Luca Guerrieri Valerio Comerci Eutizio Vittori
|
|
|
- Roland Ross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Earthquake Environmental Effects induced by the 1908 December 28 th Messina earthquake: an in-situ contribute to the Messina supersite (GEO Task DI-09-01a Vulnerability Mapping and Risk Assessment Luca Guerrieri Valerio Comerci Eutizio Vittori This document describes a dataset of in situ effects induced by the 1908 Messina earthquake on natural environment, produced by ISPRA as a contribute to the EEE Catalogue, in the frame of an INQUA (International Union for Quaternary Research) project. This dataset will contribute to the Messina supersite, as a first example of the contribute of the EEE Catalogue to the Task DI-09-01a Vulnerability Mapping and Risk Assessment of the GEO Work Plan. The EEE Catalogue The EEE Catalogue aims at collecting in a standard way all the information regarding the effects induced by paleo, historical and modern earthquakes on natural environment (Earthquake Environmental Effects). The catalogue is compiled at global level in the frame of the #0811 INQUA TERPRO Project "A global catalogue of Earthquake Environmental Effects". The implementation of the EEE Catalogue by the partners through a web interface is in progress. At the moment only a few validated records are available on the public version of the EEE Catalogue at For each earthquake information is available at different level of generalization: at earthquake level general information is available about the seismic event, including essential seismological parameters, the extent of surface faulting and total area covered by EEE, epicentral intensity assessments based on damage distribution and/or on environmental effects (ESI 2007 intensity scale). at locality level information is given about the locality where an ESI local intensity assessment is available. at site level detailed information is available about the environmental effect, including its original description, classification, major characteristics and size, references and, when available, even a picture.
2 Figure 1 Spatial distribution of the localities affected by Earthquake Environmental Effects induced by the 1908 Messina earthquake The spatial location of epicenter, localities and sites can be seen on Google Maps (Figure 1). Alphanumeric data and coordinates can be exported as a Table (Figure 2). Thus, it is possible to plot the spatial data on a GIS and, to build a web service (e.g. WMS, WFS) for the Messina supersite. Figure 2 List of descriptions of Earthquake Environmental Effects for Messina as reported in the historical documents (in Italian). Each effect has been classified according to its genesis (slope movement, ground settlement, etc.).
3 Environmental Effects induced by the 1908 December 28 th Messina earthquake The December 28, 1908, Southern Calabria - Messina earthquake (Intensity MCS XI, Mw 7.24) was the strongest seismic event of the 20th century in Italy and the most ruinous in terms of casualties (at least 80,000). Its epicenter was located at sea in the southern part of the Messina Straits. Few minutes after the earthquake, both sides of the Straits were inundated by several tsunami waves, worsening the disastrous effects due directly to the earthquake. The damages were particularly catastrophic along the Calabrian coast, between south of Reggio Calabria and south-west of Scilla, and along the eastern coast of Sicily from its easternmost tip to south of Messina. Messina and Reggio Calabria were almost totally destroyed. We have collected and catalogued all the described coseismic effects on the environment (Figure 3) by means of a careful screening of contemporary documents, i.e. technical and photographic reports, newspapers and other archive material. Inside 447 different testimonies of environmental effects, we have identified 290 independent occurrences (Figure 4). Among these effects, particularly relevant were the changes in elevation (mainly ground lowering) along both sides of the Straits, partly due to the settlement of loose sediments and artificial filling (e.g., Messina and Reggio Calabria port areas), and partly ascribed to landslides and tectonic deformation. Liquefaction phenomena, described as water, mud or sand ejection, occurred in the areas of Messina, lake Pantano (Ganzirri) and Reggio Calabria. Portions of the coast were lost, because of landslides and the combined action of the tsunami erosion and the earthquake shaking. Ground cracks were reported in 69 localities, most of them in Messina, Reggio Calabria and Villa San Giovanni. 75 slope movements occurred in many Sicilian and Calabrian localities mainly along coastal areas, but also inland. Several hydrological anomalies occurred in both regions: appearance or disappearance of springs, change of spring discharge, water temperature variations. Also descriptions of gas emissions have been found. The larger part of the collected effects is localized in the urban areas, which attracted the attention of the reporter, and along the coastal areas which were more easily accessible. To each ground effect has been attributed one of four spatial resolution values (0-1 Km, 1-10 Km, Km, Km). However, this information is not available in the EEE Catalogue.
