140 18'11" E, Elevation: 394 m (Ioyama) (Elevation Point) Izu-Torishima taken from southeast side on August 12, 2002. Courtesy of the Maritime Safety
68. Izu-Torishima Latitude: 30 29'02" N, Longitude: 140 18'11" E, Elevation: 394 m (Ioyama) (Elevation Point) Izu-Torishima taken from southeast side on August 12, 2002. Courtesy of the Maritime Safety
Seismic Activity and Crustal Deformation after the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake
 J-RAPID Symposium March 6-7, 2013 Seismic Activity and Crustal Deformation after the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Y. Honkura Tokyo Institute of Technology Japan Science and Technology
J-RAPID Symposium March 6-7, 2013 Seismic Activity and Crustal Deformation after the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Y. Honkura Tokyo Institute of Technology Japan Science and Technology
The Japanese University Joint Seismic Observations at the Niigaka-Kobe Tectonic Zone
 Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2*,**/ pp. +-- +.1 * The Japanese University Joint Seismic Observations at the Niigaka-Kobe Tectonic Zone The Japanese University Group of the Joint Seismic Observations
Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2*,**/ pp. +-- +.1 * The Japanese University Joint Seismic Observations at the Niigaka-Kobe Tectonic Zone The Japanese University Group of the Joint Seismic Observations
THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE IN JAPAN. VSU Lyuben Karavelov, Sofia, Bulgaria. Key words: Tohoku earthquake, strong ground motion, damage
 THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE IN JAPAN Radan Ivanov 1 VSU Lyuben Karavelov, Sofia, Bulgaria Abstract: This earthquake which occurred on March 11, 2011, had a magnitude of 9.0, which places it as the fourth
THE 2011 TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE IN JAPAN Radan Ivanov 1 VSU Lyuben Karavelov, Sofia, Bulgaria Abstract: This earthquake which occurred on March 11, 2011, had a magnitude of 9.0, which places it as the fourth
Occurrence of quasi-periodic slow-slip off the east coast of the Boso peninsula, Central Japan
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 9, 11 1, Occurrence of quasi-periodic slow-slip off the east coast of the Boso peninsula, Central Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, Hisashi Suito, and Mikio Tobita Geographical Survey
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 9, 11 1, Occurrence of quasi-periodic slow-slip off the east coast of the Boso peninsula, Central Japan Shinzaburo Ozawa, Hisashi Suito, and Mikio Tobita Geographical Survey
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling
 The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (April 2013)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (April 2013) Zaozan (Calm) Small-amplitude volcanic tremors were recorded on April 7 (duration: 3 min 20 sec), 9 (4 min 20 sec) and 21 (5 min 40 sec). These were the first
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (April 2013) Zaozan (Calm) Small-amplitude volcanic tremors were recorded on April 7 (duration: 3 min 20 sec), 9 (4 min 20 sec) and 21 (5 min 40 sec). These were the first
Slow slip in the focal region of the anticipated Tokai earthquake following the seismo-volcanic event in the northern Izu Islands in 2000
 Earth Planets Space, 57, 507 513, 2005 Slow slip in the focal region of the anticipated Tokai earthquake following the seismo-volcanic event in the northern Izu Islands in 2000 Akio Kobayashi 1, Akio Yoshida
Earth Planets Space, 57, 507 513, 2005 Slow slip in the focal region of the anticipated Tokai earthquake following the seismo-volcanic event in the northern Izu Islands in 2000 Akio Kobayashi 1, Akio Yoshida
REPORT ON THE TOHOKU AREA PASIFIC OFFSHORE EARTHQUAKE
 REPORT ON THE TOHOKU AREA PASIFIC OFFSHORE EARTHQUAKE GENERAL PERSPECTIVE The Highest Magnitude Ever Recorded The 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (hereafter, the 2011 Tohoku- Pacific Earthquake
REPORT ON THE TOHOKU AREA PASIFIC OFFSHORE EARTHQUAKE GENERAL PERSPECTIVE The Highest Magnitude Ever Recorded The 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (hereafter, the 2011 Tohoku- Pacific Earthquake