4 Figure 3 - Location of the environmental effects of the 1908 earthquake in the Straits area according to the collected documents CLASSIFICATION OF THE DESCRIBED EFFECTS Tsunami waves: 204 Appearance/disapp. of springs; change of springs discharge/ water temperature: 12 Coastline retreat: 19 Crack: 69 Ground lowering: 28 Water/mud/sand ejection: 8 Mass deposition on the sea floor: 11 Other: 7 Rumble: 14 Lights: 18 Gas emission: 9 Slope movement: 75 Ground uplift by levelling: 30 Differential lowering and tilting in buildings and other artificial structures: 14 Ground lowering by levelling: 91 Figure 4 - Classification of all the environmental effects of the 1908 earthquake found in contemporary documents (technical and photographic reports, newspapers and other archive material). Many testimonies are related to the same effects
5 Implications for seismic risk of the Messina area The dataset clearly points out the vulnerability of the physical environment to the occurrence of 1908 Messina like-earthquakes (and associated tsunami). The identification and characterization of the most vulnerable sites nowadays exposed to the occurrence of earthquake environmental effects is essential in the seismic risk assessment of the Messina area. The analysis of the in situ observations reported in the contemporary sources allowed us to map the spatial distribution of ground coseismic environmental effects of the 1908 earthquake. This information is essential in order to better estimate the future impact of a similar occurrence on a town like Messina that has experienced a strong urban and infrastructural growth since then. In particular, the dataset allow to know the areas prone to seismically induced landslides, liquefactions, ground settlements, etc. and to be reached by tsunami waves. Furthermore, information on Earthquake Environmental Effects is helpful also for the evaluation of the seismic intensity of the event: in fact. the EEE characteristics, size, spatial distribution and extent can be used for the definition of epicentral and local intensity through the ESI 2007 intensity scale. In 25 localities, where more diagnostic environmental effects occurred (Figures 5 and 6), we have applied the ESI 2007 scale in order to evaluate the intensity: in the Straits area the ESI values are one or two degrees lower than the MCS values (at Messina the maximum ESI value is X, while the maximum MCS value is XI). We have to consider that the ESI scale is calibrated on the MM and MSK scales, which provide intensity estimates lower than the MCS scale for the highest degrees. Moreover, the strong earthquakes that struck this area in 1894, 1905 and 1907 had certainly weakened the buildings, many of them constructed using fluvial stones and poor quality mortar, which had been badly restored afterwards. Figure 5 - ESI 2007 intensity values for several localities located in the far field area of the 1908 Messina earthquake
6 Figure 6 - ESI 2007 intensity values for several localities in the Straits area
2.3 Notes: Earthquake Damage Can Be Reduced
 2.3 Notes: Earthquake Damage Can Be Reduced Earthquakes can cause severe damage and loss of life Each year, there is about one earthquake with a magnitude of or higher-this is an extremely earthquake.
2.3 Notes: Earthquake Damage Can Be Reduced Earthquakes can cause severe damage and loss of life Each year, there is about one earthquake with a magnitude of or higher-this is an extremely earthquake.
Important Concepts. Earthquake hazards can be categorized as:
 Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Numerical investigation of the November 17, 2015 anomaly in the harbor of Crotone, Ionian Sea
 Numerical investigation of the November 17, 2015 anomaly in the harbor of Crotone, Ionian Sea F. Zaniboni, A. Armigliato, G. Pagnoni, M. A. Paparo, S. Tinti Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Alma Mater
Numerical investigation of the November 17, 2015 anomaly in the harbor of Crotone, Ionian Sea F. Zaniboni, A. Armigliato, G. Pagnoni, M. A. Paparo, S. Tinti Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Alma Mater
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Pearson Education, Inc.
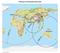 Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Earthquakes. Building Earth s Surface, Part 2. Science 330 Summer What is an earthquake?
 Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
SCENARIO DESIGN ON THE IMPACT OF A HIGH-MAGNITUDE EARTHQUAKE IN THE CITY OF LIMA, PERU
 SCENARIO DESIGN ON THE IMPACT EARTHQUAKE IN THE CITY OF LIMA, Methodology Determination of the characteristics of the probable earthquake (magnitude, intensity, acceleration). Seismic geotechnical soil
SCENARIO DESIGN ON THE IMPACT EARTHQUAKE IN THE CITY OF LIMA, Methodology Determination of the characteristics of the probable earthquake (magnitude, intensity, acceleration). Seismic geotechnical soil
NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur. Course Name Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering. Department IIT Kanpur
 NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Course Name Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Department Instructor Civil Engineering Department IIT Kanpur Prof. N.R. Patra Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Course Name Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Department Instructor Civil Engineering Department IIT Kanpur Prof. N.R. Patra Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points)
 Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Earthquake hazards. Aims 1. To know how hazards are classified 2. To be able to explain how the hazards occur 3. To be able to rank order hazards
 Earthquake hazards Aims 1. To know how hazards are classified 2. To be able to explain how the hazards occur 3. To be able to rank order hazards Types of hazard Primary A direct result of the earthquake
Earthquake hazards Aims 1. To know how hazards are classified 2. To be able to explain how the hazards occur 3. To be able to rank order hazards Types of hazard Primary A direct result of the earthquake
Tsunami and earthquake in Chile Part 2
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE GENERAL JRC JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen Global Security and Crisis Management Unit CriTech Sunday, 28 February 2010 Executive
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE GENERAL JRC JOINT RESEARCH CENTRE Institute for the Protection and Security of the Citizen Global Security and Crisis Management Unit CriTech Sunday, 28 February 2010 Executive
Dynamic Crust Regents Review
 Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Magnitude 6.3 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
Module 2, Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards
 Module 2, Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards Introduction Welcome! In the last module, you assumed the role of a volcanologist and learned how volcanoes are described and monitored. You will now assume
Module 2, Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards Introduction Welcome! In the last module, you assumed the role of a volcanologist and learned how volcanoes are described and monitored. You will now assume
Earthquakes. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
 Earthquakes Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called a. shearing. b. tension.
Earthquakes Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called a. shearing. b. tension.
Earthquakes Earth, 9th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts What is an earthquake? Earthquake focus and epicenter What is an earthquake?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic.
 Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic. IANAS GENERAL ASSEMBLY Punta Cana, 16-20 July, 2013 TECTONIC PLATES AND EARTHQUAKES Pacific
Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic. IANAS GENERAL ASSEMBLY Punta Cana, 16-20 July, 2013 TECTONIC PLATES AND EARTHQUAKES Pacific
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon
 Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
Guidelines for Site-Specific Seismic Hazard Reports for Essential and Hazardous Facilities and Major and Special-Occupancy Structures in Oregon By the Oregon Board of Geologist Examiners and the Oregon
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling
 The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
ENGINEERING-SEISMOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF EARTHQUAKE SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT ON THE EXAMPLE OF TASHKENT, UZBEKISTAN
 International Journal of Geology, Earth & Environmental Sciences ISSN: 2277-281 (Online) 218 Vol. 8 (2) May-August, pp. 3-35/Alixanovich ENGINEERING-SEISMOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF EARTHQUAKE SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT
International Journal of Geology, Earth & Environmental Sciences ISSN: 2277-281 (Online) 218 Vol. 8 (2) May-August, pp. 3-35/Alixanovich ENGINEERING-SEISMOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF EARTHQUAKE SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT
Natural Disasters Spring, LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation. Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr.
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Exam I - Reminder Feb 6 th next class details:
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Exam I - Reminder Feb 6 th next class details:
REPORT ON THE TOHOKU AREA PASIFIC OFFSHORE EARTHQUAKE
 REPORT ON THE TOHOKU AREA PASIFIC OFFSHORE EARTHQUAKE GENERAL PERSPECTIVE The Highest Magnitude Ever Recorded The 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (hereafter, the 2011 Tohoku- Pacific Earthquake
REPORT ON THE TOHOKU AREA PASIFIC OFFSHORE EARTHQUAKE GENERAL PERSPECTIVE The Highest Magnitude Ever Recorded The 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake (hereafter, the 2011 Tohoku- Pacific Earthquake
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY Sample Assessment Materials 5 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section
GCSE GEOGRAPHY Sample Assessment Materials 5 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section
Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018 Questions? Lecture Final Exam Lecture Section 1 Friday May 4, 8:00-10:00am Lecture Section 2 Friday May 4, 3:10-5:10 pm Final Exam is 70% new material
Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018 Questions? Lecture Final Exam Lecture Section 1 Friday May 4, 8:00-10:00am Lecture Section 2 Friday May 4, 3:10-5:10 pm Final Exam is 70% new material
Earthquakes. These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page.
 Earthquakes These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not
Earthquakes These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE
 PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE R.PAPADHMHTRIOU, L.PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE R.PAPADHMHTRIOU, L.PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam
 Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam Nguyen Hong Phuong Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Introduction Fault Source Model and
Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam Nguyen Hong Phuong Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Introduction Fault Source Model and
Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY
 Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY A Technical Report By MARTINEZ BRAVO Delvin Abdiel (MEE10515) Disaster
Tsukuba, Japan International Institute of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering Building Research Institute STUDY TRIP TO ITAKO CITY A Technical Report By MARTINEZ BRAVO Delvin Abdiel (MEE10515) Disaster
Monitoring Coastal Change after the Tsunami in Thailand
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Monitoring Coastal Change after the Tsunami in Thailand To cite this article: W Pantanahiran 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Monitoring Coastal Change after the Tsunami in Thailand To cite this article: W Pantanahiran 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci.
Earthquakes and Faulting
 Earthquakes and Faulting Crustal Strength Profile Quakes happen in the strong, brittle layers Great San Francisco Earthquake April 18, 1906, 5:12 AM Quake lasted about 60 seconds San Francisco was devastated
Earthquakes and Faulting Crustal Strength Profile Quakes happen in the strong, brittle layers Great San Francisco Earthquake April 18, 1906, 5:12 AM Quake lasted about 60 seconds San Francisco was devastated
Forces in Earth s Crust
 Name Date Class Earthquakes Section Summary Forces in Earth s Crust Guide for Reading How does stress in the crust change Earth s surface? Where are faults usually found, and why do they form? What land
Name Date Class Earthquakes Section Summary Forces in Earth s Crust Guide for Reading How does stress in the crust change Earth s surface? Where are faults usually found, and why do they form? What land
PLATE DEFORMATION - 2
 H4.SMR/1775-24 "8th Workshop on Three-Dimensional Modelling of Seismic Waves Generation, Propagation and their Inversion" 25 September - 7 October 2006 PLATE DEFORMATION - 2 Roberto Sabadini Dipartimento
H4.SMR/1775-24 "8th Workshop on Three-Dimensional Modelling of Seismic Waves Generation, Propagation and their Inversion" 25 September - 7 October 2006 PLATE DEFORMATION - 2 Roberto Sabadini Dipartimento
CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY A Sample Assessment Materials 5 GCSE GEOGRAPHY A COMPONENT 1 CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section Question Mark SPaG A B 1 2 Either
GCSE GEOGRAPHY A Sample Assessment Materials 5 GCSE GEOGRAPHY A COMPONENT 1 CHANGING PHYSICAL AND HUMAN LANDSCAPES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS 1 hour 30 minutes Section Question Mark SPaG A B 1 2 Either
Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami
 Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami Charitha Pattiaratchi 1 Professor of Coastal Oceanography, The University of Western Australia Email: chari.pattiaratchi@uwa.edu.au
Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami Charitha Pattiaratchi 1 Professor of Coastal Oceanography, The University of Western Australia Email: chari.pattiaratchi@uwa.edu.au
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE
 PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE E. PAPADIMITRIOU & L. PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
PROTECTING MONUMENTS AND HISTORICAL SETTINGS FROM THE NEXT EARTHQUAKE E. PAPADIMITRIOU & L. PELLI EUROPEAN CENTER OF PREVENTING & FORECASTING OF EARTHQUAKES Confronting the problem SEISMIC RISK R SEISMIC
Comparison between predicted liquefaction induced settlement and ground damage observed from the Canterbury earthquake sequence
 Power, P.M. & Jacka, M. (2013) the Canterbury earthquake sequence Proc. 19 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium. Ed. CY Chin, Queenstown Comparison between predicted liquefaction induced settlement and ground
Power, P.M. & Jacka, M. (2013) the Canterbury earthquake sequence Proc. 19 th NZGS Geotechnical Symposium. Ed. CY Chin, Queenstown Comparison between predicted liquefaction induced settlement and ground
Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk
 Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Geo-hazard Potential Mapping Using GIS and Artificial Intelligence
 Geo-hazard Potential Mapping Using GIS and Artificial Intelligence Theoretical Background and Uses Case from Namibia Andreas Knobloch 1, Dr Andreas Barth 1, Ellen Dickmayer 1, Israel Hasheela 2, Andreas
Geo-hazard Potential Mapping Using GIS and Artificial Intelligence Theoretical Background and Uses Case from Namibia Andreas Knobloch 1, Dr Andreas Barth 1, Ellen Dickmayer 1, Israel Hasheela 2, Andreas
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Overview of Consequences of the Tsunami in Thailand and Roles and Activities of the Department of Mineral Resources after the 26 December 2004 Tsunami
 Overview of Consequences of the Tsunami in Thailand and Roles and Activities of the after the 26 December 2004 Tsunami By Mr.Worawoot Tantiwanit, Thailand 1 Earthquake in NW of North Sumatra Island 580
Overview of Consequences of the Tsunami in Thailand and Roles and Activities of the after the 26 December 2004 Tsunami By Mr.Worawoot Tantiwanit, Thailand 1 Earthquake in NW of North Sumatra Island 580
Assessment Schedule 2015 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of the causes of extreme Earth events in New Zealand (91191)
 NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91191) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of the causes of extreme Earth events in New Zealand (91191) Evidence
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91191) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of the causes of extreme Earth events in New Zealand (91191) Evidence
S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura, and Y. Niwa International Research Institute of Disaster Science, Tohoku University, Japan
 The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