ANOMALOUS CRUSTAL ACTIVITY IN THE IZU PENINSULA, CENTRAL HONSHU. Kenshiro TSUMURA
 J. Phys. Earth, 25, Suppl., S 51-S 68, 1977 ANOMALOUS CRUSTAL ACTIVITY IN THE IZU PENINSULA, CENTRAL HONSHU Kenshiro TSUMURA Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan (Received June
J. Phys. Earth, 25, Suppl., S 51-S 68, 1977 ANOMALOUS CRUSTAL ACTIVITY IN THE IZU PENINSULA, CENTRAL HONSHU Kenshiro TSUMURA Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan (Received June
The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1
 The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1 Graeme BLICK, John BEAVAN, Chris CROOK, Nic DONNELLY Keywords: Darfield Earthquake, control, survey,
The Impact of the 2010 Darfield (Canterbury) Earthquake on the Geodetic Infrastructure in New Zealand 1 Graeme BLICK, John BEAVAN, Chris CROOK, Nic DONNELLY Keywords: Darfield Earthquake, control, survey,
EARTHQUAKE RELATED PROJECTS IN NIED, JAPAN. Yoshimitsu Okada NIED (National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention), Japan
 OECD/NEA WS 1/8 EARTHQUAKE RELATED PROJECTS IN NIED, JAPAN Yoshimitsu Okada NIED (National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention), Japan Abstract Earthquake related projects in NIED
OECD/NEA WS 1/8 EARTHQUAKE RELATED PROJECTS IN NIED, JAPAN Yoshimitsu Okada NIED (National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention), Japan Abstract Earthquake related projects in NIED
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March
 Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Sendai Earthquake NE Japan March 11, 2011 Some explanatory slides Bob Stern, Dave Scholl, others updated March 14 2011 Earth has 11 large plates and many more smaller ones. Plates are 100-200 km thick
Spatio-temporal variation in slip rate on the plate boundary off Sanriku, northeastern Japan, estimated from small repeating earthquakes
 Spatio-temporal variation in slip rate on the plate boundary off Sanriku, northeastern Japan, estimated from small repeating earthquakes T. Matsuzawa, N. Uchida, T. Igarashi *, N. Umino, and A. Hasegawa
Spatio-temporal variation in slip rate on the plate boundary off Sanriku, northeastern Japan, estimated from small repeating earthquakes T. Matsuzawa, N. Uchida, T. Igarashi *, N. Umino, and A. Hasegawa
4-3-1 Earthquake and Tsunami Countermeasures of Tokyo s
 4-3-1 Earthquake and Tsunami Countermeasures of Tokyo s Sewerage Masahiro Hikino* and Gaku Sato** *Planning Section, Planning and Coordinating Division, Bureau of Sewerage, Tokyo Metropolitan Government
4-3-1 Earthquake and Tsunami Countermeasures of Tokyo s Sewerage Masahiro Hikino* and Gaku Sato** *Planning Section, Planning and Coordinating Division, Bureau of Sewerage, Tokyo Metropolitan Government
Special feature: Are its lessons being adequately applied? Follow-up on the ten-year anniversary of the Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake
 Special feature: Are its lessons being adequately applied? Follow-up on the ten-year anniversary of the Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake - Are we prepared for future massive earthquakes? - Hisakazu SAKAI Member
Special feature: Are its lessons being adequately applied? Follow-up on the ten-year anniversary of the Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake - Are we prepared for future massive earthquakes? - Hisakazu SAKAI Member
Detection of Kuril subduction-zone earthquakes from remote historic records in Honshu, Japan, between 1656 and 1867
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 47, N. 2/3, April/June 2004 Detection of Kuril subduction-zone earthquakes from remote historic records in Honshu, Japan, between 1656 and 1867 Kenji Satake Active Fault Research
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 47, N. 2/3, April/June 2004 Detection of Kuril subduction-zone earthquakes from remote historic records in Honshu, Japan, between 1656 and 1867 Kenji Satake Active Fault Research
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen?