The first surface-rupturing earthquake in 20 years on a HERP major active fault: Mw=6.2 2014 Nagano, Japan, event along the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line is not characteristic S. Toda, S. Okada, D. Ishimura,
Magnitude 6.5 OFFSHORE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
What is a Tsunami? Tsu = harbor Nami = wave (Japanese terms)
 Tsunami Hazard What is a Tsunami? Tsu = harbor Nami = wave (Japanese terms) A tsunami is a series of travelling waves most commonly generated by vertical displacements of the sea floor associated with
Tsunami Hazard What is a Tsunami? Tsu = harbor Nami = wave (Japanese terms) A tsunami is a series of travelling waves most commonly generated by vertical displacements of the sea floor associated with
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
Earthquakes Science & Safety. Ms Joan L. Latchman Seismologist Seismic Research Unit
 Earthquakes Science & Safety Ms Joan L. Latchman Seismologist Seismic Research Unit Summary Trinidad lies in an area of high earthquake activity for the Caribbean. Earthquake safety tips should be practiced
Earthquakes Science & Safety Ms Joan L. Latchman Seismologist Seismic Research Unit Summary Trinidad lies in an area of high earthquake activity for the Caribbean. Earthquake safety tips should be practiced
Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 32 Number 4 2013 A METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF TSUNAMI RISK ALONG RUSSIA s FAR EAST G.V. Shevchenko, D. E. Zolotukhin,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 32 Number 4 2013 A METHOD FOR THE ESTIMATION OF TSUNAMI RISK ALONG RUSSIA s FAR EAST G.V. Shevchenko, D. E. Zolotukhin,
Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents. GNS Tsunami Reports
 Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents GNS Tsunami Reports a) Review of Tsunami Hazard and Risk in New Zealand ( National Risk Report ) b) Review of New Zealand s Preparedness
Wainui Beach Management Strategy (WBMS) Summary of Existing Documents GNS Tsunami Reports a) Review of Tsunami Hazard and Risk in New Zealand ( National Risk Report ) b) Review of New Zealand s Preparedness
Pilot service: Southern Emilia Romagna (Italy)
 Pilot service: Southern Emilia Romagna (Italy) Surface deformation service provider (PSInSAR TM ) Geodetic and optical remote sensing data integration Final user The study area The Southern Emilia-Romagna
Pilot service: Southern Emilia Romagna (Italy) Surface deformation service provider (PSInSAR TM ) Geodetic and optical remote sensing data integration Final user The study area The Southern Emilia-Romagna
Objectives. Vocabulary
 Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
Major External Processes Driven by energy from the sun and from gravity. Also create hazards and resources.
 Geologic Processes and Hazards Definition of Geology External and Internal Processes: examples of each Fundamentals of Plate Tectonics: definition, types of boundaries, general geography, hazards & resources
Geologic Processes and Hazards Definition of Geology External and Internal Processes: examples of each Fundamentals of Plate Tectonics: definition, types of boundaries, general geography, hazards & resources
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING INVESTIGATION HANDBOOK Second Edition
 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING INVESTIGATION HANDBOOK Second Edition Roy E. Hunt Taylor & Francis Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York Singapore A CRC title, part of the Taylor & Francis imprint,
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING INVESTIGATION HANDBOOK Second Edition Roy E. Hunt Taylor & Francis Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York Singapore A CRC title, part of the Taylor & Francis imprint,
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS
 SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 29 Number 3 2010 POTENTIAL DEFICIENCIES IN EDUCATION, INSTRUMENTATION, AND WARNINGS FOR LOCALLY GENERATED TSUNAMIS
SCIENCE OF TSUNAMI HAZARDS ISSN 8755-6839 Journal of Tsunami Society International Volume 29 Number 3 2010 POTENTIAL DEFICIENCIES IN EDUCATION, INSTRUMENTATION, AND WARNINGS FOR LOCALLY GENERATED TSUNAMIS
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
EC Funded Research on Tsunamis in the. Achievements and Perspectives
 EC Funded Research on Tsunamis in the FP6 and FP7 frameworks: Achievements and Perspectives Stefano Tinti University of Bologna stefano.tinti@unibo.it International Workshop on Disaster Risk Reduction
EC Funded Research on Tsunamis in the FP6 and FP7 frameworks: Achievements and Perspectives Stefano Tinti University of Bologna stefano.tinti@unibo.it International Workshop on Disaster Risk Reduction
Earthquakes 11/14/2014. Earthquakes Occur at All Boundaries. Earthquakes. Key Aspects of an Earthquake. Epicenter. Focus