 San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (July, 2012)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (July, 2012) Tokachidake [Alert Level: 1] Volcanic glows have been observed in the Taisho crater with a high-sensitivity camera at night from the night of June 30th to
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (July, 2012) Tokachidake [Alert Level: 1] Volcanic glows have been observed in the Taisho crater with a high-sensitivity camera at night from the night of June 30th to
GEO-VIII November Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories Progress Report. Document 9
 GEO-VIII 16-17 November 2011 Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories Progress Report Document 9 This document is submitted to GEO-VIII for information. Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories
GEO-VIII 16-17 November 2011 Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories Progress Report Document 9 This document is submitted to GEO-VIII for information. Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories
ACTIVITIES OF THE HEADQUARTERS FOR EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH PROMOTION
 Journal of Japan Association for Earthquake Engineering, Vol.4, No.3 (Special Issue), 2004 ACTIVITIES OF THE HEADQUARTERS FOR EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH PROMOTION Sadanori HIGASHI 1 1 Member of JAEE, Earthquake
Journal of Japan Association for Earthquake Engineering, Vol.4, No.3 (Special Issue), 2004 ACTIVITIES OF THE HEADQUARTERS FOR EARTHQUAKE RESEARCH PROMOTION Sadanori HIGASHI 1 1 Member of JAEE, Earthquake
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 56, , 2004
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 56, 353 357, 2004 Deep seismic activities preceding the three large shallow earthquakes off south-east Hokkaido, Japan the 2003 Tokachi-oki earthquake, the 1993 Kushiro-oki
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 56, 353 357, 2004 Deep seismic activities preceding the three large shallow earthquakes off south-east Hokkaido, Japan the 2003 Tokachi-oki earthquake, the 1993 Kushiro-oki
Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior
 Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior Define the Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere 2. continental crust 3. Convection current 4. Convergent plate boundary 5. Divergent plate boundary 6. earthquake
Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior Define the Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere 2. continental crust 3. Convection current 4. Convergent plate boundary 5. Divergent plate boundary 6. earthquake
Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy
 Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy Chairman Shigeru Matsuzaka, Japan - shigeru@gsi.go.jp Vice Chairman Prof. Pengfei Cheng, China - chengpf@casm.ac.cn John
Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy Chairman Shigeru Matsuzaka, Japan - shigeru@gsi.go.jp Vice Chairman Prof. Pengfei Cheng, China - chengpf@casm.ac.cn John
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on December 14, 2004. Mark answers on a scantron sheet, which will be provided.
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on December 14, 2004. Mark answers on a scantron sheet, which will be provided.
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate
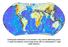 Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
JMA Tsunami Warning Services. Takeshi KOIZUMI Senior Coordinator for International Earthquake and Tsunami Information Japan Meteorological Agency
 JMA Tsunami Warning Services Takeshi KOIZUMI Senior Coordinator for International Earthquake and Tsunami Information Japan Meteorological Agency Tectonic Setting of Japan (Headquarters for Earthquake Research
JMA Tsunami Warning Services Takeshi KOIZUMI Senior Coordinator for International Earthquake and Tsunami Information Japan Meteorological Agency Tectonic Setting of Japan (Headquarters for Earthquake Research
Continuously Monitored by JMA. Latitude: 34 23'49" N, Longitude: '13" E, Elevation: 432 m (Miyatsukayama) (Spot elevation measured by JMA)
 60. Niijima Continuously Monitored by JMA Latitude: 34 23'49" N, Longitude: 139 16'13" E, Elevation: 432 m (Miyatsukayama) (Spot elevation measured by JMA) Overview of Niijima taken from southeast side
60. Niijima Continuously Monitored by JMA Latitude: 34 23'49" N, Longitude: 139 16'13" E, Elevation: 432 m (Miyatsukayama) (Spot elevation measured by JMA) Overview of Niijima taken from southeast side
MECHANISM OF THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE: INSIGHT FROM SEISMIC TOMOGRAPHY
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan MECHANISM OF THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE: INSIGHT FROM
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan MECHANISM OF THE 2011 TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE: INSIGHT FROM
Continuously Monitored by JMA. Latitude: 34 13'10" N, Longitude: '11" E, Elevation: 572 m (Tenjosan) (Triangulation Point - Kozushima)
 61. Kozushima Continuously Monitored by JMA Latitude: 34 13'10" N, Longitude: 139 09'11" E, Elevation: 572 m (Tenjosan) (Triangulation Point - Kozushima) Overview of Kozushima taken from south-southeast
61. Kozushima Continuously Monitored by JMA Latitude: 34 13'10" N, Longitude: 139 09'11" E, Elevation: 572 m (Tenjosan) (Triangulation Point - Kozushima) Overview of Kozushima taken from south-southeast
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March, 2011)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March, 2011) Japan Meteorological Agency Yakedake[ Alert Level : 1] Just after "The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake" on 11th March, seismicity became higher
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March, 2011) Japan Meteorological Agency Yakedake[ Alert Level : 1] Just after "The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake" on 11th March, seismicity became higher
Chapter 2. Earthquake and Damage
 EDM Report on the Chi-Chi, Taiwan Earthquake of September 21, 1999 2.1 Earthquake Fault 2.1.1 Tectonic Background The island of Taiwan is located in the complex junction where the Eurasian and Philippine
EDM Report on the Chi-Chi, Taiwan Earthquake of September 21, 1999 2.1 Earthquake Fault 2.1.1 Tectonic Background The island of Taiwan is located in the complex junction where the Eurasian and Philippine
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM OBSERVED STRONG-MOTION RECORDS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Plates Moving Apart Types of Boundaries
 Plates Moving Apart Types of Boundaries PLATE TECTONICS IS The theory that the Earth s crust is broken into slabs of rock that move around on top of the asthenosphere. How fast are plates moving? The Arctic
Plates Moving Apart Types of Boundaries PLATE TECTONICS IS The theory that the Earth s crust is broken into slabs of rock that move around on top of the asthenosphere. How fast are plates moving? The Arctic
A block-fault model for deformation of the Japanese Islands derived from continuous GPS observation
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 52, 1095 1100, 2000 A block-fault model for deformation of the Japanese Islands derived from continuous GPS observation Manabu Hashimoto 1, Shin ichi Miyazaki 2, and David D.
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 52, 1095 1100, 2000 A block-fault model for deformation of the Japanese Islands derived from continuous GPS observation Manabu Hashimoto 1, Shin ichi Miyazaki 2, and David D.
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February 2016)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February 2016) Japan Meteorological Agency Azumayama (Alert Level: 2) Fumarolic activity at the Oana crater has remained at relatively high levels. Aerial observation
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February 2016) Japan Meteorological Agency Azumayama (Alert Level: 2) Fumarolic activity at the Oana crater has remained at relatively high levels. Aerial observation
at IHO IRCC7 Mexico City, Mexico, June 2015
 Report on Japan s Response to Disasters presented by JHOD at IHO IRCC7 Mexico City, Mexico, 01 03 June 2015 JAPAN COAST GUARD Actions against huge earthquake Actions taken by JHOD against the Great East
Report on Japan s Response to Disasters presented by JHOD at IHO IRCC7 Mexico City, Mexico, 01 03 June 2015 JAPAN COAST GUARD Actions against huge earthquake Actions taken by JHOD against the Great East
Annual Report for Research Work in the fiscal year 2005
 JST Basic Research Programs C R E S T (Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology) Annual Report for Research Work in the fiscal year 2005 Research Area : High Performance Computing for Multi-scale
JST Basic Research Programs C R E S T (Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology) Annual Report for Research Work in the fiscal year 2005 Research Area : High Performance Computing for Multi-scale
Tsunami waves swept away houses and cars in northern Japan and pushed ships aground.
 Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Continuously Monitored by JMA. Latitude: 24 45'02" N, Longitude: '21" E, Elevation: 169 m (Suribachiyama) (GSI Measuring Point)
 74. Ioto Continuously Monitored by JMA Latitude: 24 45'02" N, Longitude: 141 17'21" E, Elevation: 169 m (Suribachiyama) (GSI Measuring Point) Overview of Ioto taken from northwest side on July 29, 2008
74. Ioto Continuously Monitored by JMA Latitude: 24 45'02" N, Longitude: 141 17'21" E, Elevation: 169 m (Suribachiyama) (GSI Measuring Point) Overview of Ioto taken from northwest side on July 29, 2008
Chapter 4 Earthquakes and Tsunamis
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Any Questions? Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Any Questions? Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Chapter 4 Earthquakes and Tsunamis. Geology of the Hawaiian Islands. Any Questions? Class March Mean = 78.
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 Any Questions? 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 Any Questions? 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Coseismic Surface GPS Displacement and Ground Shaking Associated with the 2006 Pingtung Earthquake Doublet, Offshore Southern Taiwan
 Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., Vol. 19, No. 6, 683-696, December 2008 doi: 10.3319/TAO.2008.19.6.683(PT) Coseismic Surface GPS Displacement and Ground Shaking Associated with the 2006 Pingtung Earthquake Doublet,
Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., Vol. 19, No. 6, 683-696, December 2008 doi: 10.3319/TAO.2008.19.6.683(PT) Coseismic Surface GPS Displacement and Ground Shaking Associated with the 2006 Pingtung Earthquake Doublet,
Disclaimer. This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries.
 Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update
 The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II
 Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
NTUA, Faculty of Rural and Surveying Engineering, Dionysos Satellite Observatory, Higher Geodesy Laboratory NOA, Institute of Geodynamics 1
 NOA, Institute of Geodynamics 1 Crustal Deformation from GPS measurements at the Ionian Sea : Preliminary Results Anastasiou 1 D., Paradissis 1 D., Ganas 2 A., Marinou 1 A., Papazissi 1 K., Drakatos 2
NOA, Institute of Geodynamics 1 Crustal Deformation from GPS measurements at the Ionian Sea : Preliminary Results Anastasiou 1 D., Paradissis 1 D., Ganas 2 A., Marinou 1 A., Papazissi 1 K., Drakatos 2
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Reconstruction of Geodetic Reference Frame after the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake
 Reconstruction of Geodetic Reference Frame after the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Basara MIYAHARA, Takashi TOYOFUKU Tomoaki FURUYA, Yohei HIYAMA, Atsushi YAMAGIWA, Japan Key words: GNSS/GPS,
Reconstruction of Geodetic Reference Frame after the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Basara MIYAHARA, Takashi TOYOFUKU Tomoaki FURUYA, Yohei HIYAMA, Atsushi YAMAGIWA, Japan Key words: GNSS/GPS,
Researching Earth's Moving Crust
 Chapter 3 The Changing Earth Chapter Science Investigation Researching Earth's Moving Crust Find Out Do this activity to see what evidence exists today of plate movement or volcanic eruptions. newspapers,
Chapter 3 The Changing Earth Chapter Science Investigation Researching Earth's Moving Crust Find Out Do this activity to see what evidence exists today of plate movement or volcanic eruptions. newspapers,
Magnitude 8.3 SEA OF OKHOTSK
 A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Spatiotemporal evolution of aseismic interplate slip between 1996 and 1998 and between 2002 and 2004, in Bungo channel, southwest Japan
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004643, 2007 Spatiotemporal evolution of aseismic interplate slip between 1996 and 1998 and between 2002 and 2004, in Bungo channel, southwest
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004643, 2007 Spatiotemporal evolution of aseismic interplate slip between 1996 and 1998 and between 2002 and 2004, in Bungo channel, southwest
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics
 SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY
 Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY A Technical Report By MARTINEZ BRAVO Delvin Abdiel (MEE10515) Disaster
Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY A Technical Report By MARTINEZ BRAVO Delvin Abdiel (MEE10515) Disaster
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura, and Y. Niwa International Research Institute of Disaster Science, Tohoku University, Japan
 The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
Earthquakes. Photo credit: USGS
 Earthquakes Earthquakes Photo credit: USGS Pancaked Building - 1985 Mexico City Earthquakes don t kill people - buildings do! An earthquake is the motion or trembling of the ground produced by sudden displacement
Earthquakes Earthquakes Photo credit: USGS Pancaked Building - 1985 Mexico City Earthquakes don t kill people - buildings do! An earthquake is the motion or trembling of the ground produced by sudden displacement
Dynamic Crust Regents Review
 Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p ) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by:
 Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
MAGMATIC, ERUPTIVE AND TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE ALEUTIAN ARC, ALASKA
 MAGMATIC, ERUPTIVE AND TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE ALEUTIAN ARC, ALASKA Introduction The Aleutian Arc contains roughly ten percent of the world s active volcanoes. Hardly a year goes by without a major eruption
MAGMATIC, ERUPTIVE AND TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE ALEUTIAN ARC, ALASKA Introduction The Aleutian Arc contains roughly ten percent of the world s active volcanoes. Hardly a year goes by without a major eruption
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Earthquakes and Tsunamis
 Earthquakes and Tsunamis Kenji Satake Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo 1 Part I 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami 2 Fukushima Dai ichi NPP accident Earthquake ground motion Reactors automatically
Earthquakes and Tsunamis Kenji Satake Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo 1 Part I 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami 2 Fukushima Dai ichi NPP accident Earthquake ground motion Reactors automatically
Earthquakes Modified
 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Modified Recall that the earth s crust is broken into large pieces called. These slowly moving plates each other, each other, or from each other. This causes much on the rocks.
Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Modified Recall that the earth s crust is broken into large pieces called. These slowly moving plates each other, each other, or from each other. This causes much on the rocks.
Modernization of National Geodetic Datum in China *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES
 Lab 9 Name Sec PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES 1. Fill in the blank spaces on the chart with the correct answers. Refer to figures 2.3, 2.4 p.33 (2.2 and 2.3 on p. 23) as needed. 2. With your knowledge of different
Lab 9 Name Sec PLATE TECTONIC PROCESSES 1. Fill in the blank spaces on the chart with the correct answers. Refer to figures 2.3, 2.4 p.33 (2.2 and 2.3 on p. 23) as needed. 2. With your knowledge of different
Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone Fault Systems- Phase I
 University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 4 4th Annual Report, 1980 Article 16 1-1-1980 Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone
University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 4 4th Annual Report, 1980 Article 16 1-1-1980 Contemporary Tectonics and Seismicity of the Teton and Southern Yellowstone
Collision and transform Boundaries
 Collision and transform Boundaries I. The collision boundary Sometimes when two plates move together they are both continental rather than one being continental and one being oceanic as at the destructive
Collision and transform Boundaries I. The collision boundary Sometimes when two plates move together they are both continental rather than one being continental and one being oceanic as at the destructive
Advantages of GNSS in Monitoring Crustal Deformation for Detection of Precursors to Strong Earthquakes
 Positioning, 2013, 4, 11-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/pos.2013.41003 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/pos) 11 Advantages of GNSS in Monitoring Crustal Deformation for Detection
Positioning, 2013, 4, 11-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/pos.2013.41003 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/pos) 11 Advantages of GNSS in Monitoring Crustal Deformation for Detection
The great earthquakes that have shaped Japan 日本に大きな影響を与えた地震
 The great earthquakes that have shaped Japan 日本に大きな影響を与えた地震 Brian Kennett, Research School of Earth Sciences, ANU Takashi Furumura Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo Japan tectonic plates
The great earthquakes that have shaped Japan 日本に大きな影響を与えた地震 Brian Kennett, Research School of Earth Sciences, ANU Takashi Furumura Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo Japan tectonic plates
Groundwater changes related to the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (M9.0)
 Groundwater changes related to the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (M9.0) Yuichi Kitagawa Senior Research Scientist, AIST, GSJ, Active Fault and Earthquake Research Cente Naoji Koizumi
Groundwater changes related to the 2011 Off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (M9.0) Yuichi Kitagawa Senior Research Scientist, AIST, GSJ, Active Fault and Earthquake Research Cente Naoji Koizumi
Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L
 6.10: Tectonic Plates Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L 1 On March 11, 2011, an earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale rocked the sea floor. It made a giant wave, which grew as tall as 30 feet (9.14 meters)
6.10: Tectonic Plates Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L 1 On March 11, 2011, an earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale rocked the sea floor. It made a giant wave, which grew as tall as 30 feet (9.14 meters)
Warm-up #15. How does magma move throughout the mantle? What is another example of this movement in nature?