 Earthquakes Earthquakes Caused by friction and movement between Earth s tectonic plates A release of force Often caused by a catch between two plates As plates slide by, they stick to each other When the
Earthquakes Earthquakes Caused by friction and movement between Earth s tectonic plates A release of force Often caused by a catch between two plates As plates slide by, they stick to each other When the
Groundwater and Coastal Phenomena Preceding the 1944 Tsunami (Tonankai Earthquake)
 Groundwater and Coastal Phenomena Preceding the 1944 Tsunami (Tonankai Earthquake) Masataka Ando Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica ando@earth.sinica.edu.tw Study Area Characteristics of large
Groundwater and Coastal Phenomena Preceding the 1944 Tsunami (Tonankai Earthquake) Masataka Ando Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica ando@earth.sinica.edu.tw Study Area Characteristics of large
Rapid Changes on Earth: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Landslides. Chapter 6 Study Guide
 Rapid Changes on Earth: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Landslides Chapter 6 Study Guide Magma is 1. The point underground where an earthquake starts. 2. Molten rock beneath the Earth s surface. 3. Molten rock
Rapid Changes on Earth: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Landslides Chapter 6 Study Guide Magma is 1. The point underground where an earthquake starts. 2. Molten rock beneath the Earth s surface. 3. Molten rock
3l NATURAL HAZARDS AND UNSTABLE GROUND
 Page 1 of Section 3l 3l NATURAL HAZARDS AND UNSTABLE GROUND 3l.1 Introduction A natural hazard is the result of natural processes that form, shape and change the environment and interact or potentially
Page 1 of Section 3l 3l NATURAL HAZARDS AND UNSTABLE GROUND 3l.1 Introduction A natural hazard is the result of natural processes that form, shape and change the environment and interact or potentially
An analysis on the relationship between land subsidence and floods at the Kujukuri Plain in Chiba Prefecture, Japan
 doi:10.5194/piahs-372-163-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. An analysis on the relationship between land subsidence and floods at the Kujukuri Plain in Chiba Prefecture, Japan Y. Ito 1,
doi:10.5194/piahs-372-163-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. An analysis on the relationship between land subsidence and floods at the Kujukuri Plain in Chiba Prefecture, Japan Y. Ito 1,
FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types of volcanoes.
FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types of volcanoes.
An entire branch of Earth science, called, is devoted to the study of earthquakes.
 Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Magnitude 7.0 N of ANCHORAGE, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
Storms. 3. Storm types 4. Coastal Sectors 5. Sorm Location and Seasonality 6. Storm Severity 7. Storm Frequency and grouping 8. The design storm event
 1. Introduction Storms 2. The Impact of Storms on the coast 3. Storm types 4. Coastal Sectors 5. Sorm Location and Seasonality 6. Storm Severity 7. Storm Frequency and grouping 8. The design storm event
1. Introduction Storms 2. The Impact of Storms on the coast 3. Storm types 4. Coastal Sectors 5. Sorm Location and Seasonality 6. Storm Severity 7. Storm Frequency and grouping 8. The design storm event
appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards
 appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards CONTENTS: E-2 Fault Rupture E-3 Ground Shaking E-5 Seismic Ground Deformation E-5 Liquification E-6 Seismically Induces Landslide E-6 Landslide Hazard E The following
appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards CONTENTS: E-2 Fault Rupture E-3 Ground Shaking E-5 Seismic Ground Deformation E-5 Liquification E-6 Seismically Induces Landslide E-6 Landslide Hazard E The following
Seismic risk in Romania
 Seismic risk in Romania Dr.eng. Mihaela Lazarescu National R&D Institute for Environmetal Protection ICIM Bucharest Spl. Independentei 294, cod 060031 Bucharest ROMANIA This is the list of significant
Seismic risk in Romania Dr.eng. Mihaela Lazarescu National R&D Institute for Environmetal Protection ICIM Bucharest Spl. Independentei 294, cod 060031 Bucharest ROMANIA This is the list of significant
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
Running Head: JAPANESE TSUNAMI 1. Geological Perspective of the Japanese Tsunami
 Running Head: JAPANESE TSUNAMI 1 Geological Perspective of the Japanese Tsunami JAPANESE TSUNAMI 2 JAPANESE TSUNAMI 3 Abstract Humanity is characterized with flaws, so is planet earth. Earthquakes shake
Running Head: JAPANESE TSUNAMI 1 Geological Perspective of the Japanese Tsunami JAPANESE TSUNAMI 2 JAPANESE TSUNAMI 3 Abstract Humanity is characterized with flaws, so is planet earth. Earthquakes shake
Magnitude 7.7 QUEEN CHARLOTTE ISLANDS REGION
 A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
I. Locations of Earthquakes. Announcements. Earthquakes Ch. 5. video Northridge, California earthquake, lecture on Chapter 5 Earthquakes!
 51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES
 UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
Earthquake prediction. Earthquake prediction: animals?
 Earthquake prediction Prediction: specifies that an earthquake of a specific magnitude will occur in a defined region during a particular period: There will be a M 7 or larger earthquake in southern California
Earthquake prediction Prediction: specifies that an earthquake of a specific magnitude will occur in a defined region during a particular period: There will be a M 7 or larger earthquake in southern California
SECTION 3. Housing. EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS
 SECTION 3 Housing EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS E-2 Housing Commission Attachment B Appendix E Geologic and Seismic Hazards The following definitions provide a more comprehensive discussion
SECTION 3 Housing EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS E-2 Housing Commission Attachment B Appendix E Geologic and Seismic Hazards The following definitions provide a more comprehensive discussion
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Earthquakes Science & Safety. Dr. Richard Robertson Geologist & Head Seismic Research Unit
 Earthquakes Science & Safety Dr. Richard Robertson Geologist & Head Seismic Research Unit Summary The Eastern Caribbean islands are in a seismically active part of the world. Earthquake safety tips should
Earthquakes Science & Safety Dr. Richard Robertson Geologist & Head Seismic Research Unit Summary The Eastern Caribbean islands are in a seismically active part of the world. Earthquake safety tips should
Before exploring the effects of the 1906 earthquake, watch the video on ground shaking and liquefaction at:
 Seismic Risk: Pre- Work Paper Maps Version Early on the morning of April 16, 1906, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck on the San Andreas Fault. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake revolutionized our understanding
Seismic Risk: Pre- Work Paper Maps Version Early on the morning of April 16, 1906, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck on the San Andreas Fault. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake revolutionized our understanding
Looking after Lyme Regis
 Looking after Lyme Regis Lyme Regis sits on one of the most unstable stretches of coastline in the country. The highly active and unstable nature of the land which Lyme Regis is built upon can easily be
Looking after Lyme Regis Lyme Regis sits on one of the most unstable stretches of coastline in the country. The highly active and unstable nature of the land which Lyme Regis is built upon can easily be
Study of the liquefaction phenomenon due to an earthquake: case study of Urayasu city
 Disaster Management and Human Health Risk III 311 Study of the liquefaction phenomenon due to an earthquake: case study of Urayasu city S. Kamao 1, M. Takezawa 1, K. Yamada 1, S. Jinno 1, T. Shinoda 1
Disaster Management and Human Health Risk III 311 Study of the liquefaction phenomenon due to an earthquake: case study of Urayasu city S. Kamao 1, M. Takezawa 1, K. Yamada 1, S. Jinno 1, T. Shinoda 1
Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter. Interior
 Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter Interior 8.1 What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter Focus is the point within Earth
Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter Interior 8.1 What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter Focus is the point within Earth
FIG Working Week May, Bulgaria From the wisdom of the ages to the challanges of modern world
 FIG Working Week 17-21 May, Bulgaria From the wisdom of the ages to the challanges of modern world COASTAL RISK ANALYSIS OF THE BLACK SEA UNDER THE SEA LEVEL RISE N e v i n B e t u l A V S A R, S e n o
FIG Working Week 17-21 May, Bulgaria From the wisdom of the ages to the challanges of modern world COASTAL RISK ANALYSIS OF THE BLACK SEA UNDER THE SEA LEVEL RISE N e v i n B e t u l A V S A R, S e n o
EQ Monitoring and Hazards NOTES.notebook. January 07, P-wave. S-wave. surface waves. distance
 Earthquake Monitoring and Hazards Reading a Seismogram General guidelines: P-wave First disruption of trace = Second disruption of trace = surface waves Largest disruption of trace = Not the distance to
Earthquake Monitoring and Hazards Reading a Seismogram General guidelines: P-wave First disruption of trace = Second disruption of trace = surface waves Largest disruption of trace = Not the distance to
TECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING COASTAL HAZARD AREAS FOR THE GISBORNE DISTRICT COAST
 TECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING COASTAL HAZARD AREAS FOR THE GISBORNE DISTRICT COAST July 1994 C.R. 1994/12 Jeremy G Gibb 2009 All rights reserved. This work is entitled to the full protection given by the Copyright
TECHNIQUES FOR ASSESSING COASTAL HAZARD AREAS FOR THE GISBORNE DISTRICT COAST July 1994 C.R. 1994/12 Jeremy G Gibb 2009 All rights reserved. This work is entitled to the full protection given by the Copyright
STUDY ON TSUNAMIGENIC EARTHQUAKE CRITERIA FOR THE INDONESIAN TSUNAMI EARLY WARNING SYSTEM
 STUDY ON TSUNAMIGENIC EARTHQUAKE CRITERIA FOR THE INDONESIAN TSUNAMI EARLY WARNING SYSTEM Nanang T. Puspito 1 1 Geophysics Research Group, Faculty of Mining and Petroleum Engineering, Institute of Technology
STUDY ON TSUNAMIGENIC EARTHQUAKE CRITERIA FOR THE INDONESIAN TSUNAMI EARLY WARNING SYSTEM Nanang T. Puspito 1 1 Geophysics Research Group, Faculty of Mining and Petroleum Engineering, Institute of Technology
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard.
 Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Earthquakes in Canada
 Earthquakes in Canada Maurice Lamontagne, Ph.D., ing. Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada 1 What is an Earthquake? P S P S P PS 2 2 Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger
Earthquakes in Canada Maurice Lamontagne, Ph.D., ing. Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada 1 What is an Earthquake? P S P S P PS 2 2 Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger
Preliminary report on the Canterbury Earthquake South Island of New Zealand , M 6.3
 Preliminary report on the Canterbury Earthquake South Island of New Zealand 21.02.2011, M 6.3 Kyriazis Pitilakis and the group of - Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece. General 2 General 147 people
Preliminary report on the Canterbury Earthquake South Island of New Zealand 21.02.2011, M 6.3 Kyriazis Pitilakis and the group of - Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Greece. General 2 General 147 people
Disclaimer. This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries.
 Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
20.1 Earthquakes. Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES. Earthquakes and plate boundaries 500 UNIT 6 EARTH S STRUCTURE
 Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Lecture notes Bill Engstrom: Instructor Earthquakes GLG 101 Physical Geology
 Lecture notes Bill Engstrom: Instructor Earthquakes GLG 101 Physical Geology Now that we ve seen what faults are and how mountains are built, we can look at what happens when there is movement along those
Lecture notes Bill Engstrom: Instructor Earthquakes GLG 101 Physical Geology Now that we ve seen what faults are and how mountains are built, we can look at what happens when there is movement along those
Earthquakes Web Quest
 NAME: Earthquakes Web Quest DATE: TASK #1: http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/history/historyhtml Read through the slides and answer the following questions: What did our ancient ancestors
NAME: Earthquakes Web Quest DATE: TASK #1: http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/history/historyhtml Read through the slides and answer the following questions: What did our ancient ancestors
Update on the It s Our Fault project
 Report 12.552 Date 29 October 2012 File 12/01/01 Committee Author CDEM Group Bruce Pepperell, Regional Manager, WREMO Update on the It s Our Fault project 1. Purpose To inform the CDEM Group of progress
Report 12.552 Date 29 October 2012 File 12/01/01 Committee Author CDEM Group Bruce Pepperell, Regional Manager, WREMO Update on the It s Our Fault project 1. Purpose To inform the CDEM Group of progress
ARE THE SEQUENCES OF BUS AND EARTHQUAKE ARRIVALS POISSON?
 Application Example 6 (Exponential and Poisson distributions) ARE THE SEQUENCES OF BUS AND EARTHQUAKE ARRIVALS POISSON? The Poisson Process The Poisson process is the simplest random distribution of points
Application Example 6 (Exponential and Poisson distributions) ARE THE SEQUENCES OF BUS AND EARTHQUAKE ARRIVALS POISSON? The Poisson Process The Poisson process is the simplest random distribution of points
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES. Duration of resource: 30 Minutes. Year of Production: Stock code: VEA Resource written by: Andrew Clarke BA Dip Tchg
 ADDITIONAL RESOURCES The destructive and unexpected nature of earthquakes has remained a constant threat since civilisation began. Suitable for all secondary audiences, this two-part program firstly examines
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES The destructive and unexpected nature of earthquakes has remained a constant threat since civilisation began. Suitable for all secondary audiences, this two-part program firstly examines