 Warm-up #15 How does magma move throughout the mantle? What is another example of this movement in nature? Earth s Structure Lithosphere = crust & upper mantle; tectonic plates Asthenosphere = lower mantle
Warm-up #15 How does magma move throughout the mantle? What is another example of this movement in nature? Earth s Structure Lithosphere = crust & upper mantle; tectonic plates Asthenosphere = lower mantle
22 Bulletin of the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan, Vol.59 December, 2011 Fig. 1 Crustal deformation (horizontal) associated with the 2011 o
 The Crustal Deformation and Fault Model of the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake 21 The Crustal Deformation and Fault Model of the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Tetsuro
The Crustal Deformation and Fault Model of the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake 21 The Crustal Deformation and Fault Model of the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake Tetsuro
RR#8 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and the map below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map indicates the epicenter (*) of a major earthquake that occurred at 38 N 142 E.
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and the map below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map indicates the epicenter (*) of a major earthquake that occurred at 38 N 142 E.
Name Class Date. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. mesosphere
 Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March 2013)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March 2013) Hakoneyama (Alert Level: 1) Shallow earthquake activity from the area near Mt. Komagatake to Sengokuhara has largely remained at low levels since the middle
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March 2013) Hakoneyama (Alert Level: 1) Shallow earthquake activity from the area near Mt. Komagatake to Sengokuhara has largely remained at low levels since the middle
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy
 There are more than 30,000 earthquakes worldwide each year! Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy usually because of movement of tectonic plates Most earthquakes last for
There are more than 30,000 earthquakes worldwide each year! Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy usually because of movement of tectonic plates Most earthquakes last for
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014
 Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan
 Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
The Tohoku Earthquake 2011 Case.
 Wide Area Deformation map generation with TerraSAR-X Data. The Tohoku Earthquake 2011 Case. N. Yague-Martinez (1), C. Minet (2), M. Eineder (2), B. Schättler (2) (1) Starlab, Spain (2) Remote Sensing Technology
Wide Area Deformation map generation with TerraSAR-X Data. The Tohoku Earthquake 2011 Case. N. Yague-Martinez (1), C. Minet (2), M. Eineder (2), B. Schättler (2) (1) Starlab, Spain (2) Remote Sensing Technology
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Exam Review. Part 1. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle.
 Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY. Earth Formation Plate Tectonics Sources of Earthquakes...
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY Earth Formation... 1-2 Plate Tectonics... 1-2 Sources of Earthquakes... 1-3 Earth Faults... 1-4 Fault Creep... 1-5 California Faults... 1-6 Earthquake
CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY Earth Formation... 1-2 Plate Tectonics... 1-2 Sources of Earthquakes... 1-3 Earth Faults... 1-4 Fault Creep... 1-5 California Faults... 1-6 Earthquake
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Fault Length and Direction of Rupture Propagation for the 1993 Kushiro-Oki Earthquake as Derived from Strong Motion Duration
 Letter J. Phys. Earth, 41, 319-325, 1993 Fault Length and Direction of Rupture Propagation for the 1993 Kushiro-Oki Earthquake as Derived from Strong Motion Duration Yasuo Izutani Faculty of Engineering,
Letter J. Phys. Earth, 41, 319-325, 1993 Fault Length and Direction of Rupture Propagation for the 1993 Kushiro-Oki Earthquake as Derived from Strong Motion Duration Yasuo Izutani Faculty of Engineering,
FORCES ON EARTH. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 235 241, 2001 Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake Yuichiro Tanioka 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 Meteorological Research
Earth Planets Space, 53, 235 241, 2001 Coseismic slip distribution of the 1946 Nankai earthquake and aseismic slips caused by the earthquake Yuichiro Tanioka 1 and Kenji Satake 2 1 Meteorological Research
